14.9. Running Self-Tests
The Certificate System has the added functionality to allow self-tests of the server. The self-tests are run at start up and can also be run on demand. The startup self-tests run when the server starts and keep the server from starting if a critical self-test fails. The on-demand self-tests are run by clicking the self-tests button in the subsystem console.
14.9.1. Running Self-Tests
The on-demand self-test for the CA, OCSP, KRA, or TKS subsystems are run from the console. The on-demand self-tests for the TPS system are run from the web services page.
14.9.1.1. Running Self-Tests from the Console
Note
pkiconsole is being deprecated.
- Log into the Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:admin_port/subsystem_type
- Select the subsystem name at the top of the left pane.
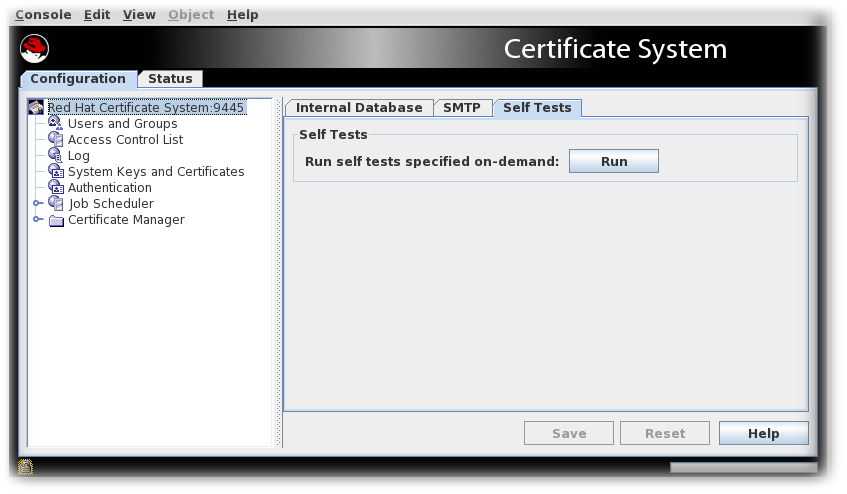
- Select the Self Tests tab.
- Click .The self-tests that are configured for the subsystem will run. If any critical self-tests fail, the server will stop.
- The On-Demand Self Tests Results window appears, showing the logged events for this run of the self-tests.
14.9.1.2. Running TPS Self-Tests
To run TPS self-tests from the command-line interface (CLI):
pki tps-selftest-findpki tps-selftest-runpki tps-selftest-show
14.9.2. Self-Test Logging
A separate log,
selftest.log, is added to the log directory that contains reports for both the start up self-tests and the on-demand self-tests. This log is configured by changing the setting for the log in the CS.cfg file. See the Modifying Self-Test Configuration section in the Red Hat Certificate System Planning, Installation, and Deployment Guide for details.
14.9.3. Configuring POSIX System ACLs
POSIX system access control rules provide finer granularity over system user permissions. These ACLs must be set for each instance after it is fully configured. For more details on ACLs, see the corresponding chapter in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux System Administration Guide.
14.9.3.1. Setting POSIX System ACLs for the CA, KRA, OCSP, TKS, and TPS
Modern file systems like ext4 and XFS enable ACLs by default, and are most likely used on modern Red Hat Enterprise Linux installations.
- Stop the instance.
pki-server stop instance_name
- Set the group readability to the pkiadmin group for the instance's directories and files.
# setfacl -R -L -m g:pkiadmin:r,d:g:pkiadmin:r /var/lib/pki/instance_name
- Apply execute (x) ACL permissions on all directories:
# find -L /var/lib/pki/instance_name -type d -exec setfacl -L -n -m g:pkiadmin:rx,d:g:pkiadmin:rx {} \; - Remove group readability for the pkiadmin group from the instance's signedAudit/ directory and its associated files:
# setfacl -R -L -x g:pkiadmin,d:g:pkiadmin /var/lib/pki/instance_name/logs/signedAudit
- Set group readability for the pkiaudit group for the instance's signedAudit/ directory and its associated files:
# setfacl -R -L -m g:pkiaudit:r,d:g:pkiaudit:r /var/lib/pki/instance_name/logs/signedAudit
- Re-apply execute (x) ACL permissions on the signedAudit/ directory and all of its subdirectories:
# find -L /var/lib/pki/instance_name/logs/signedAudit -type d -exec setfacl -L -n -m g:pkiaudit:rx,d:g:pkiaudit:rx {} \; - Start the instance.
pki-server start instance_name
- Confirm that the file access controls were properly applied by using the
getfaclcommand to show the current ACL settings:# getfacl /var/lib/pki/instance_name /var/lib/pki/instance_name/subsystem_type/logs/signedAudit/ getfacl: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names # file: var/lib/pki/instance_name # owner: pkiuser # group: pkiuser user::rwx group::rwx group:pkiadmin:r-x mask::rwx other::r-x default:user::rwx default:group::rwx default:group:pkiadmin:r-x default:mask::rwx default:other::r-x # file: var/lib/pki/instance_name/logs/signedAudit # owner: pkiuser # group: pkiaudit user::rwx group::rwx group:pkiaudit:r-x mask::rwx other::--- default:user::rwx default:group::rwx default:group:pkiaudit:r-x default:mask::rwx default:other::---