Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 3. Application Basics
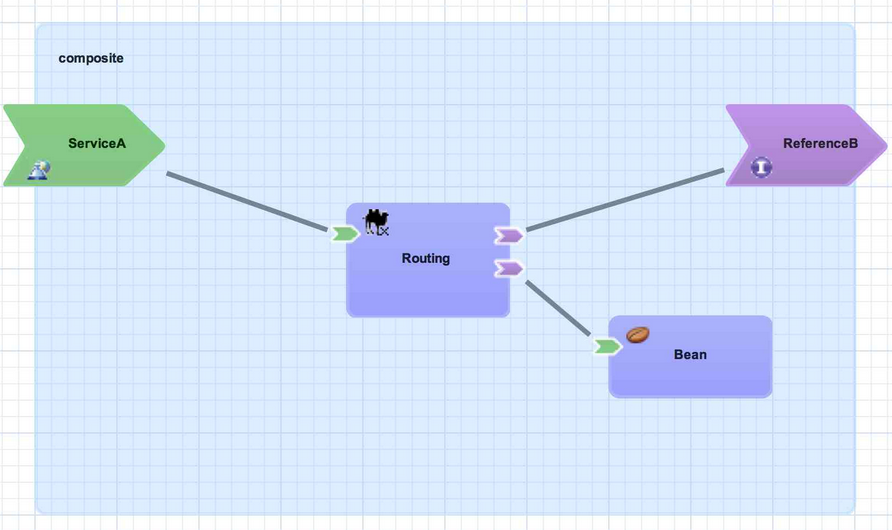
This section introduces the basic building blocks of a SwitchYard application starting from an empty application and building up to the complete application as shown below:
Figure 3.1. Composite
Each topic includes a visual representation of the
switchyard.xml configuration file as designed in the SwitchYard graphical editor and the corresponding source XML which is automatically generated from the visual design.
3.1. Composite
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
A composite is displayed as a light blue rectangle and represents the boundary between what is inside your application and what is outside your application. A SwitchYard application consists of exactly one composite that has a
name and a targetNamespace. The targetNamespace value is important as it allows names defined locally in the application (for example, service names) to be qualified and unique within a SwitchYard runtime.
Figure 3.2. Composite
Example 3.1. Sample Corresponding XML
<sca:composite name="example" targetNamespace="urn:example:switchyard:1.0"> </sca:composite>
<sca:composite name="example" targetNamespace="urn:example:switchyard:1.0">
</sca:composite>