Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
9.2. Using Add/Remove Software
To find and install a new package, on the GNOME panel click on
gpk-application command at the shell prompt.
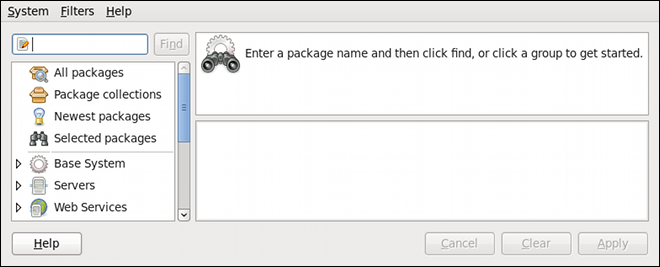
Figure 9.4. PackageKit's Add/Remove Software window
9.2.1. Refreshing Software Sources (Yum Repositories)
Link kopierenLink in die Zwischenablage kopiert!
PackageKit refers to Yum repositories as software sources. It obtains all packages from enabled software sources. You can view the list of all configured and unfiltered (see below) Yum repositories by opening Add/Remove Software and clicking
name=<My Repository Name> field of all [repository] sections in the /etc/yum.conf configuration file, and in all repository.repo files in the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory.
Entries which are checked in the Enabled column indicate that the corresponding repository will be used to locate packages to satisfy all update and installation requests (including dependency resolution). You can enable or disable any of the listed Yum repositories by selecting or clearing the check box. Note that doing so causes PolicyKit to prompt you for superuser authentication.
The Enabled column corresponds to the
enabled=<1 or 0> field in [repository] sections. When you click the check box, PackageKit inserts the enabled=<1 or 0> line into the correct [repository] section if it does not exist, or changes the value if it does. This means that enabling or disabling a repository through the Software Sources window causes that change to persist after closing the window or rebooting the system.
Note that it is not possible to add or remove Yum repositories through PackageKit.
Note
Checking the box at the bottom of the Software Sources window causes PackageKit to display source RPM, testing and debuginfo repositories as well. This box is unchecked by default.
After making a change to the available Yum repositories, click on