Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
10.3. Establishing Connections
10.3.1. Establishing a Wired (Ethernet) Connection
To establish a wired network connection, Right-click on the NetworkManager applet to open its context menu, ensure that the Enable Networking box is checked, then click on Edit Connections. This opens the Network Connections window. Note that this window can also be opened by running, as a normal user:
~]$ nm-connection-editor &
You can click on the arrow head to reveal and hide the list of connections as needed.

Figure 10.6. The Network Connections window showing the newly created System eth0 connection
The system startup scripts create and configure a single wired connection called System eth0 by default on all systems. Although you can edit System eth0, creating a new wired connection for your custom settings is recommended. You can create a new wired connection by clicking the button, selecting the Wired entry from the list that appears and then clicking the button.
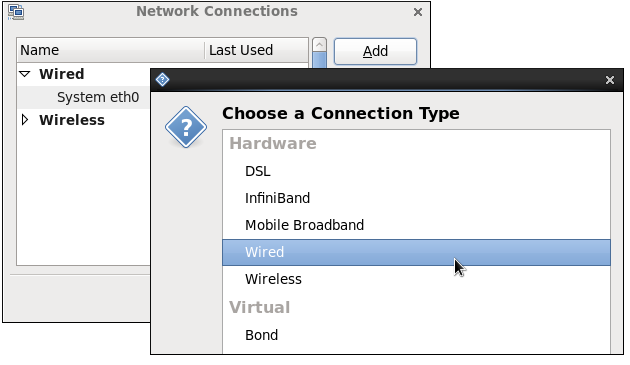
Figure 10.7. Selecting a new connection type from the "Choose a Connection Type" list
Note
When you add a new connection by clicking the button, a list of connection types appears. Once you have made a selection and clicked on the button, NetworkManager creates a new configuration file for that connection and then opens the same dialog that is used for editing an existing connection. There is no difference between these dialogs. In effect, you are always editing a connection; the difference only lies in whether that connection previously existed or was just created by NetworkManager when you clicked .
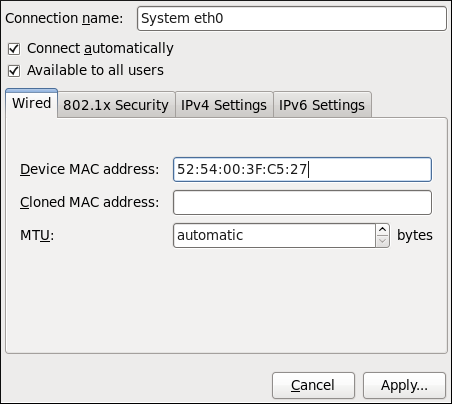
Figure 10.8. Editing the newly created Wired connection System eth0
Configuring the Connection Name, Auto-Connect Behavior, and Availability Settings
Three settings in the Editing dialog are common to all connection types:
- Connection name — Enter a descriptive name for your network connection. This name will be used to list this connection in the Wired section of the Network Connections window.
- Connect automatically — Check this box if you want NetworkManager to auto-connect to this connection when it is available. See Section 10.2.3, “Connecting to a Network Automatically” for more information.
- Available to all users — Check this box to create a connection available to all users on the system. Changing this setting may require
rootprivileges. See Section 10.2.4, “User and System Connections” for details.
Configuring the Wired Tab
The final three configurable settings are located within the Wired tab itself: the first is a text-entry field where you can specify a MAC (Media Access Control) address, and the second allows you to specify a cloned MAC address, and third allows you to specify the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value. Normally, you can leave the MAC address field blank and the MTU set to
automatic. These defaults will suffice unless you are associating a wired connection with a second or specific NIC, or performing advanced networking. In such cases, see the following descriptions:
- MAC Address
- Network hardware such as a Network Interface Card (NIC) has a unique MAC address (Media Access Control; also known as a hardware address) that identifies it to the system. Running the
ip addrcommand will show the MAC address associated with each interface. For example, in the followingip addroutput, the MAC address for the eth0 interface (which is52:54:00:26:9e:f1) immediately follows thelink/etherkeyword:~]#
ip addr1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UNKNOWN qlen 1000 link/ether 52:54:00:26:9e:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.122.251/24 brd 192.168.122.255 scope global eth0 inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fe26:9ef1/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverA single system can have one or more NICs installed on it. The MAC address field therefore allows you to associate a specific NIC with a specific connection (or connections). As mentioned, you can determine the MAC address using theip addrcommand, and then copy and paste that value into the MAC address text-entry field.The cloned MAC address field is mostly for use in such situations were a network service has been restricted to a specific MAC address and you need to emulate that MAC address. - MTU
- The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value represents the size in bytes of the largest packet that the connection will use to transmit. This value defaults to
1500when using IPv4, or a variable number1280or higher for IPv6, and does not generally need to be specified or changed.
Saving Your New (or Modified) Connection and Making Further Configurations
Once you have finished editing your wired connection, click the button and NetworkManager will immediately save your customized configuration. Given a correct configuration, you can connect to your new or customized connection by selecting it from the NetworkManager Notification Area applet. See Section 10.2.1, “Connecting to a Network” for information on using your new or altered connection.
You can further configure an existing connection by selecting it in the Network Connections window and clicking Edit to return to the Editing dialog.
Then, to configure:
- port-based Network Access Control (PNAC), click the 802.1X Security tab and proceed to Section 10.3.9.1, “Configuring 802.1X Security”;
- IPv4 settings for the connection, click the IPv4 Settings tab and proceed to Section 10.3.9.4, “Configuring IPv4 Settings”; or,
- IPv6 settings for the connection, click the IPv6 Settings tab and proceed to Section 10.3.9.5, “Configuring IPv6 Settings”.