Chapter 7. Network Configuration Reference
Network configuration is critical for building a high performance Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster. The Ceph storage cluster does not perform request routing or dispatching on behalf of the Ceph client. Instead, Ceph clients make requests directly to Ceph OSD daemons. Ceph OSDs perform data replication on behalf of Ceph clients, which means replication and other factors impose additional loads on the networks of Ceph storage clusters.
All Ceph clusters must use a "public" (front-side) network. However, unless you specify a "cluster" (back-side) network, Ceph assumes a single "public" network. Ceph functions just fine with a public network only, but you may see significant performance improvement with a second "cluster" network in a large cluster.
We recommend running a Ceph storage cluster with two networks: a public (front-side) network and a cluster (back-side) network. To support two networks, each Ceph Node will need to have more than one NIC.
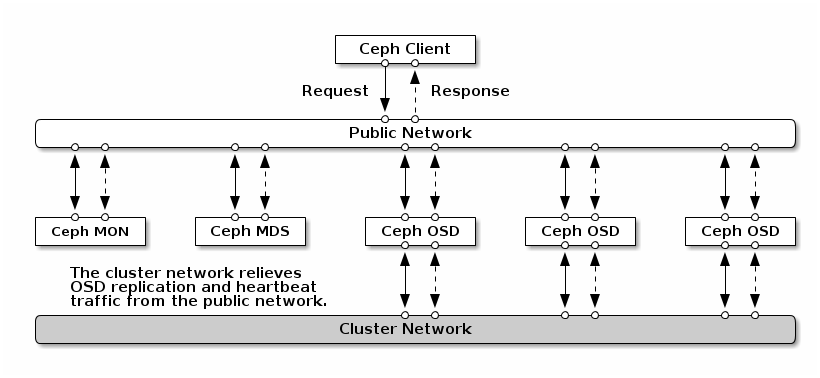
There are several reasons to consider operating two separate networks:
- Performance: Ceph OSDs handle data replication for the Ceph clients. When Ceph OSDs replicate data more than once, the network load between Ceph OSDs easily dwarfs the network load between Ceph clients and the Ceph storage cluster. This can introduce latency and create a performance problem. Recovery and re-balancing can also introduce significant latency on the public network.
-
Security: While most people are generally civil, some actors will engage in what’s known as a Denial of Service (DoS) attack. When traffic between Ceph OSDs gets disrupted, peering may fail and placement groups may no longer reflect an
active + cleanstate, which may prevent users from reading and writing data. A great way to defeat this type of attack is to maintain a completely separate cluster network that doesn’t connect directly to the internet.
7.1. IP Tables
By default, daemons bind to ports within the 6800:7100 range. You may configure this range at your discretion. Before configuring your IP tables, check the default iptables configuration. You may configure this range at your discretion.
sudo iptables -L
sudo iptables -L
For firewall.d, execute:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all-zonesSome Linux distributions include rules that reject all inbound requests except SSH from all network interfaces. For example:
REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibitedYou may need to modify or delete these rules on both your public and cluster networks initially, and replace them with appropriate rules when you are ready to harden the ports on your Ceph Nodes.
7.1.1. Monitor IP Tables
Ceph Monitors listen on port 6789 by default. Additionally, Ceph Monitors always operate on the public network. When you add the rule using the example below, make sure you replace <iface> with the public network interface (e.g., eth0, eth1, etc.), <ip-address> with the IP address of the public network and <netmask> with the netmask for the public network.
sudo iptables -A INPUT -i <iface> -p tcp -s <ip-address>/<netmask> --dport 6789 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -i <iface> -p tcp -s <ip-address>/<netmask> --dport 6789 -j ACCEPT
For firewall.d, execute:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6789/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6789/tcp --permanent7.1.2. OSD IP Tables
By default, Ceph OSDs bind to the first available ports on a Ceph node beginning at port 6800. Ensure that you open at least three ports beginning at port 6800 for each OSD that runs on the host:
- One for talking to clients and monitors.
- One for sending data to other OSDs.
- One for heartbeating.
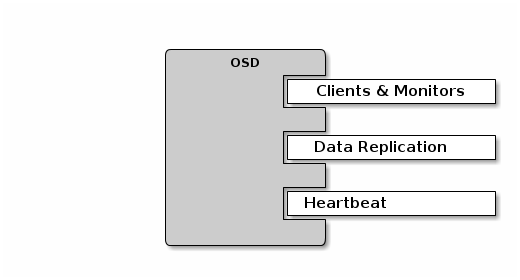
Ports are node-specific, so you don’t need to open any more ports than the number of ports needed by Ceph daemons running on that Ceph Node. You may consider opening a few additional ports in case a daemon fails and restarts without letting go of the port such that the restarted daemon binds to a new port.
If you set up separate public and cluster networks, you must add rules for both the public network and the cluster network, because clients will connect using the public network and other Ceph OSD Daemons will connect using the cluster network. When you add the rule using the example below, make sure you replace <iface> with the network interface (e.g., eth0, eth1, etc.), <ip-address> with the IP address and <netmask> with the netmask of the public or cluster network. For example:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -i <iface> -m multiport -p tcp -s <ip-address>/<netmask> --dports 6800:6810 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -i <iface> -m multiport -p tcp -s <ip-address>/<netmask> --dports 6800:6810 -j ACCEPT
For firewall.d, execute:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6800-6810/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6800-6810/tcp --permanentIf you put your cluster network into another zone, open the ports within that zone as appropriate.
7.2. Ceph Networks
To configure Ceph networks, you must add a network configuration to the [global] section of the configuration file. Ceph functions just fine with a public network only. However, Ceph allows you to establish much more specific criteria, including multiple IP network and subnet masks for your public network. You can also establish a separate cluster network to handle OSD heartbeat, object replication and recovery traffic. Don’t confuse the IP addresses you set in your configuration with the public-facing IP addresses network clients may use to access your service. Typical internal IP networks are often 192.168.0.0 or 10.0.0.0.
If you specify more than one IP address and subnet mask for either the public or the cluster network, the subnets within the network must be capable of routing to each other. Additionally, make sure you include each IP address/subnet in your IP tables and open ports for them as necessary.
Ceph uses CIDR notation for subnets (e.g., 10.0.0.0/24).
When you’ve configured your networks, you may restart your cluster or restart each daemon. Ceph daemons bind dynamically, so you do not have to restart the entire cluster at once if you change your network configuration.
7.2.1. Public Network
To configure a public network, add the following option to the [global] section of your Ceph configuration file.
[global]
...
public network = <public-network/netmask>
[global]
...
public network = <public-network/netmask>7.2.2. Cluster Network
If you declare a cluster network, OSDs will route heartbeat, object replication and recovery traffic over the cluster network. This may improve performance compared to using a single network. To configure a cluster network, add the following option to the [global] section of your Ceph configuration file.
[global]
...
cluster network = <cluster-network/netmask>
[global]
...
cluster network = <cluster-network/netmask>We prefer that the cluster network is NOT reachable from the public network or the Internet for added security.
7.3. Ceph Daemons
Ceph has one network configuration requirement that applies to all daemons: the Ceph configuration file MUST specify the host for each daemon. Ceph also requires that a Ceph configuration file specify the monitor IP address and its port.
Some deployment tools (e.g., ceph-deploy, Chef) may create a configuration file for you. DO NOT set these values if the deployment tool does it for you.
The host setting is the short name of the host (i.e., not an fqdn). It is NOT an IP address either. Enter hostname -s on the command line to retrieve the name of the host.
You do not have to set the host IP address for a daemon. If you have a static IP configuration and both public and cluster networks running, the Ceph configuration file may specify the IP address of the host for each daemon. To set a static IP address for a daemon, the following option(s) should appear in the daemon instance sections of your ceph.conf file.
[osd.0]
public addr = <host-public-ip-address>
cluster addr = <host-cluster-ip-address>
[osd.0]
public addr = <host-public-ip-address>
cluster addr = <host-cluster-ip-address>One NIC OSD in a Two Network Cluster
Generally, we do not recommend deploying an OSD host with a single NIC in a cluster with two networks. However, you may accomplish this by forcing the OSD host to operate on the public network by adding a public addr entry to the [osd.n] section of the Ceph configuration file, where n refers to the number of the OSD with one NIC. Additionally, the public network and cluster network must be able to route traffic to each other, which we don’t recommend for security reasons.
7.4. Network Config Settings
Network configuration settings are not required. Ceph assumes a public network with all hosts operating on it unless you specifically configure a cluster network.
7.4.1. Public Network
The public network configuration allows you specifically define IP addresses and subnets for the public network. You may specifically assign static IP addresses or override public network settings using the public addr setting for a specific daemon.
public network
- Description
-
The IP address and netmask of the public (front-side) network (e.g.,
192.168.0.0/24). Set in[global]. You may specify comma-delimited subnets. - Type
-
<ip-address>/<netmask> [, <ip-address>/<netmask>] - Required
- No
- Default
- N/A
public addr
- Description
- The IP address for the public (front-side) network. Set for each daemon.
- Type
- IP Address
- Required
- No
- Default
- N/A
7.4.2. Cluster Network
The cluster network configuration allows you to declare a cluster network, and specifically define IP addresses and subnets for the cluster network. You may specifically assign static IP addresses or override cluster network settings using the cluster addr setting for specific OSD daemons.
cluster network
- Description
-
The IP address and netmask of the cluster (back-side) network (e.g.,
10.0.0.0/24). Set in[global]. You may specify comma-delimited subnets. - Type
-
<ip-address>/<netmask> [, <ip-address>/<netmask>] - Required
- No
- Default
- N/A
cluster addr
- Description
- The IP address for the cluster (back-side) network. Set for each daemon.
- Type
- Address
- Required
- No
- Default
- N/A
7.4.3. Bind
Bind settings set the default port ranges Ceph OSD daemons use. The default range is 6800:7100. Ensure that your firewall configuration allows you to use the configured port range.
You may also enable Ceph daemons to bind to IPv6 addresses.
ms bind port min
- Description
- The minimum port number to which an OSD daemon will bind.
- Type
- 32-bit Integer
- Default
-
6800 - Required
- No
ms bind port max
- Description
- The maximum port number to which an OSD daemon will bind.
- Type
- 32-bit Integer
- Default
-
7100 - Required
- No.
ms bind ipv6
- Description
- Enables Ceph daemons to bind to IPv6 addresses.
- Type
- Boolean
- Default
-
false - Required
- No
7.4.4. Hosts
Ceph expects at least one monitor declared in the Ceph configuration file, with a mon addr setting under each declared monitor. Ceph expects a host setting under each declared monitor, metadata server and OSD in the Ceph configuration file.
mon addr
- Description
-
A list of
<hostname>:<port>entries that clients can use to connect to a Ceph monitor. If not set, Ceph searches[mon.*]sections. - Type
- String
- Required
- No
- Default
- N/A
host
- Description
-
The hostname. Use this setting for specific daemon instances (e.g.,
[osd.0]). - Type
- String
- Required
- Yes, for daemon instances.
- Default
-
localhost
Do not use localhost. To get your host name, execute hostname -s on your command line and use the name of your host (to the first period, not the fully-qualified domain name).
You should not specify any value for host when using a third party deployment system that retrieves the host name for you.
7.4.5. TCP
Ceph disables TCP buffering by default.
tcp nodelay
- Description
-
Ceph enables
tcp nodelayso that each request is sent immediately (no buffering). Disabling Nagle’s algorithm increases network traffic, which can introduce latency. If you experience large numbers of small packets, you may try disablingtcp nodelay. - Type
- Boolean
- Required
- No
- Default
-
true
tcp rcvbuf
- Description
- The size of the socket buffer on the receiving end of a network connection. Disable by default.
- Type
- 32-bit Integer
- Required
- No
- Default
-
0
ms tcp read timeout
- Description
-
If a client or daemon makes a request to another Ceph daemon and does not drop an unused connection, the
tcp read timeoutdefines the connection as idle after the specified number of seconds. - Type
- Unsigned 64-bit Integer
- Required
- No
- Default
-
90015 minutes.