このコンテンツは選択した言語では利用できません。
1.2. LVM Architecture Overview
For the RHEL 4 release of the Linux operating system, the original LVM1 logical volume manager was replaced by LVM2, which has a more generic kernel framework than LVM1. LVM2 provides the following improvements over LVM1:
- flexible capacity
- more efficient metadata storage
- better recovery format
- new ASCII metadata format
- atomic changes to metadata
- redundant copies of metadata
LVM2 is backwards compatible with LVM1, with the exception of snapshot and cluster support. You can convert a volume group from LVM1 format to LVM2 format with the
vgconvert command. For information on converting LVM metadata format, see the vgconvert(8) man page.
The underlying physical storage unit of an LVM logical volume is a block device such as a partition or whole disk. This device is initialized as an LVM physical volume (PV).
To create an LVM logical volume, the physical volumes are combined into a volume group (VG). This creates a pool of disk space out of which LVM logical volumes (LVs) can be allocated. This process is analogous to the way in which disks are divided into partitions. A logical volume is used by file systems and applications (such as databases).
Figure 1.1, “LVM Logical Volume Components” shows the components of a simple LVM logical volume:
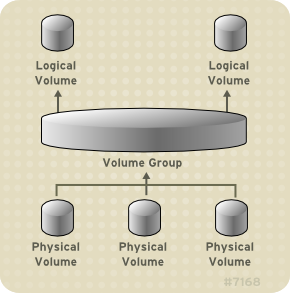
Figure 1.1. LVM Logical Volume Components
For detailed information on the components of an LVM logical volume, see Chapter 2, LVM Components.