Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 6. Requesting task recommendations
Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed is integrated into Visual Studio (VS) Code through the Ansible VS Code extension. You can request code recommendations for your task intent by using Ansible VS Code extension.
6.1. Overview
You can perform the following tasks from the Ansible VS Code extension:
Create single task or multitask requests by using natural language prompts
Create a single task prompt
Write a description of your task in the
- name:key of a new task line in your Ansible file. For example, to automate a task of installing PostgreSQL server, you can enter the prompt- name: Install postgresql-server.Create a multitask prompt
Place your cursor on a new line in your Ansible YAML file at the correct indentation, and start your prompt with a Pound key (#).
Write the descriptions of your tasks, separating each prompt by using Ampersand symbols (&). For example, to automate a multitask of installing PostgreSQL server and running the initial PostgreSQL setup command, you can enter the prompt
# Install postgresql-server & run postgresql-setup command.The Ansible Lightspeed service reads the text, interacts with the IBM watsonx Code Assistant model, and generates Ansible task recommendations based on your natural language prompt.
NoteCurrently, Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed supports user prompts in English language only. However, there could be instances where the training data that was used to train the IBM watsonx Code Assistant models included non-English language. In such scenarios, the model can generate code recommendations for prompts made in the same non-English language, but the generated code recommendations might or might not be accurate.
View the content source matching results
For each generated code recommendation, Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed lists content source matches, including details such as potential source, content author, and relevant licenses. You can use this data to gain insight into potential training data sources used to generate the code recommendations.
Provide feedback on the Ansible Lightspeed service
The Ansible Lightspeed service learns your organizational patterns and improves the code recommendation experience over time. You can provide feedback on whether the generated code recommendations were suitable for your task intent. This feedback enables Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant to improve on the quality of its suggestions.
6.1.1. Best practices to improve the recommended guidance
Follow these guidelines to improve the likelihood of a quality code recommendation.
- Ensure that your YAML file is properly formatted. See the Ansible YAML syntax guidelines for details.
Avoid context switching within a single playbook file.
The Ansible Lightspeed service attempts to correlate earlier tasks to the active recommendation, and the entire contents of the file before the cursor position are used as context by the model. If the earlier task is not relevant to your prompt, VS code provides inline suggestions instead of code recommendations.
Reword your natural language prompts to get code recommendations that match your task intent.
If you get a recommendation that does not align with the intent of your task name, then rewording your prompt to provide more information about what is desired can lead to improved results.
Use descriptive prompts and provide additional content to improve the code recommendations.
Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed reads the full Ansible YAML file when generating a code recommendation. Using descriptive prompts and having additional YAML file content related to the desired task improves the code recommendation. For example, you can add the previous Ansible tasks and appropriate playbook and variable names to improve the code recommendations.
6.2. Requesting code recommendations for a single task
You can request code recommendations for a single task by entering natural language prompts in Ansible VS Code extension. For example, to automate a task of installing a PostgreSQL server, you can enter the prompt - name: Install postgresql-server. The Ansible Lightspeed service reads the text, interacts with the IBM watsonx Code Assistant model, and generates the code recommendations.
Prerequisites
- You are part of an organization that has a trial or paid subscription to both Ansible Automation Platform and IBM watsonx Code Assistant.
- You have installed and configured the Ansible VS Code extension.
Procedure
- Log in to VS Code with your Red Hat account.
Create a new YAML file or use an existing YAML file:
Create a YAML file:
-
Select
. - From the lower right of the screen, click Plain Text, and in the language mode, select Ansible.
-
Save the file as a YAML file format extension (
.ymlor.yaml).
-
Select
Use an existing YAML file:
On the bottom right of the screen, click the existing language mode, and in the language mode settings, select Ansible.
NoteIf you do not see the language mode section in your VS Code editor, from the Command Palette, select
.
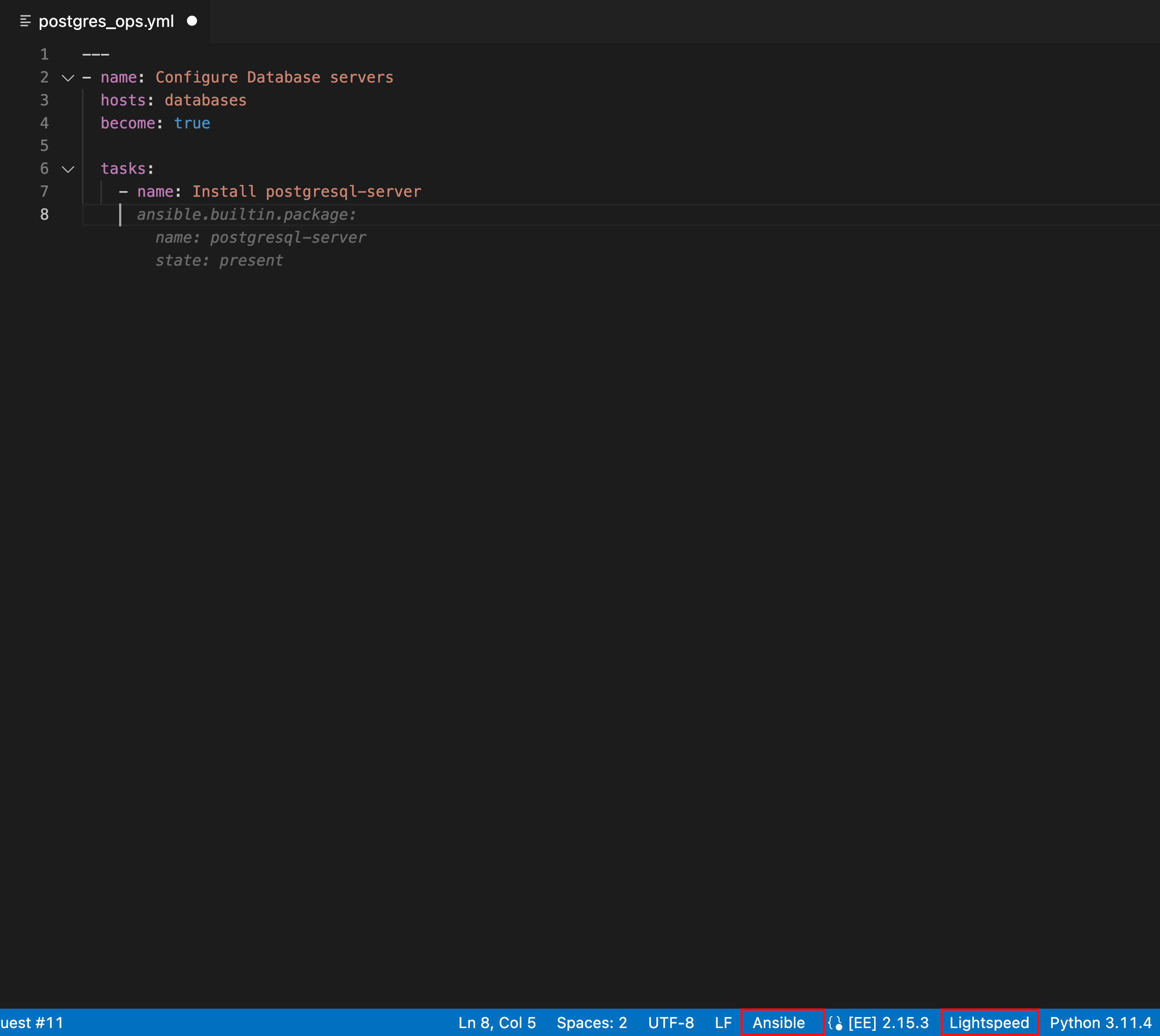
Verify that you see an entry for Lightspeed on the status bar at the lower right of VS Code.
If Ansible is already selected as the desired language but the Lightspeed entry is not displayed, re-select Ansible as the language mode. The following illustration shows Lightspeed and Ansible entries on the VS Code status bar.
Figure 6.1. Ansible and Lightspeed set as selected language mode
Optional: If you see an error message about missing Ansible lint, you can install the missing module or disable it. Perform any one of the following tasks:
- Install Ansible lint: For installation information, see the Installing section of the Ansible Lint documentation.
Disable Ansible lint:
-
From the Activity bar, click the Extensions icon
 .
.
- From the Installed extensions list, select Ansible.
- From the Ansible extension page, click the Settings icon and select Extension Settings.
- Clear the Ansible › Validation › Lint: Enabled checkbox.
-
From the Activity bar, click the Extensions icon
Create a playbook or use an existing playbook.
For more information, see Creating playbooks in the Ansible Automation Platform Creator Guide.
In the playbook, provide the following information to request code recommendations for a single task:
-
Add a new Ansible task by starting a new line with
- name:at the correct indentation. -
Add a detailed natural language prompt in the task description after
- name:on the same line. For example, you can specify the following single task prompt:- name: Install postgresql-server Press Enter directly after the task description. Keep the cursor at the same location in your file, and wait for the code recommendation results to populate.
The Ansible Lightspeed service is engaged, and it starts generating code recommendations for a single task.
ImportantAnsible Lightspeed service takes around 5 seconds per task to populate the code recommendations. If you are using a multitask prompt, the Ansible Lightspeed service takes a bit longer (number of tasks times 5 seconds) to populate the results. Do not move your cursor or press any key while the code recommendation is being generated. If you change the cursor location or press any key, Ansible VS Code extension cancels the request and the Ansible Lightspeed service does not process your request.
When the Ansible Lightspeed service is engaged, a Lightspeed processing status indicator is displayed in the lower right of the screen to denote that your code recommendation is being generated.

-
Add a new Ansible task by starting a new line with
View your code recommendations and ensure that the recommendations match your task intent.
The following illustration shows the code recommendations generated by the Ansible Lightspeed service for the single task Install postgresql-server:
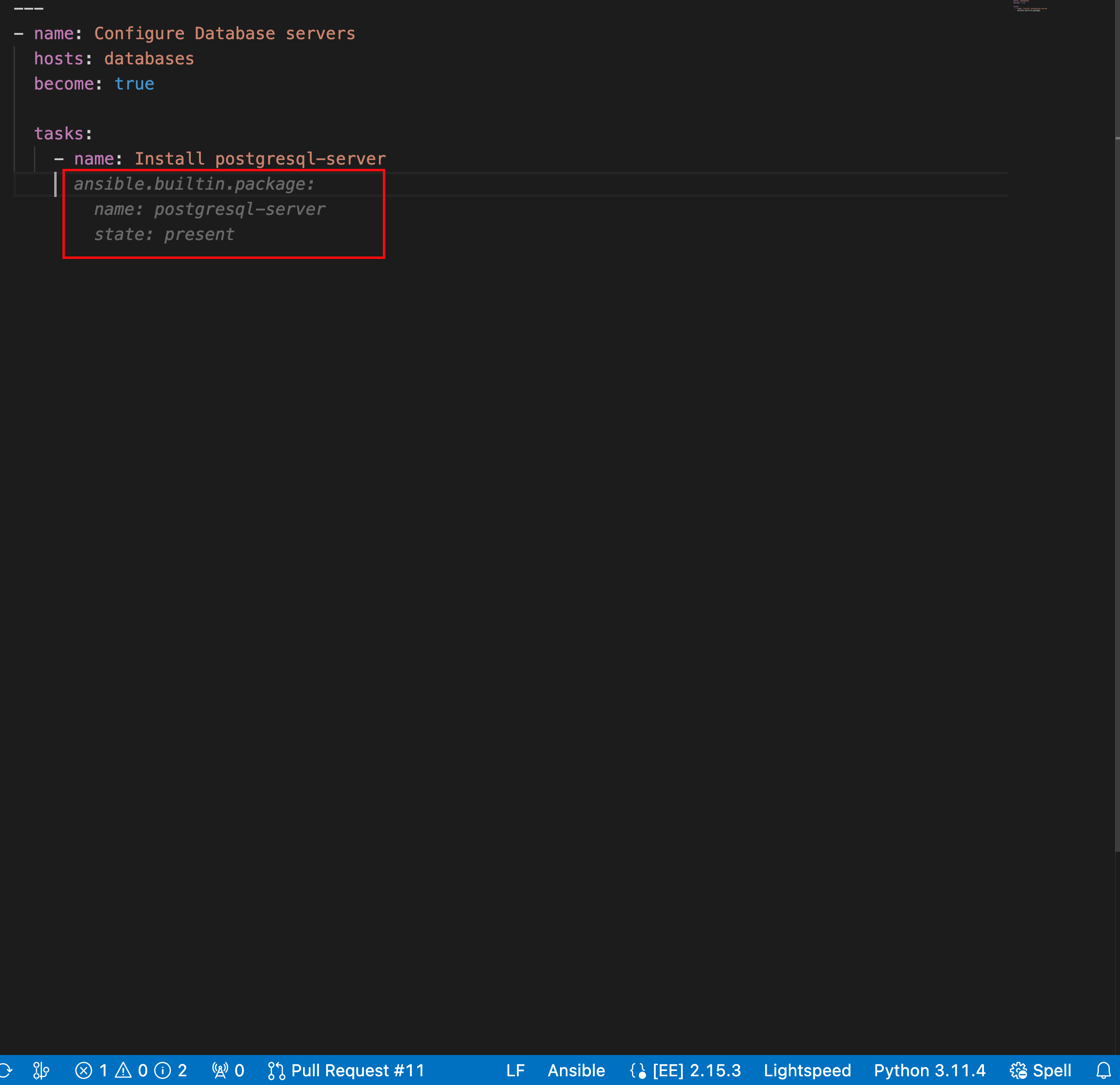
Accept or reject the code recommendations:
- To accept a code recommendation, press Tab.
To reject a code recommendation, press Esc.
NoteIf you reject a recommendation, you can modify the prompt and review the generated code recommendations once again to match your task intent.
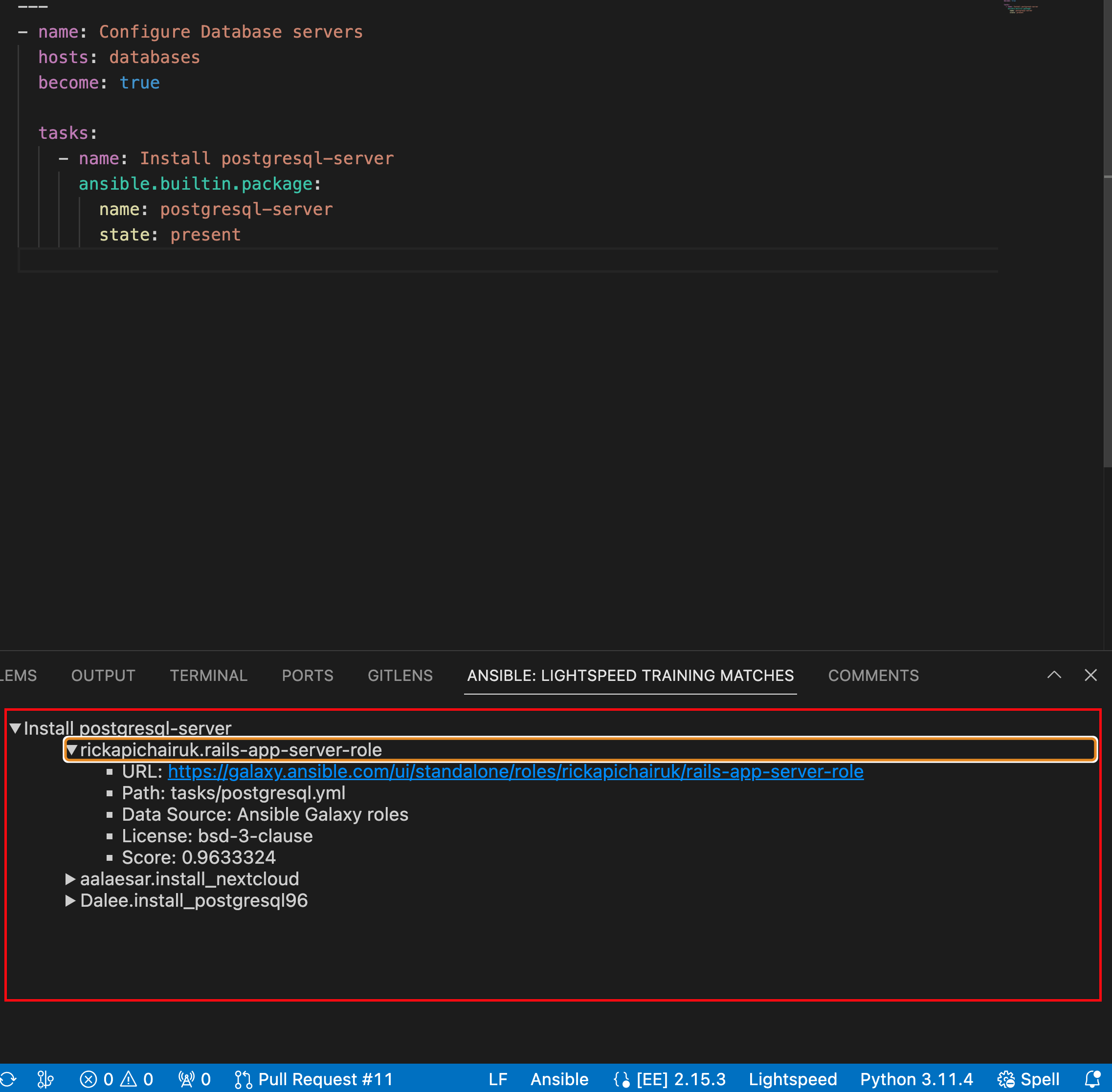
On the ANSIBLE: LIGHTSPEED TRAINING MATCHES tab, view the content source matching results.
The following illustration shows the training matches found in existing Ansible Galaxy content for the task prompt Install postgresql-server:
- Click Save to save the code recommendation changes in your Ansible YAML file.
6.3. Requesting code recommendations for multiple tasks
You can request multitask code recommendations by entering a sequence of natural language task prompts in Ansible VS Code extension. In a YAML file, start a comment by using a Pound key (#), and separate each prompt by using Ampersand (&) symbols.
For example, to automate a multitask of installing PostgreSQL server and running the initial PostgreSQL setup command, you can enter the prompt # Install postgresql-server & run postgresql-setup command. The Ansible Lightspeed service reads the text, interacts with the IBM watsonx Code Assistant models, and generates the code recommendations.
Prerequisites
- You are part of an organization that has a trial or paid subscription to both Ansible Automation Platform and IBM watsonx Code Assistant.
- You have installed and configured the Ansible VS Code extension.
Procedure
- Log in to VS Code with your Red Hat account.
Create a new YAML file or use an existing YAML file.
Create a YAML file:
-
Select
. - From the lower right of the screen, click Plain Text, and in the language mode, select Ansible.
-
Save the file as a YAML file format extension (
.ymlor.yaml).
-
Select
Use an existing YAML file:
On the bottom right of the screen, click the existing language mode, and in the language mode settings, select Ansible.
NoteIf you do not see the language mode section in your VS Code editor, from the Command Palette, select
.
Verify that you see an entry for Lightspeed on the status bar at the lower right of VS Code.
If Ansible is already selected as the desired language but the Lightspeed entry is not displayed, re-select Ansible as the language mode. The following illustration shows Lightspeed entry on the VS Code status bar.
Figure 6.2. Ansible and Lightspeed set as selected language mode
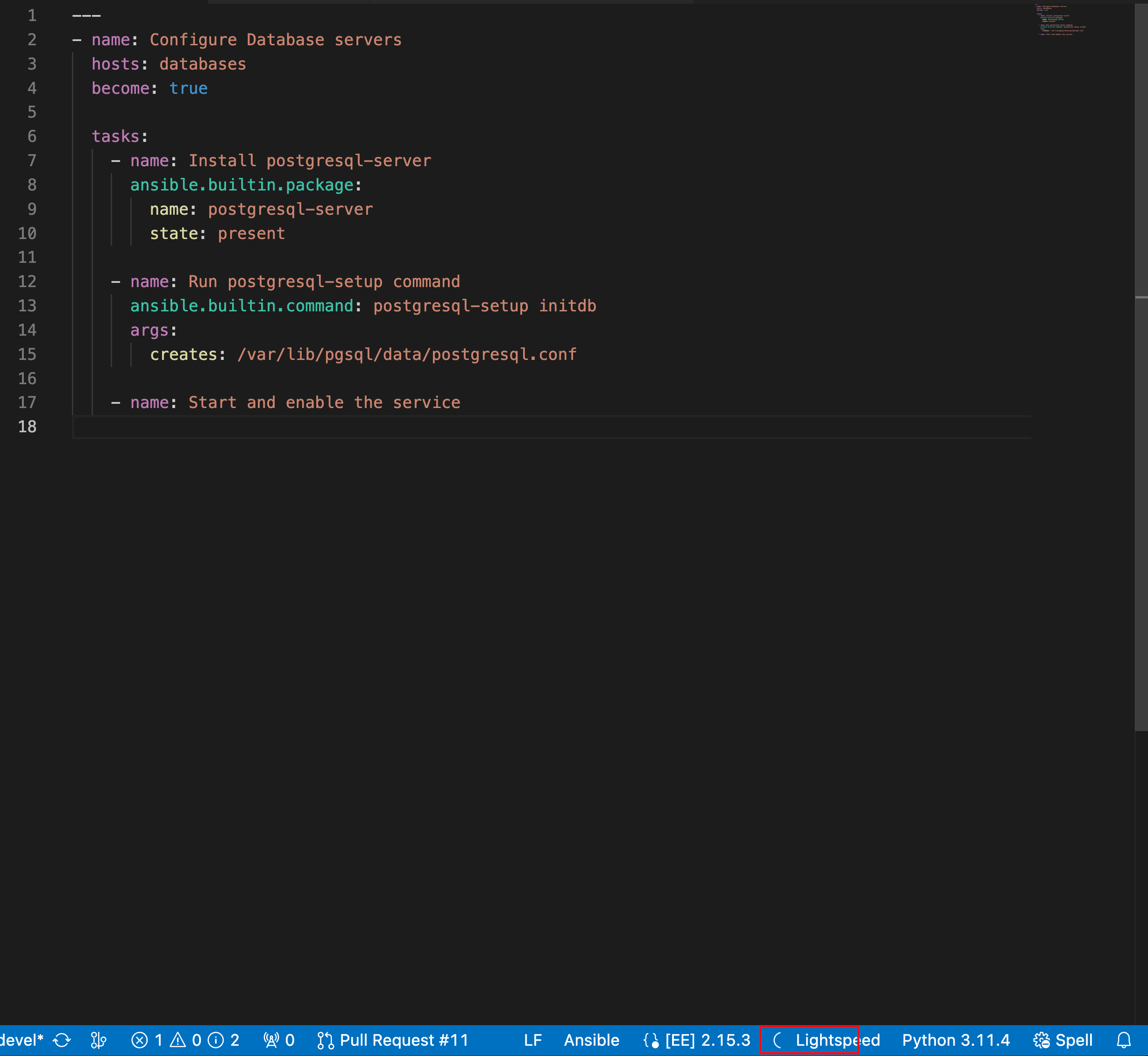
Optional: If you see an error message about missing Ansible lint, you can install the missing module or disable it. Perform any one of the following tasks:
- Install Ansible lint: For installation information, see the Installing section of the Ansible Lint documentation.
Disable Ansible lint:
-
From the Activity bar, click the Extensions icon
 .
.
- From the Installed extensions list, select Ansible.
- From the Ansible extension page, click the Settings icon and select Extension Settings.
- Clear the Ansible › Validation › Lint: Enabled checkbox.
-
From the Activity bar, click the Extensions icon
Create a playbook or use an existing playbook.
For more information, see Creating playbooks in the Ansible Automation Platform Creator Guide.
In the playbook, provide the following information to request multitask code recommendations:
- Start a new YAML file comment by entering a Pound key (#) at the correct indentation.
-
Add a detailed natural language prompt in a sequence, separating each task by using an Ampersand (&) symbol. For example, to automate the multitask of installing PostgreSQL server and running the PostgreSQL setup command, enter the following natural language prompt
# Install postgresql-server & run postgresql-setup command. Press Enter directly after the task description. Keep the cursor at the same location in your file, and wait for the code recommendation results to populate.
The Ansible Lightspeed service is engaged, and it starts generating code recommendations for multiple tasks.
ImportantAnsible Lightspeed service takes around 5 seconds per task to populate the code recommendations. If you are using a multitask prompt, the Ansible Lightspeed service takes a bit longer (number of tasks times 5 seconds) to populate the results. Do not move your cursor or press any key while the code recommendation is being generated. If you change the cursor location or press any key, Ansible VS Code extension cancels the request and the Ansible Lightspeed service does not process your request.
When the Ansible Lightspeed service is engaged, a Lightspeed processing status indicator is displayed in the lower right of the screen to denote that your code recommendation is being generated.

- Optional: If multitask code recommendations are not being generated, log out of VS Code and log in again using your Red Hat account.
View your code recommendations and ensure that the recommendations match your task intent.
The following illustration shows the code recommendations generated by the Ansible Lightspeed service for the multitask prompt Install postgresql-server & run postgresql-setup command: :
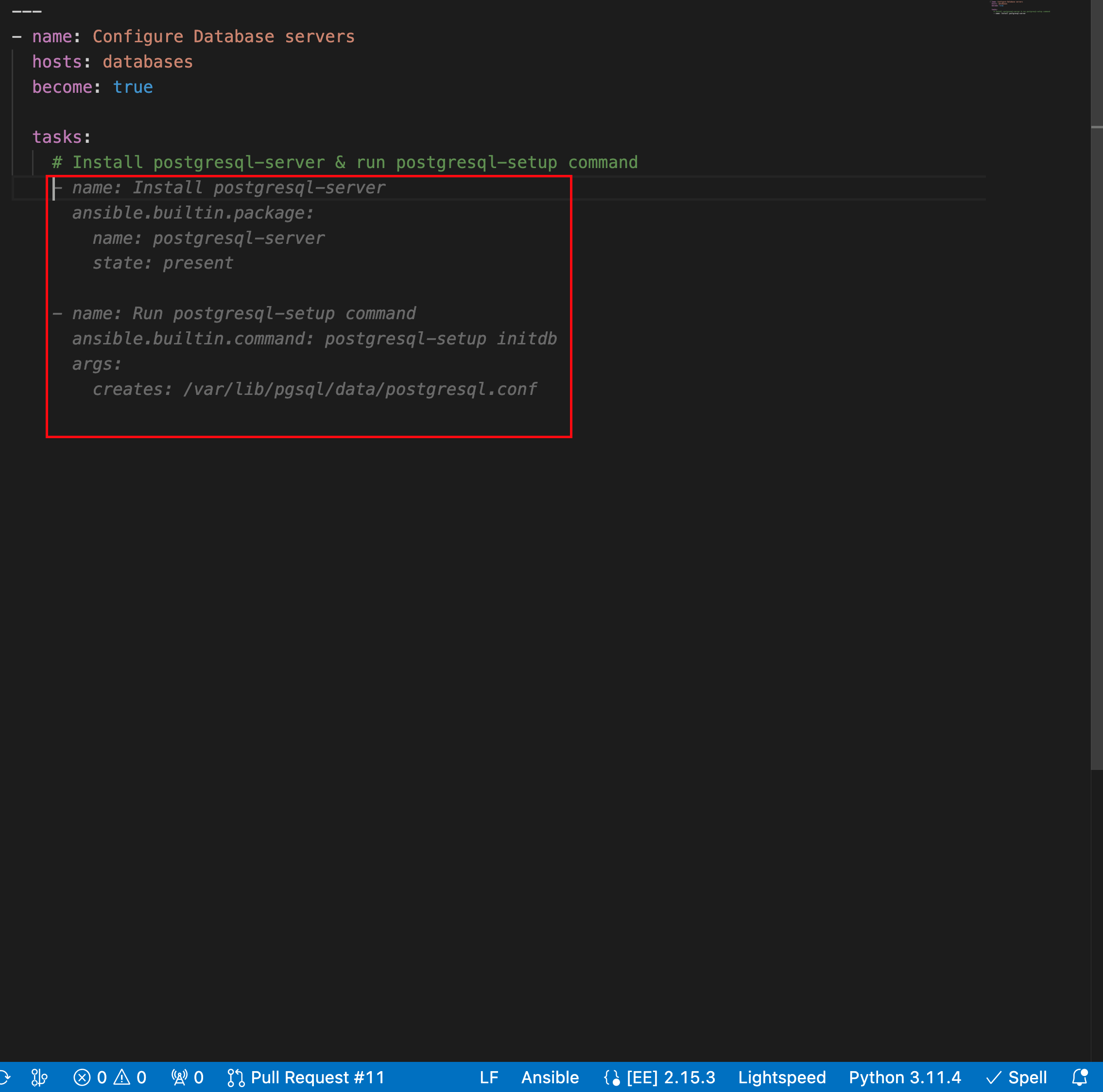
Accept or reject the code recommendations:
- To accept a code recommendation, press Tab.
To reject a code recommendation, press Esc.
NoteIf you reject a recommendation, you can modify the prompt and review the generated code recommendations once again to match your task intent.
On the ANSIBLE: LIGHTSPEED TRAINING MATCHES tab, view the content source matching results.
The following illustration shows the training matches found in existing Ansible Galaxy content for the task prompt multitask prompt Install postgresql-server & run postgresql-setup command:
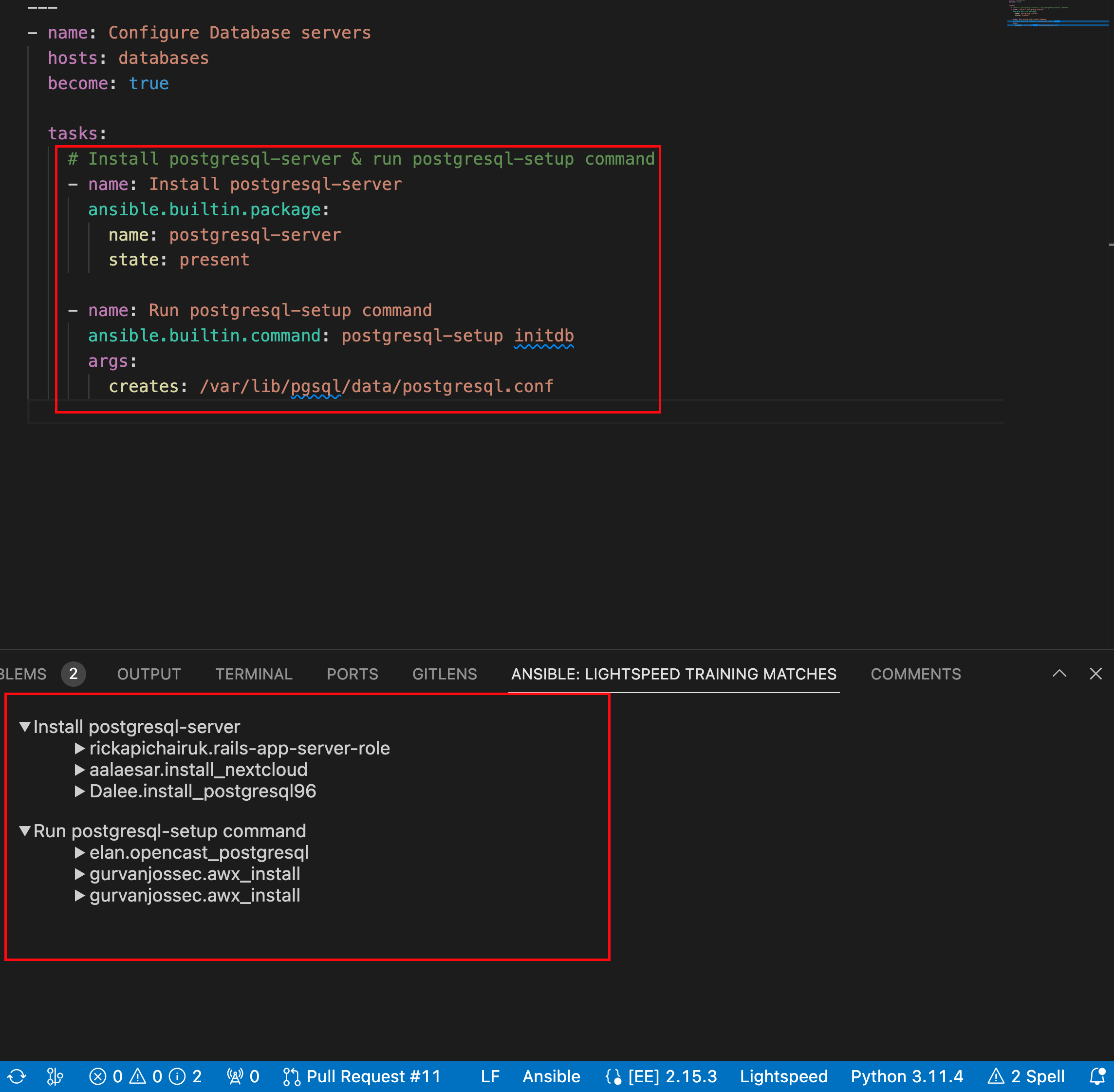
- Click Save to save the code recommendation changes in your Ansible YAML file.
6.4. Viewing Ansible Lightspeed training matches
The Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant machine learning model is trained on the following content: * Existing public or private Git repositories * Content from Ansible Galaxy
Owing to IBM watsonx Code Assistant’s generative AI technology, as well as the types of Ansible content that were used to train the model, it is not possible to identify the specific set of training data that contributed to the generated code recommendations. However, Ansible Lightspeed provides a capability that helps you to understand the possible origins of generated code recommendations.
For each generated code recommendation, Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed lists the content source matches, including details such as potential source, content author, and relevant licenses. You can use this data to gain insight into potential training data sources used to generate the code recommendations.
After you enter a natural language prompt in VS Code and see the generated code recommendations, you can view the content source matches on the ANSIBLE: LIGHTSPEED TRAINING MATCHES tab.
For example, the following illustration shows the training matches for the multitask recommendation Install postgresql-server & run postgresql-setup command:
Figure 6.3. Training matches for a multitask recommendation

This capability enables you to find out the open source license terms that are associated with related training data. However, it is unlikely that either the training data used in fine-tuning the code or the output recommendations themselves are protected by copyright, or that the output reproduces training data that is controlled by copyright licensing terms.
Red Hat does not claim any copyright or other intellectual property rights in the suggestions generated by Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant.
6.5. Providing feedback on the Ansible Lightspeed service
Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant is designed to be improved through feedback on the quality of its suggestions. The technical details of user experiences with Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed are useful in informing further improvements.
You can submit feedback through the following channels:
From the Ansible VS Code extension: Use this method to provide feedback about the quality of the suggested code recommendations.
ImportantRed Hat Support cannot assist with the suggestion quality reports. Content quality issues are routed to IBM for resolution.
- From the Red Hat customer portal: Use this method to log bug reports and service disruption incidents, and feature requests.
On the login screen of the Ansible Lightspeed Portal, there is a Chat link that redirects you to a Matrix channel. Use the Matrix channel to ask questions pertaining to your Ansible Lightspeed experience and request help to troubleshoot your issues. However, the Matrix channel is not an official Support channel, and issues raised in the Matrix chat would not be tracked through Red Hat Service Level Agreement (SLA). To raise a bug or a feature request, contact Red Hat Support and open a support ticket.
Prerequisites
- You are part of an organization that has a trial or paid subscription to both Ansible Automation Platform and IBM watsonx Code Assistant.
Procedure
- Open Visual Studio Code.
- Click the Lightspeed entry in your status bar to see options.
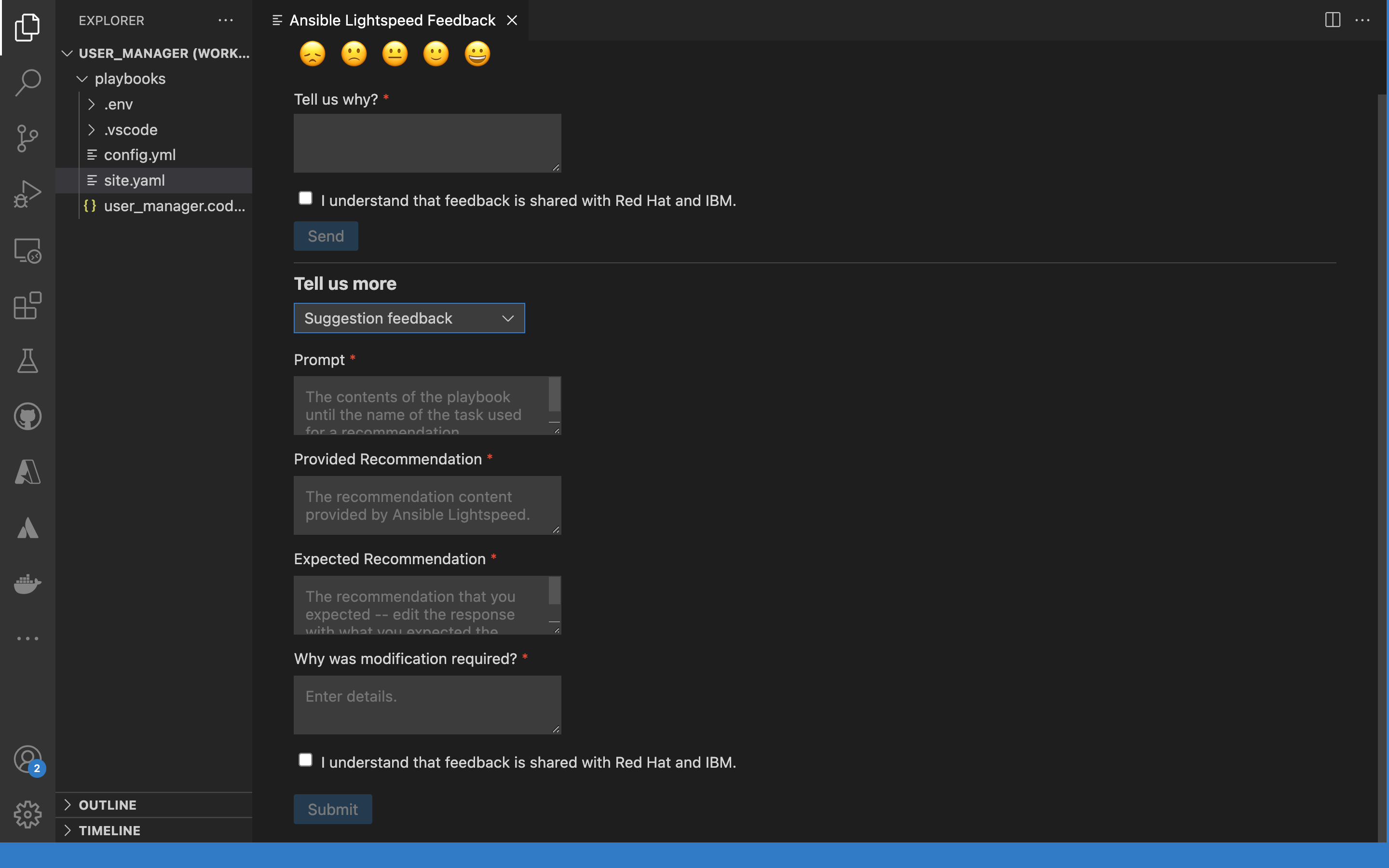
- In the Tell us why field, provide your feedback. Here, provide feedback about what results you were expecting to receive, compared to what results were generated and the training match.
Select the issue type: Bug report, Feature request, or Suggestion feedback.
NoteTo raise a bug or feature request, contact Red Hat Support and open a support ticket. Bug features and feature requests made through Ansible Lightspeed feedback are not tracked through the Red Hat Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- Select the I understand that feedback is shared with Red Hat and IBM checkbox.
Click Send.
The following image shows an example of providing suggestion feedback:
Figure 6.4. Providing feedback on Ansible Lightspeed