此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 8. LVM Configuration
LVM can be configured during the graphical installation process, the text-based installation process, or during a kickstart installation. You can use the utilities from the
lvm package to create your own LVM configuration post-installation, but these instructions focus on using Disk Druid during installation to complete this task.
Read Chapter 7, Logical Volume Manager (LVM) first to learn about LVM. An overview of the steps required to configure LVM include:
- Creating physical volumes from the hard drives.
- Creating volume groups from the physical volumes.
- Creating logical volumes from the volume groups and assign the logical volumes mount points.
Note
Although the following steps are illustrated during a GUI installation, the same can be done during a text-based installation.
Two 9.1 GB SCSI drives (
/dev/sda and /dev/sdb) are used in the following examples. They detail how to create a simple configuration using a single LVM volume group with associated logical volumes during installation.
8.1. Automatic Partitioning
On the Disk Partitioning Setup screen, select .
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux, LVM is the default method for disk partitioning. If you do not wish to have LVM implemented, or if you require RAID partitioning, manual disk partitioning through Disk Druid is required.
The following properties make up the automatically created configuration:
- The
/boot/partition resides on its own non-LVM partition. In the following example, it is the first partition on the first drive (/dev/sda1). Bootable partitions cannot reside on LVM logical volumes. - A single LVM volume group (
VolGroup00) is created, which spans all selected drives and all remaining space available. In the following example, the remainder of the first drive (/dev/sda2), and the entire second drive (/dev/sdb1) are allocated to the volume group. - Two LVM logical volumes (
LogVol00andLogVol01) are created from the newly created spanned volume group. In the following example, the recommended swap space is automatically calculated and assigned toLogVol01, and the remainder is allocated to the root file system,LogVol00.
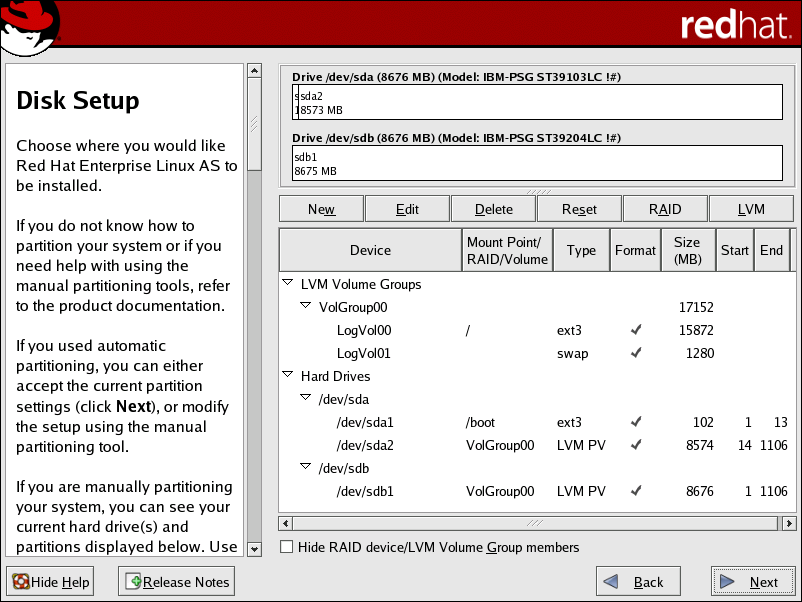
Figure 8.1. Automatic LVM Configuration With Two SCSI Drives
Note
If enabling quotas are of interest to you, it may be best to modify the automatic configuration to include other mount points, such as
/home/ or /var/, so that each file system has its own independent quota configuration limits.
In most cases, the default automatic LVM partitioning is sufficient, but advanced implementations could warrant modification or manual configuration of the LVM partition tables.
Note
If you anticipate future memory upgrades, leaving some free space in the volume group would allow for easy future expansion of the swap space logical volume on the system; in which case, the automatic LVM configuration should be modified to leave available space for future growth.