Chapter 7. Troubleshooting CodeReady Workspaces
This section provides troubleshooting procedures for most frequent issues an user can came in conflict with.
Additional resources
7.1. Troubleshooting slow workspaces
Sometimes, workspaces can take a long time to start. Tuning can reduce this start time. Depending on the options, administrators or users can do the tuning.
This section includes several tuning options for starting workspaces faster or improving workspace runtime performance.
7.1.1. Improving workspace start time
- Caching images with Image Puller
Role: Administrator
When starting a workspace, OpenShift pulls the images from the registry. A workspace can include many containers meaning that OpenShift pulls Pod’s images (one per container). Depending on the size of the image and the bandwidth, it can take a long time.
Image Puller is a tool that can cache images on each of OpenShift nodes. As such, pre-pulling images can improve start times. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/administration_guide/index#caching-images-for-faster-workspace-start_crw.
- Choosing better storage type
Role: Administrator and user
Every workspace has a shared volume attached. This volume stores the project files, so that when restarting a workspace, changes are still available. Depending on the storage, attach time can take up to a few minutes, and I/O can be slow.
To avoid this problem, use ephemeral or asynchronous storage. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#configuring-storage-types_crw.
- Installing offline
Role: Administrator
Components of CodeReady Workspaces are OCI images. Setup Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces in offline mode (air-gap scenario) to allow for reducing any extra download at runtime as everything needs to be present from the beginning. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-che-in-a-restricted-environment.adoc.
- Optimizing workspace plug-ins
Role: User
When selecting various plug-ins, each plug-in can bring its own sidecar container, which is an OCI image. OpenShift pulls the images of these sidecar containers.
Reduce the number of plug-ins, or disable them to see if start time is faster. See also https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/administration_guide/index#caching-images-for-faster-workspace-start_crw.
- Reducing the number of public endpoints
Role: Administrator
For each endpoint, OpenShift is creating OpenShift Route objects. Depending on the underlying configuration, this creation can be slow.
To avoid this problem, reduce the exposure. For example, to automatically detect a new port listening inside containers and redirect traffic for the processes using a local IP address (
127.0.0.1), the Che-Theia IDE plug-in has three optional routes.By reducing the number of endpoints and checking endpoints of all plug-ins, workspace start can be faster.
- CDN configuration
The IDE editor uses a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to serve content. Check that the content uses a CDN to the client (or a local route for offline setup).
To check that, open Developer Tools in the browser and check for
vendorsin the Network tab.vendors.<random-id>.jsoreditor.main.*should come from CDN URLs.
7.1.2. Improving workspace runtime performance
- Providing enough CPU resources
Plug-ins consume CPU resources. For example, when a plug-in provides IntelliSense features, adding more CPU resources may lead to better performance.
Ensure the CPU settings in the devfile definition (
devfile.yaml) are correct:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Providing enough memory
Plug-ins consume CPU and memory resources. For example, when a plug-in provides IntelliSense features, collecting data can consume all the memory allocated to the container.
Providing more memory to the plug-in can increase performance. Ensure the memory settings in the plug-in definition (
meta.yaml) are correct:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the memory limit for the plug-in.
In the devfile definition (
devfile.yaml):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Choosing better storage type
- Use ephemeral or asynchronous storage for faster I/O. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#configuring-storage-types_crw.
7.2. Troubleshooting network problems
Most often, connection problems occur because a firewall, proxy server, corporate network, or other network is configured in a way that blocks CodeReady Workspaces.
This section describes how to prevent or resolve issues related to corporate network policies. The network administrator may be required to enable ports or the WebSockets protocol, which CodeReady Workspaces requires for proper functionality.
Common scenarios:
- Open additional ports for a specific web site.
- Enable WebSockets on the proxy server.
7.2.1. Enabling the WebSocket protocol
Enabling the WebSocket protocol is critical for the proper functionality of CodeReady Workspaces IDE.
While the WebSocket protocol itself is unaware of proxy servers and firewalls, HTTP servers can share their default HTTP and HTTPS ports with a WebSocket server.
- HTTP: port 80
- HTTPS: port 433
Some proxy servers operate with WebSockets by default, but others prevent WebSockets from working correctly, which causes the connection to fail.
In some cases, the proxy server requires the additional configuration, and the specific proxy servers need an upgrade, which allows WebSockets support.
7.2.2. Troubleshooting WebSocket Secure connections
Secure WebSocket connections improve confidentiality and also reliability because they reduce the risk of interference by bad proxies. CodeReady Workspaces operates under WebSocket Secure connections by default and usually no action is required. Some customer’s security policy blocks some aspects of the WebSocket protocol that causes problems with proper CodeReady Workspaces functionality. Those problems are however out of scope for CodeReady Workspaces support and have to be solved by a network administrator.
To troubleshoot a failing WebSocket Secure (WSS) connection, use the instructions in this section.
Prerequisites
Using a supported web browser:
- Chrome
- Firefox
NoteUsing an unsupported web browser causes a connection interruption, followed by a warning message.
Procedure
Check browser support:
Check that the WebSocket protocol is enabled using a realtime web test in one of the supported browsers.
If the problem is not resolved, follow with the next step.
Check proxy servers and firewalls settings:
Ask the system administrator to check if there is a proxy server or firewall that blocks WebSocket Secure (WSS) connections on port 443.
Possible required actions:
- Add an exception to the firewall.
- Have the proxy intercept WebSocket connection.
Verification
Check that the WebSocket protocol is enabled using a realtime web test in one of the supported browsers.
7.3. Starting a CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode
This section describes how to start the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. See Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
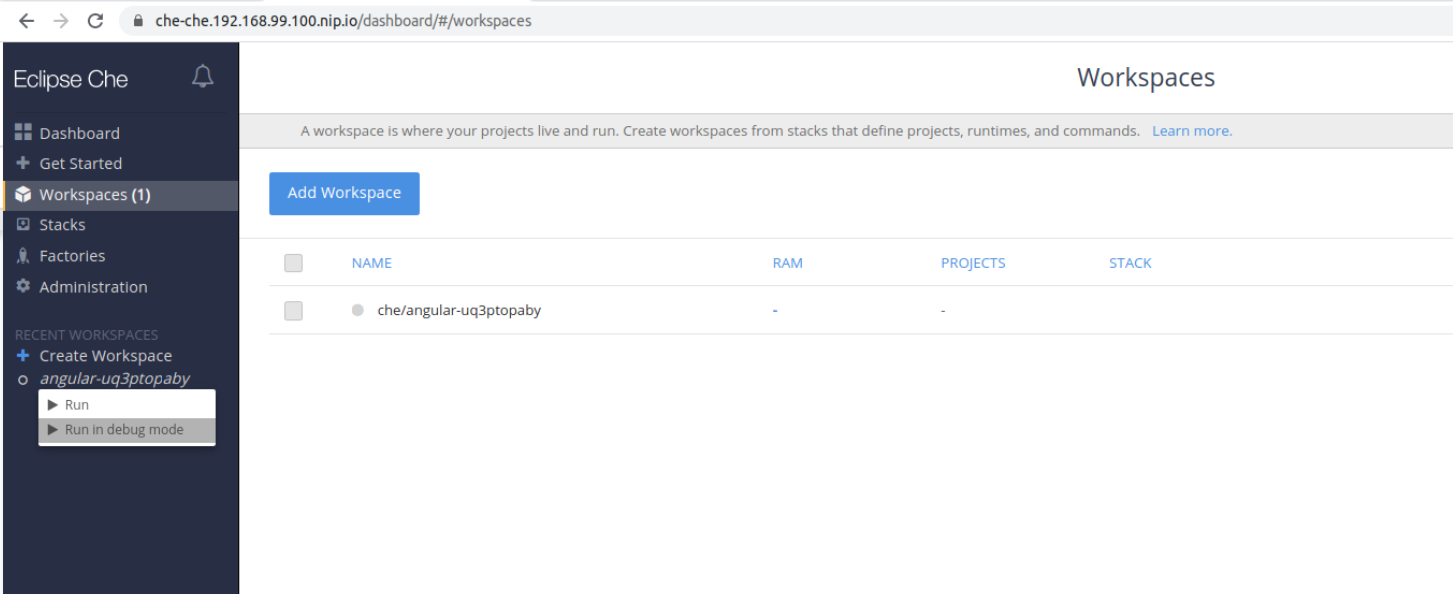
Find the target workspace from the recent workspaces. Right-click the workspace name to open a context menu. Select the Run in debug mode item:
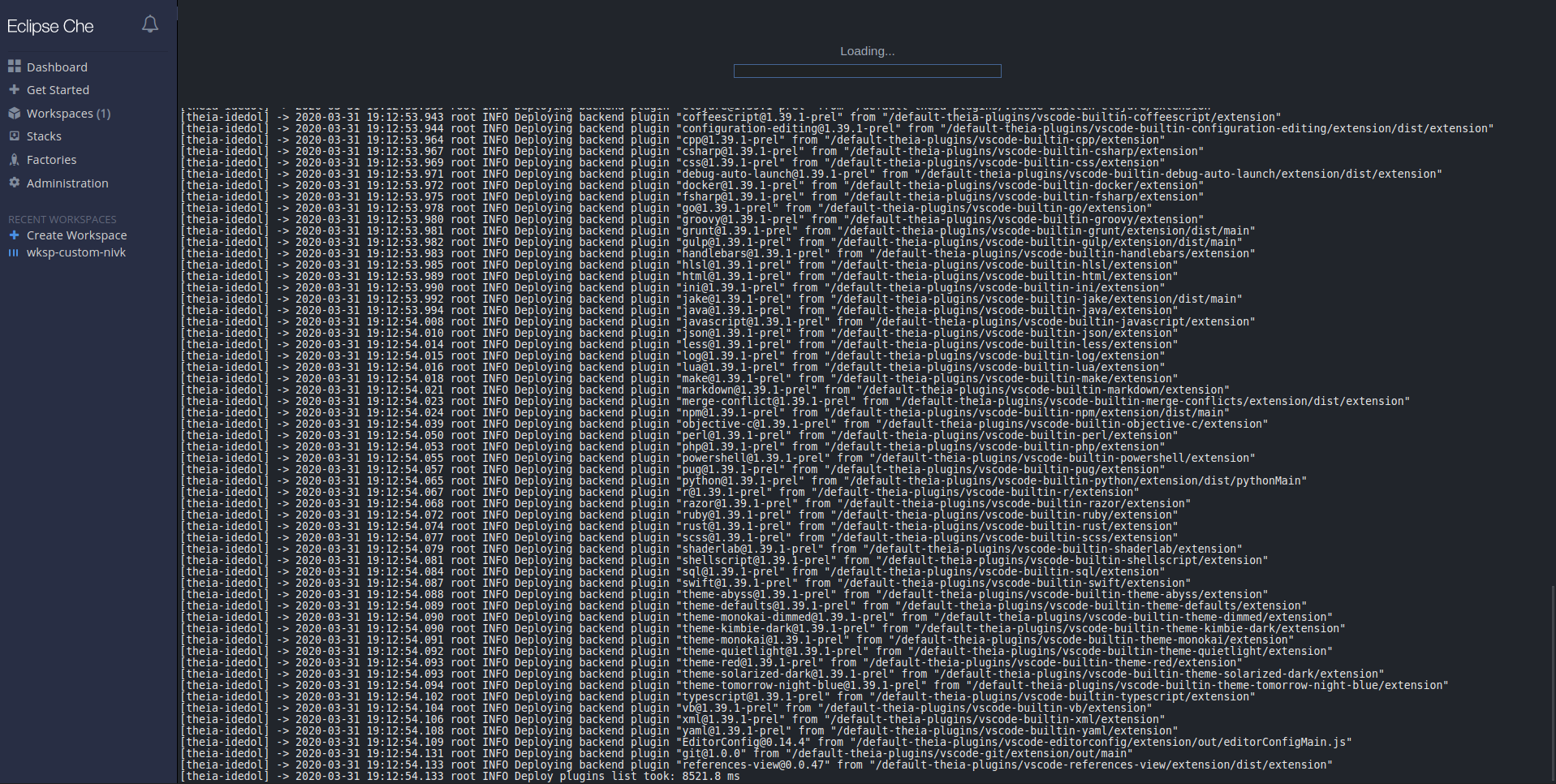
- Click the target workspace to see the logs.
The workspace logs are displayed:
7.4. Restarting a CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode after start failure
This section describes how to restart the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode after a failure during workspace start.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace that failed to start.
Procedure
Find the target workspace from the recent workspaces. Click on the target workspace to see the logs:
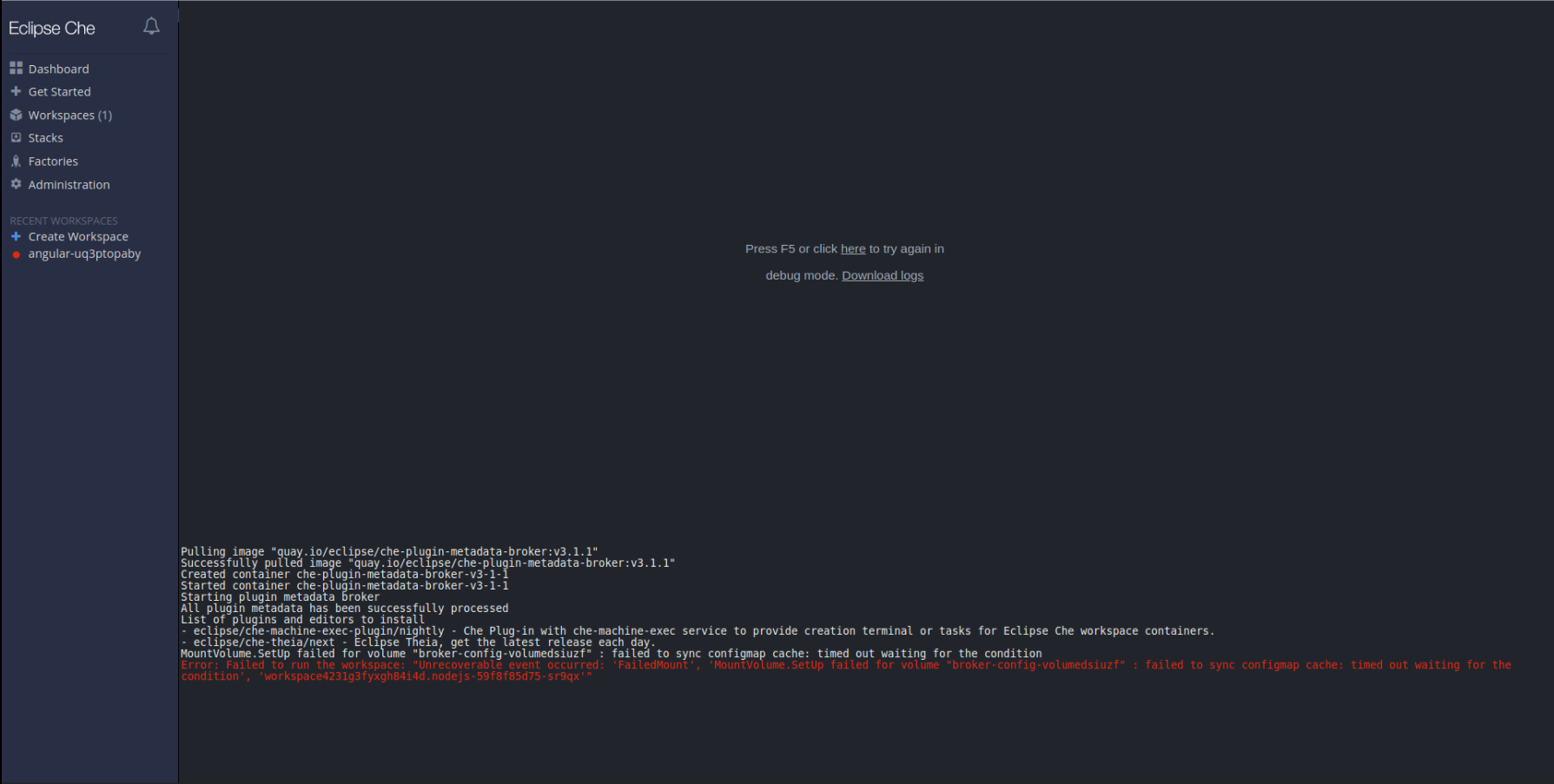
- Click the link for restarting in debug mode.
Download full logs after start fail with the Download logs link: