이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
31.5.3. Relationship Mapping
Relationships can be mapped using either a foreign key or a separate relation table. One-to-one and one-to-many relationships use the foreign key mapping style by default, and many-to-many relationships use only the relation table mapping style. The mapping of a relationship is declared in the
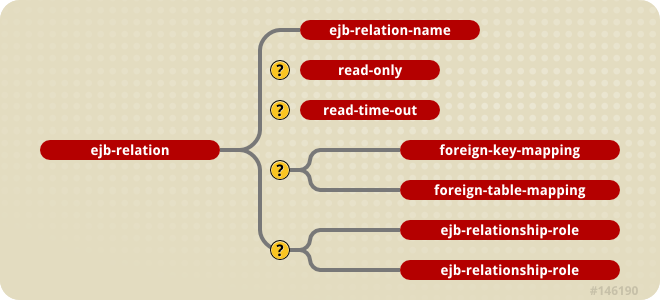
relationships section of the jbosscmp-jdbc.xml descriptor via ejb-relation elements. Relationships are identified by the ejb-relation-name from the ejb-jar.xml file. The jbosscmp-jdbc.xmlejb-relation element content model is shown in Figure 31.7, “The jbosscmp-jdbc.xml ejb-relation element content model”.
Figure 31.7. The jbosscmp-jdbc.xml ejb-relation element content model
The basic template of the relationship mapping declaration for
Organization-Gangster relationship follows:
After the
ejb-relation-name of the relationship being mapped is declared, the relationship can be declared as read only using the read-only and read-time-out elements. They have the same semantics as their counterparts in the entity element.
The
ejb-relation element must contain either a foreign-key-mapping element or a relation-table-mapping element, which are described in Section 31.5.3.2, “Foreign Key Mapping” and Section 31.5.3.3, “Relation table Mapping”. This element may also contain a pair of ejb-relationship-role elements as described in the following section.
31.5.3.1. Relationship Role Mapping
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Each of the two
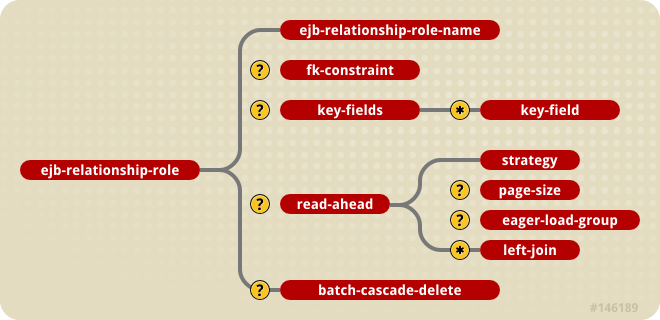
ejb-relationship-role elements contains mapping information specific to an entity in the relationship. The content model of the ejb-relationship-role element is shown in Figure 31.8, “The jbosscmp-jdbc ejb-relationship-role element content model”.
Figure 31.8. The jbosscmp-jdbc ejb-relationship-role element content model
A detailed description of the main elements follows:
- ejb-relationship-role-name: This required element gives the name of the role to which this configuration applies. It must match the name of one of the roles declared for this relationship in the
ejb-jar.xmlfile. - fk-constraint: This optional element is a true/false value that indicates whether JBoss should add a foreign key constraint to the tables for this side of the relationship. JBoss will only add generate the constraint if both the primary table and the related table were created by JBoss during deployment.
- key-fields: This optional element specifies the mapping of the primary key fields of the current entity, whether it is mapped in the relation table or in the related object. The
key-fieldselement must contain akey-fieldelement for each primary key field of the current entity. Thekey-fieldselement can be empty if no foreign key mapping is needed for this side of the relation. An example of this would be the many side of a one-to-many relationship. The details of this element are described below. - read-ahead: This optional element controls the caching of this relationship. This option is discussed in Section 31.8.3.1, “Relationships”.
- batch-cascade-delete: This indicates that a cascade delete on this relationship should be performed with a single SQL statement. This requires that the relationship be marked as
batch-deletein theejb-jar.xml.
As noted above, the
key-fields element contains a key-field for each primary key field of the current entity. The key-field element uses the same syntax as the cmp-field element of the entity, except that key-field does not support the not-null option. Key fields of a relation-table are automatically not null, because they are the primary key of the table. On the other hand, foreign key fields must be nullable by default. This is because the CMP specification requires an insert into the database after the ejbCreate method and an update to it after to pick up CMR changes made in ejbPostCreate. Since the EJB specification does not allow a relationship to be modified until ejbPostCreate, a foreign key will be initially set to null. There is a similar problem with removal. You can change this insert behavior using the jboss.xmlinsert-after-ejb-post-create container configuration flag. The following example illustrates the creation of a new bean configuration that uses insert-after-ejb-post-create by default.
An alternate means of working around the non-null foreign key issue is to map the foreign key elements onto non-null CMP fields. In this case you simply populate the foreign key fields in
ejbCreate using the associated CMP field setters.
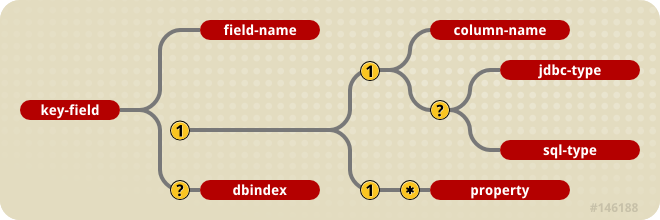
The content model of the key-fields element is Figure 31.9, “The jbosscmp-jdbc key-fields element content model”.
Figure 31.9. The jbosscmp-jdbc key-fields element content model
A detailed description of the elements contained in the
key-field element follows:
- field-name: This required element identifies the field to which this mapping applies. This name must match a primary key field of the current entity.
- column-name: Use this element to specify the column name in which this primary key field will be stored. If this is relationship uses
foreign-key-mapping, this column will be added to the table for the related entity. If this relationship usesrelation-table-mapping, this column is added to therelation-table. This element is not allowed for mapped dependent value class; instead use the property element. - jdbc-type: This is the JDBC type that is used when setting parameters in a JDBC
PreparedStatementor loading data from a JDBC ResultSet. The valid types are defined injava.sql.Types. - sql-type: This is the SQL type that is used in create table statements for this field. Valid types are only limited by your database vendor.
- property: Use this element for to specify the mapping of a primary key field which is a dependent value class.
- dbindex: The presence of this optional field indicates that the server should create an index on the corresponding column in the database, and the index name will be
fieldname_index.