이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
Chapter 3. Certificate profiles (Making Rules for Issuing Certificates)
Red Hat Certificate System provides a customizable framework to apply policies for incoming certificate requests and to control the input request types and output certificate types; these are called certificate profiles. Certificate profiles set the required information for certificate enrollment forms in the Certificate Manager end-entities page. This chapter describes how to configure certificate profiles.
3.1. About certificate profiles
A certificate profile defines everything associated with issuing a particular type of certificate, including the authentication method, the authorization method, the default certificate content, constraints for the values of the content, and the contents of the input and output for the certificate profile. Enrollment and renewal requests are submitted to a certificate profile and are then subject to the defaults and constraints set in that certificate profile. These constraints are in place whether the request is submitted through the input form associated with the certificate profile or through other means. The certificate that is issued from a certificate profile request contains the content required by the defaults with the information required by the default parameters. The constraints provide rules for what content is allowed in the certificate.
For details about using and customizing certificate profiles, see Section 3.2, “Setting up certificate profiles”.
The Certificate System contains a set of default profiles. While the default profiles are created to satisfy most deployments, every deployment can add their own new certificate profiles or modify the existing profiles.
- Authentication. In every certification profile can be specified an authentication method.
- Authorization. In every certification profile can be specified an authorization method.
- Profile inputs. Profile inputs are parameters and values that are submitted to the CA when a certificate is requested. Profile inputs include public keys for the certificate request and the certificate subject name requested by the end entity for the certificate.
- Profile outputs. Profile outputs are parameters and values that specify the format in which to provide the certificate to the end entity. Profile outputs are CMC responses which contain a PKCS#7 certificate chain, when the request was successful.
Certificate content. Each certificate defines content information, such as the name of the entity to which it is assigned (the subject name), its signing algorithm, and its validity period. What is included in a certificate is defined in the X.509 standard. With version 3 of the X509 standard, certificates can also contain extensions. For more information about certificate extensions, see Section B.3, “Standard X.509 v3 certificate extension reference”.
All of the information about a certificate profile is defined in the
setentry of the profile policy in the profile’s configuration file. When multiple certificates are expected to be requested at the same time, multiple set entries can be defined in the profile policy to satisfy needs of each certificate. Each policy set consists of a number of policy rules and each policy rule describes a field in the certificate content. A policy rule can include the following parts:- Profile defaults. These are predefined parameters and allowed values for information contained within the certificate. Profile defaults include the validity period of the certificate, and what certificate extensions appear for each type of certificate issued.
-
Profile constraints. Constraints set rules or policies for issuing certificates. Amongst other, profile constraints include rules to require the certificate subject name to have at least one CN component, to set the validity of a certificate to a maximum of 360 days, to define the allowed grace period for renewal, or to require that the
subjectaltnameextension is always set totrue.
3.1.1. The enrollment profile
The parameters for each profile defining the inputs, outputs, and policy sets are listed in more detail in Profile configuration file parameters in the Red Hat Certificate System Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide.
A profile usually contains inputs, policy sets, and outputs, as illustrated in the caUserCert profile in the following example.
Example 3.1. Example caCMCUserCert Profile
The first part of a certificate profile is the description. This shows the name, long description, whether it is enabled, and who enabled it.
desc=This certificate profile is for enrolling user certificates by using the CMC certificate request with CMC Signature authentication. visible=true enable=true enableBy=admin name=Signed CMC-Authenticated User Certificate Enrollment
desc=This certificate profile is for enrolling user certificates by using the CMC certificate request with CMC Signature authentication.
visible=true
enable=true
enableBy=admin
name=Signed CMC-Authenticated User Certificate Enrollment
The missing auth.instance_id= entry in this profile means that with this profile, authentication is not needed to submit the enrollment request. However, manual approval by an authorized CA agent will be required to get an issuance.
Next, the profile lists all of the required inputs for the profile:
input.list=i1 input.i1.class_id=cmcCertReqInputImp
input.list=i1
input.i1.class_id=cmcCertReqInputImp
For the caCMCUserCert profile, this defines the certificate request type, which is CMC.
Next, the profile must define the output, meaning the format of the final certificate. The only one available is certOutputImpl, which results in CMC response to be returned to the requestor in case of success.
output.list=o1 output.o1.class_id=certOutputImpl
output.list=o1
output.o1.class_id=certOutputImpl
The last - largest - block of configuration is the policy set for the profile. Policy sets list all of the settings that are applied to the final certificate, like its validity period, its renewal settings, and the actions the certificate can be used for. The policyset.list parameter identifies the block name of the policies that apply to one certificate; the policyset.userCertSet.list lists the individual policies to apply.
For example, the sixth policy populates the Key Usage Extension automatically in the certificate, according to the configuration in the policy. It sets the defaults and requires the certificate to use those defaults by setting the constraints:
3.1.2. Certificate extensions: defaults and constraints
An extension configures additional information to include in a certificate or rules about how the certificate can be used. These extensions can either be specified in the certificate request or taken from the profile default definition and then enforced by the constraints.
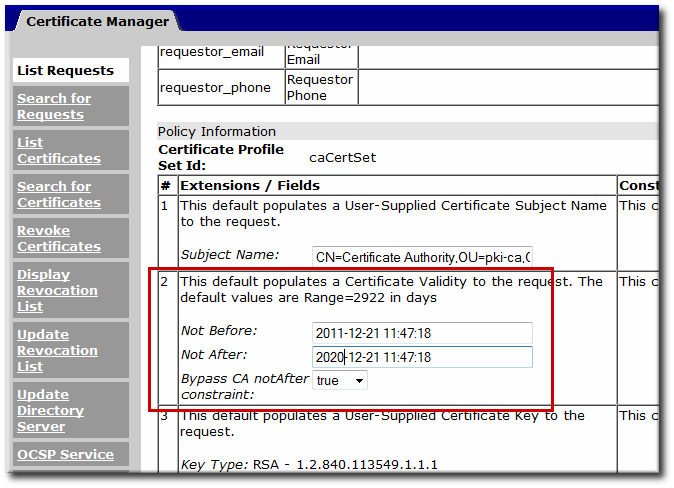
A certificate extension is added or identified in a profile by adding the default which corresponds to the extension and sets default values, if the certificate extension is not set in the request. For example, the Basic Constraints Extension identifies whether a certificate is a CA signing certificate, the maximum number of subordinate CAs that can be configured under the CA, and whether the extension is critical (required):
policyset.caCertSet.5.default.name=Basic Constraints Extension Default policyset.caCertSet.5.default.params.basicConstraintsCritical=true policyset.caCertSet.5.default.params.basicConstraintsIsCA=true policyset.caCertSet.5.default.params.basicConstraintsPathLen=-1
policyset.caCertSet.5.default.name=Basic Constraints Extension Default
policyset.caCertSet.5.default.params.basicConstraintsCritical=true
policyset.caCertSet.5.default.params.basicConstraintsIsCA=true
policyset.caCertSet.5.default.params.basicConstraintsPathLen=-1The extension can also set required values for the certificate request called constraints. If the contents of a request do not match the set constraints, then the request is rejected. The constraints generally correspond to the extension default, though not always. For example:
To allow user supplied extensions to be embedded in the certificate requests and ignore the system-defined default in the profile, the profile needs to contain the User Supplied Extension Default, which is described in Section B.1.32, “User Supplied extension default”.
3.1.3. Inputs and outputs
Inputs set information that must be submitted to receive a certificate. This can be requester information, a specific format of certificate request, or organizational information.
The outputs configured in the profile define the format of the certificate that is issued.
In Certificate System, profiles are accessed by users through enrollment forms that are accessed through the end-entities pages. (Even clients, such as TPS, submit enrollment requests through these forms.) The inputs, then, correspond to fields in the enrollment forms. The outputs correspond to the information contained on the certificate retrieval pages.
3.2. Setting up certificate profiles
In Certificate System, you can add, delete, and modify enrollment profiles:
- Using the PKI command-line interface
- Using the Java-based administration console
This section provides information on each method.
3.2.1. Managing certificate enrollment profiles using the pki command-line interface
This section describes how to manage certificate profiles using the pki utility. For further details, see the pki-ca-profile(1) man page.
Using the raw format is recommended. For details on each attribute and field of the profile, see the section Configuring certificate profiles section in the Red Hat Certificate System Planning, Installation, and Deployment Guide.
3.2.2. Enabling and disabling a certificate profile
Before you can edit a certificate profile, you must disable it. After the modification is complete, you can re-enable the profile.
Only CA agents can enable and disable certificate profiles.
For example, to disable the
caCMCECserverCertcertificate profile:pki -c password -n caagent ca-profile-disable caCMCECserverCert
# pki -c password -n caagent ca-profile-disable caCMCECserverCertCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to enable the
caCMCECserverCertcertificate profile:pki -c password -n caagent ca-profile-enable caCMCECserverCert
# pki -c password -n caagent ca-profile-enable caCMCECserverCertCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.2.2.1. Creating a certificate profile in raw format
To create a new profile in raw format:
pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-add profile_name.cfg --raw
# pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-add profile_name.cfg --rawIn raw format, specify the new profile ID as follows:
profileId=profile_name
profileId=profile_name3.2.2.2. Editing a certificate profile in raw format
CA administrators can edit a certificate profile in raw format without manually downloading the configuration file.
For example, to edit the caCMCECserverCert profile:
pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-edit caCMCECserverCert
# pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-edit caCMCECserverCert
This command automatically downloads the profile configuration in raw format and opens it in the VI editor. When you close the editor, the profile configuration is updated on the server.
You do not need to restart the CA after editing a profile.
Before you can edit a profile, disable the profile. For details, see Section 3.2.2, “Enabling and disabling a certificate profile”.
Example 3.2. Editing a certificate profile in raw format
For example, to edit the caCMCserverCert profile to accept multiple user-supplied extensions:
Disable the profile as a CA agent:
pki -c password -n caagemt ca-profile-disable caCMCserverCert
# pki -c password -n caagemt ca-profile-disable caCMCserverCertCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the profile as a CA administrator:
Download and open the profile in the
VIeditor:pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-edit caCMCserverCert
# pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-edit caCMCserverCertCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Update the configuration to accept the extensions. For details, see Example B.3, “Multiple user supplied extensions in CSR”.
Enable the profile as a CA agent:
pki -c password -n caagent ca-profile-enable caCMCserverCert
# pki -c password -n caagent ca-profile-enable caCMCserverCertCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.2.2.3. Deleting a certificate profile
To delete a certificate profile:
pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-del profile_name
# pki -c password -n caadmin ca-profile-del profile_nameBefore you can delete a profile, disable the profile. For details, see Section 3.2.2, “Enabling and disabling a certificate profile”.
3.2.3. Managing certificate enrollment profiles using the Java-based administration console
3.2.3.1. Creating certificate profiles through the CA console
For security reasons, the Certificate System enforces separation of roles whereby an existing certificate profile can only be edited by an administrator after it was allowed by an agent. To add a new certificate profile or modify an existing certificate profile, perform the following steps as the administrator:
Log in to the Certificate System CA subsystem console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Importantpkiconsoleis being deprecated.In the Configuration tab, select Certificate Manager, and then select Certificate Profiles.
The Certificate Profile Instances Management tab, which lists configured certificate profiles, opens.
To create a new certificate profile, click .
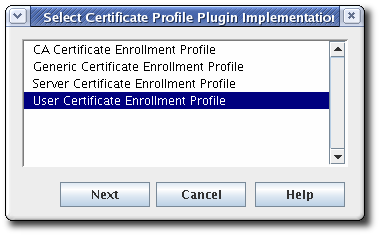
In the Select Certificate Profile Plugin Implementation window, select the type of certificate for which the profile is being created.
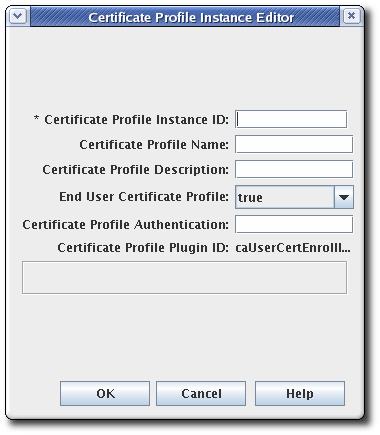
Fill in the profile information in the Certificate Profile Instance Editor.
- Certificate Profile Instance ID. This is the ID used by the system to identify the profile.
- Certificate Profile Name. This is the user-friendly name for the profile.
- Certificate Profile Description.
-
End User Certificate Profile. This sets whether the request must be made through the input form for the profile. This is usually set to
true. Setting this tofalseallows a signed request to be processed through the Certificate Manager’s certificate profile framework, rather than through the input page for the certificate profile. Certificate Profile Authentication. This sets the authentication method. An automated authentication is set by providing the instance ID for the authentication instance. If this field is blank, the authentication method is agent-approved enrollment; the request is submitted to the request queue of the agent services interface.
Unless it is for a TMS subsystem, administrators must select one of the following authentication plug-ins:
-
CMCAuth: Use this plug-in when a CA agent must approve and submit the enrollment request. -
CMCUserSignedAuth: Use this plug-in to enable non-agent users to enroll own certificates.
-
- Click . The plug-in editor closes, and the new profile is listed in the profiles tab.
- Configure the policies, inputs, and outputs for the new profile. Select the new profile from the list, and click .
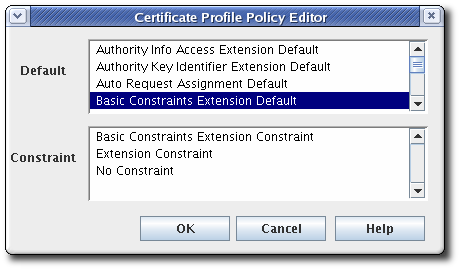
Set up policies in the Policies tab of the Certificate Profile Rule Editor window. The Policies tab lists policies that are already set by default for the profile type.
To add a policy, click .
Choose the default from the Default field, choose the constraints associated with that policy in the Constraints field, and click .
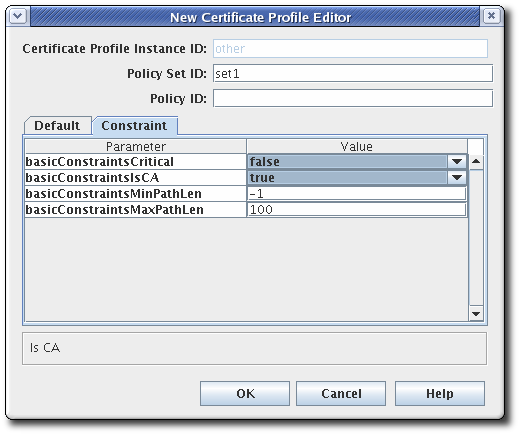
- Fill in the policy set ID. When issuing dual key pairs, separate policy sets define the policies associated with each certificate. Then fill in the certificate profile policy ID, a name or identifier for the certificate profile policy.
Configure any parameters in the Defaults and Constraints tabs.
Defaults defines attributes that populate the certificate request, which in turn determines the content of the certificate. These can be extensions, validity periods, or other fields contained in the certificates. Constraints defines valid values for the defaults.
See Section B.1, “Defaults reference” and Section B.2, “Constraints reference” for complete details for each default or constraint.
- To modify an existing policy, select a policy, and click . Then edit the default and constraints for that policy.
- To delete a policy, select the policy, and click .
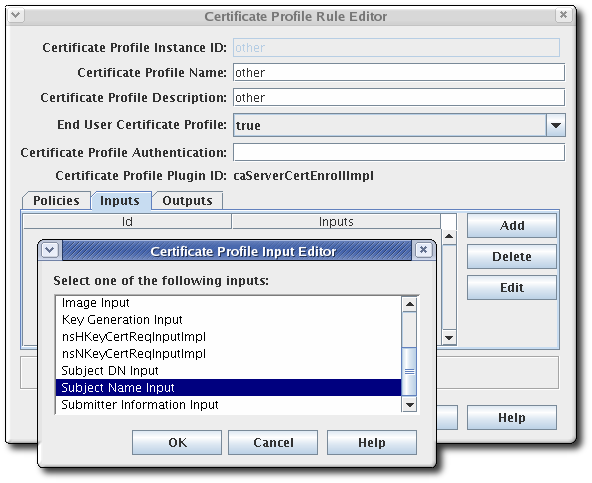
Set inputs in the Inputs tab of the Certificate Profile Rule Editor window. There can be more than one input type for a profile.
NoteUnless you configure the profile for a TMS subsystem, select only
cmcCertReqInputand delete other profiles by selecting them and clicking the button.To add an input, click .
- Choose the input from the list, and click . See Section A.1, “Input reference” for complete details of the default inputs.
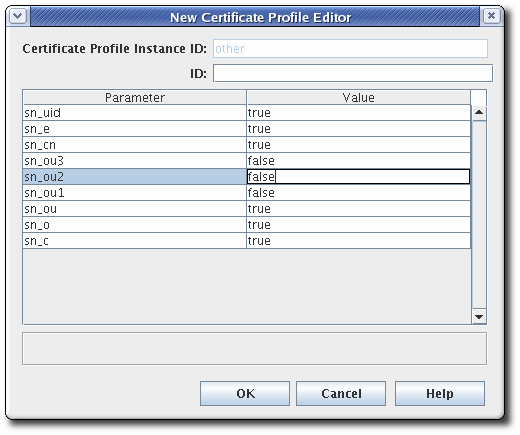
The New Certificate Profile Editor window opens. Set the input ID, and click .
Inputs can be added and deleted. It is possible to select edit for an input, but since inputs have no parameters or other settings, there is nothing to configure.
To delete an input, select the input, and click .
Set up outputs in the Outputs tab of the Certificate Profile Rule Editor window.
Outputs must be set for any certificate profile that uses an automated authentication method; no output needs to be set for any certificate profile that uses agent-approved authentication. The Certificate Output type is set by default for all profiles and is added automatically to custom profiles.
Unless you configure the profile for a TMS subsystem, select only
certOutput.Outputs can be added and deleted. It is possible to select edit for an output, but since outputs have no parameters or other settings, there is nothing to configure.
- To add an output, click .
- Choose the output from the list, and click .
Give a name or identifier for the output, and click .
This output will be listed in the output tab. You can edit it to provide values to the parameters in this output.
To delete an output, select the output from list, and click .
Restart the CA to apply the new profile.
systemctl restart pki-tomcatd-nuxwdog@instance_name.service
# systemctl restart pki-tomcatd-nuxwdog@instance_name.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After creating the profile as an administrator, a CA agent has to approve the profile in the agent services pages to enable the profile.
Open the CA’s services page.
https://server.example.com:8443/ca/services
https://server.example.com:8443/ca/servicesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click the Manage Certificate Profiles link. This page lists all of the certificate profiles that have been set up by an administrator, both active and inactive.
- Click the name of the certificate profile to approve.
At the bottom of the page, click the button.
If this profile will be used with a TPS, then the TPS must be configured to recognized the profile type. This is described in Managing smart card CA profiles section in the Red Hat Certificate System Planning, Installation, and Deployment Guide.
Authorization methods for the profiles can only be added to the profile using the command line, as described in the Configuring certificate profiles section in the Red Hat Certificate System Planning, Installation, and Deployment Guide.
3.2.3.2. Editing certificate profiles in the console
To modify an existing certificate profile:
Log into the agent services pages and disable the profile.
Once a certificate profile is enabled by an agent, that certificate profile is marked enabled in the Certificate Profile Instance Management tab, and the certificate profile cannot be edited in any way through the console.
Log in to the Certificate System CA subsystem console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the Configuration tab, select Certificate Manager, and then select Certificate Profiles.
- Select the certificate profile, and click .
The Certificate Profile Rule Editor window appears. Many any changes to the defaults, constraints, inputs, or outputs.
NOTEThe profile instance ID cannot be modified.
If necessary, enlarge the window by pulling out one of the corners of the window.
- Restart the CA to apply the changes.
- In the agent services page, re-enable the profile.
Delete any certificate profiles that will not be approved by an agent. Any certificate profile that appears in the Certificate Profile Instance Management tab also appears in the agent services interface. If a profile has already been enabled, it must be disabled by the agent before it can be deleted from the profile list.
For a list of supported profiles, see Section 8.1.2, “CMC Authentication Plug-ins”.
3.2.4. Listing certificate enrollment profiles
The following pre-defined certificate profiles are ready to use and set up in this environment when the Certificate System CA is installed. These certificate profiles have been designed for the most common types of certificates, and they provide common defaults, constraints, authentication methods, inputs, and outputs.
For a list of supported profiles, see Section 11.3, “CMC authentication plug-ins”
To list the available profiles on the command line, use the pki utility. For example:
For further details, see the pki-ca-profile(1) man page. Additional information can also be found in the Configuring certificate profiles section in the Red Hat Certificate System Planning, Installation, and Deployment Guide.
3.2.5. Displaying details of a certificate enrollment profile
For example, to display a specific certificate profile, such as caECFullCMCUserSignedCert:
For example, to display a specific certificate profile, such as caECFullCMCUserSignedCert, in raw format:
For further details, see the pki-ca-profile(1) man page.
3.3. Defining key defaults in profiles
When creating certificate profiles, the Key Default must be added before the Subject Key Identifier Default. Certificate System processes the key constraints in the Key Default before creating or applying the Subject Key Identifier Default, so if the key has not been processed yet, setting the key in the subject name fails.
For example, an object-signing profile may define both defaults:
In the policyset list, then, the Key Default (p11) must be listed before the Subject Key Identifier Default (p3).
policyset.set1.list=p1,p2,p11,p3,p4,p5,p6,p7,p8,p9,p10
policyset.set1.list=p1,p2,p11,p3,p4,p5,p6,p7,p8,p9,p103.4. Configuring profiles to enable renewal
This section discusses how to set up profiles for certificate renewals.
Renewing a certificate regenerates the certificate using the same public key as the original certificate. Renewing a certificate can be preferable to simply generating new keys and installing new certificates; for example, if a new CA signing certificate is created, all of the certificates which that CA issued and signed must be reissued. If the CA signing certificate is renewed, then all of the issued certificates are still valid. A renewed certificate is identical to the original, only with an updated validity period and expiration date. This makes renewing certificates a much simpler and cleaner option for handling the expiration of many kinds of certificates, especially CA signing certificates.
For more information on how to renew certificates, see Section 5.4, “Renewing certificates”.
3.4.1. The renewal process
There are two methods of renewing a certificate:
- Regenerating the certificate takes the original key, profile, and request of the certificate and recreates a new certificate with a new validity period and expiration date using the identical key.
- Re-keying a certificate submits a certificate request through the original profile with the same information, so that a new key pair is generated.
A profile that allows renewal is often accompanied by the renewGracePeriodConstraint entry. For example:
The Renew Grace Period Constraint should be set in the original enrollment profile. This defines the amount of time before and after the certificate’s expiration date when the user is allowed to renew the certificate. There are only a few examples of these in the default profiles, and they are mostly not enabled by default. This entry is not required; however, if no grace period is set, it is only possible to renew a certificate on the date of its expiration.
3.4.2. Renewing using the same key
A profile that allows the same key to be submitted for renewal has the allowSameKeyRenewal parameter set to true in the uniqueKeyConstraint entry. For example:
policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.constraint.class_id=uniqueKeyConstraintImpl policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.constraint.name=Unique Key Constraint policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.constraint.params.allowSameKeyRenewal=true policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.default.class_id=noDefaultImpl policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.default.name=No Default
policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.constraint.class_id=uniqueKeyConstraintImpl
policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.constraint.name=Unique Key Constraint
policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.constraint.params.allowSameKeyRenewal=true
policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.default.class_id=noDefaultImpl
policyset.cmcUserCertSet.9.default.name=No Default3.4.3. Renewing using a new key
To renew a certificate with a new key, use the same profile with a new key. Certificate System uses the subjectDN from the user signing certificate that signs the request for the new certificate.
3.5. Setting the signing algorithms for certificates
The CA’s signing certificate can sign the certificates it issues with any public key algorithm supported by the CA. For example, an ECC signing certificate can sign both ECC and RSA certificate requests, and an RSA signing certificate can sign both RSA and ECC certificate requests.
ECC and RSA are public key encryption and signing algorithms. Both public key algorithms support different cipher suites, algorithms used to encrypt and decrypt data. Part of the function of the CA signing certificate is to issue and sign certificates using one of its supported cipher suites.
Each profile can define which cipher suite the CA should use to sign certificates processed through that profile. If no signing algorithm is set, then the profile uses whatever the default signing algorithm is.
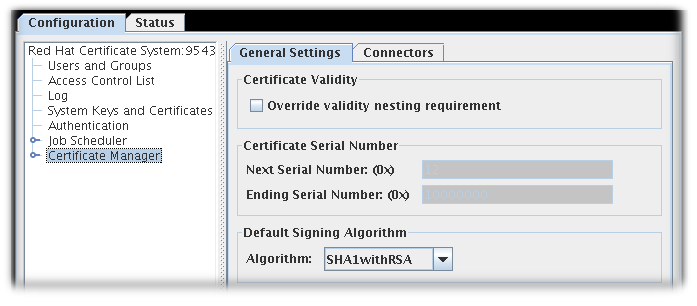
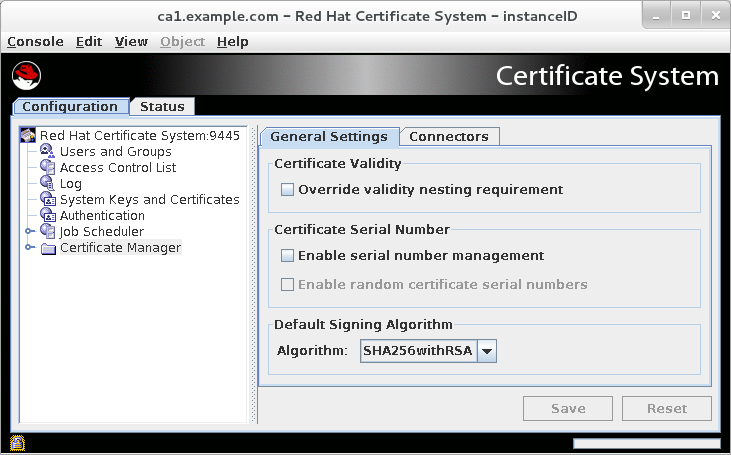
3.5.1. Setting the CA’s default signing algorithm
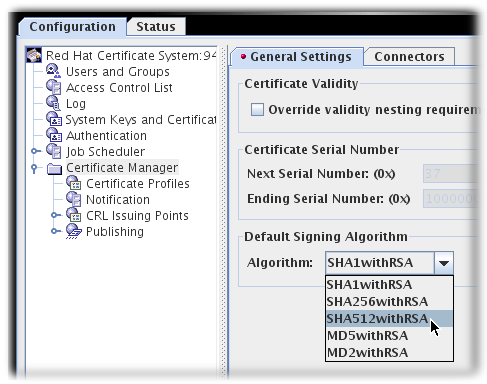
Open the CA console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.- In the Configuration tab, expand the Certificate Manager tree.
In the General Settings tab, set the algorithm to use in the Algorithm drop-down menu.
3.5.1.1. Setting the signing algorithm default in a profile
Each profile has a Signing Algorithm Default extension defined. The default has two settings: a default algorithm and a list of allowed algorithms, if the certificate request specifies a different algorithm. If no signing algorithms are specified, then the profile uses whatever is set as the default for the CA.
In the profile’s .cfg file, the algorithm is set with two parameters:
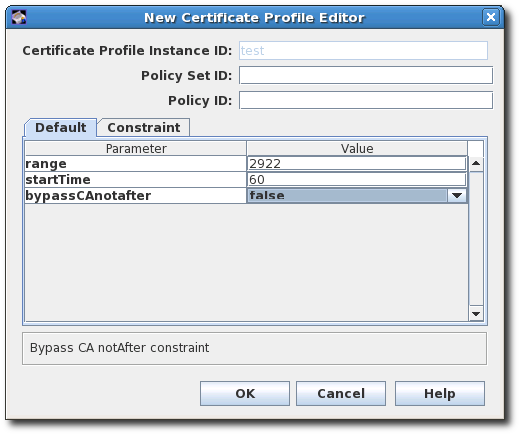
To configure the Signing Algorithm Default through the console:
Before a profile can be edited, it must first be disabled by an agent.
Open the CA console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.- In the Configuration tab, expand the Certificate Manager tree.
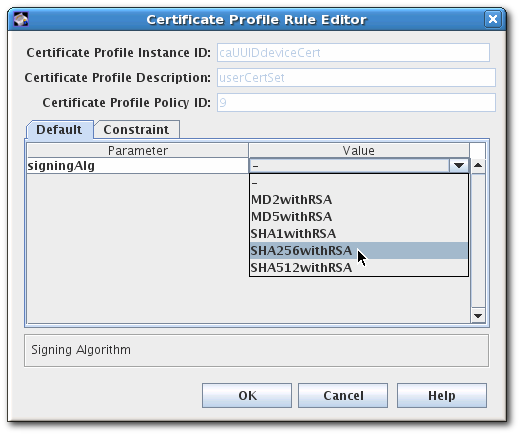
- Click the Certificate Profiles item.
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the Signing Alg policy, and click the button.
To set the default signing algorithm, set the value in the Defaults tab. If this is set to -, then the profile uses the CA’s default.
To set a list of signing algorithms allowed in a certificate request, open the Constraints tab, and set the list of algorithms in the Value field for
signingAlgsAllowed.The possible values for the constraint are listed in Section B.2.10, “Signing Algorithm constraint”.
3.7. Managing subject names and subject alternative names
The subject name of a certificate is a distinguished name (DN) that contains identifying information about the entity to which the certificate is issued. This subject name can be built from standard LDAP directory components, such as common names and organizational units. These components are defined in X.500. In addition to - or even in place of - the subject name, the certificate can have a subject alternative name, which is a kind of extension set for the certificate that includes additional information that is not defined in X.500.
The naming components for both subject names and subject alternative names can be customized.
If the subject name is empty, then the Subject Alternative Name extension must be present and marked critical.
3.7.1. Using the requester CN or UID in the subject name
The cn or uid value from a certificate request can be used to build the subject name of the issued certificate. This section demonstrates a profile that requires the naming attribute (CN or UID) being specified in the Subject Name Constraint to be present in the certificate request. If the naming attribute is missing, the request is rejected.
There are two parts to this configuration:
-
The CN or UID format is set in the
patternconfiguration in the Subject Name Constraint. - The format of the subject DN, including the CN or UID token and the specific suffix for the certificate, is set in the Subject Name Default.
For example, to use the CN in the subject DN:
In this example, if a request comes in with the CN of cn=John Smith, then the certificate will be issued with a subject DN of cn=John Smith,DC=example, DC=com. If the request comes in but it has a UID of uid=jsmith and no CN, then the request is rejected.
The same configuration is used to pull the requester UID into the subject DN:
The format for the pattern parameter is covered in Section B.2.11, “Subject Name constraint” and Section B.1.27, “Subject Name default”.
Information from an LDAP directory or that was submitted by the requester can be inserted into the subject alternative name of the certificate by using matching variables in the Subject Alt Name Extension Default configuration. This default sets the type (format) of information and then the matching pattern (variable) to use to retrieve the information. For example:
This inserts the requester’s email as the first CN component in the subject alt name. To use additional components, increment the Type_, Pattern_, and Enable_ values numerically, such as Type_1.
Configuring the subject alt name is detailed in Section B.1.23, “Subject Alternative Name extension default”, as well.
To insert LDAP components into the subject alt name of the certificate:
Inserting LDAP attribute values requires enabling the user directory authentication plug-in,
SharedSecret.Open the CA Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.- Select Authentication in the left navigation tree.
-
In the Authentication Instance tab, click , and add an instance of the
SharedSecretauthentication plug-in. Enter the following information:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the new plug-in instance.
For information on setting a CMC shared token, see Section 11.4.2, “Setting a CMC Shared Secret”.
The
ldapStringAttributesparameter instructs the authentication plug-in to read the value of themailattribute from the user’s LDAP entry and put that value in the certificate request. When the value is in the request, the certificate profile policy can be set to insert that value for an extension value.The format for the
dnpatternparameter is covered in Section B.2.11, “Subject Name constraint” and Section B.1.27, “Subject Name default”.To enable the CA to insert the LDAP attribute value in the certificate extension, edit the profile’s configuration file, and insert a policy set parameter for an extension. For example, to insert the
mailattribute value in the Subject Alternative Name extension in thecaFullCMCSharedTokenCertprofile, change the following code:policyset.setID.8.default.params.subjAltExtPattern_0=$request.auth_token.mail[0]$
policyset.setID.8.default.params.subjAltExtPattern_0=$request.auth_token.mail[0]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more details about editing a profile, see Section 3.2.2.2, “Editing a certificate profile in raw format”.
Restart the CA.
systemctl restart pki-tomcatd-nuxwdog@instance_name.service
# systemctl restart pki-tomcatd-nuxwdog@instance_name.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For this example, certificates submitted through the caFullCMCSharedTokenCert profile enrollment form will have the Subject Alternative Name extension added with the value of the requester’s mail LDAP attribute. For example:
Identifier: Subject Alternative Name - 2.5.29.17
Critical: no
Value:
RFC822Name: jsmith@example.com
Identifier: Subject Alternative Name - 2.5.29.17
Critical: no
Value:
RFC822Name: jsmith@example.com
There are many attributes which can be automatically inserted into certificates by being set as a token ($X$) in any of the Pattern_ parameters in the policy set. The common tokens are listed in Table 3.1, “Variables used to populate certificates”, and the default profiles contain examples for how these tokens are used.
| Policy Set Token | Description |
|---|---|
| $request.auth_token.cn[0]$ |
The LDAP common name ( |
| $request.auth_token.mail[0]$ |
The value of the LDAP email ( |
| $request.auth_token.tokencertsubject$ | The certificate subject name. |
| $request.auth_token.uid$ |
The LDAP user ID ( |
| $request.auth_token.userdn$ | The user DN of the user who requested the certificate. |
| $request.auth_token.userid$ | The value of the user ID attribute for the user who requested the certificate. |
| $request.uid$ | The value of the user ID attribute for the user who requested the certificate. |
| $request.requestor_email$ | The email address of the person who submitted the request. |
| $request.requestor_name$ | The person who submitted the request. |
| $request.upn$ | The Microsoft UPN. This has the format (UTF8String)1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.3,$request.upn$. |
| $server.source$ | Instructs the server to generate a version 4 UUID (random number) component in the subject name. This always has the format (IA5String)1.2.3.4,$server.source$. |
| $request.auth_token.user$ | Used when the request was submitted by TPS. The TPS subsystem trusted manager who requested the certificate. |
| $request.subject$ |
Used when the request was submitted by TPS. The subject name DN of the entity to which TPS has resolved and requested for. For example, |
3.7.3. Using the CN attribute in the SAN extension
Several client applications and libraries no longer support using the Common Name (CN) attribute of the Subject DN for domain name validation, which has been deprecated in RFC 2818. Instead, these applications and libraries use the dNSName Subject Alternative Name (SAN) value in the certificate request.
Certificate System copies the CN only if it matches the preferred name syntax according to RFC 1034 Section 3.5 and has more than one component. Additionally, existing SAN values are preserved. For example, the dNSName value based on the CN is appended to existing SANs.
To configure Certificate System to automatically use the CN attribute in the SAN extension, edit the certificate profile used to issue the certificates. For example:
Disable the profile:
pki -c password -p 8080 \ -n "PKI Administrator for example.com" ca-profile-disable profile_name# pki -c password -p 8080 \ -n "PKI Administrator for example.com" ca-profile-disable profile_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the profile:
pki -c password -p 8080 \ -n "PKI Administrator for example.com" ca-profile-edit profile_name# pki -c password -p 8080 \ -n "PKI Administrator for example.com" ca-profile-edit profile_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the following configuration with a unique set number for the profile. For example:
policyset.serverCertSet.12.constraint.class_id=noConstraintImpl policyset.serverCertSet.12.constraint.name=No Constraint policyset.serverCertSet.12.default.class_id=commonNameToSANDefaultImpl policyset.serverCertSet.12.default.name=Copy Common Name to Subject
policyset.serverCertSet.12.constraint.class_id=noConstraintImpl policyset.serverCertSet.12.constraint.name=No Constraint policyset.serverCertSet.12.default.class_id=commonNameToSANDefaultImpl policyset.serverCertSet.12.default.name=Copy Common Name to SubjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The previous example uses
12as the set number.Append the new policy set number to the
policyset.userCertSet.listparameter. For example:policyset.userCertSet.list=1,10,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,12
policyset.userCertSet.list=1,10,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,12Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the profile.
Enable the profile:
pki -c password -p 8080 \ -n "PKI Administrator for example.com" ca-profile-enable profile_name# pki -c password -p 8080 \ -n "PKI Administrator for example.com" ca-profile-enable profile_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
All default server profiles contain the commonNameToSANDefaultImpl default.
3.7.4. Accepting SAN extensions from a CSR
In certain environments, administrators want to allow specifying Subject Alternative Name (SAN) extensions in Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
3.7.4.1. Configuring a profile to retrieve SANs from a CSR
To allow retrieving SANs from a CSR, use the User Extension Default. For details, see Section B.1.32, “User Supplied extension default”.
A SAN extension can contain one or more SANs.
To accept SANs from a CSR, add the following default and constraint to a profile, such as caCMCECserverCert:
3.7.4.2. Generating a CSR with SANs
For example, to generate a CSR with two SANs using the certutil utility:
certutil -R -k ec -q nistp256 -d . -s "cn=Example Multiple SANs" --extSAN dns:www.example.com,dns:www.example.org -a -o /root/request.csr.p10
# certutil -R -k ec -q nistp256 -d . -s "cn=Example Multiple SANs" --extSAN dns:www.example.com,dns:www.example.org -a -o /root/request.csr.p10After generating the CSR, follow the steps described in Section 5.5.2, “The CMC enrollment process” to complete the CMC enrollment.