13.2. Java Persistence API (JPA)
13.2.1. About JPA
bean-validation, greeter, and kitchensink quickstarts: Section 1.4.1.1, “Access the Quickstarts”.
13.2.2. Hibernate EntityManager
13.2.3. Getting Started
13.2.3.1. Create a JPA project in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio
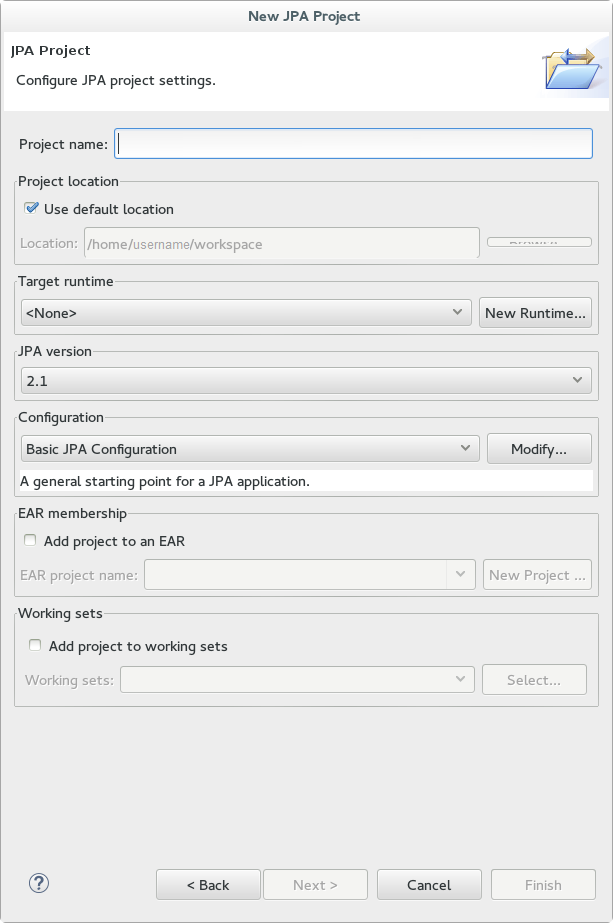
This example covers the steps required to create a JPA project in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio.
Procedure 13.1. Create a JPA project in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio
- In the Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio window, click
. Find JPA in the list, expand it, and select JPA Project. You are presented with the following dialog. - Enter a Project name.
- Select a Target runtime. If no target runtime is available, follow these instructions to define a new server and runtime: Section 1.3.1.5, “Add the JBoss EAP Server Using Define New Server”.
- Under JPA version, ensure 2.1 is selected.
- Under Configuration, choose Basic JPA Configuration.
- Click .
- If prompted, choose whether you wish to associate this type of project with the JPA perspective window.
13.2.3.2. Create the Persistence Settings File in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio
This topic covers the process for creating the persistence.xml file in a Java project using Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio.
Prerequisites
Procedure 13.2. Create and Configure a new Persistence Settings File
- Open an EJB 3.x project in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio.
- Right click the project root directory in the Project Explorer panel.
- Select
. - Select XML File from the XML folder and click .
- Select the
ejbModule/META-INFfolder as the parent directory. - Name the file
persistence.xmland click . - Select Create XML file from an XML schema file and click .
- Select http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2.0.xsd from the Select XML Catalog entry list and click .
- Click to create the file.
- Result:
- The
persistence.xmlhas been created in theMETA-INF/folder and is ready to be configured. An example file is available here: Section 13.2.3.3, “Example Persistence Settings File”
13.2.3.3. Example Persistence Settings File
Example 13.1. persistence.xml
13.2.3.4. Create the Hibernate Configuration File in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio
Prerequisites
This topic covers the process for creating the hibernate.cfg.xml file in a Java project using Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio.
Procedure 13.3. Create a New Hibernate Configuration File
- Open a Java project in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio.
- Right click the project root directory in the Project Explorer panel.
- Select
. - Select Hibernate Configuration File from the Hibernate folder and click .
- Select the
src/directory and click . - Configure the following:
- Session factory name
- Database dialect
- Driver class
- Connection URL
- Username
- Password
- Click to create the file.
- Result:
- The
hibernate.cfg.xmlhas been created in thesrc/folder. An example file is available here: Section 13.2.3.5, “Example Hibernate Configuration File”.
13.2.3.5. Example Hibernate Configuration File
Example 13.2. hibernate.cfg.xml
13.2.4. Configuration
13.2.4.1. Hibernate Configuration Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hibernate.dialect |
The classname of a Hibernate
org.hibernate.dialect.Dialect. Allows Hibernate to generate SQL optimized for a particular relational database.
In most cases Hibernate will be able to choose the correct
org.hibernate.dialect.Dialect implementation, based on the JDBC metadata returned by the JDBC driver.
|
| hibernate.show_sql |
Boolean. Writes all SQL statements to console. This is an alternative to setting the log category
org.hibernate.SQL to debug.
|
| hibernate.format_sql |
Boolean. Pretty print the SQL in the log and console.
|
| hibernate.default_schema |
Qualify unqualified table names with the given schema/tablespace in generated SQL.
|
| hibernate.default_catalog |
Qualifies unqualified table names with the given catalog in generated SQL.
|
| hibernate.session_factory_name |
The
org.hibernate.SessionFactory will be automatically bound to this name in JNDI after it has been created. For example, jndi/composite/name.
|
| hibernate.max_fetch_depth |
Sets a maximum "depth" for the outer join fetch tree for single-ended associations (one-to-one, many-to-one). A
0 disables default outer join fetching. The recommended value is between 0 and 3.
|
| hibernate.default_batch_fetch_size |
Sets a default size for Hibernate batch fetching of associations. The recommended values are
4, 8, and 16.
|
| hibernate.default_entity_mode |
Sets a default mode for entity representation for all sessions opened from this
SessionFactory. Values include: dynamic-map, dom4j, pojo.
|
| hibernate.order_updates |
Boolean. Forces Hibernate to order SQL updates by the primary key value of the items being updated. This will result in fewer transaction deadlocks in highly concurrent systems.
|
| hibernate.generate_statistics |
Boolean. If enabled, Hibernate will collect statistics useful for performance tuning.
|
| hibernate.use_identifier_rollback |
Boolean. If enabled, generated identifier properties will be reset to default values when objects are deleted.
|
| hibernate.use_sql_comments |
Boolean. If turned on, Hibernate will generate comments inside the SQL, for easier debugging. Default value is
false.
|
| hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings |
Boolean. This property is relevant when using
@GeneratedValue. It indicates whether or not the new IdentifierGenerator implementations are used for javax.persistence.GenerationType.AUTO, javax.persistence.GenerationType.TABLE and javax.persistence.GenerationType.SEQUENCE. Default value is true.
|
| hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy |
Chooses the
org.hibernate.cfg.NamingStrategy implementation when using Hibernate EntityManager. This class is deprecated and this property is only provided for backward compatibility. This property must not be used with hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy_delegator.
If the application does not use EntityManager, follow the instructions here to configure the NamingStrategy: Hibernate Reference Documentation - Implementing a Naming Strategy.
|
| hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy_delegator |
Specifies an
org.hibernate.cfg.naming.NamingStrategyDelegator implementation for database objects and schema elements when using Hibernate EntityManager. This property has the following possible values.
Note
This property must not be used with hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy. It is a temporary replacement for org.hibernate.cfg.NamingStrategy to address its limitations. A more comprehensive solution is planned for Hibernate 5.0 that replaces both org.hibernate.cfg.NamingStrategy and org.hibernate.cfg.naming.NamingStrategyDelegator.
If the application does not use EntityManager, follow the instructions here to configure the NamingStrategy: Hibernate Reference Documentation - Implementing a Naming Strategy.
|
Important
hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings, new applications should keep the default value of true. Existing applications that used Hibernate 3.3.x may need to change it to false to continue using a sequence object or table based generator, and maintain backward compatibility.
13.2.4.2. Hibernate JDBC and Connection Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hibernate.jdbc.fetch_size |
A non-zero value that determines the JDBC fetch size (calls
Statement.setFetchSize()).
|
| hibernate.jdbc.batch_size |
A non-zero value enables use of JDBC2 batch updates by Hibernate. The recommended values are between
5 and 30.
|
| hibernate.jdbc.batch_versioned_data |
Boolean. Set this property to
true if the JDBC driver returns correct row counts from executeBatch(). Hibernate will then use batched DML for automatically versioned data. Default value is to false.
|
| hibernate.jdbc.factory_class |
Select a custom
org.hibernate.jdbc.Batcher. Most applications will not need this configuration property.
|
| hibernate.jdbc.use_scrollable_resultset |
Boolean. Enables use of JDBC2 scrollable resultsets by Hibernate. This property is only necessary when using user-supplied JDBC connections. Hibernate uses connection metadata otherwise.
|
| hibernate.jdbc.use_streams_for_binary |
Boolean. This is a system-level property. Use streams when writing/reading
binary or serializable types to/from JDBC.
|
| hibernate.jdbc.use_get_generated_keys |
Boolean. Enables use of JDBC3
PreparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys() to retrieve natively generated keys after insert. Requires JDBC3+ driver and JRE1.4+. Set to false if JDBC driver has problems with the Hibernate identifier generators. By default, it tries to determine the driver capabilities using connection metadata.
|
| hibernate.connection.provider_class |
The classname of a custom
org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider which provides JDBC connections to Hibernate.
|
| hibernate.connection.isolation |
Sets the JDBC transaction isolation level. Check
java.sql.Connection for meaningful values, but note that most databases do not support all isolation levels and some define additional, non-standard isolations. Standard values are 1, 2, 4, 8.
|
| hibernate.connection.autocommit |
Boolean. This property is not recommended for use. Enables autocommit for JDBC pooled connections.
|
| hibernate.connection.release_mode |
Specifies when Hibernate should release JDBC connections. By default, a JDBC connection is held until the session is explicitly closed or disconnected. The default value
auto will choose after_statement for the JTA and CMT transaction strategies, and after_transaction for the JDBC transaction strategy.
Available values are
auto (default), on_close, after_transaction, after_statement.
This setting only affects
Session returned from SessionFactory.openSession. For Session obtained through SessionFactory.getCurrentSession, the CurrentSessionContext implementation configured for use controls the connection release mode for that Session.
|
| hibernate.connection.<propertyName> |
Pass the JDBC property <propertyName> to
DriverManager.getConnection().
|
| hibernate.jndi.<propertyName> |
Pass the property <propertyName> to the JNDI
InitialContextFactory.
|
13.2.4.3. Hibernate Cache Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
hibernate.cache.region.factory_class |
The classname of a custom
CacheProvider.
|
hibernate.cache.use_minimal_puts |
Boolean. Optimizes second-level cache operation to minimize writes, at the cost of more frequent reads. This setting is most useful for clustered caches and, in Hibernate3, is enabled by default for clustered cache implementations.
|
hibernate.cache.use_query_cache |
Boolean. Enables the query cache. Individual queries still have to be set cacheable.
|
hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache |
Boolean. Used to completely disable the second level cache, which is enabled by default for classes that specify a
<cache> mapping.
|
hibernate.cache.query_cache_factory |
The classname of a custom
QueryCache interface. The default value is the built-in StandardQueryCache.
|
hibernate.cache.region_prefix |
A prefix to use for second-level cache region names.
|
hibernate.cache.use_structured_entries |
Boolean. Forces Hibernate to store data in the second-level cache in a more human-friendly format.
|
hibernate.cache.default_cache_concurrency_strategy |
Setting used to give the name of the default
org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy to use when either @Cacheable or @Cache is used. @Cache(strategy="..") is used to override this default.
|
13.2.4.4. Hibernate Transaction Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
hibernate.transaction.factory_class |
The classname of a
TransactionFactory to use with Hibernate Transaction API. Defaults to JDBCTransactionFactory).
|
jta.UserTransaction |
A JNDI name used by
JTATransactionFactory to obtain the JTA UserTransaction from the application server.
|
hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class |
The classname of a
TransactionManagerLookup. It is required when JVM-level caching is enabled or when using hilo generator in a JTA environment.
|
hibernate.transaction.flush_before_completion |
Boolean. If enabled, the session will be automatically flushed during the before completion phase of the transaction. Built-in and automatic session context management is preferred.
|
hibernate.transaction.auto_close_session |
Boolean. If enabled, the session will be automatically closed during the after completion phase of the transaction. Built-in and automatic session context management is preferred.
|
13.2.4.5. Miscellaneous Hibernate Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
hibernate.current_session_context_class |
Supply a custom strategy for the scoping of the "current"
Session. Values include jta, thread, managed, custom.Class.
|
hibernate.query.factory_class |
Chooses the HQL parser implementation:
org.hibernate.hql.internal.ast.ASTQueryTranslatorFactory or org.hibernate.hql.internal.classic.ClassicQueryTranslatorFactory.
|
hibernate.query.substitutions |
Used to map from tokens in Hibernate queries to SQL tokens (tokens might be function or literal names). For example,
hqlLiteral=SQL_LITERAL, hqlFunction=SQLFUNC.
|
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto |
Automatically validates or exports schema DDL to the database when the
SessionFactory is created. With create-drop, the database schema will be dropped when the SessionFactory is closed explicitly. Property value options are validate, update, create, create-drop
|
hibernate.hbm2ddl.import_files |
Comma-separated names of the optional files containing SQL DML statements executed during the
SessionFactory creation. This is useful for testing or demonstrating. For example, by adding INSERT statements, the database can be populated with a minimal set of data when it is deployed. An example value is /humans.sql,/dogs.sql.
File order matters, as the statements of a given file are executed before the statements of the following files. These statements are only executed if the schema is created (i.e. if
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto is set to create or create-drop).
|
hibernate.hbm2ddl.import_files_sql_extractor |
The classname of a custom
ImportSqlCommandExtractor. Defaults to the built-in SingleLineSqlCommandExtractor. This is useful for implementing a dedicated parser that extracts a single SQL statement from each import file. Hibernate also provides MultipleLinesSqlCommandExtractor, which supports instructions/comments and quoted strings spread over multiple lines (mandatory semicolon at the end of each statement).
|
hibernate.bytecode.use_reflection_optimizer |
Boolean. This is a system-level property, which cannot be set in the
hibernate.cfg.xml file. Enables the use of bytecode manipulation instead of runtime reflection. Reflection can sometimes be useful when troubleshooting. Hibernate always requires either cglib or javassist even if the optimizer is turned off.
|
hibernate.bytecode.provider |
Both javassist or cglib can be used as byte manipulation engines. The default is
javassist. Property value is either javassist or cglib
|
13.2.4.6. Hibernate SQL Dialects
Important
hibernate.dialect property should be set to the correct org.hibernate.dialect.Dialect subclass for the application database. If a dialect is specified, Hibernate will use sensible defaults for some of the other properties. This means that they do not have to be specified manually.
| RDBMS | Dialect |
|---|---|
| DB2 | org.hibernate.dialect.DB2Dialect |
| DB2 AS/400 | org.hibernate.dialect.DB2400Dialect |
| DB2 OS390 | org.hibernate.dialect.DB2390Dialect |
| Firebird | org.hibernate.dialect.FirebirdDialect |
| FrontBase | org.hibernate.dialect.FrontbaseDialect |
| H2 Database | org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect |
| HypersonicSQL | org.hibernate.dialect.HSQLDialect |
| Informix | org.hibernate.dialect.InformixDialect |
| Ingres | org.hibernate.dialect.IngresDialect |
| Interbase | org.hibernate.dialect.InterbaseDialect |
| Mckoi SQL | org.hibernate.dialect.MckoiDialect |
| Microsoft SQL Server 2000 | org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect |
| Microsoft SQL Server 2005 | org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServer2005Dialect |
| Microsoft SQL Server 2008 | org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServer2008Dialect |
| Microsoft SQL Server 2012 | org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServer2008Dialect |
| MySQL5 | org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect |
| MySQL5 with InnoDB | org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect |
| MySQL with MyISAM | org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLMyISAMDialect |
| Oracle (any version) | org.hibernate.dialect.OracleDialect |
| Oracle 9i | org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle9iDialect |
| Oracle 10g | org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect |
| Oracle 11g | org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect |
| Pointbase | org.hibernate.dialect.PointbaseDialect |
| PostgreSQL | org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect |
| PostgreSQL 9.2 | org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL82Dialect |
| Postgres Plus Advanced Server | org.hibernate.dialect.PostgresPlusDialect |
| Progress | org.hibernate.dialect.ProgressDialect |
| SAP DB | org.hibernate.dialect.SAPDBDialect |
| Sybase | org.hibernate.dialect.SybaseASE15Dialect |
| Sybase 15.7 | org.hibernate.dialect.SybaseASE157Dialect |
| Sybase Anywhere | org.hibernate.dialect.SybaseAnywhereDialect |
13.2.5. Second-Level Caches
13.2.5.1. About Second-Level Caches
- Web Session Clustering
- Stateful Session Bean Clustering
- SSO Clustering
- Hibernate Second Level Cache
13.2.5.2. Configure a Second Level Cache for Hibernate
Procedure 13.4. Create and Edit the hibernate.cfg.xml file
Create the hibernate.cfg.xml file
Create thehibernate.cfg.xmlin the deployment's classpath. For specifics, refer to Section 13.2.3.4, “Create the Hibernate Configuration File in Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio” .- Add these lines of XML to the
hibernate.cfg.xmlfile in your application. The XML needs to be inside the <session-factory> tags:<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property> <property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property> <property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add one of the following to the <session-factory> section of the
hibernate.cfg.xmlfile:If the Infinispan CacheManager is bound to JNDI:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the Infinispan CacheManager is standalone:
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class"> org.hibernate.cache.infinispan.InfinispanRegionFactory </property><property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class"> org.hibernate.cache.infinispan.InfinispanRegionFactory </property>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Infinispan is configured as the Second Level Cache for Hibernate.