Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 4. Using SSL to protect connections to Red Hat Quay
4.1. Using SSL/TLS
To configure Red Hat Quay with a self-signed certificate, you must create a Certificate Authority (CA) and a primary key file named ssl.cert and ssl.key.
4.2. Creating a Certificate Authority
Use the following procedure to set up your own CA and use it to issue a server certificate for your domain. This allows you to secure communications with SSL/TLS using your own certificates.
Procedure
Generate the root CA key by entering the following command:
openssl genrsa -out rootCA.key 2048
$ openssl genrsa -out rootCA.key 2048Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate the root CA certificate by entering the following command:
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key rootCA.key -sha256 -days 1024 -out rootCA.pem
$ openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key rootCA.key -sha256 -days 1024 -out rootCA.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the information that will be incorporated into your certificate request, including the server hostname, for example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate the server key by entering the following command:
openssl genrsa -out ssl.key 2048
$ openssl genrsa -out ssl.key 2048Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate a signing request by entering the following command:
openssl req -new -key ssl.key -out ssl.csr
$ openssl req -new -key ssl.key -out ssl.csrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the information that will be incorporated into your certificate request, including the server hostname, for example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a configuration file
openssl.cnf, specifying the server hostname, for example:Example
openssl.cnffileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the configuration file to generate the certificate
ssl.cert:openssl x509 -req -in ssl.csr -CA rootCA.pem -CAkey rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out ssl.cert -days 356 -extensions v3_req -extfile openssl.cnf
$ openssl x509 -req -in ssl.csr -CA rootCA.pem -CAkey rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out ssl.cert -days 356 -extensions v3_req -extfile openssl.cnfCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm your created certificates and files by entering the following command:
ls /path/to/certificates
$ ls /path/to/certificatesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
rootCA.key ssl-bundle.cert ssl.key custom-ssl-config-bundle-secret.yaml rootCA.pem ssl.cert openssl.cnf rootCA.srl ssl.csr
rootCA.key ssl-bundle.cert ssl.key custom-ssl-config-bundle-secret.yaml rootCA.pem ssl.cert openssl.cnf rootCA.srl ssl.csrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.3. Configuring custom SSL/TLS certificates by using the command line interface
SSL/TLS must be configured by using the command-line interface (CLI) and updating your config.yaml file manually.
Prerequisites
- You have created a certificate authority and signed the certificate.
Procedure
Copy the certificate file and primary key file to your configuration directory, ensuring they are named
ssl.certandssl.keyrespectively:cp ~/ssl.cert ~/ssl.key /path/to/configuration_directory
cp ~/ssl.cert ~/ssl.key /path/to/configuration_directoryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the configuration directory by entering the following command:
cd /path/to/configuration_directory
$ cd /path/to/configuration_directoryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
config.yamlfile and specify that you want Red Hat Quay to handle SSL/TLS:Example
config.yamlfile# ... SERVER_HOSTNAME: <quay-server.example.com> ... PREFERRED_URL_SCHEME: https # ...
# ... SERVER_HOSTNAME: <quay-server.example.com> ... PREFERRED_URL_SCHEME: https # ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Append the contents of the
rootCA.pemfile to the end of thessl.certfile by entering the following command:cat rootCA.pem >> ssl.cert
$ cat rootCA.pem >> ssl.certCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop the
Quaycontainer by entering the following command:sudo podman stop <quay_container_name>
$ sudo podman stop <quay_container_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the registry by entering the following command:
sudo podman run -d --rm -p 80:8080 -p 443:8443 \ --name=quay \ -v $QUAY/config:/conf/stack:Z \ -v $QUAY/storage:/datastorage:Z \ registry.redhat.io/quay/quay-rhel8:v3.13.7
$ sudo podman run -d --rm -p 80:8080 -p 443:8443 \ --name=quay \ -v $QUAY/config:/conf/stack:Z \ -v $QUAY/storage:/datastorage:Z \ registry.redhat.io/quay/quay-rhel8:v3.13.7Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.4. Configuring SSL/TLS using the Red Hat Quay UI
Use the following procedure to configure SSL/TLS using the Red Hat Quay UI.
To configure SSL/TLS using the command line interface, see "Configuring SSL/TLS using the command line interface".
Prerequisites
- You have created a certificate authority and signed a certificate.
Procedure
Start the
Quaycontainer in configuration mode:sudo podman run --rm -it --name quay_config -p 80:8080 -p 443:8443 registry.redhat.io/quay/quay-rhel8:v3.13.7 config secret
$ sudo podman run --rm -it --name quay_config -p 80:8080 -p 443:8443 registry.redhat.io/quay/quay-rhel8:v3.13.7 config secretCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the Server Configuration section, select Red Hat Quay handles TLS for SSL/TLS. Upload the certificate file and private key file created earlier, ensuring that the Server Hostname matches the value used when the certificates were created.
- Validate and download the updated configuration.
Stop the
Quaycontainer and then restart the registry by entering the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.5. Testing the SSL/TLS configuration using the CLI
Your SSL/TLS configuration can be tested by using the command-line interface (CLI). Use the following procedure to test your SSL/TLS configuration.
Use the following procedure to test your SSL/TLS configuration using the CLI.
Procedure
Enter the following command to attempt to log in to the Red Hat Quay registry with SSL/TLS enabled:
sudo podman login quay-server.example.com
$ sudo podman login quay-server.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Error: error authenticating creds for "quay-server.example.com": error pinging docker registry quay-server.example.com: Get "https://quay-server.example.com/v2/": x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
Error: error authenticating creds for "quay-server.example.com": error pinging docker registry quay-server.example.com: Get "https://quay-server.example.com/v2/": x509: certificate signed by unknown authorityCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Because Podman does not trust self-signed certificates, you must use the
--tls-verify=falseoption:sudo podman login --tls-verify=false quay-server.example.com
$ sudo podman login --tls-verify=false quay-server.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Login Succeeded!
Login Succeeded!Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a subsequent section, you will configure Podman to trust the root Certificate Authority.
4.6. Testing the SSL/TLS configuration using a browser
Use the following procedure to test your SSL/TLS configuration using a browser.
Procedure
Navigate to your Red Hat Quay registry endpoint, for example,
https://quay-server.example.com. If configured correctly, the browser warns of the potential risk: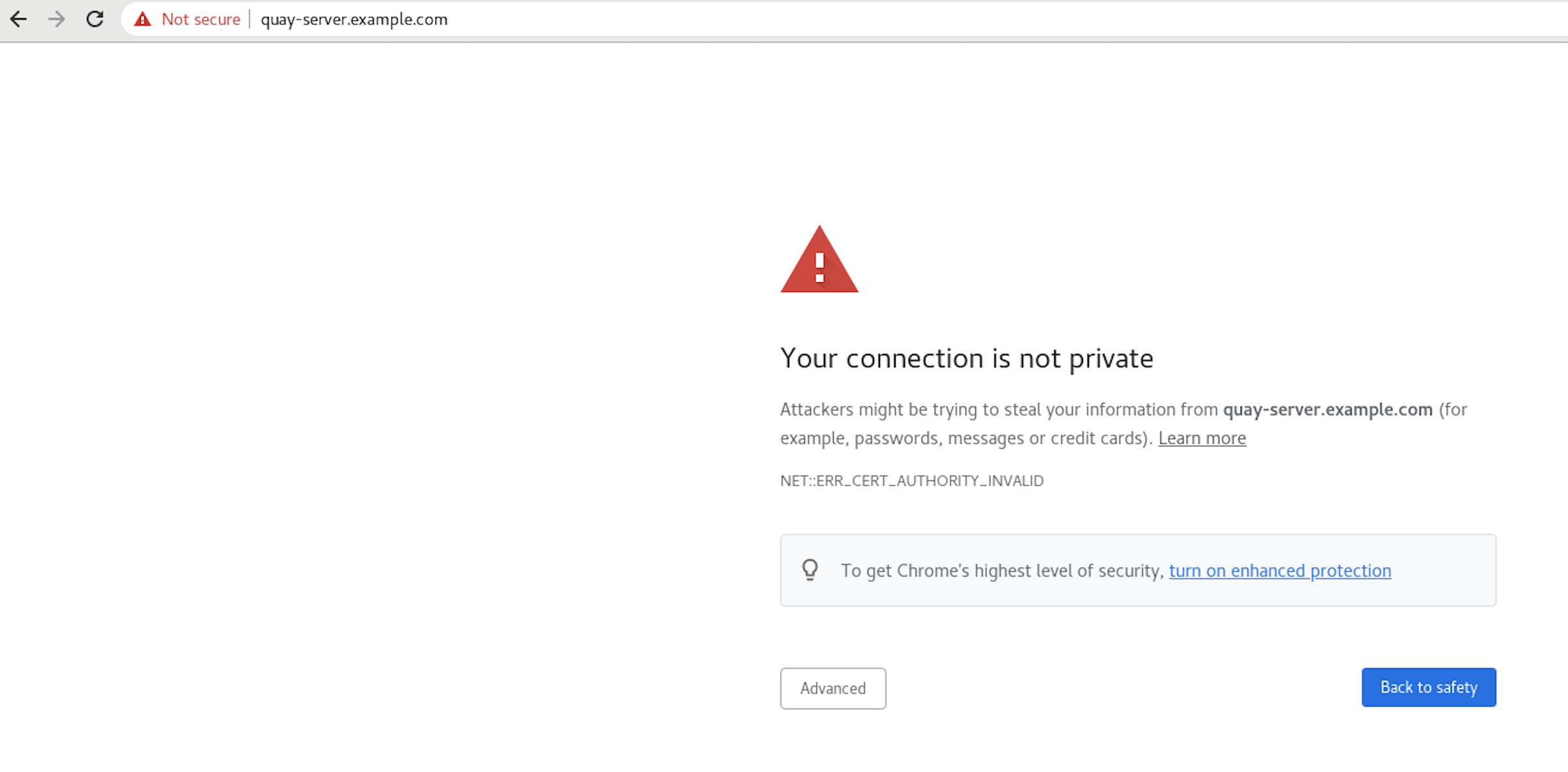
Proceed to the log in screen. The browser notifies you that the connection is not secure. For example:
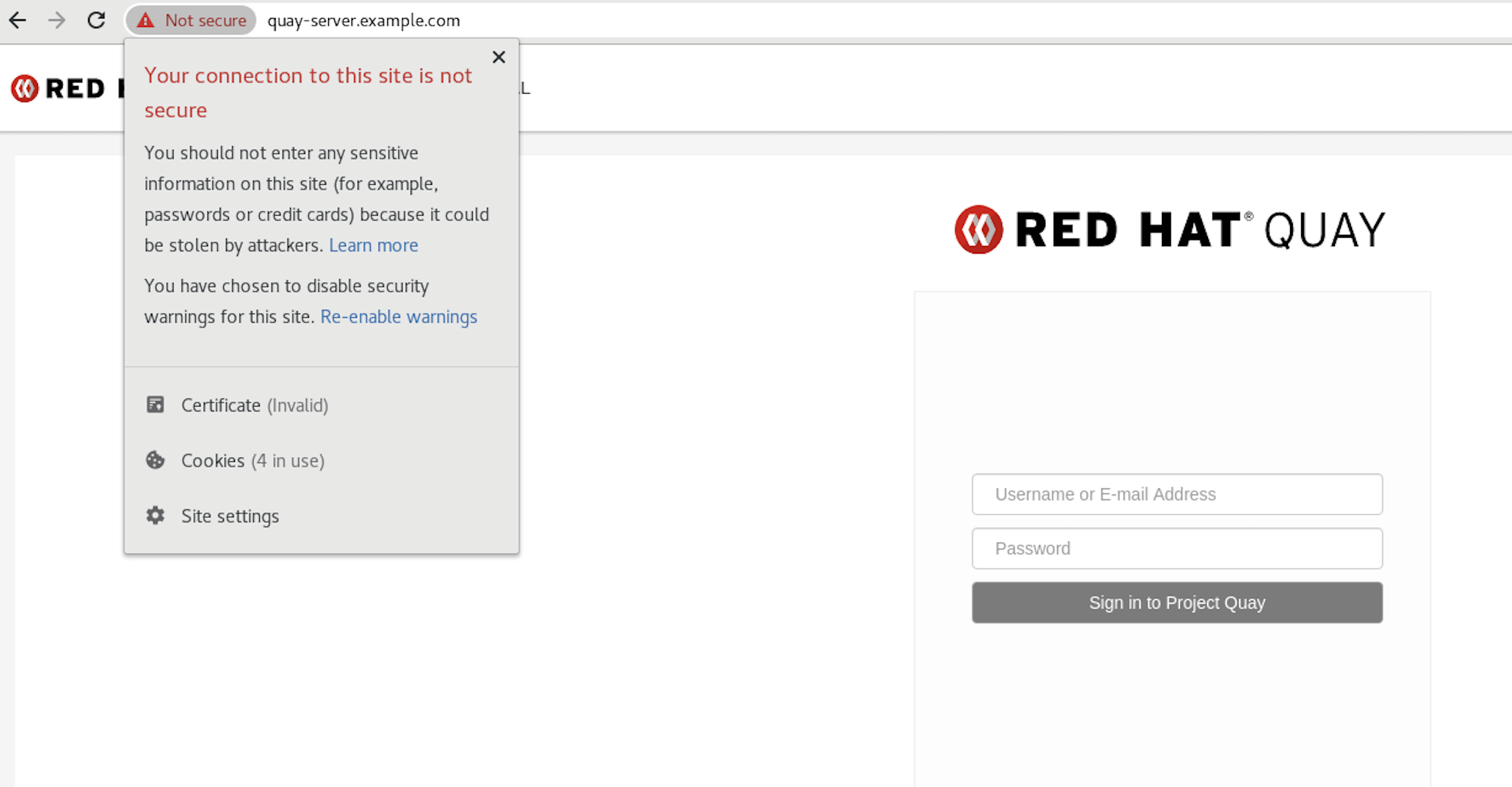
In the following section, you will configure Podman to trust the root Certificate Authority.
4.7. Configuring Podman to trust the Certificate Authority
Podman uses two paths to locate the Certificate Authority (CA) file: /etc/containers/certs.d/ and /etc/docker/certs.d/. Use the following procedure to configure Podman to trust the CA.
Procedure
Copy the root CA file to one of
/etc/containers/certs.d/or/etc/docker/certs.d/. Use the exact path determined by the server hostname, and name the fileca.crt:sudo cp rootCA.pem /etc/containers/certs.d/quay-server.example.com/ca.crt
$ sudo cp rootCA.pem /etc/containers/certs.d/quay-server.example.com/ca.crtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you no longer need to use the
--tls-verify=falseoption when logging in to your Red Hat Quay registry:sudo podman login quay-server.example.com
$ sudo podman login quay-server.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Login Succeeded!
Login Succeeded!Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.8. Configuring the system to trust the certificate authority
Use the following procedure to configure your system to trust the certificate authority.
Procedure
Enter the following command to copy the
rootCA.pemfile to the consolidated system-wide trust store:sudo cp rootCA.pem /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/
$ sudo cp rootCA.pem /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the following command to update the system-wide trust store configuration:
sudo update-ca-trust extract
$ sudo update-ca-trust extractCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional. You can use the
trust listcommand to ensure that theQuayserver has been configured:trust list | grep quay label: quay-server.example.com$ trust list | grep quay label: quay-server.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now, when you browse to the registry at
https://quay-server.example.com, the lock icon shows that the connection is secure: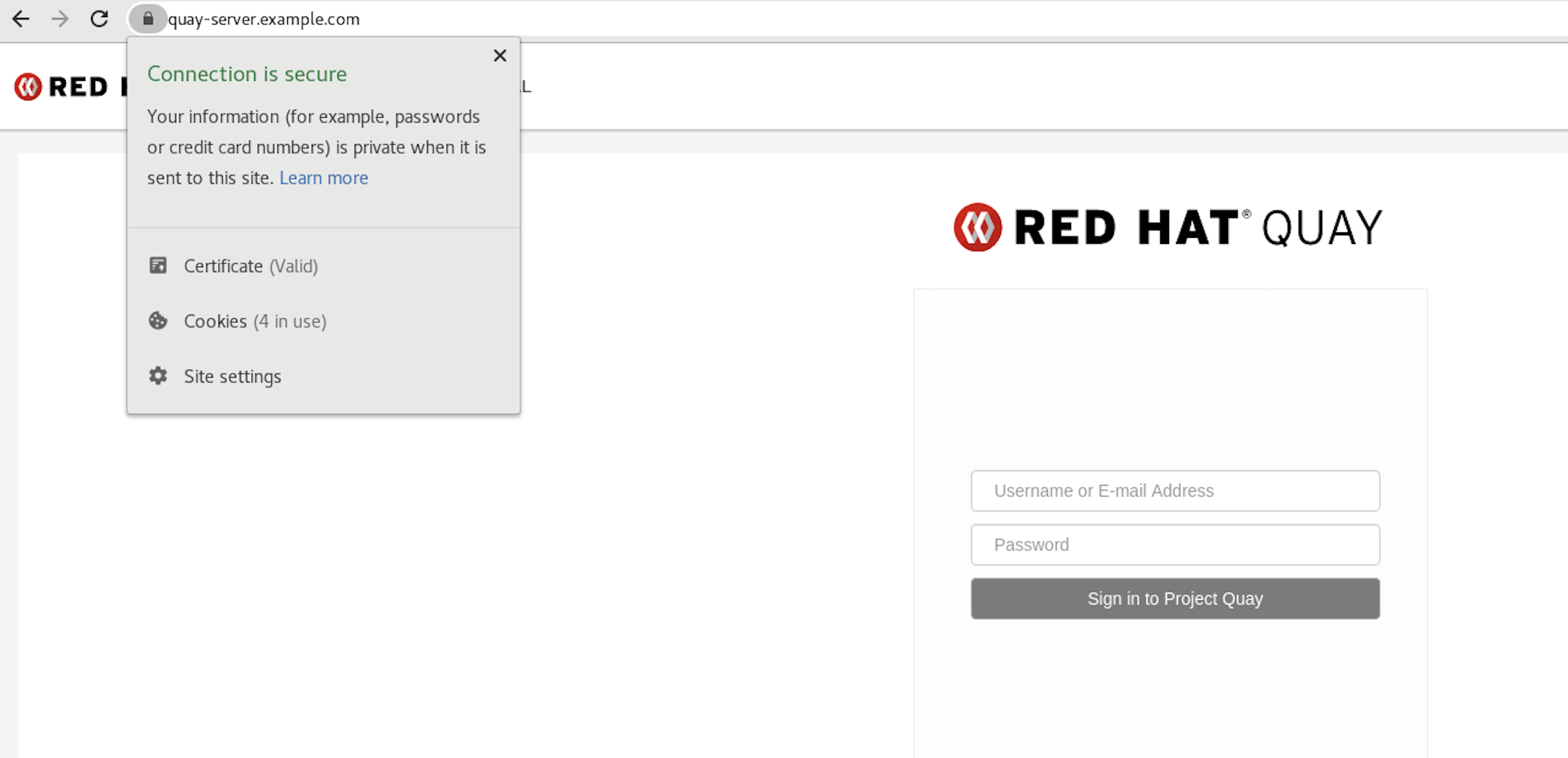
To remove the
rootCA.pemfile from system-wide trust, delete the file and update the configuration:sudo rm /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/rootCA.pem
$ sudo rm /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/rootCA.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow sudo update-ca-trust extract
$ sudo update-ca-trust extractCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow trust list | grep quay
$ trust list | grep quayCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
More information can be found in the RHEL 9 documentation in the chapter Using shared system certificates.