47.3. JAX-RS 2.0 Exception Types
Overview
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
JAX-RS 2.0 introduces a number of specific HTTP exception types that you can throw (and catch) in your application code (in addition to the existing
WebApplicationException exception type). These exception types can be used to wrap standard HTTP status codes, either for HTTP client errors (HTTP 4xx status codes), or HTTP server errors (HTTP 5xx status codes).
Exception hierarchy
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
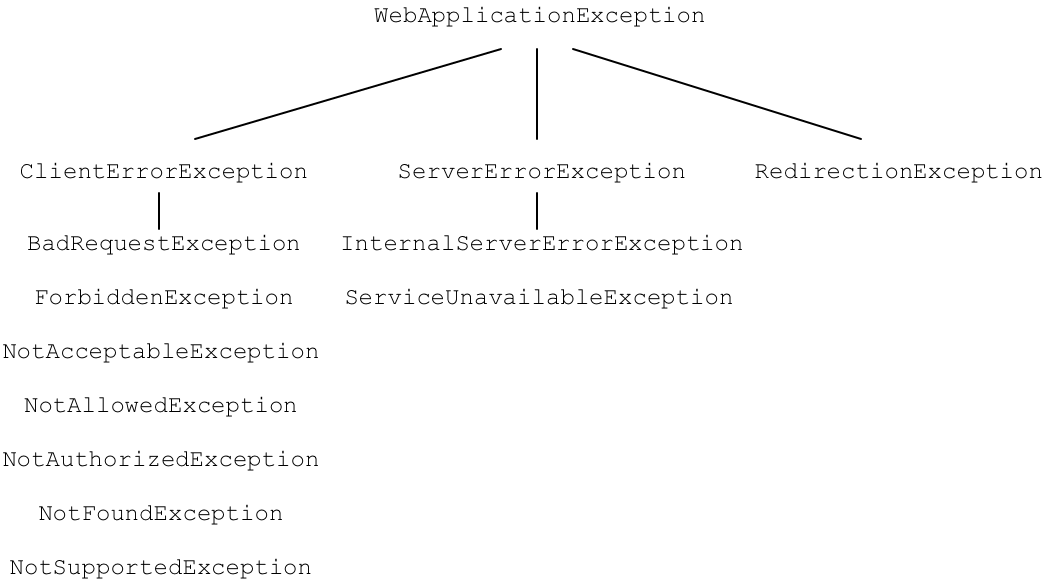
Figure 47.1, “JAX-RS 2.0 Application Exception Hierarchy” shows the hierarchy of application level exceptions supported in JAX-RS 2.0.
Figure 47.1. JAX-RS 2.0 Application Exception Hierarchy
WebApplicationException class
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The
javax.ws.rs.WebApplicationException exception class (which has been available since JAX-RS 1.x) is at the base of the JAX-RS 2.0 exception hierarchy, and is described in detail in Section 47.2, “Using WebApplicationException exceptions to report errors”.
ClientErrorException class
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The
javax.ws.rs.ClientErrorException exception class is used to encapsulate HTTP client errors (HTTP 4xx status codes). In your application code, you can throw this exception or one of its subclasses.
ServerErrorException class
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The
javax.ws.rs.ServerErrorException exception class is used to encapsulate HTTP server errors (HTTP 5xx status codes). In your application code, you can throw this exception or one of its subclasses.
RedirectionException class
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The
javax.ws.rs.RedirectionException exception class is used to encapsulate HTTP request redirection (HTTP 3xx status codes). The constructors of this class take a URI argument, which specifies the redirect location. The redirect URI is accessible through the getLocation() method. Normally, HTTP redirection is transparent on the client side.
Client exception subclasses
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
You can raise the following HTTP client exceptions (HTTP
4xx status codes) in a JAX-RS 2.0 application:
BadRequestException- Encapsulates the 400 Bad Request HTTP error status.
ForbiddenException- Encapsulates the 403 Forbidden HTTP error status.
NotAcceptableException- Encapsulates the 406 Not Acceptable HTTP error status.
NotAllowedException- Encapsulates the 405 Method Not Allowed HTTP error status.
NotAuthorizedException- Encapsulates the 401 Unauthorized HTTP error status. This exception could be raised in either of the following cases:
- The client did not send the required credentials (in a HTTP
Authorizationheader), or - The client presented the credentials, but the credentials were not valid.
NotFoundException- Encapsulates the 404 Not Found HTTP error status.
NotSupportedException- Encapsulates the 415 Unsupported Media Type HTTP error status.
Server exception subclasses
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
You can raise the following HTTP server exceptions (HTTP
5xx status codes) in a JAX-RS 2.0 application:
InternalServerErrorException- Encapsulates the 500 Internal Server Error HTTP error status.
ServiceUnavailableException- Encapsulates the 503 Service Unavailable HTTP error status.