Chapter 20. Sharing files between the host and its virtual machines
You may frequently require to share data between your host system and the virtual machines (VMs) it runs. To do so quickly and efficiently, you can set up NFS file shares on your system. Alternatively, you can also use the virtiofs to share data with your Linux and Windows VMs.
20.1. Sharing files between the host and its virtual machines by using NFS
For efficient file sharing between the RHEL 9 host system and the virtual machines (VMs), you can export an NFS share that VMs can mount and access.
However with Linux VMs, it is usually more convenient to use the virtiofs feature.
Prerequisites
The
nfs-utilspackage is installed on the host.dnf install nfs-utils -y
# dnf install nfs-utils -yCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Virtual network of
NATorbridgetype is configured to connect a host to VMs. - Optional: For improved security, ensure your VMs are compatible with NFS version 4 or later.
Procedure
On the host, export a directory with the files you want to share as a network file system (NFS):
Share an existing directory with VMs. If you do not want to share any of the existing directories, create a new one:
mkdir shared-files
# mkdir shared-filesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Obtain the IP address of each VM to share files from the host, for example, testguest1 and testguest2 :
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
/etc/exportsfile on the host and add a line that includes the directory you want to share, IPs of VMs to share, and additional options:/home/<username>/Downloads/<shared_directory>/ <VM1-IP(options)> <VM2-IP(options)> ...
/home/<username>/Downloads/<shared_directory>/ <VM1-IP(options)> <VM2-IP(options)> ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example shares the
/usr/local/shared-filesdirectory on the host with testguest1 and testguest2, and enables the VMs to edit the content of the directory:/usr/local/shared-files/ 192.0.2.2(rw,sync) 192.0.2.3(rw,sync)
/usr/local/shared-files/ 192.0.2.2(rw,sync) 192.0.2.3(rw,sync)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteTo share a directory with a Windows VM, you need to ensure the Windows NFS client has write permissions in the shared directory. You can use the
all_squash,anonuid, andanongidoptions in the/etc/exportsfile./usr/local/shared-files/ 192.0.2.2(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=<directory-owner-UID>,anongid=<directory-owner-GID>)The <directory-owner-UID> and <directory-owner-GID> are the UID and GID of the local user that owns the shared directory on the host.
For other options to manage NFS client permissions, follow the Securing the NFS service guide.
Export the updated file system:
exportfs -a
# exportfs -aCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the
nfs-serverservice:systemctl start nfs-server
# systemctl start nfs-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Obtain the IP address of the host system to mount the shared directory on the VMs:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the relevant network connects the host with VMs to share files. Usually, this is
virbr0.
Mount the shared directory on a Linux VM that is specified in the
/etc/exportsfile:mount 192.0.2.1:/usr/local/shared-files /mnt/host-share
# mount 192.0.2.1:/usr/local/shared-files /mnt/host-shareCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
192.0.2.1: The IP address of the host. -
/usr/local/shared-files: A file-system path to the exported directory on the host. /mnt/host-share: A mount point on the VMNoteThe mount point must be an empty directory.
-
To mount the shared directory on a Windows VM as mentioned in the
/etc/exportsfile:- Open a PowerShell shell prompt as an Administrator.
Install the
NFS-Clientpackage on the Windows.To install on a server version, enter:
Install-WindowsFeature NFS-Client
# Install-WindowsFeature NFS-ClientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To install on a desktop version, enter:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName ServicesForNFS-ClientOnly, ClientForNFS-Infrastructure -Online -NoRestart
# Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName ServicesForNFS-ClientOnly, ClientForNFS-Infrastructure -Online -NoRestartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Mount the directory exported by the host on a Windows VM:
C:\Windows\system32\mount.exe -o anon \\192.0.2.1\usr\local\shared-files Z:
# C:\Windows\system32\mount.exe -o anon \\192.0.2.1\usr\local\shared-files Z:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example:
-
192.0.2.1: The IP address of the host. -
/usr/local/shared-files: A file system path to the exported directory on the host. Z:: The drive letter for a mount point.NoteYou must choose a drive letter that is not in use on the system.
-
Verification
List the contents of the shared directory on the VM so that you can share files between the host and the VM:
ls <mount_point> shared-file1 shared-file2 shared-file3
$ ls <mount_point> shared-file1 shared-file2 shared-file3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, replace <mount_point> with a file system path to the mounted shared directory.
20.2. Sharing files between the host and its virtual machines by using virtiofs
Using virtiofs, you can share files between your host and your virtual machines (VM) as a directory tree that works the same as the local file system structure.
20.2.1. Sharing files between the host and its virtual machines by using virtiofs
When using RHEL 9 as your hypervisor, you can efficiently share files between your host system and its virtual machines (VM) using the virtiofs feature.
Prerequisites
- Virtualization is installed and enabled on your RHEL 9 host.
A directory that you want to share with your VMs. If you do not want to share any of your existing directories, create a new one, for example named shared-files.
mkdir /root/shared-files
# mkdir /root/shared-filesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The VM you want to share data with is using a Linux distribution as its guest operating system.
Procedure
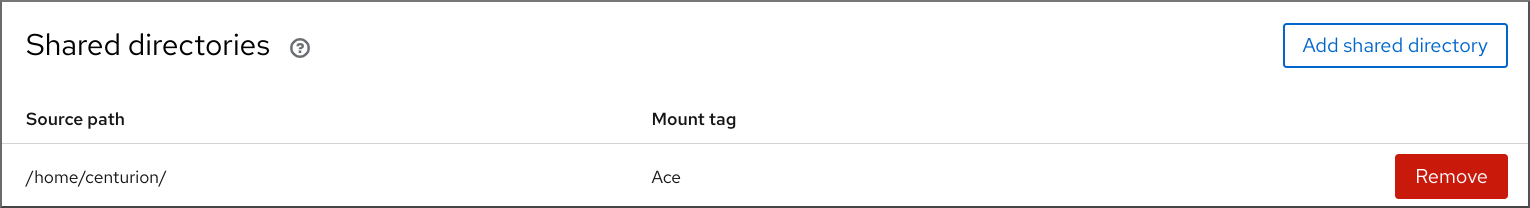
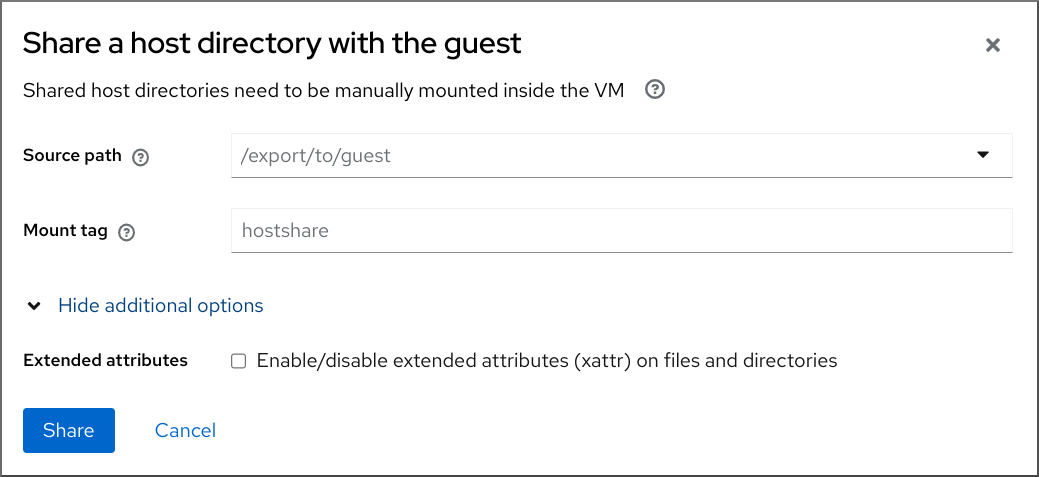
For each directory on the host that you want to share with your VM, set it as a virtiofs file system in the VM’s XML configuration.
Open the XML configuration of the intended VM.
virsh edit vm-name
# virsh edit vm-nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add an entry similar to the following to the
<devices>section of the VM’s XML configuration.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example sets the
/root/shared-filesdirectory on the host to be visible ashost-file-shareto the VM.
Set up shared memory for the VM. To do so, add shared memory backing to the
<domain>section of the XML configuration:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Boot up the VM.
virsh start vm-name
# virsh start vm-nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount the file system in the guest operating system. The following example mounts the previously configured
host-file-sharedirectory with a Linux guest operating system.mount -t virtiofs host-file-share /mnt
# mount -t virtiofs host-file-share /mntCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
- Ensure that the shared directory became accessible on the VM and that you can now open files stored in the directory.
Known issues and limitations
-
File-system mount options related to access time, such as
noatimeandstrictatime, are not likely to work with virtiofs, and Red Hat discourages their use.
Troubleshooting
-
If
virtiofsis not optimal for your usecase or supported for your system, you can use NFS instead.
20.2.2. Sharing files between the host and Windows virtual machines by using virtiofs
When using RHEL 9 as your hypervisor, you can efficiently share files between your host system and Windows virtual machines (VM) using the virtiofs feature along with the virtio-win package.
You can run the virtiofs service in case insensitive mode on a Windows VM using the virtiofs.exe command and the -i parameter.
Prerequisites
- You have configured your VM’s XML configuration file to use virtiofs. For detailed information, see Section 20.2.1, “Sharing files between the host and its virtual machines by using virtiofs”.
-
You have attached the
virtiodriver installation media to the VM. -
You have installed the
virtio-winpackage on your Windows VM. For more information, see Installing virtio drivers on a Windows guest.
Procedure
On your Windows VM, install WinFsp. To do so, mount the
virtio-winISO image, start thewinfspMSI installer, and follow the prompts.In the Custom Setup window of the installation wizard, select the features you want to install on the VM.
Start the virtiofs service:
sc start VirtioFsSvc
# sc start VirtioFsSvcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to This PC:
File Explorer
This PC Virtiofs should be available on the Windows VM as the first available drive letter starting with
z:and going backwards. For example,my_viofs (Z:).ImportantYou must restart the virtiofs service after each VM reboot to access the shared directory.
Optional: To set up additional virtiofs instances:
Stop the virtiofs service:
sc stop VirtioFsSvc sc config VirtioFsSvc start=demand
# sc stop VirtioFsSvc # sc config VirtioFsSvc start=demandCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the WinFSP.Launcher service to set up multiple virtiofs instances:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\fsreg.bat" virtiofs "<path to the binary>\virtiofs.exe" "-t %1 -m %2"
# "C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\fsreg.bat" virtiofs "<path to the binary>\virtiofs.exe" "-t %1 -m %2"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount virtiofs instances to drives.
For example, to mount virtiofs with the tag
mount_tag0to theY:drive:"C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\launchctl-x64.exe" start virtiofs viofsY mount_tag0 Y:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\launchctl-x64.exe" start virtiofs viofsY mount_tag0 Y:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Repeat the previous step to mount all of your virtiofs instances.
To unmount the virtiofs instance:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\launchctl-x64.exe" stop virtiofs viofsY
"C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\launchctl-x64.exe" stop virtiofs viofsYCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
On your Windows VM, navigate to This PC:
File Explorer
This PC -
If you did not specify a mount point when setting up the virtiofs service, it will use the first available drive letter starting with
z:and going backwards. - If you have multiple virtiofs instances set up, they will appear as drives with the letters you had assigned to the instances.
-
If you did not specify a mount point when setting up the virtiofs service, it will use the first available drive letter starting with