이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
30.4.5. Deadlock
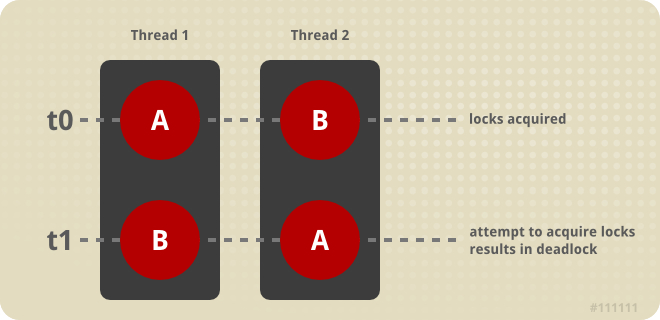
Finding deadlock problems and resolving them is the topic of this section. We will describe what deadlocking MBeans, how you can detect it within your application, and how you can resolve deadlocks. Deadlock can occur when two or more threads have locks on shared resources. Figure 30.8, “Deadlock definition example” illustrates a simple deadlock scenario. Here,
Thread 1 has the lock for Bean A, and Thread 2 has the lock for Bean B. At a later time, Thread 1 tries to lock Bean B and blocks because Thread 2 has it. Likewise, as Thread 2 tries to lock A it also blocks because Thread 1 has the lock. At this point both threads are deadlocked waiting for access to the resource already locked by the other thread.
Figure 30.8. Deadlock definition example
The default locking policy of JBoss is to lock an Entity bean when an invocation occurs in the context of a transaction until the transaction completes. Because of this, it is very easy to encounter deadlock if you have long running transactions that access many entity beans, or if you are not careful about ordering the access to them. Various techniques and advanced configurations can be used to avoid deadlocking problems. They are discussed later in this section.
30.4.5.1. Deadlock Detection
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Fortunately, JBoss is able to perform deadlock detection. JBoss holds a global internal graph of waiting transactions and what transactions they are blocking on. Whenever a thread determines that it cannot acquire an entity bean lock, it figures out what transaction currently holds the lock on the bean and add itself to the blocked transaction graph. An example of what the graph may look like is given in Table 30.1, “An example blocked transaction table”.
| Blocking TX | Tx that holds needed lock |
|---|---|
| Tx1 | Tx2 |
| Tx3 | Tx4 |
| Tx4 | Tx1 |
Before the thread actually blocks it tries to detect whether there is deadlock problem. It does this by traversing the block transaction graph. As it traverses the graph, it keeps track of what transactions are blocked. If it sees a blocked node more than once in the graph, then it knows there is deadlock and will throw an
ApplicationDeadlockException. This exception will cause a transaction rollback which will cause all locks that transaction holds to be released.