Chapter 7. Using RBAC to define and apply permissions
7.1. RBAC overview
Role-based access control (RBAC) objects determine whether a user is allowed to perform a given action within a project.
Administrators with the dedicated-admin role can use the cluster roles and bindings to control who has various access levels to the OpenShift Dedicated platform itself and all projects.
Developers can use local roles and bindings to control who has access to their projects. Note that authorization is a separate step from authentication, which is more about determining the identity of who is taking the action.
Authorization is managed using:
| Authorization object | Description |
|---|---|
| Rules |
Sets of permitted verbs on a set of objects. For example, whether a user or service account can |
| Roles | Collections of rules. You can associate, or bind, users and groups to multiple roles. |
| Bindings | Associations between users and/or groups with a role. |
There are two levels of RBAC roles and bindings that control authorization:
| RBAC level | Description |
|---|---|
| Cluster RBAC | Roles and bindings that are applicable across all projects. Cluster roles exist cluster-wide, and cluster role bindings can reference only cluster roles. |
| Local RBAC | Roles and bindings that are scoped to a given project. While local roles exist only in a single project, local role bindings can reference both cluster and local roles. |
A cluster role binding is a binding that exists at the cluster level. A role binding exists at the project level. The cluster role view must be bound to a user using a local role binding for that user to view the project. Create local roles only if a cluster role does not provide the set of permissions needed for a particular situation.
This two-level hierarchy allows reuse across multiple projects through the cluster roles while allowing customization inside of individual projects through local roles.
During evaluation, both the cluster role bindings and the local role bindings are used. For example:
- Cluster-wide "allow" rules are checked.
- Locally-bound "allow" rules are checked.
- Deny by default.
7.1.1. Default cluster roles
OpenShift Dedicated includes a set of default cluster roles that you can bind to users and groups cluster-wide or locally.
It is not recommended to manually modify the default cluster roles. Modifications to these system roles can prevent a cluster from functioning properly.
| Default cluster role | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A project manager. If used in a local binding, an |
|
| A user that can get basic information about projects and users. |
|
| A super-user that can perform any action in any project. When bound to a user with a local binding, they have full control over quota and every action on every resource in the project. |
|
| A user that can get basic cluster status information. |
|
| A user that can get or view most of the objects but cannot modify them. |
|
| A user that can modify most objects in a project but does not have the power to view or modify roles or bindings. |
|
| A user that can create their own projects. |
|
| A user who cannot make any modifications, but can see most objects in a project. They cannot view or modify roles or bindings. |
Be mindful of the difference between local and cluster bindings. For example, if you bind the cluster-admin role to a user by using a local role binding, it might appear that this user has the privileges of a cluster administrator. This is not the case. Binding the cluster-admin to a user in a project grants super administrator privileges for only that project to the user. That user has the permissions of the cluster role admin, plus a few additional permissions like the ability to edit rate limits, for that project. This binding can be confusing via the web console UI, which does not list cluster role bindings that are bound to true cluster administrators. However, it does list local role bindings that you can use to locally bind cluster-admin.
The relationships between cluster roles, local roles, cluster role bindings, local role bindings, users, groups and service accounts are illustrated below.
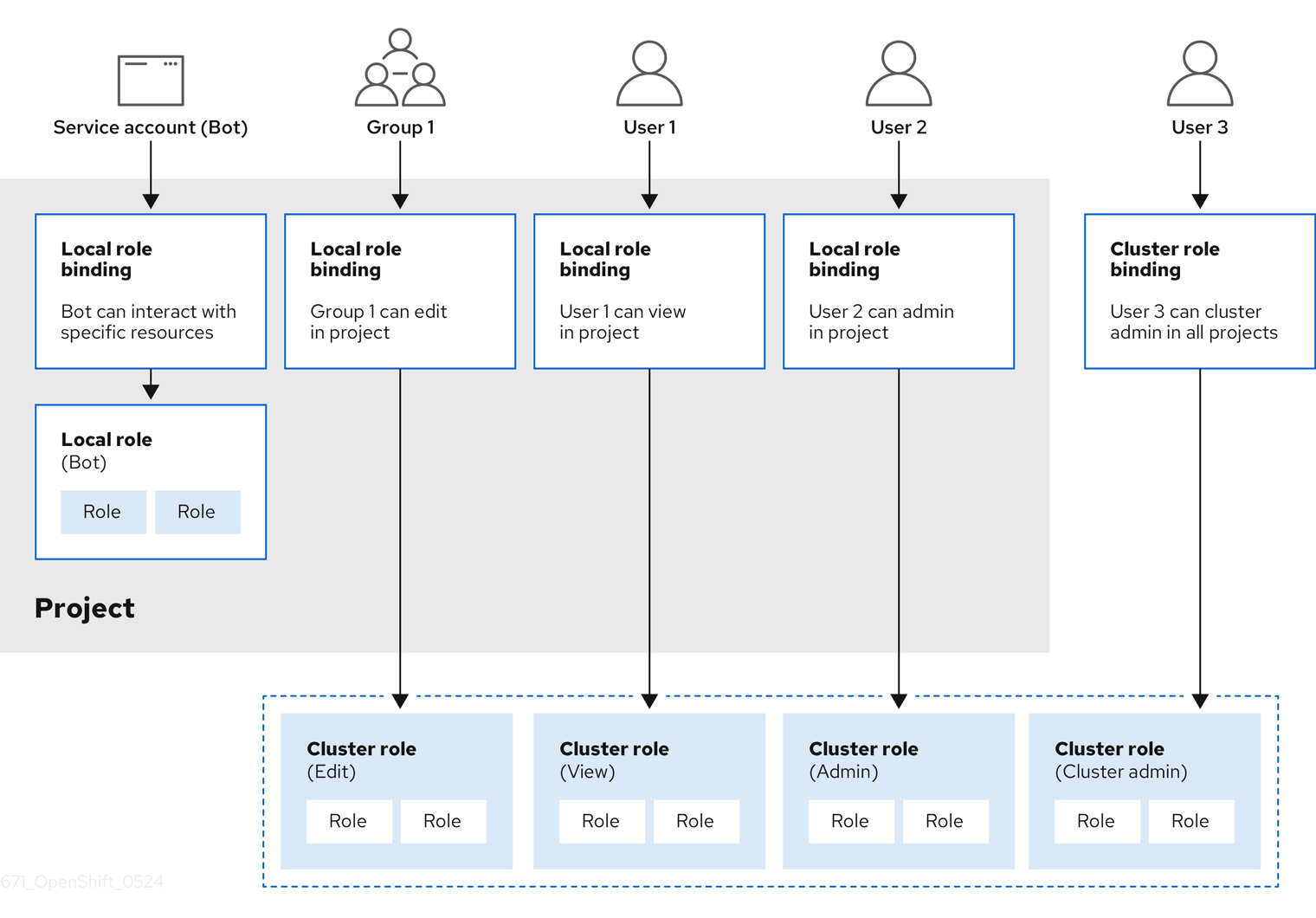
The get pods/exec, get pods/*, and get * rules grant execution privileges when they are applied to a role. Apply the principle of least privilege and assign only the minimal RBAC rights required for users and agents. For more information, see RBAC rules allow execution privileges.
7.1.2. Evaluating authorization
OpenShift Dedicated evaluates authorization by using:
- Identity
- The user name and list of groups that the user belongs to.
- Action
The action you perform. In most cases, this consists of:
- Project: The project you access. A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations that allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities.
-
Verb : The action itself:
get,list,create,update,delete,deletecollection, orwatch. - Resource name: The API endpoint that you access.
- Bindings
- The full list of bindings, the associations between users or groups with a role.
OpenShift Dedicated evaluates authorization by using the following steps:
- The identity and the project-scoped action is used to find all bindings that apply to the user or their groups.
- Bindings are used to locate all the roles that apply.
- Roles are used to find all the rules that apply.
- The action is checked against each rule to find a match.
- If no matching rule is found, the action is then denied by default.
Remember that users and groups can be associated with, or bound to, multiple roles at the same time.
Project administrators can use the CLI to view local roles and bindings, including a matrix of the verbs and resources each are associated with.
The cluster role bound to the project administrator is limited in a project through a local binding. It is not bound cluster-wide like the cluster roles granted to the cluster-admin or system:admin.
Cluster roles are roles defined at the cluster level but can be bound either at the cluster level or at the project level.
7.1.2.1. Cluster role aggregation
The default admin, edit, view, and cluster-reader cluster roles support cluster role aggregation, where the cluster rules for each role are dynamically updated as new rules are created. This feature is relevant only if you extend the Kubernetes API by creating custom resources.
7.2. Projects and namespaces
A Kubernetes namespace provides a mechanism to scope resources in a cluster. The Kubernetes documentation has more information on namespaces.
Namespaces provide a unique scope for:
- Named resources to avoid basic naming collisions.
- Delegated management authority to trusted users.
- The ability to limit community resource consumption.
Most objects in the system are scoped by namespace, but some are excepted and have no namespace, including nodes and users.
A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations and is the central vehicle by which access to resources for regular users is managed. A project allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities. Users must be given access to projects by administrators, or if allowed to create projects, automatically have access to their own projects.
Projects can have a separate name, displayName, and description.
-
The mandatory
nameis a unique identifier for the project and is most visible when using the CLI tools or API. The maximum name length is 63 characters. -
The optional
displayNameis how the project is displayed in the web console (defaults toname). -
The optional
descriptioncan be a more detailed description of the project and is also visible in the web console.
Each project scopes its own set of:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Pods, services, replication controllers, etc. |
|
| Rules for which users can or cannot perform actions on objects. |
|
| Quotas for each kind of object that can be limited. |
|
| Service accounts act automatically with designated access to objects in the project. |
Administrators with the dedicated-admin role can create projects and delegate administrative rights for the project to any member of the user community. Administrators with the dedicated-admin role can also allow developers to create their own projects.
Developers and administrators can interact with projects by using the CLI or the web console.
7.3. Default projects
OpenShift Dedicated comes with a number of default projects, and projects starting with openshift- are the most essential to users. These projects host master components that run as pods and other infrastructure components. The pods created in these namespaces that have a critical pod annotation are considered critical, and the have guaranteed admission by kubelet. Pods created for master components in these namespaces are already marked as critical.
Do not run workloads in or share access to default projects. Default projects are reserved for running core cluster components.
The following default projects are considered highly privileged: default, kube-public, kube-system, openshift, openshift-infra, openshift-node, and other system-created projects that have the openshift.io/run-level label set to 0 or 1. Functionality that relies on admission plugins, such as pod security admission, security context constraints, cluster resource quotas, and image reference resolution, does not work in highly privileged projects.
7.4. Viewing cluster roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view cluster roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. - Obtain permission to view the cluster roles and bindings.
Procedure
To view the cluster roles and their associated rule sets:
oc describe clusterrole.rbac
$ oc describe clusterrole.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the current set of cluster role bindings, which shows the users and groups that are bound to various roles:
oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.5. Viewing local roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view local roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. Obtain permission to view the local roles and bindings:
-
Users with the
admindefault cluster role bound locally can view and manage roles and bindings in that project.
-
Users with the
Procedure
To view the current set of local role bindings, which show the users and groups that are bound to various roles for the current project:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the local role bindings for a different project, add the
-nflag to the command:oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe-project
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe-projectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.6. Adding roles to users
You can use the oc adm administrator CLI to manage the roles and bindings.
Binding, or adding, a role to users or groups gives the user or group the access that is granted by the role. You can add and remove roles to and from users and groups using oc adm policy commands.
You can bind any of the default cluster roles to local users or groups in your project.
Procedure
Add a role to a user in a specific project:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, you can add the
adminrole to thealiceuser injoeproject by running:oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joe
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the role to the user:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the local role bindings and verify the addition in the output:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to view the local role bindings for the
joeproject:oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aliceuser has been added to theadminsRoleBinding.
7.7. Creating a local role
You can create a local role for a project and then bind it to a user.
Procedure
To create a local role for a project, run the following command:
oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>
$ oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role -
<resource>, the resources that the role applies to -
<project>, the project name
For example, to create a local role that allows a user to view pods in the
blueproject, run the following command:oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blue
$ oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To bind the new role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blue
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8. Local role binding commands
When you manage a user or group’s associated roles for local role bindings using the following operations, a project may be specified with the -n flag. If it is not specified, then the current project is used.
You can use the following commands for local RBAC management.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicates which users can perform an action on a resource. |
|
| Binds a specified role to specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified users and all of their roles in the current project. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified groups and all of their roles in the current project. |
7.9. Cluster role binding commands
You can also manage cluster role bindings using the following operations. The -n flag is not used for these operations because cluster role bindings use non-namespaced resources.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Binds a given role to specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
7.10. Granting administrator privileges to a user
After you have configured an identity provider for your cluster and added a user to the identity provider, you can grant dedicated-admin cluster privileges to the user.
Prerequisites
- You logged in to OpenShift Cluster Manager.
- You created an OpenShift Dedicated cluster.
- You configured an identity provider for your cluster.
Procedure
- Navigate to OpenShift Cluster Manager and select your cluster.
- Click the Access control tab.
- In the Cluster Roles and Access tab, click Add user.
- Enter the user ID of an identity provider user.
-
Click Add user to grant
dedicated-admincluster privileges to the user.
Verification
-
After granting the privileges, the user is listed as part of the
dedicated-adminsgroup under Access controlCluster Roles and Access on the OpenShift Cluster Manager page for your cluster.
7.11. Cluster role bindings for unauthenticated groups
Before OpenShift Dedicated 4.17, unauthenticated groups were allowed access to some cluster roles. Clusters updated from versions before OpenShift Dedicated 4.17 retain this access for unauthenticated groups.
For security reasons OpenShift Dedicated 4 does not allow unauthenticated groups to have default access to cluster roles.
There are use cases where it might be necessary to add system:unauthenticated to a cluster role.
Cluster administrators can add unauthenticated users to the following cluster roles:
-
system:scope-impersonation -
system:webhook -
system:oauth-token-deleter -
self-access-reviewer
Always verify compliance with your organization’s security standards when modifying unauthenticated access.