Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 6. Network security
6.1. Understanding network policy APIs
Kubernetes offers two features that users can use to enforce network security. One feature that allows users to enforce network policy is the NetworkPolicy API that is designed mainly for application developers and namespace tenants to protect their namespaces by creating namespace-scoped policies.
The second feature is AdminNetworkPolicy which consists of two APIs: the AdminNetworkPolicy (ANP) API and the BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy (BANP) API. ANP and BANP are designed for cluster and network administrators to protect their entire cluster by creating cluster-scoped policies. Cluster administrators can use ANPs to enforce non-overridable policies that take precedence over NetworkPolicy objects. Administrators can use BANP to set up and enforce optional cluster-scoped network policy rules that are overridable by users using NetworkPolicy objects when necessary. When used together, ANP, BANP, and network policy can achieve full multi-tenant isolation that administrators can use to secure their cluster.
OVN-Kubernetes CNI in Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS implements these network policies using Access Control List (ACL) Tiers to evaluate and apply them. ACLs are evaluated in descending order from Tier 1 to Tier 3.
Tier 1 evaluates AdminNetworkPolicy (ANP) objects. Tier 2 evaluates NetworkPolicy objects. Tier 3 evaluates BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy (BANP) objects.

ANPs are evaluated first. When the match is an ANP allow or deny rule, any existing NetworkPolicy and BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy (BANP) objects in the cluster are skipped from evaluation. When the match is an ANP pass rule, then evaluation moves from tier 1 of the ACL to tier 2 where the NetworkPolicy policy is evaluated. If no NetworkPolicy matches the traffic then evaluation moves from tier 2 ACLs to tier 3 ACLs where BANP is evaluated.
6.1.1. Key differences between AdminNetworkPolicy and NetworkPolicy custom resources
The following table explains key differences between the cluster scoped AdminNetworkPolicy API and the namespace scoped NetworkPolicy API.
| Policy elements | AdminNetworkPolicy | NetworkPolicy |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable user | Cluster administrator or equivalent | Namespace owners |
| Scope | Cluster | Namespaced |
| Drop traffic |
Supported with an explicit |
Supported via implicit |
| Delegate traffic |
Supported with an | Not applicable |
| Allow traffic |
Supported with an explicit | The default action for all rules is to allow. |
| Rule precedence within the policy | Depends on the order in which they appear within an ANP. The higher the rule’s position the higher the precedence. | Rules are additive |
| Policy precedence |
Among ANPs the | There is no policy ordering between policies. |
| Feature precedence | Evaluated first via tier 1 ACL and BANP is evaluated last via tier 3 ACL. | Enforced after ANP and before BANP, they are evaluated in tier 2 of the ACL. |
| Matching pod selection | Can apply different rules across namespaces. | Can apply different rules across pods in single namespace. |
| Cluster egress traffic |
Supported via |
Supported through |
| Cluster ingress traffic | Not supported | Not supported |
| Fully qualified domain names (FQDN) peer support | Not supported | Not supported |
| Namespace selectors |
Supports advanced selection of Namespaces with the use of |
Supports label based namespace selection with the use of |
6.2. Admin network policy
6.2.1. OVN-Kubernetes AdminNetworkPolicy
6.2.1.1. AdminNetworkPolicy
An AdminNetworkPolicy (ANP) is a cluster-scoped custom resource definition (CRD). As a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS administrator, you can use ANP to secure your network by creating network policies before creating namespaces. Additionally, you can create network policies on a cluster-scoped level that is non-overridable by NetworkPolicy objects.
The key difference between AdminNetworkPolicy and NetworkPolicy objects are that the former is for administrators and is cluster scoped while the latter is for tenant owners and is namespace scoped.
An ANP allows administrators to specify the following:
-
A
priorityvalue that determines the order of its evaluation. The lower the value the higher the precedence. - A set of pods that consists of a set of namespaces or namespace on which the policy is applied.
-
A list of ingress rules to be applied for all ingress traffic towards the
subject. -
A list of egress rules to be applied for all egress traffic from the
subject.
AdminNetworkPolicy example
Example 6.1. Example YAML file for an ANP
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: AdminNetworkPolicy metadata: name: sample-anp-deny-pass-rules 1 spec: priority: 50 2 subject: namespaces: matchLabels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: example.name 3 ingress: 4 - name: "deny-all-ingress-tenant-1" 5 action: "Deny" from: - pods: namespaceSelector: matchLabels: custom-anp: tenant-1 podSelector: matchLabels: custom-anp: tenant-1 6 egress:7 - name: "pass-all-egress-to-tenant-1" action: "Pass" to: - pods: namespaceSelector: matchLabels: custom-anp: tenant-1 podSelector: matchLabels: custom-anp: tenant-1
- 1
- Specify a name for your ANP.
- 2
- The
spec.priorityfield supports a maximum of 100 ANPs in the range of values0-99in a cluster. The lower the value, the higher the precedence because the range is read in order from the lowest to highest value. Because there is no guarantee which policy takes precedence when ANPs are created at the same priority, set ANPs at different priorities so that precedence is deliberate. - 3
- Specify the namespace to apply the ANP resource.
- 4
- ANP have both ingress and egress rules. ANP rules for
spec.ingressfield accepts values ofPass,Deny, andAllowfor theactionfield. - 5
- Specify a name for the
ingress.name. - 6
- Specify
podSelector.matchLabelsto select pods within the namespaces selected bynamespaceSelector.matchLabelsas ingress peers. - 7
- ANPs have both ingress and egress rules. ANP rules for
spec.egressfield accepts values ofPass,Deny, andAllowfor theactionfield.
Additional resources
6.2.1.1.1. AdminNetworkPolicy actions for rules
As an administrator, you can set Allow, Deny, or Pass as the action field for your AdminNetworkPolicy rules. Because OVN-Kubernetes uses a tiered ACLs to evaluate network traffic rules, ANP allow you to set very strong policy rules that can only be changed by an administrator modifying them, deleting the rule, or overriding them by setting a higher priority rule.
AdminNetworkPolicy Allow example
The following ANP that is defined at priority 9 ensures all ingress traffic is allowed from the monitoring namespace towards any tenant (all other namespaces) in the cluster.
Example 6.2. Example YAML file for a strong Allow ANP
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: AdminNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-monitoring
spec:
priority: 9
subject:
namespaces: {} # Use the empty selector with caution because it also selects OpenShift namespaces as well.
ingress:
- name: "allow-ingress-from-monitoring"
action: "Allow"
from:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: monitoring
# ...
This is an example of a strong Allow ANP because it is non-overridable by all the parties involved. No tenants can block themselves from being monitored using NetworkPolicy objects and the monitoring tenant also has no say in what it can or cannot monitor.
AdminNetworkPolicy Deny example
The following ANP that is defined at priority 5 ensures all ingress traffic from the monitoring namespace is blocked towards restricted tenants (namespaces that have labels security: restricted).
Example 6.3. Example YAML file for a strong Deny ANP
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: AdminNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: block-monitoring
spec:
priority: 5
subject:
namespaces:
matchLabels:
security: restricted
ingress:
- name: "deny-ingress-from-monitoring"
action: "Deny"
from:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: monitoring
# ...
This is a strong Deny ANP that is non-overridable by all the parties involved. The restricted tenant owners cannot authorize themselves to allow monitoring traffic, and the infrastructure’s monitoring service cannot scrape anything from these sensitive namespaces.
When combined with the strong Allow example, the block-monitoring ANP has a lower priority value giving it higher precedence, which ensures restricted tenants are never monitored.
AdminNetworkPolicy Pass example
The following ANP that is defined at priority 7 ensures all ingress traffic from the monitoring namespace towards internal infrastructure tenants (namespaces that have labels security: internal) are passed on to tier 2 of the ACLs and evaluated by the namespaces’ NetworkPolicy objects.
Example 6.4. Example YAML file for a strong Pass ANP
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: AdminNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: pass-monitoring
spec:
priority: 7
subject:
namespaces:
matchLabels:
security: internal
ingress:
- name: "pass-ingress-from-monitoring"
action: "Pass"
from:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: monitoring
# ...
This example is a strong Pass action ANP because it delegates the decision to NetworkPolicy objects defined by tenant owners. This pass-monitoring ANP allows all tenant owners grouped at security level internal to choose if their metrics should be scraped by the infrastructures' monitoring service using namespace scoped NetworkPolicy objects.
6.2.2. OVN-Kubernetes BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy
6.2.2.1. BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy
BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy (BANP) is a cluster-scoped custom resource definition (CRD). As a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS administrator, you can use BANP to setup and enforce optional baseline network policy rules that are overridable by users using NetworkPolicy objects if need be. Rule actions for BANP are allow or deny.
The BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy resource is a cluster singleton object that can be used as a guardrail policy incase a passed traffic policy does not match any NetworkPolicy objects in the cluster. A BANP can also be used as a default security model that provides guardrails that intra-cluster traffic is blocked by default and a user will need to use NetworkPolicy objects to allow known traffic. You must use default as the name when creating a BANP resource.
A BANP allows administrators to specify:
-
A
subjectthat consists of a set of namespaces or namespace. -
A list of ingress rules to be applied for all ingress traffic towards the
subject. -
A list of egress rules to be applied for all egress traffic from the
subject.
BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy example
Example 6.5. Example YAML file for BANP
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy metadata: name: default 1 spec: subject: namespaces: matchLabels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: example.name 2 ingress: 3 - name: "deny-all-ingress-from-tenant-1" 4 action: "Deny" from: - pods: namespaceSelector: matchLabels: custom-banp: tenant-1 5 podSelector: matchLabels: custom-banp: tenant-1 6 egress: - name: "allow-all-egress-to-tenant-1" action: "Allow" to: - pods: namespaceSelector: matchLabels: custom-banp: tenant-1 podSelector: matchLabels: custom-banp: tenant-1
- 1
- The policy name must be
defaultbecause BANP is a singleton object. - 2
- Specify the namespace to apply the ANP to.
- 3
- BANP have both ingress and egress rules. BANP rules for
spec.ingressandspec.egressfields accepts values ofDenyandAllowfor theactionfield. - 4
- Specify a name for the
ingress.name - 5
- Specify the namespaces to select the pods from to apply the BANP resource.
- 6
- Specify
podSelector.matchLabelsname of the pods to apply the BANP resource.
BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy Deny example
The following BANP singleton ensures that the administrator has set up a default deny policy for all ingress monitoring traffic coming into the tenants at internal security level. When combined with the "AdminNetworkPolicy Pass example", this deny policy acts as a guardrail policy for all ingress traffic that is passed by the ANP pass-monitoring policy.
Example 6.6. Example YAML file for a guardrail Deny rule
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: default
spec:
subject:
namespaces:
matchLabels:
security: internal
ingress:
- name: "deny-ingress-from-monitoring"
action: "Deny"
from:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: monitoring
# ...
You can use an AdminNetworkPolicy resource with a Pass value for the action field in conjunction with the BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy resource to create a multi-tenant policy. This multi-tenant policy allows one tenant to collect monitoring data on their application while simultaneously not collecting data from a second tenant.
As an administrator, if you apply both the "AdminNetworkPolicy Pass action example" and the "BaselineAdminNetwork Policy Deny example", tenants are then left with the ability to choose to create a NetworkPolicy resource that will be evaluated before the BANP.
For example, Tenant 1 can set up the following NetworkPolicy resource to monitor ingress traffic:
Example 6.7. Example NetworkPolicy
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-monitoring
namespace: tenant 1
spec:
podSelector:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: monitoring
# ...
In this scenario, Tenant 1’s policy would be evaluated after the "AdminNetworkPolicy Pass action example" and before the "BaselineAdminNetwork Policy Deny example", which denies all ingress monitoring traffic coming into tenants with security level internal. With Tenant 1’s NetworkPolicy object in place, they will be able to collect data on their application. Tenant 2, however, who does not have any NetworkPolicy objects in place, will not be able to collect data. As an administrator, you have not by default monitored internal tenants, but instead, you created a BANP that allows tenants to use NetworkPolicy objects to override the default behavior of your BANP.
6.3. Network policy
6.3.1. About network policy
As a developer, you can define network policies that restrict traffic to pods in your cluster.
6.3.1.1. About network policy
By default, all pods in a project are accessible from other pods and network endpoints. To isolate one or more pods in a project, you can create NetworkPolicy objects in that project to indicate the allowed incoming connections. Project administrators can create and delete NetworkPolicy objects within their own project.
If a pod is matched by selectors in one or more NetworkPolicy objects, then the pod will accept only connections that are allowed by at least one of those NetworkPolicy objects. A pod that is not selected by any NetworkPolicy objects is fully accessible.
A network policy applies to only the TCP, UDP, ICMP, and SCTP protocols. Other protocols are not affected.
Network policy does not apply to the host network namespace. Pods with host networking enabled are unaffected by network policy rules. However, pods connecting to the host-networked pods might be affected by the network policy rules.
Network policies cannot block traffic from localhost or from their resident nodes.
The following example NetworkPolicy objects demonstrate supporting different scenarios:
Deny all traffic:
To make a project deny by default, add a
NetworkPolicyobject that matches all pods but accepts no traffic:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: deny-by-default spec: podSelector: {} ingress: []Only allow connections from the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS Ingress Controller:
To make a project allow only connections from the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS Ingress Controller, add the following
NetworkPolicyobject.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-openshift-ingress spec: ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: network.openshift.io/policy-group: ingress podSelector: {} policyTypes: - IngressOnly accept connections from pods within a project:
ImportantTo allow ingress connections from
hostNetworkpods in the same namespace, you need to apply theallow-from-hostnetworkpolicy together with theallow-same-namespacepolicy.To make pods accept connections from other pods in the same project, but reject all other connections from pods in other projects, add the following
NetworkPolicyobject:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-same-namespace spec: podSelector: {} ingress: - from: - podSelector: {}Only allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic based on pod labels:
To enable only HTTP and HTTPS access to the pods with a specific label (
role=frontendin following example), add aNetworkPolicyobject similar to the following:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-http-and-https spec: podSelector: matchLabels: role: frontend ingress: - ports: - protocol: TCP port: 80 - protocol: TCP port: 443Accept connections by using both namespace and pod selectors:
To match network traffic by combining namespace and pod selectors, you can use a
NetworkPolicyobject similar to the following:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-pod-and-namespace-both spec: podSelector: matchLabels: name: test-pods ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: project: project_name podSelector: matchLabels: name: test-pods
NetworkPolicy objects are additive, which means you can combine multiple NetworkPolicy objects together to satisfy complex network requirements.
For example, for the NetworkPolicy objects defined in previous samples, you can define both allow-same-namespace and allow-http-and-https policies within the same project. Thus allowing the pods with the label role=frontend, to accept any connection allowed by each policy. That is, connections on any port from pods in the same namespace, and connections on ports 80 and 443 from pods in any namespace.
6.3.1.1.1. Using the allow-from-router network policy
Use the following NetworkPolicy to allow external traffic regardless of the router configuration:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-from-router
spec:
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
policy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress: ""1
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress- 1
policy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress:""label supports OVN-Kubernetes.
6.3.1.1.2. Using the allow-from-hostnetwork network policy
Add the following allow-from-hostnetwork NetworkPolicy object to direct traffic from the host network pods.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-from-hostnetwork
spec:
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
policy-group.network.openshift.io/host-network: ""
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress6.3.1.2. Optimizations for network policy with OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
When designing your network policy, refer to the following guidelines:
-
For network policies with the same
spec.podSelectorspec, it is more efficient to use one network policy with multipleingressoregressrules, than multiple network policies with subsets ofingressoregressrules. Every
ingressoregressrule based on thepodSelectorornamespaceSelectorspec generates the number of OVS flows proportional tonumber of pods selected by network policy + number of pods selected by ingress or egress rule. Therefore, it is preferable to use thepodSelectorornamespaceSelectorspec that can select as many pods as you need in one rule, instead of creating individual rules for every pod.For example, the following policy contains two rules:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: test-network-policy spec: podSelector: {} ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: role: frontend - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: role: backendThe following policy expresses those same two rules as one:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: test-network-policy spec: podSelector: {} ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchExpressions: - {key: role, operator: In, values: [frontend, backend]}The same guideline applies to the
spec.podSelectorspec. If you have the sameingressoregressrules for different network policies, it might be more efficient to create one network policy with a commonspec.podSelectorspec. For example, the following two policies have different rules:apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: policy1 spec: podSelector: matchLabels: role: db ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: role: frontend --- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: policy2 spec: podSelector: matchLabels: role: client ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: role: frontendThe following network policy expresses those same two rules as one:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: policy3 spec: podSelector: matchExpressions: - {key: role, operator: In, values: [db, client]} ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: role: frontendYou can apply this optimization when only multiple selectors are expressed as one. In cases where selectors are based on different labels, it may not be possible to apply this optimization. In those cases, consider applying some new labels for network policy optimization specifically.
6.3.1.2.1. NetworkPolicies and external IPs in OVN-Kubernetes
In OVN-Kubernetes, NetworkPolicies enforce strict isolation rules. If a service is exposed using an external IP, NetworkPolicies can block access from other namespaces unless explicitly configured.
To allow access to external IPs across namespaces, create a NetworkPolicy that explicitly permits ingress from the required namespaces and ensures traffic is allowed to the designated service ports. Without allowing traffic to the required ports, access might still be restricted.
Example output
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
annotations:
name: <policy_name> 1
namespace: openshift-ingress
spec:
ingress:
- ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
- ports:
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: <namespace_name> 2
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
For more details, see "About network policy".
6.3.1.3. Next steps
6.3.2. Creating a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can create a network policy for a namespace.
6.3.2.1. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-27107 1 spec: podSelector: 2 matchLabels: app: mongodb ingress: - from: - podSelector: 3 matchLabels: app: app ports: 4 - protocol: TCP port: 27017
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
6.3.2.2. Creating a network policy using the CLI
To define granular rules describing ingress or egress network traffic allowed for namespaces in your cluster, you can create a network policy.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy rule:
Create a
<policy_name>.yamlfile:$ touch <policy_name>.yaml
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the network policy file name.
Define a network policy in the file that you just created, such as in the following examples:
Deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces
This is a fundamental policy, blocking all cross-pod networking other than cross-pod traffic allowed by the configuration of other Network Policies.
kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: deny-by-default spec: podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: []Allow ingress from all pods in the same namespace
kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-same-namespace spec: podSelector: ingress: - from: - podSelector: {}Allow ingress traffic to one pod from a particular namespace
This policy allows traffic to pods labelled
pod-afrom pods running innamespace-y.kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-traffic-pod spec: podSelector: matchLabels: pod: pod-a policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: namespace-y
To create the network policy object, enter the following command:
$ oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the network policy file name.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default created
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of creating a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
6.3.2.3. Creating a default deny all network policy
This policy blocks all cross-pod networking other than network traffic allowed by the configuration of other deployed network policies and traffic between host-networked pods. This procedure enforces a strong deny policy by applying a deny-by-default policy in the my-project namespace.
Without configuring a NetworkPolicy custom resource (CR) that allows traffic communication, the following policy might cause communication problems across your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create the following YAML that defines a
deny-by-defaultpolicy to deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces. Save the YAML in thedeny-by-default.yamlfile:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: deny-by-default namespace: my-project 1 spec: podSelector: {} 2 ingress: [] 3
- 1
Specifies the namespace in which to deploy the policy. For example, the `my-projectnamespace.- 2
- If this field is empty, the configuration matches all the pods. Therefore, the policy applies to all pods in the
my-projectnamespace. - 3
- There are no
ingressrules specified. This causes incoming traffic to be dropped to all pods.
Apply the policy by entering the following command:
$ oc apply -f deny-by-default.yaml
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default created
6.3.2.4. Creating a network policy to allow traffic from external clients
With the deny-by-default policy in place you can proceed to configure a policy that allows traffic from external clients to a pod with the label app=web.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows external service from the public Internet directly or by using a Load Balancer to access the pod. Traffic is only allowed to a pod with the label app=web.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from the public Internet directly or by using a load balancer to access the pod. Save the YAML in the
web-allow-external.yamlfile:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: web-allow-external namespace: default spec: policyTypes: - Ingress podSelector: matchLabels: app: web ingress: - {}Apply the policy by entering the following command:
$ oc apply -f web-allow-external.yaml
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-external created
This policy allows traffic from all resources, including external traffic as illustrated in the following diagram:
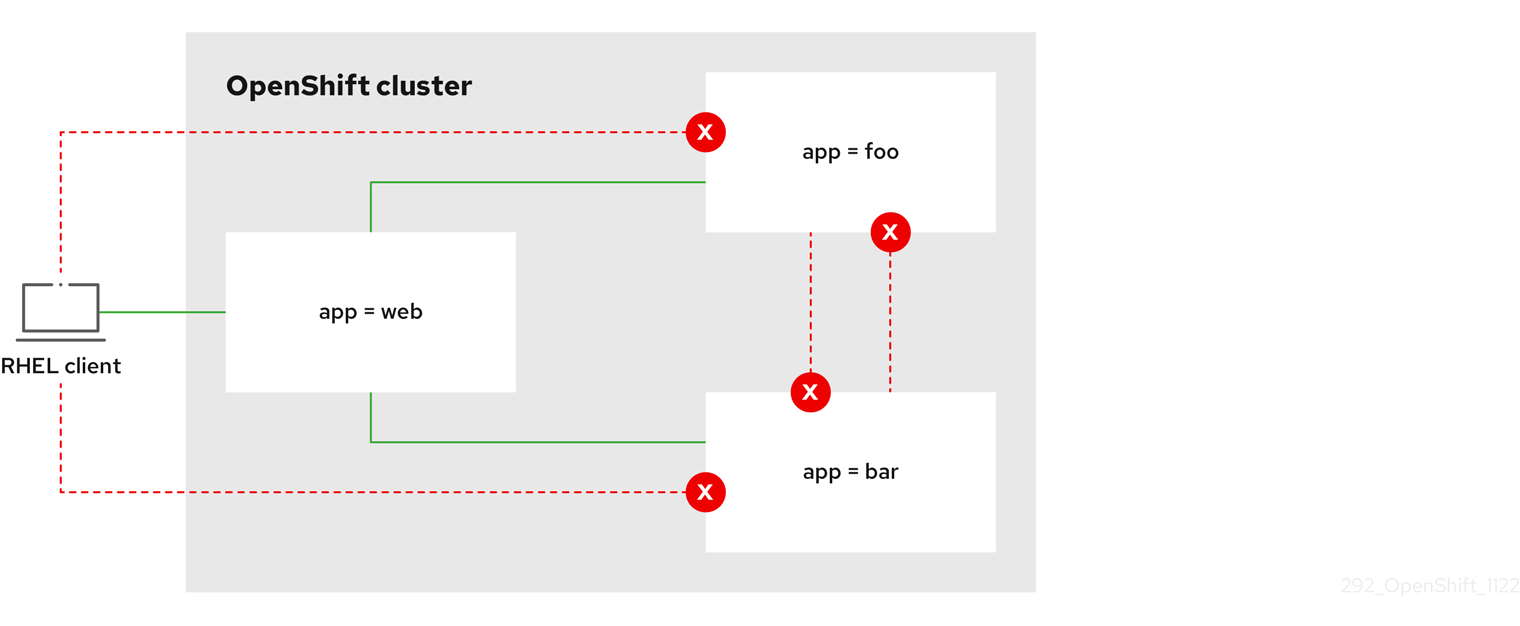
6.3.2.5. Creating a network policy allowing traffic to an application from all namespaces
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows traffic from all pods in all namespaces to a particular application.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in all namespaces to a particular application. Save the YAML in the
web-allow-all-namespaces.yamlfile:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: web-allow-all-namespaces namespace: default spec: podSelector: matchLabels: app: web 1 policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: {} 2NoteBy default, if you omit specifying a
namespaceSelectorit does not select any namespaces, which means the policy allows traffic only from the namespace the network policy is deployed to.Apply the policy by entering the following command:
$ oc apply -f web-allow-all-namespaces.yaml
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-all-namespaces created
Verification
Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in thesecondarynamespace and to start a shell:$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=secondary --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is allowed:
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
Expected output
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p> </body> </html>
6.3.2.6. Creating a network policy allowing traffic to an application from a namespace
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows traffic to a pod with the label app=web from a particular namespace. You might want to do this to:
- Restrict traffic to a production database only to namespaces where production workloads are deployed.
- Enable monitoring tools deployed to a particular namespace to scrape metrics from the current namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in a particular namespaces with a label
purpose=production. Save the YAML in theweb-allow-prod.yamlfile:kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: web-allow-prod namespace: default spec: podSelector: matchLabels: app: web 1 policyTypes: - Ingress ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: purpose: production 2Apply the policy by entering the following command:
$ oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yaml
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-prod created
Verification
Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
Run the following command to create the
prodnamespace:$ oc create namespace prod
Run the following command to label the
prodnamespace:$ oc label namespace/prod purpose=production
Run the following command to create the
devnamespace:$ oc create namespace dev
Run the following command to label the
devnamespace:$ oc label namespace/dev purpose=testing
Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in thedevnamespace and to start a shell:$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=dev --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is blocked:
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
Expected output
wget: download timed out
Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in theprodnamespace and start a shell:$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is allowed:
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
Expected output
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> html { color-scheme: light dark; } body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p> </body> </html>
6.3.2.7. Creating a network policy using OpenShift Cluster Manager
To define granular rules describing the ingress or egress network traffic allowed for namespaces in your cluster, you can create a network policy.
Prerequisites
- You logged in to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
- You created an Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
- You configured an identity provider for your cluster.
- You added your user account to the configured identity provider.
- You created a project within your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
Procedure
- From OpenShift Cluster Manager, click on the cluster you want to access.
- Click Open console to navigate to the OpenShift web console.
- Click on your identity provider and provide your credentials to log in to the cluster.
- From the administrator perspective, under Networking, click NetworkPolicies.
- Click Create NetworkPolicy.
- Provide a name for the policy in the Policy name field.
- Optional: You can provide the label and selector for a specific pod if this policy applies only to one or more specific pods. If you do not select a specific pod, then this policy will be applicable to all pods on the cluster.
- Optional: You can block all ingress and egress traffic by using the Deny all ingress traffic or Deny all egress traffic checkboxes.
- You can also add any combination of ingress and egress rules, allowing you to specify the port, namespace, or IP blocks you want to approve.
Add ingress rules to your policy:
Select Add ingress rule to configure a new rule. This action creates a new Ingress rule row with an Add allowed source drop-down menu that enables you to specify how you want to limit inbound traffic. The drop-down menu offers three options to limit your ingress traffic:
- Allow pods from the same namespace limits traffic to pods within the same namespace. You can specify the pods in a namespace, but leaving this option blank allows all of the traffic from pods in the namespace.
- Allow pods from inside the cluster limits traffic to pods within the same cluster as the policy. You can specify namespaces and pods from which you want to allow inbound traffic. Leaving this option blank allows inbound traffic from all namespaces and pods within this cluster.
- Allow peers by IP block limits traffic from a specified Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) IP block. You can block certain IPs with the exceptions option. Leaving the CIDR field blank allows all inbound traffic from all external sources.
- You can restrict all of your inbound traffic to a port. If you do not add any ports then all ports are accessible to traffic.
Add egress rules to your network policy:
Select Add egress rule to configure a new rule. This action creates a new Egress rule row with an Add allowed destination"* drop-down menu that enables you to specify how you want to limit outbound traffic. The drop-down menu offers three options to limit your egress traffic:
- Allow pods from the same namespace limits outbound traffic to pods within the same namespace. You can specify the pods in a namespace, but leaving this option blank allows all of the traffic from pods in the namespace.
- Allow pods from inside the cluster limits traffic to pods within the same cluster as the policy. You can specify namespaces and pods from which you want to allow outbound traffic. Leaving this option blank allows outbound traffic from all namespaces and pods within this cluster.
- Allow peers by IP block limits traffic from a specified CIDR IP block. You can block certain IPs with the exceptions option. Leaving the CIDR field blank allows all outbound traffic from all external sources.
- You can restrict all of your outbound traffic to a port. If you do not add any ports then all ports are accessible to traffic.
6.3.3. Viewing a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can view a network policy for a namespace.
6.3.3.1. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-27107 1 spec: podSelector: 2 matchLabels: app: mongodb ingress: - from: - podSelector: 3 matchLabels: app: app ports: 4 - protocol: TCP port: 27017
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
6.3.3.2. Viewing network policies using the CLI
You can examine the network policies in a namespace.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can view any network policy in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the network policy exists.
Procedure
List network policies in a namespace:
To view network policy objects defined in a namespace, enter the following command:
$ oc get networkpolicy
Optional: To examine a specific network policy, enter the following command:
$ oc describe networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy to inspect.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
For example:
$ oc describe networkpolicy allow-same-namespace
Output for
oc describecommandName: allow-same-namespace Namespace: ns1 Created on: 2021-05-24 22:28:56 -0400 EDT Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Spec: PodSelector: <none> (Allowing the specific traffic to all pods in this namespace) Allowing ingress traffic: To Port: <any> (traffic allowed to all ports) From: PodSelector: <none> Not affecting egress traffic Policy Types: Ingress
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of viewing a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
6.3.3.3. Viewing network policies using OpenShift Cluster Manager
You can view the configuration details of your network policy in Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager.
Prerequisites
- You logged in to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
- You created an Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
- You configured an identity provider for your cluster.
- You added your user account to the configured identity provider.
- You created a network policy.
Procedure
- From the Administrator perspective in the OpenShift Cluster Manager web console, under Networking, click NetworkPolicies.
- Select the desired network policy to view.
- In the Network Policy details page, you can view all of the associated ingress and egress rules.
Select YAML on the network policy details to view the policy configuration in YAML format.
NoteYou can only view the details of these policies. You cannot edit these policies.
6.3.4. Editing a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can edit an existing network policy for a namespace.
6.3.4.1. Editing a network policy
You can edit a network policy in a namespace.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can edit a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the network policy exists.
Procedure
Optional: To list the network policy objects in a namespace, enter the following command:
$ oc get networkpolicy
where:
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Edit the network policy object.
If you saved the network policy definition in a file, edit the file and make any necessary changes, and then enter the following command.
$ oc apply -n <namespace> -f <policy_file>.yaml
where:
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
<policy_file>- Specifies the name of the file containing the network policy.
If you need to update the network policy object directly, enter the following command:
$ oc edit networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Confirm that the network policy object is updated.
$ oc describe networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of editing a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from the policy in the web console through the Actions menu.
6.3.4.2. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-27107 1 spec: podSelector: 2 matchLabels: app: mongodb ingress: - from: - podSelector: 3 matchLabels: app: app ports: 4 - protocol: TCP port: 27017
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
6.3.4.3. Additional resources
6.3.5. Deleting a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can delete a network policy from a namespace.
6.3.5.1. Deleting a network policy using the CLI
You can delete a network policy in a namespace.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can delete any network policy in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the network policy exists.
Procedure
To delete a network policy object, enter the following command:
$ oc delete networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/default-deny deleted
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of deleting a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from the policy in the web console through the Actions menu.
6.3.5.2. Deleting a network policy using OpenShift Cluster Manager
You can delete a network policy in a namespace.
Prerequisites
- You logged in to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
- You created an Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster.
- You configured an identity provider for your cluster.
- You added your user account to the configured identity provider.
Procedure
- From the Administrator perspective in the OpenShift Cluster Manager web console, under Networking, click NetworkPolicies.
Use one of the following methods for deleting your network policy:
Delete the policy from the Network Policies table:
- From the Network Policies table, select the stack menu on the row of the network policy you want to delete and then, click Delete NetworkPolicy.
Delete the policy using the Actions drop-down menu from the individual network policy details:
- Click on Actions drop-down menu for your network policy.
- Select Delete NetworkPolicy from the menu.
6.3.6. Defining a default network policy for projects
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the new project template to automatically include network policies when you create a new project. If you do not yet have a customized template for new projects, you must first create one.
6.3.6.1. Modifying the template for new projects
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the default project template so that new projects are created using your custom requirements.
To create your own custom project template:
Prerequisites
-
You have access to an Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using an account with
dedicated-adminpermissions.
Procedure
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. Generate the default project template:
$ oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yaml
-
Use a text editor to modify the generated
template.yamlfile by adding objects or modifying existing objects. The project template must be created in the
openshift-confignamespace. Load your modified template:$ oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-config
Edit the project configuration resource using the web console or CLI.
Using the web console:
-
Navigate to the Administration
Cluster Settings page. - Click Configuration to view all configuration resources.
- Find the entry for Project and click Edit YAML.
-
Navigate to the Administration
Using the CLI:
Edit the
project.config.openshift.io/clusterresource:$ oc edit project.config.openshift.io/cluster
Update the
specsection to include theprojectRequestTemplateandnameparameters, and set the name of your uploaded project template. The default name isproject-request.Project configuration resource with custom project template
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Project metadata: # ... spec: projectRequestTemplate: name: <template_name> # ...- After you save your changes, create a new project to verify that your changes were successfully applied.
6.3.6.2. Adding network policies to the new project template
As a cluster administrator, you can add network policies to the default template for new projects. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS will automatically create all the NetworkPolicy objects specified in the template in the project.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a default CNI network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You must have created a custom default project template for new projects.
Procedure
Edit the default template for a new project by running the following command:
$ oc edit template <project_template> -n openshift-config
Replace
<project_template>with the name of the default template that you configured for your cluster. The default template name isproject-request.In the template, add each
NetworkPolicyobject as an element to theobjectsparameter. Theobjectsparameter accepts a collection of one or more objects.In the following example, the
objectsparameter collection includes severalNetworkPolicyobjects.objects: - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-same-namespace spec: podSelector: {} ingress: - from: - podSelector: {} - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-openshift-ingress spec: ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: network.openshift.io/policy-group: ingress podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Ingress - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-kube-apiserver-operator spec: ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: openshift-kube-apiserver-operator podSelector: matchLabels: app: kube-apiserver-operator policyTypes: - Ingress ...Optional: Create a new project to confirm that your network policy objects are created successfully by running the following commands:
Create a new project:
$ oc new-project <project> 1- 1
- Replace
<project>with the name for the project you are creating.
Confirm that the network policy objects in the new project template exist in the new project:
$ oc get networkpolicy NAME POD-SELECTOR AGE allow-from-openshift-ingress <none> 7s allow-from-same-namespace <none> 7s
6.3.7. Configuring multitenant isolation with network policy
As a cluster administrator, you can configure your network policies to provide multitenant network isolation.
Configuring network policies as described in this section provides network isolation similar to the multitenant mode of OpenShift SDN in previous versions of Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
6.3.7.1. Configuring multitenant isolation by using network policy
You can configure your project to isolate it from pods and services in other project namespaces.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, withmode: NetworkPolicyset. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the following
NetworkPolicyobjects:A policy named
allow-from-openshift-ingress.$ cat << EOF| oc create -f - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-openshift-ingress spec: ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: policy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress: "" podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Ingress EOFNotepolicy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress: ""is the preferred namespace selector label for OVN-Kubernetes.A policy named
allow-from-openshift-monitoring:$ cat << EOF| oc create -f - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-openshift-monitoring spec: ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: network.openshift.io/policy-group: monitoring podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Ingress EOFA policy named
allow-same-namespace:$ cat << EOF| oc create -f - kind: NetworkPolicy apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: allow-same-namespace spec: podSelector: ingress: - from: - podSelector: {} EOFA policy named
allow-from-kube-apiserver-operator:$ cat << EOF| oc create -f - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-kube-apiserver-operator spec: ingress: - from: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: openshift-kube-apiserver-operator podSelector: matchLabels: app: kube-apiserver-operator policyTypes: - Ingress EOFFor more details, see New
kube-apiserver-operatorwebhook controller validating health of webhook.
Optional: To confirm that the network policies exist in your current project, enter the following command:
$ oc describe networkpolicy
Example output
Name: allow-from-openshift-ingress Namespace: example1 Created on: 2020-06-09 00:28:17 -0400 EDT Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Spec: PodSelector: <none> (Allowing the specific traffic to all pods in this namespace) Allowing ingress traffic: To Port: <any> (traffic allowed to all ports) From: NamespaceSelector: network.openshift.io/policy-group: ingress Not affecting egress traffic Policy Types: Ingress Name: allow-from-openshift-monitoring Namespace: example1 Created on: 2020-06-09 00:29:57 -0400 EDT Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Spec: PodSelector: <none> (Allowing the specific traffic to all pods in this namespace) Allowing ingress traffic: To Port: <any> (traffic allowed to all ports) From: NamespaceSelector: network.openshift.io/policy-group: monitoring Not affecting egress traffic Policy Types: Ingress
6.4. Audit logging for network security
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin uses Open Virtual Network (OVN) access control lists (ACLs) to manage AdminNetworkPolicy, BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy, NetworkPolicy, and EgressFirewall objects. Audit logging exposes allow and deny ACL events for NetworkPolicy, EgressFirewall and BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy custom resources (CR). Logging also exposes allow, deny, and pass ACL events for AdminNetworkPolicy (ANP) CR.
Audit logging is available for only the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
6.4.1. Audit configuration
The configuration for audit logging is specified as part of the OVN-Kubernetes cluster network provider configuration. The following YAML illustrates the default values for the audit logging:
Audit logging configuration
apiVersion: operator.openshift.io/v1
kind: Network
metadata:
name: cluster
spec:
defaultNetwork:
ovnKubernetesConfig:
policyAuditConfig:
destination: "null"
maxFileSize: 50
rateLimit: 20
syslogFacility: local0
The following table describes the configuration fields for audit logging.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| integer |
The maximum number of messages to generate every second per node. The default value is |
|
| integer |
The maximum size for the audit log in bytes. The default value is |
|
| integer | The maximum number of log files that are retained. |
|
| string | One of the following additional audit log targets:
|
|
| string |
The syslog facility, such as |
6.4.2. Audit logging
You can configure the destination for audit logs, such as a syslog server or a UNIX domain socket. Regardless of any additional configuration, an audit log is always saved to /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log on each OVN-Kubernetes pod in the cluster.
You can enable audit logging for each namespace by annotating each namespace configuration with a k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging section. In the k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging section, you must specify allow, deny, or both values to enable audit logging for a namespace.
A network policy does not support setting the Pass action set as a rule.
The ACL-logging implementation logs access control list (ACL) events for a network. You can view these logs to analyze any potential security issues.
Example namespace annotation
kind: Namespace
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: example1
annotations:
k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging: |-
{
"deny": "info",
"allow": "info"
}
To view the default ACL logging configuration values, see the policyAuditConfig object in the cluster-network-03-config.yml file. If required, you can change the ACL logging configuration values for log file parameters in this file.
The logging message format is compatible with syslog as defined by RFC5424. The syslog facility is configurable and defaults to local0. The following example shows key parameters and their values outputted in a log message:
Example logging message that outputs parameters and their values
<timestamp>|<message_serial>|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|<severity>|name="<acl_name>", verdict="<verdict>", severity="<severity>", direction="<direction>": <flow>
Where:
-
<timestamp>states the time and date for the creation of a log message. -
<message_serial>lists the serial number for a log message. -
acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)is a literal string that prints the location of the log message in the OVN-Kubernetes plugin. -
<severity>sets the severity level for a log message. If you enable audit logging that supportsallowanddenytasks then two severity levels show in the log message output. -
<name>states the name of the ACL-logging implementation in the OVN Network Bridging Database (nbdb) that was created by the network policy. -
<verdict>can be eitherallowordrop. -
<direction>can be eitherto-lportorfrom-lportto indicate that the policy was applied to traffic going to or away from a pod. -
<flow>shows packet information in a format equivalent to theOpenFlowprotocol. This parameter comprises Open vSwitch (OVS) fields.
The following example shows OVS fields that the flow parameter uses to extract packet information from system memory:
Example of OVS fields used by the flow parameter to extract packet information
<proto>,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=<src_mac>,dl_dst=<source_mac>,nw_src=<source_ip>,nw_dst=<target_ip>,nw_tos=<tos_dscp>,nw_ecn=<tos_ecn>,nw_ttl=<ip_ttl>,nw_frag=<fragment>,tp_src=<tcp_src_port>,tp_dst=<tcp_dst_port>,tcp_flags=<tcp_flags>
Where:
-
<proto>states the protocol. Valid values aretcpandudp. -
vlan_tci=0x0000states the VLAN header as0because a VLAN ID is not set for internal pod network traffic. -
<src_mac>specifies the source for the Media Access Control (MAC) address. -
<source_mac>specifies the destination for the MAC address. -
<source_ip>lists the source IP address -
<target_ip>lists the target IP address. -
<tos_dscp>states Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) values to classify and prioritize certain network traffic over other traffic. -
<tos_ecn>states Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) values that indicate any congested traffic in your network. -
<ip_ttl>states the Time To Live (TTP) information for an packet. -
<fragment>specifies what type of IP fragments or IP non-fragments to match. -
<tcp_src_port>shows the source for the port for TCP and UDP protocols. -
<tcp_dst_port>lists the destination port for TCP and UDP protocols. -
<tcp_flags>supports numerous flags such asSYN,ACK,PSHand so on. If you need to set multiple values then each value is separated by a vertical bar (|). The UDP protocol does not support this parameter.
For more information about the previous field descriptions, go to the OVS manual page for ovs-fields.
Example ACL deny log entry for a network policy
2023-11-02T16:28:54.139Z|00004|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:Ingress", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:01,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.131.0.39,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=62,nw_frag=no,tp_src=58496,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2023-11-02T16:28:55.187Z|00005|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:Ingress", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:01,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.131.0.39,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=62,nw_frag=no,tp_src=58496,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2023-11-02T16:28:57.235Z|00006|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:Ingress", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:01,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.131.0.39,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=62,nw_frag=no,tp_src=58496,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn
The following table describes namespace annotation values:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Blocks namespace access to any traffic that matches an ACL rule with the |
|
|
Permits namespace access to any traffic that matches an ACL rule with the |
|
|
A |
Additional resources
6.4.3. AdminNetworkPolicy audit logging
Audit logging is enabled per AdminNetworkPolicy CR by annotating an ANP policy with the k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging key such as in the following example:
Example 6.8. Example of annotation for AdminNetworkPolicy CR
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: AdminNetworkPolicy
metadata:
annotations:
k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging: '{ "deny": "alert", "allow": "alert", "pass" : "warning" }'
name: anp-tenant-log
spec:
priority: 5
subject:
namespaces:
matchLabels:
tenant: backend-storage # Selects all pods owned by storage tenant.
ingress:
- name: "allow-all-ingress-product-development-and-customer" # Product development and customer tenant ingress to backend storage.
action: "Allow"
from:
- pods:
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: tenant
operator: In
values:
- product-development
- customer
podSelector: {}
- name: "pass-all-ingress-product-security"
action: "Pass"
from:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
tenant: product-security
- name: "deny-all-ingress" # Ingress to backend from all other pods in the cluster.
action: "Deny"
from:
- namespaces: {}
egress:
- name: "allow-all-egress-product-development"
action: "Allow"
to:
- pods:
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
tenant: product-development
podSelector: {}
- name: "pass-egress-product-security"
action: "Pass"
to:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
tenant: product-security
- name: "deny-all-egress" # Egress from backend denied to all other pods.
action: "Deny"
to:
- namespaces: {}
Logs are generated whenever a specific OVN ACL is hit and meets the action criteria set in your logging annotation. For example, an event in which any of the namespaces with the label tenant: product-development accesses the namespaces with the label tenant: backend-storage, a log is generated.
ACL logging is limited to 60 characters. If your ANP name field is long, the rest of the log will be truncated.
The following is a direction index for the examples log entries that follow:
| Direction | Rule |
|---|---|
| Ingress |
|
| Egress |
|
Example 6.9. Example ACL log entry for Allow action of the AdminNetworkPolicy named anp-tenant-log with Ingress:0 and Egress:0
2024-06-10T16:27:45.194Z|00052|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:1a,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,nw_src=10.128.2.26,nw_dst=10.128.2.25,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=57814,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T16:28:23.130Z|00059|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:18,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,nw_src=10.128.2.24,nw_dst=10.128.2.25,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=38620,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack 2024-06-10T16:28:38.293Z|00069|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Egress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:1a,nw_src=10.128.2.25,nw_dst=10.128.2.26,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=47566,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=fin|ack=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=55704,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack
Example 6.10. Example ACL log entry for Pass action of the AdminNetworkPolicy named anp-tenant-log with Ingress:1 and Egress:1
2024-06-10T16:33:12.019Z|00075|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Ingress:1", verdict=pass, severity=warning, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:1b,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,nw_src=10.128.2.27,nw_dst=10.128.2.25,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=37394,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack 2024-06-10T16:35:04.209Z|00081|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Egress:1", verdict=pass, severity=warning, direction=from-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:1b,nw_src=10.128.2.25,nw_dst=10.128.2.27,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=34018,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack
Example 6.11. Example ACL log entry for Deny action of the AdminNetworkPolicy named anp-tenant-log with Egress:2 and Ingress2
2024-06-10T16:43:05.287Z|00087|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Egress:2", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:18,nw_src=10.128.2.25,nw_dst=10.128.2.24,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=51598,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T16:44:43.591Z|00090|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="ANP:anp-tenant-log:Ingress:2", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:80:02:1c,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:80:02:19,nw_src=10.128.2.28,nw_dst=10.128.2.25,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=33774,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn
The following table describes ANP annotation:
| Annotation | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
You must specify at least one of
|
6.4.4. BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy audit logging
Audit logging is enabled in the BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy CR by annotating an BANP policy with the k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging key such as in the following example:
Example 6.12. Example of annotation for BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy CR
apiVersion: policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: BaselineAdminNetworkPolicy
metadata:
annotations:
k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging: '{ "deny": "alert", "allow": "alert"}'
name: default
spec:
subject:
namespaces:
matchLabels:
tenant: workloads # Selects all workload pods in the cluster.
ingress:
- name: "default-allow-dns" # This rule allows ingress from dns tenant to all workloads.
action: "Allow"
from:
- namespaces:
matchLabels:
tenant: dns
- name: "default-deny-dns" # This rule denies all ingress from all pods to workloads.
action: "Deny"
from:
- namespaces: {} # Use the empty selector with caution because it also selects OpenShift namespaces as well.
egress:
- name: "default-deny-dns" # This rule denies all egress from workloads. It will be applied when no ANP or network policy matches.
action: "Deny"
to:
- namespaces: {} # Use the empty selector with caution because it also selects OpenShift namespaces as well.
In the example, an event in which any of the namespaces with the label tenant: dns accesses the namespaces with the label tenant: workloads, a log is generated.
The following is a direction index for the examples log entries that follow:
| Direction | Rule |
|---|---|
| Ingress |
|
| Egress |
|
Example 6.13. Example ACL allow log entry for Allow action of default BANP with Ingress:0
2024-06-10T18:11:58.263Z|00022|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.87,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=60510,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T18:11:58.264Z|00023|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.87,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=60510,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=psh|ack 2024-06-10T18:11:58.264Z|00024|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.87,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=60510,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack 2024-06-10T18:11:58.264Z|00025|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.87,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=60510,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack 2024-06-10T18:11:58.264Z|00026|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.87,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=60510,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=fin|ack 2024-06-10T18:11:58.264Z|00027|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.87,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=60510,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=ack
Example 6.14. Example ACL allow log entry for Allow action of default BANP with Egress:0 and Ingress:1
2024-06-10T18:09:57.774Z|00016|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Egress:0", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,nw_src=10.130.2.86,nw_dst=10.130.2.87,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=45614,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T18:09:58.809Z|00017|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Egress:0", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,nw_src=10.130.2.86,nw_dst=10.130.2.87,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=45614,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T18:10:00.857Z|00018|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Egress:0", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:57,nw_src=10.130.2.86,nw_dst=10.130.2.87,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=45614,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T18:10:25.414Z|00019|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:1", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:58,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.88,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=40630,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T18:10:26.457Z|00020|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:1", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:58,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.88,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=40630,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2024-06-10T18:10:28.505Z|00021|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="BANP:default:Ingress:1", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:82:02:58,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:82:02:56,nw_src=10.130.2.88,nw_dst=10.130.2.86,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,tp_src=40630,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn
The following table describes BANP annotation:
| Annotation | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
You must specify at least one of
|
6.4.5. Configuring egress firewall and network policy auditing for a cluster
As a cluster administrator, you can customize audit logging for your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To customize the audit logging configuration, enter the following command:
$ oc edit network.operator.openshift.io/cluster
TipYou can alternatively customize and apply the following YAML to configure audit logging:
apiVersion: operator.openshift.io/v1 kind: Network metadata: name: cluster spec: defaultNetwork: ovnKubernetesConfig: policyAuditConfig: destination: "null" maxFileSize: 50 rateLimit: 20 syslogFacility: local0
Verification
To create a namespace with network policies complete the following steps:
Create a namespace for verification:
$ cat <<EOF| oc create -f - kind: Namespace apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: verify-audit-logging annotations: k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging: '{ "deny": "alert", "allow": "alert" }' EOFExample output
namespace/verify-audit-logging created
Create network policies for the namespace:
$ cat <<EOF| oc create -n verify-audit-logging -f - apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: deny-all spec: podSelector: matchLabels: policyTypes: - Ingress - Egress --- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-from-same-namespace namespace: verify-audit-logging spec: podSelector: {} policyTypes: - Ingress - Egress ingress: - from: - podSelector: {} egress: - to: - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: verify-audit-logging EOFExample output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-all created networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/allow-from-same-namespace created
Create a pod for source traffic in the
defaultnamespace:$ cat <<EOF| oc create -n default -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: client spec: containers: - name: client image: registry.access.redhat.com/rhel7/rhel-tools command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"] args: ["sleep inf"] EOFCreate two pods in the
verify-audit-loggingnamespace:$ for name in client server; do cat <<EOF| oc create -n verify-audit-logging -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: ${name} spec: containers: - name: ${name} image: registry.access.redhat.com/rhel7/rhel-tools command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"] args: ["sleep inf"] EOF doneExample output
pod/client created pod/server created
To generate traffic and produce network policy audit log entries, complete the following steps:
Obtain the IP address for pod named
serverin theverify-audit-loggingnamespace:$ POD_IP=$(oc get pods server -n verify-audit-logging -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')Ping the IP address from the previous command from the pod named
clientin thedefaultnamespace and confirm that all packets are dropped:$ oc exec -it client -n default -- /bin/ping -c 2 $POD_IP
Example output
PING 10.128.2.55 (10.128.2.55) 56(84) bytes of data. --- 10.128.2.55 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2041ms
Ping the IP address saved in the
POD_IPshell environment variable from the pod namedclientin theverify-audit-loggingnamespace and confirm that all packets are allowed:$ oc exec -it client -n verify-audit-logging -- /bin/ping -c 2 $POD_IP
Example output
PING 10.128.0.86 (10.128.0.86) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.128.0.86: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=2.21 ms 64 bytes from 10.128.0.86: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.440 ms --- 10.128.0.86 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.440/1.329/2.219/0.890 ms
Display the latest entries in the network policy audit log:
$ for pod in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node --no-headers=true | awk '{ print $1 }') ; do oc exec -it $pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -- tail -4 /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log doneExample output
2023-11-02T16:28:54.139Z|00004|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:Ingress", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:01,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.131.0.39,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=62,nw_frag=no,tp_src=58496,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2023-11-02T16:28:55.187Z|00005|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:Ingress", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:01,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.131.0.39,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=62,nw_frag=no,tp_src=58496,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2023-11-02T16:28:57.235Z|00006|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:Ingress", verdict=drop, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: tcp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:01,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.131.0.39,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=62,nw_frag=no,tp_src=58496,tp_dst=8080,tcp_flags=syn 2023-11-02T16:49:57.909Z|00028|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Egress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0 2023-11-02T16:49:57.909Z|00029|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0 2023-11-02T16:49:58.932Z|00030|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Egress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0 2023-11-02T16:49:58.932Z|00031|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0
6.4.6. Enabling egress firewall and network policy audit logging for a namespace
As a cluster administrator, you can enable audit logging for a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To enable audit logging for a namespace, enter the following command:
$ oc annotate namespace <namespace> \ k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging='{ "deny": "alert", "allow": "notice" }'where:
<namespace>- Specifies the name of the namespace.
TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to enable audit logging:
kind: Namespace apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: <namespace> annotations: k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging: |- { "deny": "alert", "allow": "notice" }Example output
namespace/verify-audit-logging annotated
Verification
Display the latest entries in the audit log:
$ for pod in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node --no-headers=true | awk '{ print $1 }') ; do oc exec -it $pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -- tail -4 /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log doneExample output
2023-11-02T16:49:57.909Z|00028|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Egress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0 2023-11-02T16:49:57.909Z|00029|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0 2023-11-02T16:49:58.932Z|00030|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Egress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=from-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0 2023-11-02T16:49:58.932Z|00031|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|INFO|name="NP:verify-audit-logging:allow-from-same-namespace:Ingress:0", verdict=allow, severity=alert, direction=to-lport: icmp,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=0a:58:0a:81:02:22,dl_dst=0a:58:0a:81:02:23,nw_src=10.129.2.34,nw_dst=10.129.2.35,nw_tos=0,nw_ecn=0,nw_ttl=64,nw_frag=no,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0
6.4.7. Disabling egress firewall and network policy audit logging for a namespace
As a cluster administrator, you can disable audit logging for a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To disable audit logging for a namespace, enter the following command:
$ oc annotate --overwrite namespace <namespace> k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging-
where:
<namespace>- Specifies the name of the namespace.
TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to disable audit logging:
kind: Namespace apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: <namespace> annotations: k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging: nullExample output
namespace/verify-audit-logging annotated