Chapter 6. Customizing the web console in OpenShift Container Platform
You can customize the OpenShift Container Platform web console to set a custom logo, product name, links, notifications, and command-line downloads. This is especially helpful if you need to tailor the web console to meet specific corporate or government requirements.
6.1. Adding a custom logo and product name
You can create custom branding by adding a custom logo or custom product name. You can set both or one without the other, as these settings are independent of each other.
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
-
Create a file of the logo that you want to use. The logo can be a file in any common image format, including GIF, JPG, PNG, or SVG, and is constrained to a
max-heightof60px. Image size must not exceed 1 MB due to constraints on theConfigMapobject size.
Procedure
Import your logo file into a config map in the
openshift-confignamespace:oc create configmap console-custom-logo --from-file /path/to/console-custom-logo.png -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap console-custom-logo --from-file /path/to/console-custom-logo.png -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to create the config map:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Provide a valid base64-encoded logo.
Edit the web console’s Operator configuration to include
customLogoFileandcustomProductName:oc edit consoles.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit consoles.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Once the Operator configuration is updated, it will sync the custom logo config map into the console namespace, mount it to the console pod, and redeploy.
Check for success. If there are any issues, the console cluster Operator will report a
Degradedstatus, and the console Operator configuration will also report aCustomLogoDegradedstatus, but with reasons likeKeyOrFilenameInvalidorNoImageProvided.To check the
clusteroperator, run:oc get clusteroperator console -o yaml
$ oc get clusteroperator console -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check the console Operator configuration, run:
oc get consoles.operator.openshift.io -o yaml
$ oc get consoles.operator.openshift.io -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2. Creating custom links in the web console
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
From Administration
Custom Resource Definitions, click on ConsoleLink. - Select Instances tab
Click Create Console Link and edit the file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Valid location settings are
HelpMenu,UserMenu,ApplicationMenu, andNamespaceDashboard.
To make the custom link appear in all namespaces, follow this example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To make the custom link appear in only some namespaces, follow this example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To make the custom link appear in the application menu, follow this example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Save to apply your changes.
6.3. Customizing console routes
For console and downloads routes, custom routes functionality uses the ingress config route configuration API. If the console custom route is set up in both the ingress config and console-operator config, then the new ingress config custom route configuration takes precedent. The route configuration with the console-operator config is deprecated.
6.3.1. Customizing the console route
You can customize the console route by setting the custom hostname and TLS certificate in the spec.componentRoutes field of the cluster Ingress configuration.
Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
You have created a secret in the
openshift-confignamespace containing the TLS certificate and key. This is required if the domain for the custom hostname suffix does not match the cluster domain suffix. The secret is optional if the suffix matches.TipYou can create a TLS secret by using the
oc create secret tlscommand.
Procedure
Edit the cluster
Ingressconfiguration:oc edit ingress.config.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit ingress.config.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the custom hostname and optionally the serving certificate and key:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file to apply the changes.
Add a DNS record for the custom console route that points to the application ingress load balancer.
6.3.2. Customizing the download route
You can customize the download route by setting the custom hostname and TLS certificate in the spec.componentRoutes field of the cluster Ingress configuration.
Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
You have created a secret in the
openshift-confignamespace containing the TLS certificate and key. This is required if the domain for the custom hostname suffix does not match the cluster domain suffix. The secret is optional if the suffix matches.TipYou can create a TLS secret by using the
oc create secret tlscommand.
Procedure
Edit the cluster
Ingressconfiguration:oc edit ingress.config.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit ingress.config.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the custom hostname and optionally the serving certificate and key:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file to apply the changes.
Add a DNS record for the custom downloads route that points to the application ingress load balancer.
6.4. Customizing the login page
Create Terms of Service information with custom login pages. Custom login pages can also be helpful if you use a third-party login provider, such as GitHub or Google, to show users a branded page that they trust and expect before being redirected to the authentication provider. You can also render custom error pages during the authentication process.
Customizing the error template is limited to identity providers (IDPs) that use redirects, such as request header and OIDC-based IDPs. It does not have an effect on IDPs that use direct password authentication, such as LDAP and htpasswd.
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
Run the following commands to create templates you can modify:
oc adm create-login-template > login.html
$ oc adm create-login-template > login.htmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc adm create-provider-selection-template > providers.html
$ oc adm create-provider-selection-template > providers.htmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc adm create-error-template > errors.html
$ oc adm create-error-template > errors.htmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the secrets:
oc create secret generic login-template --from-file=login.html -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic login-template --from-file=login.html -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc create secret generic providers-template --from-file=providers.html -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic providers-template --from-file=providers.html -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc create secret generic error-template --from-file=errors.html -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic error-template --from-file=errors.html -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run:
oc edit oauths cluster
$ oc edit oauths clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the specification:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run
oc explain oauths.spec.templatesto understand the options.
6.5. Defining a template for an external log link
If you are connected to a service that helps you browse your logs, but you need to generate URLs in a particular way, then you can define a template for your link.
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
From Administration
Custom Resource Definitions, click on ConsoleExternalLogLink. - Select Instances tab
Click Create Console External Log Link and edit the file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.6. Creating custom notification banners
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
From Administration
Custom Resource Definitions, click on ConsoleNotification. - Select Instances tab
Click Create Console Notification and edit the file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Valid location settings are
BannerTop,BannerBottom, andBannerTopBottom.
- Click Create to apply your changes.
6.7. Customizing CLI downloads
You can configure links for downloading the CLI with custom link text and URLs, which can point directly to file packages or to an external page that provides the packages.
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
Navigate to Administration
Custom Resource Definitions. - Select ConsoleCLIDownload from the list of Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs).
Click the YAML tab, and then make your edits:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click the Save button.
6.8. Adding YAML examples to Kubernetes resources
You can dynamically add YAML examples to any Kubernetes resources at any time.
Prerequisites
- You must have cluster administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
From Administration
Custom Resource Definitions, click on ConsoleYAMLSample. Click YAML and edit the file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use
spec.snippetto indicate that the YAML sample is not the full YAML resource definition, but a fragment that can be inserted into the existing YAML document at the user’s cursor.- Click Save.
6.9. Customizing user perspectives
The OpenShift Container Platform web console provides two perspectives by default, Administrator and Developer. You might have more perspectives available depending on installed console plugins. As a cluster administrator, you can show or hide a perspective for all users or for a specific user role. Customizing perspectives ensures that users can view only the perspectives that are applicable to their role and tasks. For example, you can hide the Administrator perspective from unprivileged users so that they cannot manage cluster resources, users, and projects. Similarly, you can show the Developer perspective to users with the developer role so that they can create, deploy, and monitor applications.
You can also customize the perspective visibility for users based on role-based access control (RBAC). For example, if you customize a perspective for monitoring purposes, which requires specific permissions, you can define that the perspective is visible only to users with required permissions.
Each perspective includes the following mandatory parameters, which you can edit in the YAML view:
-
id: Defines the ID of the perspective to show or hide -
visibility: Defines the state of the perspective along with access review checks, if needed -
state: Defines whether the perspective is enabled, disabled, or needs an access review check
By default, all perspectives are enabled. When you customize the user perspective, your changes are applicable to the entire cluster.
6.9.1. Customizing a perspective using YAML view
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
In the Administrator perspective, navigate to Administration
Cluster Settings. - Select the Configuration tab and click the Console (operator.openshift.io) resource.
Click the YAML tab and make your customization:
To enable or disable a perspective, insert the snippet for Add user perspectives and edit the YAML code as needed:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To hide a perspective based on RBAC permissions, insert the snippet for Hide user perspectives and edit the YAML code as needed:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To customize a perspective based on your needs, create your own YAML snippet:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Click Save.
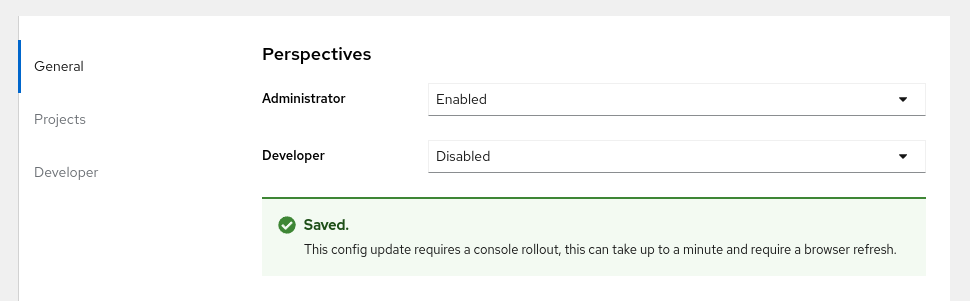
6.9.2. Customizing a perspective using form view
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
In the Administrator perspective, navigate to Administration
Cluster Settings. - Select the Configuration tab and click the Console (operator.openshift.io) resource.
-
Click Actions
Customize on the right side of the page. In the General settings, customize the perspective by selecting one of the following options from the dropdown list:
- Enabled: Enables the perspective for all users
- Only visible for privileged users: Enables the perspective for users who can list all namespaces
- Only visible for unprivileged users: Enables the perspective for users who cannot list all namespaces
Disabled: Disables the perspective for all users
A notification opens to confirm that your changes are saved.
 Note
NoteWhen you customize the user perspective, your changes are automatically saved and take effect after a browser refresh.
6.10. Developer catalog and sub-catalog customization
As a cluster administrator, you have the ability to organize and manage the Developer catalog or its sub-catalogs. You can enable or disable the sub-catalog types or disable the entire developer catalog.
The developerCatalog.types object includes the following parameters that you must define in a snippet to use them in the YAML view:
-
state: Defines if a list of developer catalog types should be enabled or disabled. -
enabled: Defines a list of developer catalog types (sub-catalogs) that are visible to users. -
disabled: Defines a list of developer catalog types (sub-catalogs) that are not visible to users.
You can enable or disable the following developer catalog types (sub-catalogs) using the YAML view or the form view.
-
Builder Images -
Templates -
Devfiles -
Samples -
Helm Charts -
Event Sources -
Event Sinks -
Operator Backed
6.10.1. Customizing a developer catalog or its sub-catalogs using the YAML view
You can customize a developer catalog by editing the YAML content in the YAML view.
Prerequisites
- An OpenShift web console session with cluster administrator privileges.
Procedure
-
In the Administrator perspective of the web console, navigate to Administration
Cluster Settings. - Select the Configuration tab, click the Console (operator.openshift.io) resource and view the Details page.
Click the YAML tab to open the editor and edit the YAML content as needed.
For example, to disable a developer catalog type, insert the following snippet that defines a list of disabled developer catalog resources:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Save.
By default, the developer catalog types are enabled in the Administrator view of the Web Console.
6.10.2. Customizing a developer catalog or its sub-catalogs using the form view
You can customize a developer catalog by using the form view in the Web Console.
Prerequisites
- An OpenShift web console session with cluster administrator privileges.
- The Developer perspective is enabled.
Procedure
-
In the Administrator perspective, navigate to Administration
Cluster Settings. - Select the Configuration tab and click the Console (operator.openshift.io) resource.
-
Click Actions
Customize. Enable or disable items in the Pre-pinned navigation items, Add page, and Developer Catalog sections.
Verification
After you have customized the developer catalog, your changes are automatically saved in the system and take effect in the browser after a refresh.

As an administrator, you can define the navigation items that appear by default for all users. You can also reorder the navigation items.
You can use a similar procedure to customize Web UI items such as Quick starts, Cluster roles, and Actions.
6.10.2.1. Example YAML file changes
You can dynamically add the following snippets in the YAML editor for customizing a developer catalog.
Use the following snippet to display all the sub-catalogs by setting the state type to Enabled.
Use the following snippet to disable all sub-catalogs by setting the state type to Disabled:
Use the following snippet when a cluster administrator defines a list of sub-catalogs, which are enabled in the Web Console.