13.4.3. サービス間でのファイルの共有
Type Enforcement は、プロセスが別のプロセスで使用することを目的としたファイルにアクセスするのを防ぐのに役立ちます。たとえば、Samba は、デフォルトでは、
httpd_sys_content_t のタイプでラベルが付いたファイル (Apache HTTP サーバーが使用するファイル) を読み込むことができません。ファイルに public_content_t または public_content_rw_t のタイプのラベルが付けられている場合は、Apache HTTP サーバー、FTP、rsync、および Samba との間でファイルを共有できます。
以下の例では、ディレクトリーとファイルを作成し、Apache HTTP Server、FTP、rsync、および Samba でディレクトリーとファイルを共有 (読み取り専用) できるようにします。
- root で
mkdirユーティリティーを使用して、複数のサービス間でファイルを共有するための新しいトップレベルディレクトリーを作成します。~]# mkdir /shares - file-context 設定のパターンに一致しないファイルおよびディレクトリーには、
default_tタイプのラベルが付けられます。このタイプは、制限のあるサービスからはアクセスできません。~]$ ls -dZ /shares drwxr-xr-x root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /shares - root で、
/shares/index.htmlファイルを作成します。以下の内容を/shares/index.htmlにコピーアンドペーストします。<html> <body> <p>Hello</p> </body> </html>
public_content_tタイプでの/shares/のラベル付けでは、Apache HTTP サーバー、FTP、rsync、および Samba による読み取り専用アクセスが許可されます。root で以下のコマンドを入力し、ラベルの変更を file-context 設定に追加します。~]# semanage fcontext -a -t public_content_t "/shares(/.*)?"restoreconユーティリティーを root で使用し、ラベルの変更を適用します。~]# restorecon -R -v /shares/ restorecon reset /shares context unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0->system_u:object_r:public_content_t:s0 restorecon reset /shares/index.html context unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0->system_u:object_r:public_content_t:s0
Samba 経由で
/shares/を共有するには、以下を行います。
- samba パッケージ、samba-common パッケージ、および samba-client パッケージがインストールされていることを確認します (バージョン番号が異なる場合があります)。
~]$ rpm -q samba samba-common samba-client samba-3.4.0-0.41.el6.3.i686 samba-common-3.4.0-0.41.el6.3.i686 samba-client-3.4.0-0.41.el6.3.i686これらのパッケージのいずれかがインストールされていない場合は、root で以下のコマンドを実行してインストールします。~]# yum install package-name /etc/samba/smb.confを root で編集します。このファイルの下部に以下のエントリーを追加し、Samba で/shares/ディレクトリーを共有します。[shares] comment = Documents for Apache HTTP Server, FTP, rsync, and Samba path = /shares public = yes writable = no
- Samba ファイルシステムをマウントするには、Samba アカウントが必要です。root で次のコマンドを入力して、Samba アカウントを作成します。username は、既存の Linux ユーザーです。たとえば、smbpasswd -a testuser は、Linux
testuserユーザーの Samba アカウントを作成します。~]# smbpasswd -a testuser New SMB password: Enter a password Retype new SMB password: Enter the same password again Added user testuser.上記のコマンドを実行し、システムに存在しないアカウントのユーザー名を指定すると、Cannot locate Unix account for 'username'!エラーが発生します。 - Samba サービスを再起動します。
~]# systemctl start smb.service - 利用可能な共有を一覧表示するには、次のコマンドを入力します。username は、手順 3 で追加した Samba アカウントです。パスワードを求められたら、手順 3 で Samba アカウントに割り当てたパスワードを入力します (バージョン番号は異なる場合があります)。
~]$ smbclient -U username -L localhost Enter username's password: Domain=[HOSTNAME] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.4.0-0.41.el6] Sharename Type Comment --------- ---- ------- shares Disk Documents for Apache HTTP Server, FTP, rsync, and Samba IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba Server Version 3.4.0-0.41.el6) username Disk Home Directories Domain=[HOSTNAME] OS=[Unix] Server=[Samba 3.4.0-0.41.el6] Server Comment --------- ------- Workgroup Master --------- ------- mkdirユーティリティーを使用して、新しいディレクトリーを作成します。このディレクトリーは、sharesの Samba 共有をマウントするために使用されます。~]# mkdir /test/- root で次のコマンドを入力して、
sharesの Samba 共有を/test/にマウントし、username を、手順 3 のユーザー名に置き換えます。~]# mount //localhost/shares /test/ -o user=username手順 3 で設定した username のパスワードを入力します。 - Samba で共有されているファイルの内容を表示します。
~]$ cat /test/index.html <html> <body> <p>Hello</p> </body> </html>
Apache HTTP サーバー経由で
/shares/ を共有するには、次のコマンドを実行します。
- httpd パッケージがインストールされていることを確認します (バージョン番号が異なる場合があります)。
~]$ rpm -q httpd httpd-2.2.11-6.i386このパッケージがインストールされていない場合は、root でyumユーティリティーを使用してインストールします。~]# yum install httpd /var/www/html/ディレクトリーに変更します。root で以下のコマンドを入力し、/shares/ディレクトリーへのリンク (名前はshares) を作成します。html]# ln -s /shares/ shares- Apache HTTP サーバーを起動します。
~]# systemctl start httpd.service - Web ブラウザーを使用して
http://localhost/sharesに移動します。/shares/index.htmlが表示されます。
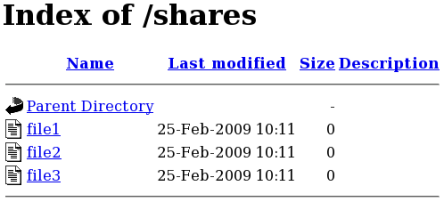
既定では、
index.html ファイルが存在する場合は読み込まれます。/shares/ にindex.html がなく、代わりに file1、file2、および file3 があった場合は、http://localhost/shares へのアクセス時にディレクトリーの一覧が表示されます。
index.htmlファイルを削除します。~]# rm -i /shares/index.htmltouchユーティリティーを root で使用し、/shares/に 3 つのファイルを作成します。~]# touch /shares/file{1,2,3} ~]# ls -Z /shares/ -rw-r--r-- root root system_u:object_r:public_content_t:s0 file1 -rw-r--r-- root root unconfined_u:object_r:public_content_t:s0 file2 -rw-r--r-- root root unconfined_u:object_r:public_content_t:s0 file3
- root で以下のコマンドを入力して、Apache HTTP サーバーのステータスを確認します。
~]# systemctl status httpd.service httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled) Active: inactive (dead)サーバーが停止している場合は、起動します。~]# systemctl start httpd.service - Web ブラウザーを使用して
http://localhost/sharesに移動します。ディレクトリーの一覧が表示されます。