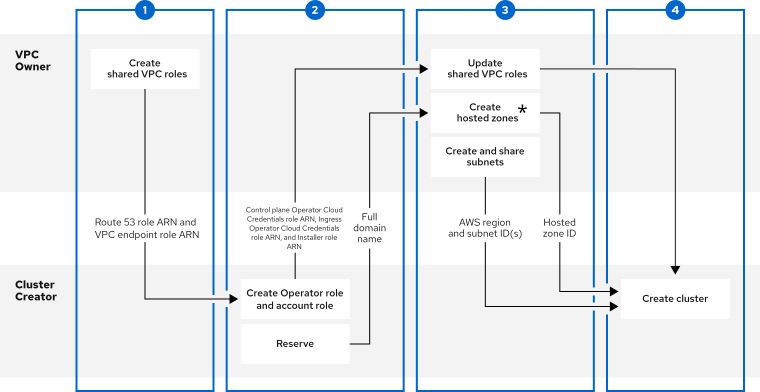
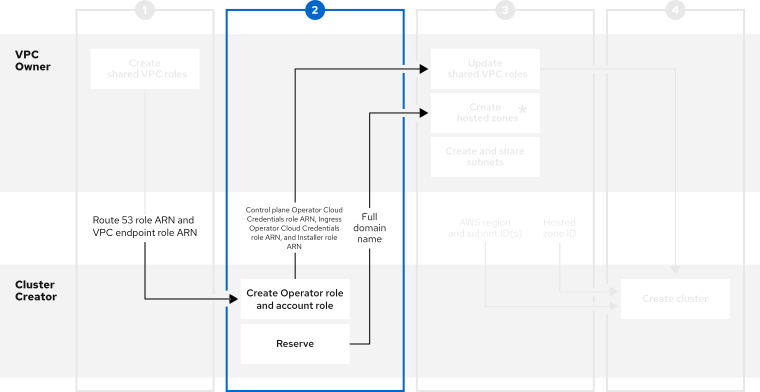
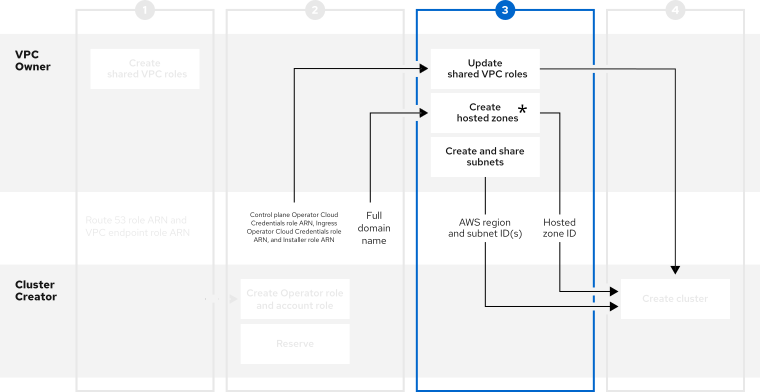
Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Install clusters
Installing, accessing, and deleting Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) clusters.
Abstract
Chapter 1. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS quick start guide
Follow this guide to quickly create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using the ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (rosa), grant user access, deploy your first application, and learn how to revoke user access and delete your cluster.
1.1. Overview of the default cluster specifications
You can quickly create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using the default installation options.
The following summary describes the default cluster specifications.
| Component | Default specifications |
|---|---|
| Accounts and roles |
|
| Cluster settings |
|
| Compute node machine pool |
|
| Networking configuration |
|
| Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) ranges |
|
| Cluster roles and policies |
|
| Storage |
|
| Cluster update strategy |
|
1.2. Setting up the environment
Before you create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must set up your environment by completing the following tasks:
- Verify Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS prerequisites against your AWS and Red Hat accounts.
- Install and configure the required command-line interface (CLI) tools.
- Verify the configuration of the CLI tools.
You can follow the procedures in this section to complete these setup requirements.
1.2.1. Verifying Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS prerequisites
Use the steps in this procedure to enable Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in your AWS account.
Prerequisites
- You have a Red Hat account.
You have an AWS account.
NoteConsider using a dedicated AWS account to run production clusters. If you are using AWS Organizations, you can use an AWS account within your organization or create a new one.
Procedure
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to the ROSA service.
Click Get started.
The Verify ROSA prerequisites page opens.
Under ROSA enablement, ensure that a green check mark and
You previously enabled ROSAare displayed.If not, follow these steps:
-
Select the checkbox beside
I agree to share my contact information with Red Hat. Click Enable ROSA.
After a short wait, a green check mark and
You enabled ROSAmessage are displayed.
-
Select the checkbox beside
Under Service Quotas, ensure that a green check and
Your quotas meet the requirements for ROSAare displayed.If you see
Your quotas don’t meet the minimum requirements, take note of the quota type and the minimum listed in the error message. See Amazon’s documentation on requesting a quota increase for guidance. It may take several hours for Amazon to approve your quota request.-
Under ELB service-linked role, ensure that a green check mark and
AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing already existsare displayed. Click Continue to Red Hat.
The Get started with Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) page opens in a new tab. You have already completed Step 1 on this page, and can now continue with Step 2.
1.2.2. Installing and configuring the required CLI tools
Several command-line interface (CLI) tools are required to deploy and work with your cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have an AWS account.
- You have a Red Hat account.
Procedure
Log in to your Red Hat and AWS accounts to access the download page for each required tool.
- Log in to your Red Hat account at console.redhat.com.
- Log in to your AWS account at aws.amazon.com.
Install and configure the latest AWS CLI (
aws).- Install the AWS CLI by following the AWS Command Line Interface documentation appropriate for your workstation.
Configure the AWS CLI by specifying your
aws_access_key_id,aws_secret_access_key, andregionin the.aws/credentialsfile. For more information, see AWS Configuration basics in the AWS documentation.NoteYou can optionally use the
AWS_DEFAULT_REGIONenvironment variable to set the default AWS region.Query the AWS API to verify if the AWS CLI is installed and configured correctly:
aws sts get-caller-identity --output text
$ aws sts get-caller-identity --output textCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
<aws_account_id> arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:user/<username> <aws_user_id>
<aws_account_id> arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:user/<username> <aws_user_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Install and configure the latest ROSA CLI.
- Navigate to Downloads.
Find Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS command line interface (
rosa) in the list of tools and click Download.The
rosa-linux.tar.gzfile is downloaded to your default download location.Extract the
rosabinary file from the downloaded archive. The following example extracts the binary from a Linux tar archive:tar xvf rosa-linux.tar.gz
$ tar xvf rosa-linux.tar.gzCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Move the
rosabinary file to a directory in your execution path. In the following example, the/usr/local/bindirectory is included in the path of the user:sudo mv rosa /usr/local/bin/rosa
$ sudo mv rosa /usr/local/bin/rosaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the ROSA CLI is installed correctly by querying the
rosaversion:rosa version
$ rosa versionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
1.2.47 Your ROSA CLI is up to date.
1.2.47 Your ROSA CLI is up to date.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Log in to the ROSA CLI using an offline access token.
Run the login command:
rosa login
$ rosa loginCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
To login to your Red Hat account, get an offline access token at https://console.redhat.com/openshift/token/rosa ? Copy the token and paste it here:
To login to your Red Hat account, get an offline access token at https://console.redhat.com/openshift/token/rosa ? Copy the token and paste it here:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Navigate to the URL listed in the command output to view your offline access token.
Enter the offline access token at the command-line prompt to log in.
? Copy the token and paste it here: ******************* [full token length omitted]
? Copy the token and paste it here: ******************* [full token length omitted]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn the future you can specify the offline access token by using the
--token="<offline_access_token>"argument when you run therosa logincommand.Verify that you are logged in and confirm that your credentials are correct before proceeding:
rosa whoami
$ rosa whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Install and configure the latest OpenShift CLI (
oc).Use the ROSA CLI to download the
ocCLI.The following command downloads the latest version of the CLI to the current working directory:
rosa download openshift-client
$ rosa download openshift-clientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Extract the
ocbinary file from the downloaded archive. The following example extracts the files from a Linux tar archive:tar xvf openshift-client-linux.tar.gz
$ tar xvf openshift-client-linux.tar.gzCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Move the
ocbinary to a directory in your execution path. In the following example, the/usr/local/bindirectory is included in the path of the user:sudo mv oc /usr/local/bin/oc
$ sudo mv oc /usr/local/bin/ocCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
ocCLI is installed correctly:rosa verify openshift-client
$ rosa verify openshift-clientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
I: Verifying whether OpenShift command-line tool is available... I: Current OpenShift Client Version: 4.17.3
I: Verifying whether OpenShift command-line tool is available... I: Current OpenShift Client Version: 4.17.3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Next steps
Before you can use the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console to deploy Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, you must associate your AWS account with your Red Hat organization and create the required account-wide AWS IAM STS roles and policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
1.3. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters
You must have an AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. You can use the following methods to create a VPC:
- Create a VPC using the ROSA CLI
- Create a VPC by using a Terraform template
- Manually create the VPC resources in the AWS console
The Terraform instructions are for testing and demonstration purposes. Your own installation requires some modifications to the VPC for your own use. You should also ensure that when you use this linked Terraform configuration, it is in the same region that you intend to install your cluster. In these examples, us-east-2 is used.
1.3.1. Creating an AWS VPC using the ROSA CLI
The rosa create network command is available in v.1.2.48 or later of the ROSA CLI. The command uses AWS CloudFormation to create a VPC and associated networking components necessary to install a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. CloudFormation is a native AWS infrastructure-as-code tool and is compatible with the AWS CLI.
If you do not specify a template, CloudFormation uses a default template that creates resources with the following parameters:
| VPC parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Availability zones | 1 |
| Region |
|
| VPC CIDR |
|
You can create and customize CloudFormation templates to use with the rosa create network command. See the additional resources of this section for information on the default VPC template.
Prerequisites
- You have configured your AWS account
- You have configured your Red Hat accounts
- You have installed the ROSA CLI and configured it to the latest version
Procedure
Create an AWS VPC using the default CloudFormations template by running the following command:
rosa create network
$ rosa create networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Customize your VPC by specifying additional parameters.
You can use the
--paramflag to specify changes to the default VPC template. The following example command specifies custom values forregion,Name,AvailabilityZoneCountandVpcCidr.rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16
$ rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command takes about 5 minutes to run and provides regular status updates from AWS as resources are created. If there is an issue with CloudFormation, a rollback is attempted. For all other errors that are encountered, please follow the error message instructions or contact AWS support.
Verification
When completed, you receive a summary of the created resources:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
<private_subnet_id-1>and<public_subnet_id-1>subnet IDs are used to create your cluster when using therosa create clustercommand. -
The network stack name (
rosa-network-stack-5555) is used to delete the resource later.
-
The
1.3.1.1. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud using Terraform
Terraform is a tool that allows you to create various resources using an established template. The following process uses the default options as required to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. For more information about using Terraform, see the additional resources.
Prerequisites
- You have installed Terraform version 1.4.0 or newer on your machine.
- You have installed Git on your machine.
Procedure
Open a shell prompt and clone the Terraform VPC repository by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-example
$ git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the created directory by running the following command:
cd terraform-vpc-example
$ cd terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Initiate the Terraform file by running the following command:
terraform init
$ terraform initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A message confirming the initialization appears when this process completes.
To build your VPC Terraform plan based on the existing Terraform template, run the
plancommand. You must include your AWS region. You can choose to specify a cluster name. Arosa.tfplanfile is added to thehypershift-tfdirectory after theterraform plancompletes. For more detailed options, see the Terraform VPC repository’s README file.terraform plan -out rosa.tfplan -var region=<region>
$ terraform plan -out rosa.tfplan -var region=<region>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply this plan file to build your VPC by running the following command:
terraform apply rosa.tfplan
$ terraform apply rosa.tfplanCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: You can capture the values of the Terraform-provisioned private, public, and machinepool subnet IDs as environment variables to use when creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by running the following commands:
export SUBNET_IDS=$(terraform output -raw cluster-subnets-string)
$ export SUBNET_IDS=$(terraform output -raw cluster-subnets-string)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the variables were correctly set with the following command:
echo $SUBNET_IDS
$ echo $SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
subnet-0a6a57e0f784171aa,subnet-078e84e5b10ecf5b0
$ subnet-0a6a57e0f784171aa,subnet-078e84e5b10ecf5b0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.3.2. Creating an AWS Virtual Private Cloud manually
If you choose to manually create your AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) instead of using Terraform, go to the VPC page in the AWS console.
Your VPC must meet the requirements shown in the following table.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| VPC name | You need to have the specific VPC name and ID when creating your cluster. |
| CIDR range | Your VPC CIDR range should match your machine CIDR. |
| Availability zone | You need one availability zone for a single zone, and you need three for availability zones for multi-zone. |
| Public subnet | You must have one public subnet with a NAT gateway for public clusters. Private clusters do not need a public subnet. |
| DNS hostname and resolution | You must ensure that the DNS hostname and resolution are enabled. |
1.4. Creating an OpenID Connect configuration
When creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you can create the OpenID Connect (OIDC) configuration before creating your cluster. This configuration is registered to be used with OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host.
Procedure
To create your OIDC configuration alongside the AWS resources, run the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command returns the following information.
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When creating your cluster, you must supply the OIDC config ID. The CLI output provides this value for
--mode auto, otherwise you must determine these values based onawsCLI output for--mode manual.Optional: you can save the OIDC configuration ID as a variable to use later. Run the following command to save the variable:
export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>
$ export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <oidc_config_id>-
In this example output, the OIDC configuration ID is
13cdr6b.
View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $OIDC_ID
$ echo $OIDC_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
13cdr6b
13cdr6bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can list the possible OIDC configurations available for your clusters that are associated with your user organization. Run the following command:
rosa list oidc-config
$ rosa list oidc-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDN
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.5. Creating Operator roles and policies
When you deploy a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the Operator IAM roles. The cluster Operators use the Operator roles and policies to obtain the temporary permissions required to carry out cluster operations, such as managing back-end storage and external access to a cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host. - You created the account-wide AWS roles.
Procedure
To create your Operator roles, run the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following breakdown provides options for the Operator role creation.
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
--prefix=- You must supply a prefix when creating these Operator roles. Failing to do so produces an error. See the Additional resources of this section for information on the Operator prefix.
--oidc-config-id=- This value is the OIDC configuration ID that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
--installer-role-arn- This value is the installer role ARN that you created when you created the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account roles.
You must include the
--hosted-cpparameter to create the correct roles for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. This command returns the following information.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
Operator roles prefix- This field is prepopulated with the prefix that you set in the initial creation command.
OIDC Configuration ID- This field requires you to select an OIDC configuration that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
The Operator roles are now created and ready to use for creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Verification
You can list the Operator roles associated with your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account. Run the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the command runs, it displays all the prefixes associated with your AWS account and notes how many roles are associated with this prefix. If you need to see all of these roles and their details, enter "Yes" on the detail prompt to have these roles listed out with specifics.
1.6. Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using the CLI
When using the ROSA CLI, rosa, to create a cluster, you can select the default options to create the cluster quickly.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. Runrosa versionto see your currently installed version of the ROSA CLI. If a newer version is available, the CLI provides a link to download this upgrade. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
- You have created an OIDC configuration.
- You have verified that the AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service role exists in your AWS account.
Procedure
Use one of the following commands to create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster:
NoteWhen creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, the default machine Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is
10.0.0.0/16. If this does not correspond to the CIDR range for your VPC subnets, add--machine-cidr <address_block>to the following commands. To learn more about the default CIDR ranges for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see CIDR range definitions.If you did not set environmental variables, run the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<cluster_name>-
Specify the name of your cluster. If your cluster name is longer than 15 characters, it will contain an autogenerated domain prefix as a subdomain for your provisioned cluster on openshiftapps.com. To customize the subdomain, use the
--domain-prefixflag. The domain prefix cannot be longer than 15 characters, must be unique, and cannot be changed after cluster creation. --private-
Optional. The
--privateargument is used to create private Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. If you use this argument, ensure that you only use your private subnet ID for--subnet-ids. <operator-role-prefix>-
By default, the cluster-specific Operator role names are prefixed with the cluster name and a random 4-digit hash. You can optionally specify a custom prefix to replace
<cluster_name>-<hash>in the role names. The prefix is applied when you create the cluster-specific Operator IAM roles. For information about the prefix, see About custom Operator IAM role prefixes. <external-id>- Optional. A unique identifier that might be required when you assume a role in another account.
NoteIf you specified custom ARN paths when you created the associated account-wide roles, the custom path is automatically detected. The custom path is applied to the cluster-specific Operator roles when you create them in a later step.
If you set the environmental variables, create a cluster with a single, initial machine pool, using either a publicly or privately available API, and a publicly or privately available Ingress by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS$ rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you set the environmental variables, create a cluster with a single, initial machine pool, a publicly available API, and a publicly available Ingress by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --mode=auto \ --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS$ rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --mode=auto \ --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check the status of your cluster by running the following command:
rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following
Statefield changes are listed in the output as the cluster installation progresses:-
pending (Preparing account) -
installing (DNS setup in progress) -
installing readyNoteIf the installation fails or the
Statefield does not change toreadyafter more than 10 minutes, check the installation troubleshooting documentation for details. For more information, see Troubleshooting installations. For steps to contact Red Hat Support for assistance, see Getting support for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
Track the progress of the cluster creation by watching the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS installation program logs. To check the logs, run the following command:
rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To watch for new log messages as the installation progresses, use the
--watchargument.
1.7. Granting user access to a cluster
You can grant a user access to your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by adding them to your configured identity provider.
You can configure different types of identity providers for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. The following example procedure adds a user to a GitHub organization that is configured for identity provision to the cluster.
Procedure
- Navigate to github.com and log in to your GitHub account.
- Invite users that require access to the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster to your GitHub organization. Follow the steps in Inviting users to join your organization in the GitHub documentation.
1.8. Granting administrator privileges to a user
After you have added a user to your configured identity provider, you can grant the user cluster-admin or dedicated-admin privileges for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Procedure
To configure
cluster-adminprivileges for an identity provider user:Grant the user
cluster-adminprivileges:rosa grant user cluster-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa grant user cluster-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Granted role 'cluster-admins' to user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'
I: Granted role 'cluster-admins' to user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify if the user is listed as a member of the
cluster-adminsgroup:rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ID GROUPS <idp_user_name> cluster-admins
ID GROUPS <idp_user_name> cluster-adminsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To configure
dedicated-adminprivileges for an identity provider user:Grant the user
dedicated-adminprivileges:rosa grant user dedicated-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa grant user dedicated-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Granted role 'dedicated-admins' to user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'
I: Granted role 'dedicated-admins' to user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify if the user is listed as a member of the
dedicated-adminsgroup:rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ID GROUPS <idp_user_name> dedicated-admins
ID GROUPS <idp_user_name> dedicated-adminsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.9. Accessing a cluster through the web console
After you have created a cluster administrator user or added a user to your configured identity provider, you can log into your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster through the web console.
Procedure
Obtain the console URL for your cluster:
rosa describe cluster -c <cluster_name> | grep Console
$ rosa describe cluster -c <cluster_name> | grep ConsoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Console URL: https://console-openshift-console.apps.example-cluster.wxyz.p1.openshiftapps.com
Console URL: https://console-openshift-console.apps.example-cluster.wxyz.p1.openshiftapps.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Go to the console URL in the output of the preceding step and log in.
-
If you created a
cluster-adminuser, log in by using the provided credentials. - If you configured an identity provider for your cluster, select the identity provider name in the Log in with… dialog and complete any authorization requests that are presented by your provider.
-
If you created a
1.10. Deploying an application from the Developer Catalog
From the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS web console, you can deploy a test application from the Developer Catalog and expose it with a route.
Prerequisites
- You logged in to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console.
- You created a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
- You configured an identity provider for your cluster.
- You added your user account to the configured identity provider.
Procedure
- Go to the Cluster List page in OpenShift Cluster Manager.
- Click the options icon (⋮) next to the cluster you want to view.
- Click Open console.
- Your cluster console opens in a new browser window. Log in to your Red Hat account with your configured identity provider credentials.
- In the Administrator perspective, select Home → Projects → Create Project.
- Enter a name for your project and optionally add a Display Name and Description.
- Click Create to create the project.
- Switch to the Developer perspective and select +Add. Verify that the selected Project is the one that you just created.
- In the Developer Catalog dialog, select All services.
- In the Developer Catalog page, select Languages → JavaScript from the menu.
Click Node.js, and then click Create to open the Create Source-to-Image application page.
NoteYou might need to click Clear All Filters to display the Node.js option.
- In the Git section, click Try sample.
- Add a unique name in the Name field. The value will be used to name the associated resources.
- Confirm that Deployment and Create a route are selected.
- Click Create to deploy the application. It will take a few minutes for the pods to deploy.
-
Optional: Check the status of the pods in the Topology pane by selecting your Node.js app and reviewing its sidebar. You must wait for the
nodejsbuild to complete and for thenodejspod to be in a Running state before continuing. When the deployment is complete, click the route URL for the application, which has a format similar to the following:
https://nodejs-<project>.<cluster_name>.<hash>.<region>.openshiftapps.com/
https://nodejs-<project>.<cluster_name>.<hash>.<region>.openshiftapps.com/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A new tab in your browser opens with a message similar to the following:
Welcome to your Node.js application on OpenShift
Welcome to your Node.js application on OpenShiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Delete the application and clean up the resources that you created:
- In the Administrator perspective, navigate to Home → Projects.
- Click the action menu for your project and select Delete Project.
1.11. Revoking administrator privileges and user access
You can revoke cluster-admin or dedicated-admin privileges from a user by using the ROSA CLI, rosa.
To revoke cluster access from a user, you must remove the user from your configured identity provider.
Follow the procedures in this section to revoke administrator privileges or cluster access from a user.
1.11.1. Revoking administrator privileges from a user
Follow the steps in this section to revoke cluster-admin or dedicated-admin privileges from a user.
Procedure
To revoke
cluster-adminprivileges from an identity provider user:Revoke the
cluster-adminprivilege:rosa revoke user cluster-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa revoke user cluster-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
? Are you sure you want to revoke role cluster-admins from user <idp_user_name> in cluster <cluster_name>? Yes I: Revoked role 'cluster-admins' from user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'
? Are you sure you want to revoke role cluster-admins from user <idp_user_name> in cluster <cluster_name>? Yes I: Revoked role 'cluster-admins' from user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the user is not listed as a member of the
cluster-adminsgroup:rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
W: There are no users configured for cluster '<cluster_name>'
W: There are no users configured for cluster '<cluster_name>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To revoke
dedicated-adminprivileges from an identity provider user:Revoke the
dedicated-adminprivilege:rosa revoke user dedicated-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa revoke user dedicated-admin --user=<idp_user_name> --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
? Are you sure you want to revoke role dedicated-admins from user <idp_user_name> in cluster <cluster_name>? Yes I: Revoked role 'dedicated-admins' from user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'
? Are you sure you want to revoke role dedicated-admins from user <idp_user_name> in cluster <cluster_name>? Yes I: Revoked role 'dedicated-admins' from user '<idp_user_name>' on cluster '<cluster_name>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the user is not listed as a member of the
dedicated-adminsgroup:rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa list users --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
W: There are no users configured for cluster '<cluster_name>'
W: There are no users configured for cluster '<cluster_name>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.11.2. Revoking user access to a cluster
You can revoke cluster access for an identity provider user by removing them from your configured identity provider.
You can configure different types of identity providers for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. The following example procedure revokes cluster access for a member of a GitHub organization that is configured for identity provision to the cluster.
Procedure
- Navigate to github.com and log in to your GitHub account.
- Remove the user from your GitHub organization. Follow the steps in Removing a member from your organization in the GitHub documentation.
1.12. Deleting a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster and the AWS IAM STS resources
You can delete a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using the ROSA CLI, rosa. You can also use the ROSA CLI to delete the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) account-wide roles, the cluster-specific Operator roles, and the OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider. To delete the account-wide and Operator policies, you can use the AWS IAM Console or the AWS CLI.
Account-wide IAM roles and policies might be used by other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. You must only remove the resources if they are not required by other clusters.
Procedure
Delete a cluster and watch the logs, replacing
<cluster_name>with the name or ID of your cluster:rosa delete cluster --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa delete cluster --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantYou must wait for the cluster deletion to complete before you remove the IAM roles, policies, and OIDC provider. The account-wide roles are required to delete the resources created by the installer. The cluster-specific Operator roles are required to clean-up the resources created by the OpenShift Operators. The Operators use the OIDC provider to authenticate with AWS APIs.
After the cluster is deleted, delete the OIDC provider that the cluster Operators use to authenticate:
rosa delete oidc-provider -c <cluster_id> --mode auto
$ rosa delete oidc-provider -c <cluster_id> --mode autoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can use the
-yoption to automatically answer yes to the prompts.Delete the cluster-specific Operator IAM roles:
rosa delete operator-roles -c <cluster_id> --mode auto
$ rosa delete operator-roles -c <cluster_id> --mode autoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the account-wide roles:
ImportantAccount-wide IAM roles and policies might be used by other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. You must only remove the resources if they are not required by other clusters.
rosa delete account-roles --prefix <prefix> --mode auto
$ rosa delete account-roles --prefix <prefix> --mode autoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<prefix>with the prefix of the account-wide roles to delete. If you did not specify a custom prefix when you created the account-wide roles, specify the default prefix, depending on how they were created,HCP-ROSAorManagedOpenShift.Delete the account-wide and Operator IAM policies that you created for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS deployments:
- Log in to the AWS IAM Console.
- Navigate to Access management → Policies and select the checkbox for one of the account-wide policies.
- With the policy selected, click on Actions → Delete to open the delete policy dialog.
- Enter the policy name to confirm the deletion and select Delete to delete the policy.
- Repeat this step to delete each of the account-wide and Operator policies for the cluster.
Chapter 2. Creating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters using the default options
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS that use hosted control planes offer a more efficient and reliable architecture for creating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. With hosted control planes, each cluster has a dedicated control plane that is isolated in the AWS account.
Create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster quickly by using the default options and automatic AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resource creation. You can deploy your cluster by using the ROSA CLI (rosa).
Since it is not possible to upgrade or convert existing Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (classic architecture) clusters to hosted control plane architecture, you must create a new cluster to use Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS functionality.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters only support AWS IAM Security Token Service (STS) authentication.
2.1. Considerations regarding auto creation mode
The procedures in this document use the auto mode in the ROSA CLI to immediately create the required IAM resources using the current AWS account. The required resources include the account-wide IAM roles and policies, cluster-specific Operator roles and policies, and OpenID Connect (OIDC) identity provider.
Alternatively, you can use manual mode, which outputs the aws commands needed to create the IAM resources instead of deploying them automatically.
2.2. Next steps
- Ensure that you have completed the AWS prerequisites.
2.3. Overview of the default cluster specifications
You can quickly create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using the default installation options.
The following summary describes the default cluster specifications.
| Component | Default specifications |
|---|---|
| Accounts and roles |
|
| Cluster settings |
|
| Compute node machine pool |
|
| Networking configuration |
|
| Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) ranges |
|
| Cluster roles and policies |
|
| Storage |
|
| Cluster update strategy |
|
2.4. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS Prerequisites
To create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must have the following items:
- A configured virtual private cloud (VPC)
- Account-wide roles
- An OIDC configuration
- Operator roles
2.4.1. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters
You must have a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. You can use the following methods to create a VPC:
- Create a VPC using the ROSA CLI
- Create a VPC by using a Terraform template
- Manually create the VPC resources in the AWS console
The Terraform instructions are for testing and demonstration purposes. Your own installation requires some modifications to the VPC for your own use. You should also ensure that when you use this Terraform configuration, it is in the same region that you intend to install your cluster. In these examples, us-east-2 is used.
2.4.1.1. Creating an AWS VPC using the ROSA CLI
The rosa create network command is available in v.1.2.48 or later of the ROSA CLI. The command uses AWS CloudFormation to create a VPC and associated networking components necessary to install a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. CloudFormation is a native AWS infrastructure-as-code tool and is compatible with the AWS CLI.
If you do not specify a template, CloudFormation uses a default template that creates resources with the following parameters:
| VPC parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Availability zones | 1 |
| Region |
|
| VPC CIDR |
|
You can create and customize CloudFormation templates to use with the rosa create network command. See the additional resources of this section for information on the default VPC template.
Prerequisites
- You have configured your AWS account
- You have configured your Red Hat accounts
- You have installed the ROSA CLI and configured it to the latest version
Procedure
Create an AWS VPC using the default CloudFormations template by running the following command:
rosa create network
$ rosa create networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Customize your VPC by specifying additional parameters.
You can use the
--paramflag to specify changes to the default VPC template. The following example command specifies custom values forregion,Name,AvailabilityZoneCountandVpcCidr.rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16
$ rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command takes about 5 minutes to run and provides regular status updates from AWS as resources are created. If there is an issue with CloudFormation, a rollback is attempted. For all other errors that are encountered, please follow the error message instructions or contact AWS support.
Verification
When completed, you receive a summary of the created resources:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
<private_subnet_id-1>and<public_subnet_id-1>subnet IDs are used to create your cluster when using therosa create clustercommand. -
The network stack name (
rosa-network-stack-5555) is used to delete the resource later.
-
The
2.4.1.2. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud using Terraform
Terraform is a tool that allows you to create various resources using an established template. The following process uses the default options as required to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. For more information about using Terraform, see the additional resources.
Prerequisites
- You have installed Terraform version 1.4.0 or newer on your machine.
- You have installed Git on your machine.
Procedure
Open a shell prompt and clone the Terraform VPC repository by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-example
$ git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the created directory by running the following command:
cd terraform-vpc-example
$ cd terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Initiate the Terraform file by running the following command:
terraform init
$ terraform initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A message confirming the initialization appears when this process completes.
To build your VPC Terraform plan based on the existing Terraform template, run the
plancommand. You must include your AWS region. You can choose to specify a cluster name. Arosa.tfplanfile is added to thehypershift-tfdirectory after theterraform plancompletes. For more detailed options, see the Terraform VPC repository’s README file.terraform plan -out rosa.tfplan -var region=<region>
$ terraform plan -out rosa.tfplan -var region=<region>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply this plan file to build your VPC by running the following command:
terraform apply rosa.tfplan
$ terraform apply rosa.tfplanCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: You can capture the values of the Terraform-provisioned private, public, and machinepool subnet IDs as environment variables to use when creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by running the following commands:
export SUBNET_IDS=$(terraform output -raw cluster-subnets-string)
$ export SUBNET_IDS=$(terraform output -raw cluster-subnets-string)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the variables were correctly set with the following command:
echo $SUBNET_IDS
$ echo $SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
subnet-0a6a57e0f784171aa,subnet-078e84e5b10ecf5b0
$ subnet-0a6a57e0f784171aa,subnet-078e84e5b10ecf5b0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4.2. Creating an AWS Virtual Private Cloud manually
If you choose to manually create your AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) instead of using Terraform, go to the VPC page in the AWS console.
Your VPC must meet the requirements shown in the following table.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| VPC name | You need to have the specific VPC name and ID when creating your cluster. |
| CIDR range | Your VPC CIDR range should match your machine CIDR. |
| Availability zone | You need one availability zone for a single zone, and you need three for availability zones for multi-zone. |
| Public subnet | You must have one public subnet with a NAT gateway for public clusters. Private clusters do not need a public subnet. |
| DNS hostname and resolution | You must ensure that the DNS hostname and resolution are enabled. |
2.4.4. Creating the account-wide STS roles and policies
Before you create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the required account-wide roles and policies.
Specific AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS must be attached to each role. Customer-managed policies must not be used with these required account roles. For more information regarding AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, see AWS managed policies for ROSA.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
Procedure
If they do not exist in your AWS account, create the required account-wide STS roles and attach the policies by running the following command:
rosa create account-roles --hosted-cp
$ rosa create account-roles --hosted-cpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Set your prefix as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>
$ export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX
$ echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIXCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ManagedOpenShift
ManagedOpenShiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information regarding AWS managed IAM policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see AWS managed IAM policies for ROSA.
2.4.5. Creating an OpenID Connect configuration
When creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you can create the OpenID Connect (OIDC) configuration before creating your cluster. This configuration is registered to be used with OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host.
Procedure
To create your OIDC configuration alongside the AWS resources, run the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command returns the following information.
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When creating your cluster, you must supply the OIDC config ID. The CLI output provides this value for
--mode auto, otherwise you must determine these values based onawsCLI output for--mode manual.Optional: you can save the OIDC configuration ID as a variable to use later. Run the following command to save the variable:
export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>
$ export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <oidc_config_id>-
In this example output, the OIDC configuration ID is
13cdr6b.
View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $OIDC_ID
$ echo $OIDC_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
13cdr6b
13cdr6bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can list the possible OIDC configurations available for your clusters that are associated with your user organization. Run the following command:
rosa list oidc-config
$ rosa list oidc-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDN
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4.6. Creating Operator roles and policies
When you deploy a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the Operator IAM roles. The cluster Operators use the Operator roles and policies to obtain the temporary permissions required to carry out cluster operations, such as managing back-end storage and external access to a cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host. - You created the account-wide AWS roles.
Procedure
To create your Operator roles, run the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following breakdown provides options for the Operator role creation.
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
--prefix=- You must supply a prefix when creating these Operator roles. Failing to do so produces an error. See the Additional resources of this section for information on the Operator prefix.
--oidc-config-id=- This value is the OIDC configuration ID that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
--installer-role-arn- This value is the installer role ARN that you created when you created the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account roles.
You must include the
--hosted-cpparameter to create the correct roles for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. This command returns the following information.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
Operator roles prefix- This field is prepopulated with the prefix that you set in the initial creation command.
OIDC Configuration ID- This field requires you to select an OIDC configuration that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
The Operator roles are now created and ready to use for creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Verification
You can list the Operator roles associated with your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account. Run the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the command runs, it displays all the prefixes associated with your AWS account and notes how many roles are associated with this prefix. If you need to see all of these roles and their details, enter "Yes" on the detail prompt to have these roles listed out with specifics.
2.5. Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using the CLI
When using the ROSA CLI, rosa, to create a cluster, you can select the default options to create the cluster quickly.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. Runrosa versionto see your currently installed version of the ROSA CLI. If a newer version is available, the CLI provides a link to download this upgrade. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
- You have created an OIDC configuration.
- You have verified that the AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service role exists in your AWS account.
Procedure
Use one of the following commands to create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster:
NoteWhen creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, the default machine Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is
10.0.0.0/16. If this does not correspond to the CIDR range for your VPC subnets, add--machine-cidr <address_block>to the following commands. To learn more about the default CIDR ranges for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see CIDR range definitions.If you did not set environmental variables, run the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<cluster_name>-
Specify the name of your cluster. If your cluster name is longer than 15 characters, it will contain an autogenerated domain prefix as a subdomain for your provisioned cluster on openshiftapps.com. To customize the subdomain, use the
--domain-prefixflag. The domain prefix cannot be longer than 15 characters, must be unique, and cannot be changed after cluster creation. --private-
Optional. The
--privateargument is used to create private Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. If you use this argument, ensure that you only use your private subnet ID for--subnet-ids. <operator-role-prefix>-
By default, the cluster-specific Operator role names are prefixed with the cluster name and a random 4-digit hash. You can optionally specify a custom prefix to replace
<cluster_name>-<hash>in the role names. The prefix is applied when you create the cluster-specific Operator IAM roles. For information about the prefix, see About custom Operator IAM role prefixes. <external-id>- Optional. A unique identifier that might be required when you assume a role in another account.
NoteIf you specified custom ARN paths when you created the associated account-wide roles, the custom path is automatically detected. The custom path is applied to the cluster-specific Operator roles when you create them in a later step.
If you set the environmental variables, create a cluster with a single, initial machine pool, using either a publicly or privately available API, and a publicly or privately available Ingress by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS$ rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you set the environmental variables, create a cluster with a single, initial machine pool, a publicly available API, and a publicly available Ingress by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --mode=auto \ --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS$ rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --mode=auto \ --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check the status of your cluster by running the following command:
rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following
Statefield changes are listed in the output as the cluster installation progresses:-
pending (Preparing account) -
installing (DNS setup in progress) -
installing readyNoteIf the installation fails or the
Statefield does not change toreadyafter more than 10 minutes, check the installation troubleshooting documentation for details. For more information, see Troubleshooting installations. For steps to contact Red Hat Support for assistance, see Getting support for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
Track the progress of the cluster creation by watching the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS installation program logs. To check the logs, run the following command:
rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To watch for new log messages as the installation progresses, use the
--watchargument.
Chapter 3. Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with Terraform
3.1. Creating a default Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with Terraform
Create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with a Terraform cluster template that is configured with the default cluster options.
The following process for creating a cluster uses a Terraform configuration that prepares a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with these resources:
-
An OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider with a managed
oidc-configconfiguration - Prerequisite IAM Operator roles with associated AWS Managed Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS Policies
- IAM account roles with associated AWS Managed Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS Policies
- All other AWS resources required to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
3.1.1. Overview of Terraform
Terraform is an infrastructure-as-code tool that provides a way to configure your resources once and replicate those resources as desired. Terraform accomplishes the creation tasks by using declarative language. You declare what you want the final state of the infrastructure resource to be, and Terraform creates these resources to your specifications.
3.1.2. Prerequisites
To use the Red Hat Cloud Services provider inside your Terraform configuration, you must meet the following prerequisites:
- You have installed the ROSA CLI tool.
- You have your offline Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager token.
- You have installed Terraform version 1.4.6 or newer.
You have created your AWS account-wide IAM roles.
The specific account-wide IAM roles and policies provide the STS permissions required for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS support, installation, control plane, and compute functionality. This includes account-wide Operator policies. See the Additional resources for more information on the AWS account roles.
- You have an AWS account and associated credentials that allow you to create resources. The credentials are configured for the AWS provider. See the Authentication and Configuration section in AWS Terraform provider documentation.
You have, at minimum, the following permissions in your AWS IAM role policy that is operating Terraform. Check for these permissions in the AWS console.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.1.3. Considerations when using Terraform
In general, using Terraform to manage cloud resources should be done with the expectation that any changes should be done using the Terraform methodology. Use caution when using tools outside of Terraform, such as the AWS console or Red Hat console, to modify cloud resources created by Terraform. Using tools outside Terraform to manage cloud resources that are already managed by Terraform introduces configuration drift from your declared Terraform configuration.
For example, if you upgrade your Terraform-created cluster by using the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console, you need to reconcile your Terraform state before applying any forthcoming configuration changes. For more information, see Manage resources in Terraform state in the HashiCorp Developer documentation.
3.1.4. Overview of the default cluster specifications
You can quickly create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using the default installation options.
The following summary describes the default cluster specifications.
| Component | Default specifications |
|---|---|
| Accounts and roles |
|
| Cluster settings |
|
| Compute node machine pool |
|
| Networking configuration |
|
| Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) ranges |
|
| Cluster roles and policies |
|
| Storage |
|
| Cluster update strategy |
|
3.1.5. Creating a default Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using Terraform
The cluster creation process outlined below shows how to use Terraform to create your account-wide IAM roles and a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with a managed OIDC configuration.
3.1.5.1. Preparing your environment for Terraform
Before you can create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using Terraform, you need to export your offline Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager token.
Procedure
Optional: Because the Terraform files get created in your current directory during this procedure, you can create a new directory to store these files and navigate into it by running the following command:
mkdir terraform-cluster && cd terraform-cluster
$ mkdir terraform-cluster && cd terraform-clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Grant permissions to your account by using an offline Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager token.
Copy your offline token, and set the token as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export RHCS_TOKEN=<your_offline_token>
$ export RHCS_TOKEN=<your_offline_token>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis environmental variable resets at the end of each session, such as restarting your machine or closing the terminal.
Verification
After you export your token, verify the value by running the following command:
echo $RHCS_TOKEN
$ echo $RHCS_TOKENCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.1.5.2. Creating your Terraform files locally
After you set up your offline Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager token, you need to create the Terraform files locally to build your cluster. You can create these files by using the following code templates.
Procedure
Create the
main.tffile by running the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you want to create an administrator user during cluster creation, uncomment the appropriate parameters in the
Optional: Configure a cluster administrator usersection and edit their values.Create the
variables.tffile by running the following command:NoteCopy and edit this file before running the command to build your cluster.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
vpc.tffile by running the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You are ready to initiate Terraform.
3.1.5.3. Using Terraform to create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
After you create the Terraform files, you must initiate Terraform to provide all of the required dependencies. Then apply the Terraform plan.
Do not modify Terraform state files. For more information, see Considerations when using Terraform
Procedure
Set up Terraform to create your resources based on your Terraform files, run the following command:
terraform init
$ terraform initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Verify that the Terraform you copied is correct by running the following command:
terraform validate
$ terraform validateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Success! The configuration is valid.
Success! The configuration is valid.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create your cluster with Terraform by running the following command:
terraform apply
$ terraform applyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Terraform interface asks two questions to create your cluster, similar to the following:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter
yesto proceed ornoto cancel when the Terraform interface lists the resources to be created or changed and prompts for confirmation:Plan: 63 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Plan: 63 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you enter
yes, your Terraform plan starts, creating your AWS account roles, Operator roles, and your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Verification
Verify that your cluster was created by running the following command:
rosa list clusters
$ rosa list clustersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example shows a cluster in the
readystate:ID NAME STATE TOPOLOGY 27c3snjsupa9obua74ba8se5kcj11269 rosa-tf-demo ready Hosted CP
ID NAME STATE TOPOLOGY 27c3snjsupa9obua74ba8se5kcj11269 rosa-tf-demo ready Hosted CPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that your account roles were created by running the following command:
rosa list account-roles
$ rosa list account-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example shows the account roles that were created:
I: Fetching account roles ROLE NAME ROLE TYPE ROLE ARN OPENSHIFT VERSION AWS Managed ROSA-demo-Installer-Role Installer arn:aws:iam::<ID>:role/ROSA-demo-Installer-Role 4.14 No ROSA-demo-Support-Role Support arn:aws:iam::<ID>:role/ROSA-demo-Support-Role 4.14 No ROSA-demo-Worker-Role Worker arn:aws:iam::<ID>:role/ROSA-demo-Worker-Role 4.14 No
I: Fetching account roles ROLE NAME ROLE TYPE ROLE ARN OPENSHIFT VERSION AWS Managed ROSA-demo-Installer-Role Installer arn:aws:iam::<ID>:role/ROSA-demo-Installer-Role 4.14 No ROSA-demo-Support-Role Support arn:aws:iam::<ID>:role/ROSA-demo-Support-Role 4.14 No ROSA-demo-Worker-Role Worker arn:aws:iam::<ID>:role/ROSA-demo-Worker-Role 4.14 NoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that your Operator roles were created by running the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example shows the Terraform-created Operator roles:
I: Fetching operator roles ROLE PREFIX AMOUNT IN BUNDLE rosa-demo 8
I: Fetching operator roles ROLE PREFIX AMOUNT IN BUNDLE rosa-demo 8Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.1.5.4. Configuring an htpasswd identity provider with Terraform
After creating your cluster with Terraform, you can permit users access to your cluster by using an htpasswd identity provider (IDP) with the Terraform tool.
Prerequisites
- You have installed and configured the latest version of the ROSA CLI.
- You have installed and configured the latest version of Terraform.
Procedure
Create the
htpasswd_idp.tffile by running one of the following commands:Option 1: To create a user with a generated, randomized password, run:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You must replace the
<cluster_id>placeholder with the 32-digit ID for your cluster. To find that value, runrosa list clusters | awk '{print $1}'. You also must replace the<user_name>placeholder with the username you want to create. The randomized password is then stored in your AWS Secrets manager to be used when logging in to the cluster.Run the following command to view your password after setting it:
terraform output password_output
$ terraform output password_outputCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The CLI returns your generated password in plain text.
Option 2: To specify your passwords when creating a user, run:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You must replace the
<cluster_id>placeholder with the 32-digit ID for your cluster. To find that value, runrosa list clusters | awk '{print $1}'. You also must replace the<user_name>placeholder with the username you want to create as well as a password for the<password>placeholder.
Run the following command to set up Terraform to create your resources based on your Terraform files:
terraform init
$ terraform initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the Terraform you copied is correct by running the following command:
terraform validate
$ terraform validateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Success! The configuration is valid.
Success! The configuration is valid.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create your cluster with Terraform by running the following command:
terraform apply
$ terraform applyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter
yesto proceed ornoto cancel when the Terraform interface lists the resources to be created or changed and prompts for confirmation:Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve. Enter a value: yes
Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve. Enter a value: yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You see a confirmation that your IDP has been created.
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you used the randomized password template, then the generated password is stored in your AWS Secrets manager.
3.1.5.5. Deleting your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with Terraform
Use the terraform destroy command to remove all resources you create with the terraform apply command.
Keep your Terraform .tf files unchanged before destroying your resources. These variables are matched to resources to delete.
Procedure
In the directory where you ran the
terraform applycommand to create your cluster, run the following command to delete the cluster:terraform destroy
$ terraform destroyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Terraform interface prompts you for two variables. These should match the answers you provided when creating a cluster:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter
yesto start the role and cluster deletion:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that your cluster was destroyed by running the following command:
rosa list clusters
$ rosa list clustersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output showing no cluster
I: No clusters available
I: No clusters availableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the account roles were destroyed by running the following command:
rosa list account-roles
$ rosa list account-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output showing no Terraform-created account roles
I: Fetching account roles I: No account roles available
I: Fetching account roles I: No account roles availableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the Operator roles were destroyed by running the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output showing no Terraform-created Operator roles
I: Fetching operator roles I: No operator roles available
I: Fetching operator roles I: No operator roles availableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 4. Creating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters using a custom AWS KMS encryption key
Create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using a custom AWS Key Management Service (KMS) key.
4.1. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS Prerequisites
To create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must have the following items:
- A configured virtual private cloud (VPC)
- Account-wide roles
- An OIDC configuration
- Operator roles
4.2. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters
You must have an AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. You can use the following methods to create a VPC:
- Create a VPC using the ROSA CLI
- Create a VPC by using a Terraform template
- Manually create the VPC resources in the AWS console
The Terraform instructions are for testing and demonstration purposes. Your own installation requires some modifications to the VPC for your own use. You should also ensure that when you use this linked Terraform configuration, it is in the same region that you intend to install your cluster. In these examples, us-east-2 is used.
4.2.1. Creating an AWS VPC using the ROSA CLI
The rosa create network command is available in v.1.2.48 or later of the ROSA CLI. The command uses AWS CloudFormation to create a VPC and associated networking components necessary to install a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. CloudFormation is a native AWS infrastructure-as-code tool and is compatible with the AWS CLI.
If you do not specify a template, CloudFormation uses a default template that creates resources with the following parameters:
| VPC parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Availability zones | 1 |
| Region |
|
| VPC CIDR |
|
You can create and customize CloudFormation templates to use with the rosa create network command. See the additional resources of this section for information on the default VPC template.
Prerequisites
- You have configured your AWS account
- You have configured your Red Hat accounts
- You have installed the ROSA CLI and configured it to the latest version
Procedure
Create an AWS VPC using the default CloudFormations template by running the following command:
rosa create network
$ rosa create networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Customize your VPC by specifying additional parameters.
You can use the
--paramflag to specify changes to the default VPC template. The following example command specifies custom values forregion,Name,AvailabilityZoneCountandVpcCidr.rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16
$ rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command takes about 5 minutes to run and provides regular status updates from AWS as resources are created. If there is an issue with CloudFormation, a rollback is attempted. For all other errors that are encountered, please follow the error message instructions or contact AWS support.
Verification
When completed, you receive a summary of the created resources:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
<private_subnet_id-1>and<public_subnet_id-1>subnet IDs are used to create your cluster when using therosa create clustercommand. -
The network stack name (
rosa-network-stack-5555) is used to delete the resource later.
-
The
4.2.2. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud using Terraform
Terraform is a tool that allows you to create various resources using an established template. The following process uses the default options as required to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. For more information about using Terraform, see the additional resources.
Prerequisites
- You have installed Terraform version 1.4.0 or newer on your machine.
- You have installed Git on your machine.
Procedure
Open a shell prompt and clone the Terraform VPC repository by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-example
$ git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the created directory by running the following command:
cd terraform-vpc-example
$ cd terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Initiate the Terraform file by running the following command:
terraform init
$ terraform initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A message confirming the initialization appears when this process completes.
To build your VPC Terraform plan based on the existing Terraform template, run the
plancommand. You must include your AWS region. You can choose to specify a cluster name. Arosa.tfplanfile is added to thehypershift-tfdirectory after theterraform plancompletes. For more detailed options, see the Terraform VPC repository’s README file.terraform plan -out rosa.tfplan -var region=<region>
$ terraform plan -out rosa.tfplan -var region=<region>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply this plan file to build your VPC by running the following command:
terraform apply rosa.tfplan
$ terraform apply rosa.tfplanCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: You can capture the values of the Terraform-provisioned private, public, and machinepool subnet IDs as environment variables to use when creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by running the following commands:
export SUBNET_IDS=$(terraform output -raw cluster-subnets-string)
$ export SUBNET_IDS=$(terraform output -raw cluster-subnets-string)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the variables were correctly set with the following command:
echo $SUBNET_IDS
$ echo $SUBNET_IDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
subnet-0a6a57e0f784171aa,subnet-078e84e5b10ecf5b0
$ subnet-0a6a57e0f784171aa,subnet-078e84e5b10ecf5b0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.2.3. Creating an AWS Virtual Private Cloud manually
If you choose to manually create your AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) instead of using Terraform, go to the VPC page in the AWS console.
Your VPC must meet the requirements shown in the following table.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| VPC name | You need to have the specific VPC name and ID when creating your cluster. |
| CIDR range | Your VPC CIDR range should match your machine CIDR. |
| Availability zone | You need one availability zone for a single zone, and you need three for availability zones for multi-zone. |
| Public subnet | You must have one public subnet with a NAT gateway for public clusters. Private clusters do not need a public subnet. |
| DNS hostname and resolution | You must ensure that the DNS hostname and resolution are enabled. |
4.2.5. Creating the account-wide STS roles and policies
Before you create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the required account-wide roles and policies.
Specific AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS must be attached to each role. Customer-managed policies must not be used with these required account roles. For more information regarding AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, see AWS managed policies for ROSA.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
Procedure
If they do not exist in your AWS account, create the required account-wide STS roles and attach the policies by running the following command:
rosa create account-roles --hosted-cp
$ rosa create account-roles --hosted-cpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Set your prefix as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>
$ export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX
$ echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIXCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ManagedOpenShift
ManagedOpenShiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information regarding AWS managed IAM policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see AWS managed IAM policies for ROSA.
4.2.6. Creating an OpenID Connect configuration
When creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you can create the OpenID Connect (OIDC) configuration before creating your cluster. This configuration is registered to be used with OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host.
Procedure
To create your OIDC configuration alongside the AWS resources, run the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command returns the following information.
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When creating your cluster, you must supply the OIDC config ID. The CLI output provides this value for
--mode auto, otherwise you must determine these values based onawsCLI output for--mode manual.Optional: you can save the OIDC configuration ID as a variable to use later. Run the following command to save the variable:
export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>
$ export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <oidc_config_id>-
In this example output, the OIDC configuration ID is
13cdr6b.
View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $OIDC_ID
$ echo $OIDC_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
13cdr6b
13cdr6bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can list the possible OIDC configurations available for your clusters that are associated with your user organization. Run the following command:
rosa list oidc-config
$ rosa list oidc-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDN
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.2.7. Creating Operator roles and policies
When you deploy a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the Operator IAM roles. The cluster Operators use the Operator roles and policies to obtain the temporary permissions required to carry out cluster operations, such as managing back-end storage and external access to a cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host. - You created the account-wide AWS roles.
Procedure
To create your Operator roles, run the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following breakdown provides options for the Operator role creation.
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
--prefix=- You must supply a prefix when creating these Operator roles. Failing to do so produces an error. See the Additional resources of this section for information on the Operator prefix.
--oidc-config-id=- This value is the OIDC configuration ID that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
--installer-role-arn- This value is the installer role ARN that you created when you created the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account roles.
You must include the
--hosted-cpparameter to create the correct roles for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. This command returns the following information.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
Operator roles prefix- This field is prepopulated with the prefix that you set in the initial creation command.
OIDC Configuration ID- This field requires you to select an OIDC configuration that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
The Operator roles are now created and ready to use for creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Verification
You can list the Operator roles associated with your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account. Run the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the command runs, it displays all the prefixes associated with your AWS account and notes how many roles are associated with this prefix. If you need to see all of these roles and their details, enter "Yes" on the detail prompt to have these roles listed out with specifics.
4.2.8. Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using a custom AWS KMS key
You can create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with a customer-provided KMS key that is used to encrypt either node root volumes, the etcd database, or both. A different KMS key ARN can be provided for each option.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS does not automatically configure the default storage class to encrypt persistent volumes with the customer-provided KMS key. This is something that can be configured in-cluster after installation.
Procedure
Create a custom AWS customer-managed KMS key by running the following command:
KMS_ARN=$(aws kms create-key --region $AWS_REGION --description 'Custom ROSA Encryption Key' --tags TagKey=red-hat,TagValue=true --query KeyMetadata.Arn --output text)
$ KMS_ARN=$(aws kms create-key --region $AWS_REGION --description 'Custom ROSA Encryption Key' --tags TagKey=red-hat,TagValue=true --query KeyMetadata.Arn --output text)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command saves the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) output of this custom key for further steps.
NoteCustomers must provide the
--tags TagKey=red-hat,TagValue=trueargument that is required for a customer KMS key.Verify the KMS key has been created by running the following command:
echo $KMS_ARN
$ echo $KMS_ARNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set your AWS account ID to an environment variable.
AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=<aws_account_id>
$ AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=<aws_account_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the ARN for the account-wide installer role and operator roles that you created in the preceding step to the
Statement.Principal.AWSsection in the file. In the following example, the ARN for the defaultManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Rolerole is added:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm the details of the policy file created by running the following command:
cat rosa-key-policy.json
$ cat rosa-key-policy.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the newly generated key policy to the custom KMS key by running the following command:
aws kms put-key-policy --key-id $KMS_ARN \ --policy file://rosa-key-policy.json \ --policy-name default
$ aws kms put-key-policy --key-id $KMS_ARN \ --policy file://rosa-key-policy.json \ --policy-name defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the cluster by running the following command:
NoteIf your cluster name is longer than 15 characters, it will contain an autogenerated domain prefix as a sub-domain for your provisioned cluster on
*.openshiftapps.com.To customize the subdomain, use the
--domain-prefixflag. The domain prefix cannot be longer than 15 characters, must be unique, and cannot be changed after cluster creation.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
--kms-key-arn- This KMS key ARN is used to encrypt all worker node root volumes. It is not required if only etcd database encryption is needed.
--etcd-encryption-kms-arn- This KMS key ARN is used to encrypt the etcd database. The etcd database is always encrypted by default with an AES cipher block, but can be encrypted instead with a KMS key. It is not required if only node root volume encryption is needed.
Verification
You can verify that your KMS key works by using OpenShift Cluster Manager.
- Navigate to OpenShift Cluster Manager and select Instances.
- Select your instance.
- Click the Storage tab.
- Copy the KMS key ID.
- Search and select Key Management Service.
- Enter your copied KMS key ID in the Filter field.
Chapter 6. Creating a private cluster on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS
For Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS workloads that do not require public internet access, you can create a private cluster.
6.1. Creating a private Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using the ROSA CLI
You can create a private cluster with multiple availability zones (Multi-AZ) on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS using the ROSA command-line interface (CLI), rosa.
Creating a cluster with hosted control planes can take around 10 minutes.
Prerequisites
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
- You have installed and configured the latest version of the ROSA CLI on your installation host.
Procedure
Create a VPC with at least one private subnet. Ensure that your machine’s classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) matches your virtual private cloud’s CIDR. For more information, see Requirements for using your own VPC and VPC Validation.
ImportantIf you use a firewall, you must configure it so that ROSA can access the sites that required to function.
For more information, see the "AWS PrivateLink firewall prerequisites" section.
Create the account-wide IAM roles by running the following command:
rosa create account-roles --hosted-cp
$ rosa create account-roles --hosted-cpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the OIDC configuration by running the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the OIDC configuration ID because you need it to create the Operator roles.
Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Operator roles by running the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix <operator_roles_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$<account_roles_prefix>:role/$<account_roles_prefix>-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix <operator_roles_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$<account_roles_prefix>:role/$<account_roles_prefix>-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a private Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster-name> --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator_role_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> [--machine-cidr=<VPC CIDR>/16] --subnet-ids=<private-subnet-id1>[,<private-subnet-id2>,<private-subnet-id3>]
$ rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster-name> --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator_role_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> [--machine-cidr=<VPC CIDR>/16] --subnet-ids=<private-subnet-id1>[,<private-subnet-id2>,<private-subnet-id3>]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the following command to check the status of your cluster. During cluster creation, the
Statefield from the output will transition frompendingtoinstalling, and finally, toready.rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf installation fails or the
Statefield does not change toreadyafter 10 minutes, see the "Troubleshooting Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS installations" documentation in the Additional resources section.Enter the following command to follow the OpenShift installer logs to track the progress of your cluster:
rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2. Adding additional AWS security groups to the AWS PrivateLink endpoint
With Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, the AWS PrivateLink endpoint exposed in the host’s Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) has a security group that limits access to requests that originate from within the cluster’s Machine CIDR range. You must create and attach another security group to the PrivateLink endpoint to grant API access to entities outside of the VPC through VPC peering, transit gateways, or other network connectivity.
Adding additional AWS security groups to the AWS PrivateLink endpoint is only supported on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS version 4.17.2 and later.
Prerequisites
- Your corporate network or other VPC has connectivity.
- You have permission to create and attach security groups within the VPC.
Procedure
Set your cluster name as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster_name>
$ export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the variable exists by running the following command:
echo $CLUSTER_NAME
$ echo $CLUSTER_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
hcp-private
hcp-privateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the VPC endpoint (VPCE) ID and VPC ID by running the following command:
read -r VPCE_ID VPC_ID <<< $(aws ec2 describe-vpc-endpoints --filters "Name=tag:api.openshift.com/id,Values=$(rosa describe cluster -c ${CLUSTER_NAME} -o yaml | grep '^id: ' | cut -d' ' -f2)" --query 'VpcEndpoints[].[VpcEndpointId,VpcId]' --output text)$ read -r VPCE_ID VPC_ID <<< $(aws ec2 describe-vpc-endpoints --filters "Name=tag:api.openshift.com/id,Values=$(rosa describe cluster -c ${CLUSTER_NAME} -o yaml | grep '^id: ' | cut -d' ' -f2)" --query 'VpcEndpoints[].[VpcEndpointId,VpcId]' --output text)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningModifying or removing the default AWS PrivateLink endpoint security group is not supported and might result in unexpected behavior.
Create an additional security group by running the following command:
export SG_ID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group --description "Granting API access to ${CLUSTER_NAME} from outside of VPC" --group-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-api-sg" --vpc-id $VPC_ID --output text)$ export SG_ID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group --description "Granting API access to ${CLUSTER_NAME} from outside of VPC" --group-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-api-sg" --vpc-id $VPC_ID --output text)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add an inbound (ingress) rule to the security group by running the following command:
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id $SG_ID --ip-permissions FromPort=443,ToPort=443,IpProtocol=tcp,IpRanges=[{CidrIp=<cidr-to-allow>}]$ aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id $SG_ID --ip-permissions FromPort=443,ToPort=443,IpProtocol=tcp,IpRanges=[{CidrIp=<cidr-to-allow>}]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the new security group to the VPCE by running the following command:
aws ec2 modify-vpc-endpoint --vpc-endpoint-id $VPCE_ID --add-security-group-ids $SG_ID
$ aws ec2 modify-vpc-endpoint --vpc-endpoint-id $VPCE_ID --add-security-group-ids $SG_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can now access the API of your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS private cluster from the specified CIDR block.
6.3. Additional principals on your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
You can allow AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles as additional principals to connect to your cluster’s private API server endpoint.
You can access your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster’s API Server endpoint from either the public internet or the interface endpoint that was created within the VPC private subnets. By default, you can privately access your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API Server by using the -kube-system-kube-controller-manager Operator role. To be able to access Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API server from another account directly without using the primary account where cluster is installed, you must include cross-account IAM roles as additional principals. This feature allows you to simplify your network architecture and reduce data transfer costs by avoiding peering or attaching cross-account VPCs to cluster’s VPC.
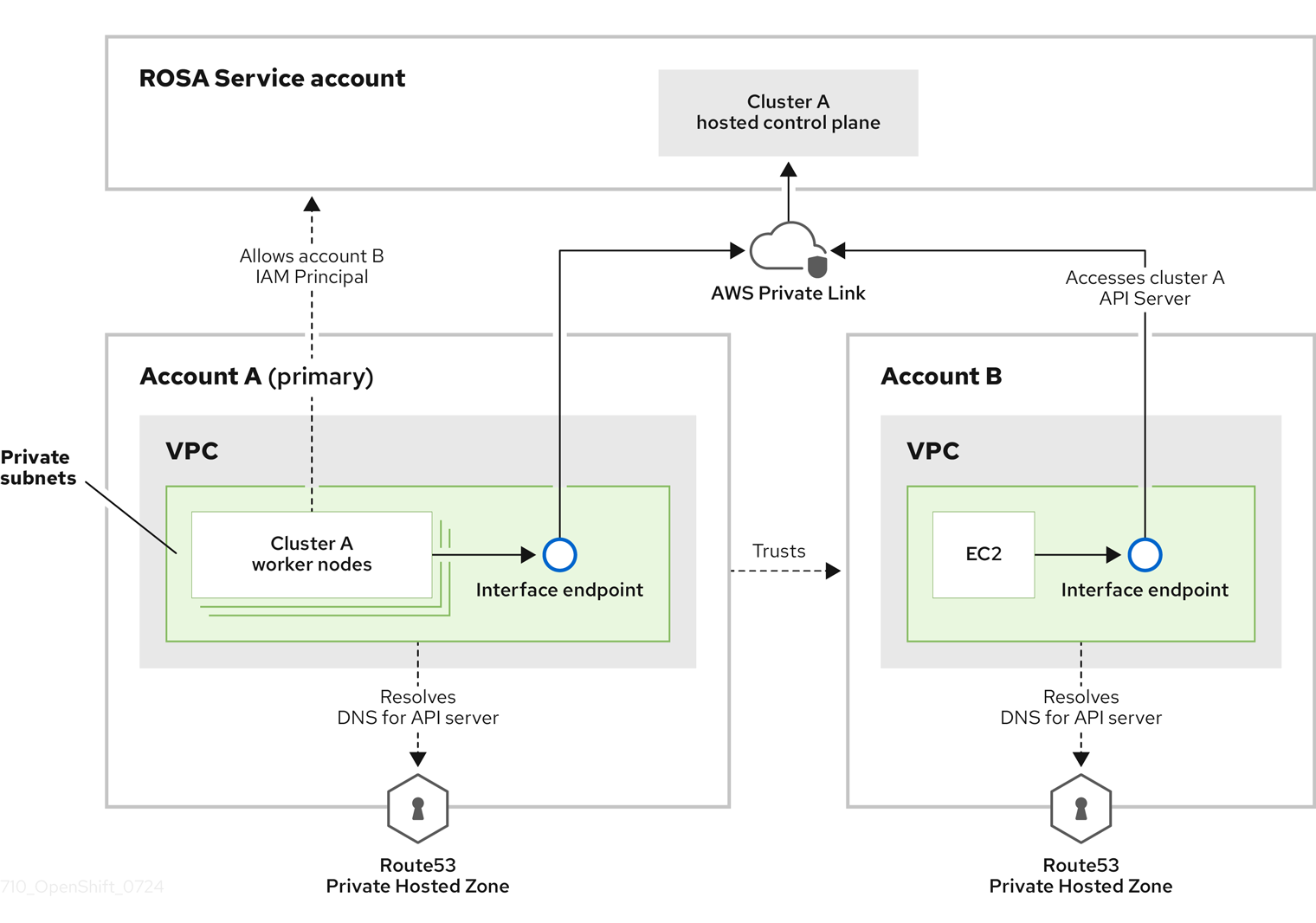
In this diagram, the cluster creating account is designated as Account A. This account designates that another account, Account B, should have access to the API server.
After you have configured additional allowed principals, you must create the interface VPC endpoint in the VPC from where you want to access the cross-account Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API server. Then, create a private hosted zone in Route53 to route calls made to cross-account Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API server to pass through the created VPC endpoint.
6.3.1. Adding additional principals while creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
Use the --additional-allowed-principals argument to permit access through other roles.
Procedure
Add the
--additional-allowed-principalsargument to therosa create clustercommand, similar to the following:rosa create cluster [...] --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>
$ rosa create cluster [...] --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can use
arn:aws:iam::account_id:role/role_nameto approve a specific role.When the cluster creation command runs, you receive a summary of your cluster with the
--additional-allowed-principalsspecified:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.2. Adding additional principals to your existing Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
You can add additional principals to your cluster by using the command-line interface (CLI).
Procedure
Run the following command to edit your cluster and add an additional principal who can access this cluster’s endpoint:
rosa edit cluster -c <cluster_name> --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>
$ rosa edit cluster -c <cluster_name> --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can use
arn:aws:iam::account_id:role/role_nameto approve a specific role.
Next steps
- Configure an identity provider.
Chapter 7. Creating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters with egress zero
Creating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS with egress zero provides a way to enhance your cluster’s stability and security by allowing your cluster to use the image registry in the local region if the cluster cannot access the internet. Your cluster first tries to pull the images from Quay, and when they aren’t reached, it instead pulls the images from the image registry in the local region.
All public and private clusters with egress zero get their Red Hat container images from an Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) located in the local region of the cluster instead of gathering these images from various endpoints and registries on the internet. ECR provides storage for OpenShift release images as well as Red Hat Operators. All requests for ECR are kept within your AWS network by serving them over a VPC endpoint within your cluster.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters with egress zero use AWS ECR to provision your clusters without the need for public internet. Because necessary cluster lifecycle processes occur over AWS private networking, AWS ECR serves as a critical service for core cluster platform images. For more information on AWS ECR, see Amazon Elastic Container Registry.
You can create a fully operational cluster that does not require a public egress by configuring a virtual private cloud (VPC) and using the --properties zero_egress:true flag when creating your cluster.
See Upgrading Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters to upgrade clusters using egress zero.
Clusters created in restricted network environments may be unable to use certain Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS features including Red Hat Lightspeed and Telemetry. These clusters may also experience potential failures for workloads that require public access to registries such as quay.io. When using clusters installed with egress zero, you can also install Red Hat-owned Operators from the software catalog. For a complete list of Red Hat-owned Operators, see the Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog. Only the default Operator channel is mirrored for any Operator that is installed with egress zero.
7.1. Prerequisites
- You have an AWS account with sufficient permissions to create VPCs, subnets, and other required infrastructure.
- You have installed the Terraform v1.4.0+ CLI.
- You have installed the ROSA v1.2.45+ CLI.
- You have installed and configured the AWS CLI with the necessary credentials.
- You have installed the git CLI.
- You have enabled the necessary ROSA CLI firewall rules and Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console firewall rules.
- You can use egress zero on all supported versions of Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS that use the hosted control plane architecture; however, Red Hat suggests using the latest available z-stream release for each OpenShift Container Platform version.
- While you may install and upgrade your clusters as you would a regular cluster, due to an upstream issue with how the internal image registry functions in disconnected environments, your cluster that uses egress zero will not be able to fully use all platform components, such as the image registry. You can restore these features by using the latest ROSA version when upgrading or installing your cluster.
7.2. Glossary of network environment terms
Although it is used throughout the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS documentation, disconnected environment is a broad term that can refer to environments with various levels of internet connectivity. Other terms are sometimes used to refer to a specific level of internet connectivity, and these environments might require additional unique configurations. These network types differ from a "standard network," which has full access to the internet.
The following table describes the different terms used to refer to environments without a full internet connection:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Air-gapped network | An environment or network that is completely isolated from an external network. This isolation depends on a physical separation, or an "air gap", between machines on the internal network and any part of an external network. Air-gapped environments are often used in industries with strict security or regulatory requirements. |
| Disconnected environment | An environment or network that has some level of isolation from an external network. This isolation could be enabled by physical or logical separation between machines on the internal network and an external network. Regardless of the level of isolation from the external network, a cluster in a disconnected environment does not have access to public services hosted by Red Hat and requires additional setup to maintain full cluster functionality. |
| Restricted network | An environment or network with limited connection to an external network. A physical connection might exist between machines on the internal network and an external network, but network traffic is limited by additional configurations, such as firewalls and proxies. |
7.3. Setting Environment Variables
Set the following environment variables to streamline resource creation.
Procedure
Set your environment variable by running the following command:
export <variable_name>=<variable_value>
$ export <variable_name>=<variable_value>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can confirm that your variable has been set by running the following command:
echo <variable_name>
$ echo <variable_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expand Table 7.2. Suggested variables for disconnected Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters Variable name Variable value Notes AWS_ACCOUNT_ID$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query Account --output text)You must be logged in to your AWS account with
rosa login.CLUSTER_NAMEThe name you want for your cluster.
Your cluster name cannot exceed 26 characters.
OIDC_IDThe 32-digit ID for your OpenID Connect (OIDC) configuration.
You generate this ID by running
rosa create oidc-config.OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIXThe Operator role prefix.
If you want to make your AWS account roles use the same prefix as your Operator roles, you can run
ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIXafter setting your Operator role prefix variable.PRIVATE_SUBNETThe ID of your private subnets.
You must enclose this value in quotation marks (") and separate the subnet IDs with commas.
REGIONYour AWS region.
-
SUBNET_IDSThe IDs of all your subnets.
You must enclose this value in quotation marks (") and separate the subnet IDs with commas.
7.3.1. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters
You must have a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. To pull images from the local ECR mirror over your VPC endpoint, you must configure a privatelink service connection and modify the default security groups with specific tags. Use one of the following methods to create a VPC:
- Create a VPC using the ROSA command-line interface (CLI)
- Create a VPC by using a Terraform template
- Create a VPC using the AWS CLI
- Manually create the VPC resources in the AWS console
7.3.2. Creating an AWS VPC using the ROSA CLI
The rosa create network command is available in v.1.2.48 or later of the ROSA CLI. The command uses AWS CloudFormation to create a VPC and associated networking components necessary to install a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. CloudFormation is a native AWS infrastructure-as-code tool and is compatible with the AWS CLI.
If you do not specify a template, CloudFormation uses a default template that creates resources with the following parameters:
| VPC parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Availability zones | 1 |
| Region |
|
| VPC CIDR |
|
You can create and customize CloudFormation templates to use with the rosa create network command. See the additional resources of this section for information on the default VPC template.
Prerequisites
- You have configured your AWS account
- You have configured your Red Hat accounts
- You have installed the ROSA CLI and configured it to the latest version
Procedure
Create an AWS VPC using the default CloudFormations template by running the following command:
rosa create network
$ rosa create networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Customize your VPC by specifying additional parameters.
You can use the
--paramflag to specify changes to the default VPC template. The following example command specifies custom values forregion,Name,AvailabilityZoneCountandVpcCidr.rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16
$ rosa create network --param Region=us-east-2 --param Name=quickstart-stack --param AvailabilityZoneCount=3 --param VpcCidr=10.0.0.0/16Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command takes about 5 minutes to run and provides regular status updates from AWS as resources are created. If there is an issue with CloudFormation, a rollback is attempted. For all other errors that are encountered, please follow the error message instructions or contact AWS support.
Verification
When completed, you receive a summary of the created resources:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
<private_subnet_id-1>and<public_subnet_id-1>subnet IDs are used to create your cluster when using therosa create clustercommand. -
The network stack name (
rosa-network-stack-5555) is used to delete the resource later.
-
The
7.3.2.1. Tagging your subnets
Before you can use your VPC to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must tag your VPC subnets. Automated service preflight checks verify that these resources are tagged correctly.
The following table shows how to tag your resources:
| Resource | Key | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Public subnet |
|
|
| Private subnet |
|
|
You must tag at least one private subnet and one public subnet, if applicable.
Procedure
Tag your resources in your terminal:
For public subnets, run the following command:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources <public_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/elb,Value=1
$ aws ec2 create-tags --resources <public_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/elb,Value=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For private subnets, run the following command:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources <private_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb,Value=1
$ aws ec2 create-tags --resources <private_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb,Value=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the tag is correct by running the following command:
aws ec2 describe-tags --filters "Name=resource-id,Values=<subnet_id>"
$ aws ec2 describe-tags --filters "Name=resource-id,Values=<subnet_id>"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
TAGS Name <subnet_id> subnet <prefix>-subnet-public1-us-east-1a TAGS kubernetes.io/role/elb <subnet_id> subnet 1
TAGS Name <subnet_id> subnet <prefix>-subnet-public1-us-east-1a TAGS kubernetes.io/role/elb <subnet_id> subnet 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.3. Creating a Virtual Private Cloud using Terraform
Terraform is a tool that allows you to create various resources using an established template. The following process uses the default options as required to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. For more information about using Terraform, see the additional resources.
The Terraform instructions are for testing and demonstration purposes. Your own installation requires some modifications to the VPC for your own use. You should also ensure that when you use this Terraform script, it is in the same region that you intend to install your cluster. These examples use us-east-2.
Prerequisites
- You have installed Terraform version 1.4.0 or newer on your machine.
- You have installed Git on your machine.
Procedure
Open a shell prompt and clone the Terraform VPC repository by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-example
$ git clone https://github.com/openshift-cs/terraform-vpc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the created directory by running the following command:
cd terraform-vpc-example/zero-egress
$ cd terraform-vpc-example/zero-egressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Initiate the Terraform file by running the following command:
terraform init
$ terraform initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A message confirming the initialization appears when this process completes.
To build your VPC Terraform plan based on the existing Terraform template, run the
plancommand. You must include your AWS region, availability zones, CIDR blocks, and private subnets. You can choose to specify a cluster name. Arosa-zero-egress.tfplanfile is added to thehypershift-tfdirectory after theterraform plancompletes. For more detailed options, see the Terraform VPC repository’s README file.terraform plan -out rosa-zero-egress.tfplan -var region=<aws_region> \ -var 'availability_zones=<availability_zones>' \ -var vpc_cidr_block=<vpc_cidr_block> \ -var 'private_subnets=<private_subnets>'$ terraform plan -out rosa-zero-egress.tfplan -var region=<aws_region> \ -var 'availability_zones=<availability_zones>' \ -var vpc_cidr_block=<vpc_cidr_block> \ -var 'private_subnets=<private_subnets>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<aws_region>- Enter your AWS region.
<availability_zones>-
Enter the availability zones for the VPC. For example, for a VPC that uses
ap-southeast-1, you would use the following as availability zones:["ap-southeast-1a", "ap-southeast-1b", "ap-southeast-1c"]. <vpc_cidr_block>-
Enter the CIDR block for your VPC. For example,
10.0.0.0/16. <private_subnets>-
Enter each of the subnets that are created for the VPC. For example,
["10.0.0.0/24", "10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24"].
Apply this plan file to build your VPC by running the following command:
terraform apply rosa-zero-egress.tfplan
$ terraform apply rosa-zero-egress.tfplanCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.3.1. Tagging your subnets
Before you can use your VPC to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must tag your VPC subnets. Automated service preflight checks verify that these resources are tagged correctly.
The following table shows how to tag your resources:
| Resource | Key | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Public subnet |
|
|
| Private subnet |
|
|
You must tag at least one private subnet and one public subnet, if applicable.
Procedure
Tag your resources in your terminal:
For public subnets, run the following command:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources <public_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/elb,Value=1
$ aws ec2 create-tags --resources <public_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/elb,Value=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For private subnets, run the following command:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources <private_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb,Value=1
$ aws ec2 create-tags --resources <private_subnet_id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb,Value=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the tag is correct by running the following command:
aws ec2 describe-tags --filters "Name=resource-id,Values=<subnet_id>"
$ aws ec2 describe-tags --filters "Name=resource-id,Values=<subnet_id>"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
TAGS Name <subnet_id> subnet <prefix>-subnet-public1-us-east-1a TAGS kubernetes.io/role/elb <subnet_id> subnet 1
TAGS Name <subnet_id> subnet <prefix>-subnet-public1-us-east-1a TAGS kubernetes.io/role/elb <subnet_id> subnet 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.4. Creating a VPC using the AWS CLI
You can create a VPC by using the AWS CLI. For information on using this CLI, see the AWS create-vpc documentation.
7.3.5. Creating an AWS Virtual Private Cloud manually
If you choose to manually create your AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) instead of using Terraform, go to the VPC page in the AWS console.
Your VPC must meet the requirements shown in the following table.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| VPC name | You need to have the specific VPC name and ID when creating your cluster. |
| CIDR range | Your VPC CIDR range should match your machine CIDR. |
| Availability zone | You need one availability zone for a single zone, and you need three for availability zones for multi-zone. |
| Public subnet | You must have one public subnet with a NAT gateway for public clusters. Private clusters do not need a public subnet. |
| DNS hostname and resolution | You must ensure that the DNS hostname and resolution are enabled. |
7.3.5.1. Tagging your subnets
Before you can use your VPC to create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must tag your VPC subnets. Automated service preflight checks verify that these resources are tagged correctly before you can use these resources for a cluster. The following table shows how your resources should be tagged:
| Resource | Key | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Public subnet |
|
|
| Private subnet |
|
|
You must tag at least one private subnet and, if applicable, one public subnet.
Prerequisites
- You have created a VPC.
-
You have installed the
awsCLI.
Procedure
Tag your resources in your terminal by running the following commands:
For public subnets, run:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources <public-subnet-id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/elb,Value=1
$ aws ec2 create-tags --resources <public-subnet-id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/elb,Value=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For private subnets, run:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources <private-subnet-id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb,Value=1
$ aws ec2 create-tags --resources <private-subnet-id> --region <aws_region> --tags Key=kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb,Value=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the tag is correctly applied by running the following command:
aws ec2 describe-tags --filters "Name=resource-id,Values=<subnet_id>"
$ aws ec2 describe-tags --filters "Name=resource-id,Values=<subnet_id>"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
TAGS Name <subnet-id> subnet <prefix>-subnet-public1-us-east-1a TAGS kubernetes.io/role/elb <subnet-id> subnet 1
TAGS Name <subnet-id> subnet <prefix>-subnet-public1-us-east-1a TAGS kubernetes.io/role/elb <subnet-id> subnet 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4. Creating the account-wide STS roles and policies
Before you create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the required account-wide roles and policies.
Specific AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS must be attached to each role. Customer-managed policies must not be used with these required account roles. For more information regarding AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, see AWS managed policies for ROSA.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
Procedure
If they do not exist in your AWS account, create the required account-wide STS roles and attach the policies by running the following command:
rosa create account-roles --hosted-cp
$ rosa create account-roles --hosted-cpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure that the your worker role has the correct AWS policy by running the following command:
aws iam attach-role-policy \ --role-name ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role \ --policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly"
$ aws iam attach-role-policy \ --role-name ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role \ --policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow --role-name ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role::This role needs to include the prefix that was created in the previous step.Optional: Set your prefix as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>
$ export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX
$ echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIXCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ManagedOpenShift
ManagedOpenShiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information regarding AWS managed IAM policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see AWS managed IAM policies for ROSA.
7.5. Creating an OpenID Connect configuration
When creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you can create the OpenID Connect (OIDC) configuration before creating your cluster. This configuration is registered to be used with OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host.
Procedure
To create your OIDC configuration alongside the AWS resources, run the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command returns the following information.
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When creating your cluster, you must supply the OIDC config ID. The CLI output provides this value for
--mode auto, otherwise you must determine these values based onawsCLI output for--mode manual.Optional: you can save the OIDC configuration ID as a variable to use later. Run the following command to save the variable:
export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>
$ export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <oidc_config_id>-
In this example output, the OIDC configuration ID is
13cdr6b.
View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $OIDC_ID
$ echo $OIDC_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
13cdr6b
13cdr6bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can list the possible OIDC configurations available for your clusters that are associated with your user organization. Run the following command:
rosa list oidc-config
$ rosa list oidc-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDN
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.6. Creating Operator roles and policies
When you deploy a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the Operator IAM roles. The cluster Operators use the Operator roles and policies to obtain the temporary permissions required to carry out cluster operations, such as managing back-end storage and external access to a cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host. - You created the account-wide AWS roles.
Procedure
To create your Operator roles, run the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following breakdown provides options for the Operator role creation.
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
--prefix=- You must supply a prefix when creating these Operator roles. Failing to do so produces an error. See the Additional resources of this section for information on the Operator prefix.
--oidc-config-id=- This value is the OIDC configuration ID that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
--installer-role-arn- This value is the installer role ARN that you created when you created the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account roles.
You must include the
--hosted-cpparameter to create the correct roles for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. This command returns the following information.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
Operator roles prefix- This field is prepopulated with the prefix that you set in the initial creation command.
OIDC Configuration ID- This field requires you to select an OIDC configuration that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
The Operator roles are now created and ready to use for creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Verification
You can list the Operator roles associated with your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account. Run the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the command runs, it displays all the prefixes associated with your AWS account and notes how many roles are associated with this prefix. If you need to see all of these roles and their details, enter "Yes" on the detail prompt to have these roles listed out with specifics.
7.7. Creating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters with egress zero using the CLI
When using the ROSA CLI, rosa, to create a cluster, you can select the default options to create the cluster quickly.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. Runrosa versionto see your currently installed version of the ROSA CLI. If a newer version is available, the CLI provides a link to download this upgrade. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
- You have created an OIDC configuration.
- You have verified that the AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service role exists in your AWS account.
Procedure
Use one of the following commands to create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster:
NoteWhen creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, the default machine Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is
10.0.0.0/16. If this does not correspond to the CIDR range for your VPC subnets, add--machine-cidr <address_block>to the following commands. To learn more about the default CIDR ranges for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see the CIDR range definitions.If you did not set environment variables, run the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<cluster_name>-
Specify the name of your cluster. If your cluster name is longer than 15 characters, it will contain an autogenerated domain prefix as a subdomain for your provisioned cluster on openshiftapps.com. To customize the subdomain, use the
--domain-prefixflag. The domain prefix cannot be longer than 15 characters, must be unique, and cannot be changed after cluster creation. <operator-role-prefix>By default, the cluster-specific Operator role names are prefixed with the cluster name and a random 4-digit hash. You can optionally specify a custom prefix to replace
<cluster_name>-<hash>in the role names. The prefix is applied when you create the cluster-specific Operator IAM roles. For information about the prefix, see About custom Operator IAM role prefixes.NoteIf you specified custom ARN paths when you created the associated account-wide roles, the custom path is automatically detected. The custom path is applied to the cluster-specific Operator roles when you create them in a later step.
<root-acct-id>- If your billing account is different from your user account, add this argument and specify the AWS account that is responsible for all billing.
If you set the environment variables, create a cluster with egress zero that has a single, initial machine pool, using a privately available API, and a privately available Ingress by running the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check the status of your cluster by running the following command:
rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following
Statefield changes are listed in the output as cluster installation progresses:-
pending (Preparing account) -
installing (DNS setup in progress) -
installing readyNoteIf the installation fails or the
Statefield does not change toreadyafter more than 10 minutes, check the installation troubleshooting documentation for details. For more information, see Troubleshooting installations. For steps to contact Red Hat Support for assistance, see Getting support for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
Track the cluster creation progress by watching the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS installation program logs. To check the logs, run the following command:
rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> [--watch]
$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> [--watch]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To watch for new log messages as the installation progresses, use the
--watchargument.
Chapter 8. Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster that uses direct authentication with an external OIDC identity provider
You can create Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters that use an external OpenID Connect (OIDC) identity provider to issue tokens for authentication, replacing the built-in OpenShift OAuth server. While the built-in OpenShift OAuth server supports integration with a variety of identity providers, including external OIDC identity providers, it is limited to the capabilities of the OAuth server itself. You can directly integrate external OIDC identity providers with Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in order to facilitate machine-to-machine workflows, such as CLI, and provide additional capabilities which are not available when using the built-in OpenShift OAuth server.
Since it is not possible to upgrade or convert existing Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (classic architecture) clusters to a hosted control planes architecture, you must create a new cluster to use Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS functionality. You also cannot convert a cluster that was created to use external authentication providers to use the internal OAuth2 server. You must also create a new cluster.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters only support Security Token Service (STS) authentication.
8.1. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS prerequisites
To create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must have completed the following steps:
- Configured virtual private cloud (VPC)
- Created Account-wide roles
- Created an OIDC configuration
- Created Operator roles
8.2. Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster that uses direct authentication with an external OIDC identity provider
Use the --external-auth-providers-enabled flag in the ROSA CLI to create a cluster that uses an external authentication service.
When creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, the default machine Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is 10.0.0.0/16. If this does not correspond to the CIDR range for your VPC subnets, add --machine-cidr <address_block> to the following commands.
Procedure
If you used the
OIDC_ID,SUBNET_IDS, andOPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIXvariables to prepare your environment, you can continue to use those variables when creating your cluster. For example, run the following command:rosa create cluster --hosted-cp --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --external-auth-providers-enabled
$ rosa create cluster --hosted-cp --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS \ --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX \ --external-auth-providers-enabledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you did not set environmental variables, run the following command:
rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --sts --mode=auto \ --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator-role-prefix> \ --oidc-config-id <ID-of-OIDC-configuration> \ --external-auth-providers-enabled \ --subnet-ids=<public-subnet-id>,<private-subnet-id>$ rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --sts --mode=auto \ --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator-role-prefix> \ --oidc-config-id <ID-of-OIDC-configuration> \ --external-auth-providers-enabled \ --subnet-ids=<public-subnet-id>,<private-subnet-id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that your external authentication is enabled in the cluster details by running the following command:
rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example output, the
External Authenticationfield shows that the external authentication is enabled:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3. Creating an external authentication provider
After you have created a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with the enabled option for external authentication providers, you must create a provider using the ROSA CLI.
Similar to the rosa create|delete|list idp[s] command in the ROSA CLI, you cannot edit an existing identity provider that you created using rosa create external-auth-provider. Instead, you must delete the external authentication provider and create a new one.
Procedure
Do one of the following:
To create your external authentication provider using interactive mode, run the following command:
rosa create external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa create external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create your external authentication provider by entering each argument, run the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<cluster_id>- The name or the ID of your cluster.
<provider_name>- The name of your external authentication provider. This name should be a lower-case with numbers and dashes.
<issuing_url>- The URL of the token issuer.
<audience_id>- The audience IDs that this authentication provider issues tokens for. This is a comma-separated list of token audiences.
<ca_file_path>- Optional. The certificate file to use when making requests.
<claim_username>-
The name of the claim that is used to construct the user names for cluster identity, such as using
email. <method>-
The method with which to transform the ID token into a cluster identity, such as using
groups. <client_id_for_app_registration>- Optional. The application or client ID that your app registration uses for the console.
<client_secret>- The client secret that is used to associate your account with the application. If you do not include the client secret, this command uses a public OIDC OAuthClient.
<claim_validation_rule>-
Optional. The rules that help validate token claims which authenticate your users. This field should be formatted as
:<required_value>.
Example output
I: Successfully created an external authentication provider for cluster 'ext-auth-test'
I: Successfully created an external authentication provider for cluster 'ext-auth-test'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3.1. Example Microsoft Entra ID configuration
You can use Microsoft Entra ID as an external provider. You must have already configured a Microsoft Entra ID server before using it as an external provider. See the Microsoft Entra ID documentation for more information.
The following example shows a configured Microsoft Entra ID external authentication provider.
Procedure
Create an external authentication provider that uses Microsoft Entra ID by running the following command:
NoteYou must set your own environment variables with values specific to your Microsoft Entra ID server.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should indicate that the external authentication provider was successfully created.
I: Successfully created an external authentication provider for cluster 'ext-auth-test'. It can take a few minutes for the creation of an external authentication provider to become fully effective.
I: Successfully created an external authentication provider for cluster 'ext-auth-test'. It can take a few minutes for the creation of an external authentication provider to become fully effective.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the external authentication provider for your cluster to see the issuer URL or use the
rosa describecommand to see all details related to this external authentication provider by running one of the following commands:List the external authentication configuration on a specified cluster by running the following command:
rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should show the issuer URL for the external authentication provider.
NAME ISSUER URL m-entra-id https://login.microsoftonline.com/<group_id>/v2.0
NAME ISSUER URL m-entra-id https://login.microsoftonline.com/<group_id>/v2.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the external authentication configuration on a specified cluster by running the following command:
rosa describe external-auth-provider \ -c <cluster_name> --name <name_of_external_authentication>$ rosa describe external-auth-provider \ -c <cluster_name> --name <name_of_external_authentication>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output displays the details of the external authentication provider.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3.2. Example Keycloak configuration
You can use Keycloak as an external provider. You must have already configured a Keycloak server before using it as an external provider. See the Keycloak documentation for more information.
Procedure
Create an external authentication provider that uses Keycloak by running the following command:
NoteYou must set your own environment variables with values specific to your Keycloak server.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should indicate that the external authentication provider was successfully created.
I: Successfully created an external authentication provider for cluster 'ext-auth-test'. It can take a few minutes for the creation of an external authentication provider to become fully effective.
I: Successfully created an external authentication provider for cluster 'ext-auth-test'. It can take a few minutes for the creation of an external authentication provider to become fully effective.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the external authentication provider for your cluster to see the issuer URL or use the
rosa describecommand to see all details related to this external authentication provider by running one of the following commands:List the external authentication configuration on a specified cluster by running the following command:
rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should display the issuer URL for the external authentication provider.
NAME ISSUER URL keycloak https://keycloak-keycloak.apps.<keycloak_id>.openshift.org/realms/master
NAME ISSUER URL keycloak https://keycloak-keycloak.apps.<keycloak_id>.openshift.org/realms/masterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the external authentication configuration on a specified cluster by running the following command:
rosa describe external-auth-provider \ -c <cluster_name> --name <name_of_external_authentication>$ rosa describe external-auth-provider \ -c <cluster_name> --name <name_of_external_authentication>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output displays the details of the external authentication provider.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.4. Creating a break glass credential for a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
As a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster owner, you can use the break glass credential to create temporary administrative client credentials to access your clusters that are configured with custom OpenID Connect (OIDC) token issuers. Creating a break glass credential generates a new cluster-admin kubeconfig file. The kubeconfig file contains information about the cluster that the CLI uses to connect a client to the correct cluster and API server. You can use the newly generated kubeconfig file to allow access to the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have created a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with external authentication enabled. For more information, see Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS with HCP cluster that uses external authentication providers.
- You have created an external authentication provider. For more information, see Creating an external authentication provider.
-
You have an account with
cluster adminpermissions.
Procedure
Create a break glass credential by using one of the following commands:
To create a break glass credential by using the interactive command interface to interactively specify custom settings, run the following command:
rosa create break-glass-credential -c <cluster_name> -i
$ rosa create break-glass-credential -c <cluster_name> -iCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command starts an interactive CLI process:
I: Enabling interactive mode ? Username (optional): ? Expiration duration (optional): I: Successfully created a break glass credential for cluster 'ac-hcp-test'.
I: Enabling interactive mode ? Username (optional): ? Expiration duration (optional): I: Successfully created a break glass credential for cluster 'ac-hcp-test'.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
Username-
If left blank, the value in the
usernamewill have a randomly generated username value. Expiration duration- The minimum validity of the break glass credential is 10 minutes, and the maximum validity is 24 hours. If left blank, the expiration duration value defaults to 24 hours.
To create a break glass credential for cluster called
myclusterwith specified values:rosa create break-glass-credential -c mycluster --username test-username --expiration 1h
$ rosa create break-glass-credential -c mycluster --username test-username --expiration 1hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
List the break glass credential IDs, status, and associated users that are available for a cluster called
myclusterby running the following command:rosa list break-glass-credential -c mycluster
$ rosa list break-glass-credential -c myclusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ID USERNAME STATUS 2a7jli9n4phe6c02ul7ti91djtv2o51d test-user issued
ID USERNAME STATUS 2a7jli9n4phe6c02ul7ti91djtv2o51d test-user issuedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can also view the credentials in a JSON output by adding the
-o jsonargument to the command.To view the status of a break glass credential, run the following command, replacing
<break_glass_credential_id>with the break glass credential ID:rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ID: 2a7jli9n4phe6c02ul7ti91djtv2o51d Username: test-user Expire at: Dec 28 2026 10:23:05 EDT Status: issued
ID: 2a7jli9n4phe6c02ul7ti91djtv2o51d Username: test-user Expire at: Dec 28 2026 10:23:05 EDT Status: issuedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following is a list of possible
Statusfield values:-
issuedThe break glass credential has been issued and is ready to use. -
expiredThe break glass credential has expired and can no longer be used. -
failedThe break glass credential has failed to create. In this case, you receive a service log detailing the failure. For more information about service logs, see Accessing the service logs for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. For steps to contact Red Hat Support for assistance, see Getting support. -
awaiting_revocationThe break glass credential is currently being revoked, meaning it cannot be used. -
revokedThe break glass credential has been revoked and can no longer be used.
-
To retrieve the
kubeconfig, run the following commands:Create a
kubeconfigsdirectory:mkdir ~/kubeconfigs
$ mkdir ~/kubeconfigsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Export the newly generated
kubeconfigfile, replacing <cluster_name> with the name of your cluster:export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster_name> && export KUBECONFIG=~/kubeconfigs/break-glass-${CLUSTER_NAME}.kubeconfig$ export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster_name> && export KUBECONFIG=~/kubeconfigs/break-glass-${CLUSTER_NAME}.kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the
kubeconfig:rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c mycluster --kubeconfig
$ rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c mycluster --kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
users.user.client-certificate-data- The client-certificate contains a certificate for the user signed by the Kubernetes certificate authorities (CA).
users.user.client-key-data- The client-key contains the key that signed the client certificate.
Optional: To save the
kubeconfig, run the following command :rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c mycluster --kubeconfig > $KUBECONFIG
$ rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c mycluster --kubeconfig > $KUBECONFIGCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.5. Accessing a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using a break glass credential
Use the new kubeconfig from the break glass credential to gain temporary admin access to a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have access to a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with external authentication enabled. For more information, see Creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster that uses direct authentication with an external OIDC identity provider.
-
You have installed the
ocand thekubectlCLIs. -
You have configured the new
kubeconfig. For more information, see Creating a break glass credential for a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Procedure
Access the details for the cluster:
rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c <cluster_name> --kubeconfig > $KUBECONFIG
$ rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c <cluster_name> --kubeconfig > $KUBECONFIGCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the nodes from the cluster:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-0-27.ec2.internal Ready worker 8m v1.28.7+f1b5f6c ip-10-0-0-67.ec2.internal Ready worker 9m v1.28.7+f1b5f6c
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-0-27.ec2.internal Ready worker 8m v1.28.7+f1b5f6c ip-10-0-0-67.ec2.internal Ready worker 9m v1.28.7+f1b5f6cCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify you have the correct credentials:
kubectl auth whoami
$ kubectl auth whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ATTRIBUTE VALUE Username system:customer-break-glass:test-user Groups [system:masters system:authenticated]
ATTRIBUTE VALUE Username system:customer-break-glass:test-user Groups [system:masters system:authenticated]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the
ClusterRoleBindingfor the groups defined in the external OIDC provider. TheClusterRoleBindingmaps therosa-hcp-adminsgroup that is created in Microsoft Entra ID to a group in the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output of this command is:
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/rosa-hcp-admins created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/rosa-hcp-admins createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteAfter the
ClusterRoleBindinghas been applied, the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster is configured, and therosaCLI and the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console are authenticated through the external OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider. You can now start assigning roles and deploying applications on the cluster.
8.6. Revoking a break glass credential for a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
You can revoke access to any break glass credentials that you have provisioned at any time by using the revoke break-glass-credentials command.
Prerequisites
- You have created a break glass credential.
- You are the cluster owner.
Procedure
Revoke the break glass credentials for a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by running the following command.
ImportantRunning this command will revoke access for all break glass credentials related to the cluster.
rosa revoke break-glass-credentials -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa revoke break-glass-credentials -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
? Are you sure you want to revoke all the break glass credentials on cluster 'my-cluster'?: Yes I: Successfully requested revocation for all break glass credentials from cluster 'my-cluster'
? Are you sure you want to revoke all the break glass credentials on cluster 'my-cluster'?: Yes I: Successfully requested revocation for all break glass credentials from cluster 'my-cluster'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
The revocation process can take several minutes. You can verify that the break glass credentials for your clusters have been revoked by running one of the following commands:
List all break glass credentials and check the status of each:
rosa list break-glass-credential -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa list break-glass-credential -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ID USERNAME STATUS 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 test-user awaiting_revocation
ID USERNAME STATUS 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 test-user awaiting_revocationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also verify the status by checking the individual credential:
rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa describe break-glass-credential <break_glass_credential_id> -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ID: 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 Username: test-user Expire at: Dec 28 2026 10:23:05 EDT Status: issued Revoked at: Dec 27 2026 15:30:33 EDT
ID: 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 Username: test-user Expire at: Dec 28 2026 10:23:05 EDT Status: issued Revoked at: Dec 27 2026 15:30:33 EDTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.7. Deleting an external authentication provider
Delete external authentication providers by using the ROSA CLI.
Procedure
Display your external authentication provider on your cluster by running the following command:
rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME ISSUER URL entra-test https://login.microsoftonline.com/<group_id>/v2.0
NAME ISSUER URL entra-test https://login.microsoftonline.com/<group_id>/v2.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the external authentication provider by running the following command:
rosa delete external-auth-provider <name_of_provider> -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa delete external-auth-provider <name_of_provider> -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
? Are you sure you want to delete external authentication provider entra-test on cluster rosa-ext-test? Yes I: Successfully deleted external authentication provider 'entra-test' from cluster 'rosa-ext-test'
? Are you sure you want to delete external authentication provider entra-test on cluster rosa-ext-test? Yes I: Successfully deleted external authentication provider 'entra-test' from cluster 'rosa-ext-test'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Query for any external authentication providers on your cluster by running the following command:
rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>
$ rosa list external-auth-provider -c <cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
E: there are no external authentication providers for this cluster
E: there are no external authentication providers for this clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 9. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters without a CNI plugin
You can use your own Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin when creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster. You can create a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster without a CNI and install your own CNI plugin after cluster creation.
For customers who choose to use their own CNI, the responsibility of CNI plugin support belongs to the customer in coordination with their chosen CNI vendor.
The default plugin for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS is the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. This plugin is the only Red Hat supported CNI plugin for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
If you choose to use your own CNI for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, it is strongly recommended that you obtain commercial support from the plugin vendor before creating your clusters. Red Hat support cannot assist with CNI-related issues such as pod to pod traffic for customers who choose to use their own CNI. Red Hat still provides support for all non-CNI issues. If you want CNI-related support from Red Hat, you must install the cluster with the default OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. For more information, see the responsibility matrix.
9.1. Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have completed the AWS prerequisites.
- Ensure that you have a configured virtual private cloud (VPC).
9.2. Creating the account-wide STS roles and policies
Before you create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the required account-wide roles and policies.
Specific AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS must be attached to each role. Customer-managed policies must not be used with these required account roles. For more information regarding AWS-managed policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, see AWS managed policies for ROSA.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
Procedure
If they do not exist in your AWS account, create the required account-wide STS roles and attach the policies by running the following command:
rosa create account-roles --hosted-cp
$ rosa create account-roles --hosted-cpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Set your prefix as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>
$ export ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX=<account_role_prefix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX
$ echo $ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIXCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ManagedOpenShift
ManagedOpenShiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information regarding AWS managed IAM policies for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, see AWS managed IAM policies for ROSA.
9.3. Creating an OpenID Connect configuration
When creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you can create the OpenID Connect (OIDC) configuration before creating your cluster. This configuration is registered to be used with OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host.
Procedure
To create your OIDC configuration alongside the AWS resources, run the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command returns the following information.
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When creating your cluster, you must supply the OIDC config ID. The CLI output provides this value for
--mode auto, otherwise you must determine these values based onawsCLI output for--mode manual.Optional: you can save the OIDC configuration ID as a variable to use later. Run the following command to save the variable:
export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>
$ export OIDC_ID=<oidc_config_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <oidc_config_id>-
In this example output, the OIDC configuration ID is
13cdr6b.
View the value of the variable by running the following command:
echo $OIDC_ID
$ echo $OIDC_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
13cdr6b
13cdr6bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can list the possible OIDC configurations available for your clusters that are associated with your user organization. Run the following command:
rosa list oidc-config
$ rosa list oidc-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDN
ID MANAGED ISSUER URL SECRET ARN 2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 true https://dvbwgdztaeq9o.cloudfront.net/2330dbs0n8m3chkkr25gkkcd8pnj3lk2 233hvnrjoqu14jltk6lhbhf2tj11f8un false https://oidc-r7u1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:242819244:secret:rosa-private-key-oidc-r7u1-tM3MDNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.4. Creating Operator roles and policies
When you deploy a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you must create the Operator IAM roles. The cluster Operators use the Operator roles and policies to obtain the temporary permissions required to carry out cluster operations, such as managing back-end storage and external access to a cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (
rosa) on your installation host. - You created the account-wide AWS roles.
Procedure
To create your Operator roles, run the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/${ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX}-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following breakdown provides options for the Operator role creation.
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ACCOUNT_ROLES_PREFIX-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
--prefix=- You must supply a prefix when creating these Operator roles. Failing to do so produces an error. See the Additional resources of this section for information on the Operator prefix.
--oidc-config-id=- This value is the OIDC configuration ID that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
--installer-role-arn- This value is the installer role ARN that you created when you created the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account roles.
You must include the
--hosted-cpparameter to create the correct roles for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters. This command returns the following information.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
Operator roles prefix- This field is prepopulated with the prefix that you set in the initial creation command.
OIDC Configuration ID- This field requires you to select an OIDC configuration that you created for your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
The Operator roles are now created and ready to use for creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Verification
You can list the Operator roles associated with your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS account. Run the following command:
rosa list operator-roles
$ rosa list operator-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the command runs, it displays all the prefixes associated with your AWS account and notes how many roles are associated with this prefix. If you need to see all of these roles and their details, enter "Yes" on the detail prompt to have these roles listed out with specifics.
9.5. Creating the cluster
When using the ROSA command-line interface (CLI), rosa, to create a cluster, you can add an optional flag --no-cni to create a cluster without a CNI plugin.
Prerequisites
- You have completed the AWS prerequisites for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. Runrosa versionto see your currently installed version of the ROSA CLI. If a newer version is available, the CLI provides a link to download this upgrade. - You have logged in to your Red Hat account by using the ROSA CLI.
- You have created an OIDC configuration.
- You have verified that the AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service role exists in your AWS account.
Procedure
You can create your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster with one of the following commands.
NoteWhen creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, the default machine Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is
10.0.0.0/16. If this does not correspond to the CIDR range for your VPC subnets, add--machine-cidr <address_block>to the following commands.Create a cluster with a single, initial machine pool, publicly available API, publicly available Ingress, and no CNI plugin by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator-role-prefix> \ --oidc-config-id <ID-of-OIDC-configuration> --subnet-ids=<public-subnet-id>,<private-subnet-id> --no-cni$ rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator-role-prefix> \ --oidc-config-id <ID-of-OIDC-configuration> --subnet-ids=<public-subnet-id>,<private-subnet-id> --no-cniCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a cluster with a single, initial machine pool, privately available API, privately available Ingress, and no CNI plugin by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --subnet-ids=<private-subnet-id> --no-cni$ rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster_name> \ --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --subnet-ids=<private-subnet-id> --no-cniCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you used the
OIDC_ID,SUBNET_IDS, andOPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIXvariables to prepare your environment, you can continue to use those variables when creating your cluster without a CNI plugin. For example, run the following command:rosa create cluster --hosted-cp --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --no-cni
$ rosa create cluster --hosted-cp --subnet-ids=$SUBNET_IDS --oidc-config-id=$OIDC_ID --cluster-name=<cluster_name> --operator-roles-prefix=$OPERATOR_ROLES_PREFIX --no-cniCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check the status of your cluster by running the following command:
rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantWhen you first log in to the cluster after it reaches
readystatus, the nodes will still be in thenot readystate until you install your own CNI plugin. After CNI installation, the nodes will change toready.The following
Statefield changes are listed in the output as the cluster installation progresses:-
pending (Preparing account) -
installing (DNS setup in progress) -
installing readyNoteIf the installation fails or the
Statefield does not change toreadyafter more than 10 minutes, check the installation troubleshooting documentation for details. For more information, see Troubleshooting installations. For steps to contact Red Hat Support for assistance, see Getting support for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
-
Track the progress of the cluster creation by watching the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS installation program logs. To check the logs, run the following command:
rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To watch for new log messages as the installation progresses, use the
--watchargument.
9.6. Installing a CNI plugin
After creating a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster without a CNI plugin, you must install the CNI plugin before the cluster can operate. Because the nodes are not ready, the workloads cannot deploy. For example, the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster web console is not available, so you must use the OpenShift CLI (oc) to log in to the cluster. Additionally, other OpenShift components such as the HAProxy-based Ingress Controller, image registry, and prometheus-based monitoring stack are not running. This is expected behavior until you install a CNI provider.
Procedure
Install your CNI plugin.
The nodes change from the
not readytoreadystate.
Chapter 10. Deleting a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
If you want to delete a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster, you can use either the Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager or the ROSA command-line interface (CLI) (rosa). After deleting your cluster, you can also delete the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources that are used by the cluster.
10.1. Deleting a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster and the cluster-specific IAM resources
You can delete a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using the ROSA CLI or Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager.
After deleting the cluster, you can clean up the cluster-specific Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources in your AWS account by using the ROSA CLI. The cluster-specific resources include the Operator roles and the OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider.
The cluster deletion must complete before you remove the IAM resources, because the resources are used in the cluster deletion and clean up processes.
If add-ons are installed, the cluster deletion takes longer because add-ons are uninstalled before the cluster is deleted. The amount of time depends on the number and size of the add-ons.
Prerequisites
- You have installed a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
- You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI on your installation host.
Procedure
Get the cluster ID, the Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) for the cluster-specific Operator roles, and the endpoint URL for the OIDC provider by running the following command:
rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
-
The
IDfield lists the cluster ID. -
The
Operator IAM Rolesfield specifies the ARNs for the cluster-specific Operator roles. For example, in the sample output the ARN for the role required by the Machine Config Operator isarn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/mycluster-x4q9-openshift-machine-api-aws-cloud-credentials. The
OIDC Endpoint URLfield displays the endpoint URL for the cluster-specific OIDC provider.ImportantAfter the cluster is deleted, you need the cluster ID to delete the cluster-specific STS resources using the ROSA CLI.
-
The
Delete the cluster by using either the OpenShift Cluster Manager or the ROSA CLI:
To delete the cluster by using the OpenShift Cluster Manager:
- Navigate to the OpenShift Cluster Manager.
-
Click the Options menu
 next to your cluster and select Delete cluster.
next to your cluster and select Delete cluster.
- Type the name of your cluster into the prompt and click Delete.
To delete the cluster using the ROSA CLI:
Run the following command, replacing
<cluster_name>with the name or ID of your cluster:rosa delete cluster --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa delete cluster --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantYou must wait for cluster deletion to complete before you remove the Operator roles and the OIDC provider.
Delete the cluster-specific Operator IAM roles by running one of the following commands:
For clusters without a shared Virtual Private Cloud (VPC):
rosa delete operator-roles --prefix <operator_role_prefix>
$ rosa delete operator-roles --prefix <operator_role_prefix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For clusters with a shared VPC:
rosa delete operator-roles --prefix <operator_role_prefix> --delete-hosted-shared-vpc-policies
$ rosa delete operator-roles --prefix <operator_role_prefix> --delete-hosted-shared-vpc-policiesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Delete the OIDC provider by running the following command:
rosa delete oidc-provider --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id>
$ rosa delete oidc-provider --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Troubleshooting
- Ensure that there are no add-ons for your cluster pending in the Hybrid Cloud Console.
- Ensure that all AWS resources and dependencies have been deleted in the Amazon Web Console.
10.2. Deleting the account-wide IAM resources
After you have deleted all Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters that depend on the account-wide AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources, you can delete the account-wide resources.
If you no longer need to install a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager, you can also delete the OpenShift Cluster Manager and user IAM roles.
The account-wide IAM roles and policies might be used by other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. Only remove the resources if they are not required by other clusters.
The OpenShift Cluster Manager and user IAM roles are required if you want to install, manage, and delete other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account by using OpenShift Cluster Manager. Only remove the roles if you no longer need to install Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in your account by using OpenShift Cluster Manager. For more information about repairing your cluster if these roles are removed before deletion, see "Repairing a cluster that cannot be deleted" in Troubleshooting cluster deployments.
10.2.1. Deleting the account-wide IAM roles and policies
This section provides steps to delete the account-wide IAM roles and policies that you created for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS deployments, along with the account-wide Operator policies. You can delete the account-wide AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and policies only after deleting all of the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters that depend on them.
The account-wide IAM roles and policies might be used by other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. Only remove the roles if they are not required by other clusters.
Prerequisites
- You have account-wide IAM roles that you want to delete.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host.
Procedure
Delete the account-wide roles:
List the account-wide roles in your AWS account by using the ROSA CLI (
rosa):rosa list account-roles
$ rosa list account-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Fetching account roles ROLE NAME ROLE TYPE ROLE ARN OPENSHIFT VERSION AWS Managed ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role Installer arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role 4.21 Yes ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Support-Role Support arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Support-Role 4.21 Yes ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role Worker arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role 4.21 Yes
I: Fetching account roles ROLE NAME ROLE TYPE ROLE ARN OPENSHIFT VERSION AWS Managed ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role Installer arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role 4.21 Yes ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Support-Role Support arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Support-Role 4.21 Yes ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role Worker arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-HCP-ROSA-Worker-Role 4.21 YesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the account-wide roles by running one of the following commands:
For clusters without a shared Virtual Private Cloud (VPC):
rosa delete account-roles --prefix <prefix> --mode auto
$ rosa delete account-roles --prefix <prefix> --mode autoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You must include the
--<prefix>argument. Replace<prefix>with the prefix of the account-wide roles to delete. If you did not specify a custom prefix when you created the account-wide roles, specify the default prefix,ManagedOpenShift.For clusters with a shared VPC:
rosa delete account-roles --prefix <prefix> --delete-hosted-shared-vpc-policies --mode auto
$ rosa delete account-roles --prefix <prefix> --delete-hosted-shared-vpc-policies --mode autoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You must include the
--<prefix>argument. Replace<prefix>with the prefix of the account-wide roles to delete. If you did not specify a custom prefix when you created the account-wide roles, specify the default prefix,ManagedOpenShift.ImportantThe account-wide IAM roles might be used by other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. Only remove the roles if they are not required by other clusters.
Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Delete the account-wide in-line and Operator policies:
Under the Policies page in the AWS IAM Console, filter the list of policies by the prefix that you specified when you created the account-wide roles and policies.
NoteIf you did not specify a custom prefix when you created the account-wide roles, search for the default prefix,
ManagedOpenShift.Delete the account-wide policies and Operator policies by using the AWS IAM Console. For more information about deleting IAM policies by using the AWS IAM Console, see Deleting IAM policies in the AWS documentation.
ImportantThe account-wide and Operator IAM policies might be used by other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. Only remove the roles if they are not required by other clusters.
10.2.2. Unlinking and deleting the OpenShift Cluster Manager and user IAM roles
When you install a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by using Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager, you also create OpenShift Cluster Manager and user Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles that link to your Red Hat organization. After deleting your cluster, you can unlink and delete the roles by using the ROSA CLI (rosa).
The OpenShift Cluster Manager and user IAM roles are required if you want to use OpenShift Cluster Manager to install and manage other Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters in the same AWS account. Only remove the roles if you no longer need to use the OpenShift Cluster Manager to install Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters.
Prerequisites
- You created OpenShift Cluster Manager and user IAM roles and linked them to your Red Hat organization.
-
You have installed and configured the latest ROSA CLI (
rosa) on your installation host. - You have organization administrator privileges in your Red Hat organization.
Procedure
Unlink the OpenShift Cluster Manager IAM role from your Red Hat organization and delete the role:
List the OpenShift Cluster Manager IAM roles in your AWS account:
rosa list ocm-roles
$ rosa list ocm-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Fetching ocm roles ROLE NAME ROLE ARN LINKED ADMIN AWS Managed ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id> arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id> Yes Yes Yes
I: Fetching ocm roles ROLE NAME ROLE ARN LINKED ADMIN AWS Managed ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id> arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id> Yes Yes YesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If your OpenShift Cluster Manager IAM role is listed as linked in the output of the preceding command, unlink the role from your Red Hat organization by running the following command:
rosa unlink ocm-role --role-arn <arn>
$ rosa unlink ocm-role --role-arn <arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<arn>with the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for your OpenShift Cluster Manager IAM role. The ARN is specified in the output of the preceding command. In the preceding example, the ARN is in the formatarn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>.Example output
I: Unlinking OCM role ? Unlink the 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>' role from organization '<red_hat_organization_id>'? Yes I: Successfully unlinked role-arn 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>' from organization account '<red_hat_organization_id>'
I: Unlinking OCM role ? Unlink the 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>' role from organization '<red_hat_organization_id>'? Yes I: Successfully unlinked role-arn 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>' from organization account '<red_hat_organization_id>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the OpenShift Cluster Manager IAM role and policies:
rosa delete ocm-role --role-arn <arn>
$ rosa delete ocm-role --role-arn <arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Deleting OCM role ? OCM Role ARN: arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id> ? Delete 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>' ocm role? Yes ? OCM role deletion mode: auto I: Successfully deleted the OCM role
I: Deleting OCM role ? OCM Role ARN: arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id> ? Delete 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-<red_hat_organization_external_id>' ocm role? Yes ? OCM role deletion mode: auto I: Successfully deleted the OCM roleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
OCM role deletion modefield specifies the deletion mode. You can useautomode to automatically delete the OpenShift Cluster Manager IAM role and policies. Inmanualmode, the ROSA CLI generates theawscommands needed to delete the role and policies.manualmode enables you to review the details before running theawscommands manually.
Unlink the user IAM role from your Red Hat organization and delete the role:
List the user IAM roles in your AWS account:
rosa list user-roles
$ rosa list user-rolesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Fetching user roles ROLE NAME ROLE ARN LINKED ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role Yes
I: Fetching user roles ROLE NAME ROLE ARN LINKED ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role YesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If your user IAM role is listed as linked in the output of the preceding command, unlink the role from your Red Hat organization:
rosa unlink user-role --role-arn <arn>
$ rosa unlink user-role --role-arn <arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<arn>with the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for your user IAM role. The ARN is specified in the output of the preceding command. In the preceding example, the ARN is in the formatarn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role.Example output
I: Unlinking user role ? Unlink the 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role' role from the current account '<ocm_user_account_id>'? Yes I: Successfully unlinked role ARN 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role' from account '<ocm_user_account_id>'
I: Unlinking user role ? Unlink the 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role' role from the current account '<ocm_user_account_id>'? Yes I: Successfully unlinked role ARN 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role' from account '<ocm_user_account_id>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the user IAM role:
rosa delete user-role --role-arn <arn>
$ rosa delete user-role --role-arn <arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I: Deleting user role ? User Role ARN: arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role ? Delete the 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role' role from the AWS account? Yes ? User role deletion mode: auto I: Successfully deleted the user role
I: Deleting user role ? User Role ARN: arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role ? Delete the 'arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-<ocm_user_name>-Role' role from the AWS account? Yes ? User role deletion mode: auto I: Successfully deleted the user roleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
User role deletion modefield specifies the deletion mode. You can useautomode to automatically delete the user IAM role. Inmanualmode, the ROSA CLI generates theawscommand needed to delete the role.manualmode enables you to review the details before running theawscommand manually.
Legal Notice
Copyright © Red Hat
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of the OpenJS Foundation.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.