12.2. Configuring the Services
To allow you to configure which services are started at boot time, Red Hat Enterprise Linux is shipped with the following utilities: the Service Configuration graphical application, the ntsysv text user interface, and the chkconfig command-line tool.
Important
To ensure optimal performance on POWER architecture, it is recommended that the
irqbalance service is enabled. In most cases, this service is installed and configured to run during the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 installation. To verify that irqbalance is running, as root, type the following at a shell prompt:
service irqbalance status irqbalance (pid 1234) is running...
~]# service irqbalance status
irqbalance (pid 1234) is running...
For information on how to enable and run a service using a graphical user interface, see Section 12.2.1, “Using the Service Configuration Utility”. For instructions on how to perform these task on the command line, see Section 12.2.3, “Using the chkconfig Utility” and Section 12.3, “Running Services” respectively.
12.2.1. Using the Service Configuration Utility
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The Service Configuration utility is a graphical application developed by Red Hat to configure which services are started in a particular runlevel, as well as to start, stop, and restart them from the menu. To start the utility, select
system-config-services at a shell prompt.
Note
The
system-config-services utility is provided by the system-config-services package, which may not be installed by default on your version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. To ensure that, first run the following command:
rpm -q system-config-services
~]$ rpm -q system-config-services
If the package is not installed by default, install it manually by running the following command as root:
yum install system-config-services
~]# yum install system-config-services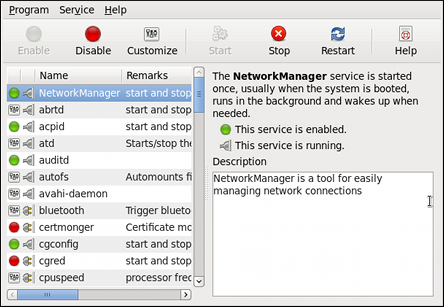
Figure 12.1. The Service Configuration utility
The utility displays the list of all available services (services from the
/etc/rc.d/init.d/ directory, as well as services controlled by xinetd) along with their description and the current status. For a complete list of used icons and an explanation of their meaning, see Table 12.2, “Possible service states”.
Note that unless you are already authenticated, you will be prompted to enter the superuser password the first time you make a change.
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|

| The service is enabled. |

| The service is disabled. |

| The service is enabled for selected runlevels only. |

| The service is running. |

| The service is stopped. |

| There is something wrong with the service. |

| The status of the service is unknown. |
12.2.1.1. Enabling and Disabling a Service
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To enable a service, select it from the list and either click the Enable button on the toolbar, or choose
To disable a service, select it from the list and either click the Disable button on the toolbar, or choose
12.2.1.2. Starting, Restarting, and Stopping a Service
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To start a service, select it from the list and either click the Start button on the toolbar, or choose
To restart a running service, select it from the list and either click the Restart button on the toolbar, or choose
To stop a service, select it from the list and either click the Stop button on the toolbar, or choose
12.2.1.3. Selecting Runlevels
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To enable the service for certain runlevels only, select it from the list and either click the Customize button on the toolbar, or choose