Chapter 4. Decision Model and Notation (DMN)
Decision Model and Notation (DMN) is a standard established by the Object Management Group (OMG) for describing and modeling operational decisions. DMN defines an XML schema that enables DMN models to be shared between DMN-compliant platforms and across organizations so that business analysts and business rules developers can collaborate in designing and implementing DMN decision services. The DMN standard is similar to and can be used together with the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard for designing and modeling business processes.
For more information about the background and applications of DMN, see the OMG Decision Model and Notation specification.
4.1. DMN conformance levels
The DMN specification defines three incremental levels of conformance in a software implementation. A product that claims compliance at one level must also be compliant with any preceding levels. For example, a conformance level 3 implementation must also include the supported components in conformance levels 1 and 2. For the formal definitions of each conformance level, see the OMG Decision Model and Notation specification.
The following list summarizes the three DMN conformance levels:
- Conformance level 1
- A DMN conformance level 1 implementation supports decision requirement diagrams (DRDs), decision logic, and decision tables, but decision models are not executable. Any language can be used to define the expressions, including natural, unstructured languages.
- Conformance level 2
- A DMN conformance level 2 implementation includes the requirements in conformance level 1, and supports Simplified Friendly Enough Expression Language (S-FEEL) expressions and fully executable decision models.
- Conformance level 3
- A DMN conformance level 3 implementation includes the requirements in conformance levels 1 and 2, and supports Friendly Enough Expression Language (FEEL) expressions, the full set of boxed expressions, and fully executable decision models.
Red Hat Decision Manager provides runtime support for DMN 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and 1.4 models at conformance level 3, and design support for DMN 1.2 models at conformance level 3. You can design your DMN models directly in Business Central or with the Red Hat Decision Manager DMN modeler in VS Code, or import existing DMN models into your Red Hat Decision Manager projects for deployment and execution. Any DMN 1.1 and 1.3 models (do not contain DMN 1.3 features) that you import into Business Central, open in the DMN designer, and save are converted to DMN 1.2 models.
4.2. DMN decision requirements diagram (DRD) components
A decision requirements diagram (DRD) is a visual representation of your DMN model. A DRD can represent part or all of the overall decision requirements graph (DRG) for the DMN model. DRDs trace business decisions using decision nodes, business knowledge models, sources of business knowledge, input data, and decision services.
The following table summarizes the components in a DRD:
| Component | Description | Notation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elements | Decision | Node where one or more input elements determine an output based on defined decision logic. | 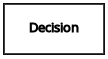 |
| Business knowledge model | Reusable function with one or more decision elements. Decisions that have the same logic but depend on different sub-input data or sub-decisions use business knowledge models to determine which procedure to follow. |  | |
| Knowledge source | External authorities, documents, committees, or policies that regulate a decision or business knowledge model. Knowledge sources are references to real-world factors rather than executable business rules. |  | |
| Input data | Information used in a decision node or a business knowledge model. Input data usually includes business-level concepts or objects relevant to the business, such as loan applicant data used in a lending strategy. |  | |
| Decision service | Top-level decision containing a set of reusable decisions published as a service for invocation. A decision service can be invoked from an external application or a BPMN business process. |  | |
| Requirement connectors | Information requirement | Connection from an input data node or decision node to another decision node that requires the information. |  |
| Knowledge requirement | Connection from a business knowledge model to a decision node or to another business knowledge model that invokes the decision logic. |  | |
| Authority requirement | Connection from an input data node or a decision node to a dependent knowledge source or from a knowledge source to a decision node, business knowledge model, or another knowledge source. |  | |
| Artifacts | Text annotation | Explanatory note associated with an input data node, decision node, business knowledge model, or knowledge source. |  |
| Association | Connection from an input data node, decision node, business knowledge model, or knowledge source to a text annotation. |  | |
The following table summarizes the permitted connectors between DRD elements:
| Starts from | Connects to | Connection type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision | Decision | Information requirement | 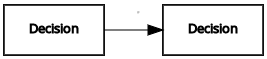 |
| Business knowledge model | Decision | Knowledge requirement | 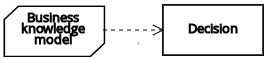 |
| Business knowledge model | 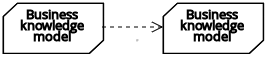 | ||
| Decision service | Decision | Knowledge requirement | 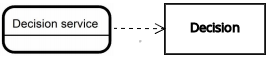 |
| Business knowledge model | 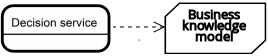 | ||
| Input data | Decision | Information requirement | 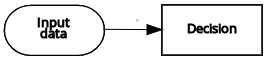 |
| Knowledge source | Authority requirement | 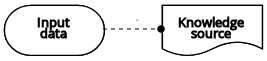 | |
| Knowledge source | Decision | Authority requirement | 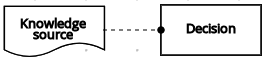 |
| Business knowledge model | 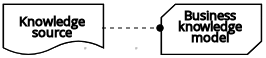 | ||
| Knowledge source | 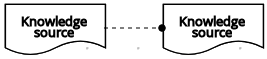 | ||
| Decision | Text annotation | Association | 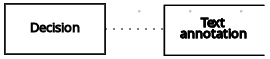 |
| Business knowledge model |  | ||
| Knowledge source |  | ||
| Input data |  |
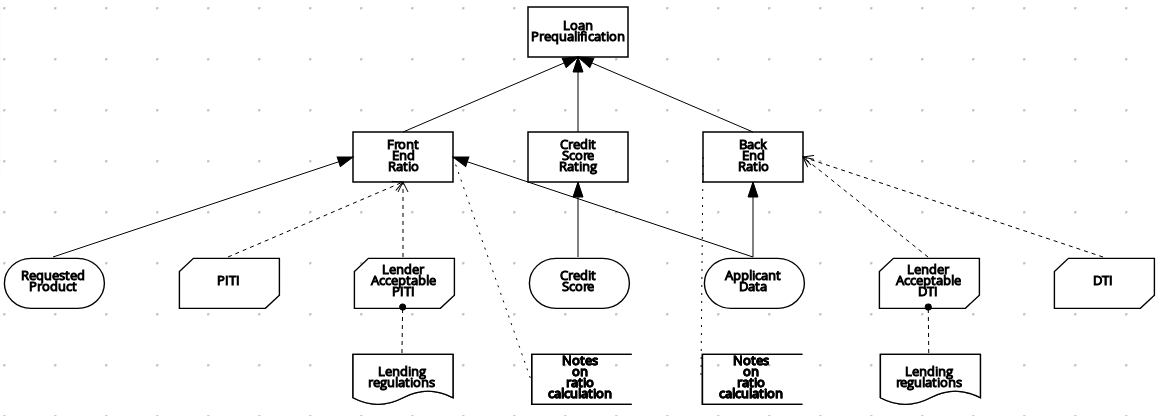
The following example DRD illustrates some of these DMN components in practice:
Figure 4.1. Example DRD: Loan prequalification
The following example DRD illustrates DMN components that are part of a reusable decision service:
Figure 4.2. Example DRD: Phone call handling as a decision service
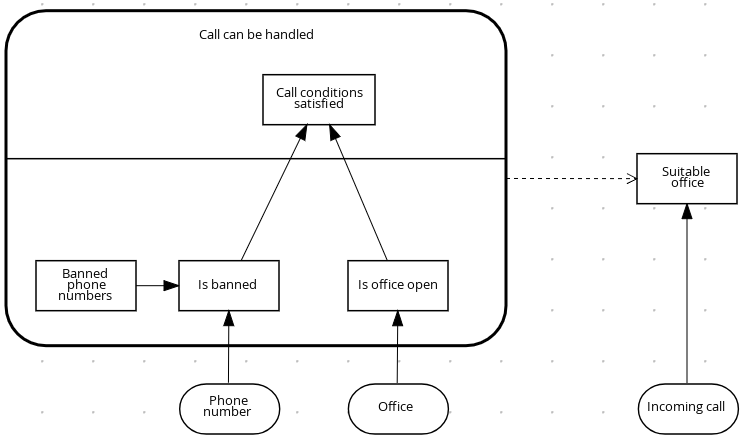
In a DMN decision service node, the decision nodes in the bottom segment incorporate input data from outside of the decision service to arrive at a final decision in the top segment of the decision service node. The resulting top-level decisions from the decision service are then implemented in any subsequent decisions or business knowledge requirements of the DMN model. You can reuse DMN decision services in other DMN models to apply the same decision logic with different input data and different outgoing connections.
4.3. Rule expressions in FEEL
Friendly Enough Expression Language (FEEL) is an expression language defined by the Object Management Group (OMG) DMN specification. FEEL expressions define the logic of a decision in a DMN model. FEEL is designed to facilitate both decision modeling and execution by assigning semantics to the decision model constructs. FEEL expressions in decision requirements diagrams (DRDs) occupy table cells in boxed expressions for decision nodes and business knowledge models.
For more information about FEEL in DMN, see the OMG Decision Model and Notation specification.
4.3.1. Data types in FEEL
Friendly Enough Expression Language (FEEL) supports the following data types:
- Numbers
- Strings
- Boolean values
- Dates
- Time
- Date and time
- Days and time duration
- Years and months duration
- Functions
- Contexts
- Ranges (or intervals)
- Lists
The DMN specification currently does not provide an explicit way of declaring a variable as a function, context, range, or list, but Red Hat Decision Manager extends the DMN built-in types to support variables of these types.
The following list describes each data type:
- Numbers
Numbers in FEEL are based on the IEEE 754-2008 Decimal 128 format, with 34 digits of precision. Internally, numbers are represented in Java as
BigDecimalswithMathContext DECIMAL128. FEEL supports only one number data type, so the same type is used to represent both integers and floating point numbers.FEEL numbers use a dot (
.) as a decimal separator. FEEL does not support-INF,+INF, orNaN. FEEL usesnullto represent invalid numbers.Red Hat Decision Manager extends the DMN specification and supports additional number notations:
-
Scientific: You can use scientific notation with the suffix
e<exp>orE<exp>. For example,1.2e3is the same as writing the expression1.2*10**3, but is a literal instead of an expression. -
Hexadecimal: You can use hexadecimal numbers with the prefix
0x. For example,0xffis the same as the decimal number255. Both uppercase and lowercase letters are supported. For example,0XFFis the same as0xff. -
Type suffixes: You can use the type suffixes
f,F,d,D,l, andL. These suffixes are ignored.
-
Scientific: You can use scientific notation with the suffix
- Strings
Strings in FEEL are any sequence of characters delimited by double quotation marks.
Example
"John Doe"
- Boolean values
-
FEEL uses three-valued boolean logic, so a boolean logic expression may have values
true,false, ornull. - Dates
Date literals are not supported in FEEL, but you can use the built-in
date()function to construct date values. Date strings in FEEL follow the format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document. The format is"YYYY-MM-DD"whereYYYYis the year with four digits,MMis the number of the month with two digits, andDDis the number of the day.Example:
date( "2017-06-23" )
Date objects have time equal to
"00:00:00", which is midnight. The dates are considered to be local, without a timezone.- Time
Time literals are not supported in FEEL, but you can use the built-in
time()function to construct time values. Time strings in FEEL follow the format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document. The format is"hh:mm:ss[.uuu][(+-)hh:mm]"wherehhis the hour of the day (from00to23),mmis the minutes in the hour, andssis the number of seconds in the minute. Optionally, the string may define the number of milliseconds (uuu) within the second and contain a positive (+) or negative (-) offset from UTC time to define its timezone. Instead of using an offset, you can use the letterzto represent the UTC time, which is the same as an offset of-00:00. If no offset is defined, the time is considered to be local.Examples:
time( "04:25:12" ) time( "14:10:00+02:00" ) time( "22:35:40.345-05:00" ) time( "15:00:30z" )
Time values that define an offset or a timezone cannot be compared to local times that do not define an offset or a timezone.
- Date and time
Date and time literals are not supported in FEEL, but you can use the built-in
date and time()function to construct date and time values. Date and time strings in FEEL follow the format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document. The format is"<date>T<time>", where<date>and<time>follow the prescribed XML schema formatting, conjoined byT.Examples:
date and time( "2017-10-22T23:59:00" ) date and time( "2017-06-13T14:10:00+02:00" ) date and time( "2017-02-05T22:35:40.345-05:00" ) date and time( "2017-06-13T15:00:30z" )
Date and time values that define an offset or a timezone cannot be compared to local date and time values that do not define an offset or a timezone.
ImportantIf your implementation of the DMN specification does not support spaces in the XML schema, use the keyword
dateTimeas a synonym ofdate and time.- Days and time duration
Days and time duration literals are not supported in FEEL, but you can use the built-in
duration()function to construct days and time duration values. Days and time duration strings in FEEL follow the format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document, but are restricted to only days, hours, minutes and seconds. Months and years are not supported.Examples:
duration( "P1DT23H12M30S" ) duration( "P23D" ) duration( "PT12H" ) duration( "PT35M" )
ImportantIf your implementation of the DMN specification does not support spaces in the XML schema, use the keyword
dayTimeDurationas a synonym ofdays and time duration.- Years and months duration
Years and months duration literals are not supported in FEEL, but you can use the built-in
duration()function to construct days and time duration values. Years and months duration strings in FEEL follow the format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document, but are restricted to only years and months. Days, hours, minutes, or seconds are not supported.Examples:
duration( "P3Y5M" ) duration( "P2Y" ) duration( "P10M" ) duration( "P25M" )
ImportantIf your implementation of the DMN specification does not support spaces in the XML schema, use the keyword
yearMonthDurationas a synonym ofyears and months duration.- Functions
FEEL has
functionliterals (or anonymous functions) that you can use to create functions. The DMN specification currently does not provide an explicit way of declaring a variable as afunction, but Red Hat Decision Manager extends the DMN built-in types to support variables of functions.Example:
function(a, b) a + b
In this example, the FEEL expression creates a function that adds the parameters
aandband returns the result.- Contexts
FEEL has
contextliterals that you can use to create contexts. Acontextin FEEL is a list of key and value pairs, similar to maps in languages like Java. The DMN specification currently does not provide an explicit way of declaring a variable as acontext, but Red Hat Decision Manager extends the DMN built-in types to support variables of contexts.Example:
{ x : 5, y : 3 }In this example, the expression creates a context with two entries,
xandy, representing a coordinate in a chart.In DMN 1.2, another way to create contexts is to create an item definition that contains the list of keys as attributes, and then declare the variable as having that item definition type.
The Red Hat Decision Manager DMN API supports DMN
ItemDefinitionstructural types in aDMNContextrepresented in two ways:-
User-defined Java type: Must be a valid JavaBeans object defining properties and getters for each of the components in the DMN
ItemDefinition. If necessary, you can also use the@FEELPropertyannotation for those getters representing a component name which would result in an invalid Java identifier. -
java.util.Mapinterface: The map needs to define the appropriate entries, with the keys corresponding to the component name in the DMNItemDefinition.
-
User-defined Java type: Must be a valid JavaBeans object defining properties and getters for each of the components in the DMN
- Ranges (or intervals)
FEEL has
rangeliterals that you can use to create ranges or intervals. Arangein FEEL is a value that defines a lower and an upper bound, where either can be open or closed. The DMN specification currently does not provide an explicit way of declaring a variable as arange, but Red Hat Decision Manager extends the DMN built-in types to support variables of ranges.The syntax of a range is defined in the following formats:
range := interval_start endpoint '..' endpoint interval_end interval_start := open_start | closed_start open_start := '(' | ']' closed_start := '[' interval_end := open_end | closed_end open_end := ')' | '[' closed_end := ']' endpoint := expressionThe expression for the endpoint must return a comparable value, and the lower bound endpoint must be lower than the upper bound endpoint.
For example, the following literal expression defines an interval between
1and10, including the boundaries (a closed interval on both endpoints):[ 1 .. 10 ]
The following literal expression defines an interval between 1 hour and 12 hours, including the lower boundary (a closed interval), but excluding the upper boundary (an open interval):
[ duration("PT1H") .. duration("PT12H") )You can use ranges in decision tables to test for ranges of values, or use ranges in simple literal expressions. For example, the following literal expression returns
trueif the value of a variablexis between0and100:x in [ 1 .. 100 ]
- Lists
FEEL has
listliterals that you can use to create lists of items. Alistin FEEL is represented by a comma-separated list of values enclosed in square brackets. The DMN specification currently does not provide an explicit way of declaring a variable as alist, but Red Hat Decision Manager extends the DMN built-in types to support variables of lists.Example:
[ 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
All lists in FEEL contain elements of the same type and are immutable. Elements in a list can be accessed by index, where the first element is
1. Negative indexes can access elements starting from the end of the list so that-1is the last element.For example, the following expression returns the second element of a list
x:x[2]
The following expression returns the second-to-last element of a list
x:x[-2]
Elements in a list can also be counted by the function
count, which uses the list of elements as the parameter.For example, the following expression returns
4:count([ 2, 3, 4, 5 ])
4.3.2. Built-in functions in FEEL
To promote interoperability with other platforms and systems, Friendly Enough Expression Language (FEEL) includes a library of built-in functions. The built-in FEEL functions are implemented in the Drools Decision Model and Notation (DMN) engine so that you can use the functions in your DMN decision services.
The following sections describe each built-in FEEL function, listed in the format NAME( PARAMETERS ). For more information about FEEL functions in DMN, see the OMG Decision Model and Notation specification.
4.3.2.1. Conversion functions
The following functions support conversion between values of different types. Some of these functions use specific string formats, such as the following examples:
-
date string: Follows the format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document, such as2020-06-01 time string: Follows one of the following formats:-
Format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document, such as
23:59:00z -
Format for a local time defined by ISO 8601 followed by
@and an IANA Timezone, such as00:01:00@Etc/UTC
-
Format defined in the XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes document, such as
-
date time string: Follows the format of adate stringfollowed byTand atime string, such as2012-12-25T11:00:00Z -
duration string: Follows the format ofdays and time durationandyears and months durationdefined in the XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Data Model, such asP1Y2M
- date( from ) - using date
Converts
fromto adatevalue.Table 4.3. Parameters Parameter Type Format fromstringdate stringExample
date( "2012-12-25" ) - date( "2012-12-24" ) = duration( "P1D" )
- date( from ) - using date and time
Converts
fromto adatevalue and sets time components to null.Table 4.4. Parameters Parameter Type fromdate and timeExample
date(date and time( "2012-12-25T11:00:00Z" )) = date( "2012-12-25" )
- date( year, month, day )
Produces a
datefrom the specified year, month, and day values.Table 4.5. Parameters Parameter Type yearnumbermonthnumberdaynumberExample
date( 2012, 12, 25 ) = date( "2012-12-25" )
- date and time( date, time )
Produces a
date and timefrom the specified date and ignores any time components and the specified time.Table 4.6. Parameters Parameter Type datedateordate and timetimetimeExample
date and time ( "2012-12-24T23:59:00" ) = date and time(date( "2012-12-24" ), time( "23:59:00" ))
- date and time( from )
Produces a
date and timefrom the specified string.Table 4.7. Parameters Parameter Type Format fromstringdate time stringExample
date and time( "2012-12-24T23:59:00" ) + duration( "PT1M" ) = date and time( "2012-12-25T00:00:00" )
- time( from )
Produces a
timefrom the specified string.Table 4.8. Parameters Parameter Type Format fromstringtime stringExample
time( "23:59:00z" ) + duration( "PT2M" ) = time( "00:01:00@Etc/UTC" )
- time( from )
Produces a
timefrom the specified parameter and ignores any date components.Table 4.9. Parameters Parameter Type fromtimeordate and timeExample
time(date and time( "2012-12-25T11:00:00Z" )) = time( "11:00:00Z" )
- time( hour, minute, second, offset? )
Produces a
timefrom the specified hour, minute, and second component values.Table 4.10. Parameters Parameter Type hournumberminutenumbersecondnumberoffset(Optional)days and time durationor nullExample
time( "23:59:00z" ) = time(23, 59, 0, duration( "PT0H" ))
- number( from, grouping separator, decimal separator )
Converts
fromto anumberusing the specified separators.Table 4.11. Parameters Parameter Type fromstringrepresenting a valid numbergrouping separatorSpace ( ), comma (
,), period (.), or nulldecimal separatorSame types as
grouping separator, but the values cannot matchExample
number( "1 000,0", " ", "," ) = number( "1,000.0", ",", "." )
- string( from )
Provides a string representation of the specified parameter.
Table 4.12. Parameters Parameter Type fromNon-null value
Examples
string( 1.1 ) = "1.1" string( null ) = null
- duration( from )
Converts
fromto adays and time durationvalue oryears and months durationvalue.Table 4.13. Parameters Parameter Type Format fromstringduration stringExamples
date and time( "2012-12-24T23:59:00" ) - date and time( "2012-12-22T03:45:00" ) = duration( "P2DT20H14M" ) duration( "P2Y2M" ) = duration( "P26M" )
- years and months duration( from, to )
Calculates the
years and months durationbetween the two specified parameters.Table 4.14. Parameters Parameter Type fromdateordate and timetodateordate and timeExample
years and months duration( date( "2011-12-22" ), date( "2013-08-24" ) ) = duration( "P1Y8M" )
4.3.2.2. Boolean functions
The following functions support Boolean operations.
- not( negand )
Performs the logical negation of the
negandoperand.Table 4.15. Parameters Parameter Type negandbooleanExamples
not( true ) = false not( null ) = null
4.3.2.3. String functions
The following functions support string operations.
In FEEL, Unicode characters are counted based on their code points.
- substring( string, start position, length? )
Returns the substring from the start position for the specified length. The first character is at position value
1.Table 4.16. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringstart positionnumberlength(Optional)numberExamples
substring( "testing",3 ) = "sting" substring( "testing",3,3 ) = "sti" substring( "testing", -2, 1 ) = "n" substring( "\U01F40Eab", 2 ) = "ab"
NoteIn FEEL, the string literal
"\U01F40Eab"is the🐎abstring (horse symbol followed byaandb).
- string length( string )
Calculates the length of the specified string.
Table 4.17. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringExamples
string length( "tes" ) = 3 string length( "\U01F40Eab" ) = 3
- upper case( string )
Produces an uppercase version of the specified string.
Table 4.18. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringExample
upper case( "aBc4" ) = "ABC4"
- lower case( string )
Produces a lowercase version of the specified string.
Table 4.19. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringExample
lower case( "aBc4" ) = "abc4"
- substring before( string, match )
Calculates the substring before the match.
Table 4.20. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringmatchstringExamples
substring before( "testing", "ing" ) = "test" substring before( "testing", "xyz" ) = ""
- substring after( string, match )
Calculates the substring after the match.
Table 4.21. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringmatchstringExamples
substring after( "testing", "test" ) = "ing" substring after( "", "a" ) = ""
- replace( input, pattern, replacement, flags? )
Calculates the regular expression replacement.
Table 4.22. Parameters Parameter Type inputstringpatternstringreplacementstringflags(Optional)stringNoteThis function uses regular expression parameters as defined in XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Functions and Operators.
Example
replace( "abcd", "(ab)|(a)", "[1=$1][2=$2]" ) = "[1=ab][2=]cd"
- contains( string, match )
Returns
trueif the string contains the match.Table 4.23. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringmatchstringExample
contains( "testing", "to" ) = false
- starts with( string, match )
Returns
trueif the string starts with the matchTable 4.24. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringmatchstringExample
starts with( "testing", "te" ) = true
- ends with( string, match )
Returns
trueif the string ends with the match.Table 4.25. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringmatchstringExample
ends with( "testing", "g" ) = true
- matches( input, pattern, flags? )
Returns
trueif the input matches the regular expression.Table 4.26. Parameters Parameter Type inputstringpatternstringflags(Optional)stringNoteThis function uses regular expression parameters as defined in XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Functions and Operators.
Example
matches( "teeesting", "^te*sting" ) = true
- split( string, delimiter )
Returns a list of the original string and splits it at the delimiter regular expression pattern.
Table 4.27. Parameters Parameter Type stringstringdelimiterstringfor a regular expression patternNoteThis function uses regular expression parameters as defined in XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Functions and Operators.
Examples
split( "John Doe", "\\s" ) = ["John", "Doe"] split( "a;b;c;;", ";" ) = ["a","b","c","",""]
4.3.2.4. List functions
The following functions support list operations.
In FEEL, the index of the first element in a list is 1. The index of the last element in a list can be identified as -1.
- list contains( list, element )
Returns
trueif the list contains the element.Table 4.28. Parameters Parameter Type listlistelementAny type, including null
Example
list contains( [1,2,3], 2 ) = true
- count( list )
Counts the elements in the list.
Table 4.29. Parameters Parameter Type listlistExamples
count( [1,2,3] ) = 3 count( [] ) = 0 count( [1,[2,3]] ) = 2
- min( list )
Returns the minimum comparable element in the list.
Table 4.30. Parameters Parameter Type listlistAlternative signature
min( e1, e2, ..., eN )
Examples
min( [1,2,3] ) = 1 min( 1 ) = 1 min( [1] ) = 1
- max( list )
Returns the maximum comparable element in the list.
Table 4.31. Parameters Parameter Type listlistAlternative signature
max( e1, e2, ..., eN )
Examples
max( 1,2,3 ) = 3 max( [] ) = null
- sum( list )
Returns the sum of the numbers in the list.
Table 4.32. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofnumberelementsAlternative signature
sum( n1, n2, ..., nN )
Examples
sum( [1,2,3] ) = 6 sum( 1,2,3 ) = 6 sum( 1 ) = 1 sum( [] ) = null
- mean( list )
Calculates the average (arithmetic mean) of the elements in the list.
Table 4.33. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofnumberelementsAlternative signature
mean( n1, n2, ..., nN )
Examples
mean( [1,2,3] ) = 2 mean( 1,2,3 ) = 2 mean( 1 ) = 1 mean( [] ) = null
- all( list )
Returns
trueif all elements in the list are true.Table 4.34. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofbooleanelementsAlternative signature
all( b1, b2, ..., bN )
Examples
all( [false,null,true] ) = false all( true ) = true all( [true] ) = true all( [] ) = true all( 0 ) = null
- any( list )
Returns
trueif any element in the list is true.Table 4.35. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofbooleanelementsAlternative signature
any( b1, b2, ..., bN )
Examples
any( [false,null,true] ) = true any( false ) = false any( [] ) = false any( 0 ) = null
- sublist( list, start position, length? )
Returns the sublist from the start position, limited to the length elements.
Table 4.36. Parameters Parameter Type listliststart positionnumberlength(Optional)numberExample
sublist( [4,5,6], 1, 2 ) = [4,5]
- append( list, item )
Creates a list that is appended to the item or items.
Table 4.37. Parameters Parameter Type listlistitemAny type
Example
append( [1], 2, 3 ) = [1,2,3]
- concatenate( list )
Creates a list that is the result of the concatenated lists.
Table 4.38. Parameters Parameter Type listlistExample
concatenate( [1,2],[3] ) = [1,2,3]
- insert before( list, position, newItem )
Creates a list with the
newIteminserted at the specified position.Table 4.39. Parameters Parameter Type listlistpositionnumbernewItemAny type
Example
insert before( [1,3],1,2 ) = [2,1,3]
- remove( list, position )
Creates a list with the removed element excluded from the specified position.
Table 4.40. Parameters Parameter Type listlistpositionnumberExample
remove( [1,2,3], 2 ) = [1,3]
- reverse( list )
Returns a reversed list.
Table 4.41. Parameters Parameter Type listlistExample
reverse( [1,2,3] ) = [3,2,1]
- index of( list, match )
Returns indexes matching the element.
Parameters
-
listof typelist -
matchof any type
Table 4.42. Parameters Parameter Type listlistmatchAny type
Example
index of( [1,2,3,2],2 ) = [2,4]
-
- union( list )
Returns a list of all the elements from multiple lists and excludes duplicates.
Table 4.43. Parameters Parameter Type listlistExample
union( [1,2],[2,3] ) = [1,2,3]
- distinct values( list )
Returns a list of elements from a single list and excludes duplicates.
Table 4.44. Parameters Parameter Type listlistExample
distinct values( [1,2,3,2,1] ) = [1,2,3]
- flatten( list )
Returns a flattened list.
Table 4.45. Parameters Parameter Type listlistExample
flatten( [[1,2],[[3]], 4] ) = [1,2,3,4]
- product( list )
Returns the product of the numbers in the list.
Table 4.46. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofnumberelementsAlternative signature
product( n1, n2, ..., nN )
Examples
product( [2, 3, 4] ) = 24 product( 2, 3, 4 ) = 24
- median( list )
Returns the median of the numbers in the list. If the number of elements is odd, the result is the middle element. If the number of elements is even, the result is the average of the two middle elements.
Table 4.47. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofnumberelementsAlternative signature
median( n1, n2, ..., nN )
Examples
median( 8, 2, 5, 3, 4 ) = 4 median( [6, 1, 2, 3] ) = 2.5 median( [ ] ) = null
- stddev( list )
Returns the standard deviation of the numbers in the list.
Table 4.48. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofnumberelementsAlternative signature
stddev( n1, n2, ..., nN )
Examples
stddev( 2, 4, 7, 5 ) = 2.081665999466132735282297706979931 stddev( [47] ) = null stddev( 47 ) = null stddev( [ ] ) = null
- mode( list )
Returns the mode of the numbers in the list. If multiple elements are returned, the numbers are sorted in ascending order.
Table 4.49. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofnumberelementsAlternative signature
mode( n1, n2, ..., nN )
Examples
mode( 6, 3, 9, 6, 6 ) = [6] mode( [6, 1, 9, 6, 1] ) = [1, 6] mode( [ ] ) = [ ]
4.3.2.4.1. Loop statements
Loop statements can transform lists or verify if some elements satisfy a specific condition:
- for in (list)
Iterates the elements of the list.
Table 4.50. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofAnyelementsExamples
for i in [1, 2, 3] return i * i = [1, 4, 9] for i in [1,2,3], j in [1,2,3] return i*j = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 6, 3, 6, 9]
- some in (list) satisfies (condition)
Returns to single boolean value (true or false), if any element in the list satisfies the condition.
Table 4.51. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofAnyelementsconditionboolean expression evaluated to true or false
Examples
some i in [1, 2, 3] satisfies i > 3 = true some i in [1, 2, 3] satisfies i > 4 = false
- every in (list) satisfies (condition)
Returns to single boolean value (true or false), if every element in the list satisfies the condition.
Table 4.52. Parameters Parameter Type listlistofAnyelementsconditionboolean expression evaluated to true or false
Examples
every i in [1, 2, 3] satisfies i > 1 = false every i in [1, 2, 3] satisfies i > 0 = true
4.3.2.5. Numeric functions
The following functions support number operations.
- decimal( n, scale )
Returns a number with the specified scale.
Table 4.53. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberscalenumberin the range[−6111..6176]NoteThis function is implemented to be consistent with the
FEEL:numberdefinition for rounding decimal numbers to the nearest even decimal number.Examples
decimal( 1/3, 2 ) = .33 decimal( 1.5, 0 ) = 2 decimal( 2.5, 0 ) = 2 decimal( 1.035, 2 ) = 1.04 decimal( 1.045, 2 ) = 1.04 decimal( 1.055, 2 ) = 1.06 decimal( 1.065, 2 ) = 1.06
- floor( n )
Returns the greatest integer that is less than or equal to the specified number.
Table 4.54. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExamples
floor( 1.5 ) = 1 floor( -1.5 ) = -2
- ceiling( n )
Returns the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the specified number.
Table 4.55. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExamples
ceiling( 1.5 ) = 2 ceiling( -1.5 ) = -1
- abs( n )
Returns the absolute value.
Table 4.56. Parameters Parameter Type nnumber,days and time duration, oryears and months durationExamples
abs( 10 ) = 10 abs( -10 ) = 10 abs( @"PT5H" ) = @"PT5H" abs( @"-PT5H" ) = @"PT5H"
- modulo( dividend, divisor )
Returns the remainder of the division of the dividend by the divisor. If either the dividend or divisor is negative, the result is of the same sign as the divisor.
NoteThis function is also expressed as
modulo(dividend, divisor) = dividend - divisor*floor(dividen d/divisor).Table 4.57. Parameters Parameter Type dividendnumberdivisornumberExamples
modulo( 12, 5 ) = 2 modulo( -12,5 )= 3 modulo( 12,-5 )= -3 modulo( -12,-5 )= -2 modulo( 10.1, 4.5 )= 1.1 modulo( -10.1, 4.5 )= 3.4 modulo( 10.1, -4.5 )= -3.4 modulo( -10.1, -4.5 )= -1.1
- sqrt( number )
Returns the square root of the specified number.
Table 4.58. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExample
sqrt( 16 ) = 4
- log( number )
Returns the logarithm of the specified number.
Table 4.59. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExample
decimal( log( 10 ), 2 ) = 2.30
- exp( number )
Returns Euler’s number
eraised to the power of the specified number.Table 4.60. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExample
decimal( exp( 5 ), 2 ) = 148.41
- odd( number )
Returns
trueif the specified number is odd.Table 4.61. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExamples
odd( 5 ) = true odd( 2 ) = false
- even( number )
Returns
trueif the specified number is even.Table 4.62. Parameters Parameter Type nnumberExamples
even( 5 ) = false even ( 2 ) = true
4.3.2.6. Date and time functions
The following functions support date and time operations.
- is( value1, value2 )
Returns
trueif both values are the same element in the FEEL semantic domain.Table 4.63. Parameters Parameter Type value1Any type
value2Any type
Examples
is( date( "2012-12-25" ), time( "23:00:50" ) ) = false is( date( "2012-12-25" ), date( "2012-12-25" ) ) = true is( time( "23:00:50z" ), time( "23:00:50" ) ) = false
4.3.2.7. Range functions
The following functions support temporal ordering operations to establish relationships between single scalar values and ranges of such values. These functions are similar to the components in the Health Level Seven (HL7) International Clinical Quality Language (CQL) 1.4 syntax.
- before( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAis before an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
before( point1 point2 ) -
before( point range ) -
before( range point ) -
before( range1,range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
point1 < point2 -
point < range.start or ( point = range.start and not(range.start included) ) -
range.end < point or ( range.end = point and not(range.end included) ) -
range1.end < range2.start or (( not(range1.end included) or not(range2.start included) ) and range1.end = range2.start )
Examples
before( 1, 10 ) = true before( 10, 1 ) = false before( 1, [1..10] ) = false before( 1, (1..10] ) = true before( 1, [5..10] ) = true before( [1..10], 10 ) = false before( [1..10), 10 ) = true before( [1..10], 15 ) = true before( [1..10], [15..20] ) = true before( [1..10], [10..20] ) = false before( [1..10), [10..20] ) = true before( [1..10], (10..20] ) = true
-
- after( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAis after an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
after( point1 point2 ) -
after( point range ) -
after( range, point ) -
after( range1 range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
point1 > point2 -
point > range.end or ( point = range.end and not(range.end included) ) -
range.start > point or ( range.start = point and not(range.start included) ) -
range1.start > range2.end or (( not(range1.start included) or not(range2.end included) ) and range1.start = range2.end )
Examples
after( 10, 5 ) = true after( 5, 10 ) = false after( 12, [1..10] ) = true after( 10, [1..10) ) = true after( 10, [1..10] ) = false after( [11..20], 12 ) = false after( [11..20], 10 ) = true after( (11..20], 11 ) = true after( [11..20], 11 ) = false after( [11..20], [1..10] ) = true after( [1..10], [11..20] ) = false after( [11..20], [1..11) ) = true after( (11..20], [1..11] ) = true
-
- meets( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAmeets an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
meets( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
range1.end included and range2.start included and range1.end = range2.start
Examples
meets( [1..5], [5..10] ) = true meets( [1..5), [5..10] ) = false meets( [1..5], (5..10] ) = false meets( [1..5], [6..10] ) = false
-
- met by( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAis met by an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
met by( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
range1.start included and range2.end included and range1.start = range2.end
Examples
met by( [5..10], [1..5] ) = true met by( [5..10], [1..5) ) = false met by( (5..10], [1..5] ) = false met by( [6..10], [1..5] ) = false
-
- overlaps( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAoverlaps an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
overlaps( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
( range1.end > range2.start or (range1.end = range2.start and (range1.end included or range2.end included)) ) and ( range1.start < range2.end or (range1.start = range2.end and range1.start included and range2.end included) )
Examples
overlaps( [1..5], [3..8] ) = true overlaps( [3..8], [1..5] ) = true overlaps( [1..8], [3..5] ) = true overlaps( [3..5], [1..8] ) = true overlaps( [1..5], [6..8] ) = false overlaps( [6..8], [1..5] ) = false overlaps( [1..5], [5..8] ) = true overlaps( [1..5], (5..8] ) = false overlaps( [1..5), [5..8] ) = false overlaps( [1..5), (5..8] ) = false overlaps( [5..8], [1..5] ) = true overlaps( (5..8], [1..5] ) = false overlaps( [5..8], [1..5) ) = false overlaps( (5..8], [1..5) ) = false
-
- overlaps before( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAoverlaps before an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
overlaps before( range1 range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
( range1.start < range2.start or (range1.start = range2.start and range1.start included and range2.start included) ) and ( range1.end > range2.start or (range1.end = range2.start and range1.end included and range2.start included) ) and ( range1.end < range2.end or (range1.end = range2.end and (not(range1.end included) or range2.end included )) )
Examples
overlaps before( [1..5], [3..8] ) = true overlaps before( [1..5], [6..8] ) = false overlaps before( [1..5], [5..8] ) = true overlaps before( [1..5], (5..8] ) = false overlaps before( [1..5), [5..8] ) = false overlaps before( [1..5), (1..5] ) = true overlaps before( [1..5], (1..5] ) = true overlaps before( [1..5), [1..5] ) = false overlaps before( [1..5], [1..5] ) = false
-
- overlaps after( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAoverlaps after an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
overlaps after( range1 range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
( range2.start < range1.start or (range2.start = range1.start and range2.start included and not( range1.start included)) ) and ( range2.end > range1.start or (range2.end = range1.start and range2.end included and range1.start included) ) and ( range2.end < range1.end or (range2.end = range1.end and (not(range2.end included) or range1.end included)) )
Examples
overlaps after( [3..8], [1..5] )= true overlaps after( [6..8], [1..5] )= false overlaps after( [5..8], [1..5] )= true overlaps after( (5..8], [1..5] )= false overlaps after( [5..8], [1..5) )= false overlaps after( (1..5], [1..5) )= true overlaps after( (1..5], [1..5] )= true overlaps after( [1..5], [1..5) )= false overlaps after( [1..5], [1..5] )= false overlaps after( (1..5), [1..5] )= false overlaps after( (1..5], [1..6] )= false overlaps after( (1..5], (1..5] )= false overlaps after( (1..5], [2..5] )= false
-
- finishes( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAfinishes an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
finishes( point, range ) -
finishes( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
range.end included and range.end = point -
range1.end included = range2.end included and range1.end = range2.end and ( range1.start > range2.start or (range1.start = range2.start and (not(range1.start included) or range2.start included)) )
Examples
finishes( 10, [1..10] ) = true finishes( 10, [1..10) ) = false finishes( [5..10], [1..10] ) = true finishes( [5..10), [1..10] ) = false finishes( [5..10), [1..10) ) = true finishes( [1..10], [1..10] ) = true finishes( (1..10], [1..10] ) = true
-
- finished by( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAis finished by an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
finished by( range, point ) -
finished by( range1 range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
range.end included and range.end = point -
range1.end included = range2.end included and range1.end = range2.end and ( range1.start < range2.start or (range1.start = range2.start and (range1.start included or not(range2.start included))) )
Examples
finished by( [1..10], 10 ) = true finished by( [1..10), 10 ) = false finished by( [1..10], [5..10] ) = true finished by( [1..10], [5..10) ) = false finished by( [1..10), [5..10) ) = true finished by( [1..10], [1..10] ) = true finished by( [1..10], (1..10] ) = true
-
- includes( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAincludes an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
includes( range, point ) -
includes( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
(range.start < point and range.end > point) or (range.start = point and range.start included) or (range.end = point and range.end included) -
( range1.start < range2.start or (range1.start = range2.start and (range1.start included or not(range2.start included))) ) and ( range1.end > range2.end or (range1.end = range2.end and (range1.end included or not(range2.end included))) )
Examples
includes( [1..10], 5 ) = true includes( [1..10], 12 ) = false includes( [1..10], 1 ) = true includes( [1..10], 10 ) = true includes( (1..10], 1 ) = false includes( [1..10), 10 ) = false includes( [1..10], [4..6] ) = true includes( [1..10], [1..5] ) = true includes( (1..10], (1..5] ) = true includes( [1..10], (1..10) ) = true includes( [1..10), [5..10) ) = true includes( [1..10], [1..10) ) = true includes( [1..10], (1..10] ) = true includes( [1..10], [1..10] ) = true
-
- during( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAis during an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
during( point, range ) -
during( range1 range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
(range.start < point and range.end > point) or (range.start = point and range.start included) or (range.end = point and range.end included) -
( range2.start < range1.start or (range2.start = range1.start and (range2.start included or not(range1.start included))) ) and ( range2.end > range1.end or (range2.end = range1.end and (range2.end included or not(range1.end included))) )
Examples
during( 5, [1..10] ) = true during( 12, [1..10] ) = false during( 1, [1..10] ) = true during( 10, [1..10] ) = true during( 1, (1..10] ) = false during( 10, [1..10) ) = false during( [4..6], [1..10] ) = true during( [1..5], [1..10] ) = true during( (1..5], (1..10] ) = true during( (1..10), [1..10] ) = true during( [5..10), [1..10) ) = true during( [1..10), [1..10] ) = true during( (1..10], [1..10] ) = true during( [1..10], [1..10] ) = true
-
- starts( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAstarts an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
starts( point, range ) -
starts( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
range.start = point and range.start included -
range1.start = range2.start and range1.start included = range2.start included and ( range1.end < range2.end or (range1.end = range2.end and (not(range1.end included) or range2.end included)) )
Examples
starts( 1, [1..10] ) = true starts( 1, (1..10] ) = false starts( 2, [1..10] ) = false starts( [1..5], [1..10] ) = true starts( (1..5], (1..10] ) = true starts( (1..5], [1..10] ) = false starts( [1..5], (1..10] ) = false starts( [1..10], [1..10] ) = true starts( [1..10), [1..10] ) = true starts( (1..10), (1..10) ) = true
-
- started by( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAis started by an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
started by( range, point ) -
started by( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
range.start = point and range.start included -
range1.start = range2.start and range1.start included = range2.start included and ( range2.end < range1.end or (range2.end = range1.end and (not(range2.end included) or range1.end included)) )
Examples
started by( [1..10], 1 ) = true started by( (1..10], 1 ) = false started by( [1..10], 2 ) = false started by( [1..10], [1..5] ) = true started by( (1..10], (1..5] ) = true started by( [1..10], (1..5] ) = false started by( (1..10], [1..5] ) = false started by( [1..10], [1..10] ) = true started by( [1..10], [1..10) ) = true started by( (1..10), (1..10) ) = true
-
- coincides( )
Returns
truewhen an elementAcoincides with an elementBand when the relevant requirements for evaluating totrueare also met.Signatures
-
coincides( point1, point2 ) -
coincides( range1, range2 )
Requirements for evaluating to
true-
point1 = point2 -
range1.start = range2.start and range1.start included = range2.start included and range1.end = range2.end and range1.end included = range2.end included
Examples
coincides( 5, 5 ) = true coincides( 3, 4 ) = false coincides( [1..5], [1..5] ) = true coincides( (1..5), [1..5] ) = false coincides( [1..5], [2..6] ) = false
-
4.3.2.8. Temporal functions
The following functions support general temporal operations.
- day of year( date )
Returns the Gregorian number of the day of the year.
Table 4.64. Parameters Parameter Type datedateordate and timeExample
day of year( date(2019, 9, 17) ) = 260
- day of week( date )
Returns the Gregorian day of the week:
"Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday", or"Sunday".Table 4.65. Parameters Parameter Type datedateordate and timeExample
day of week( date(2019, 9, 17) ) = "Tuesday"
- month of year( date )
Returns the Gregorian month of the year:
"January","February","March","April","May","June","July","August","September","October","November", or"December".Table 4.66. Parameters Parameter Type datedateordate and timeExample
month of year( date(2019, 9, 17) ) = "September"
- month of year( date )
Returns the Gregorian week of the year as defined by ISO 8601.
Table 4.67. Parameters Parameter Type datedateordate and timeExamples
week of year( date(2019, 9, 17) ) = 38 week of year( date(2003, 12, 29) ) = 1 week of year( date(2004, 1, 4) ) = 1 week of year( date(2005, 1, 1) ) = 53 week of year( date(2005, 1, 3) ) = 1 week of year( date(2005, 1, 9) ) = 1
4.3.2.9. Sort functions
The following functions support sorting operations.
- sort( list, precedes )
Returns a list of the same elements but ordered according to the sorting function.
Table 4.68. Parameters Parameter Type listlistprecedesfunctionExample
sort( list: [3,1,4,5,2], precedes: function(x,y) x < y ) = [1,2,3,4,5]
4.3.2.10. Context functions
The following functions support context operations.
- get value( m, key )
Returns the value from the context for the specified entry key.
Table 4.69. Parameters Parameter Type mcontextkeystringExamples
get value( {key1 : "value1"}, "key1" ) = "value1" get value( {key1 : "value1"}, "unexistent-key" ) = null- get entries( m )
Returns a list of key-value pairs for the specified context.
Table 4.70. Parameters Parameter Type mcontextExample
get entries( {key1 : "value1", key2 : "value2"} ) = [ { key : "key1", value : "value1" }, {key : "key2", value : "value2"} ]
4.3.3. Variable and function names in FEEL
Unlike many traditional expression languages, Friendly Enough Expression Language (FEEL) supports spaces and a few special characters as part of variable and function names. A FEEL name must start with a letter, ?, or _ element. The unicode letter characters are also allowed. Variable names cannot start with a language keyword, such as and, true, or every. The remaining characters in a variable name can be any of the starting characters, as well as digits, white spaces, and special characters such as +, -, /, *, ', and ..
For example, the following names are all valid FEEL names:
- Age
- Birth Date
- Flight 234 pre-check procedure
Several limitations apply to variable and function names in FEEL:
- Ambiguity
-
The use of spaces, keywords, and other special characters as part of names can make FEEL ambiguous. The ambiguities are resolved in the context of the expression, matching names from left to right. The parser resolves the variable name as the longest name matched in scope. You can use
( )to disambiguate names if necessary. - Spaces in names
The DMN specification limits the use of spaces in FEEL names. According to the DMN specification, names can contain multiple spaces but not two consecutive spaces.
In order to make the language easier to use and avoid common errors due to spaces, Red Hat Decision Manager removes the limitation on the use of consecutive spaces. Red Hat Decision Manager supports variable names with any number of consecutive spaces, but normalizes them into a single space. For example, the variable references
First Namewith one space andFirst Namewith two spaces are both acceptable in Red Hat Decision Manager.Red Hat Decision Manager also normalizes the use of other white spaces, like the non-breakable white space that is common in web pages, tabs, and line breaks. From a Red Hat Decision Manager FEEL engine perspective, all of these characters are normalized into a single white space before processing.
- The keyword
in -
The keyword
inis the only keyword in the language that cannot be used as part of a variable name. Although the specifications allow the use of keywords in the middle of variable names, the use ofinin variable names conflicts with the grammar definition offor,everyandsomeexpression constructs.
4.4. DMN decision logic in boxed expressions
Boxed expressions in DMN are tables that you use to define the underlying logic of decision nodes and business knowledge models in a decision requirements diagram (DRD). Some boxed expressions can contain other boxed expressions, but the top-level boxed expression corresponds to the decision logic of a single DRD artifact. While DRDs represent the flow of a DMN decision model, boxed expressions define the actual decision logic of individual nodes. DRDs and boxed expressions together form a complete and functional DMN decision model.
The following are the types of DMN boxed expressions:
- Decision tables
- Literal expressions
- Contexts
- Relations
- Functions
- Invocations
- Lists
Red Hat Decision Manager does not provide boxed list expressions in Business Central, but supports a FEEL list data type that you can use in boxed literal expressions. For more information about the list data type and other FEEL data types in Red Hat Decision Manager, see Section 4.3.1, “Data types in FEEL”.
All Friendly Enough Expression Language (FEEL) expressions that you use in your boxed expressions must conform to the FEEL syntax requirements in the OMG Decision Model and Notation specification.
4.4.1. DMN decision tables
A decision table in DMN is a visual representation of one or more business rules in a tabular format. You use decision tables to define rules for a decision node that applies those rules at a given point in the decision model. Each rule consists of a single row in the table, and includes columns that define the conditions (input) and outcome (output) for that particular row. The definition of each row is precise enough to derive the outcome using the values of the conditions. Input and output values can be FEEL expressions or defined data type values.
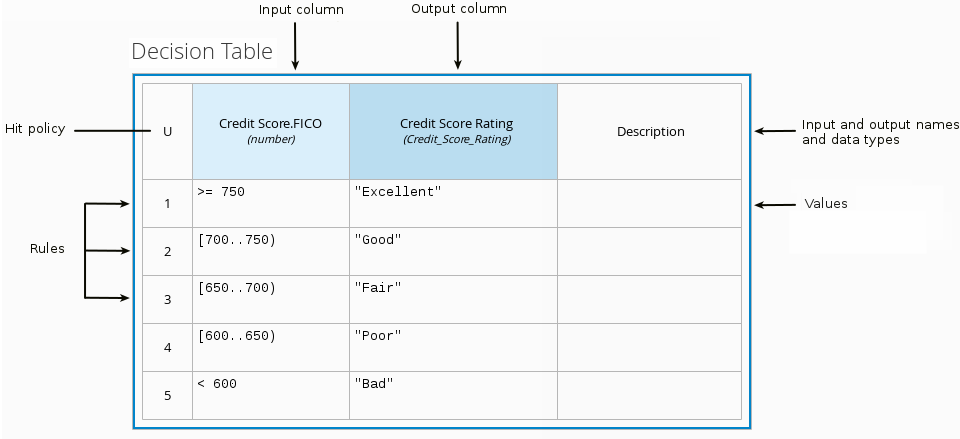
For example, the following decision table determines credit score ratings based on a defined range of a loan applicant’s credit score:
Figure 4.3. Decision table for credit score rating
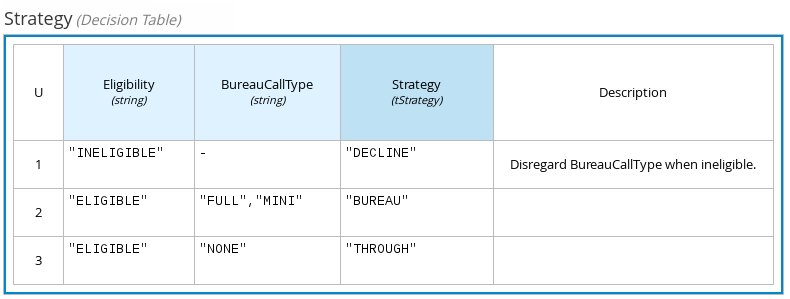
The following decision table determines the next step in a lending strategy for applicants depending on applicant loan eligibility and the bureau call type:
Figure 4.4. Decision table for lending strategy
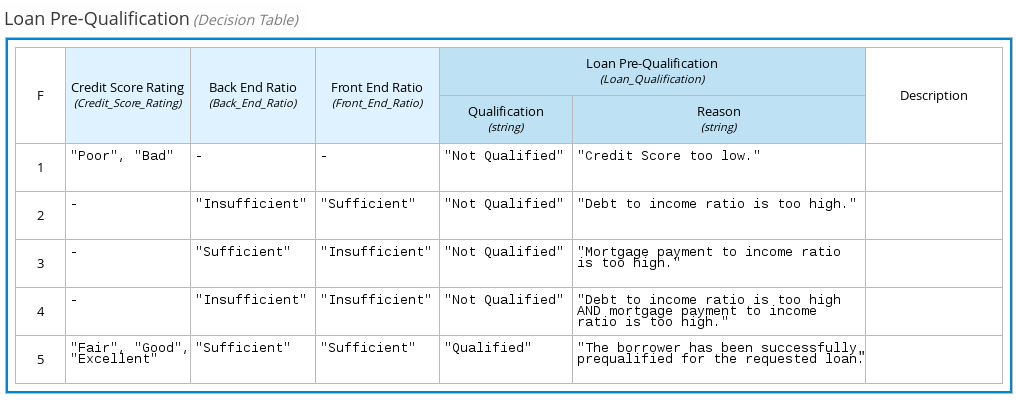
The following decision table determines applicant qualification for a loan as the concluding decision node in a loan prequalification decision model:
Figure 4.5. Decision table for loan prequalification
Decision tables are a popular way of modeling rules and decision logic, and are used in many methodologies (such as DMN) and implementation frameworks (such as Drools).
Red Hat Decision Manager supports both DMN decision tables and Drools-native decision tables, but they are different types of assets with different syntax requirements and are not interchangeable. For more information about Drools-native decision tables in Red Hat Decision Manager, see Designing a decision service using spreadsheet decision tables.
4.4.1.1. Hit policies in DMN decision tables
Hit policies determine how to reach an outcome when multiple rules in a decision table match the provided input values. For example, if one rule in a decision table applies a sales discount to military personnel and another rule applies a discount to students, then when a customer is both a student and in the military, the decision table hit policy must indicate whether to apply one discount or the other (Unique, First) or both discounts (Collect Sum). You specify the single character of the hit policy (U, F, C+) in the upper-left corner of the decision table.
The following decision table hit policies are supported in DMN:
- Unique (U): Permits only one rule to match. Any overlap raises an error.
- Any (A): Permits multiple rules to match, but they must all have the same output. If multiple matching rules do not have the same output, an error is raised.
- Priority (P): Permits multiple rules to match, with different outputs. The output that comes first in the output values list is selected.
- First (F): Uses the first match in rule order.
Collect (C+, C>, C<, C#): Aggregates output from multiple rules based on an aggregation function.
- Collect ( C ): Aggregates values in an arbitrary list.
- Collect Sum (C+): Outputs the sum of all collected values. Values must be numeric.
- Collect Min (C<): Outputs the minimum value among the matches. The resulting values must be comparable, such as numbers, dates, or text (lexicographic order).
- Collect Max (C>): Outputs the maximum value among the matches. The resulting values must be comparable, such as numbers, dates or text (lexicographic order).
- Collect Count (C#): Outputs the number of matching rules.
4.4.2. Boxed literal expressions
A boxed literal expression in DMN is a literal FEEL expression as text in a table cell, typically with a labeled column and an assigned data type. You use boxed literal expressions to define simple or complex node logic or decision data directly in FEEL for a particular node in a decision. Literal FEEL expressions must conform to FEEL syntax requirements in the OMG Decision Model and Notation specification.
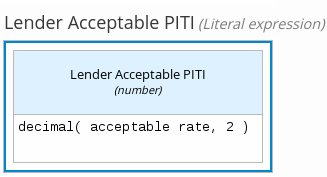
For example, the following boxed literal expression defines the minimum acceptable PITI calculation (principal, interest, taxes, and insurance) in a lending decision, where acceptable rate is a variable defined in the DMN model:
Figure 4.6. Boxed literal expression for minimum PITI value
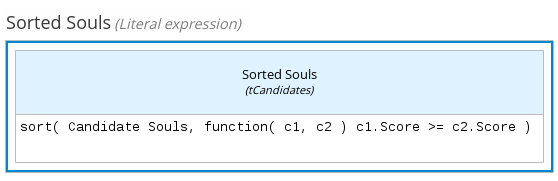
The following boxed literal expression sorts a list of possible dating candidates (soul mates) in an online dating application based on their score on criteria such as age, location, and interests:
Figure 4.7. Boxed literal expression for matching online dating candidates
4.4.3. Boxed context expressions
A boxed context expression in DMN is a set of variable names and values with a result value. Each name-value pair is a context entry. You use context expressions to represent data definitions in decision logic and set a value for a desired decision element within the DMN decision model. A value in a boxed context expression can be a data type value or FEEL expression, or can contain a nested sub-expression of any type, such as a decision table, a literal expression, or another context expression.
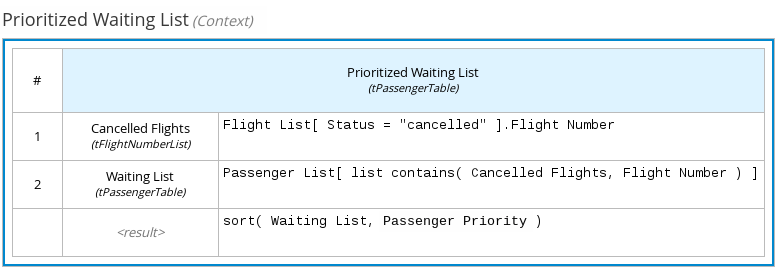
For example, the following boxed context expression defines the factors for sorting delayed passengers in a flight-rebooking decision model, based on defined data types (tPassengerTable, tFlightNumberList):
Figure 4.8. Boxed context expression for flight passenger waiting list
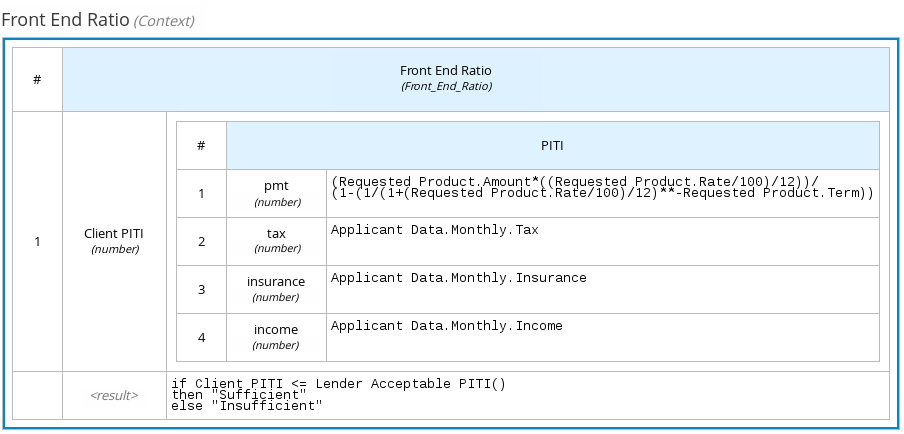
The following boxed context expression defines the factors that determine whether a loan applicant can meet minimum mortgage payments based on principal, interest, taxes, and insurance (PITI), represented as a front-end ratio calculation with a sub-context expression:
Figure 4.9. Boxed context expression for front-end client PITI ratio
4.4.4. Boxed relation expressions
A boxed relation expression in DMN is a traditional data table with information about given entities, listed as rows. You use boxed relation tables to define decision data for relevant entities in a decision at a particular node. Boxed relation expressions are similar to context expressions in that they set variable names and values, but relation expressions contain no result value and list all variable values based on a single defined variable in each column.
For example, the following boxed relation expression provides information about employees in an employee rostering decision:
Figure 4.10. Boxed relation expression with employee information
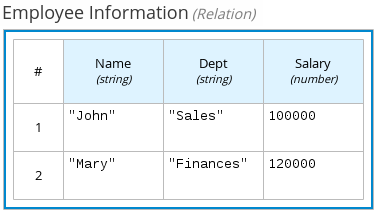
4.4.5. Boxed function expressions
A boxed function expression in DMN is a parameterized boxed expression containing a literal FEEL expression, a nested context expression of an external JAVA or PMML function, or a nested boxed expression of any type. By default, all business knowledge models are defined as boxed function expressions. You use boxed function expressions to call functions on your decision logic and to define all business knowledge models.
For example, the following boxed function expression determines airline flight capacity in a flight-rebooking decision model:
Figure 4.11. Boxed function expression for flight capacity

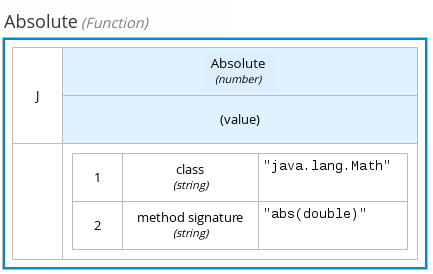
The following boxed function expression contains a basic Java function as a context expression for determining absolute value in a decision model calculation:
Figure 4.12. Boxed function expression for absolute value
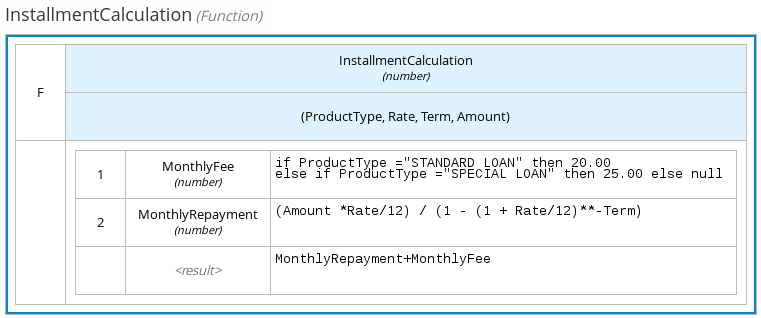
The following boxed function expression determines a monthly mortgage installment as a business knowledge model in a lending decision, with the function value defined as a nested context expression:
Figure 4.13. Boxed function expression for installment calculation in business knowledge model
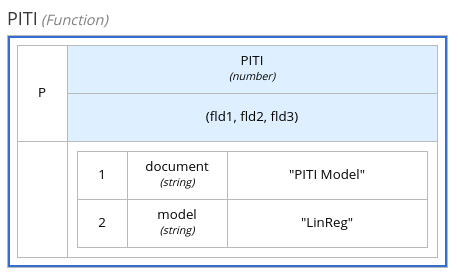
The following boxed function expression uses a PMML model included in the DMN file to define the minimum acceptable PITI calculation (principal, interest, taxes, and insurance) in a lending decision:
Figure 4.14. Boxed function expression with an included PMML model in business knowledge model
4.4.6. Boxed invocation expressions
A boxed invocation expression in DMN is a boxed expression that invokes a business knowledge model. A boxed invocation expression contains the name of the business knowledge model to be invoked and a list of parameter bindings. Each binding is represented by two boxed expressions on a row: The box on the left contains the name of a parameter and the box on the right contains the binding expression whose value is assigned to the parameter to evaluate the invoked business knowledge model. You use boxed invocations to invoke at a particular decision node a business knowledge model defined in the decision model.
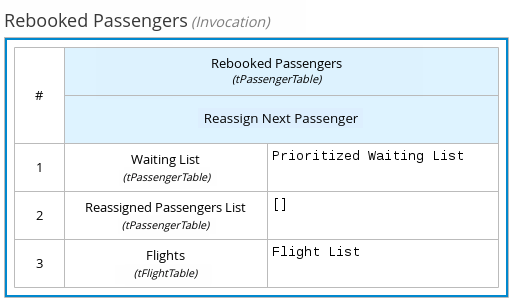
For example, the following boxed invocation expression invokes a Reassign Next Passenger business knowledge model as the concluding decision node in a flight-rebooking decision model:
Figure 4.15. Boxed invocation expression to reassign flight passengers
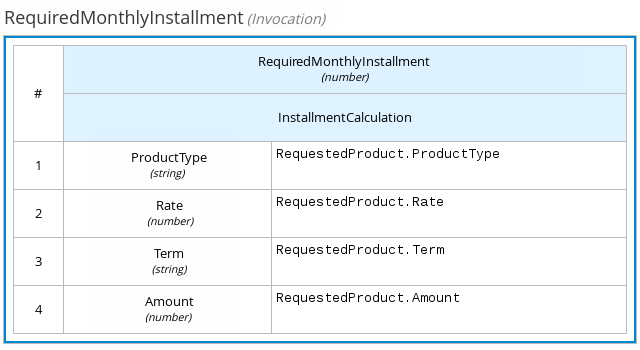
The following boxed invocation expression invokes an InstallmentCalculation business knowledge model to calculate a monthly installment amount for a loan before proceeding to affordability decisions:
Figure 4.16. Boxed invocation expression for required monthly installment
4.4.7. Boxed list expressions
A boxed list expression in DMN represents a FEEL list of items. You use boxed lists to define lists of relevant items for a particular node in a decision. You can also use literal FEEL expressions for list items in cells to create more complex lists.
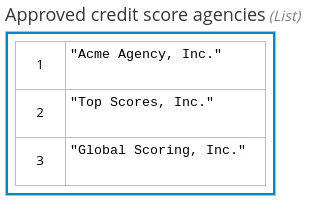
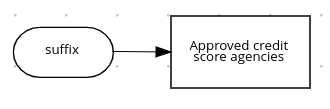
For example, the following boxed list expression identifies approved credit score agencies in a loan application decision service:
Figure 4.17. Boxed list expression for approved credit score agencies
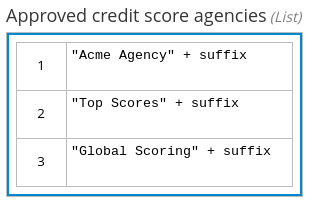
The following boxed list expression also identifies approved credit score agencies but uses FEEL logic to define the agency status (Inc., LLC, SA, GA) based on a DMN input node:
Figure 4.18. Boxed list expression using FEEL logic for approved credit score agency status
4.5. DMN model example
The following is a real-world DMN model example that demonstrates how you can use decision modeling to reach a decision based on input data, circumstances, and company guidelines. In this scenario, a flight from San Diego to New York is canceled, requiring the affected airline to find alternate arrangements for its inconvenienced passengers.
First, the airline collects the information necessary to determine how best to get the travelers to their destinations:
- Input data
- List of flights
- List of passengers
- Decisions
- Prioritize the passengers who will get seats on a new flight
- Determine which flights those passengers will be offered
- Business knowledge models
- The company process for determining passenger priority
- Any flights that have space available
- Company rules for determining how best to reassign inconvenienced passengers
The airline then uses the DMN standard to model its decision process in the following decision requirements diagram (DRD) for determining the best rebooking solution:
Figure 4.19. DRD for flight rebooking
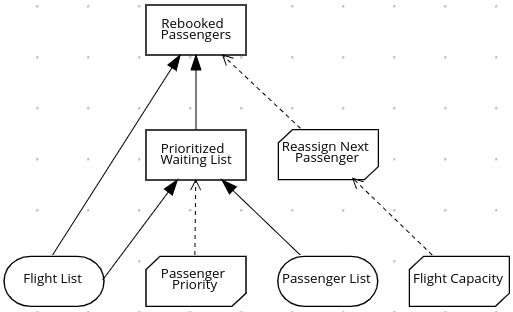
Similar to flowcharts, DRDs use shapes to represent the different elements in a process. Ovals contain the two necessary input data, rectangles contain the decision points in the model, and rectangles with clipped corners (business knowledge models) contain reusable logic that can be repeatedly invoked.
The DRD draws logic for each element from boxed expressions that provide variable definitions using FEEL expressions or data type values.
Some boxed expressions are basic, such as the following decision for establishing a prioritized waiting list:
Figure 4.20. Boxed context expression example for prioritized wait list

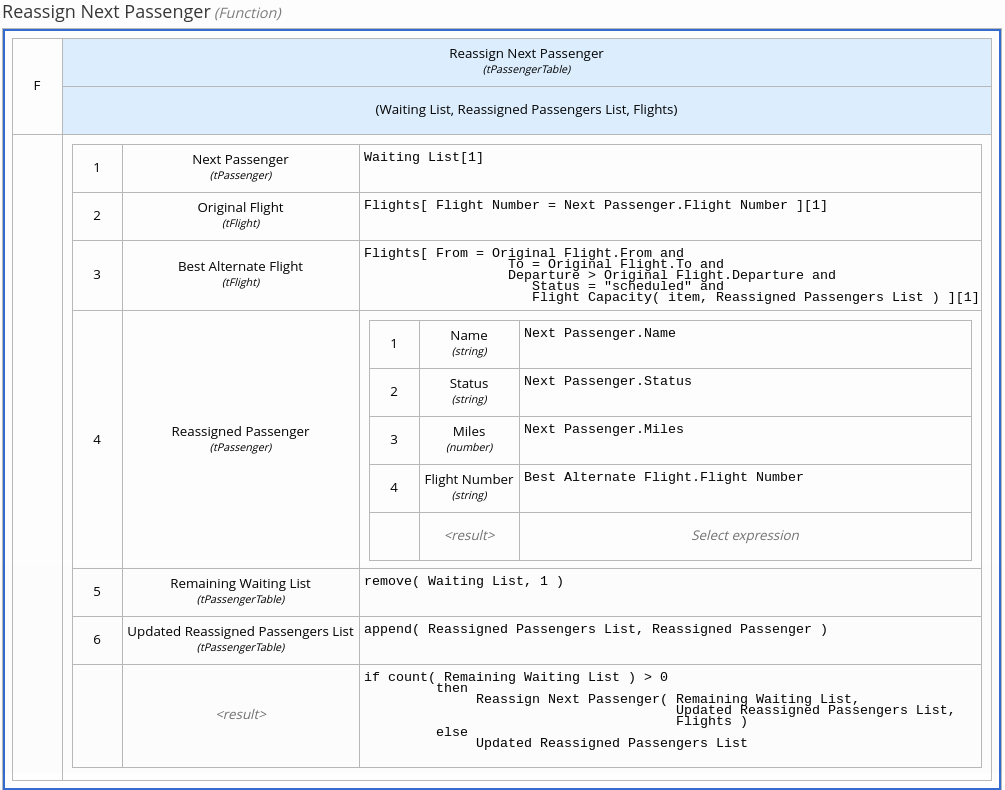
Some boxed expressions are more complex with greater detail and calculation, such as the following business knowledge model for reassigning the next delayed passenger:
Figure 4.21. Boxed function expression for passenger reassignment
The following is the DMN source file for this decision model:
<dmn:definitions xmlns="https://www.drools.org/kie-dmn/Flight-rebooking" xmlns:dmn="http://www.omg.org/spec/DMN/20151101/dmn.xsd" xmlns:feel="http://www.omg.org/spec/FEEL/20140401" id="_0019_flight_rebooking" name="0019-flight-rebooking" namespace="https://www.drools.org/kie-dmn/Flight-rebooking">
<dmn:itemDefinition id="_tFlight" name="tFlight">
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_Flight" name="Flight Number">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_From" name="From">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_To" name="To">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_Dep" name="Departure">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:dateTime</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_Arr" name="Arrival">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:dateTime</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_Capacity" name="Capacity">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:number</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tFlight_Status" name="Status">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
</dmn:itemDefinition>
<dmn:itemDefinition id="_tFlightTable" isCollection="true" name="tFlightTable">
<dmn:typeRef>tFlight</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemDefinition>
<dmn:itemDefinition id="_tPassenger" name="tPassenger">
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tPassenger_Name" name="Name">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tPassenger_Status" name="Status">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tPassenger_Miles" name="Miles">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:number</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
<dmn:itemComponent id="_tPassenger_Flight" name="Flight Number">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemComponent>
</dmn:itemDefinition>
<dmn:itemDefinition id="_tPassengerTable" isCollection="true" name="tPassengerTable">
<dmn:typeRef>tPassenger</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemDefinition>
<dmn:itemDefinition id="_tFlightNumberList" isCollection="true" name="tFlightNumberList">
<dmn:typeRef>feel:string</dmn:typeRef>
</dmn:itemDefinition>
<dmn:inputData id="i_Flight_List" name="Flight List">
<dmn:variable name="Flight List" typeRef="tFlightTable"/>
</dmn:inputData>
<dmn:inputData id="i_Passenger_List" name="Passenger List">
<dmn:variable name="Passenger List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
</dmn:inputData>
<dmn:decision name="Prioritized Waiting List" id="d_PrioritizedWaitingList">
<dmn:variable name="Prioritized Waiting List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:requiredInput href="#i_Passenger_List"/>
</dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:requiredInput href="#i_Flight_List"/>
</dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:knowledgeRequirement>
<dmn:requiredKnowledge href="#b_PassengerPriority"/>
</dmn:knowledgeRequirement>
<dmn:context>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Cancelled Flights" typeRef="tFlightNumberList"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Flight List[ Status = "cancelled" ].Flight Number</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Waiting List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Passenger List[ list contains( Cancelled Flights, Flight Number ) ]</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>sort( Waiting List, passenger priority )</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
</dmn:context>
</dmn:decision>
<dmn:decision name="Rebooked Passengers" id="d_RebookedPassengers">
<dmn:variable name="Rebooked Passengers" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:requiredDecision href="#d_PrioritizedWaitingList"/>
</dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:requiredInput href="#i_Flight_List"/>
</dmn:informationRequirement>
<dmn:knowledgeRequirement>
<dmn:requiredKnowledge href="#b_ReassignNextPassenger"/>
</dmn:knowledgeRequirement>
<dmn:invocation>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>reassign next passenger</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:binding>
<dmn:parameter name="Waiting List"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Prioritized Waiting List</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:binding>
<dmn:binding>
<dmn:parameter name="Reassigned Passengers List"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>[]</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:binding>
<dmn:binding>
<dmn:parameter name="Flights"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Flight List</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:binding>
</dmn:invocation>
</dmn:decision>
<dmn:businessKnowledgeModel id="b_PassengerPriority" name="passenger priority">
<dmn:encapsulatedLogic>
<dmn:formalParameter name="Passenger1" typeRef="tPassenger"/>
<dmn:formalParameter name="Passenger2" typeRef="tPassenger"/>
<dmn:decisionTable hitPolicy="UNIQUE">
<dmn:input id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_i_P1_Status" label="Passenger1.Status">
<dmn:inputExpression typeRef="feel:string">
<dmn:text>Passenger1.Status</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputExpression>
<dmn:inputValues>
<dmn:text>"gold", "silver", "bronze"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputValues>
</dmn:input>
<dmn:input id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_i_P2_Status" label="Passenger2.Status">
<dmn:inputExpression typeRef="feel:string">
<dmn:text>Passenger2.Status</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputExpression>
<dmn:inputValues>
<dmn:text>"gold", "silver", "bronze"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputValues>
</dmn:input>
<dmn:input id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_i_P1_Miles" label="Passenger1.Miles">
<dmn:inputExpression typeRef="feel:string">
<dmn:text>Passenger1.Miles</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputExpression>
</dmn:input>
<dmn:output id="b_Status_Priority_dt_o" label="Passenger1 has priority">
<dmn:outputValues>
<dmn:text>true, false</dmn:text>
</dmn:outputValues>
<dmn:defaultOutputEntry>
<dmn:text>false</dmn:text>
</dmn:defaultOutputEntry>
</dmn:output>
<dmn:rule id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r1">
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r1_i1">
<dmn:text>"gold"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r1_i2">
<dmn:text>"gold"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r1_i3">
<dmn:text>>= Passenger2.Miles</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:outputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r1_o1">
<dmn:text>true</dmn:text>
</dmn:outputEntry>
</dmn:rule>
<dmn:rule id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r2">
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r2_i1">
<dmn:text>"gold"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r2_i2">
<dmn:text>"silver","bronze"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r2_i3">
<dmn:text>-</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:outputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r2_o1">
<dmn:text>true</dmn:text>
</dmn:outputEntry>
</dmn:rule>
<dmn:rule id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r3">
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r3_i1">
<dmn:text>"silver"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r3_i2">
<dmn:text>"silver"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r3_i3">
<dmn:text>>= Passenger2.Miles</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:outputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r3_o1">
<dmn:text>true</dmn:text>
</dmn:outputEntry>
</dmn:rule>
<dmn:rule id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r4">
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r4_i1">
<dmn:text>"silver"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r4_i2">
<dmn:text>"bronze"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r4_i3">
<dmn:text>-</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:outputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r4_o1">
<dmn:text>true</dmn:text>
</dmn:outputEntry>
</dmn:rule>
<dmn:rule id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r5">
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r5_i1">
<dmn:text>"bronze"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r5_i2">
<dmn:text>"bronze"</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:inputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r5_i3">
<dmn:text>>= Passenger2.Miles</dmn:text>
</dmn:inputEntry>
<dmn:outputEntry id="b_Passenger_Priority_dt_r5_o1">
<dmn:text>true</dmn:text>
</dmn:outputEntry>
</dmn:rule>
</dmn:decisionTable>
</dmn:encapsulatedLogic>
<dmn:variable name="passenger priority" typeRef="feel:boolean"/>
</dmn:businessKnowledgeModel>
<dmn:businessKnowledgeModel id="b_ReassignNextPassenger" name="reassign next passenger">
<dmn:encapsulatedLogic>
<dmn:formalParameter name="Waiting List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:formalParameter name="Reassigned Passengers List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:formalParameter name="Flights" typeRef="tFlightTable"/>
<dmn:context>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Next Passenger" typeRef="tPassenger"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Waiting List[1]</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Original Flight" typeRef="tFlight"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Flights[ Flight Number = Next Passenger.Flight Number ][1]</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Best Alternate Flight" typeRef="tFlight"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Flights[ From = Original Flight.From and To = Original Flight.To and Departure > Original Flight.Departure and Status = "scheduled" and has capacity( item, Reassigned Passengers List ) ][1]</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Reassigned Passenger" typeRef="tPassenger"/>
<dmn:context>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Name" typeRef="feel:string"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Next Passenger.Name</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Status" typeRef="feel:string"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Next Passenger.Status</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Miles" typeRef="feel:number"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Next Passenger.Miles</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Flight Number" typeRef="feel:string"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>Best Alternate Flight.Flight Number</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
</dmn:context>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Remaining Waiting List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>remove( Waiting List, 1 )</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:variable name="Updated Reassigned Passengers List" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>append( Reassigned Passengers List, Reassigned Passenger )</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:contextEntry>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>if count( Remaining Waiting List ) > 0 then reassign next passenger( Remaining Waiting List, Updated Reassigned Passengers List, Flights ) else Updated Reassigned Passengers List</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:contextEntry>
</dmn:context>
</dmn:encapsulatedLogic>
<dmn:variable name="reassign next passenger" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:knowledgeRequirement>
<dmn:requiredKnowledge href="#b_HasCapacity"/>
</dmn:knowledgeRequirement>
</dmn:businessKnowledgeModel>
<dmn:businessKnowledgeModel id="b_HasCapacity" name="has capacity">
<dmn:encapsulatedLogic>
<dmn:formalParameter name="flight" typeRef="tFlight"/>
<dmn:formalParameter name="rebooked list" typeRef="tPassengerTable"/>
<dmn:literalExpression>
<dmn:text>flight.Capacity > count( rebooked list[ Flight Number = flight.Flight Number ] )</dmn:text>
</dmn:literalExpression>
</dmn:encapsulatedLogic>
<dmn:variable name="has capacity" typeRef="feel:boolean"/>
</dmn:businessKnowledgeModel>
</dmn:definitions>