Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
4.4. Smart Cards
Authentication based on smart cards is an alternative to password-based authentication. User credentials are stored on the smart card, and special software and hardware is then used to access them. In order to authenticate using a smart card, the user must place the smart card into a smart card reader and then supply the PIN code for the smart card.
Important
The following sections describe how to configure a single system for smart card authentication with local users by using the pam_pkcs11 and pam_krb5 packages. Note that these packages are now deprecated, as described in Deprecated Functionality in the 7.4 Release Notes.
To configure smart card authentication centrally, use the enhanced smart card functionality provided by the System Security Services Daemon (SSSD). For details, see Smart-card Authentication in Identity Management in the Linux Domain Identity, Authentication, and Policy Guide.
4.4.1. Configuring Smart Cards Using authconfig
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Once the Enable smart card support option is selected, additional controls for configuring behavior of smart cards appear.
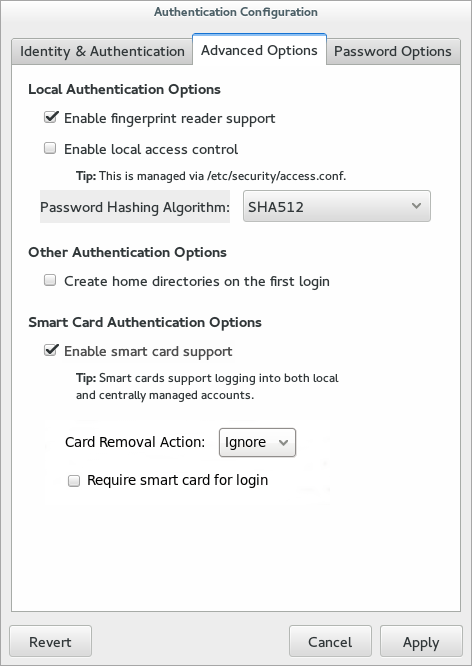
Figure 4.3. Smart Card Options
Note that smart card login for Red Hat Enterprise Linux servers and workstations is not enabled by default and must be enabled in the system settings.
Note
Using single sign-on when logging into Red Hat Enterprise Linux requires these packages:
- nss-tools
- nss-pam-ldapd
- esc
- pam_pkcs11
- pam_krb5
- opensc
- pcsc-lite-ccid
- gdm
- authconfig
- authconfig-gtk
- krb5-libs
- krb5-workstation
- krb5-pkinit
- pcsc-lite
- pcsc-lite-libs
4.4.1.1. Enabling Smart Card Authentication from the UI
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
- Log into the system as root.
- Download the root CA certificates for the network in base 64 format, and install them on the server. The certificates are installed in the appropriate system database using the
certutilcommand. For example:certutil -A -d /etc/pki/nssdb -n "root CA cert" -t "CT,C,C" -i /tmp/ca_cert.crt
[root@server ~]# certutil -A -d /etc/pki/nssdb -n "root CA cert" -t "CT,C,C" -i /tmp/ca_cert.crtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Do not be concerned that the imported certificate is not displayed in theauthconfigUI later during the process. You cannot see the certificate in the UI; it is obtained from the/etc/pki/nssdb/directory during authentication. - In the top menu, select the menu, select , and then click .
- Open the Advanced Options tab.
- Click the Enable Smart Card Support check box.
- There are two behaviors that can be configured for smart cards:
- The Card removal action menu sets the response that the system takes if the smart card is removed during an active session. The
Ignoreoption means that the system continues functioning as normal if the smart card is removed, whileLockimmediately locks the screen. - The Require smart card for login check box sets whether a smart card is required for logins. When this option is selected, all other methods of authentication are blocked.
Warning
Do not select this until after you have successfully logged in using a smart card.
- By default, the mechanisms to check whether a certificate has been revoked (Online Certificate Status Protocol, or OCSP, responses) are disabled. To validate whether a certificate has been revoked before its expiration period, enable OCSP checking by adding the
ocsp_onoption to thecert_policydirective.- Open the
pam_pkcs11.conffile.vim /etc/pam_pkcs11/pam_pkcs11.conf
vim /etc/pam_pkcs11/pam_pkcs11.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change every
cert_policyline so that it contains theocsp_onoption.cert_policy = ca, ocsp_on, signature;
cert_policy = ca, ocsp_on, signature;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Because of the way the file is parsed, there must be a space betweencert_policyand the equals sign. Otherwise, parsing the parameter fails.
- If the smart card has not yet been enrolled (set up with personal certificates and keys), enroll the smart card.
- If the smart card is a CAC card, create the
.k5loginfile in the CAC user's home directory. The.k5loginfile is required to have the Microsoft Principal Name on the CAC card. - Add the following line to the
/etc/pam.d/smartcard-authand/etc/pam.d/system-authfiles:auth optional pam_krb5.so use_first_pass no_subsequent_prompt preauth_options=X509_user_identity=PKCS11:/usr/lib64/pkcs11/opensc-pkcs11.so
auth optional pam_krb5.so use_first_pass no_subsequent_prompt preauth_options=X509_user_identity=PKCS11:/usr/lib64/pkcs11/opensc-pkcs11.soCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the OpenSC module does not work as expected, use the module from the coolkey package:/usr/lib64/pkcs11/libcoolkeypk11.so. In this case, consider contacting Red Hat Technical Support or filing a Bugzilla report about the problem. - Configure the
/etc/krb5.conffile. The settings vary depending on whether you are using a CAC card or a Gemalto 64K card.- With CAC cards, specify all the root certificates related to the CAC card usage in
pkinit_anchors. In the following example/etc/krb5.conffile for configuring a CAC card, EXAMPLE.COM is the realm name for the CAC cards, and kdc.server.hostname.com is the KDC server host name.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the following example
/etc/krb5.conffile for configuring a Gemalto 64K card, EXAMPLE.COM is the realm created on the KDC server, kdc-ca.pem is the CA certificate, and kdc.server.hostname.com is the KDC server host name.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
When a smart card is inserted, the
pklogin_finder utility, when run in debug mode, first maps the login ID to the certificates on the card and then attempts to output information about the validity of certificates:
pklogin_finder debug
pklogin_finder debug
The command is useful for diagnosing problems with using a smart card to log into the system.
4.4.1.2. Configuring Smart Card Authentication from the Command Line
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
All that is required to use smart cards with a system is to set the
--enablesmartcard option:
authconfig --enablesmartcard --update
[root@server ~]# authconfig --enablesmartcard --update
There are other configuration options for smart cards, such as changing the default smart card module, setting the behavior of the system when the smart card is removed, and requiring smart cards for login.
A value of
0 instructs the system to lock out a user immediately if the smart card is removed; a setting of 1 ignores it if the smart card is removed:
authconfig --enablesmartcard --smartcardaction=0 --update
[root@server ~]# authconfig --enablesmartcard --smartcardaction=0 --update
Once smart card authentication has been successfully configured and tested, then the system can be configured to require smart card authentication for users rather than simple password-based authentication.
authconfig --enablerequiresmartcard --update
[root@server ~]# authconfig --enablerequiresmartcard --updateWarning
Do not use the
--enablerequiresmartcard option until you have successfully authenticated to the system using a smart card. Otherwise, users may be unable to log into the system.
4.4.2. Smart Card Authentication in Identity Management
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Red Hat Identity Management supports smart card authentication for IdM users. For more information, see the Smart-card Authentication in Identity Management section in the Linux Domain Identity, Authentication, and Policy Guide.
If you want to start using smart card authentication, see the hardware requirements: Smart-card support in RHEL 7.4+.