このコンテンツは選択した言語では利用できません。
18.2. WS-Transaction
WS-Transaction (WS-T) comprises the pair of transaction coordination protocols, WS-Atomic Transaction (WS-AT) and WS-Business Activity (WS-BA), which utilize the coordination framework provided by WS-Coordination (WS-C).
WS-Transactions was developed to unify existing traditional transaction processing systems, allowing them to communicate reliably with one another without changes to the systems' own function.
18.2.1. WS-Transaction Foundations
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
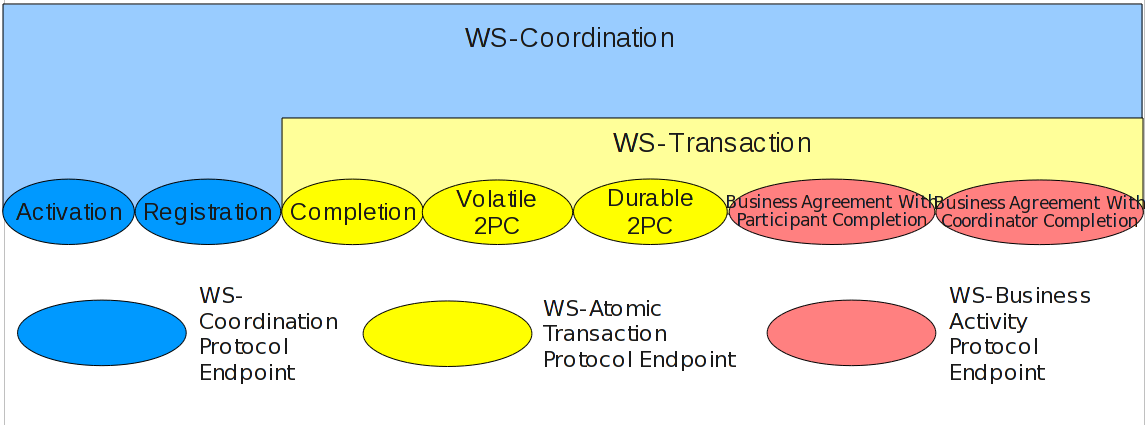
WS-Transaction is layered upon the WS-Coordination protocol, as shown in as shown in Figure 18.3, “WS-Coordination, WS-Transaction, and WS-Business Activity”.
Figure 18.3. WS-Coordination, WS-Transaction, and WS-Business Activity
WS-C provides a generic framework for specific coordination protocols, like WS-Transaction, used in a modular fashion. WS-C provides only context management, allowing contexts to be created and activities to be registered with those contexts. WS-Transaction leverages the context management framework provided by WS-C in two ways.
- It extends the WS-C context to create a transaction context.
- It augments the activation and registration services with a number of additional services (Completion, Volatile2PC, Durable2PC, BusinessAgreementWithParticipantCompletion, and BusinessAgreementWithCoordinatorCompletion) and two protocol message sets (one for each of the transaction models supported in WS-Transaction), to build a fully-fledged transaction coordinator on top of the WS-C protocol infrastructure.
- An important aspect of WS-Transaction that differs from traditional transaction protocols is that a synchronous request/response model is not assumed. Sequences of one way messages are used to implement communications between the client/participant and the coordination services appropriate to the transaction's coordination and participant protocols. This is significant because it means that the client and participant containers must deploy XTS service endpoints to receive messages from the coordinator service.This requirement is visible in the details of the
RegisterandRegisterResponsemessages declared in the Registration Service WSDL in Example 18.2, “Registration ServiceWSDL Interface”. TheRegistermessage contains the URL of an endpoint in the client or web service container. This URL is used when a WS-Transaction coordination service wishes to dispatch a message to the client or web service. Similarly, theRegisterResponsemessage contains a URL identifying an endpoint for the protocol-specific WS-Transaction coordination service for which the client/web service is registered, allowing messages to be addressed to the transaction coordinator.