Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
4.2. Locating Maven Artifacts at Build Time
Overview
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
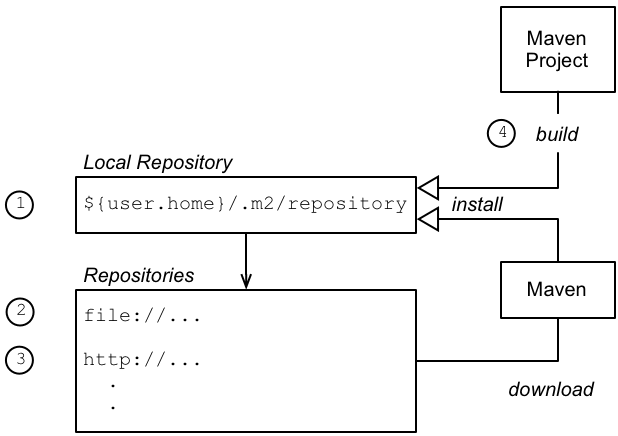
When building projects, Maven implements a simple caching scheme: artifacts are downloaded from remote repositories on the Internet and then cached in the local repository. Figure 4.1, “How Maven Locates Artifacts at Build Time” shows an overview of the procedure that Maven follows when locating artifacts at build time.
Figure 4.1. How Maven Locates Artifacts at Build Time
Locating artifacts at build time
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
While building a project, Maven locates required artifacts (OSGi bundles, Karaf features, required plug-ins, and so on) as follows:
- The first place that Maven looks for artifacts is in the local repository,
~/.m2/repository/(which is effectively a cache where Maven stores the artifacts it has already downloaded or found elsewhere). - If an artifact is not available in the local repository, Maven attempts to download the artifact from one of the repositories listed in its configuration. This repository list can include both internal and remote repositories.
- If the artifact is not available from an internal repository, the next repositories to try are the remote repositories (accessible through HTTP or HTTPS).
- When a Maven project is built locally using the
mvn installcommand, the project's Maven artifacts are installed into the local repository.
Adding a remote Maven repository
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Remote repositories are configured in the same way as internal repositories, except that they should be listed after any internal repositories.
Adding an internal Maven repository
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Maven enables you to specify the location of internal repositories either in your
settings.xml file (which applies to all projects) or in a pom.xml (which applies to that project only). Typically, the location of an internal repository is specified using either a file:// URL or a http:// URL (assuming you have set up a local Web server to serve up the artifacts) and you should generally ensure that internal repositories are listed before remote repositories. Otherwise, there is nothing special about an internal repository: it is just a repository that happens to be located in your internal network.
For an example of how to specify a repository in your
settings.xml file, see the section called “Adding the Red Hat JBoss Fuse repository”.
Customizing the location of the local repository
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Maven resolves the location of the local repository, by checking the following settings:
- The location specified by the
localRepositoryelement in the~/.m2/settings.xmlfile (UNIX and Linux) orC:\Documents and Settings\UserName\.m2\settings.xml(Windows). - Otherwise, the location specified by the
localRepositoryelement in theM2_HOME/conf/settings.xmlfile. - Otherwise, the default location is in the user's home directory,
~/.m2/repository/(UNIX and Linux) orC:\Documents and Settings\UserName\.m2\repository(Windows).