Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
Chapter 4. Managing user accounts using Ansible playbooks
You can manage users in IdM using Ansible playbooks. After presenting the user life cycle, learn how to use Ansible playbooks to ensure the presence or absence of users listed directly directly in the YML file.
4.1. User life cycle
Identity Management (IdM) supports three user account states:
- Stage users are not allowed to authenticate. This is an initial state. Some of the user account properties required for active users cannot be set, for example, group membership.
- Active users are allowed to authenticate. All required user account properties must be set in this state.
- Preserved users are former active users that are considered inactive and cannot authenticate to IdM. Preserved users retain most of the account properties they had as active users, but they are not part of any user groups.
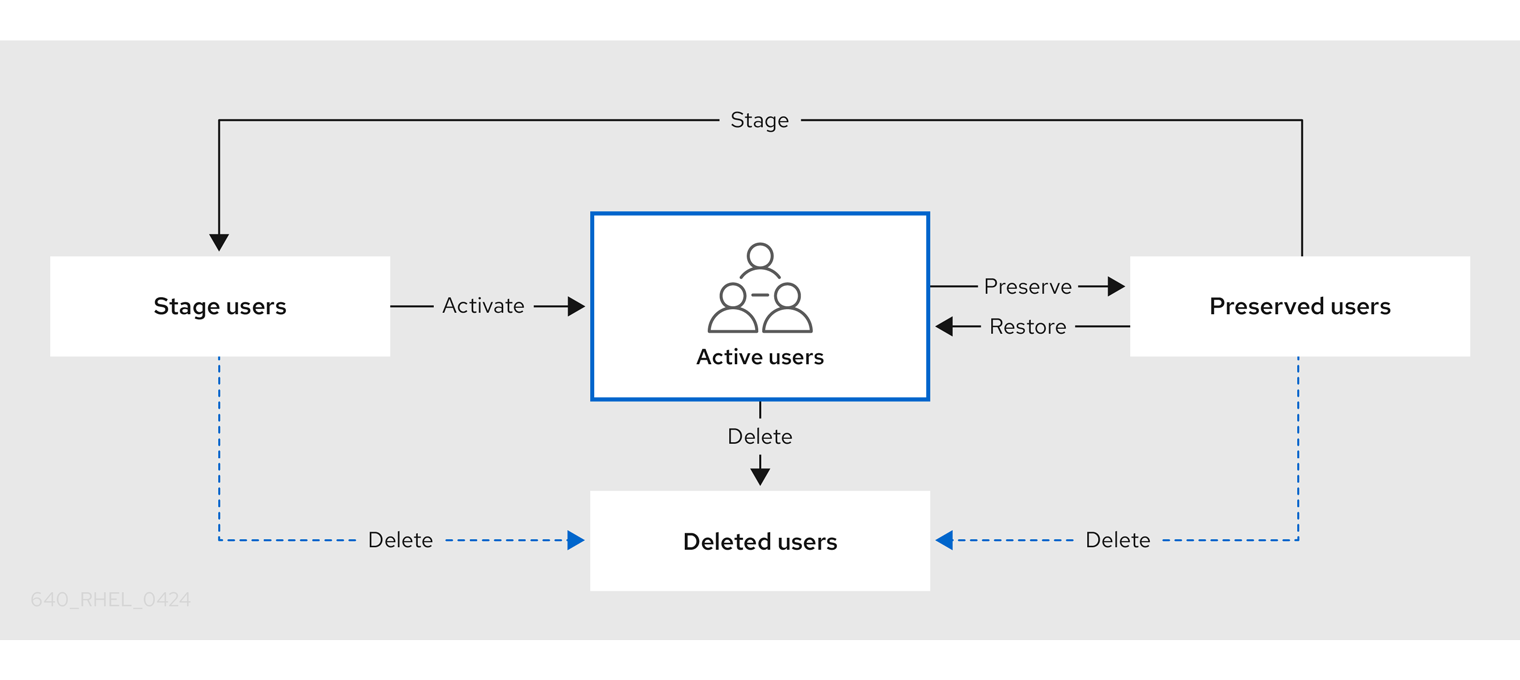
You can delete user entries permanently from the IdM database.
Deleted user accounts cannot be restored. When you delete a user account, all the information associated with the account is permanently lost.
A new administrator can only be created by a user with administrator rights, such as the default admin user. If you accidentally delete all administrator accounts, the Directory Manager must create a new administrator manually in the Directory Server.
Do not delete the admin user. As admin is a pre-defined user required by IdM, this operation causes problems with certain commands. If you want to define and use an alternative admin user, disable the pre-defined admin user with ipa user-disable admin after you granted admin permissions to at least one different user.
Do not add local users to IdM. The Name Service Switch (NSS) always resolves IdM users and groups before resolving local users and groups. This means that, for example, IdM group membership does not work for local users.
4.2. Ensuring the presence of an IdM user using an Ansible playbook
The following procedure describes ensuring the presence of a user in IdM using an Ansible playbook.
Prerequisites
On the control node:
- You are using Ansible version 2.13 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Create an inventory file, for example
inventory.file, and defineipaserverin it:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an Ansible playbook file with the data of the user whose presence in IdM you want to ensure. To simplify this step, you can copy and modify the example in the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/user/add-user.ymlfile. For example, to create user named idm_user and add Password123 as the user password:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You must use the following options to add a user:
- name: the login name
- first: the first name string
- last: the last name string
For the full list of available user options, see the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/README-user.mdMarkdown file.NoteIf you use the
update_password: on_createoption, Ansible only creates the user password when it creates the user. If the user is already created with a password, Ansible does not generate a new password.Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/add-IdM-user.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/add-IdM-user.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can verify if the new user account exists in IdM by using the
ipa user-showcommand:Log into
ipaserveras admin:ssh admin@server.idm.example.com
$ ssh admin@server.idm.example.com Password: [admin@server /]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Request a Kerberos ticket for admin:
kinit admin
$ kinit admin Password for admin@IDM.EXAMPLE.COM:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Request information about idm_user:
ipa user-show idm_user
$ ipa user-show idm_user User login: idm_user First name: Alice Last name: Acme ....Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The user named idm_user is present in IdM.
4.3. Ensuring the presence of multiple IdM users using Ansible playbooks
The following procedure describes ensuring the presence of multiple users in IdM using an Ansible playbook.
Prerequisites
On the control node:
- You are using Ansible version 2.13 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Create an inventory file, for example
inventory.file, and defineipaserverin it:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an Ansible playbook file with the data of the users whose presence you want to ensure in IdM. To simplify this step, you can copy and modify the example in the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/user/ensure-users-present.ymlfile. For example, to create users idm_user_1, idm_user_2, and idm_user_3, and add Password123 as the password of idm_user_1:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do not specify the update_password: on_create option, Ansible resets the user password every time the playbook is run: if the user has changed the password since the last time the playbook was run, Ansible resets password.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/add-users.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/add-users.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can verify if the user account exists in IdM by using the
ipa user-showcommand:Log into
ipaserveras administrator:ssh administrator@server.idm.example.com
$ ssh administrator@server.idm.example.com Password: [admin@server /]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display information about idm_user_1:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The user named idm_user_1 is present in IdM.
4.4. Ensuring the presence of multiple IdM users from a JSON file using Ansible playbooks
The following procedure describes how you can ensure the presence of multiple users in IdM using an Ansible playbook. The users are stored in a JSON file.
Prerequisites
On the control node:
- You are using Ansible version 2.13 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Create an inventory file, for example
inventory.file, and defineipaserverin it:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Create an Ansible playbook file with the necessary tasks. Reference the
JSONfile with the data of the users whose presence you want to ensure. To simplify this step, you can copy and modify the example in the/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/README-user.mdfile:
Create the
users.jsonfile, and add the IdM users into it. To simplify this step, you can copy and modify the example in the/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/README-user.mdfile. For example, to create users idm_user_1, idm_user_2, and idm_user_3, and add Password123 as the password of idm_user_1:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/ensure-users-present-jsonfile.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/ensure-users-present-jsonfile.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can verify if the user accounts are present in IdM using the
ipa user-showcommand:Log into
ipaserveras administrator:ssh administrator@server.idm.example.com
$ ssh administrator@server.idm.example.com Password: [admin@server /]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display information about idm_user_1:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The user named idm_user_1 is present in IdM.
4.5. Ensuring the absence of users using Ansible playbooks
The following procedure describes how you can use an Ansible playbook to ensure that specific users are absent from IdM.
Prerequisites
On the control node:
- You are using Ansible version 2.13 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Create an inventory file, for example
inventory.file, and defineipaserverin it:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an Ansible playbook file with the users whose absence from IdM you want to ensure. To simplify this step, you can copy and modify the example in the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/user/ensure-users-present.ymlfile. For example, to delete users idm_user_1, idm_user_2, and idm_user_3:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/delete-users.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i path_to_inventory_directory/inventory.file path_to_playbooks_directory/delete-users.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can verify that the user accounts do not exist in IdM by using the ipa user-show command:
Log into
ipaserveras administrator:ssh administrator@server.idm.example.com
$ ssh administrator@server.idm.example.com Password: [admin@server /]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Request information about idm_user_1:
ipa user-show idm_user_1
$ ipa user-show idm_user_1 ipa: ERROR: idm_user_1: user not foundCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The user named idm_user_1 does not exist in IdM.