Chapter 5. Network Observability Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
The Network Observability Operator for OpenShift Container Platform deploys a monitoring pipeline. This pipeline collects and enriches network traffic flows generated by the eBPF agent.
5.1. Viewing statuses
The Network Observability Operator provides the Flow Collector API. When a Flow Collector resource is created, it deploys pods and services to create and store network flows in the Loki log store, as well as to display dashboards, metrics, and flows in the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
Procedure
Run the following command to view the state of
FlowCollector:oc get flowcollector/cluster
$ oc get flowcollector/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGENT SAMPLING (EBPF) DEPLOYMENT MODEL STATUS cluster EBPF 50 DIRECT Ready
NAME AGENT SAMPLING (EBPF) DEPLOYMENT MODEL STATUS cluster EBPF 50 DIRECT ReadyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the status of pods running in the
netobservnamespace by entering the following command:oc get pods -n netobserv
$ oc get pods -n netobservCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
flowlogs-pipelinepods collect flows, enriches the collected flows, then send flows to the Loki storage.netobserv-pluginpods create a visualization plugin for the OpenShift Container Platform Console.Check the status of pods running in the namespace
netobserv-privilegedby entering the following command:oc get pods -n netobserv-privileged
$ oc get pods -n netobserv-privilegedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
netobserv-ebpf-agentpods monitor network interfaces of the nodes to get flows and send them toflowlogs-pipelinepods.If you are using the Loki Operator, check the status of the
componentpods ofLokiStackcustom resource in thenetobservnamespace by entering the following command:oc get pods -n netobserv
$ oc get pods -n netobservCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2. Network Observablity Operator architecture
The Network Observability Operator provides the FlowCollector API, which is instantiated at installation and configured to reconcile the eBPF agent, the flowlogs-pipeline, and the netobserv-plugin components. Only a single FlowCollector per cluster is supported.
The eBPF agent runs on each cluster node with some privileges to collect network flows. The flowlogs-pipeline receives the network flows data and enriches the data with Kubernetes identifiers. If you choose to use Loki, the flowlogs-pipeline sends flow logs data to Loki for storing and indexing. The netobserv-plugin, which is a dynamic OpenShift Container Platform web console plugin, queries Loki to fetch network flows data. Cluster-admins can view the data in the web console.
If you do not use Loki, you can generate metrics with Prometheus. Those metrics and their related dashboards are accessible in the web console. For more information, see "Network Observability without Loki".
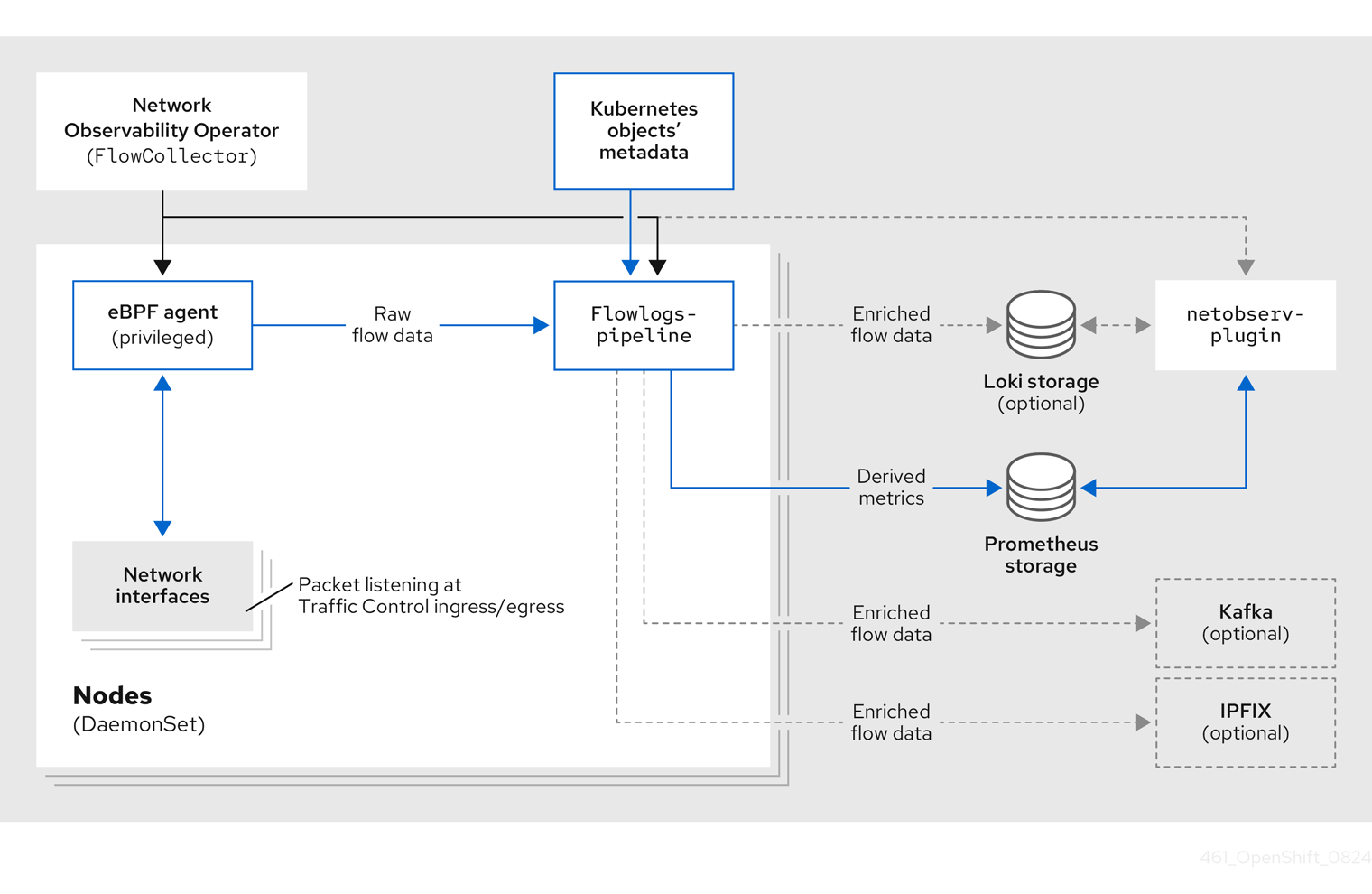
There are three deployment model options for the Network Observability Operator.
The Network Observability Operator does not manage Loki or other data stores. You must install Loki separately by using the Loki Operator. If you use Kafka, you must install it separately by using the Kafka Operator.
- Service deployment model
-
When the
spec.deploymentModelfield in theFlowCollectorresource is set toService, agents are deployed per node as daemon sets. Theflowlogs-pipelineis a standard deployment with a service. You can scale theflowlogs-pipelinecomponent by using thespec.processor.consumerReplicasfield. - Direct deployment model
-
When the
spec.deploymentModelfield is set toDirect, agents and theflowlogs-pipelineare both deployed per node as daemon sets. This model is suitable for technology assessments and small clusters. However, it is less memory-efficient in large clusters because each instance offlowlogs-pipelinecaches the same cluster information. - Kafka deployment model (optional)
If you use the Kafka option, the
eBPF agentsends the network flow data to Kafka. You can scale theflowlogs-pipelinecomponent by using thespec.processor.consumerReplicasfield. Theflowlogs-pipelinecomponent reads from the Kafka topic before sending data to Loki, as shown in the following diagram.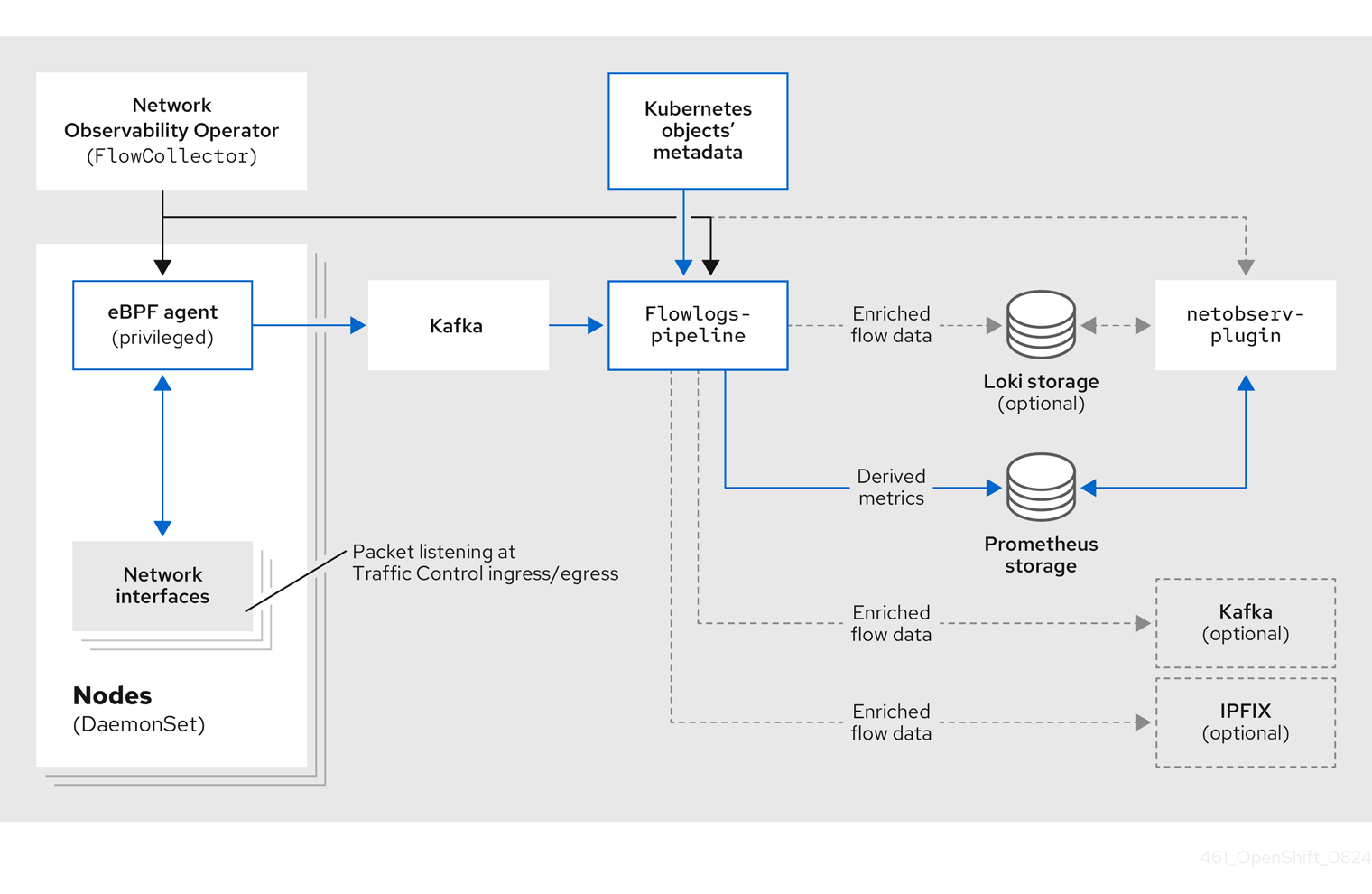
5.3. Viewing Network Observability Operator status and configuration
You can inspect the status and view the details of the FlowCollector using the oc describe command.
Procedure
Run the following command to view the status and configuration of the Network Observability Operator:
oc describe flowcollector/cluster
$ oc describe flowcollector/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow