1.6. 群集逻辑卷管理器
群集逻辑卷管理器(Cluster Logical Volume Manager,CLVM)提供了 LVM2 的群集版本。CLVM 具备和单节点上的 LVM2 相同的能力,但它可以使逻辑卷为 Red Hat 群集里的所有节点所用。用 CLVM 创建的逻辑卷可为群集里的所有节点所用。
The key component in CLVM is
clvmd. clvmd is a daemon that provides clustering extensions to the standard LVM2 tool set and allows LVM2 commands to manage shared storage. clvmd runs in each cluster node and distributes LVM metadata updates in a cluster, thereby presenting each cluster node with the same view of the logical volumes (refer to 图 1.14 “CLVM Overview”). Logical volumes created with CLVM on shared storage are visible to all nodes that have access to the shared storage. CLVM allows a user to configure logical volumes on shared storage by locking access to physical storage while a logical volume is being configured. CLVM uses the lock-management service provided by the cluster infrastructure (refer to 第 1.3 节 “Cluster Infrastructure”).
注意
在红帽群集套件中使用的共享存储要求您运行群集逻辑卷管理器守护进程(
clvmd)或者高可用性逻辑卷管理代理(HA-LVM)。如果您无法使用 clvmd 守护进程或者 HA-LVM,无论是因为操作原因还是您没有正确的权利,您就一定不能在共享磁盘中使用单一事件 LVM,因为这将导致数据崩溃。如果您有任何疑问,请联络您的红帽服务代表。
注意
使用 CLVM 需要对
/etc/lvm/lvm.conf 进行群集范围的锁定方面的少许修改。
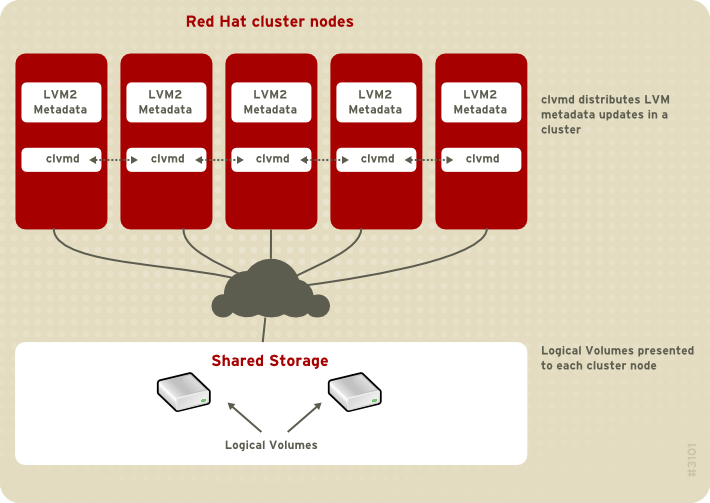
图 1.14. CLVM Overview
You can configure CLVM using the same commands as LVM2, using the LVM graphical user interface (refer to 图 1.15 “LVM Graphical User Interface”), or using the storage configuration function of the Conga cluster configuration graphical user interface (refer to 图 1.16 “Conga LVM Graphical User Interface”) . 图 1.17 “Creating Logical Volumes” shows the basic concept of creating logical volumes from Linux partitions and shows the commands used to create logical volumes.
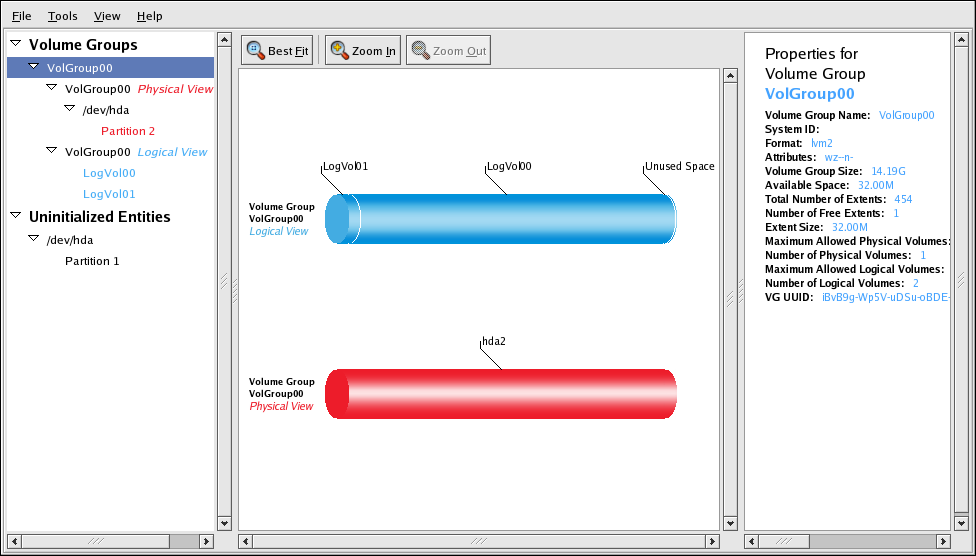
图 1.15. LVM Graphical User Interface
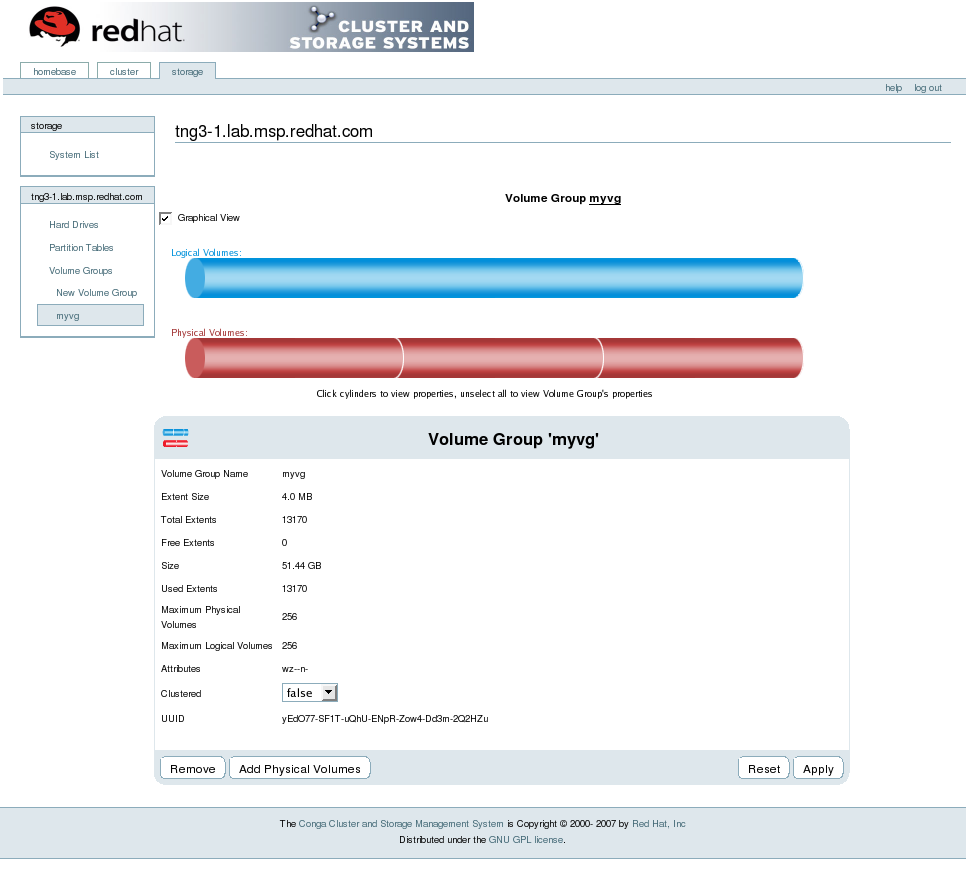
图 1.16. Conga LVM Graphical User Interface
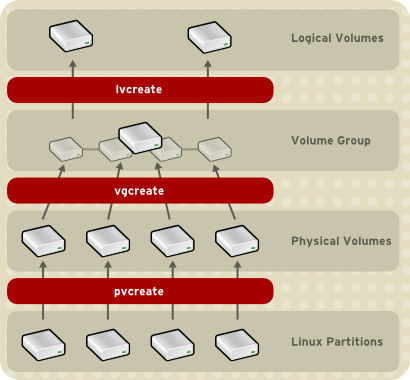
图 1.17. Creating Logical Volumes