이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
8.3. Snapshot Creation
In Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization the initial snapshot for a virtual machine is different from subsequent snapshots in that the initial snapshot retains its format, either QCOW2 or RAW. The first snapshot for a virtual machine designates existing volumes as a base image. Additional snapshots are additional COW layers tracking the changes made to the data stored in the image since the previous snapshot.
In Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization, a guest virtual machine usually interacts with a RAW disk image unless the image is created as a thinly provisioned image or the user specifically asked for it to be QCOW2. As depicted in Figure 8.1, “Initial Snapshot Creation”, the creation of a snapshot causes the volumes that comprise a virtual machine disk image to serve as the base image for all subsequent snapshots.
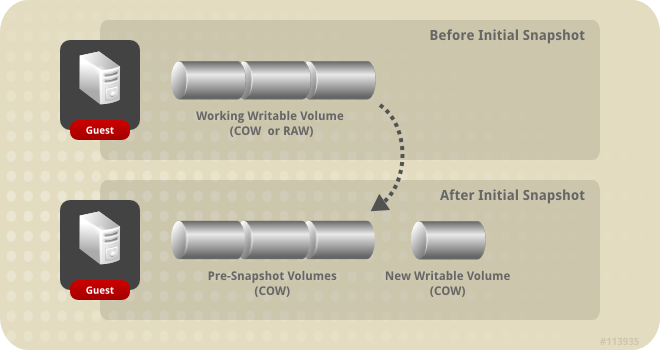
Figure 8.1. Initial Snapshot Creation
Snapshots taken after the initial snapshot result in the creation of new COW volumes in which data that is created or changed after the snapshot is taken will be stored. Each new COW layer begins containing only COW metadata. Data that is created through virtual machine use and operation after a snapshot is written to a new COW layer. When a virtual machine is used to modify data that exists in a previous COW layer, the data is read from the previous layer, and written into the newest layer. Virtual machines locate data by checking each COW layer from most recent to oldest, transparently to the virtual machine.
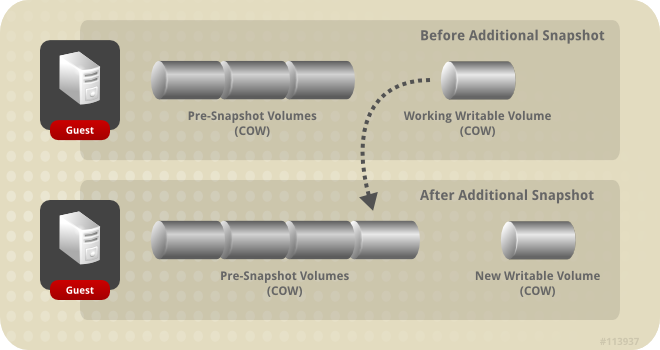
Figure 8.2. Additional Snapshot Creation