Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
8.12. Composed Message Processor
Composed Message Processor
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
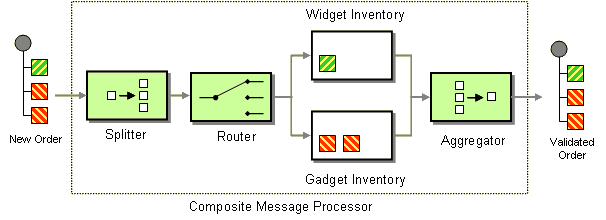
The composed message processor pattern, as shown in Figure 8.11, “Composed Message Processor Pattern”, allows you to process a composite message by splitting it up, routing the sub-messages to appropriate destinations, and then re-aggregating the responses back into a single message.
Figure 8.11. Composed Message Processor Pattern
Java DSL example
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
The following example checks that a multipart order can be filled, where each part of the order requires a check to be made at a different inventory:
XML DSL example
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
The preceding route can also be written in XML DSL, as follows:
Processing steps
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Processing starts by splitting the order, using a Splitter. The Splitter then sends individual
OrderItems to a Content Based Router, which routes messages based on the item type. Widget items get sent for checking in the widgetInventory bean and gadget items get sent to the gadgetInventory bean. Once these OrderItems have been validated by the appropriate bean, they are sent on to the Aggregator which collects and re-assembles the validated OrderItems into an order again.
Each received order has a header containing an order ID. We make use of the order ID during the aggregation step: the
.header("orderId") qualifier on the aggregate() DSL command instructs the aggregator to use the header with the key, orderId, as the correlation expression.
For full details, check the
ComposedMessageProcessorTest.java example source at camel-core/src/test/java/org/apache/camel/processor.