Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
Chapter 50. Producer Interface
Abstract
This chapter describes how to implement the
Producer interface, which is an essential step in the implementation of a Apache Camel component.
50.1. The Producer Interface
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Overview
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
An instance of
org.apache.camel.Producer type represents a target endpoint in a route. The role of the producer is to send requests (In messages) to a specific physical endpoint and to receive the corresponding response (Out or Fault message). A Producer object is essentially a special kind of Processor that appears at the end of a processor chain (equivalent to a route). Figure 50.1, “Producer Inheritance Hierarchy” shows the inheritance hierarchy for producers.
Figure 50.1. Producer Inheritance Hierarchy
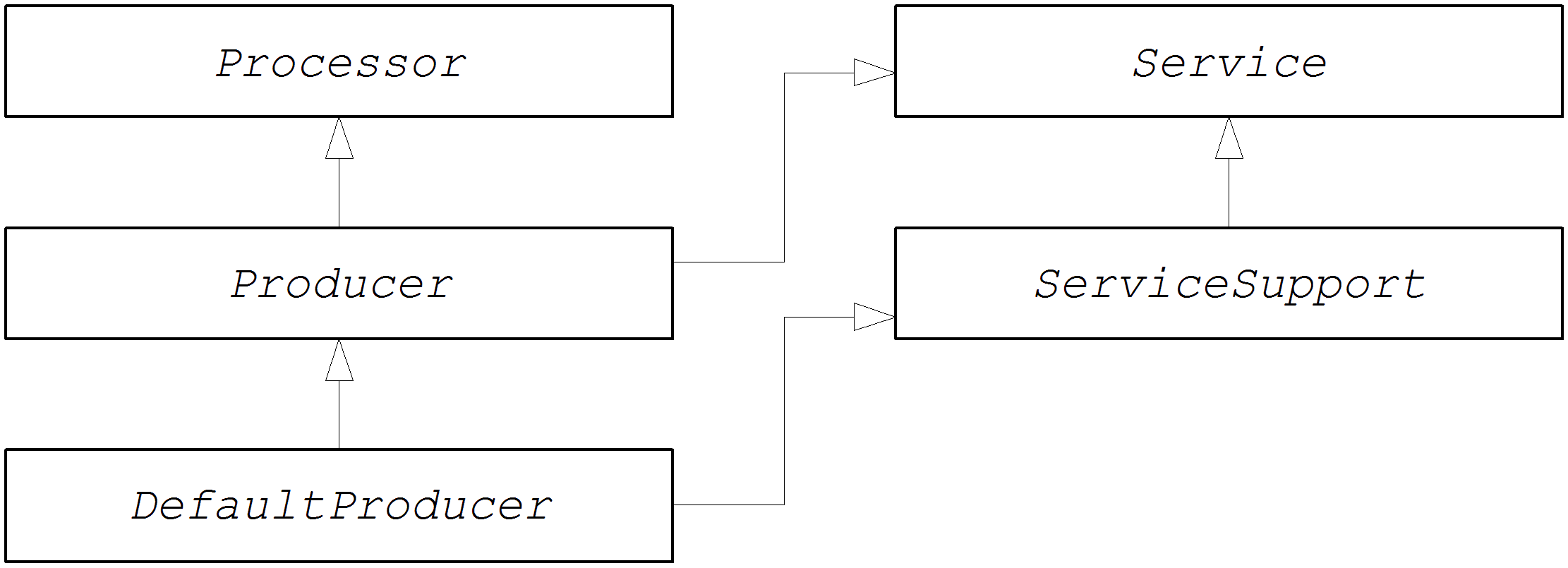
The Producer interface
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Example 50.1, “Producer Interface” shows the definition of the
org.apache.camel.Producer interface.
Example 50.1. Producer Interface
Producer methods
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
The
Producer interface defines the following methods:
process()(inherited from Processor)—The most important method. A producer is essentially a special type of processor that sends a request to an endpoint, instead of forwarding the exchange object to another processor. By overriding theprocess()method, you define how the producer sends and receives messages to and from the relevant endpoint.getEndpoint()—Returns a reference to the parent endpoint instance.createExchange()—These overloaded methods are analogous to the corresponding methods defined in theEndpointinterface. Normally, these methods delegate to the corresponding methods defined on the parentEndpointinstance (this is what theDefaultEndpointclass does by default). Occasionally, you might need to override these methods.
Asynchronous processing
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Processing an exchange object in a producer—which usually involves sending a message to a remote destination and waiting for a reply—can potentially block for a significant length of time. If you want to avoid blocking the current thread, you can opt to implement the producer as an asynchronous processor. The asynchronous processing pattern decouples the preceding processor from the producer, so that the
process() method returns without delay. See Section 46.1.4, “Asynchronous Processing”.
When implementing a producer, you can support the asynchronous processing model by implementing the
org.apache.camel.AsyncProcessor interface. On its own, this is not enough to ensure that the asynchronous processing model will be used: it is also necessary for the preceding processor in the chain to call the asynchronous version of the process() method. The definition of the AsyncProcessor interface is shown in Example 50.2, “AsyncProcessor Interface”.
Example 50.2. AsyncProcessor Interface
package org.apache.camel;
public interface AsyncProcessor extends Processor {
boolean process(Exchange exchange, AsyncCallback callback);
}
package org.apache.camel;
public interface AsyncProcessor extends Processor {
boolean process(Exchange exchange, AsyncCallback callback);
}
The asynchronous version of the
process() method takes an extra argument, callback, of org.apache.camel.AsyncCallback type. The corresponding AsyncCallback interface is defined as shown in Example 50.3, “AsyncCallback Interface”.
Example 50.3. AsyncCallback Interface
package org.apache.camel;
public interface AsyncCallback {
void done(boolean doneSynchronously);
}
package org.apache.camel;
public interface AsyncCallback {
void done(boolean doneSynchronously);
}
The caller of
AsyncProcessor.process() must provide an implementation of AsyncCallback to receive the notification that processing has finished. The AsyncCallback.done() method takes a boolean argument that indicates whether the processing was performed synchronously or not. Normally, the flag would be false, to indicate asynchronous processing. In some cases, however, it can make sense for the producer not to process asynchronously (in spite of being asked to do so). For example, if the producer knows that the processing of the exchange will complete rapidly, it could optimise the processing by doing it synchronously. In this case, the doneSynchronously flag should be set to true.
ExchangeHelper class
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
When implementing a producer, you might find it helpful to call some of the methods in the
org.apache.camel.util.ExchangeHelper utility class. For full details of the ExchangeHelper class, see Section 43.4, “The ExchangeHelper Class”.