此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
1.8.2. Three-Tier LVS Topology
Figure 1.22, “Three-Tier LVS Topology” shows a typical three-tier LVS configuration. In the example, the active LVS router routes the requests from the public network (Internet) to the second tier — real servers. Each real server then accesses a shared data source of a Red Hat cluster in the third tier over the private network.
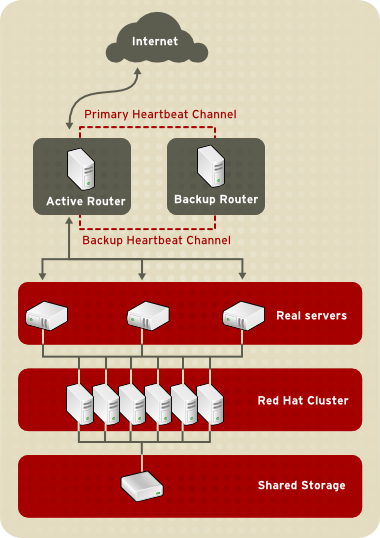
Figure 1.22. Three-Tier LVS Topology
This topology is suited well for busy FTP servers, where accessible data is stored on a central, highly available server and accessed by each real server via an exported NFS directory or Samba share. This topology is also recommended for websites that access a central, high-availability database for transactions. Additionally, using an active-active configuration with a Red Hat cluster, you can configure one high-availability cluster to serve both of these roles simultaneously.