Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 40. Provider-Based Route
40.1. Provider-Based JAX-WS Endpoint
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Overview
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Use the provider-based approach, if you need to process very large Web services messages. The provider-based approach is a variant of the PAYLOAD data format that enables you to encode the message body as an XML streaming type, such as
SAXSource. Since the XMLstreaming types are more efficient than DOM objects, the provider-based approach is ideal for large XML messages.
Demonstration location
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
The code presented in this chapter is taken from the following demonstration:
cxf-webinars-jboss-fuse-6.3/customer-ws-camel-cxf-provider
cxf-webinars-jboss-fuse-6.3/customer-ws-camel-cxf-provider
For details of how to download and install the demonstration code, see Chapter 34, Demonstration Code for Camel/CXF
Camel CXF component
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
The Camel CXF component is an Apache CXF component that integrates Web services with routes. You can use it either to instantiate consumer endpoints (at the start of a route), which behave like Web service instances, or to instantiate producer endpoints (at any other points in the route), which behave like WS clients.
Note
Came CXF endpoints—which are instantiated using the
cxf:cxfEndpoint XML element and are implemented by the Apache Camel project—are not to be confused with the Apache CXF JAX-WS endpoints—which are instantiated using the jaxws:endpoint XML element and are implemented by the Apache CXF project.
Provider-based approach and the PAYLOAD data format
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
The provider-based approach is a variant of the PAYLOAD data format, which is enabled as follows:
- Define a custom
javax.xml.ws.Provider<StreamType>class, where the StreamType type is an XML streaming type, such asSAXSource. - The PAYLOAD data format is selected by an annotation on the custom
Provider<?>class (see the section called “The SAXSourceService provider class”). - The custom
Provider<?>class is referenced by setting theserviceClassattribute of thecxf:cxfEndpointelement in XML configuration.
The provider-based approach has the following characteristics:
- Enables you to access the message body as a streamed XML type—for example,
javax.xml.transform.sax.SAXSource. - No JAX-WS or JAXB stub code required.
- The SOAP body is marshalled into a stream-based
SAXSourcetype. - The SOAP headers are converted into headers in the exchange's In message, of
org.apache.cxf.binding.soap.SoapHeadertype.
Implementing and building a provider-based route
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
To implement and build the demonstration provider-based route, starting from scratch, you would perform the following steps:
- Define a custom
javax.xml.ws.Provider<StreamType>class (the current demonstration usesSAXSourceas the StreamType type). - Instantiate the Camel CXF endpoint in Spring, using the
cxf:cxfEndpointelement and reference the custom provider class (using theserviceClassattribute). - Implement the route in XML, where you can use the content-based router to sort requests by operation name.
- For each operation, define a processor bean to process the request.
- Define velocity templates for generating the response messages.
- Define a custom type converter, to support converting a
Stringmessage body to aSAXSourcemessage body.
Sample provider-based route
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
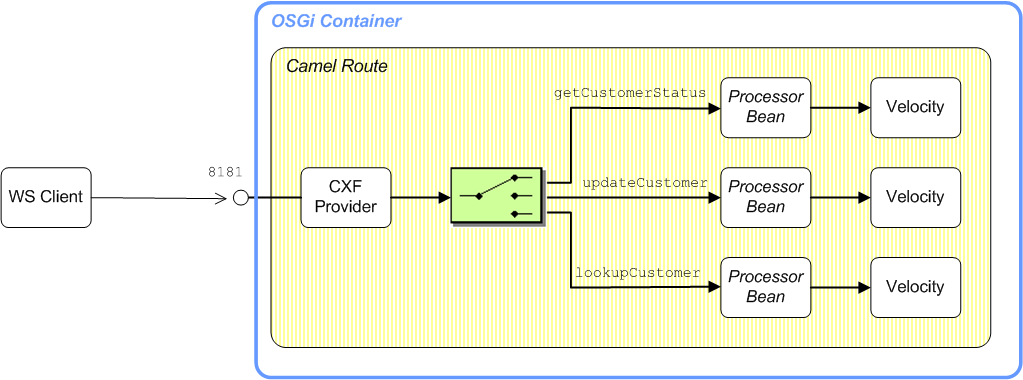
Figure 40.1, “Sample Provider-Based Route” shows an outline of the route that is used to process the operations of the
CustomerService Web service using the provider-based approach. After sorting the request messages by operation name, an operation-specific processor bean reads the incoming request parameters. Finally, the response messages are generated using Velocity templates.
Figure 40.1. Sample Provider-Based Route