このコンテンツは選択した言語では利用できません。
Chapter 2. Quick Start
2.1. Cloud Balancing Tutorial
2.1.1. Problem Description
Suppose your company owns a number of cloud computers and needs to run a number of processes on those computers. Assign each process to a computer under the following four constraints.
The following hard constraints must be fulfilled:
Every computer must be able to handle the minimum hardware requirements of the sum of its processes:
- The CPU power of a computer must be at least the sum of the CPU power required by the processes assigned to that computer.
- The RAM memory of a computer must be at least the sum of the RAM memory required by the processes assigned to that computer.
- The network bandwidth of a computer must be at least the sum of the network bandwidth required by the processes assigned to that computer.
The following soft constraints should be optimized:
Each computer that has one or more processes assigned, incurs a maintenance cost (which is fixed per computer).
- Minimize the total maintenance cost.
This problem is a form of bin packing. The following is a simplified example, where we assign four processes to two computers with two constraints (CPU and RAM) with a simple algorithm:
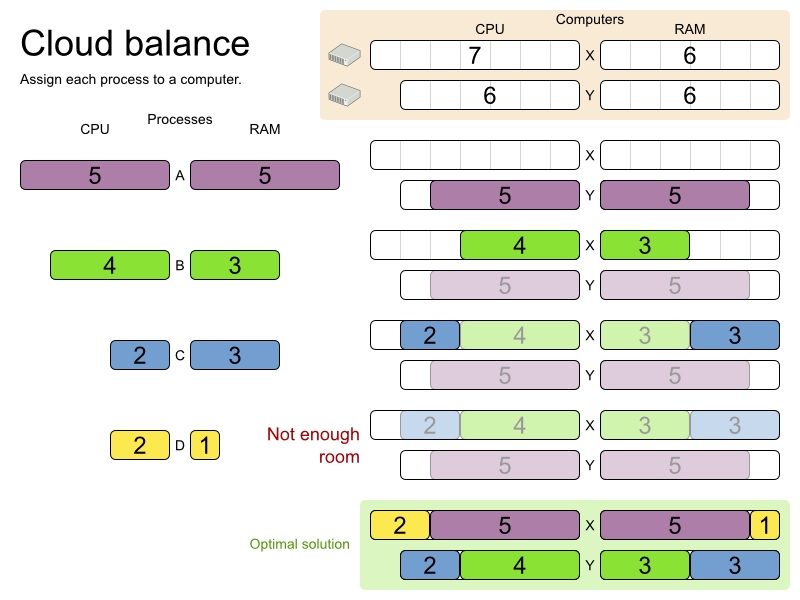
The simple algorithm used here is the First Fit Decreasing algorithm, which assigns the bigger processes first and assigns the smaller processes to the remaining space. As you can see, it is not optimal, as it does not leave enough room to assign the yellow process “D”.
Planner does find the more optimal solution fast by using additional, smarter algorithms. It also scales: both in data (more processes, more computers) and constraints (more hardware requirements, other constraints). So see how Planner can be used in this scenario.
2.1.2. Problem Size
| Problem Size | Computers | Processes | Search Space |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2computers-6processes | 2 | 6 | 64 |
| 3computers-9processes | 3 | 9 | 104 |
| 4computers-012processes | 4 | 12 | 107 |
| 100computers-300processes | 100 | 300 | 10600 |
| 200computers-600processes | 200 | 600 | 101380 |
| 400computers-1200processes | 400 | 1200 | 103122 |
| 800computers-2400processes | 800 | 2400 | 106967 |
2.1.3. Domain Model Design
Beginning with the domain model:
-
Computer: represents a computer with certain hardware (CPU power, RAM memory, network bandwidth) and maintenance cost. -
Process: represents a process with a demand. Needs to be assigned to aComputerby Planner. -
CloudBalance: represents a problem. Contains everyComputerandProcessfor a certain data set.
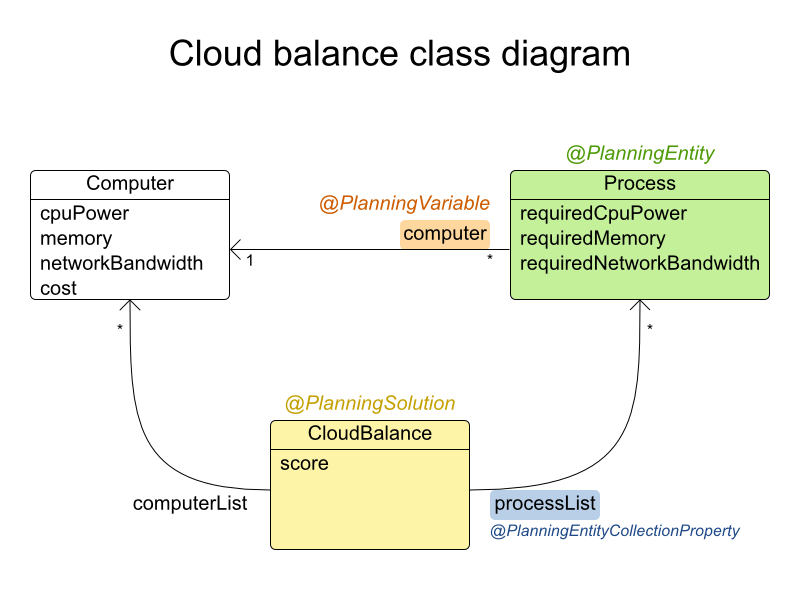
In the UML class diagram above, the Planner concepts are already annotated:
-
Planning entity: the class (or classes) that changes during planning. In this example, it is the class
Process. -
Planning variable: the property (or properties) of a planning entity class that changes during planning. In this example, it is the property
computeron the classProcess. -
Solution: the class that represents a data set and contains all planning entities. In this example that is the class
CloudBalance.
2.1.4. Main Method
Try it yourself. Download and configure the examples in your preferred IDE. Run org.optaplanner.examples.cloudbalancing.app.CloudBalancingHelloWorld. By default, it is configured to run for 120 seconds. It will execute this code:
Example 2.1. CloudBalancingHelloWorld.java
The code example does the following:
Build the
Solverbased on a solver configuration (in this case an XML file from the classpath).SolverFactory<CloudBalance> solverFactory = SolverFactory.createFromXmlResource( "org/optaplanner/examples/cloudbalancing/solver/cloudBalancingSolverConfig.xml"); Solver solver<CloudBalance> = solverFactory.buildSolver();SolverFactory<CloudBalance> solverFactory = SolverFactory.createFromXmlResource( "org/optaplanner/examples/cloudbalancing/solver/cloudBalancingSolverConfig.xml"); Solver solver<CloudBalance> = solverFactory.buildSolver();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Load the problem.
CloudBalancingGeneratorgenerates a random problem: you will replace this with a class that loads a real problem, for example from a database.CloudBalance unsolvedCloudBalance = new CloudBalancingGenerator().createCloudBalance(400, 1200);
CloudBalance unsolvedCloudBalance = new CloudBalancingGenerator().createCloudBalance(400, 1200);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Solve the problem.
CloudBalance solvedCloudBalance = solver.solve(unsolvedCloudBalance);
CloudBalance solvedCloudBalance = solver.solve(unsolvedCloudBalance);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the result.
System.out.println("\nSolved cloudBalance with 400 computers and 1200 processes:\n" + toDisplayString(solvedCloudBalance));System.out.println("\nSolved cloudBalance with 400 computers and 1200 processes:\n" + toDisplayString(solvedCloudBalance));Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The only complicated part is building the Solver, as detailed in the next section.
2.1.5. Solver Configuration
Take a look at the solver configuration:
Example 2.2. cloudBalancingSolverConfig.xml
This solver configuration consists of three parts:
Domain model configuration: What can Planner change? We need to make Planner aware of our domain classes. In this configuration, it will automatically scan all classes in your classpath (for an
@PlanningEntityor@PlanningSolutionannotation):<scanAnnotatedClasses/>
<scanAnnotatedClasses/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Score configuration: How should Planner optimize the planning variables? What is our goal? Since we have hard and soft constraints, we use a
HardSoftScore. But we also need to tell Planner how to calculate the score, depending on our business requirements. Further down, we will look into two alternatives to calculate the score: using an easy Java implementation, or using Drools DRL.<scoreDirectorFactory> <scoreDefinitionType>HARD_SOFT</scoreDefinitionType> <easyScoreCalculatorClass>org.optaplanner.examples.cloudbalancing.solver.score.CloudBalancingEasyScoreCalculator</easyScoreCalculatorClass> <!--<scoreDrl>org/optaplanner/examples/cloudbalancing/solver/cloudBalancingScoreRules.drl</scoreDrl>--> </scoreDirectorFactory><scoreDirectorFactory> <scoreDefinitionType>HARD_SOFT</scoreDefinitionType> <easyScoreCalculatorClass>org.optaplanner.examples.cloudbalancing.solver.score.CloudBalancingEasyScoreCalculator</easyScoreCalculatorClass> <!--<scoreDrl>org/optaplanner/examples/cloudbalancing/solver/cloudBalancingScoreRules.drl</scoreDrl>--> </scoreDirectorFactory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optimization algorithms configuration: How should Planner optimize it? In this case, we use the default optimization algorithms (because no explicit optimization algorithms are configured) for 30 seconds:
<termination> <secondsSpentLimit>30</secondsSpentLimit> </termination><termination> <secondsSpentLimit>30</secondsSpentLimit> </termination>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Planner should get a good result in seconds (and even in less than 15 milliseconds with real-time planning), but the more time it has, the better the result will be. Advanced use cases will likely use a different termination criteria than a hard time limit.
The default algorithms will already easily surpass human planners and most in-house implementations. Use the Benchmarker to power tweak to get even better results.
Let’s examine the domain model classes and the score configuration.
2.1.6. Domain Model Implementation
2.1.6.1. The Computer Class
The Computer class is a POJO (Plain Old Java Object). Usually, you will have more of this kind of classes.
Example 2.3. CloudComputer.java
2.1.6.2. The Process Class
The Process class is particularly important. We need to tell Planner that it can change the field computer, so we annotate the class with @PlanningEntity and the getter getComputer() with @PlanningVariable:
Example 2.4. CloudProcess.java
The values that Planner can choose from for the field computer, are retrieved from a method on the Solution implementation: CloudBalance.getComputerList(), which returns a list of all computers in the current data set. The valueRangeProviderRefs property is used to pass this information to the Planner.
Instead of getter annotations, it is also possible to use field annotations.
2.1.6.3. The CloudBalance Class
The CloudBalance class implements the Solution interface. It holds a list of all computers and processes. We need to tell Planner how to retrieve the collection of processes that it can change, therefore we must annotate the getter getProcessList with @PlanningEntityCollectionProperty.
The CloudBalance class also has a property score, which is the Score of that Solution instance in its current state:
Example 2.5. CloudBalance.java
The getProblemFacts() method is only needed for score calculation with Drools. It is not needed for the other score calculation types.
2.1.7. Score Configuration
Planner will search for the Solution with the highest Score. This example uses a HardSoftScore, which means Planner will look for the solution with no hard constraints broken (fulfill hardware requirements) and as little as possible soft constraints broken (minimize maintenance cost).
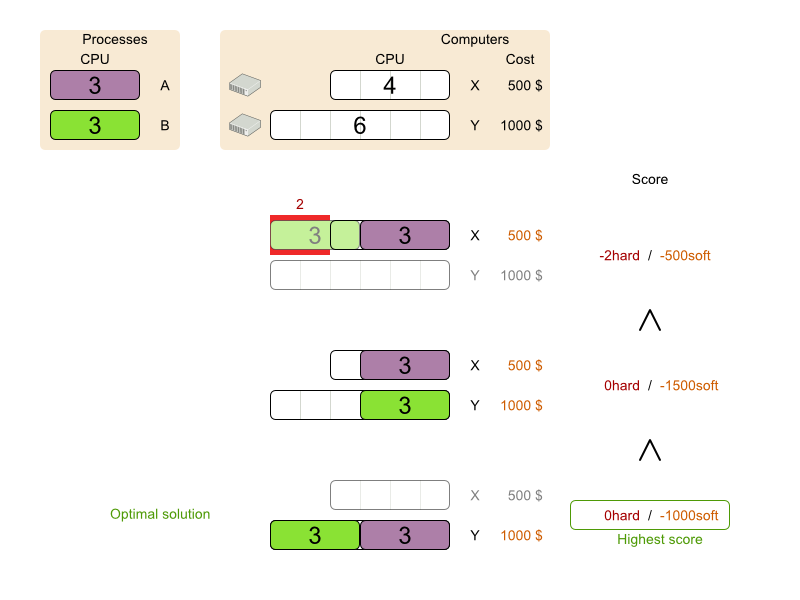
Of course, Planner needs to be told about these domain-specific score constraints. There are several ways to implement such a score function:
- Easy Java
- Incremental Java
- Drools
Let’s take a look at two different implementations:
2.1.7.1. Easy Java Score Configuration
One way to define a score function is to implement the interface EasyScoreCalculator in plain Java.
<scoreDirectorFactory>
<scoreDefinitionType>HARD_SOFT</scoreDefinitionType>
<easyScoreCalculatorClass>org.optaplanner.examples.cloudbalancing.solver.score.CloudBalancingEasyScoreCalculator</easyScoreCalculatorClass>
</scoreDirectorFactory>
<scoreDirectorFactory>
<scoreDefinitionType>HARD_SOFT</scoreDefinitionType>
<easyScoreCalculatorClass>org.optaplanner.examples.cloudbalancing.solver.score.CloudBalancingEasyScoreCalculator</easyScoreCalculatorClass>
</scoreDirectorFactory>
Just implement the calculateScore(Solution) method to return a HardSoftScore instance.
Example 2.6. CloudBalancingEasyScoreCalculator.java
Even if we optimize the code above to use Maps to iterate through the processList only once, it is still slow because it does not do incremental score calculation. To fix that, either use an incremental Java score function or a Drools score function. Let’s take a look at the latter.
2.1.7.2. Drools Score Configuration
To use the Drools rule engine as a score function, simply add a scoreDrl resource in the classpath:
<scoreDirectorFactory>
<scoreDefinitionType>HARD_SOFT</scoreDefinitionType>
<scoreDrl>org/optaplanner/examples/cloudbalancing/solver/cloudBalancingScoreRules.drl</scoreDrl>
</scoreDirectorFactory>
<scoreDirectorFactory>
<scoreDefinitionType>HARD_SOFT</scoreDefinitionType>
<scoreDrl>org/optaplanner/examples/cloudbalancing/solver/cloudBalancingScoreRules.drl</scoreDrl>
</scoreDirectorFactory>First, we want to make sure that all computers have enough CPU, RAM and network bandwidth to support all their processes, so we make these hard constraints:
Example 2.7. cloudBalancingScoreRules.drl - Hard Constraints
Next, if those constraints are met, we want to minimize the maintenance cost, so we add that as a soft constraint:
Example 2.8. cloudBalancingScoreRules.drl - Soft Constraints
If you use the Drools rule engine for score calculation, you can integrate with other Drools technologies, such as decision tables (XLS or web based), the KIE Workbench, …
2.1.8. Beyond this Tutorial
Now that this simple example works, try going further. Enrich the domain model and add extra constraints such as these:
-
Each
Processbelongs to aService. A computer might crash, so processes running the same service should be assigned to different computers. -
Each
Computeris located in aBuilding. A building might burn down, so processes of the same services should be assigned to computers in different buildings.