2.3. Kickstart Profiles
Kickstart profiles specify the configuration options to be used for the installation.
Kickstart profiles can be created using a wizard interface, which generates a profile based on the answers you give to a series of questions. They can also be created using the raw method, which gives complete control over the contents of the profile.
Procedure 2.3. Creating a Kickstart Profile with a Wizard
- Select
- Provide an appropriate Label, and select the desired Base Channel and Kickstartable Tree
- Select the desired Virtualization Type. See Virtualization Types for more information about virtualization types. Click next to continue.
- Select the download location for the kickstart profile. For custom distributions, enter the location of its tree as a URL (both HTTP and FTP are supported), otherwise, use the default option. Click next to continue.
- Enter the root password and click finish to complete the profile creation.
- The complete kickstart profile will be created. View the profile by clicking Kickstart File.
Procedure 2.4. Creating a Kickstart Profile with the Raw Method
- Select
- Provide an appropriate label, and select the desired distribution
- Select the desired Virtualization Type. See Virtualization Types for more information about virtualization types.
- If there is an existing kickstart profile, upload the file. Otherwise, write the kickstart profile in the File Contents text box.Here is a sample raw kickstart that can be used as a starting point:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The RHN Satellite server does not handle the specified distribution as the
urlin the kickstart, so remember to include theurl --urloption in the profile, similar to the following:url --url http://satellite.example.com/ks/dist/org/1/my_distro
url --url http://satellite.example.com/ks/dist/org/1/my_distroCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replacemy_distrowith the distribution label and1with your org id. - Raw kickstart profiles use
$http_serverinstead of the Satellite's host name. This will be filled in automatically when the kickstart template is rendered. - The
redhat_registersnippet is used to handle registration.
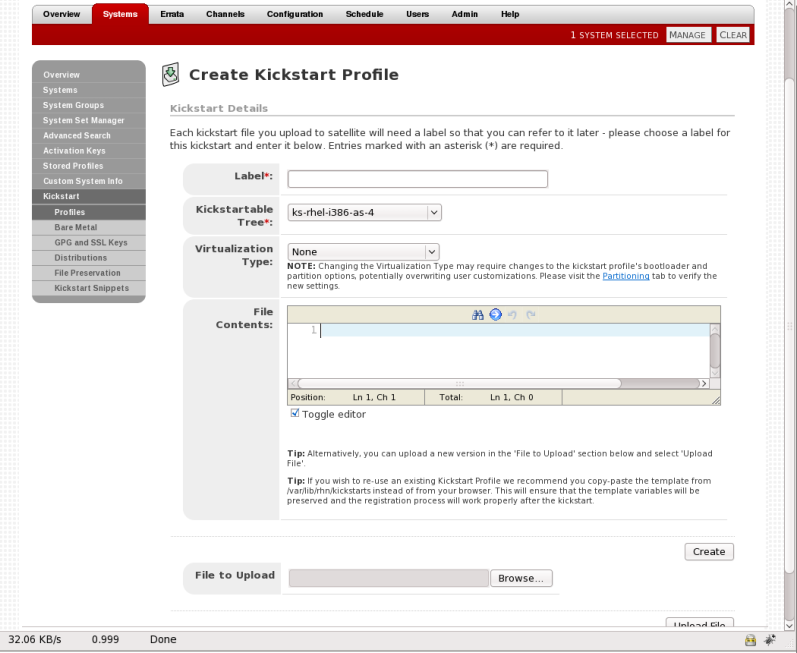
Figure 2.2. Raw Kickstart
Virtualization Types
All kickstart profiles have a virtualization type associated with them. This table outlines the different options:
| Type | Description | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| none | No virtualization | Use this type for normal provisioning, bare metal installations, and virtualized installation that are not Xen or KVM (such as VMware, or Virtage) |
| KVM Virtualized Guest | KVM guests | Use this type for provisioning KVM guests |
| Xen Fully-Virtualized Guest | Xen guests | Use this type for provisioning Xen guests
Note
This option requires hardware support on the host, but does not require a modified operating system on the guest.
|
| Xen Para-Virtualized Guest | Xen Guests | Use this type for provisioning a virtual guest with Xen para-virtualization. Para-virtualization is the fastest virtualization mode. It requires a PAE flag on the system CPU, and a modified operating system. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 supports guests under para-virtualization. |
| Xen Virtualization Host | Xen hosts | Use this type for provisioning a virtual host with Xen para-virtualization. Xen para-virtualized guests and hosts are supported, if the hardware is compatible. |
Kickstart profiles created to be used as Xen hosts must include the
kernel-xen package in the %packages section.
Kickstart profiles created to be used as KVM hosts must include the
qemu package in the %packages section.
Fully virtualized systems may require virtualization support to be turned on in the computer's BIOS menu.
Note
For more information about kickstart, see the Kickstart Installations chapter in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Installation Guide.