Chapter 4. Creating a new Apache Camel JUnit test case
Overview
A common way of testing routes is to use JUnit. The design time tooling includes a wizard that simplifies creating a JUnit test case for your routes. The wizard uses the endpoints you specify to generate the starting point code and configuration for the test.
After you create the boilerplate JUnit test case, you need to modify it to add expectations and assertions specific to the route that you’ve created or modified, so the test is valid for the route.
Prerequisites
Before you create a new JUnit test case, you need to perform a preliminary task:
- If you are replacing an existing JUnit test case, you need to delete it before you create a new one. See the section called “Deleting and existing JUnit test case”.
-
If you are creating a new JUnit test case in a project that hasn’t one, you need to first create the project_root
/src/test/javafolder for the test case that is included in the build path. See the section called “Creating and adding thesrc/test/javafolder to the build path”.
Deleting and existing JUnit test case
-
In the Project Explorer view, expand the project’s root node to expose the <root_project>
/src/test/javafolder. Locate the JUnit test case file in the
/src/test/javafolder.Depending on which DSL the project is based on, the JUnit test case file is named
BlueprintXmlTest.javaorCamelContextXmlTest.java.Right-click the JUnit test case
.javafile to open the context menu, and then select Delete.The JUnit test case
.javafile disappears from the Project Explorer view.You can now create a new JUnit test case.
Creating and adding the src/test/java folder to the build path
- In the Project Explorer view, right-click the project’s root to open the context menu.
-
Select New
Folder to open the Create a new folder resource wizard. In the wizard’s project tree pane, expand the project’s root node and select the
srcfolder.Make sure <project_root>
/srcappears in the Enter or select the parent folder field.-
In Folder name, enter
/test/java. This folder will store the new JUnit test case you create. Click Finish.
In the Project Explorer view, the new
src/test/javafolder appears under thesrc/main/resourcesfolder. You can verify that this folder is on the class path by opening its context menu and selecting Build Path. If Remove from Build Path is a menu option, you know thesrc/test/javafolder is on the class path.You can now create a new JUnit test case.
Creating a JUnit test case
To create a new JUnit test case for your route:
-
In the Project Explorer view, select the routing context
.xmlfile in your project. Right-click it to open the context menu, and then select New
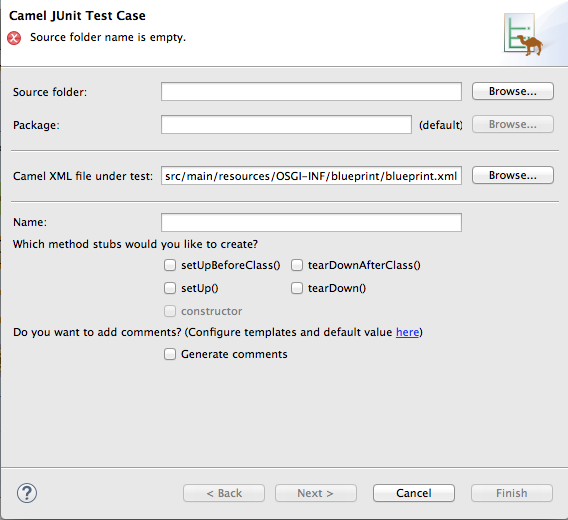
Camel Test Case to open the New Camel JUnit Test Case wizard, as shown in Figure 4.1, “New Camel JUnit Test Case wizard”. Figure 4.1. New Camel JUnit Test Case wizard
Alternatively, you can open the wizard by selecting File
New Other > Fuse > Camel Test Case from the menu bar. In Source folder, accept the default location of the source code for the test case, or enter another location.
You can click
 to search for a location.
to search for a location.
In Package, accept the default package name for the generated test code, or enter another package name.
You can click
 to search for a package.
to search for a package.
In Camel XML file under test, accept the default pathname of the routing context file that contains the route you want to test, or enter another pathname.
You can click
 to search for a context file.
to search for a context file.
- In Name, accept the default name for the generated test class, or enter another name.
- Select the method stubs you want to include in the generated code.
- If you want to include the default generated comments in the generated code, check the Generate comments box.
Click
 to open the Test Endpoints page. For example, Figure 4.2, “New Camel JUnit Test Case page” shows a route’s input and output file endpoints selected.
to open the Test Endpoints page. For example, Figure 4.2, “New Camel JUnit Test Case page” shows a route’s input and output file endpoints selected.
Figure 4.2. New Camel JUnit Test Case page

- Under Available endpoints, select the endpoints you want to test. Click the checkbox next to any selected endpoint to deselect it.
Click
 .
Note
.
NoteIf prompted, add JUnit to the build path.
The artifacts for the test are added to your project and appear in the Project Explorer view under src/test/java. The class implementing the test case opens in the Java editor.