此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
5.2. Starting the Cluster Configuration Tool
You can start the Cluster Configuration Tool by logging in to a cluster node as root with the
ssh -Y command and issuing the system-config-cluster command. For example, to start the Cluster Configuration Tool on cluster node nano-01, do the following:
- Log in to a cluster node and run
system-config-cluster. For example:ssh -Y root@nano-01 . . . system-config-cluster
$ ssh -Y root@nano-01 . . . # system-config-clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If this is the first time you have started the Cluster Configuration Tool, the program prompts you to either open an existing configuration or create a new one. Click to start a new configuration file (refer to Figure 5.1, “Starting a New Configuration File”).
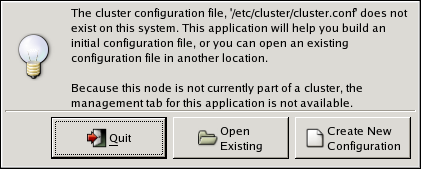
Figure 5.1. Starting a New Configuration File
Note
The tab for the Red Hat Cluster Suite management GUI is available after you save the configuration file with the Cluster Configuration Tool, exit, and restart the the Red Hat Cluster Suite management GUI (system-config-cluster). (The tab displays the status of the cluster service manager, cluster nodes, and resources, and shows statistics concerning cluster service operation. To manage the cluster system further, choose the tab.) - Clicking causes the New Configuration dialog box to be displayed (refer to Figure 5.2, “Creating A New Configuration”). The New Configuration dialog box provides a text box for a cluster name and group boxes for the following configuration options: , (DLM clusters only), and (DLM clusters only). In most circumstances you only need to configure a cluster name and a lock method. is the default lock method. To configure a GULM cluster, select . (Selecting disables and , which are applicable only to DLM clusters). specifies whether a multicast address is used for cluster management communication among cluster nodes. is disabled (checkbox unchecked) by default. To use a multicast address for cluster management communication among cluster nodes, click the checkbox (enabled when checked). When is enabled, the text boxes are enabled; enter the multicast address into the text boxes. To use a quorum disk, click the checkbox and enter quorum disk parameters. The following quorum-disk parameters are available in the dialog box if you enable : , , , , , , and . Table 5.1, “Quorum-Disk Parameters” describes the parameters.
Important
Quorum-disk parameters and heuristics depend on the site environment and special requirements needed. To understand the use of quorum-disk parameters and heuristics, refer to the qdisk(5) man page. If you require assistance understanding and using quorum disk, contact an authorized Red Hat support representative.Note
It is probable that configuring a quorum disk requires changing quorum-disk parameters after the initial configuration. The Cluster Configuration Tool (system-config-cluster) provides only the display of quorum-disk parameters after initial configuration. If you need to configure quorum disk, consider using Conga instead; Conga allows modification of quorum disk parameters.Overall:Whilesystem-config-clusterprovides several convenient tools for configuring and managing a Red Hat Cluster, the newer, more comprehensive tool, Conga, provides more convenience and flexibility thansystem-config-cluster. You may want to consider using Conga instead (refer to Chapter 3, Configuring Red Hat Cluster With Conga and Chapter 4, Managing Red Hat Cluster With Conga).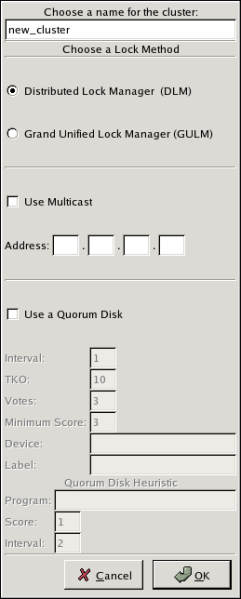
Figure 5.2. Creating A New Configuration
- When you have completed entering the cluster name and other parameters in the New Configuration dialog box, click . Clicking starts the Cluster Configuration Tool, displaying a graphical representation of the configuration (Figure 5.3, “The Cluster Configuration Tool”).
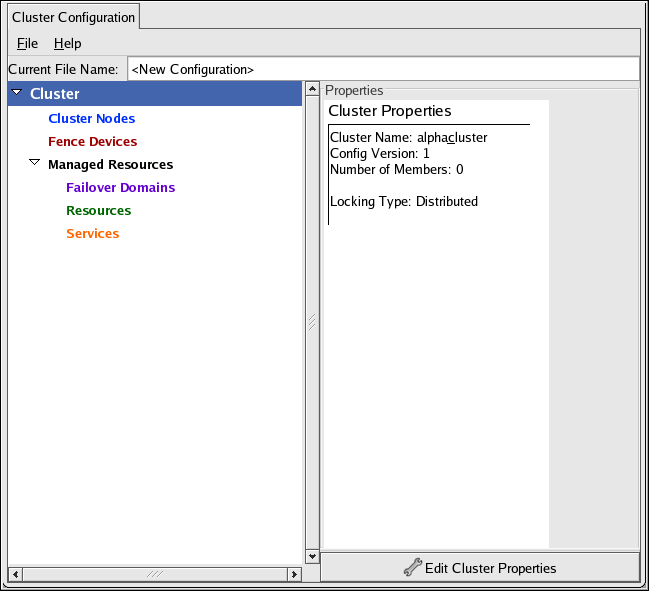
Figure 5.3. The Cluster Configuration Tool
| Parameter | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enables quorum disk. Enables quorum-disk parameters in the New Configuration dialog box. | ||||
| The frequency of read/write cycles, in seconds. | ||||
| The number of cycles a node must miss in order to be declared dead. | ||||
| The number of votes the quorum daemon advertises to CMAN when it has a high enough score. | ||||
The minimum score for a node to be considered "alive". If omitted or set to 0, the default function, floor((n+1)/2), is used, where n is the sum of the heuristics scores. The value must never exceed the sum of the heuristic scores; otherwise, the quorum disk cannot be available. | ||||
| The storage device the quorum daemon uses. The device must be the same on all nodes. | ||||
Specifies the quorum disk label created by the mkqdisk utility. If this field contains an entry, the label overrides the field. If this field is used, the quorum daemon reads /proc/partitions and checks for qdisk signatures on every block device found, comparing the label against the specified label. This is useful in configurations where the quorum device name differs among nodes. | ||||
|