1.2. Red Hat Virtualization Host
A Red Hat Virtualization environment has one or more hosts attached to it. A host is a server that provides the physical hardware that virtual machines make use of.
Red Hat Virtualization Host (RHVH) runs an optimized operating system installed using a special, customized installation media specifically for creating virtualization hosts.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux hosts are servers running a standard Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating system that has been configured after installation to permit use as a host.
Both methods of host installation result in hosts that interact with the rest of the virtualized environment in the same way, and so, will both referred to as hosts.
Figure 1.2. Host Architecture
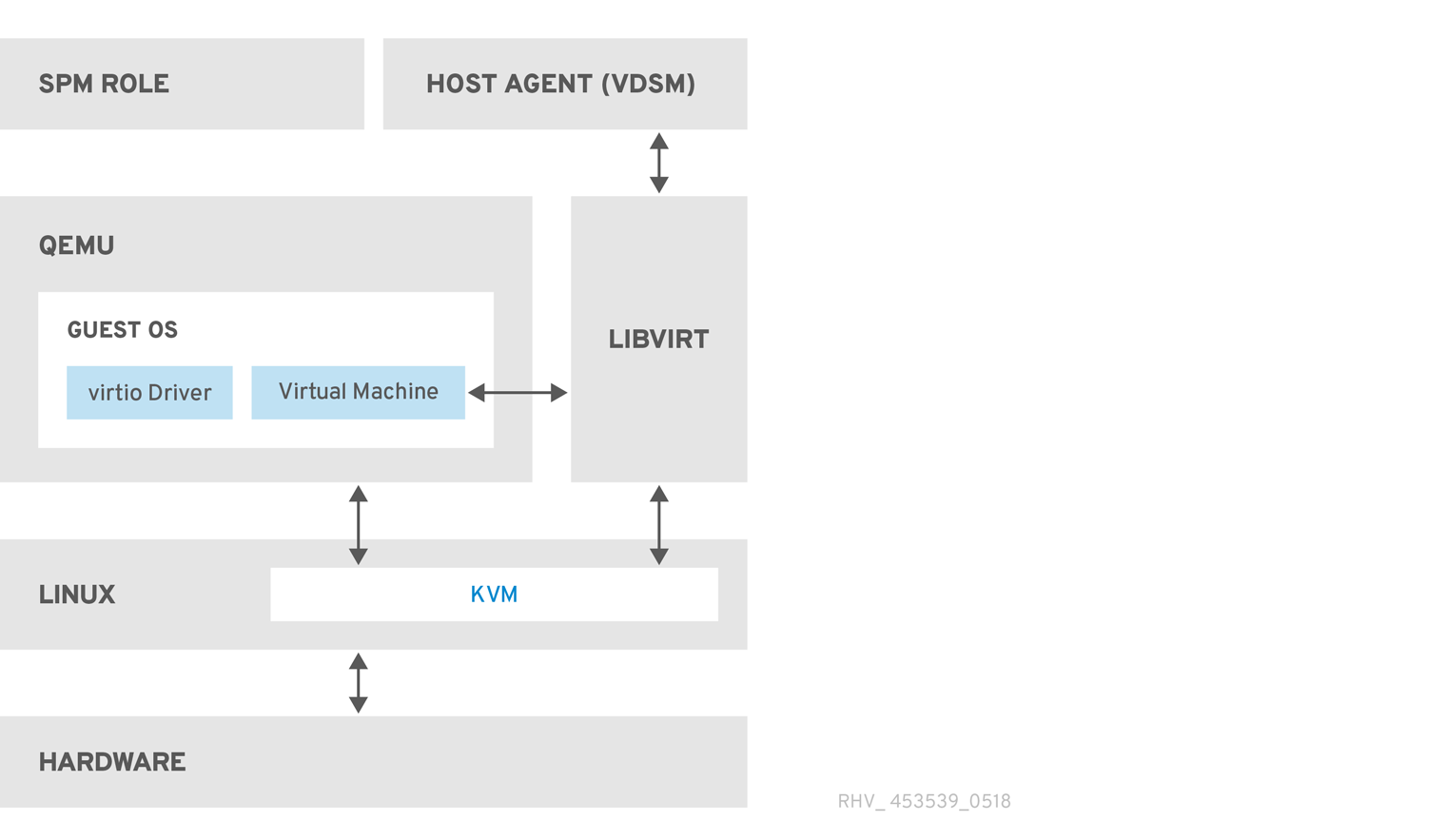
- Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM)
- The Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is a loadable kernel module that provides full virtualization through the use of the Intel VT or AMD-V hardware extensions. Though KVM itself runs in kernel space, the guests running upon it run as individual QEMU processes in user space. KVM allows a host to make its physical hardware available to virtual machines.
- QEMU
- QEMU is a multi-platform emulator used to provide full system emulation. QEMU emulates a full system, for example a PC, including one or more processors, and peripherals. QEMU can be used to launch different operating systems or to debug system code. QEMU, working in conjunction with KVM and a processor with appropriate virtualization extensions, provides full hardware assisted virtualization.
- Red Hat Virtualization Manager Host Agent, VDSM
-
In Red Hat Virtualization, VDSM initiates actions on virtual machines and storage. It also facilitates inter-host communication. VDSM monitors host resources such as memory, storage, and networking. Additionally, VDSM manages tasks such as virtual machine creation, statistics accumulation, and log collection. A VDSM instance runs on each host and receives management commands from the Red Hat Virtualization Manager using the re-configurable port
54321.
- VDSM-REG
-
VDSM uses VDSM-REG to register each host with the Red Hat Virtualization Manager. VDSM-REG supplies information about itself and its host using port
80or port443. - libvirt
- Libvirt facilitates the management of virtual machines and their associated virtual devices. When Red Hat Virtualization Manager initiates virtual machine life-cycle commands (start, stop, reboot), VDSM invokes libvirt on the relevant host machines to execute them.
- Storage Pool Manager, SPM
The Storage Pool Manager (SPM) is a role assigned to one host in a data center. The SPM host has sole authority to make all storage domain structure metadata changes for the data center. This includes creation, deletion, and manipulation of virtual disks, snapshots, and templates. It also includes allocation of storage for sparse block devices on a Storage Area Network(SAN). The role of SPM can be migrated to any host in a data center. As a result, all hosts in a data center must have access to all the storage domains defined in the data center.
Red Hat Virtualization Manager ensures that the SPM is always available. In case of storage connectivity errors, the Manager re-assigns the SPM role to another host.
- Guest Operating System
Guest operating systems do not need to be modified to be installed on virtual machines in a Red Hat Virtualization environment. The guest operating system, and any applications on the guest, are unaware of the virtualized environment and run normally.
Red Hat provides enhanced device drivers that allow faster and more efficient access to virtualized devices. You can also install the Red Hat Virtualization Guest Agent on guests, which provides enhanced guest information to the management console.