6.3. External Provider Networks
6.3.1. Importing Networks From External Providers
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To use networks from an external network provider (OpenStack Networking or any third-party provider that implements the OpenStack Neutron REST API), register the provider with the Manager. See Section 12.2.3, “Adding an OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Instance for Network Provisioning” or Section 12.2.6, “Adding an External Network Provider” for more information. Then, use the following procedure to import the networks provided by that provider into the Manager so the networks can be used by virtual machines.
Procedure 6.14. Importing a Network From an External Provider
- Click the Networks tab.
- Click the button to open the Import Networks window.
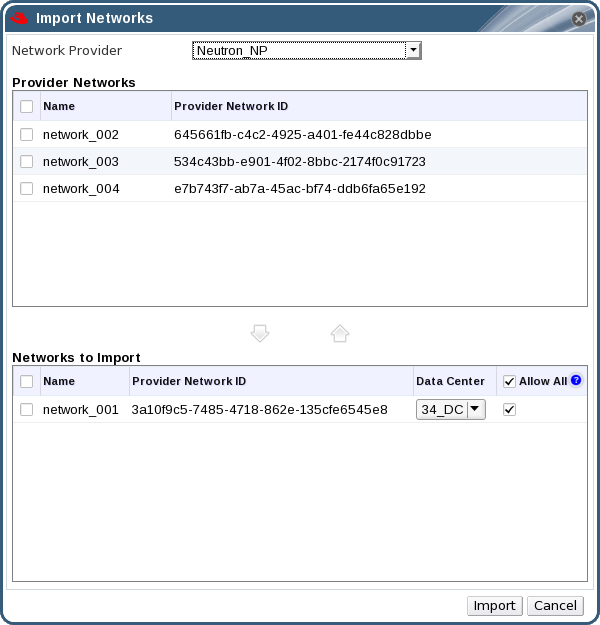
Figure 6.3. The Import Networks Window
- From the Network Provider drop-down list, select an external provider. The networks offered by that provider are automatically discovered and listed in the Provider Networks list.
- Using the check boxes, select the networks to import in the Provider Networks list and click the down arrow to move those networks into the Networks to Import list.
- It is possible to customize the name of the network that you are importing. To customize the name, click on the network's name in the Name column, and change the text.
- From the Data Center drop-down list, select the data center into which the networks will be imported.
- Optionally, clear the Allow All check box for a network in the Networks to Import list to prevent that network from being available to all users.
- Click the button.
The selected networks are imported into the target data center and can be attached to virtual machines. See Adding a New Network Interface in the Virtual Machine Management Guide for more information.
6.3.2. Limitations to Using External Provider Networks
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The following limitations apply to using logical networks imported from an external provider in a Red Hat Virtualization environment.
- Logical networks offered by external providers must be used as virtual machine networks, and cannot be used as display networks.
- The same logical network can be imported more than once, but only to different data centers.
- You cannot edit logical networks offered by external providers in the Manager. To edit the details of a logical network offered by an external provider, you must edit the logical network directly from the external provider that provides that logical network.
- Port mirroring is not available for virtual network interface cards connected to logical networks offered by external providers.
- If a virtual machine uses a logical network offered by an external provider, that provider cannot be deleted from the Manager while the logical network is still in use by the virtual machine.
- Networks offered by external providers are non-required. As such, scheduling for clusters in which such logical networks have been imported will not take those logical networks into account during host selection. Moreover, it is the responsibility of the user to ensure the availability of the logical network on hosts in clusters in which such logical networks have been imported.
6.3.3. Configuring Subnets on External Provider Logical Networks
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
6.3.3.1. Configuring Subnets on External Provider Logical Networks
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A logical network provided by an external provider can only assign IP addresses to virtual machines if one or more subnets have been defined on that logical network. If no subnets are defined, virtual machines will not be assigned IP addresses. If there is one subnet, virtual machines will be assigned an IP address from that subnet, and if there are multiple subnets, virtual machines will be assigned an IP address from any of the available subnets. The DHCP service provided by the external network provider on which the logical network is hosted is responsible for assigning these IP addresses.
While the Red Hat Virtualization Manager automatically discovers predefined subnets on imported logical networks, you can also add or remove subnets to or from logical networks from within the Manager.
6.3.3.2. Adding Subnets to External Provider Logical Networks
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Create a subnet on a logical network provided by an external provider.
Procedure 6.15. Adding Subnets to External Provider Logical Networks
- Click the Networks tab.
- Click the logical network provided by an external provider to which the subnet will be added.
- Click the Subnets tab in the details pane.
- Click the button to open the New External Subnet window.

Figure 6.4. The New External Subnet Window
- Enter a Name and CIDR for the new subnet.
- From the IP Version drop-down menu, select either IPv4 or IPv6.
- Click .
6.3.3.3. Removing Subnets from External Provider Logical Networks
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Remove a subnet from a logical network provided by an external provider.
Procedure 6.16. Removing Subnets from External Provider Logical Networks
- Click the Networks tab.
- Click the logical network provided by an external provider from which the subnet will be removed.
- Click the Subnets tab in the details pane.
- Click the subnet to remove.
- Click the button and click when prompted.