This documentation is for a release that is no longer maintained
See documentation for the latest supported version 3 or the latest supported version 4.Post-installation configuration
Day 2 operations for OpenShift Container Platform
Abstract
Chapter 1. Postinstallation configuration overview
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, a cluster administrator can configure and customize the following components:
- Machine
- Bare metal
- Cluster
- Node
- Network
- Storage
- Users
- Alerts and notifications
1.1. Configuration tasks to perform after installation
Cluster administrators can perform the following postinstallation configuration tasks:
Configure operating system features: Machine Config Operator (MCO) manages
MachineConfigobjects. By using MCO, you can perform the following tasks on an OpenShift Container Platform cluster:-
Configure nodes by using
MachineConfigobjects - Configure MCO-related custom resources
-
Configure nodes by using
Configure bare metal nodes: The Bare Metal Operator (BMO) implements a Kubernetes API for managing bare metal hosts. It maintains an inventory of available bare metal hosts as instances of the BareMetalHost Custom Resource Definition (CRD). The Bare Metal Operator can:
- Inspect the host’s hardware details and report them on the corresponding BareMetalHost. This includes information about CPUs, RAM, disks, NICs, and more.
- Inspect the host’s firmware and configure BIOS settings.
- Provision hosts with a desired image.
- Clean a host’s disk contents before or after provisioning.
Configure cluster features: As a cluster administrator, you can modify the configuration resources of the major features of an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. These features include:
- Image registry
- Networking configuration
- Image build behavior
- Identity provider
- The etcd configuration
- Machine set creation to handle the workloads
- Cloud provider credential management
Configure cluster components to be private: By default, the installation program provisions OpenShift Container Platform by using a publicly accessible DNS and endpoints. If you want your cluster to be accessible only from within an internal network, configure the following components to be private:
- DNS
- Ingress Controller
- API server
Perform node operations: By default, OpenShift Container Platform uses Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute machines. As a cluster administrator, you can perform the following operations with the machines in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster:
- Add and remove compute machines
- Add and remove taints and tolerations to the nodes
- Configure the maximum number of pods per node
- Enable Device Manager
Configure network: After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can configure the following:
- Ingress cluster traffic
- Node port service range
- Network policy
- Enabling the cluster-wide proxy
Configure storage: By default, containers operate using ephemeral storage or transient local storage. The ephemeral storage has a lifetime limitation. TO store the data for a long time, you must configure persistent storage. You can configure storage by using one of the following methods:
- Dynamic provisioning: You can dynamically provision storage on demand by defining and creating storage classes that control different levels of storage, including storage access.
- Static provisioning: You can use Kubernetes persistent volumes to make existing storage available to a cluster. Static provisioning can support various device configurations and mount options.
- Configure users: OAuth access tokens allow users to authenticate themselves to the API. As a cluster administrator, you can configure OAuth to perform the following tasks:
- Specify an identity provider
- Use role-based access control to define and supply permissions to users
- Install an Operator from OperatorHub
- Manage alerts and notifications: By default, firing alerts are displayed on the Alerting UI of the web console. You can also configure OpenShift Container Platform to send alert notifications to external systems.
Chapter 2. Configuring a private cluster
After you install an OpenShift Container Platform version 4.11 cluster, you can set some of its core components to be private.
2.1. About private clusters
By default, OpenShift Container Platform is provisioned using publicly-accessible DNS and endpoints. You can set the DNS, Ingress Controller, and API server to private after you deploy your private cluster.
If the cluster has any public subnets, load balancer services created by administrators might be publicly accessible. To ensure cluster security, verify that these services are explicitly annotated as private.
DNS
If you install OpenShift Container Platform on installer-provisioned infrastructure, the installation program creates records in a pre-existing public zone and, where possible, creates a private zone for the cluster’s own DNS resolution. In both the public zone and the private zone, the installation program or cluster creates DNS entries for *.apps, for the Ingress object, and api, for the API server.
The *.apps records in the public and private zone are identical, so when you delete the public zone, the private zone seamlessly provides all DNS resolution for the cluster.
Ingress Controller
Because the default Ingress object is created as public, the load balancer is internet-facing and in the public subnets.
The Ingress Operator generates a default certificate for an Ingress Controller to serve as a placeholder until you configure a custom default certificate. Do not use Operator-generated default certificates in production clusters. The Ingress Operator does not rotate its own signing certificate or the default certificates that it generates. Operator-generated default certificates are intended as placeholders for custom default certificates that you configure.
API server
By default, the installation program creates appropriate network load balancers for the API server to use for both internal and external traffic.
On Amazon Web Services (AWS), separate public and private load balancers are created. The load balancers are identical except that an additional port is available on the internal one for use within the cluster. Although the installation program automatically creates or destroys the load balancer based on API server requirements, the cluster does not manage or maintain them. As long as you preserve the cluster’s access to the API server, you can manually modify or move the load balancers. For the public load balancer, port 6443 is open and the health check is configured for HTTPS against the /readyz path.
On Google Cloud Platform, a single load balancer is created to manage both internal and external API traffic, so you do not need to modify the load balancer.
On Microsoft Azure, both public and private load balancers are created. However, because of limitations in current implementation, you just retain both load balancers in a private cluster.
2.2. Setting DNS to private
After you deploy a cluster, you can modify its DNS to use only a private zone.
Procedure
Review the
DNScustom resource for your cluster:oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the
specsection contains both a private and a public zone.Patch the
DNScustom resource to remove the public zone:oc patch dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge --patch='{"spec": {"publicZone": null}}' dns.config.openshift.io/cluster patched$ oc patch dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge --patch='{"spec": {"publicZone": null}}' dns.config.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Because the Ingress Controller consults the
DNSdefinition when it createsIngressobjects, when you create or modifyIngressobjects, only private records are created.ImportantDNS records for the existing Ingress objects are not modified when you remove the public zone.
Optional: Review the
DNScustom resource for your cluster and confirm that the public zone was removed:oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.3. Setting the Ingress Controller to private
After you deploy a cluster, you can modify its Ingress Controller to use only a private zone.
Procedure
Modify the default Ingress Controller to use only an internal endpoint:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io "default" deleted ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io/default replaced
ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io "default" deleted ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io/default replacedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The public DNS entry is removed, and the private zone entry is updated.
2.4. Restricting the API server to private
After you deploy a cluster to Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, you can reconfigure the API server to use only the private zone.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Have access to the web console as a user with
adminprivileges.
Procedure
In the web portal or console for AWS or Azure, take the following actions:
Locate and delete appropriate load balancer component.
- For AWS, delete the external load balancer. The API DNS entry in the private zone already points to the internal load balancer, which uses an identical configuration, so you do not need to modify the internal load balancer.
-
For Azure, delete the
api-internalrule for the load balancer.
-
Delete the
api.$clustername.$yourdomainDNS entry in the public zone.
Remove the external load balancers:
ImportantYou can run the following steps only for an installer-provisioned infrastructure (IPI) cluster. For a user-provisioned infrastructure (UPI) cluster, you must manually remove or disable the external load balancers.
From your terminal, list the cluster machines:
oc get machine -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machine -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You modify the control plane machines, which contain
masterin the name, in the following step.Remove the external load balancer from each control plane machine.
Edit a control plane
Machineobject to remove the reference to the external load balancer:oc edit machines -n openshift-machine-api <master_name>
$ oc edit machines -n openshift-machine-api <master_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the name of the control plane, or master,
Machineobject to modify.
Remove the lines that describe the external load balancer, which are marked in the following example, and save and exit the object specification:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Repeat this process for each of the machines that contains
masterin the name.
2.4.1. Configuring the Ingress Controller endpoint publishing scope to Internal
When a cluster administrator installs a new cluster without specifying that the cluster is private, the default Ingress Controller is created with a scope set to External. Cluster administrators can change an External scoped Ingress Controller to Internal.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
To change an
Externalscoped Ingress Controller toInternal, enter the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/default --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"scope":"Internal"}}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/default --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"scope":"Internal"}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check the status of the Ingress Controller, enter the following command:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers/default -o yaml
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers/default -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
Progressingstatus condition indicates whether you must take further action. For example, the status condition can indicate that you need to delete the service by entering the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress delete services/router-default
$ oc -n openshift-ingress delete services/router-defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you delete the service, the Ingress Operator recreates it as
Internal.
Chapter 3. Bare metal configuration
When deploying OpenShift Container Platform on bare metal hosts, there are times when you need to make changes to the host either before or after provisioning. This can include inspecting the host’s hardware, firmware, and firmware details. It can also include formatting disks or changing modifiable firmware settings.
3.1. About the Bare Metal Operator
Use the Bare Metal Operator (BMO) to provision, manage, and inspect bare-metal hosts in your cluster.
The BMO uses three resources to complete these tasks:
-
BareMetalHost -
HostFirmwareSettings -
FirmwareSchema
The BMO maintains an inventory of the physical hosts in the cluster by mapping each bare-metal host to an instance of the BareMetalHost custom resource definition. Each BareMetalHost resource features hardware, software, and firmware details. The BMO continually inspects the bare-metal hosts in the cluster to ensure each BareMetalHost resource accurately details the components of the corresponding host.
The BMO also uses the HostFirmwareSettings resource and the FirmwareSchema resource to detail firmware specifications for the bare-metal host.
The BMO interfaces with bare-metal hosts in the cluster by using the Ironic API service. The Ironic service uses the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) on the host to interface with the machine.
Some common tasks you can complete by using the BMO include the following:
- Provision bare-metal hosts to the cluster with a specific image
- Format a host’s disk contents before provisioning or after deprovisioning
- Turn on or off a host
- Change firmware settings
- View the host’s hardware details
3.1.1. Bare Metal Operator architecture
The Bare Metal Operator (BMO) uses three resources to provision, manage, and inspect bare-metal hosts in your cluster. The following diagram illustrates the architecture of these resources:
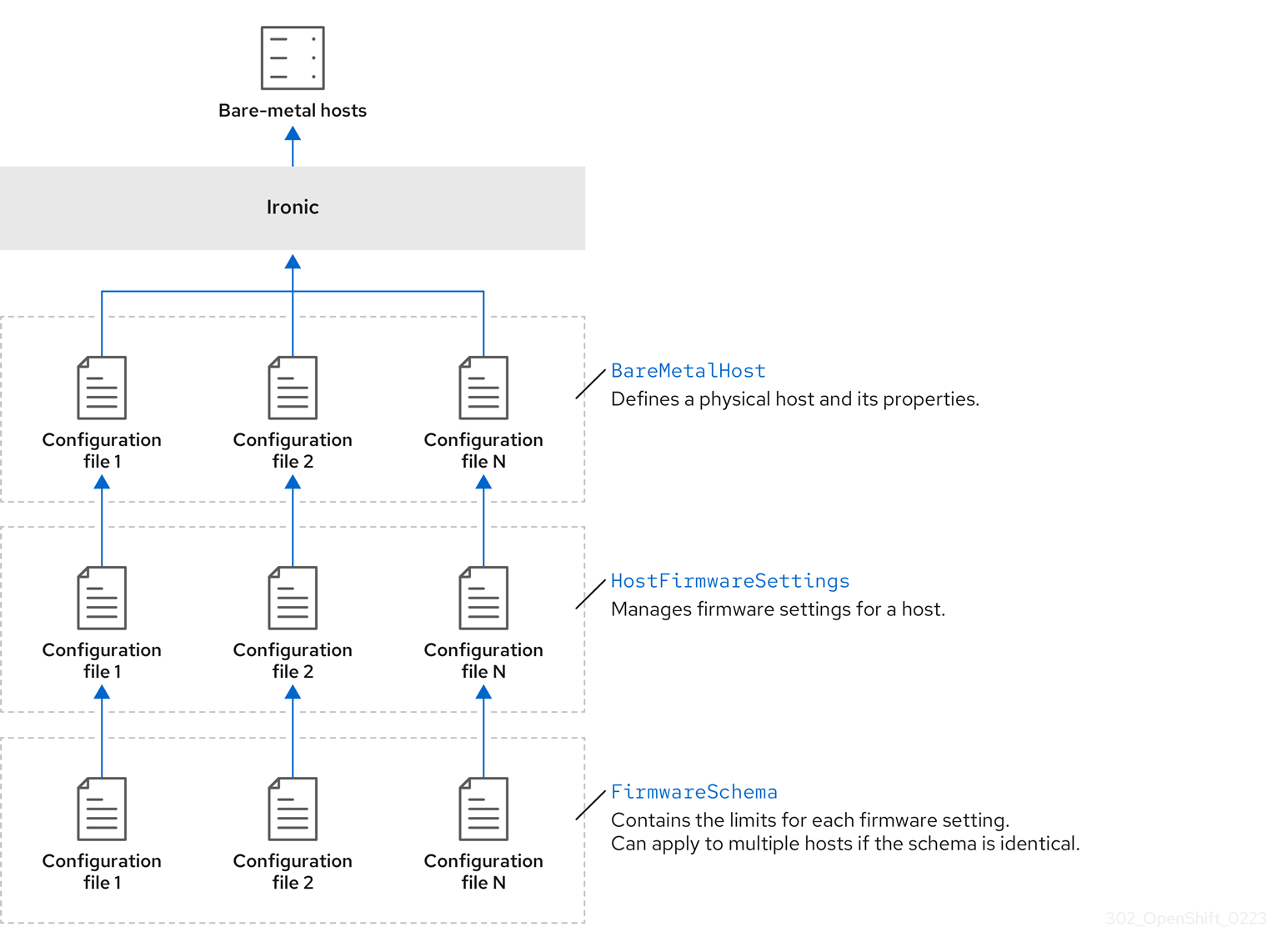
BareMetalHost
The BareMetalHost resource defines a physical host and its properties. When you provision a bare-metal host to the cluster, you must define a BareMetalHost resource for that host. For ongoing management of the host, you can inspect the information in the BareMetalHost or update this information.
The BareMetalHost resource features provisioning information such as the following:
- Deployment specifications such as the operating system boot image or the custom RAM disk
- Provisioning state
- Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) address
- Desired power state
The BareMetalHost resource features hardware information such as the following:
- Number of CPUs
- MAC address of a NIC
- Size of the host’s storage device
- Current power state
HostFirmwareSettings
You can use the HostFirmwareSettings resource to retrieve and manage the firmware settings for a host. When a host moves to the Available state, the Ironic service reads the host’s firmware settings and creates the HostFirmwareSettings resource. There is a one-to-one mapping between the BareMetalHost resource and the HostFirmwareSettings resource.
You can use the HostFirmwareSettings resource to inspect the firmware specifications for a host or to update a host’s firmware specifications.
You must adhere to the schema specific to the vendor firmware when you edit the spec field of the HostFirmwareSettings resource. This schema is defined in the read-only FirmwareSchema resource.
FirmwareSchema
Firmware settings vary among hardware vendors and host models. A FirmwareSchema resource is a read-only resource that contains the types and limits for each firmware setting on each host model. The data comes directly from the BMC by using the Ironic service. The FirmwareSchema resource enables you to identify valid values you can specify in the spec field of the HostFirmwareSettings resource.
A FirmwareSchema resource can apply to many BareMetalHost resources if the schema is the same.
3.2. About the BareMetalHost resource
Metal3 introduces the concept of the BareMetalHost resource, which defines a physical host and its properties. The BareMetalHost resource contains two sections:
-
The
BareMetalHostspec -
The
BareMetalHoststatus
3.2.1. The BareMetalHost spec
The spec section of the BareMetalHost resource defines the desired state of the host.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
An interface to enable or disable automated cleaning during provisioning and de-provisioning. When set to |
bmc: address: credentialsName: disableCertificateVerification: |
The
|
|
| The MAC address of the NIC used for provisioning the host. |
|
|
The boot mode of the host. It defaults to |
|
|
A reference to another resource that is using the host. It could be empty if another resource is not currently using the host. For example, a |
|
| A human-provided string to help identify the host. |
|
| A boolean indicating whether the host provisioning and deprovisioning are managed externally. When set:
|
|
|
Contains information about the BIOS configuration of bare metal hosts. Currently,
|
image: url: checksum: checksumType: format: |
The
|
|
| A reference to the secret containing the network configuration data and its namespace, so that it can be attached to the host before the host boots to set up the network. |
|
|
A boolean indicating whether the host should be powered on ( |
raid: hardwareRAIDVolumes: softwareRAIDVolumes: | (Optional) Contains the information about the RAID configuration for bare metal hosts. If not specified, it retains the current configuration. Note OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 supports hardware RAID for BMCs using the iRMC protocol only. OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 does not support software RAID. See the following configuration settings:
You can set the spec:
raid:
hardwareRAIDVolume: []
If you receive an error message indicating that the driver does not support RAID, set the |
|
|
The
|
3.2.2. The BareMetalHost status
The BareMetalHost status represents the host’s current state, and includes tested credentials, current hardware details, and other information.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
| A reference to the secret and its namespace holding the last set of baseboard management controller (BMC) credentials the system was able to validate as working. |
|
| Details of the last error reported by the provisioning backend, if any. |
|
| Indicates the class of problem that has caused the host to enter an error state. The error types are:
|
|
|
The
|
hardware: firmware: | Contains BIOS firmware information. For example, the hardware vendor and version. |
|
|
The
|
hardware: ramMebibytes: | The host’s amount of memory in Mebibytes (MiB). |
|
|
The
|
hardware:
systemVendor:
manufacturer:
productName:
serialNumber:
|
Contains information about the host’s |
|
| The timestamp of the last time the status of the host was updated. |
|
| The status of the server. The status is one of the following:
|
|
| Boolean indicating whether the host is powered on. |
|
|
The
|
|
| A reference to the secret and its namespace holding the last set of BMC credentials that were sent to the provisioning backend. |
3.3. Getting the BareMetalHost resource
The BareMetalHost resource contains the properties of a physical host. You must get the BareMetalHost resource for a physical host to review its properties.
Procedure
Get the list of
BareMetalHostresources:oc get bmh -n openshift-machine-api -o yaml
$ oc get bmh -n openshift-machine-api -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can use
baremetalhostas the long form ofbmhwithoc getcommand.Get the list of hosts:
oc get bmh -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get bmh -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the
BareMetalHostresource for a specific host:oc get bmh <host_name> -n openshift-machine-api -o yaml
$ oc get bmh <host_name> -n openshift-machine-api -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<host_name>is the name of the host.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.4. About the HostFirmwareSettings resource
You can use the HostFirmwareSettings resource to retrieve and manage the BIOS settings for a host. When a host moves to the Available state, Ironic reads the host’s BIOS settings and creates the HostFirmwareSettings resource. The resource contains the complete BIOS configuration returned from the baseboard management controller (BMC). Whereas, the firmware field in the BareMetalHost resource returns three vendor-independent fields, the HostFirmwareSettings resource typically comprises many BIOS settings of vendor-specific fields per host.
The HostFirmwareSettings resource contains two sections:
-
The
HostFirmwareSettingsspec. -
The
HostFirmwareSettingsstatus.
3.4.1. The HostFirmwareSettings spec
The spec section of the HostFirmwareSettings resource defines the desired state of the host’s BIOS, and it is empty by default. Ironic uses the settings in the spec.settings section to update the baseboard management controller (BMC) when the host is in the Preparing state. Use the FirmwareSchema resource to ensure that you do not send invalid name/value pairs to hosts. See "About the FirmwareSchema resource" for additional details.
Example
spec:
settings:
ProcTurboMode: Disabled
spec:
settings:
ProcTurboMode: Disabled- 1
- In the foregoing example, the
spec.settingssection contains a name/value pair that will set theProcTurboModeBIOS setting toDisabled.
Integer parameters listed in the status section appear as strings. For example, "1". When setting integers in the spec.settings section, the values should be set as integers without quotes. For example, 1.
3.4.2. The HostFirmwareSettings status
The status represents the current state of the host’s BIOS.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The
|
status:
schema:
name:
namespace:
lastUpdated:
|
The
|
status: settings: |
The |
3.5. Getting the HostFirmwareSettings resource
The HostFirmwareSettings resource contains the vendor-specific BIOS properties of a physical host. You must get the HostFirmwareSettings resource for a physical host to review its BIOS properties.
Procedure
Get the detailed list of
HostFirmwareSettingsresources:oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-api -o yaml
$ oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-api -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can use
hostfirmwaresettingsas the long form ofhfswith theoc getcommand.Get the list of
HostFirmwareSettingsresources:oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the
HostFirmwareSettingsresource for a particular hostoc get hfs <host_name> -n openshift-machine-api -o yaml
$ oc get hfs <host_name> -n openshift-machine-api -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<host_name>is the name of the host.
3.6. Editing the HostFirmwareSettings resource
You can edit the HostFirmwareSettings of provisioned hosts.
You can only edit hosts when they are in the provisioned state, excluding read-only values. You cannot edit hosts in the externally provisioned state.
Procedure
Get the list of
HostFirmwareSettingsresources:oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit a host’s
HostFirmwareSettingsresource:oc edit hfs <host_name> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc edit hfs <host_name> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<host_name>is the name of a provisioned host. TheHostFirmwareSettingsresource will open in the default editor for your terminal.Add name/value pairs to the
spec.settingssection:Example
spec: settings: name: valuespec: settings: name: value1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Use the
FirmwareSchemaresource to identify the available settings for the host. You cannot set values that are read-only.
- Save the changes and exit the editor.
Get the host’s machine name:
oc get bmh <host_name> -n openshift-machine name
$ oc get bmh <host_name> -n openshift-machine nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<host_name>is the name of the host. The machine name appears under theCONSUMERfield.Annotate the machine to delete it from the machineset:
oc annotate machine <machine_name> machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine=yes -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc annotate machine <machine_name> machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine=yes -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<machine_name>is the name of the machine to delete.Get a list of nodes and count the number of worker nodes:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the machineset:
oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Scale the machineset:
oc scale machineset <machineset_name> -n openshift-machine-api --replicas=<n-1>
$ oc scale machineset <machineset_name> -n openshift-machine-api --replicas=<n-1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<machineset_name>is the name of the machineset and<n-1>is the decremented number of worker nodes.When the host enters the
Availablestate, scale up the machineset to make theHostFirmwareSettingsresource changes take effect:oc scale machineset <machineset_name> -n openshift-machine-api --replicas=<n>
$ oc scale machineset <machineset_name> -n openshift-machine-api --replicas=<n>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<machineset_name>is the name of the machineset and<n>is the number of worker nodes.
3.7. Verifying the HostFirmware Settings resource is valid
When the user edits the spec.settings section to make a change to the HostFirmwareSetting(HFS) resource, the Bare Metal Operator (BMO) validates the change against the FimwareSchema resource, which is a read-only resource. If the setting is invalid, the BMO will set the Type value of the status.Condition setting to False and also generate an event and store it in the HFS resource. Use the following procedure to verify that the resource is valid.
Procedure
Get a list of
HostFirmwareSettingresources:oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get hfs -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
HostFirmwareSettingsresource for a particular host is valid:oc describe hfs <host_name> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc describe hfs <host_name> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<host_name>is the name of the host.Example output
Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal ValidationFailed 2m49s metal3-hostfirmwaresettings-controller Invalid BIOS setting: Setting ProcTurboMode is invalid, unknown enumeration value - Foo
Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal ValidationFailed 2m49s metal3-hostfirmwaresettings-controller Invalid BIOS setting: Setting ProcTurboMode is invalid, unknown enumeration value - FooCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantIf the response returns
ValidationFailed, there is an error in the resource configuration and you must update the values to conform to theFirmwareSchemaresource.
3.8. About the FirmwareSchema resource
BIOS settings vary among hardware vendors and host models. A FirmwareSchema resource is a read-only resource that contains the types and limits for each BIOS setting on each host model. The data comes directly from the BMC through Ironic. The FirmwareSchema enables you to identify valid values you can specify in the spec field of the HostFirmwareSettings resource. The FirmwareSchema resource has a unique identifier derived from its settings and limits. Identical host models use the same FirmwareSchema identifier. It is likely that multiple instances of HostFirmwareSettings use the same FirmwareSchema.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The
|
3.9. Getting the FirmwareSchema resource
Each host model from each vendor has different BIOS settings. When editing the HostFirmwareSettings resource’s spec section, the name/value pairs you set must conform to that host’s firmware schema. To ensure you are setting valid name/value pairs, get the FirmwareSchema for the host and review it.
Procedure
To get a list of
FirmwareSchemaresource instances, execute the following:oc get firmwareschema -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get firmwareschema -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To get a particular
FirmwareSchemainstance, execute:oc get firmwareschema <instance_name> -n openshift-machine-api -o yaml
$ oc get firmwareschema <instance_name> -n openshift-machine-api -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
<instance_name>is the name of the schema instance stated in theHostFirmwareSettingsresource (see Table 3).
Chapter 4. Configuring multi-architecture compute machines on an OpenShift Container Platform cluster
An OpenShift Container Platform cluster with multi-architecture compute machines is a cluster that supports compute machines with different architectures. You can deploy a cluster with multi-architecture compute machines by creating an Azure installer-provisioned cluster using the multi-architecture installer binary. For Azure installation, see Installing a cluster on Azure with customizations.
The multi-architecture compute machines Technology Preview feature has limited usability with installing, upgrading, and running payloads.
The following procedures explain how to generate an ARM64 boot image and create an Azure compute machine set with the ARM64 boot image. This adds ARM64 compute nodes to your cluster and deploys the desired amount of ARM64 virtual machines (VM). This section also shows how to upgrade your existing cluster to a cluster that supports multi-architecture compute machines. Clusters with multi-architecture compute machines are only available on Azure installer-provisioned infrastructures with x86_64 control plane machines.
OpenShift Container Platform clusters with multi-architecture compute machines on Azure installer-provisioned infrastructure installations is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
4.1. Creating an ARM64 boot image using the Azure image gallery
To configure your cluster with multi-architecture compute machines, you must create an ARM64 boot image and add it to your Azure compute machine set. The following procedure describes how to manually generate an ARM64 boot image.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the Azure CLI (
az). - You created a single-architecture Azure installer-provisioned cluster with the multi-architecture installer binary.
Procedure
Log in to your Azure account:
az login
$ az loginCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a storage account and upload the ARM64 virtual hard disk (VHD) to your storage account. The OpenShift Container Platform installation program creates a resource group, however, the boot image can also be uploaded to a custom named resource group:
az storage account create -n ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} -g ${RESOURCE_GROUP} -l westus --sku Standard_LRS$ az storage account create -n ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} -g ${RESOURCE_GROUP} -l westus --sku Standard_LRS1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
westusobject is an example region.
Create a storage container using the storage account you generated:
az storage container create -n ${CONTAINER_NAME} --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME}$ az storage container create -n ${CONTAINER_NAME} --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You must use the OpenShift Container Platform installation program JSON file to extract the URL and
aarch64VHD name:Extract the
URLfield and set it toRHCOS_VHD_ORIGIN_URLas the file name by running the following command:RHCOS_VHD_ORIGIN_URL=$(oc -n openshift-machine-config-operator get configmap/coreos-bootimages -o jsonpath='{.data.stream}' | jq -r '.architectures.aarch64."rhel-coreos-extensions"."azure-disk".url')$ RHCOS_VHD_ORIGIN_URL=$(oc -n openshift-machine-config-operator get configmap/coreos-bootimages -o jsonpath='{.data.stream}' | jq -r '.architectures.aarch64."rhel-coreos-extensions"."azure-disk".url')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Extract the
aarch64VHD name and set it toBLOB_NAMEas the file name by running the following command:BLOB_NAME=rhcos-$(oc -n openshift-machine-config-operator get configmap/coreos-bootimages -o jsonpath='{.data.stream}' | jq -r '.architectures.aarch64."rhel-coreos-extensions"."azure-disk".release')-azure.aarch64.vhd$ BLOB_NAME=rhcos-$(oc -n openshift-machine-config-operator get configmap/coreos-bootimages -o jsonpath='{.data.stream}' | jq -r '.architectures.aarch64."rhel-coreos-extensions"."azure-disk".release')-azure.aarch64.vhdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Generate a shared access signature (SAS) token. Use this token to upload the RHCOS VHD to your storage container with the following commands:
end=`date -u -d "30 minutes" '+%Y-%m-%dT%H:%MZ'`
$ end=`date -u -d "30 minutes" '+%Y-%m-%dT%H:%MZ'`Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow sas=`az storage container generate-sas -n ${CONTAINER_NAME} --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} --https-only --permissions dlrw --expiry $end -o tsv`$ sas=`az storage container generate-sas -n ${CONTAINER_NAME} --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} --https-only --permissions dlrw --expiry $end -o tsv`Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the RHCOS VHD into the storage container:
az storage blob copy start --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} --sas-token "$sas" \ --source-uri "${RHCOS_VHD_ORIGIN_URL}" \ --destination-blob "${BLOB_NAME}" --destination-container ${CONTAINER_NAME}$ az storage blob copy start --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} --sas-token "$sas" \ --source-uri "${RHCOS_VHD_ORIGIN_URL}" \ --destination-blob "${BLOB_NAME}" --destination-container ${CONTAINER_NAME}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can check the status of the copying process with the following command:
az storage blob show -c ${CONTAINER_NAME} -n ${BLOB_NAME} --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} | jq .properties.copy$ az storage blob show -c ${CONTAINER_NAME} -n ${BLOB_NAME} --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} | jq .properties.copyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If the status parameter displays the
successobject, the copying process is complete.
Create an image gallery using the following command:
az sig create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --gallery-name ${GALLERY_NAME}$ az sig create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --gallery-name ${GALLERY_NAME}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the image gallery to create an image definition. In the following example command,
rhcos-arm64is the name of the image definition.az sig image-definition create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --gallery-name ${GALLERY_NAME} --gallery-image-definition rhcos-arm64 --publisher RedHat --offer arm --sku arm64 --os-type linux --architecture Arm64 --hyper-v-generation V2$ az sig image-definition create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --gallery-name ${GALLERY_NAME} --gallery-image-definition rhcos-arm64 --publisher RedHat --offer arm --sku arm64 --os-type linux --architecture Arm64 --hyper-v-generation V2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To get the URL of the VHD and set it to
RHCOS_VHD_URLas the file name, run the following command:RHCOS_VHD_URL=$(az storage blob url --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} -c ${CONTAINER_NAME} -n "${BLOB_NAME}" -o tsv)$ RHCOS_VHD_URL=$(az storage blob url --account-name ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} -c ${CONTAINER_NAME} -n "${BLOB_NAME}" -o tsv)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
RHCOS_VHD_URLfile, your storage account, resource group, and image gallery to create an image version. In the following example,1.0.0is the image version.az sig image-version create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --gallery-name ${GALLERY_NAME} --gallery-image-definition rhcos-arm64 --gallery-image-version 1.0.0 --os-vhd-storage-account ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} --os-vhd-uri ${RHCOS_VHD_URL}$ az sig image-version create --resource-group ${RESOURCE_GROUP} --gallery-name ${GALLERY_NAME} --gallery-image-definition rhcos-arm64 --gallery-image-version 1.0.0 --os-vhd-storage-account ${STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME} --os-vhd-uri ${RHCOS_VHD_URL}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your ARM64 boot image is now generated. You can access the ID of your image with the following command:
az sig image-version show -r $GALLERY_NAME -g $RESOURCE_GROUP -i rhcos-arm64 -e 1.0.0
$ az sig image-version show -r $GALLERY_NAME -g $RESOURCE_GROUP -i rhcos-arm64 -e 1.0.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example image ID is used in the
recourseIDparameter of the machine set:Example
resourceID/resourceGroups/${RESOURCE_GROUP}/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/${GALLERY_NAME}/images/rhcos-arm64/versions/1.0.0/resourceGroups/${RESOURCE_GROUP}/providers/Microsoft.Compute/galleries/${GALLERY_NAME}/images/rhcos-arm64/versions/1.0.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.2. Adding a multi-architecture compute machine set to your cluster using the ARM64 boot image
To add ARM64 compute nodes to your cluster, you must create an Azure compute machine set that uses the ARM64 boot image. To create your own custom compute machine set on Azure, see "Creating a compute machine set on Azure".
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a machine set and modify the
resourceIDandvmSizeparameters with the following command. This machine set will control the ARM64 worker nodes in your cluster:oc create -f arm64-machine-set-0.yaml
$ oc create -f arm64-machine-set-0.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample YAML machine set with ARM64 boot image
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the new ARM64 machines are running by entering the following command:
oc get machineset -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machineset -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE <infrastructure_id>-arm64-machine-set-0 2 2 2 2 10m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE <infrastructure_id>-arm64-machine-set-0 2 2 2 2 10mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can check that the nodes are ready and scheduable with the following command:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.3. Upgrading a cluster with multi-architecture compute machines
You must perform an explicit upgrade command to upgrade your existing cluster to a cluster that supports multi-architecture compute machines.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
To manually upgrade your cluster, use the following command:
oc adm upgrade --allow-explicit-upgrade --to-image <image-pullspec>
$ oc adm upgrade --allow-explicit-upgrade --to-image <image-pullspec>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 5. Postinstallation machine configuration tasks
There are times when you need to make changes to the operating systems running on OpenShift Container Platform nodes. This can include changing settings for network time service, adding kernel arguments, or configuring journaling in a specific way.
Aside from a few specialized features, most changes to operating systems on OpenShift Container Platform nodes can be done by creating what are referred to as MachineConfig objects that are managed by the Machine Config Operator.
Tasks in this section describe how to use features of the Machine Config Operator to configure operating system features on OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
5.1. Understanding the Machine Config Operator
5.1.1. Machine Config Operator
Purpose
The Machine Config Operator manages and applies configuration and updates of the base operating system and container runtime, including everything between the kernel and kubelet.
There are four components:
-
machine-config-server: Provides Ignition configuration to new machines joining the cluster. -
machine-config-controller: Coordinates the upgrade of machines to the desired configurations defined by aMachineConfigobject. Options are provided to control the upgrade for sets of machines individually. -
machine-config-daemon: Applies new machine configuration during update. Validates and verifies the state of the machine to the requested machine configuration. -
machine-config: Provides a complete source of machine configuration at installation, first start up, and updates for a machine.
Currently, there is no supported way to block or restrict the machine config server endpoint. The machine config server must be exposed to the network so that newly-provisioned machines, which have no existing configuration or state, are able to fetch their configuration. In this model, the root of trust is the certificate signing requests (CSR) endpoint, which is where the kubelet sends its certificate signing request for approval to join the cluster. Because of this, machine configs should not be used to distribute sensitive information, such as secrets and certificates.
To ensure that the machine config server endpoints, ports 22623 and 22624, are secured in bare metal scenarios, customers must configure proper network policies.
Additional resources
Project
5.1.2. Machine config overview
The Machine Config Operator (MCO) manages updates to systemd, CRI-O and Kubelet, the kernel, Network Manager and other system features. It also offers a MachineConfig CRD that can write configuration files onto the host (see machine-config-operator). Understanding what MCO does and how it interacts with other components is critical to making advanced, system-level changes to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. Here are some things you should know about MCO, machine configs, and how they are used:
- Machine configs are processed alphabetically, in lexicographically increasing order, of their name. The render controller uses the first machine config in the list as the base and appends the rest to the base machine config.
- A machine config can make a specific change to a file or service on the operating system of each system representing a pool of OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
MCO applies changes to operating systems in pools of machines. All OpenShift Container Platform clusters start with worker and control plane node pools. By adding more role labels, you can configure custom pools of nodes. For example, you can set up a custom pool of worker nodes that includes particular hardware features needed by an application. However, examples in this section focus on changes to the default pool types.
ImportantA node can have multiple labels applied that indicate its type, such as
masterorworker, however it can be a member of only a single machine config pool.-
After a machine config change, the MCO updates the affected nodes alphabetically by zone, based on the
topology.kubernetes.io/zonelabel. If a zone has more than one node, the oldest nodes are updated first. For nodes that do not use zones, such as in bare metal deployments, the nodes are upgraded by age, with the oldest nodes updated first. The MCO updates the number of nodes as specified by themaxUnavailablefield on the machine configuration pool at a time. - Some machine configuration must be in place before OpenShift Container Platform is installed to disk. In most cases, this can be accomplished by creating a machine config that is injected directly into the OpenShift Container Platform installer process, instead of running as a postinstallation machine config. In other cases, you might need to do bare metal installation where you pass kernel arguments at OpenShift Container Platform installer startup, to do such things as setting per-node individual IP addresses or advanced disk partitioning.
- MCO manages items that are set in machine configs. Manual changes you do to your systems will not be overwritten by MCO, unless MCO is explicitly told to manage a conflicting file. In other words, MCO only makes specific updates you request, it does not claim control over the whole node.
- Manual changes to nodes are strongly discouraged. If you need to decommission a node and start a new one, those direct changes would be lost.
-
MCO is only supported for writing to files in
/etcand/vardirectories, although there are symbolic links to some directories that can be writeable by being symbolically linked to one of those areas. The/optand/usr/localdirectories are examples. - Ignition is the configuration format used in MachineConfigs. See the Ignition Configuration Specification v3.2.0 for details.
- Although Ignition config settings can be delivered directly at OpenShift Container Platform installation time, and are formatted in the same way that MCO delivers Ignition configs, MCO has no way of seeing what those original Ignition configs are. Therefore, you should wrap Ignition config settings into a machine config before deploying them.
-
When a file managed by MCO changes outside of MCO, the Machine Config Daemon (MCD) sets the node as
degraded. It will not overwrite the offending file, however, and should continue to operate in adegradedstate. -
A key reason for using a machine config is that it will be applied when you spin up new nodes for a pool in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. The
machine-api-operatorprovisions a new machine and MCO configures it.
MCO uses Ignition as the configuration format. OpenShift Container Platform 4.6 moved from Ignition config specification version 2 to version 3.
5.1.2.1. What can you change with machine configs?
The kinds of components that MCO can change include:
config: Create Ignition config objects (see the Ignition configuration specification) to do things like modify files, systemd services, and other features on OpenShift Container Platform machines, including:
-
Configuration files: Create or overwrite files in the
/varor/etcdirectory. - systemd units: Create and set the status of a systemd service or add to an existing systemd service by dropping in additional settings.
users and groups: Change SSH keys in the passwd section postinstallation.
Important-
Changing SSH keys by using a machine config is supported only for the
coreuser. - Adding new users by using a machine config is not supported.
-
Changing SSH keys by using a machine config is supported only for the
-
Configuration files: Create or overwrite files in the
- kernelArguments: Add arguments to the kernel command line when OpenShift Container Platform nodes boot.
-
kernelType: Optionally identify a non-standard kernel to use instead of the standard kernel. Use
realtimeto use the RT kernel (for RAN). This is only supported on select platforms. - fips: Enable FIPS mode. FIPS should be set at installation-time setting and not a postinstallation procedure.
To enable FIPS mode for your cluster, you must run the installation program from a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) computer configured to operate in FIPS mode. For more information about configuring FIPS mode on RHEL, see Installing the system in FIPS mode. The use of FIPS validated or Modules In Process cryptographic libraries is only supported on OpenShift Container Platform deployments on the x86_64 architecture.
- extensions: Extend RHCOS features by adding selected pre-packaged software. For this feature, available extensions include usbguard and kernel modules.
-
Custom resources (for
ContainerRuntimeandKubelet): Outside of machine configs, MCO manages two special custom resources for modifying CRI-O container runtime settings (ContainerRuntimeCR) and the Kubelet service (KubeletCR).
The MCO is not the only Operator that can change operating system components on OpenShift Container Platform nodes. Other Operators can modify operating system-level features as well. One example is the Node Tuning Operator, which allows you to do node-level tuning through Tuned daemon profiles.
Tasks for the MCO configuration that can be done postinstallation are included in the following procedures. See descriptions of RHCOS bare metal installation for system configuration tasks that must be done during or before OpenShift Container Platform installation.
There might be situations where the configuration on a node does not fully match what the currently-applied machine config specifies. This state is called configuration drift. The Machine Config Daemon (MCD) regularly checks the nodes for configuration drift. If the MCD detects configuration drift, the MCO marks the node degraded until an administrator corrects the node configuration. A degraded node is online and operational, but, it cannot be updated. For more information on configuration drift, see Understanding configuration drift detection.
5.1.2.2. Project
See the openshift-machine-config-operator GitHub site for details.
5.1.3. Understanding configuration drift detection
There might be situations when the on-disk state of a node differs from what is configured in the machine config. This is known as configuration drift. For example, a cluster admin might manually modify a file, a systemd unit file, or a file permission that was configured through a machine config. This causes configuration drift. Configuration drift can cause problems between nodes in a Machine Config Pool or when the machine configs are updated.
The Machine Config Operator (MCO) uses the Machine Config Daemon (MCD) to check nodes for configuration drift on a regular basis. If detected, the MCO sets the node and the machine config pool (MCP) to Degraded and reports the error. A degraded node is online and operational, but, it cannot be updated.
The MCD performs configuration drift detection upon each of the following conditions:
- When a node boots.
- After any of the files (Ignition files and systemd drop-in units) specified in the machine config are modified outside of the machine config.
Before a new machine config is applied.
NoteIf you apply a new machine config to the nodes, the MCD temporarily shuts down configuration drift detection. This shutdown is needed because the new machine config necessarily differs from the machine config on the nodes. After the new machine config is applied, the MCD restarts detecting configuration drift using the new machine config.
When performing configuration drift detection, the MCD validates that the file contents and permissions fully match what the currently-applied machine config specifies. Typically, the MCD detects configuration drift in less than a second after the detection is triggered.
If the MCD detects configuration drift, the MCD performs the following tasks:
- Emits an error to the console logs
- Emits a Kubernetes event
- Stops further detection on the node
-
Sets the node and MCP to
degraded
You can check if you have a degraded node by listing the MCPs:
oc get mcp worker
$ oc get mcp worker
If you have a degraded MCP, the DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT field is non-zero, similar to the following output:
Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-404caf3180818d8ac1f50c32f14b57c3 False True True 2 1 1 1 5h51m
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE
worker rendered-worker-404caf3180818d8ac1f50c32f14b57c3 False True True 2 1 1 1 5h51mYou can determine if the problem is caused by configuration drift by examining the machine config pool:
oc describe mcp worker
$ oc describe mcp workerExample output
Or, if you know which node is degraded, examine that node:
oc describe node/ci-ln-j4h8nkb-72292-pxqxz-worker-a-fjks4
$ oc describe node/ci-ln-j4h8nkb-72292-pxqxz-worker-a-fjks4Example output
- 1
- The error message indicating that configuration drift was detected between the node and the listed machine config. Here the error message indicates that the contents of the
/etc/mco-test-file, which was added by the machine config, has changed outside of the machine config. - 2
- The state of the node is
Degraded.
You can correct configuration drift and return the node to the Ready state by performing one of the following remediations:
- Ensure that the contents and file permissions of the files on the node match what is configured in the machine config. You can manually rewrite the file contents or change the file permissions.
Generate a force file on the degraded node. The force file causes the MCD to bypass the usual configuration drift detection and reapplies the current machine config.
NoteGenerating a force file on a node causes that node to reboot.
5.1.4. Checking machine config pool status
To see the status of the Machine Config Operator (MCO), its sub-components, and the resources it manages, use the following oc commands:
Procedure
To see the number of MCO-managed nodes available on your cluster for each machine config pool (MCP), run the following command:
oc get machineconfigpool
$ oc get machineconfigpoolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-06c9c4… True False False 3 3 3 0 4h42m worker rendered-worker-f4b64… False True False 3 2 2 0 4h42m
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-06c9c4… True False False 3 3 3 0 4h42m worker rendered-worker-f4b64… False True False 3 2 2 0 4h42mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- UPDATED
-
The
Truestatus indicates that the MCO has applied the current machine config to the nodes in that MCP. The current machine config is specified in theSTATUSfield in theoc get mcpoutput. TheFalsestatus indicates a node in the MCP is updating. - UPDATING
-
The
Truestatus indicates that the MCO is applying the desired machine config, as specified in theMachineConfigPoolcustom resource, to at least one of the nodes in that MCP. The desired machine config is the new, edited machine config. Nodes that are updating might not be available for scheduling. TheFalsestatus indicates that all nodes in the MCP are updated. - DEGRADED
-
A
Truestatus indicates the MCO is blocked from applying the current or desired machine config to at least one of the nodes in that MCP, or the configuration is failing. Nodes that are degraded might not be available for scheduling. AFalsestatus indicates that all nodes in the MCP are ready. - MACHINECOUNT
- Indicates the total number of machines in that MCP.
- READYMACHINECOUNT
- Indicates the total number of machines in that MCP that are ready for scheduling.
- UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT
- Indicates the total number of machines in that MCP that have the current machine config.
- DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT
- Indicates the total number of machines in that MCP that are marked as degraded or unreconcilable.
In the previous output, there are three control plane (master) nodes and three worker nodes. The control plane MCP and the associated nodes are updated to the current machine config. The nodes in the worker MCP are being updated to the desired machine config. Two of the nodes in the worker MCP are updated and one is still updating, as indicated by the
UPDATEDMACHINECOUNTbeing2. There are no issues, as indicated by theDEGRADEDMACHINECOUNTbeing0andDEGRADEDbeingFalse.While the nodes in the MCP are updating, the machine config listed under
CONFIGis the current machine config, which the MCP is being updated from. When the update is complete, the listed machine config is the desired machine config, which the MCP was updated to.NoteIf a node is being cordoned, that node is not included in the
READYMACHINECOUNT, but is included in theMACHINECOUNT. Also, the MCP status is set toUPDATING. Because the node has the current machine config, it is counted in theUPDATEDMACHINECOUNTtotal:Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-06c9c4… True False False 3 3 3 0 4h42m worker rendered-worker-c1b41a… False True False 3 2 3 0 4h42m
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-06c9c4… True False False 3 3 3 0 4h42m worker rendered-worker-c1b41a… False True False 3 2 3 0 4h42mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check the status of the nodes in an MCP by examining the
MachineConfigPoolcustom resource, run the following command: :oc describe mcp worker
$ oc describe mcp workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a node is being cordoned, the node is not included in the
Ready Machine Count. It is included in theUnavailable Machine Count:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To see each existing
MachineConfigobject, run the following command:oc get machineconfigs
$ oc get machineconfigsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the
MachineConfigobjects listed asrenderedare not meant to be changed or deleted.To view the contents of a particular machine config (in this case,
01-master-kubelet), run the following command:oc describe machineconfigs 01-master-kubelet
$ oc describe machineconfigs 01-master-kubeletCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output from the command shows that this
MachineConfigobject contains both configuration files (cloud.confandkubelet.conf) and a systemd service (Kubernetes Kubelet):Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If something goes wrong with a machine config that you apply, you can always back out that change. For example, if you had run oc create -f ./myconfig.yaml to apply a machine config, you could remove that machine config by running the following command:
oc delete -f ./myconfig.yaml
$ oc delete -f ./myconfig.yamlIf that was the only problem, the nodes in the affected pool should return to a non-degraded state. This actually causes the rendered configuration to roll back to its previously rendered state.
If you add your own machine configs to your cluster, you can use the commands shown in the previous example to check their status and the related status of the pool to which they are applied.
5.2. Using MachineConfig objects to configure nodes
You can use the tasks in this section to create MachineConfig objects that modify files, systemd unit files, and other operating system features running on OpenShift Container Platform nodes. For more ideas on working with machine configs, see content related to updating SSH authorized keys, verifying image signatures, enabling SCTP, and configuring iSCSI initiatornames for OpenShift Container Platform.
OpenShift Container Platform supports Ignition specification version 3.2. All new machine configs you create going forward should be based on Ignition specification version 3.2. If you are upgrading your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, any existing Ignition specification version 2.x machine configs will be translated automatically to specification version 3.2.
There might be situations where the configuration on a node does not fully match what the currently-applied machine config specifies. This state is called configuration drift. The Machine Config Daemon (MCD) regularly checks the nodes for configuration drift. If the MCD detects configuration drift, the MCO marks the node degraded until an administrator corrects the node configuration. A degraded node is online and operational, but, it cannot be updated. For more information on configuration drift, see Understanding configuration drift detection.
Use the following "Configuring chrony time service" procedure as a model for how to go about adding other configuration files to OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
5.2.1. Configuring chrony time service
You can set the time server and related settings used by the chrony time service (chronyd) by modifying the contents of the chrony.conf file and passing those contents to your nodes as a machine config.
Procedure
Create a Butane config including the contents of the
chrony.conffile. For example, to configure chrony on worker nodes, create a99-worker-chrony.bufile.NoteSee "Creating machine configs with Butane" for information about Butane.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1 2
- On control plane nodes, substitute
masterforworkerin both of these locations. - 3
- Specify an octal value mode for the
modefield in the machine config file. After creating the file and applying the changes, themodeis converted to a decimal value. You can check the YAML file with the commandoc get mc <mc-name> -o yaml. - 4
- Specify any valid, reachable time source, such as the one provided by your DHCP server. Alternately, you can specify any of the following NTP servers:
1.rhel.pool.ntp.org,2.rhel.pool.ntp.org, or3.rhel.pool.ntp.org.
Use Butane to generate a
MachineConfigobject file,99-worker-chrony.yaml, containing the configuration to be delivered to the nodes:butane 99-worker-chrony.bu -o 99-worker-chrony.yaml
$ butane 99-worker-chrony.bu -o 99-worker-chrony.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configurations in one of two ways:
-
If the cluster is not running yet, after you generate manifest files, add the
MachineConfigobject file to the<installation_directory>/openshiftdirectory, and then continue to create the cluster. If the cluster is already running, apply the file:
oc apply -f ./99-worker-chrony.yaml
$ oc apply -f ./99-worker-chrony.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
If the cluster is not running yet, after you generate manifest files, add the
5.2.2. Disabling the chrony time service
You can disable the chrony time service (chronyd) for nodes with a specific role by using a MachineConfig custom resource (CR).
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the
MachineConfigCR that disableschronydfor the specified node role.Save the following YAML in the
disable-chronyd.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Node role where you want to disable
chronyd, for example,master.
Create the
MachineConfigCR by running the following command:oc create -f disable-chronyd.yaml
$ oc create -f disable-chronyd.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.3. Adding kernel arguments to nodes
In some special cases, you might want to add kernel arguments to a set of nodes in your cluster. This should only be done with caution and clear understanding of the implications of the arguments you set.
Improper use of kernel arguments can result in your systems becoming unbootable.
Examples of kernel arguments you could set include:
-
nosmt: Disables symmetric multithreading (SMT) in the kernel. Multithreading allows multiple logical threads for each CPU. You could consider
nosmtin multi-tenant environments to reduce risks from potential cross-thread attacks. By disabling SMT, you essentially choose security over performance. systemd.unified_cgroup_hierarchy: Enables Linux control group version 2 (cgroup v2). cgroup v2 is the next version of the kernel control group and offers multiple improvements.
ImportantThe OpenShift Container Platform cgroups version 2 feature is in Developer Preview and is not supported by Red Hat at this time.
enforcing=0: Configures Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) to run in permissive mode. In permissive mode, the system acts as if SELinux is enforcing the loaded security policy, including labeling objects and emitting access denial entries in the logs, but it does not actually deny any operations. While not supported for production systems, permissive mode can be helpful for debugging.
WarningDisabling SELinux on RHCOS in production is not supported. Once SELinux has been disabled on a node, it must be re-provisioned before re-inclusion in a production cluster.
See Kernel.org kernel parameters for a list and descriptions of kernel arguments.
In the following procedure, you create a MachineConfig object that identifies:
- A set of machines to which you want to add the kernel argument. In this case, machines with a worker role.
- Kernel arguments that are appended to the end of the existing kernel arguments.
- A label that indicates where in the list of machine configs the change is applied.
Prerequisites
- Have administrative privilege to a working OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
List existing
MachineConfigobjects for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to determine how to label your machine config:oc get MachineConfig
$ oc get MachineConfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
MachineConfigobject file that identifies the kernel argument (for example,05-worker-kernelarg-selinuxpermissive.yaml)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the new machine config:
oc create -f 05-worker-kernelarg-selinuxpermissive.yaml
$ oc create -f 05-worker-kernelarg-selinuxpermissive.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the machine configs to see that the new one was added:
oc get MachineConfig
$ oc get MachineConfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the nodes:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can see that scheduling on each worker node is disabled as the change is being applied.
Check that the kernel argument worked by going to one of the worker nodes and listing the kernel command line arguments (in
/proc/cmdlineon the host):oc debug node/ip-10-0-141-105.ec2.internal
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-141-105.ec2.internalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You should see the
enforcing=0argument added to the other kernel arguments.
5.2.4. Enabling multipathing with kernel arguments on RHCOS
Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) supports multipathing on the primary disk, allowing stronger resilience to hardware failure to achieve higher host availability. Postinstallation support is available by activating multipathing via the machine config.
Enabling multipathing during installation is supported and recommended for nodes provisioned in OpenShift Container Platform 4.8 or higher. In setups where any I/O to non-optimized paths results in I/O system errors, you must enable multipathing at installation time. For more information about enabling multipathing during installation time, see "Enabling multipathing with kernel arguments on RHCOS" in the Installing on bare metal documentation.
On IBM Z and LinuxONE, you can enable multipathing only if you configured your cluster for it during installation. For more information, see "Installing RHCOS and starting the OpenShift Container Platform bootstrap process" in Installing a cluster with z/VM on IBM Z and LinuxONE.
Prerequisites
- You have a running OpenShift Container Platform cluster that uses version 4.7 or later.
- You are logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
- You have confirmed that the disk is enabled for multipathing. Multipathing is only supported on hosts that are connected to a SAN via an HBA adapter.
Procedure
To enable multipathing postinstallation on control plane nodes:
Create a machine config file, such as
99-master-kargs-mpath.yaml, that instructs the cluster to add themasterlabel and that identifies the multipath kernel argument, for example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To enable multipathing postinstallation on worker nodes:
Create a machine config file, such as
99-worker-kargs-mpath.yaml, that instructs the cluster to add theworkerlabel and that identifies the multipath kernel argument, for example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create the new machine config by using either the master or worker YAML file you previously created:
oc create -f ./99-worker-kargs-mpath.yaml
$ oc create -f ./99-worker-kargs-mpath.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the machine configs to see that the new one was added:
oc get MachineConfig
$ oc get MachineConfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the nodes:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can see that scheduling on each worker node is disabled as the change is being applied.
Check that the kernel argument worked by going to one of the worker nodes and listing the kernel command line arguments (in
/proc/cmdlineon the host):oc debug node/ip-10-0-141-105.ec2.internal
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-141-105.ec2.internalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You should see the added kernel arguments.
5.3. Enabling Linux control groups version 2 (cgroups v2)
You can enable Linux control groups version 2 (cgroups v2) on specific nodes in your cluster by using a machine config. The OpenShift Container Platform process for enabling cgroups v2 disables all cgroups version 1 controllers and hierarchies.
The OpenShift Container Platform cgroups version 2 feature is in Developer Preview and is not supported by Red Hat at this time.
Prerequisites
- You have a running OpenShift Container Platform cluster that uses version 4.10 or later.
- You are logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
You have the
node-role.kubernetes.iovalue for the node(s) you want to configure.oc describe node <node-name>
$ oc describe node <node-name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This value is the node role you need.
Procedure
Enable cgroups v2 on nodes:
Create a machine config file YAML, such as
worker-cgroups-v2.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the new machine config:
oc create -f worker-enable-cgroups-v2.yaml
$ oc create -f worker-enable-cgroups-v2.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check the machine configs to see that the new one was added:
oc get MachineConfig
$ oc get MachineConfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the nodes to see that scheduling on each affected node is disabled. This indicates that the change is being applied:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After a node returns to the
Readystate, you can verify that cgroups v2 is enabled by checking that thesys/fs/cgroup/cgroup.controllersfile is present on the node. This file is created by cgroups v2.Start a debug session for that node:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Locate the
sys/fs/cgroup/cgroup.controllersfile. If this file is present, cgroups v2 is enabled on that node.Example output
cgroup.controllers cgroup.stat cpuset.cpus.effective io.stat pids cgroup.max.depth cgroup.subtree_control cpuset.mems.effective kubepods.slice system.slice cgroup.max.descendants cgroup.threads init.scope memory.pressure user.slice cgroup.procs cpu.pressure io.pressure memory.stat
cgroup.controllers cgroup.stat cpuset.cpus.effective io.stat pids cgroup.max.depth cgroup.subtree_control cpuset.mems.effective kubepods.slice system.slice cgroup.max.descendants cgroup.threads init.scope memory.pressure user.slice cgroup.procs cpu.pressure io.pressure memory.statCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.3.1. Adding a real-time kernel to nodes
Some OpenShift Container Platform workloads require a high degree of determinism.While Linux is not a real-time operating system, the Linux real-time kernel includes a preemptive scheduler that provides the operating system with real-time characteristics.
If your OpenShift Container Platform workloads require these real-time characteristics, you can switch your machines to the Linux real-time kernel. For OpenShift Container Platform, 4.11 you can make this switch using a MachineConfig object. Although making the change is as simple as changing a machine config kernelType setting to realtime, there are a few other considerations before making the change:
- Currently, real-time kernel is supported only on worker nodes, and only for radio access network (RAN) use.
- The following procedure is fully supported with bare metal installations that use systems that are certified for Red Hat Enterprise Linux for Real Time 8.
- Real-time support in OpenShift Container Platform is limited to specific subscriptions.
- The following procedure is also supported for use with Google Cloud Platform.
Prerequisites
- Have a running OpenShift Container Platform cluster (version 4.4 or later).
- Log in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
Procedure
Create a machine config for the real-time kernel: Create a YAML file (for example,
99-worker-realtime.yaml) that contains aMachineConfigobject for therealtimekernel type. This example tells the cluster to use a real-time kernel for all worker nodes:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the machine config to the cluster. Type the following to add the machine config to the cluster:
oc create -f 99-worker-realtime.yaml
$ oc create -f 99-worker-realtime.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the real-time kernel: Once each impacted node reboots, log in to the cluster and run the following commands to make sure that the real-time kernel has replaced the regular kernel for the set of nodes you configured:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-143-147.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 103m v1.24.0 ip-10-0-146-92.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 101m v1.24.0 ip-10-0-169-2.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 102m v1.24.0
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-143-147.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 103m v1.24.0 ip-10-0-146-92.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 101m v1.24.0 ip-10-0-169-2.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 102m v1.24.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc debug node/ip-10-0-143-147.us-east-2.compute.internal
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-143-147.us-east-2.compute.internalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The kernel name contains
rtand text “PREEMPT RT” indicates that this is a real-time kernel.To go back to the regular kernel, delete the
MachineConfigobject:oc delete -f 99-worker-realtime.yaml
$ oc delete -f 99-worker-realtime.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.3.2. Configuring journald settings
If you need to configure settings for the journald service on OpenShift Container Platform nodes, you can do that by modifying the appropriate configuration file and passing the file to the appropriate pool of nodes as a machine config.
This procedure describes how to modify journald rate limiting settings in the /etc/systemd/journald.conf file and apply them to worker nodes. See the journald.conf man page for information on how to use that file.
Prerequisites
- Have a running OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Log in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
Procedure
Create a Butane config file,
40-worker-custom-journald.bu, that includes an/etc/systemd/journald.conffile with the required settings.NoteSee "Creating machine configs with Butane" for information about Butane.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use Butane to generate a
MachineConfigobject file,40-worker-custom-journald.yaml, containing the configuration to be delivered to the worker nodes:butane 40-worker-custom-journald.bu -o 40-worker-custom-journald.yaml
$ butane 40-worker-custom-journald.bu -o 40-worker-custom-journald.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the machine config to the pool:
oc apply -f 40-worker-custom-journald.yaml
$ oc apply -f 40-worker-custom-journald.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the new machine config is applied and that the nodes are not in a degraded state. It might take a few minutes. The worker pool will show the updates in progress, as each node successfully has the new machine config applied:
oc get machineconfigpool NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-35 True False False 3 3 3 0 34m worker rendered-worker-d8 False True False 3 1 1 0 34m
$ oc get machineconfigpool NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-35 True False False 3 3 3 0 34m worker rendered-worker-d8 False True False 3 1 1 0 34mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check that the change was applied, you can log in to a worker node:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.3.3. Adding extensions to RHCOS
RHCOS is a minimal container-oriented RHEL operating system, designed to provide a common set of capabilities to OpenShift Container Platform clusters across all platforms. While adding software packages to RHCOS systems is generally discouraged, the MCO provides an extensions feature you can use to add a minimal set of features to RHCOS nodes.
Currently, the following extensions are available:
-
usbguard: Adding the
usbguardextension protects RHCOS systems from attacks from intrusive USB devices. See USBGuard for details. -
kerberos: Adding the
kerberosextension provides a mechanism that allows both users and machines to identify themselves to the network to receive defined, limited access to the areas and services that an administrator has configured. See Using Kerberos for details, including how to set up a Kerberos client and mount a Kerberized NFS share.
The following procedure describes how to use a machine config to add one or more extensions to your RHCOS nodes.
Prerequisites
- Have a running OpenShift Container Platform cluster (version 4.6 or later).
- Log in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
Procedure
Create a machine config for extensions: Create a YAML file (for example,
80-extensions.yaml) that contains aMachineConfigextensionsobject. This example tells the cluster to add theusbguardextension.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the machine config to the cluster. Type the following to add the machine config to the cluster:
oc create -f 80-extensions.yaml
$ oc create -f 80-extensions.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This sets all worker nodes to have rpm packages for
usbguardinstalled.Check that the extensions were applied:
oc get machineconfig 80-worker-extensions
$ oc get machineconfig 80-worker-extensionsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME GENERATEDBYCONTROLLER IGNITIONVERSION AGE 80-worker-extensions 3.2.0 57s
NAME GENERATEDBYCONTROLLER IGNITIONVERSION AGE 80-worker-extensions 3.2.0 57sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the new machine config is now applied and that the nodes are not in a degraded state. It may take a few minutes. The worker pool will show the updates in progress, as each machine successfully has the new machine config applied:
oc get machineconfigpool
$ oc get machineconfigpoolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-35 True False False 3 3 3 0 34m worker rendered-worker-d8 False True False 3 1 1 0 34m
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE master rendered-master-35 True False False 3 3 3 0 34m worker rendered-worker-d8 False True False 3 1 1 0 34mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the extensions. To check that the extension was applied, run:
oc get node | grep worker
$ oc get node | grep workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-169-2.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 102m v1.24.0
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-169-2.us-east-2.compute.internal Ready worker 102m v1.24.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc debug node/ip-10-0-169-2.us-east-2.compute.internal
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-169-2.us-east-2.compute.internalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` sh-4.4# chroot /host sh-4.4# rpm -q usbguard usbguard-0.7.4-4.el8.x86_64.rpm
... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` sh-4.4# chroot /host sh-4.4# rpm -q usbguard usbguard-0.7.4-4.el8.x86_64.rpmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.3.4. Loading custom firmware blobs in the machine config manifest
Because the default location for firmware blobs in /usr/lib is read-only, you can locate a custom firmware blob by updating the search path. This enables you to load local firmware blobs in the machine config manifest when the blobs are not managed by RHCOS.
Procedure
Create a Butane config file,
98-worker-firmware-blob.bu, that updates the search path so that it is root-owned and writable to local storage. The following example places the custom blob file from your local workstation onto nodes under/var/lib/firmware.NoteSee "Creating machine configs with Butane" for information about Butane.
Butane config file for custom firmware blob
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Sets the path on the node where the firmware package is copied to.
- 2
- Specifies a file with contents that are read from a local file directory on the system running Butane. The path of the local file is relative to a
files-dirdirectory, which must be specified by using the--files-diroption with Butane in the following step. - 3
- Sets the permissions for the file on the RHCOS node. It is recommended to set
0644permissions. - 4
- The
firmware_class.pathparameter customizes the kernel search path of where to look for the custom firmware blob that was copied from your local workstation onto the root file system of the node. This example uses/var/lib/firmwareas the customized path.
Run Butane to generate a
MachineConfigobject file that uses a copy of the firmware blob on your local workstation named98-worker-firmware-blob.yaml. The firmware blob contains the configuration to be delivered to the nodes. The following example uses the--files-diroption to specify the directory on your workstation where the local file or files are located:butane 98-worker-firmware-blob.bu -o 98-worker-firmware-blob.yaml --files-dir <directory_including_package_name>
$ butane 98-worker-firmware-blob.bu -o 98-worker-firmware-blob.yaml --files-dir <directory_including_package_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configurations to the nodes in one of two ways:
-
If the cluster is not running yet, after you generate manifest files, add the
MachineConfigobject file to the<installation_directory>/openshiftdirectory, and then continue to create the cluster. If the cluster is already running, apply the file:
oc apply -f 98-worker-firmware-blob.yaml
$ oc apply -f 98-worker-firmware-blob.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A
MachineConfigobject YAML file is created for you to finish configuring your machines.
-
If the cluster is not running yet, after you generate manifest files, add the
-
Save the Butane config in case you need to update the
MachineConfigobject in the future.
5.4. Configuring MCO-related custom resources
Besides managing MachineConfig objects, the MCO manages two custom resources (CRs): KubeletConfig and ContainerRuntimeConfig. Those CRs let you change node-level settings impacting how the Kubelet and CRI-O container runtime services behave.
5.4.1. Creating a KubeletConfig CRD to edit kubelet parameters
The kubelet configuration is currently serialized as an Ignition configuration, so it can be directly edited. However, there is also a new kubelet-config-controller added to the Machine Config Controller (MCC). This lets you use a KubeletConfig custom resource (CR) to edit the kubelet parameters.
As the fields in the kubeletConfig object are passed directly to the kubelet from upstream Kubernetes, the kubelet validates those values directly. Invalid values in the kubeletConfig object might cause cluster nodes to become unavailable. For valid values, see the Kubernetes documentation.
Consider the following guidance:
-
Create one
KubeletConfigCR for each machine config pool with all the config changes you want for that pool. If you are applying the same content to all of the pools, you need only oneKubeletConfigCR for all of the pools. -
Edit an existing
KubeletConfigCR to modify existing settings or add new settings, instead of creating a CR for each change. It is recommended that you create a CR only to modify a different machine config pool, or for changes that are intended to be temporary, so that you can revert the changes. -
As needed, create multiple
KubeletConfigCRs with a limit of 10 per cluster. For the firstKubeletConfigCR, the Machine Config Operator (MCO) creates a machine config appended withkubelet. With each subsequent CR, the controller creates anotherkubeletmachine config with a numeric suffix. For example, if you have akubeletmachine config with a-2suffix, the nextkubeletmachine config is appended with-3.
If you want to delete the machine configs, delete them in reverse order to avoid exceeding the limit. For example, you delete the kubelet-3 machine config before deleting the kubelet-2 machine config.
If you have a machine config with a kubelet-9 suffix, and you create another KubeletConfig CR, a new machine config is not created, even if there are fewer than 10 kubelet machine configs.
Example KubeletConfig CR
oc get kubeletconfig
$ oc get kubeletconfigNAME AGE set-max-pods 15m
NAME AGE
set-max-pods 15mExample showing a KubeletConfig machine config
oc get mc | grep kubelet
$ oc get mc | grep kubelet... 99-worker-generated-kubelet-1 b5c5119de007945b6fe6fb215db3b8e2ceb12511 3.2.0 26m ...
...
99-worker-generated-kubelet-1 b5c5119de007945b6fe6fb215db3b8e2ceb12511 3.2.0 26m
...The following procedure is an example to show how to configure the maximum number of pods per node on the worker nodes.
Prerequisites
Obtain the label associated with the static
MachineConfigPoolCR for the type of node you want to configure. Perform one of the following steps:View the machine config pool:
oc describe machineconfigpool <name>
$ oc describe machineconfigpool <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc describe machineconfigpool worker
$ oc describe machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If a label has been added it appears under
labels.
If the label is not present, add a key/value pair:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
View the available machine configuration objects that you can select:
oc get machineconfig
$ oc get machineconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, the two kubelet-related configs are
01-master-kubeletand01-worker-kubelet.Check the current value for the maximum pods per node:
oc describe node <node_name>
$ oc describe node <node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc describe node ci-ln-5grqprb-f76d1-ncnqq-worker-a-mdv94
$ oc describe node ci-ln-5grqprb-f76d1-ncnqq-worker-a-mdv94Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Look for
value: pods: <value>in theAllocatablestanza:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the maximum pods per node on the worker nodes by creating a custom resource file that contains the kubelet configuration:
ImportantKubelet configurations that target a specific machine config pool also affect any dependent pools. For example, creating a kubelet configuration for the pool containing worker nodes will also apply to any subset pools, including the pool containing infrastructure nodes. To avoid this, you must create a new machine config pool with a selection expression that only includes worker nodes, and have your kubelet configuration target this new pool.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe rate at which the kubelet talks to the API server depends on queries per second (QPS) and burst values. The default values,
50forkubeAPIQPSand100forkubeAPIBurst, are sufficient if there are limited pods running on each node. It is recommended to update the kubelet QPS and burst rates if there are enough CPU and memory resources on the node.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the machine config pool for workers with the label:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
KubeletConfigobject:oc create -f change-maxPods-cr.yaml
$ oc create -f change-maxPods-cr.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
KubeletConfigobject is created:oc get kubeletconfig
$ oc get kubeletconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE set-max-pods 15m
NAME AGE set-max-pods 15mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Depending on the number of worker nodes in the cluster, wait for the worker nodes to be rebooted one by one. For a cluster with 3 worker nodes, this could take about 10 to 15 minutes.
Verify that the changes are applied to the node:
Check on a worker node that the
maxPodsvalue changed:oc describe node <node_name>
$ oc describe node <node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Locate the
Allocatablestanza:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the
podsparameter should report the value you set in theKubeletConfigobject.
Verify the change in the
KubeletConfigobject:oc get kubeletconfigs set-max-pods -o yaml
$ oc get kubeletconfigs set-max-pods -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This should show a status of
Trueandtype:Success, as shown in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.4.2. Creating a ContainerRuntimeConfig CR to edit CRI-O parameters
You can change some of the settings associated with the OpenShift Container Platform CRI-O runtime for the nodes associated with a specific machine config pool (MCP). Using a ContainerRuntimeConfig custom resource (CR), you set the configuration values and add a label to match the MCP. The MCO then rebuilds the crio.conf and storage.conf configuration files on the associated nodes with the updated values.
To revert the changes implemented by using a ContainerRuntimeConfig CR, you must delete the CR. Removing the label from the machine config pool does not revert the changes.
You can modify the following settings by using a ContainerRuntimeConfig CR:
PIDs limit: Setting the PIDs limit in the
ContainerRuntimeConfigis expected to be deprecated. If PIDs limits are required, it is recommended to use thepodPidsLimitfield in theKubeletConfigCR instead. The default value of thepodPidsLimitfield is4096.NoteThe CRI-O flag is applied on the cgroup of the container, while the Kubelet flag is set on the cgroup of the pod. Please adjust the PIDs limit accordingly.
-
Log level: The
logLevelparameter sets the CRI-Olog_levelparameter, which is the level of verbosity for log messages. The default isinfo(log_level = info). Other options includefatal,panic,error,warn,debug, andtrace. -
Overlay size: The
overlaySizeparameter sets the CRI-O Overlay storage driversizeparameter, which is the maximum size of a container image. -
Maximum log size: Setting the maximum log size in the
ContainerRuntimeConfigis expected to be deprecated. If a maximum log size is required, it is recommended to use thecontainerLogMaxSizefield in theKubeletConfigCR instead. -
Container runtime: The
defaultRuntimeparameter sets the container runtime to eitherruncorcrun. The default isrunc.
Support for the crun container runtime is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
You should have one ContainerRuntimeConfig CR for each machine config pool with all the config changes you want for that pool. If you are applying the same content to all the pools, you only need one ContainerRuntimeConfig CR for all the pools.
You should edit an existing ContainerRuntimeConfig CR to modify existing settings or add new settings instead of creating a new CR for each change. It is recommended to create a new ContainerRuntimeConfig CR only to modify a different machine config pool, or for changes that are intended to be temporary so that you can revert the changes.
You can create multiple ContainerRuntimeConfig CRs, as needed, with a limit of 10 per cluster. For the first ContainerRuntimeConfig CR, the MCO creates a machine config appended with containerruntime. With each subsequent CR, the controller creates a new containerruntime machine config with a numeric suffix. For example, if you have a containerruntime machine config with a -2 suffix, the next containerruntime machine config is appended with -3.
If you want to delete the machine configs, you should delete them in reverse order to avoid exceeding the limit. For example, you should delete the containerruntime-3 machine config before deleting the containerruntime-2 machine config.
If you have a machine config with a containerruntime-9 suffix, and you create another ContainerRuntimeConfig CR, a new machine config is not created, even if there are fewer than 10 containerruntime machine configs.
Example showing multiple ContainerRuntimeConfig CRs
oc get ctrcfg
$ oc get ctrcfgExample output
NAME AGE ctr-pid 24m ctr-overlay 15m ctr-level 5m45s
NAME AGE
ctr-pid 24m
ctr-overlay 15m
ctr-level 5m45sExample showing multiple containerruntime machine configs
oc get mc | grep container
$ oc get mc | grep containerExample output
The following example raises the pids_limit to 2048, sets the log_level to debug, sets the overlay size to 8 GB, and sets the log_size_max to unlimited:
Example ContainerRuntimeConfig CR
- 1
- Specifies the machine config pool label.
- 2
- Optional: Specifies the maximum number of processes allowed in a container.
- 3
- Optional: Specifies the level of verbosity for log messages.
- 4
- Optional: Specifies the maximum size of a container image.
- 5
- Optional: Specifies the maximum size allowed for the container log file. If set to a positive number, it must be at least 8192.
Procedure
To change CRI-O settings using the ContainerRuntimeConfig CR:
Create a YAML file for the
ContainerRuntimeConfigCR:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
ContainerRuntimeConfigCR:oc create -f <file_name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the CR is created:
oc get ContainerRuntimeConfig
$ oc get ContainerRuntimeConfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE overlay-size 3m19s
NAME AGE overlay-size 3m19sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that a new
containerruntimemachine config is created:oc get machineconfigs | grep containerrun
$ oc get machineconfigs | grep containerrunCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
99-worker-generated-containerruntime 2c9371fbb673b97a6fe8b1c52691999ed3a1bfc2 3.2.0 31s
99-worker-generated-containerruntime 2c9371fbb673b97a6fe8b1c52691999ed3a1bfc2 3.2.0 31sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Monitor the machine config pool until all are shown as ready:
oc get mcp worker
$ oc get mcp workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-169 False True False 3 1 1 0 9h
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-169 False True False 3 1 1 0 9hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the settings were applied in CRI-O:
Open an
oc debugsession to a node in the machine config pool and runchroot /host.oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow chroot /host
sh-4.4# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the changes in the
crio.conffile:crio config | egrep 'log_level|pids_limit|log_size_max'
sh-4.4# crio config | egrep 'log_level|pids_limit|log_size_max'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
pids_limit = 2048 log_size_max = -1 log_level = "debug"
pids_limit = 2048 log_size_max = -1 log_level = "debug"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the changes in the `storage.conf`file:
head -n 7 /etc/containers/storage.conf
sh-4.4# head -n 7 /etc/containers/storage.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.4.3. Setting the default maximum container root partition size for Overlay with CRI-O
The root partition of each container shows all of the available disk space of the underlying host. Follow this guidance to set a maximum partition size for the root disk of all containers.
To configure the maximum Overlay size, as well as other CRI-O options like the log level and PID limit, you can create the following ContainerRuntimeConfig custom resource definition (CRD):
Procedure
Create the configuration object:
oc apply -f overlaysize.yml
$ oc apply -f overlaysize.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To apply the new CRI-O configuration to your worker nodes, edit the worker machine config pool:
oc edit machineconfigpool worker
$ oc edit machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
custom-criolabel based on thematchLabelsname you set in theContainerRuntimeConfigCRD:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the changes, then view the machine configs:
oc get machineconfigs
$ oc get machineconfigsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow New
99-worker-generated-containerruntimeandrendered-worker-xyzobjects are created:Example output
99-worker-generated-containerruntime 4173030d89fbf4a7a0976d1665491a4d9a6e54f1 3.2.0 7m42s rendered-worker-xyz 4173030d89fbf4a7a0976d1665491a4d9a6e54f1 3.2.0 7m36s
99-worker-generated-containerruntime 4173030d89fbf4a7a0976d1665491a4d9a6e54f1 3.2.0 7m42s rendered-worker-xyz 4173030d89fbf4a7a0976d1665491a4d9a6e54f1 3.2.0 7m36sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After those objects are created, monitor the machine config pool for the changes to be applied:
oc get mcp worker
$ oc get mcp workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The worker nodes show
UPDATINGasTrue, as well as the number of machines, the number updated, and other details:Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-xyz False True False 3 2 2 0 20h
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-xyz False True False 3 2 2 0 20hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When complete, the worker nodes transition back to
UPDATINGasFalse, and theUPDATEDMACHINECOUNTnumber matches theMACHINECOUNT:Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-xyz True False False 3 3 3 0 20h
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE worker rendered-worker-xyz True False False 3 3 3 0 20hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Looking at a worker machine, you see that the new 8 GB max size configuration is applied to all of the workers:
Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Looking inside a container, you see that the root partition is now 8 GB:
Example output
~ $ df -h Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on overlay 8.0G 8.0K 8.0G 0% /
~ $ df -h Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on overlay 8.0G 8.0K 8.0G 0% /Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 6. Postinstallation cluster tasks
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can further expand and customize your cluster to your requirements.
6.1. Available cluster customizations
You complete most of the cluster configuration and customization after you deploy your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. A number of configuration resources are available.
If you install your cluster on IBM Z, not all features and functions are available.
You modify the configuration resources to configure the major features of the cluster, such as the image registry, networking configuration, image build behavior, and the identity provider.
For current documentation of the settings that you control by using these resources, use the oc explain command, for example oc explain builds --api-version=config.openshift.io/v1
6.1.1. Cluster configuration resources
All cluster configuration resources are globally scoped (not namespaced) and named cluster.
| Resource name | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Provides API server configuration such as certificates and certificate authorities. |
|
| Controls the identity provider and authentication configuration for the cluster. |
|
| Controls default and enforced configuration for all builds on the cluster. |
|
| Configures the behavior of the web console interface, including the logout behavior. |
|
| Enables FeatureGates so that you can use Tech Preview features. |
|
| Configures how specific image registries should be treated (allowed, disallowed, insecure, CA details). |
|
| Configuration details related to routing such as the default domain for routes. |
|
| Configures identity providers and other behavior related to internal OAuth server flows. |
|
| Configures how projects are created including the project template. |
|
| Defines proxies to be used by components needing external network access. Note: not all components currently consume this value. |
|
| Configures scheduler behavior such as profiles and default node selectors. |
6.1.2. Operator configuration resources
These configuration resources are cluster-scoped instances, named cluster, which control the behavior of a specific component as owned by a particular Operator.
| Resource name | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Controls console appearance such as branding customizations |
|
| Configures OpenShift image registry settings such as public routing, log levels, proxy settings, resource constraints, replica counts, and storage type. |
|
| Configures the Samples Operator to control which example image streams and templates are installed on the cluster. |
6.1.3. Additional configuration resources
These configuration resources represent a single instance of a particular component. In some cases, you can request multiple instances by creating multiple instances of the resource. In other cases, the Operator can use only a specific resource instance name in a specific namespace. Reference the component-specific documentation for details on how and when you can create additional resource instances.
| Resource name | Instance name | Namespace | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Controls the Alertmanager deployment parameters. |
|
|
|
| Configures Ingress Operator behavior such as domain, number of replicas, certificates, and controller placement. |
6.1.4. Informational Resources
You use these resources to retrieve information about the cluster. Some configurations might require you to edit these resources directly.
| Resource name | Instance name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11, you must not customize the |
|
|
| You cannot modify the DNS settings for your cluster. You can view the DNS Operator status. |
|
|
| Configuration details allowing the cluster to interact with its cloud provider. |
|
|
| You cannot modify your cluster networking after installation. To customize your network, follow the process to customize networking during installation. |
6.2. Updating the global cluster pull secret
You can update the global pull secret for your cluster by either replacing the current pull secret or appending a new pull secret.
The procedure is required when users use a separate registry to store images than the registry used during installation.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Optional: To append a new pull secret to the existing pull secret, complete the following steps:
Enter the following command to download the pull secret:
oc get secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --template='{{index .data ".dockerconfigjson" | base64decode}}' ><pull_secret_location>$ oc get secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --template='{{index .data ".dockerconfigjson" | base64decode}}' ><pull_secret_location>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Provide the path to the pull secret file.
Enter the following command to add the new pull secret:
oc registry login --registry="<registry>" \ --auth-basic="<username>:<password>" \ --to=<pull_secret_location>
$ oc registry login --registry="<registry>" \1 --auth-basic="<username>:<password>" \2 --to=<pull_secret_location>3 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, you can perform a manual update to the pull secret file.
Enter the following command to update the global pull secret for your cluster:
oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=<pull_secret_location>
$ oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=<pull_secret_location>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Provide the path to the new pull secret file.
This update is rolled out to all nodes, which can take some time depending on the size of your cluster.
NoteAs of OpenShift Container Platform 4.7.4, changes to the global pull secret no longer trigger a node drain or reboot.
6.3. Adjust worker nodes
If you incorrectly sized the worker nodes during deployment, adjust them by creating one or more new machine sets, scale them up, then scale the original machine set down before removing them.
6.3.1. Understanding the difference between machine sets and the machine config pool
MachineSet objects describe OpenShift Container Platform nodes with respect to the cloud or machine provider.
The MachineConfigPool object allows MachineConfigController components to define and provide the status of machines in the context of upgrades.
The MachineConfigPool object allows users to configure how upgrades are rolled out to the OpenShift Container Platform nodes in the machine config pool.
The NodeSelector object can be replaced with a reference to the MachineSet object.
6.3.2. Scaling a machine set manually
To add or remove an instance of a machine in a machine set, you can manually scale the machine set.
This guidance is relevant to fully automated, installer-provisioned infrastructure installations. Customized, user-provisioned infrastructure installations do not have machine sets.
Prerequisites
-
Install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster and the
occommand line. -
Log in to
ocas a user withcluster-adminpermission.
Procedure
View the machine sets that are in the cluster:
oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The machine sets are listed in the form of
<clusterid>-worker-<aws-region-az>.View the machines that are in the cluster:
oc get machine -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machine -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the annotation on the machine that you want to delete:
oc annotate machine/<machine_name> -n openshift-machine-api machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine="true"
$ oc annotate machine/<machine_name> -n openshift-machine-api machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine="true"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Scale the machine set by running one of the following commands:
oc scale --replicas=2 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc scale --replicas=2 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Or:
oc edit machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc edit machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to scale the machine set:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can scale the machine set up or down. It takes several minutes for the new machines to be available.
ImportantBy default, the machine controller tries to drain the node that is backed by the machine until it succeeds. In some situations, such as with a misconfigured pod disruption budget, the drain operation might not be able to succeed. If the drain operation fails, the machine controller cannot proceed removing the machine.
You can skip draining the node by annotating
machine.openshift.io/exclude-node-drainingin a specific machine.
Verification
Verify the deletion of the intended machine:
oc get machines
$ oc get machinesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.3. The machine set deletion policy
Random, Newest, and Oldest are the three supported deletion options. The default is Random, meaning that random machines are chosen and deleted when scaling machine sets down. The deletion policy can be set according to the use case by modifying the particular machine set:
spec: deletePolicy: <delete_policy> replicas: <desired_replica_count>
spec:
deletePolicy: <delete_policy>
replicas: <desired_replica_count>
Specific machines can also be prioritized for deletion by adding the annotation machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine=true to the machine of interest, regardless of the deletion policy.
By default, the OpenShift Container Platform router pods are deployed on workers. Because the router is required to access some cluster resources, including the web console, do not scale the worker machine set to 0 unless you first relocate the router pods.
Custom machine sets can be used for use cases requiring that services run on specific nodes and that those services are ignored by the controller when the worker machine sets are scaling down. This prevents service disruption.
6.3.4. Creating default cluster-wide node selectors
You can use default cluster-wide node selectors on pods together with labels on nodes to constrain all pods created in a cluster to specific nodes.
With cluster-wide node selectors, when you create a pod in that cluster, OpenShift Container Platform adds the default node selectors to the pod and schedules the pod on nodes with matching labels.
You configure cluster-wide node selectors by editing the Scheduler Operator custom resource (CR). You add labels to a node, a machine set, or a machine config. Adding the label to the machine set ensures that if the node or machine goes down, new nodes have the label. Labels added to a node or machine config do not persist if the node or machine goes down.
You can add additional key/value pairs to a pod. But you cannot add a different value for a default key.
Procedure
To add a default cluster-wide node selector:
Edit the Scheduler Operator CR to add the default cluster-wide node selectors:
oc edit scheduler cluster
$ oc edit scheduler clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example Scheduler Operator CR with a node selector
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add a node selector with the appropriate
<key>:<value>pairs.
After making this change, wait for the pods in the
openshift-kube-apiserverproject to redeploy. This can take several minutes. The default cluster-wide node selector does not take effect until the pods redeploy.Add labels to a node by using a machine set or editing the node directly:
Use a machine set to add labels to nodes managed by the machine set when a node is created:
Run the following command to add labels to a
MachineSetobject:oc patch MachineSet <name> --type='json' -p='[{"op":"add","path":"/spec/template/spec/metadata/labels", "value":{"<key>"="<value>","<key>"="<value>"}}]' -n openshift-machine-api$ oc patch MachineSet <name> --type='json' -p='[{"op":"add","path":"/spec/template/spec/metadata/labels", "value":{"<key>"="<value>","<key>"="<value>"}}]' -n openshift-machine-api1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add a
<key>/<value>pair for each label.
For example:
oc patch MachineSet ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c --type='json' -p='[{"op":"add","path":"/spec/template/spec/metadata/labels", "value":{"type":"user-node","region":"east"}}]' -n openshift-machine-api$ oc patch MachineSet ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c --type='json' -p='[{"op":"add","path":"/spec/template/spec/metadata/labels", "value":{"type":"user-node","region":"east"}}]' -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add labels to a machine set:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the labels are added to the
MachineSetobject by using theoc editcommand:For example:
oc edit MachineSet abc612-msrtw-worker-us-east-1c -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc edit MachineSet abc612-msrtw-worker-us-east-1c -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
MachineSetobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Redeploy the nodes associated with that machine set by scaling down to
0and scaling up the nodes:For example:
oc scale --replicas=0 MachineSet ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc scale --replicas=0 MachineSet ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc scale --replicas=1 MachineSet ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc scale --replicas=1 MachineSet ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When the nodes are ready and available, verify that the label is added to the nodes by using the
oc getcommand:oc get nodes -l <key>=<value>
$ oc get nodes -l <key>=<value>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc get nodes -l type=user-node
$ oc get nodes -l type=user-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c-vmqzp Ready worker 61s v1.24.0
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-c-vmqzp Ready worker 61s v1.24.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Add labels directly to a node:
Edit the
Nodeobject for the node:oc label nodes <name> <key>=<value>
$ oc label nodes <name> <key>=<value>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to label a node:
oc label nodes ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-b-tgq49 type=user-node region=east
$ oc label nodes ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-b-tgq49 type=user-node region=eastCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add labels to a node:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the labels are added to the node using the
oc getcommand:oc get nodes -l <key>=<value>,<key>=<value>
$ oc get nodes -l <key>=<value>,<key>=<value>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc get nodes -l type=user-node,region=east
$ oc get nodes -l type=user-node,region=eastCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-b-tgq49 Ready worker 17m v1.24.0
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ci-ln-l8nry52-f76d1-hl7m7-worker-b-tgq49 Ready worker 17m v1.24.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4. Improving cluster stability in high latency environments using worker latency profiles
If the cluster administrator has performed latency tests for platform verification, they can discover the need to adjust the operation of the cluster to ensure stability in cases of high latency. The cluster administrator need change only one parameter, recorded in a file, which controls four parameters affecting how supervisory processes read status and interpret the health of the cluster. Changing only the one parameter provides cluster tuning in an easy, supportable manner.
The Kubelet process provides the starting point for monitoring cluster health. The Kubelet sets status values for all nodes in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. The Kubernetes Controller Manager (kube controller) reads the status values every 10 seconds, by default. If the kube controller cannot read a node status value, it loses contact with that node after a configured period. The default behavior is:
-
The node controller on the control plane updates the node health to
Unhealthyand marks the nodeReadycondition`Unknown`. - In response, the scheduler stops scheduling pods to that node.
-
The Node Lifecycle Controller adds a
node.kubernetes.io/unreachabletaint with aNoExecuteeffect to the node and schedules any pods on the node for eviction after five minutes, by default.
This behavior can cause problems if your network is prone to latency issues, especially if you have nodes at the network edge. In some cases, the Kubernetes Controller Manager might not receive an update from a healthy node due to network latency. The Kubelet evicts pods from the node even though the node is healthy.
To avoid this problem, you can use worker latency profiles to adjust the frequency that the Kubelet and the Kubernetes Controller Manager wait for status updates before taking action. These adjustments help to ensure that your cluster runs properly if network latency between the control plane and the worker nodes is not optimal.
These worker latency profiles contain three sets of parameters that are pre-defined with carefully tuned values to control the reaction of the cluster to increased latency. No need to experimentally find the best values manually.
You can configure worker latency profiles when installing a cluster or at any time you notice increased latency in your cluster network.
6.4.1. Understanding worker latency profiles
Worker latency profiles are four different categories of carefully-tuned parameters. The four parameters which implement these values are node-status-update-frequency, node-monitor-grace-period, default-not-ready-toleration-seconds and default-unreachable-toleration-seconds. These parameters can use values which allow you control the reaction of the cluster to latency issues without needing to determine the best values using manual methods.
Setting these parameters manually is not supported. Incorrect parameter settings adversely affect cluster stability.
All worker latency profiles configure the following parameters:
- node-status-update-frequency
- Specifies how often the kubelet posts node status to the API server.
- node-monitor-grace-period
-
Specifies the amount of time in seconds that the Kubernetes Controller Manager waits for an update from a kubelet before marking the node unhealthy and adding the
node.kubernetes.io/not-readyornode.kubernetes.io/unreachabletaint to the node. - default-not-ready-toleration-seconds
- Specifies the amount of time in seconds after marking a node unhealthy that the Kube API Server Operator waits before evicting pods from that node.
- default-unreachable-toleration-seconds
- Specifies the amount of time in seconds after marking a node unreachable that the Kube API Server Operator waits before evicting pods from that node.
The following Operators monitor the changes to the worker latency profiles and respond accordingly:
-
The Machine Config Operator (MCO) updates the
node-status-update-frequencyparameter on the worker nodes. -
The Kubernetes Controller Manager updates the
node-monitor-grace-periodparameter on the control plane nodes. -
The Kubernetes API Server Operator updates the
default-not-ready-toleration-secondsanddefault-unreachable-toleration-secondsparameters on the control plane nodes.
While the default configuration works in most cases, OpenShift Container Platform offers two other worker latency profiles for situations where the network is experiencing higher latency than usual. The three worker latency profiles are described in the following sections:
- Default worker latency profile
With the
Defaultprofile, eachKubeletupdates it’s status every 10 seconds (node-status-update-frequency). TheKube Controller Managerchecks the statuses ofKubeletevery 5 seconds (node-monitor-grace-period).The Kubernetes Controller Manager waits 40 seconds for a status update from
Kubeletbefore considering theKubeletunhealthy. If no status is made available to the Kubernetes Controller Manager, it then marks the node with thenode.kubernetes.io/not-readyornode.kubernetes.io/unreachabletaint and evicts the pods on that node.If a pod on that node has the
NoExecutetaint, the pod is run according totolerationSeconds. If the pod has no taint, it will be evicted in 300 seconds (default-not-ready-toleration-secondsanddefault-unreachable-toleration-secondssettings of theKube API Server).Expand Profile Component Parameter Value Default
kubelet
node-status-update-frequency10s
Kubelet Controller Manager
node-monitor-grace-period40s
Kubernetes API Server Operator
default-not-ready-toleration-seconds300s
Kubernetes API Server Operator
default-unreachable-toleration-seconds300s
- Medium worker latency profile
Use the
MediumUpdateAverageReactionprofile if the network latency is slightly higher than usual.The
MediumUpdateAverageReactionprofile reduces the frequency of kubelet updates to 20 seconds and changes the period that the Kubernetes Controller Manager waits for those updates to 2 minutes. The pod eviction period for a pod on that node is reduced to 60 seconds. If the pod has thetolerationSecondsparameter, the eviction waits for the period specified by that parameter.The Kubernetes Controller Manager waits for 2 minutes to consider a node unhealthy. In another minute, the eviction process starts.
Expand Profile Component Parameter Value MediumUpdateAverageReaction
kubelet
node-status-update-frequency20s
Kubelet Controller Manager
node-monitor-grace-period2m
Kubernetes API Server Operator
default-not-ready-toleration-seconds60s
Kubernetes API Server Operator
default-unreachable-toleration-seconds60s
- Low worker latency profile
Use the
LowUpdateSlowReactionprofile if the network latency is extremely high.The
LowUpdateSlowReactionprofile reduces the frequency of kubelet updates to 1 minute and changes the period that the Kubernetes Controller Manager waits for those updates to 5 minutes. The pod eviction period for a pod on that node is reduced to 60 seconds. If the pod has thetolerationSecondsparameter, the eviction waits for the period specified by that parameter.The Kubernetes Controller Manager waits for 5 minutes to consider a node unhealthy. In another minute, the eviction process starts.
Expand Profile Component Parameter Value LowUpdateSlowReaction
kubelet
node-status-update-frequency1m
Kubelet Controller Manager
node-monitor-grace-period5m
Kubernetes API Server Operator
default-not-ready-toleration-seconds60s
Kubernetes API Server Operator
default-unreachable-toleration-seconds60s
6.4.2. Using and changing worker latency profiles
To change a worker latency profile to deal with network latency, edit the node.config object to add the name of the profile. You can change the profile at any time as latency increases or decreases.
You must move one worker latency profile at a time. For example, you cannot move directly from the Default profile to the LowUpdateSlowReaction worker latency profile. You must move from the Default worker latency profile to the MediumUpdateAverageReaction profile first, then to LowUpdateSlowReaction. Similarly, when returning to the Default profile, you must move from the low profile to the medium profile first, then to Default.
You can also configure worker latency profiles upon installing an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
To move from the default worker latency profile:
Move to the medium worker latency profile:
Edit the
node.configobject:oc edit nodes.config/cluster
$ oc edit nodes.config/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add
spec.workerLatencyProfile: MediumUpdateAverageReaction:Example
node.configobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the medium worker latency policy.
Scheduling on each worker node is disabled as the change is being applied.
Optional: Move to the low worker latency profile:
Edit the
node.configobject:oc edit nodes.config/cluster
$ oc edit nodes.config/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change the
spec.workerLatencyProfilevalue toLowUpdateSlowReaction:Example
node.configobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies use of the low worker latency policy.
Scheduling on each worker node is disabled as the change is being applied.
Verification
When all nodes return to the
Readycondition, you can use the following command to look in the Kubernetes Controller Manager to ensure it was applied:oc get KubeControllerManager -o yaml | grep -i workerlatency -A 5 -B 5
$ oc get KubeControllerManager -o yaml | grep -i workerlatency -A 5 -B 5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies that the profile is applied and active.
To change the medium profile to default or change the default to medium, edit the node.config object and set the spec.workerLatencyProfile parameter to the appropriate value.
6.5. Creating infrastructure machine sets for production environments
You can create a machine set to create machines that host only infrastructure components, such as the default router, the integrated container image registry, and components for cluster metrics and monitoring. These infrastructure machines are not counted toward the total number of subscriptions that are required to run the environment.
In a production deployment, it is recommended that you deploy at least three machine sets to hold infrastructure components. Both OpenShift Logging and Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh deploy Elasticsearch, which requires three instances to be installed on different nodes. Each of these nodes can be deployed to different availability zones for high availability. A configuration like this requires three different machine sets, one for each availability zone. In global Azure regions that do not have multiple availability zones, you can use availability sets to ensure high availability.
For information on infrastructure nodes and which components can run on infrastructure nodes, see Creating infrastructure machine sets.
To create an infrastructure node, you can use a machine set, post_installation_configuration/cluster-tasks.adoc#creating-an-infra-node_post-install-cluster-tasks[assign a label to the nodes], or use a machine config pool.
For sample machine sets that you can use with these procedures, see Creating machine sets for different clouds.
Applying a specific node selector to all infrastructure components causes OpenShift Container Platform to schedule those workloads on nodes with that label.
6.5.1. Creating a machine set
In addition to the compute machine sets created by the installation program, you can create your own to dynamically manage the machine compute resources for specific workloads of your choice.
Prerequisites
- Deploy an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to
ocas a user withcluster-adminpermission.
Procedure
Create a new YAML file that contains the machine set custom resource (CR) sample and is named
<file_name>.yaml.Ensure that you set the
<clusterID>and<role>parameter values.Optional: If you are not sure which value to set for a specific field, you can check an existing compute machine set from your cluster.
To list the compute machine sets in your cluster, run the following command:
oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view values of a specific compute machine set custom resource (CR), run the following command:
oc get machineset <machineset_name> \ -n openshift-machine-api -o yaml
$ oc get machineset <machineset_name> \ -n openshift-machine-api -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The cluster infrastructure ID.
- 2
- A default node label.Note
For clusters that have user-provisioned infrastructure, a compute machine set can only create
workerandinfratype machines. - 3
- The values in the
<providerSpec>section of the compute machine set CR are platform-specific. For more information about<providerSpec>parameters in the CR, see the sample compute machine set CR configuration for your provider.
Create a
MachineSetCR by running the following command:oc create -f <file_name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
View the list of compute machine sets by running the following command:
oc get machineset -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machineset -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When the new machine set is available, the
DESIREDandCURRENTvalues match. If the machine set is not available, wait a few minutes and run the command again.
6.5.2. Creating an infrastructure node
See Creating infrastructure machine sets for installer-provisioned infrastructure environments or for any cluster where the control plane nodes are managed by the machine API.
Requirements of the cluster dictate that infrastructure, also called infra nodes, be provisioned. The installer only provides provisions for control plane and worker nodes. Worker nodes can be designated as infrastructure nodes or application, also called app, nodes through labeling.
Procedure
Add a label to the worker node that you want to act as application node:
oc label node <node-name> node-role.kubernetes.io/app=""
$ oc label node <node-name> node-role.kubernetes.io/app=""Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a label to the worker nodes that you want to act as infrastructure nodes:
oc label node <node-name> node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=""
$ oc label node <node-name> node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=""Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check to see if applicable nodes now have the
infrarole andapproles:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a default cluster-wide node selector. The default node selector is applied to pods created in all namespaces. This creates an intersection with any existing node selectors on a pod, which additionally constrains the pod’s selector.
ImportantIf the default node selector key conflicts with the key of a pod’s label, then the default node selector is not applied.
However, do not set a default node selector that might cause a pod to become unschedulable. For example, setting the default node selector to a specific node role, such as
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra="", when a pod’s label is set to a different node role, such asnode-role.kubernetes.io/master="", can cause the pod to become unschedulable. For this reason, use caution when setting the default node selector to specific node roles.You can alternatively use a project node selector to avoid cluster-wide node selector key conflicts.
Edit the
Schedulerobject:oc edit scheduler cluster
$ oc edit scheduler clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
defaultNodeSelectorfield with the appropriate node selector:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This example node selector deploys pods on nodes in the
us-east-1region by default.
- Save the file to apply the changes.
You can now move infrastructure resources to the newly labeled infra nodes.
6.5.3. Creating a machine config pool for infrastructure machines
If you need infrastructure machines to have dedicated configurations, you must create an infra pool.
Procedure
Add a label to the node you want to assign as the infra node with a specific label:
oc label node <node_name> <label>
$ oc label node <node_name> <label>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc label node ci-ln-n8mqwr2-f76d1-xscn2-worker-c-6fmtx node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=
$ oc label node ci-ln-n8mqwr2-f76d1-xscn2-worker-c-6fmtx node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a machine config pool that contains both the worker role and your custom role as machine config selector:
cat infra.mcp.yaml
$ cat infra.mcp.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteCustom machine config pools inherit machine configs from the worker pool. Custom pools use any machine config targeted for the worker pool, but add the ability to also deploy changes that are targeted at only the custom pool. Because a custom pool inherits resources from the worker pool, any change to the worker pool also affects the custom pool.
After you have the YAML file, you can create the machine config pool:
oc create -f infra.mcp.yaml
$ oc create -f infra.mcp.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the machine configs to ensure that the infrastructure configuration rendered successfully:
oc get machineconfig
$ oc get machineconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You should see a new machine config, with the
rendered-infra-*prefix.Optional: To deploy changes to a custom pool, create a machine config that uses the custom pool name as the label, such as
infra. Note that this is not required and only shown for instructional purposes. In this manner, you can apply any custom configurations specific to only your infra nodes.NoteAfter you create the new machine config pool, the MCO generates a new rendered config for that pool, and associated nodes of that pool reboot to apply the new configuration.
Create a machine config:
cat infra.mc.yaml
$ cat infra.mc.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add the label you added to the node as a
nodeSelector.
Apply the machine config to the infra-labeled nodes:
oc create -f infra.mc.yaml
$ oc create -f infra.mc.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Confirm that your new machine config pool is available:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE infra rendered-infra-60e35c2e99f42d976e084fa94da4d0fc True False False 1 1 1 0 4m20s master rendered-master-9360fdb895d4c131c7c4bebbae099c90 True False False 3 3 3 0 91m worker rendered-worker-60e35c2e99f42d976e084fa94da4d0fc True False False 2 2 2 0 91m
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE infra rendered-infra-60e35c2e99f42d976e084fa94da4d0fc True False False 1 1 1 0 4m20s master rendered-master-9360fdb895d4c131c7c4bebbae099c90 True False False 3 3 3 0 91m worker rendered-worker-60e35c2e99f42d976e084fa94da4d0fc True False False 2 2 2 0 91mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, a worker node was changed to an infra node.
6.6. Assigning machine set resources to infrastructure nodes
After creating an infrastructure machine set, the worker and infra roles are applied to new infra nodes. Nodes with the infra role are not counted toward the total number of subscriptions that are required to run the environment, even when the worker role is also applied.
However, when an infra node is assigned the worker role, there is a chance that user workloads can get assigned inadvertently to the infra node. To avoid this, you can apply a taint to the infra node and tolerations for the pods that you want to control.
6.6.1. Binding infrastructure node workloads using taints and tolerations
If you have an infra node that has the infra and worker roles assigned, you must configure the node so that user workloads are not assigned to it.
It is recommended that you preserve the dual infra,worker label that is created for infra nodes and use taints and tolerations to manage nodes that user workloads are scheduled on. If you remove the worker label from the node, you must create a custom pool to manage it. A node with a label other than master or worker is not recognized by the MCO without a custom pool. Maintaining the worker label allows the node to be managed by the default worker machine config pool, if no custom pools that select the custom label exists. The infra label communicates to the cluster that it does not count toward the total number of subscriptions.
Prerequisites
-
Configure additional
MachineSetobjects in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
Add a taint to the infra node to prevent scheduling user workloads on it:
Determine if the node has the taint:
oc describe nodes <node_name>
$ oc describe nodes <node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example shows that the node has a taint. You can proceed with adding a toleration to your pod in the next step.
If you have not configured a taint to prevent scheduling user workloads on it:
oc adm taint nodes <node_name> <key>=<value>:<effect>
$ oc adm taint nodes <node_name> <key>=<value>:<effect>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc adm taint nodes node1 node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=reserved:NoExecute
$ oc adm taint nodes node1 node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=reserved:NoExecuteCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the taint:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example places a taint on
node1that has keynode-role.kubernetes.io/infraand taint effectNoSchedule. Nodes with theNoScheduleeffect schedule only pods that tolerate the taint, but allow existing pods to remain scheduled on the node.NoteIf a descheduler is used, pods violating node taints could be evicted from the cluster.
Add tolerations for the pod configurations you want to schedule on the infra node, like router, registry, and monitoring workloads. Add the following code to the
Podobject specification:tolerations: - effect: NoExecute key: node-role.kubernetes.io/infra operator: Exists value: reservedtolerations: - effect: NoExecute1 key: node-role.kubernetes.io/infra2 operator: Exists3 value: reserved4 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This toleration matches the taint created by the
oc adm taintcommand. A pod with this toleration can be scheduled onto the infra node.NoteMoving pods for an Operator installed via OLM to an infra node is not always possible. The capability to move Operator pods depends on the configuration of each Operator.
- Schedule the pod to the infra node using a scheduler. See the documentation for Controlling pod placement onto nodes for details.
6.7. Moving resources to infrastructure machine sets
Some of the infrastructure resources are deployed in your cluster by default. You can move them to the infrastructure machine sets that you created.
6.7.1. Moving the router
You can deploy the router pod to a different machine set. By default, the pod is deployed to a worker node.
Prerequisites
- Configure additional machine sets in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
View the
IngressControllercustom resource for the router Operator:oc get ingresscontroller default -n openshift-ingress-operator -o yaml
$ oc get ingresscontroller default -n openshift-ingress-operator -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command output resembles the following text:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
ingresscontrollerresource and change thenodeSelectorto use theinfralabel:oc edit ingresscontroller default -n openshift-ingress-operator
$ oc edit ingresscontroller default -n openshift-ingress-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add a
nodeSelectorparameter with the appropriate value to the component you want to move. You can use anodeSelectorin the format shown or use<key>: <value>pairs, based on the value specified for the node. If you added a taint to the infrastructure node, also add a matching toleration.
Confirm that the router pod is running on the
infranode.View the list of router pods and note the node name of the running pod:
oc get pod -n openshift-ingress -o wide
$ oc get pod -n openshift-ingress -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES router-default-86798b4b5d-bdlvd 1/1 Running 0 28s 10.130.2.4 ip-10-0-217-226.ec2.internal <none> <none> router-default-955d875f4-255g8 0/1 Terminating 0 19h 10.129.2.4 ip-10-0-148-172.ec2.internal <none> <none>
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES router-default-86798b4b5d-bdlvd 1/1 Running 0 28s 10.130.2.4 ip-10-0-217-226.ec2.internal <none> <none> router-default-955d875f4-255g8 0/1 Terminating 0 19h 10.129.2.4 ip-10-0-148-172.ec2.internal <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the running pod is on the
ip-10-0-217-226.ec2.internalnode.View the node status of the running pod:
oc get node <node_name>
$ oc get node <node_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the
<node_name>that you obtained from the pod list.
Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-217-226.ec2.internal Ready infra,worker 17h v1.24.0
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-10-0-217-226.ec2.internal Ready infra,worker 17h v1.24.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Because the role list includes
infra, the pod is running on the correct node.
6.7.2. Moving the default registry
You configure the registry Operator to deploy its pods to different nodes.
Prerequisites
- Configure additional machine sets in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Procedure
View the
config/instanceobject:oc get configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
config/instanceobject:oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add a
nodeSelectorparameter with the appropriate value to the component you want to move. You can use anodeSelectorin the format shown or use<key>: <value>pairs, based on the value specified for the node. If you added a taint to the infrasructure node, also add a matching toleration.
Verify the registry pod has been moved to the infrastructure node.
Run the following command to identify the node where the registry pod is located:
oc get pods -o wide -n openshift-image-registry
$ oc get pods -o wide -n openshift-image-registryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm the node has the label you specified:
oc describe node <node_name>
$ oc describe node <node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the command output and confirm that
node-role.kubernetes.io/infrais in theLABELSlist.
6.7.3. Moving the monitoring solution
The monitoring stack includes multiple components, including Prometheus, Thanos Querier, and Alertmanager. The Cluster Monitoring Operator manages this stack. To redeploy the monitoring stack to infrastructure nodes, you can create and apply a custom config map.
Procedure
Edit the
cluster-monitoring-configconfig map and change thenodeSelectorto use theinfralabel:oc edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config -n openshift-monitoring
$ oc edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config -n openshift-monitoringCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add a
nodeSelectorparameter with the appropriate value to the component you want to move. You can use anodeSelectorin the format shown or use<key>: <value>pairs, based on the value specified for the node. If you added a taint to the infrasructure node, also add a matching toleration.
Watch the monitoring pods move to the new machines:
watch 'oc get pod -n openshift-monitoring -o wide'
$ watch 'oc get pod -n openshift-monitoring -o wide'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If a component has not moved to the
infranode, delete the pod with this component:oc delete pod -n openshift-monitoring <pod>
$ oc delete pod -n openshift-monitoring <pod>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The component from the deleted pod is re-created on the
infranode.
6.7.4. Moving logging resources
You can configure the Red Hat OpenShift Logging Operator to deploy the pods for logging components, such as Elasticsearch and Kibana, to different nodes. You cannot move the Red Hat OpenShift Logging Operator pod from its installed location.
For example, you can move the Elasticsearch pods to a separate node because of high CPU, memory, and disk requirements.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the Red Hat OpenShift Logging Operator and the OpenShift Elasticsearch Operator.
Procedure
Edit the
ClusterLoggingcustom resource (CR) in theopenshift-loggingproject:oc edit ClusterLogging instance
$ oc edit ClusterLogging instanceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
ClusterLoggingCRCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that a component has moved, you can use the oc get pod -o wide command.
For example:
You want to move the Kibana pod from the
ip-10-0-147-79.us-east-2.compute.internalnode:oc get pod kibana-5b8bdf44f9-ccpq9 -o wide
$ oc get pod kibana-5b8bdf44f9-ccpq9 -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES kibana-5b8bdf44f9-ccpq9 2/2 Running 0 27s 10.129.2.18 ip-10-0-147-79.us-east-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES kibana-5b8bdf44f9-ccpq9 2/2 Running 0 27s 10.129.2.18 ip-10-0-147-79.us-east-2.compute.internal <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You want to move the Kibana pod to the
ip-10-0-139-48.us-east-2.compute.internalnode, a dedicated infrastructure node:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the node has a
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra: ''label:oc get node ip-10-0-139-48.us-east-2.compute.internal -o yaml
$ oc get node ip-10-0-139-48.us-east-2.compute.internal -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To move the Kibana pod, edit the
ClusterLoggingCR to add a node selector:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add a node selector to match the label in the node specification.
After you save the CR, the current Kibana pod is terminated and new pod is deployed:
oc get pods
$ oc get podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The new pod is on the
ip-10-0-139-48.us-east-2.compute.internalnode:oc get pod kibana-7d85dcffc8-bfpfp -o wide
$ oc get pod kibana-7d85dcffc8-bfpfp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES kibana-7d85dcffc8-bfpfp 2/2 Running 0 43s 10.131.0.22 ip-10-0-139-48.us-east-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES kibana-7d85dcffc8-bfpfp 2/2 Running 0 43s 10.131.0.22 ip-10-0-139-48.us-east-2.compute.internal <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After a few moments, the original Kibana pod is removed.
oc get pods
$ oc get podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.8. About the cluster autoscaler
The cluster autoscaler adjusts the size of an OpenShift Container Platform cluster to meet its current deployment needs. It uses declarative, Kubernetes-style arguments to provide infrastructure management that does not rely on objects of a specific cloud provider. The cluster autoscaler has a cluster scope, and is not associated with a particular namespace.
The cluster autoscaler increases the size of the cluster when there are pods that fail to schedule on any of the current worker nodes due to insufficient resources or when another node is necessary to meet deployment needs. The cluster autoscaler does not increase the cluster resources beyond the limits that you specify.
The cluster autoscaler computes the total memory, CPU, and GPU on all nodes the cluster, even though it does not manage the control plane nodes. These values are not single-machine oriented. They are an aggregation of all the resources in the entire cluster. For example, if you set the maximum memory resource limit, the cluster autoscaler includes all the nodes in the cluster when calculating the current memory usage. That calculation is then used to determine if the cluster autoscaler has the capacity to add more worker resources.
Ensure that the maxNodesTotal value in the ClusterAutoscaler resource definition that you create is large enough to account for the total possible number of machines in your cluster. This value must encompass the number of control plane machines and the possible number of compute machines that you might scale to.
Every 10 seconds, the cluster autoscaler checks which nodes are unnecessary in the cluster and removes them. The cluster autoscaler considers a node for removal if the following conditions apply:
-
The node utilization is less than the node utilization level threshold for the cluster. The node utilization level is the sum of the requested resources divided by the allocated resources for the node. If you do not specify a value in the
ClusterAutoscalercustom resource, the cluster autoscaler uses a default value of0.5, which corresponds to 50% utilization. - The cluster autoscaler can move all pods running on the node to the other nodes. The Kubernetes scheduler is responsible for scheduling pods on the nodes.
- The cluster autoscaler does not have scale down disabled annotation.
If the following types of pods are present on a node, the cluster autoscaler will not remove the node:
- Pods with restrictive pod disruption budgets (PDBs).
- Kube-system pods that do not run on the node by default.
- Kube-system pods that do not have a PDB or have a PDB that is too restrictive.
- Pods that are not backed by a controller object such as a deployment, replica set, or stateful set.
- Pods with local storage.
- Pods that cannot be moved elsewhere because of a lack of resources, incompatible node selectors or affinity, matching anti-affinity, and so on.
-
Unless they also have a
"cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/safe-to-evict": "true"annotation, pods that have a"cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/safe-to-evict": "false"annotation.
For example, you set the maximum CPU limit to 64 cores and configure the cluster autoscaler to only create machines that have 8 cores each. If your cluster starts with 30 cores, the cluster autoscaler can add up to 4 more nodes with 32 cores, for a total of 62.
If you configure the cluster autoscaler, additional usage restrictions apply:
- Do not modify the nodes that are in autoscaled node groups directly. All nodes within the same node group have the same capacity and labels and run the same system pods.
- Specify requests for your pods.
- If you have to prevent pods from being deleted too quickly, configure appropriate PDBs.
- Confirm that your cloud provider quota is large enough to support the maximum node pools that you configure.
- Do not run additional node group autoscalers, especially the ones offered by your cloud provider.
The horizontal pod autoscaler (HPA) and the cluster autoscaler modify cluster resources in different ways. The HPA changes the deployment’s or replica set’s number of replicas based on the current CPU load. If the load increases, the HPA creates new replicas, regardless of the amount of resources available to the cluster. If there are not enough resources, the cluster autoscaler adds resources so that the HPA-created pods can run. If the load decreases, the HPA stops some replicas. If this action causes some nodes to be underutilized or completely empty, the cluster autoscaler deletes the unnecessary nodes.
The cluster autoscaler takes pod priorities into account. The Pod Priority and Preemption feature enables scheduling pods based on priorities if the cluster does not have enough resources, but the cluster autoscaler ensures that the cluster has resources to run all pods. To honor the intention of both features, the cluster autoscaler includes a priority cutoff function. You can use this cutoff to schedule "best-effort" pods, which do not cause the cluster autoscaler to increase resources but instead run only when spare resources are available.
Pods with priority lower than the cutoff value do not cause the cluster to scale up or prevent the cluster from scaling down. No new nodes are added to run the pods, and nodes running these pods might be deleted to free resources.
Cluster autoscaling is supported for the platforms that have machine API available on it.
6.8.1. Cluster autoscaler resource definition
This ClusterAutoscaler resource definition shows the parameters and sample values for the cluster autoscaler.
- 1
- Specify the priority that a pod must exceed to cause the cluster autoscaler to deploy additional nodes. Enter a 32-bit integer value. The
podPriorityThresholdvalue is compared to the value of thePriorityClassthat you assign to each pod. - 2
- Specify the maximum number of nodes to deploy. This value is the total number of machines that are deployed in your cluster, not just the ones that the autoscaler controls. Ensure that this value is large enough to account for all of your control plane and compute machines and the total number of replicas that you specify in your
MachineAutoscalerresources. - 3
- Specify the minimum number of cores to deploy in the cluster.
- 4
- Specify the maximum number of cores to deploy in the cluster.
- 5
- Specify the minimum amount of memory, in GiB, in the cluster.
- 6
- Specify the maximum amount of memory, in GiB, in the cluster.
- 7
- Optional: Specify the type of GPU node to deploy. Only
nvidia.com/gpuandamd.com/gpuare valid types. - 8
- Specify the minimum number of GPUs to deploy in the cluster.
- 9
- Specify the maximum number of GPUs to deploy in the cluster.
- 10
- In this section, you can specify the period to wait for each action by using any valid ParseDuration interval, including
ns,us,ms,s,m, andh. - 11
- Specify whether the cluster autoscaler can remove unnecessary nodes.
- 12
- Optional: Specify the period to wait before deleting a node after a node has recently been added. If you do not specify a value, the default value of
10mis used. - 13
- Optional: Specify the period to wait before deleting a node after a node has recently been deleted. If you do not specify a value, the default value of
0sis used. - 14
- Optional: Specify the period to wait before deleting a node after a scale down failure occurred. If you do not specify a value, the default value of
3mis used. - 15
- Optional: Specify the period before an unnecessary node is eligible for deletion. If you do not specify a value, the default value of
10mis used. - 16
- Optional: Specify the node utilization level below which an unnecessary node is eligible for deletion. The node utilization level is the sum of the requested resources divided by the allocated resources for the node, and must be a value greater than
"0"but less than"1". If you do not specify a value, the cluster autoscaler uses a default value of"0.5", which corresponds to 50% utilization. This value must be expressed as a string.
When performing a scaling operation, the cluster autoscaler remains within the ranges set in the ClusterAutoscaler resource definition, such as the minimum and maximum number of cores to deploy or the amount of memory in the cluster. However, the cluster autoscaler does not correct the current values in your cluster to be within those ranges.
The minimum and maximum CPUs, memory, and GPU values are determined by calculating those resources on all nodes in the cluster, even if the cluster autoscaler does not manage the nodes. For example, the control plane nodes are considered in the total memory in the cluster, even though the cluster autoscaler does not manage the control plane nodes.
6.8.2. Deploying a cluster autoscaler
To deploy a cluster autoscaler, you create an instance of the ClusterAutoscaler resource.
Procedure
-
Create a YAML file for a
ClusterAutoscalerresource that contains the custom resource definition. Create the custom resource in the cluster by running the following command:
oc create -f <filename>.yaml
$ oc create -f <filename>.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
<filename>is the name of the custom resource file.
6.9. About the machine autoscaler
The machine autoscaler adjusts the number of Machines in the machine sets that you deploy in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. You can scale both the default worker machine set and any other machine sets that you create. The machine autoscaler makes more Machines when the cluster runs out of resources to support more deployments. Any changes to the values in MachineAutoscaler resources, such as the minimum or maximum number of instances, are immediately applied to the machine set they target.
You must deploy a machine autoscaler for the cluster autoscaler to scale your machines. The cluster autoscaler uses the annotations on machine sets that the machine autoscaler sets to determine the resources that it can scale. If you define a cluster autoscaler without also defining machine autoscalers, the cluster autoscaler will never scale your cluster.
6.9.1. Machine autoscaler resource definition
This MachineAutoscaler resource definition shows the parameters and sample values for the machine autoscaler.
- 1
- Specify the machine autoscaler name. To make it easier to identify which machine set this machine autoscaler scales, specify or include the name of the machine set to scale. The machine set name takes the following form:
<clusterid>-<machineset>-<region>. - 2
- Specify the minimum number machines of the specified type that must remain in the specified zone after the cluster autoscaler initiates cluster scaling. If running in AWS, GCP, Azure, RHOSP, or vSphere, this value can be set to
0. For other providers, do not set this value to0.You can save on costs by setting this value to
0for use cases such as running expensive or limited-usage hardware that is used for specialized workloads, or by scaling a machine set with extra large machines. The cluster autoscaler scales the machine set down to zero if the machines are not in use.ImportantDo not set the
spec.minReplicasvalue to0for the three compute machine sets that are created during the OpenShift Container Platform installation process for an installer provisioned infrastructure. - 3
- Specify the maximum number machines of the specified type that the cluster autoscaler can deploy in the specified zone after it initiates cluster scaling. Ensure that the
maxNodesTotalvalue in theClusterAutoscalerresource definition is large enough to allow the machine autoscaler to deploy this number of machines. - 4
- In this section, provide values that describe the existing machine set to scale.
- 5
- The
kindparameter value is alwaysMachineSet. - 6
- The
namevalue must match the name of an existing machine set, as shown in themetadata.nameparameter value.
6.9.2. Deploying a machine autoscaler
To deploy a machine autoscaler, you create an instance of the MachineAutoscaler resource.
Procedure
-
Create a YAML file for a
MachineAutoscalerresource that contains the custom resource definition. Create the custom resource in the cluster by running the following command:
oc create -f <filename>.yaml
$ oc create -f <filename>.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
<filename>is the name of the custom resource file.
6.10. Enabling Technology Preview features using FeatureGates
You can turn on a subset of the current Technology Preview features on for all nodes in the cluster by editing the FeatureGate custom resource (CR).
6.10.1. Understanding feature gates
You can use the FeatureGate custom resource (CR) to enable specific feature sets in your cluster. A feature set is a collection of OpenShift Container Platform features that are not enabled by default.
You can activate the following feature set by using the FeatureGate CR:
TechPreviewNoUpgrade. This feature set is a subset of the current Technology Preview features. This feature set allows you to enable these tech preview features on test clusters, where you can fully test them, while leaving the features disabled on production clusters. Enabling this feature set cannot be undone and prevents minor version updates. This feature set is not recommended on production clusters.WarningEnabling the
TechPreviewNoUpgradefeature set on your cluster cannot be undone and prevents minor version updates. You should not enable this feature set on production clusters.The following Technology Preview features are enabled by this feature set:
- Microsoft Azure File CSI Driver Operator. Enables the provisioning of persistent volumes (PVs) by using the Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver for Microsoft Azure File Storage.
CSI automatic migration. Enables automatic migration for supported in-tree volume plugins to their equivalent Container Storage Interface (CSI) drivers. Supported for:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
- Google Compute Engine Persistent Disk
- Azure File
- VMware vSphere
Cluster Cloud Controller Manager Operator. Enables the Cluster Cloud Controller Manager Operator rather than the in-tree cloud controller. Available as a Technology Preview for:
- Alibaba Cloud
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)
- VMware vSphere
- Shared resource CSI driver
- CSI volume support for the OpenShift Container Platform build system
- Swap memory on nodes
Cluster API. Enables the integrated upstream Cluster API in OpenShift Container Platform with the
ClusterAPIEnabledfeature gate. Available as a Technology Preview for:- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Managing alerting rules for core platform monitoring
6.10.2. Enabling feature sets using the web console
You can use the OpenShift Container Platform web console to enable feature sets for all of the nodes in a cluster by editing the FeatureGate custom resource (CR).
Procedure
To enable feature sets:
- In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, switch to the Administration → Custom Resource Definitions page.
- On the Custom Resource Definitions page, click FeatureGate.
- On the Custom Resource Definition Details page, click the Instances tab.
- Click the cluster feature gate, then click the YAML tab.
Edit the cluster instance to add specific feature sets:
WarningEnabling the
TechPreviewNoUpgradefeature set on your cluster cannot be undone and prevents minor version updates. You should not enable this feature set on production clusters.Sample Feature Gate custom resource
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you save the changes, new machine configs are created, the machine config pools are updated, and scheduling on each node is disabled while the change is being applied.
Verification
You can verify that the feature gates are enabled by looking at the kubelet.conf file on a node after the nodes return to the ready state.
- From the Administrator perspective in the web console, navigate to Compute → Nodes.
- Select a node.
- In the Node details page, click Terminal.
In the terminal window, change your root directory to
/host:chroot /host
sh-4.2# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the
kubelet.conffile:cat /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf
sh-4.2# cat /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
# ... featureGates: InsightsOperatorPullingSCA: true, LegacyNodeRoleBehavior: false # ...
# ... featureGates: InsightsOperatorPullingSCA: true, LegacyNodeRoleBehavior: false # ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The features that are listed as
trueare enabled on your cluster.NoteThe features listed vary depending upon the OpenShift Container Platform version.
6.10.3. Enabling feature sets using the CLI
You can use the OpenShift CLI (oc) to enable feature sets for all of the nodes in a cluster by editing the FeatureGate custom resource (CR).
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
To enable feature sets:
Edit the
FeatureGateCR namedcluster:oc edit featuregate cluster
$ oc edit featuregate clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningEnabling the
TechPreviewNoUpgradefeature set on your cluster cannot be undone and prevents minor version updates. You should not enable this feature set on production clusters.Sample FeatureGate custom resource
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you save the changes, new machine configs are created, the machine config pools are updated, and scheduling on each node is disabled while the change is being applied.
Verification
You can verify that the feature gates are enabled by looking at the kubelet.conf file on a node after the nodes return to the ready state.
- From the Administrator perspective in the web console, navigate to Compute → Nodes.
- Select a node.
- In the Node details page, click Terminal.
In the terminal window, change your root directory to
/host:chroot /host
sh-4.2# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the
kubelet.conffile:cat /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf
sh-4.2# cat /etc/kubernetes/kubelet.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
# ... featureGates: InsightsOperatorPullingSCA: true, LegacyNodeRoleBehavior: false # ...
# ... featureGates: InsightsOperatorPullingSCA: true, LegacyNodeRoleBehavior: false # ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The features that are listed as
trueare enabled on your cluster.NoteThe features listed vary depending upon the OpenShift Container Platform version.
6.11. etcd tasks
Back up etcd, enable or disable etcd encryption, or defragment etcd data.
6.11.1. About etcd encryption
By default, etcd data is not encrypted in OpenShift Container Platform. You can enable etcd encryption for your cluster to provide an additional layer of data security. For example, it can help protect the loss of sensitive data if an etcd backup is exposed to the incorrect parties.
When you enable etcd encryption, the following OpenShift API server and Kubernetes API server resources are encrypted:
- Secrets
- Config maps
- Routes
- OAuth access tokens
- OAuth authorize tokens
When you enable etcd encryption, encryption keys are created. These keys are rotated on a weekly basis. You must have these keys to restore from an etcd backup.
Etcd encryption only encrypts values, not keys. Resource types, namespaces, and object names are unencrypted.
If etcd encryption is enabled during a backup, the static_kuberesources_<datetimestamp>.tar.gz file contains the encryption keys for the etcd snapshot. For security reasons, store this file separately from the etcd snapshot. However, this file is required to restore a previous state of etcd from the respective etcd snapshot.
6.11.2. Enabling etcd encryption
You can enable etcd encryption to encrypt sensitive resources in your cluster.
Do not back up etcd resources until the initial encryption process is completed. If the encryption process is not completed, the backup might be only partially encrypted.
After you enable etcd encryption, several changes can occur:
- The etcd encryption might affect the memory consumption of a few resources.
- You might notice a transient affect on backup performance because the leader must serve the backup.
- A disk I/O can affect the node that receives the backup state.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Modify the
APIServerobject:oc edit apiserver
$ oc edit apiserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
encryptionfield type toaescbc:spec: encryption: type: aescbcspec: encryption: type: aescbc1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aescbctype means that AES-CBC with PKCS#7 padding and a 32 byte key is used to perform the encryption.
Save the file to apply the changes.
The encryption process starts. It can take 20 minutes or longer for this process to complete, depending on the size of your cluster.
Verify that etcd encryption was successful.
Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the OpenShift API server to verify that its resources were successfully encrypted:oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
EncryptionCompletedupon successful encryption:EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: routes.route.openshift.io
EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: routes.route.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
EncryptionInProgress, encryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the Kubernetes API server to verify that its resources were successfully encrypted:oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
EncryptionCompletedupon successful encryption:EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: secrets, configmaps
EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: secrets, configmapsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
EncryptionInProgress, encryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the OpenShift OAuth API server to verify that its resources were successfully encrypted:oc get authentication.operator.openshift.io -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get authentication.operator.openshift.io -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
EncryptionCompletedupon successful encryption:EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: oauthaccesstokens.oauth.openshift.io, oauthauthorizetokens.oauth.openshift.io
EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: oauthaccesstokens.oauth.openshift.io, oauthauthorizetokens.oauth.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
EncryptionInProgress, encryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.
6.11.3. Disabling etcd encryption
You can disable encryption of etcd data in your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Modify the
APIServerobject:oc edit apiserver
$ oc edit apiserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
encryptionfield type toidentity:spec: encryption: type: identityspec: encryption: type: identity1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
identitytype is the default value and means that no encryption is performed.
Save the file to apply the changes.
The decryption process starts. It can take 20 minutes or longer for this process to complete, depending on the size of your cluster.
Verify that etcd decryption was successful.
Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the OpenShift API server to verify that its resources were successfully decrypted:oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
DecryptionCompletedupon successful decryption:DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decrypted
DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decryptedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
DecryptionInProgress, decryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the Kubernetes API server to verify that its resources were successfully decrypted:oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
DecryptionCompletedupon successful decryption:DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decrypted
DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decryptedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
DecryptionInProgress, decryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the OpenShift OAuth API server to verify that its resources were successfully decrypted:oc get authentication.operator.openshift.io -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get authentication.operator.openshift.io -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
DecryptionCompletedupon successful decryption:DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decrypted
DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decryptedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
DecryptionInProgress, decryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.
6.11.4. Backing up etcd data
Follow these steps to back up etcd data by creating an etcd snapshot and backing up the resources for the static pods. This backup can be saved and used at a later time if you need to restore etcd.
Only save a backup from a single control plane host. Do not take a backup from each control plane host in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. You have checked whether the cluster-wide proxy is enabled.
TipYou can check whether the proxy is enabled by reviewing the output of
oc get proxy cluster -o yaml. The proxy is enabled if thehttpProxy,httpsProxy, andnoProxyfields have values set.
Procedure
Start a debug session for a control plane node:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change your root directory to
/host:chroot /host
sh-4.2# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
If the cluster-wide proxy is enabled, be sure that you have exported the
NO_PROXY,HTTP_PROXY, andHTTPS_PROXYenvironment variables. Run the
cluster-backup.shscript and pass in the location to save the backup to.TipThe
cluster-backup.shscript is maintained as a component of the etcd Cluster Operator and is a wrapper around theetcdctl snapshot savecommand./usr/local/bin/cluster-backup.sh /home/core/assets/backup
sh-4.4# /usr/local/bin/cluster-backup.sh /home/core/assets/backupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example script output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, two files are created in the
/home/core/assets/backup/directory on the control plane host:-
snapshot_<datetimestamp>.db: This file is the etcd snapshot. Thecluster-backup.shscript confirms its validity. static_kuberesources_<datetimestamp>.tar.gz: This file contains the resources for the static pods. If etcd encryption is enabled, it also contains the encryption keys for the etcd snapshot.NoteIf etcd encryption is enabled, it is recommended to store this second file separately from the etcd snapshot for security reasons. However, this file is required to restore from the etcd snapshot.
Keep in mind that etcd encryption only encrypts values, not keys. This means that resource types, namespaces, and object names are unencrypted.
-
6.11.5. Defragmenting etcd data
For large and dense clusters, etcd can suffer from poor performance if the keyspace grows too large and exceeds the space quota. Periodically maintain and defragment etcd to free up space in the data store. Monitor Prometheus for etcd metrics and defragment it when required; otherwise, etcd can raise a cluster-wide alarm that puts the cluster into a maintenance mode that accepts only key reads and deletes.
Monitor these key metrics:
-
etcd_server_quota_backend_bytes, which is the current quota limit -
etcd_mvcc_db_total_size_in_use_in_bytes, which indicates the actual database usage after a history compaction -
etcd_mvcc_db_total_size_in_bytes, which shows the database size, including free space waiting for defragmentation
Defragment etcd data to reclaim disk space after events that cause disk fragmentation, such as etcd history compaction.
History compaction is performed automatically every five minutes and leaves gaps in the back-end database. This fragmented space is available for use by etcd, but is not available to the host file system. You must defragment etcd to make this space available to the host file system.
Defragmentation occurs automatically, but you can also trigger it manually.
Automatic defragmentation is good for most cases, because the etcd operator uses cluster information to determine the most efficient operation for the user.
6.11.5.1. Automatic defragmentation
The etcd Operator automatically defragments disks. No manual intervention is needed.
Verify that the defragmentation process is successful by viewing one of these logs:
- etcd logs
- cluster-etcd-operator pod
- operator status error log
Automatic defragmentation can cause leader election failure in various OpenShift core components, such as the Kubernetes controller manager, which triggers a restart of the failing component. The restart is harmless and either triggers failover to the next running instance or the component resumes work again after the restart.
Example log output for successful defragmentation
etcd member has been defragmented: <member_name>, memberID: <member_id>
etcd member has been defragmented: <member_name>, memberID: <member_id>Example log output for unsuccessful defragmentation
failed defrag on member: <member_name>, memberID: <member_id>: <error_message>
failed defrag on member: <member_name>, memberID: <member_id>: <error_message>6.11.5.2. Manual defragmentation
A Prometheus alert indicates when you need to use manual defragmentation. The alert is displayed in two cases:
- When etcd uses more than 50% of its available space for more than 10 minutes
- When etcd is actively using less than 50% of its total database size for more than 10 minutes
You can also determine whether defragmentation is needed by checking the etcd database size in MB that will be freed by defragmentation with the PromQL expression: (etcd_mvcc_db_total_size_in_bytes - etcd_mvcc_db_total_size_in_use_in_bytes)/1024/1024
Defragmenting etcd is a blocking action. The etcd member will not respond until defragmentation is complete. For this reason, wait at least one minute between defragmentation actions on each of the pods to allow the cluster to recover.
Follow this procedure to defragment etcd data on each etcd member.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Determine which etcd member is the leader, because the leader should be defragmented last.
Get the list of etcd pods:
oc -n openshift-etcd get pods -l k8s-app=etcd -o wide
$ oc -n openshift-etcd get pods -l k8s-app=etcd -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
etcd-ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com 3/3 Running 0 175m 10.0.159.225 ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com <none> <none> etcd-ip-10-0-191-37.example.redhat.com 3/3 Running 0 173m 10.0.191.37 ip-10-0-191-37.example.redhat.com <none> <none> etcd-ip-10-0-199-170.example.redhat.com 3/3 Running 0 176m 10.0.199.170 ip-10-0-199-170.example.redhat.com <none> <none>
etcd-ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com 3/3 Running 0 175m 10.0.159.225 ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com <none> <none> etcd-ip-10-0-191-37.example.redhat.com 3/3 Running 0 173m 10.0.191.37 ip-10-0-191-37.example.redhat.com <none> <none> etcd-ip-10-0-199-170.example.redhat.com 3/3 Running 0 176m 10.0.199.170 ip-10-0-199-170.example.redhat.com <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Choose a pod and run the following command to determine which etcd member is the leader:
oc rsh -n openshift-etcd etcd-ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com etcdctl endpoint status --cluster -w table
$ oc rsh -n openshift-etcd etcd-ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com etcdctl endpoint status --cluster -w tableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Based on the
IS LEADERcolumn of this output, thehttps://10.0.199.170:2379endpoint is the leader. Matching this endpoint with the output of the previous step, the pod name of the leader isetcd-ip-10-0-199-170.example.redhat.com.
Defragment an etcd member.
Connect to the running etcd container, passing in the name of a pod that is not the leader:
oc rsh -n openshift-etcd etcd-ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.com
$ oc rsh -n openshift-etcd etcd-ip-10-0-159-225.example.redhat.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Unset the
ETCDCTL_ENDPOINTSenvironment variable:unset ETCDCTL_ENDPOINTS
sh-4.4# unset ETCDCTL_ENDPOINTSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Defragment the etcd member:
etcdctl --command-timeout=30s --endpoints=https://localhost:2379 defrag
sh-4.4# etcdctl --command-timeout=30s --endpoints=https://localhost:2379 defragCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Finished defragmenting etcd member[https://localhost:2379]
Finished defragmenting etcd member[https://localhost:2379]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If a timeout error occurs, increase the value for
--command-timeoutuntil the command succeeds.Verify that the database size was reduced:
etcdctl endpoint status -w table --cluster
sh-4.4# etcdctl endpoint status -w table --clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example shows that the database size for this etcd member is now 41 MB as opposed to the starting size of 104 MB.
Repeat these steps to connect to each of the other etcd members and defragment them. Always defragment the leader last.
Wait at least one minute between defragmentation actions to allow the etcd pod to recover. Until the etcd pod recovers, the etcd member will not respond.
If any
NOSPACEalarms were triggered due to the space quota being exceeded, clear them.Check if there are any
NOSPACEalarms:etcdctl alarm list
sh-4.4# etcdctl alarm listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
memberID:12345678912345678912 alarm:NOSPACE
memberID:12345678912345678912 alarm:NOSPACECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Clear the alarms:
etcdctl alarm disarm
sh-4.4# etcdctl alarm disarmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.11.6. Restoring to a previous cluster state
You can use a saved etcd backup to restore a previous cluster state or restore a cluster that has lost the majority of control plane hosts.
If your cluster uses a control plane machine set, see "Troubleshooting the control plane machine set" for a more simple etcd recovery procedure.
When you restore your cluster, you must use an etcd backup that was taken from the same z-stream release. For example, an OpenShift Container Platform 4.7.2 cluster must use an etcd backup that was taken from 4.7.2.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole through a certificate-basedkubeconfigfile, like the one that was used during installation. - A healthy control plane host to use as the recovery host.
- SSH access to control plane hosts.
-
A backup directory containing both the
etcdsnapshot and the resources for the static pods, which were from the same backup. The file names in the directory must be in the following formats:snapshot_<datetimestamp>.dbandstatic_kuberesources_<datetimestamp>.tar.gz.
For non-recovery control plane nodes, it is not required to establish SSH connectivity or to stop the static pods. You can delete and recreate other non-recovery, control plane machines, one by one.
Procedure
- Select a control plane host to use as the recovery host. This is the host that you will run the restore operation on.
Establish SSH connectivity to each of the control plane nodes, including the recovery host.
kube-apiserverbecomes inaccessible after the restore process starts, so you cannot access the control plane nodes. For this reason, it is recommended to establish SSH connectivity to each control plane host in a separate terminal.ImportantIf you do not complete this step, you will not be able to access the control plane hosts to complete the restore procedure, and you will be unable to recover your cluster from this state.
Copy the
etcdbackup directory to the recovery control plane host.This procedure assumes that you copied the
backupdirectory containing theetcdsnapshot and the resources for the static pods to the/home/core/directory of your recovery control plane host.Stop the static pods on any other control plane nodes.
NoteYou do not need to stop the static pods on the recovery host.
- Access a control plane host that is not the recovery host.
Move the existing etcd pod file out of the kubelet manifest directory by running:
sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd-pod.yaml /tmp
$ sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd-pod.yaml /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
etcdpods are stopped by using:sudo crictl ps | grep etcd | egrep -v "operator|etcd-guard"
$ sudo crictl ps | grep etcd | egrep -v "operator|etcd-guard"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output of this command is not empty, wait a few minutes and check again.
Move the existing
kube-apiserverfile out of the kubelet manifest directory by running:sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver-pod.yaml /tmp
$ sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver-pod.yaml /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
kube-apiservercontainers are stopped by running:sudo crictl ps | grep kube-apiserver | egrep -v "operator|guard"
$ sudo crictl ps | grep kube-apiserver | egrep -v "operator|guard"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output of this command is not empty, wait a few minutes and check again.
Move the existing
kube-controller-managerfile out of the kubelet manifest directory by using:sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager-pod.yaml /tmp
$ sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager-pod.yaml /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
kube-controller-managercontainers are stopped by running:sudo crictl ps | grep kube-controller-manager | egrep -v "operator|guard"
$ sudo crictl ps | grep kube-controller-manager | egrep -v "operator|guard"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output of this command is not empty, wait a few minutes and check again.
Move the existing
kube-schedulerfile out of the kubelet manifest directory by using:sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler-pod.yaml /tmp
$ sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-scheduler-pod.yaml /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
kube-schedulercontainers are stopped by using:sudo crictl ps | grep kube-scheduler | egrep -v "operator|guard"
$ sudo crictl ps | grep kube-scheduler | egrep -v "operator|guard"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output of this command is not empty, wait a few minutes and check again.
Move the
etcddata directory to a different location with the following example:sudo mv /var/lib/etcd/ /tmp
$ sudo mv /var/lib/etcd/ /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the
/etc/kubernetes/manifests/keepalived.yamlfile exists, follow these steps:Move the
/etc/kubernetes/manifests/keepalived.yamlfile out of the kubelet manifest directory:sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/keepalived.yaml /tmp
$ sudo mv /etc/kubernetes/manifests/keepalived.yaml /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that any containers managed by the
keepaliveddaemon are stopped:sudo crictl ps --name keepalived
$ sudo crictl ps --name keepalivedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output of this command should be empty. If it is not empty, wait a few minutes and check again.
Check if the control plane has any Virtual IPs (VIPs) assigned to it:
ip -o address | egrep '<api_vip>|<ingress_vip>'
$ ip -o address | egrep '<api_vip>|<ingress_vip>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For each reported VIP, run the following command to remove it:
sudo ip address del <reported_vip> dev <reported_vip_device>
$ sudo ip address del <reported_vip> dev <reported_vip_device>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Repeat this step on each of the other control plane hosts that is not the recovery host.
- Access the recovery control plane host.
If the
keepaliveddaemon is in use, verify that the recovery control plane node owns the VIP:ip -o address | grep <api_vip>
$ ip -o address | grep <api_vip>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The address of the VIP is highlighted in the output if it exists. This command returns an empty string if the VIP is not set or configured incorrectly.
If the cluster-wide proxy is enabled, be sure that you have exported the
NO_PROXY,HTTP_PROXY, andHTTPS_PROXYenvironment variables.TipYou can check whether the proxy is enabled by reviewing the output of
oc get proxy cluster -o yaml. The proxy is enabled if thehttpProxy,httpsProxy, andnoProxyfields have values set.Run the restore script on the recovery control plane host and pass in the path to the
etcdbackup directory:sudo -E /usr/local/bin/cluster-restore.sh /home/core/backup
$ sudo -E /usr/local/bin/cluster-restore.sh /home/core/backupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example script output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The cluster-restore.sh script must show that
etcd,kube-apiserver,kube-controller-manager, andkube-schedulerpods are stopped and then started at the end of the restore process.NoteThe restore process can cause nodes to enter the
NotReadystate if the node certificates were updated after the lastetcdbackup.Check the nodes to ensure they are in the
Readystate.Run the following command:
oc get nodes -w
$ oc get nodes -wCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow It can take several minutes for all nodes to report their state.
If any nodes are in the
NotReadystate, log in to the nodes and remove all of the PEM files from the/var/lib/kubelet/pkidirectory on each node. You can SSH into the nodes or use the terminal window in the web console.ssh -i <ssh-key-path> core@<master-hostname>
$ ssh -i <ssh-key-path> core@<master-hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample
pkidirectorypwd /var/lib/kubelet/pki ls kubelet-client-2022-04-28-11-24-09.pem kubelet-server-2022-04-28-11-24-15.pem kubelet-client-current.pem kubelet-server-current.pem
sh-4.4# pwd /var/lib/kubelet/pki sh-4.4# ls kubelet-client-2022-04-28-11-24-09.pem kubelet-server-2022-04-28-11-24-15.pem kubelet-client-current.pem kubelet-server-current.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Restart the kubelet service on all control plane hosts.
From the recovery host, run:
sudo systemctl restart kubelet.service
$ sudo systemctl restart kubelet.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Repeat this step on all other control plane hosts.
Approve the pending Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs):
NoteClusters with no worker nodes, such as single-node clusters or clusters consisting of three schedulable control plane nodes, will not have any pending CSRs to approve. You can skip all the commands listed in this step.
CSR (for user-provisioned installations). <2> A pending node-bootstrapper CSR.
Review the details of a CSR to verify that it is valid by running:
oc describe csr <csr_name>
$ oc describe csr <csr_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
<csr_name>is the name of a CSR from the list of current CSRs.
Approve each valid
node-bootstrapperCSR by running:oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>
$ oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For user-provisioned installations, approve each valid kubelet service CSR by running:
oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>
$ oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify that the single member control plane has started successfully.
From the recovery host, verify that the
etcdcontainer is running by using:sudo crictl ps | grep etcd | egrep -v "operator|etcd-guard"
$ sudo crictl ps | grep etcd | egrep -v "operator|etcd-guard"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
3ad41b7908e32 36f86e2eeaaffe662df0d21041eb22b8198e0e58abeeae8c743c3e6e977e8009 About a minute ago Running etcd 0 7c05f8af362f0
3ad41b7908e32 36f86e2eeaaffe662df0d21041eb22b8198e0e58abeeae8c743c3e6e977e8009 About a minute ago Running etcd 0 7c05f8af362f0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the recovery host, verify that the
etcdpod is running by using:oc -n openshift-etcd get pods -l k8s-app=etcd
$ oc -n openshift-etcd get pods -l k8s-app=etcdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE etcd-ip-10-0-143-125.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 1 2m47s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE etcd-ip-10-0-143-125.ec2.internal 1/1 Running 1 2m47sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the status is
Pending, or the output lists more than one runningetcdpod, wait a few minutes and check again.-
If you are using the
OVNKubernetesnetwork plugin, you must restartovnkube-controlplanepods.
-
If you are using the
Delete all of the
ovnkube-controlplanepods by running:oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes delete pod -l app=ovnkube-control-plane
$ oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes delete pod -l app=ovnkube-control-planeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that all of the
ovnkube-controlplanepods were redeployed by using:oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes get pod -l app=ovnkube-control-plane
$ oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes get pod -l app=ovnkube-control-planeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) redeploys the OVN-Kubernetes control plane and that it no longer references the non-recovery controller IP addresses. To verify this result, regularly check the output of the following command. Wait until it returns an empty result before you proceed to restart the Open Virtual Network (OVN) Kubernetes pods on all of the hosts in the next step.
oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes get ds/ovnkube-master -o yaml | grep -E '<non-recovery_controller_ip_1>|<non-recovery_controller_ip_2>'
$ oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes get ds/ovnkube-master -o yaml | grep -E '<non-recovery_controller_ip_1>|<non-recovery_controller_ip_2>'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIt can take at least 5-10 minutes for the OVN-Kubernetes control plane to be redeployed and the previous command to return empty output.
Restart the Open Virtual Network (OVN) Kubernetes pods on all the hosts.
NoteValidating and mutating admission webhooks can reject pods. If you add any additional webhooks with the
failurePolicyset toFail, then they can reject pods and the restoration process can fail. You can avoid this by saving and deleting webhooks while restoring the cluster state. After the cluster state is restored successfully, you can enable the webhooks again.Alternatively, you can temporarily set the
failurePolicytoIgnorewhile restoring the cluster state. After the cluster state is restored successfully, you can set thefailurePolicytoFail.
Remove the northbound database (nbdb) and southbound database (sbdb). Access the recovery host and the remaining control plane nodes by using Secure Shell (SSH) and run:
sudo rm -f /var/lib/ovn/etc/*.db
$ sudo rm -f /var/lib/ovn/etc/*.dbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete all OVN-Kubernetes control plane pods by running the following command:
oc delete pods -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc delete pods -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure that any OVN-Kubernetes control plane pods are deployed again and are in a
Runningstate by running the following command:oc get pods -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get pods -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ovnkube-master-nb24h 4/4 Running 0 48s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ovnkube-master-nb24h 4/4 Running 0 48sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
ovnkube-nodepod is running again with:oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -o name | grep ovnkube-node | while read p ; do oc delete $p -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes ; done
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -o name | grep ovnkube-node | while read p ; do oc delete $p -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes ; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure that all the
ovnkube-nodepods are deployed again and are in aRunningstate by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep ovnkube-node
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep ovnkube-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete and re-create other non-recovery, control plane machines, one by one. After the machines are re-created, a new revision is forced and
etcdautomatically scales up.If you use a user-provisioned bare metal installation, you can re-create a control plane machine by using the same method that you used to originally create it. For more information, see "Installing a user-provisioned cluster on bare metal".
WarningDo not delete and re-create the machine for the recovery host.
If you are running installer-provisioned infrastructure, or you used the Machine API to create your machines, follow these steps:
WarningDo not delete and re-create the machine for the recovery host.
For bare metal installations on installer-provisioned infrastructure, control plane machines are not re-created. For more information, see "Replacing a bare-metal control plane node".
Obtain the machine for one of the lost control plane hosts.
In a terminal that has access to the cluster as a cluster-admin user, run the following command:
oc get machines -n openshift-machine-api -o wide
$ oc get machines -n openshift-machine-api -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This is the control plane machine for the lost control plane host,
ip-10-0-131-183.ec2.internal.
Save the machine configuration to a file on your file system by running:
oc get machine clustername-8qw5l-master-0 \ -n openshift-machine-api \ -o yaml \ > new-master-machine.yaml$ oc get machine clustername-8qw5l-master-0 \1 -n openshift-machine-api \ -o yaml \ > new-master-machine.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the name of the control plane machine for the lost control plane host.
Edit the
new-master-machine.yamlfile that was created in the previous step to assign a new name and remove unnecessary fields.Remove the entire
statussection by running:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change the
metadata.namefield to a new name by running:It is recommended to keep the same base name as the old machine and change the ending number to the next available number. In this example,
clustername-8qw5l-master-0is changed toclustername-8qw5l-master-3:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the
spec.providerIDfield by running:providerID: aws:///us-east-1a/i-0fdb85790d76d0c3f
providerID: aws:///us-east-1a/i-0fdb85790d76d0c3fCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the
metadata.annotationsandmetadata.generationfields by running:annotations: machine.openshift.io/instance-state: running ... generation: 2
annotations: machine.openshift.io/instance-state: running ... generation: 2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the
metadata.resourceVersionandmetadata.uidfields by running:resourceVersion: "13291" uid: a282eb70-40a2-4e89-8009-d05dd420d31a
resourceVersion: "13291" uid: a282eb70-40a2-4e89-8009-d05dd420d31aCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Delete the machine of the lost control plane host by running:
oc delete machine -n openshift-machine-api clustername-8qw5l-master-0
$ oc delete machine -n openshift-machine-api clustername-8qw5l-master-01 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the name of the control plane machine for the lost control plane host.
Verify that the machine was deleted by running:
oc get machines -n openshift-machine-api -o wide
$ oc get machines -n openshift-machine-api -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a machine by using the
new-master-machine.yamlfile by running:oc apply -f new-master-machine.yaml
$ oc apply -f new-master-machine.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the new machine has been created by running:
oc get machines -n openshift-machine-api -o wide
$ oc get machines -n openshift-machine-api -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The new machine,
clustername-8qw5l-master-3is being created and is ready after the phase changes fromProvisioningtoRunning.
It might take a few minutes for the new machine to be created. The
etcdcluster Operator will automatically sync when the machine or node returns to a healthy state.Repeat these steps for each lost control plane host that is not the recovery host.
Turn off the quorum guard by entering:
oc patch etcd/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec": {"unsupportedConfigOverrides": {"useUnsupportedUnsafeNonHANonProductionUnstableEtcd": true}}}'$ oc patch etcd/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec": {"unsupportedConfigOverrides": {"useUnsupportedUnsafeNonHANonProductionUnstableEtcd": true}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command ensures that you can successfully re-create secrets and roll out the static pods.
In a separate terminal window within the recovery host, export the recovery
kubeconfigfile by running:export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/static-pod-resources/kube-apiserver-certs/secrets/node-kubeconfigs/localhost-recovery.kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/static-pod-resources/kube-apiserver-certs/secrets/node-kubeconfigs/localhost-recovery.kubeconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Force
etcdredeployment.In the same terminal window where you exported the recovery
kubeconfigfile, run:oc patch etcd cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch etcd cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=merge1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
forceRedeploymentReasonvalue must be unique, which is why a timestamp is appended.
When the
etcdcluster Operator performs a redeployment, the existing nodes are started with new pods similar to the initial bootstrap scale up.Turn the quorum guard back on by entering:
oc patch etcd/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec": {"unsupportedConfigOverrides": null}}'$ oc patch etcd/cluster --type=merge -p '{"spec": {"unsupportedConfigOverrides": null}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can verify that the
unsupportedConfigOverridessection is removed from the object by running:oc get etcd/cluster -oyaml
$ oc get etcd/cluster -oyamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all nodes are updated to the latest revision.
In a terminal that has access to the cluster as a
cluster-adminuser, run:oc get etcd -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get etcd -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the
NodeInstallerProgressingstatus condition foretcdto verify that all nodes are at the latest revision. The output showsAllNodesAtLatestRevisionupon successful update:AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 7
AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 71 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the latest revision number is
7.
If the output includes multiple revision numbers, such as
2 nodes are at revision 6; 1 nodes are at revision 7, this means that the update is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.After
etcdis redeployed, force new rollouts for the control plane.kube-apiserverwill reinstall itself on the other nodes because the kubelet is connected to API servers using an internal load balancer.In a terminal that has access to the cluster as a
cluster-adminuser, run:
Force a new rollout for
kube-apiserver:oc patch kubeapiserver cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch kubeapiserver cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all nodes are updated to the latest revision.
oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the
NodeInstallerProgressingstatus condition to verify that all nodes are at the latest revision. The output showsAllNodesAtLatestRevisionupon successful update:AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 7
AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 71 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the latest revision number is
7.
If the output includes multiple revision numbers, such as
2 nodes are at revision 6; 1 nodes are at revision 7, this means that the update is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Force a new rollout for the Kubernetes controller manager by running the following command:
oc patch kubecontrollermanager cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch kubecontrollermanager cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all nodes are updated to the latest revision by running:
oc get kubecontrollermanager -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubecontrollermanager -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the
NodeInstallerProgressingstatus condition to verify that all nodes are at the latest revision. The output showsAllNodesAtLatestRevisionupon successful update:AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 7
AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 71 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the latest revision number is
7.
If the output includes multiple revision numbers, such as
2 nodes are at revision 6; 1 nodes are at revision 7, this means that the update is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Force a new rollout for the
kube-schedulerby running:oc patch kubescheduler cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch kubescheduler cluster -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date --rfc-3339=ns )"'"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all nodes are updated to the latest revision by using:
oc get kubescheduler -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubescheduler -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="NodeInstallerProgressing")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the
NodeInstallerProgressingstatus condition to verify that all nodes are at the latest revision. The output showsAllNodesAtLatestRevisionupon successful update:AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 7
AllNodesAtLatestRevision 3 nodes are at revision 71 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the latest revision number is
7.
If the output includes multiple revision numbers, such as
2 nodes are at revision 6; 1 nodes are at revision 7, this means that the update is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Verify that all control plane hosts have started and joined the cluster.
In a terminal that has access to the cluster as a
cluster-adminuser, run the following command:oc -n openshift-etcd get pods -l k8s-app=etcd
$ oc -n openshift-etcd get pods -l k8s-app=etcdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
etcd-ip-10-0-143-125.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 9h etcd-ip-10-0-154-194.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 9h etcd-ip-10-0-173-171.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 9h
etcd-ip-10-0-143-125.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 9h etcd-ip-10-0-154-194.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 9h etcd-ip-10-0-173-171.ec2.internal 2/2 Running 0 9hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To ensure that all workloads return to normal operation following a recovery procedure, restart each pod that stores kube-apiserver information. This includes OpenShift Container Platform components such as routers, Operators, and third-party components.
On completion of the previous procedural steps, you might need to wait a few minutes for all services to return to their restored state. For example, authentication by using oc login might not immediately work until the OAuth server pods are restarted.
Consider using the system:admin kubeconfig file for immediate authentication. This method basis its authentication on SSL/TLS client certificates as against OAuth tokens. You can authenticate with this file by issuing the following command:
export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfig
$ export KUBECONFIG=<installation_directory>/auth/kubeconfigIssue the following command to display your authenticated user name:
oc whoami
$ oc whoami6.11.7. Issues and workarounds for restoring a persistent storage state
If your OpenShift Container Platform cluster uses persistent storage of any form, a state of the cluster is typically stored outside etcd. It might be an Elasticsearch cluster running in a pod or a database running in a StatefulSet object. When you restore from an etcd backup, the status of the workloads in OpenShift Container Platform is also restored. However, if the etcd snapshot is old, the status might be invalid or outdated.
The contents of persistent volumes (PVs) are never part of the etcd snapshot. When you restore an OpenShift Container Platform cluster from an etcd snapshot, non-critical workloads might gain access to critical data, or vice-versa.
The following are some example scenarios that produce an out-of-date status:
- MySQL database is running in a pod backed up by a PV object. Restoring OpenShift Container Platform from an etcd snapshot does not bring back the volume on the storage provider, and does not produce a running MySQL pod, despite the pod repeatedly attempting to start. You must manually restore this pod by restoring the volume on the storage provider, and then editing the PV to point to the new volume.
- Pod P1 is using volume A, which is attached to node X. If the etcd snapshot is taken while another pod uses the same volume on node Y, then when the etcd restore is performed, pod P1 might not be able to start correctly due to the volume still being attached to node Y. OpenShift Container Platform is not aware of the attachment, and does not automatically detach it. When this occurs, the volume must be manually detached from node Y so that the volume can attach on node X, and then pod P1 can start.
- Cloud provider or storage provider credentials were updated after the etcd snapshot was taken. This causes any CSI drivers or Operators that depend on the those credentials to not work. You might have to manually update the credentials required by those drivers or Operators.
A device is removed or renamed from OpenShift Container Platform nodes after the etcd snapshot is taken. The Local Storage Operator creates symlinks for each PV that it manages from
/dev/disk/by-idor/devdirectories. This situation might cause the local PVs to refer to devices that no longer exist.To fix this problem, an administrator must:
- Manually remove the PVs with invalid devices.
- Remove symlinks from respective nodes.
-
Delete
LocalVolumeorLocalVolumeSetobjects (see Storage → Configuring persistent storage → Persistent storage using local volumes → Deleting the Local Storage Operator Resources).
6.12. Pod disruption budgets
Understand and configure pod disruption budgets.
6.12.1. Understanding how to use pod disruption budgets to specify the number of pods that must be up
A pod disruption budget allows the specification of safety constraints on pods during operations, such as draining a node for maintenance.
PodDisruptionBudget is an API object that specifies the minimum number or percentage of replicas that must be up at a time. Setting these in projects can be helpful during node maintenance (such as scaling a cluster down or a cluster upgrade) and is only honored on voluntary evictions (not on node failures).
A PodDisruptionBudget object’s configuration consists of the following key parts:
- A label selector, which is a label query over a set of pods.
An availability level, which specifies the minimum number of pods that must be available simultaneously, either:
-
minAvailableis the number of pods must always be available, even during a disruption. -
maxUnavailableis the number of pods can be unavailable during a disruption.
-
Available refers to the number of pods that has condition Ready=True. Ready=True refers to the pod that is able to serve requests and should be added to the load balancing pools of all matching services.
A maxUnavailable of 0% or 0 or a minAvailable of 100% or equal to the number of replicas is permitted but can block nodes from being drained.
You can check for pod disruption budgets across all projects with the following:
oc get poddisruptionbudget --all-namespaces
$ oc get poddisruptionbudget --all-namespacesExample output
The PodDisruptionBudget is considered healthy when there are at least minAvailable pods running in the system. Every pod above that limit can be evicted.
Depending on your pod priority and preemption settings, lower-priority pods might be removed despite their pod disruption budget requirements.
6.12.2. Specifying the number of pods that must be up with pod disruption budgets
You can use a PodDisruptionBudget object to specify the minimum number or percentage of replicas that must be up at a time.
Procedure
To configure a pod disruption budget:
Create a YAML file with the an object definition similar to the following:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
PodDisruptionBudgetis part of thepolicy/v1API group.- 2
- The minimum number of pods that must be available simultaneously. This can be either an integer or a string specifying a percentage, for example,
20%. - 3
- A label query over a set of resources. The result of
matchLabelsandmatchExpressionsare logically conjoined. Leave this paramter blank, for exampleselector {}, to select all pods in the project.
Or:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
PodDisruptionBudgetis part of thepolicy/v1API group.- 2
- The maximum number of pods that can be unavailable simultaneously. This can be either an integer or a string specifying a percentage, for example,
20%. - 3
- A label query over a set of resources. The result of
matchLabelsandmatchExpressionsare logically conjoined. Leave this paramter blank, for exampleselector {}, to select all pods in the project.
Run the following command to add the object to project:
oc create -f </path/to/file> -n <project_name>
$ oc create -f </path/to/file> -n <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.13. Rotating or removing cloud provider credentials
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, some organizations require the rotation or removal of the cloud provider credentials that were used during the initial installation.
To allow the cluster to use the new credentials, you must update the secrets that the Cloud Credential Operator (CCO) uses to manage cloud provider credentials.
6.13.1. Rotating cloud provider credentials with the Cloud Credential Operator utility
The Cloud Credential Operator (CCO) utility ccoctl supports updating secrets for clusters installed on IBM Cloud.
6.13.1.1. Rotating API keys for IBM Cloud
You can rotate API keys for your existing service IDs and update the corresponding secrets.
Prerequisites
-
You have configured the
ccoctlbinary. - You have existing service IDs in a live OpenShift Container Platform cluster installed on IBM Cloud.
Procedure
Use the
ccoctlutility to rotate your API keys for the service IDs and update the secrets:ccoctl ibmcloud refresh-keys \ --kubeconfig <openshift_kubeconfig_file> \ --credentials-requests-dir <path_to_credential_requests_directory> \ --name <name>$ ccoctl ibmcloud refresh-keys \ --kubeconfig <openshift_kubeconfig_file> \1 --credentials-requests-dir <path_to_credential_requests_directory> \2 --name <name>3 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf your cluster uses Technology Preview features that are enabled by the
TechPreviewNoUpgradefeature set, you must include the--enable-tech-previewparameter.
6.13.2. Rotating cloud provider credentials manually
If your cloud provider credentials are changed for any reason, you must manually update the secret that the Cloud Credential Operator (CCO) uses to manage cloud provider credentials.
The process for rotating cloud credentials depends on the mode that the CCO is configured to use. After you rotate credentials for a cluster that is using mint mode, you must manually remove the component credentials that were created by the removed credential.
Prerequisites
Your cluster is installed on a platform that supports rotating cloud credentials manually with the CCO mode that you are using:
- For mint mode, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are supported.
- For passthrough mode, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), and VMware vSphere are supported.
- You have changed the credentials that are used to interface with your cloud provider.
- The new credentials have sufficient permissions for the mode CCO is configured to use in your cluster.
Procedure
- In the Administrator perspective of the web console, navigate to Workloads → Secrets.
In the table on the Secrets page, find the root secret for your cloud provider.
Expand Platform Secret name AWS
aws-credsAzure
azure-credentialsGCP
gcp-credentialsRHOSP
openstack-credentialsRHV
ovirt-credentialsVMware vSphere
vsphere-creds-
Click the Options menu
 in the same row as the secret and select Edit Secret.
in the same row as the secret and select Edit Secret.
- Record the contents of the Value field or fields. You can use this information to verify that the value is different after updating the credentials.
- Update the text in the Value field or fields with the new authentication information for your cloud provider, and then click Save.
If you are updating the credentials for a vSphere cluster that does not have the vSphere CSI Driver Operator enabled, you must force a rollout of the Kubernetes controller manager to apply the updated credentials.
NoteIf the vSphere CSI Driver Operator is enabled, this step is not required.
To apply the updated vSphere credentials, log in to the OpenShift Container Platform CLI as a user with the
cluster-adminrole and run the following command:oc patch kubecontrollermanager cluster \ -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date )"'"}}' \ --type=merge$ oc patch kubecontrollermanager cluster \ -p='{"spec": {"forceRedeploymentReason": "recovery-'"$( date )"'"}}' \ --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow While the credentials are rolling out, the status of the Kubernetes Controller Manager Operator reports
Progressing=true. To view the status, run the following command:oc get co kube-controller-manager
$ oc get co kube-controller-managerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the CCO for your cluster is configured to use mint mode, delete each component secret that is referenced by the individual
CredentialsRequestobjects.-
Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform CLI as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. Get the names and namespaces of all referenced component secrets:
oc -n openshift-cloud-credential-operator get CredentialsRequest \ -o json | jq -r '.items[] | select (.spec.providerSpec.kind=="<provider_spec>") | .spec.secretRef'
$ oc -n openshift-cloud-credential-operator get CredentialsRequest \ -o json | jq -r '.items[] | select (.spec.providerSpec.kind=="<provider_spec>") | .spec.secretRef'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<provider_spec>is the corresponding value for your cloud provider:-
AWS:
AWSProviderSpec -
GCP:
GCPProviderSpec
Partial example output for AWS
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
AWS:
Delete each of the referenced component secrets:
oc delete secret <secret_name> \ -n <secret_namespace>
$ oc delete secret <secret_name> \1 -n <secret_namespace>2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example deletion of an AWS secret
oc delete secret ebs-cloud-credentials -n openshift-cluster-csi-drivers
$ oc delete secret ebs-cloud-credentials -n openshift-cluster-csi-driversCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You do not need to manually delete the credentials from your provider console. Deleting the referenced component secrets will cause the CCO to delete the existing credentials from the platform and create new ones.
-
Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform CLI as a user with the
Verification
To verify that the credentials have changed:
- In the Administrator perspective of the web console, navigate to Workloads → Secrets.
- Verify that the contents of the Value field or fields have changed.
6.13.3. Removing cloud provider credentials
After installing an OpenShift Container Platform cluster with the Cloud Credential Operator (CCO) in mint mode, you can remove the administrator-level credential secret from the kube-system namespace in the cluster. The administrator-level credential is required only during changes that require its elevated permissions, such as upgrades.
Prior to a non z-stream upgrade, you must reinstate the credential secret with the administrator-level credential. If the credential is not present, the upgrade might be blocked.
Prerequisites
- Your cluster is installed on a platform that supports removing cloud credentials from the CCO. Supported platforms are AWS and GCP.
Procedure
- In the Administrator perspective of the web console, navigate to Workloads → Secrets.
In the table on the Secrets page, find the root secret for your cloud provider.
Expand Platform Secret name AWS
aws-credsGCP
gcp-credentials-
Click the Options menu
 in the same row as the secret and select Delete Secret.
in the same row as the secret and select Delete Secret.
6.14. Configuring image streams for a disconnected cluster
After installing OpenShift Container Platform in a disconnected environment, configure the image streams for the Cluster Samples Operator and the must-gather image stream.
6.14.1. Cluster Samples Operator assistance for mirroring
During installation, OpenShift Container Platform creates a config map named imagestreamtag-to-image in the openshift-cluster-samples-operator namespace. The imagestreamtag-to-image config map contains an entry, the populating image, for each image stream tag.
The format of the key for each entry in the data field in the config map is <image_stream_name>_<image_stream_tag_name>.
During a disconnected installation of OpenShift Container Platform, the status of the Cluster Samples Operator is set to Removed. If you choose to change it to Managed, it installs samples.
The use of samples in a network-restricted or discontinued environment may require access to services external to your network. Some example services include: Github, Maven Central, npm, RubyGems, PyPi and others. There might be additional steps to take that allow the cluster samples operators’s objects to reach the services they require.
You can use this config map as a reference for which images need to be mirrored for your image streams to import.
-
While the Cluster Samples Operator is set to
Removed, you can create your mirrored registry, or determine which existing mirrored registry you want to use. - Mirror the samples you want to the mirrored registry using the new config map as your guide.
-
Add any of the image streams you did not mirror to the
skippedImagestreamslist of the Cluster Samples Operator configuration object. -
Set
samplesRegistryof the Cluster Samples Operator configuration object to the mirrored registry. -
Then set the Cluster Samples Operator to
Managedto install the image streams you have mirrored.
6.14.2. Using Cluster Samples Operator image streams with alternate or mirrored registries
Most image streams in the openshift namespace managed by the Cluster Samples Operator point to images located in the Red Hat registry at registry.redhat.io. Mirroring will not apply to these image streams.
The cli, installer, must-gather, and tests image streams, while part of the install payload, are not managed by the Cluster Samples Operator. These are not addressed in this procedure.
The Cluster Samples Operator must be set to Managed in a disconnected environment. To install the image streams, you have a mirrored registry.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - Create a pull secret for your mirror registry.
Procedure
Access the images of a specific image stream to mirror, for example:
oc get is <imagestream> -n openshift -o json | jq .spec.tags[].from.name | grep registry.redhat.io
$ oc get is <imagestream> -n openshift -o json | jq .spec.tags[].from.name | grep registry.redhat.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mirror images from registry.redhat.io associated with any image streams you need in the restricted network environment into one of the defined mirrors, for example:
oc image mirror registry.redhat.io/rhscl/ruby-25-rhel7:latest ${MIRROR_ADDR}/rhscl/ruby-25-rhel7:latest$ oc image mirror registry.redhat.io/rhscl/ruby-25-rhel7:latest ${MIRROR_ADDR}/rhscl/ruby-25-rhel7:latestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the cluster’s image configuration object:
oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=${MIRROR_ADDR_HOSTNAME}..5000=$path/ca.crt -n openshift-config$ oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=${MIRROR_ADDR_HOSTNAME}..5000=$path/ca.crt -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the required trusted CAs for the mirror in the cluster’s image configuration object:
oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"registry-config"}}}' --type=merge$ oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"registry-config"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the
samplesRegistryfield in the Cluster Samples Operator configuration object to contain thehostnameportion of the mirror location defined in the mirror configuration:oc edit configs.samples.operator.openshift.io -n openshift-cluster-samples-operator
$ oc edit configs.samples.operator.openshift.io -n openshift-cluster-samples-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis is required because the image stream import process does not use the mirror or search mechanism at this time.
Add any image streams that are not mirrored into the
skippedImagestreamsfield of the Cluster Samples Operator configuration object. Or if you do not want to support any of the sample image streams, set the Cluster Samples Operator toRemovedin the Cluster Samples Operator configuration object.NoteThe Cluster Samples Operator issues alerts if image stream imports are failing but the Cluster Samples Operator is either periodically retrying or does not appear to be retrying them.
Many of the templates in the
openshiftnamespace reference the image streams. So usingRemovedto purge both the image streams and templates will eliminate the possibility of attempts to use them if they are not functional because of any missing image streams.
6.14.3. Preparing your cluster to gather support data
Clusters using a restricted network must import the default must-gather image to gather debugging data for Red Hat support. The must-gather image is not imported by default, and clusters on a restricted network do not have access to the internet to pull the latest image from a remote repository.
Procedure
If you have not added your mirror registry’s trusted CA to your cluster’s image configuration object as part of the Cluster Samples Operator configuration, perform the following steps:
Create the cluster’s image configuration object:
oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=${MIRROR_ADDR_HOSTNAME}..5000=$path/ca.crt -n openshift-config$ oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=${MIRROR_ADDR_HOSTNAME}..5000=$path/ca.crt -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the required trusted CAs for the mirror in the cluster’s image configuration object:
oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"registry-config"}}}' --type=merge$ oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"registry-config"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Import the default must-gather image from your installation payload:
oc import-image is/must-gather -n openshift
$ oc import-image is/must-gather -n openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When running the oc adm must-gather command, use the --image flag and point to the payload image, as in the following example:
oc adm must-gather --image=$(oc adm release info --image-for must-gather)
$ oc adm must-gather --image=$(oc adm release info --image-for must-gather)6.15. Configuring periodic importing of Cluster Sample Operator image stream tags
You can ensure that you always have access to the latest versions of the Cluster Sample Operator images by periodically importing the image stream tags when new versions become available.
Procedure
Fetch all the imagestreams in the
openshiftnamespace by running the following command:oc get imagestreams -nopenshift
oc get imagestreams -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Fetch the tags for every imagestream in the
openshiftnamespace by running the following command:oc get is <image-stream-name> -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}{.name}{'\t'}{.from.name}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshift$ oc get is <image-stream-name> -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}{.name}{'\t'}{.from.name}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc get is ubi8-openjdk-17 -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}{.name}{'\t'}{.from.name}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshift$ oc get is ubi8-openjdk-17 -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}{.name}{'\t'}{.from.name}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
1.11 registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.11 1.12 registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.12
1.11 registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.11 1.12 registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.12Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Schedule periodic importing of images for each tag present in the image stream by running the following command:
oc tag <repository/image> <image-stream-name:tag> --scheduled -nopenshift
$ oc tag <repository/image> <image-stream-name:tag> --scheduled -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc tag registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.11 ubi8-openjdk-17:1.11 --scheduled -nopenshift oc tag registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.12 ubi8-openjdk-17:1.12 --scheduled -nopenshift
$ oc tag registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.11 ubi8-openjdk-17:1.11 --scheduled -nopenshift $ oc tag registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/openjdk-17:1.12 ubi8-openjdk-17:1.12 --scheduled -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command causes OpenShift Container Platform to periodically update this particular image stream tag. This period is a cluster-wide setting set to 15 minutes by default.
Verify the scheduling status of the periodic import by running the following command:
oc get imagestream <image-stream-name> -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}Tag: {.name}{'\t'}Scheduled: {.importPolicy.scheduled}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshiftoc get imagestream <image-stream-name> -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}Tag: {.name}{'\t'}Scheduled: {.importPolicy.scheduled}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc get imagestream ubi8-openjdk-17 -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}Tag: {.name}{'\t'}Scheduled: {.importPolicy.scheduled}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshiftoc get imagestream ubi8-openjdk-17 -o jsonpath="{range .spec.tags[*]}Tag: {.name}{'\t'}Scheduled: {.importPolicy.scheduled}{'\n'}{end}" -nopenshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Tag: 1.11 Scheduled: true Tag: 1.12 Scheduled: true
Tag: 1.11 Scheduled: true Tag: 1.12 Scheduled: trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 7. Postinstallation node tasks
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can further expand and customize your cluster to your requirements through certain node tasks.
7.1. Adding RHEL compute machines to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster
Understand and work with RHEL compute nodes.
7.1.1. About adding RHEL compute nodes to a cluster
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11, you have the option of using Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) machines as compute machines in your cluster if you use a user-provisioned or installer-provisioned infrastructure installation on the x86_64 architecture. You must use Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) machines for the control plane machines in your cluster.
If you choose to use RHEL compute machines in your cluster, you are responsible for all operating system life cycle management and maintenance. You must perform system updates, apply patches, and complete all other required tasks.
For installer-provisioned infrastructure clusters, you must manually add RHEL compute machines because automatic scaling in installer-provisioned infrastructure clusters adds Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute machines by default.
- Because removing OpenShift Container Platform from a machine in the cluster requires destroying the operating system, you must use dedicated hardware for any RHEL machines that you add to the cluster.
- Swap memory is disabled on all RHEL machines that you add to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. You cannot enable swap memory on these machines.
You must add any RHEL compute machines to the cluster after you initialize the control plane.
7.1.2. System requirements for RHEL compute nodes
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) compute machine hosts in your OpenShift Container Platform environment must meet the following minimum hardware specifications and system-level requirements:
- You must have an active OpenShift Container Platform subscription on your Red Hat account. If you do not, contact your sales representative for more information.
- Production environments must provide compute machines to support your expected workloads. As a cluster administrator, you must calculate the expected workload and add about 10% for overhead. For production environments, allocate enough resources so that a node host failure does not affect your maximum capacity.
Each system must meet the following hardware requirements:
- Physical or virtual system, or an instance running on a public or private IaaS.
Base OS: RHEL 8.6 and later with "Minimal" installation option.
ImportantAdding RHEL 7 compute machines to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster is not supported.
If you have RHEL 7 compute machines that were previously supported in a past OpenShift Container Platform version, you cannot upgrade them to RHEL 8. You must deploy new RHEL 8 hosts, and the old RHEL 7 hosts should be removed. See the "Deleting nodes" section for more information.
For the most recent list of major functionality that has been deprecated or removed within OpenShift Container Platform, refer to the Deprecated and removed features section of the OpenShift Container Platform release notes.
- If you deployed OpenShift Container Platform in FIPS mode, you must enable FIPS on the RHEL machine before you boot it. See Installing a RHEL 8 system with FIPS mode enabled in the RHEL 8 documentation.
To enable FIPS mode for your cluster, you must run the installation program from a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) computer configured to operate in FIPS mode. For more information about configuring FIPS mode on RHEL, see Installing the system in FIPS mode. The use of FIPS validated or Modules In Process cryptographic libraries is only supported on OpenShift Container Platform deployments on the x86_64 architecture.
- NetworkManager 1.0 or later.
- 1 vCPU.
- Minimum 8 GB RAM.
-
Minimum 15 GB hard disk space for the file system containing
/var/. -
Minimum 1 GB hard disk space for the file system containing
/usr/local/bin/. Minimum 1 GB hard disk space for the file system containing its temporary directory. The temporary system directory is determined according to the rules defined in the tempfile module in the Python standard library.
-
Each system must meet any additional requirements for your system provider. For example, if you installed your cluster on VMware vSphere, your disks must be configured according to its storage guidelines and the
disk.enableUUID=trueattribute must be set. - Each system must be able to access the cluster’s API endpoints by using DNS-resolvable hostnames. Any network security access control that is in place must allow system access to the cluster’s API service endpoints.
-
Each system must meet any additional requirements for your system provider. For example, if you installed your cluster on VMware vSphere, your disks must be configured according to its storage guidelines and the
7.1.2.1. Certificate signing requests management
Because your cluster has limited access to automatic machine management when you use infrastructure that you provision, you must provide a mechanism for approving cluster certificate signing requests (CSRs) after installation. The kube-controller-manager only approves the kubelet client CSRs. The machine-approver cannot guarantee the validity of a serving certificate that is requested by using kubelet credentials because it cannot confirm that the correct machine issued the request. You must determine and implement a method of verifying the validity of the kubelet serving certificate requests and approving them.
7.1.3. Preparing the machine to run the playbook
Before you can add compute machines that use Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) as the operating system to an OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 cluster, you must prepare a RHEL 8 machine to run an Ansible playbook that adds the new node to the cluster. This machine is not part of the cluster but must be able to access it.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc) on the machine that you run the playbook on. -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminpermission.
Procedure
-
Ensure that the
kubeconfigfile for the cluster and the installation program that you used to install the cluster are on the RHEL 8 machine. One way to accomplish this is to use the same machine that you used to install the cluster. - Configure the machine to access all of the RHEL hosts that you plan to use as compute machines. You can use any method that your company allows, including a bastion with an SSH proxy or a VPN.
Configure a user on the machine that you run the playbook on that has SSH access to all of the RHEL hosts.
ImportantIf you use SSH key-based authentication, you must manage the key with an SSH agent.
If you have not already done so, register the machine with RHSM and attach a pool with an
OpenShiftsubscription to it:Register the machine with RHSM:
subscription-manager register --username=<user_name> --password=<password>
# subscription-manager register --username=<user_name> --password=<password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pull the latest subscription data from RHSM:
subscription-manager refresh
# subscription-manager refreshCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the available subscriptions:
subscription-manager list --available --matches '*OpenShift*'
# subscription-manager list --available --matches '*OpenShift*'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the output for the previous command, find the pool ID for an OpenShift Container Platform subscription and attach it:
subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_id>
# subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Enable the repositories required by OpenShift Container Platform 4.11:
subscription-manager repos \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms" \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms" \ --enable="rhocp-4.11-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms"# subscription-manager repos \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms" \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms" \ --enable="rhocp-4.11-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Install the required packages, including
openshift-ansible:yum install openshift-ansible openshift-clients jq
# yum install openshift-ansible openshift-clients jqCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
openshift-ansiblepackage provides installation program utilities and pulls in other packages that you require to add a RHEL compute node to your cluster, such as Ansible, playbooks, and related configuration files. Theopenshift-clientsprovides theocCLI, and thejqpackage improves the display of JSON output on your command line.
7.1.4. Preparing a RHEL compute node
Before you add a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) machine to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, you must register each host with Red Hat Subscription Manager (RHSM), attach an active OpenShift Container Platform subscription, and enable the required repositories. Ensure NetworkManager is enabled and configured to control all interfaces on the host.
On each host, register with RHSM:
subscription-manager register --username=<user_name> --password=<password>
# subscription-manager register --username=<user_name> --password=<password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pull the latest subscription data from RHSM:
subscription-manager refresh
# subscription-manager refreshCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the available subscriptions:
subscription-manager list --available --matches '*OpenShift*'
# subscription-manager list --available --matches '*OpenShift*'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the output for the previous command, find the pool ID for an OpenShift Container Platform subscription and attach it:
subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_id>
# subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable all yum repositories:
Disable all the enabled RHSM repositories:
subscription-manager repos --disable="*"
# subscription-manager repos --disable="*"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the remaining yum repositories and note their names under
repo id, if any:yum repolist
# yum repolistCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use
yum-config-managerto disable the remaining yum repositories:yum-config-manager --disable <repo_id>
# yum-config-manager --disable <repo_id>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, disable all repositories:
yum-config-manager --disable \*
# yum-config-manager --disable \*Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that this might take a few minutes if you have a large number of available repositories
Enable only the repositories required by OpenShift Container Platform 4.11:
subscription-manager repos \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms" \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms" \ --enable="rhocp-4.11-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms" \ --enable="fast-datapath-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms"# subscription-manager repos \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-baseos-rpms" \ --enable="rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms" \ --enable="rhocp-4.11-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms" \ --enable="fast-datapath-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop and disable firewalld on the host:
systemctl disable --now firewalld.service
# systemctl disable --now firewalld.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou must not enable firewalld later. If you do, you cannot access OpenShift Container Platform logs on the worker.
7.1.5. Adding a RHEL compute machine to your cluster
You can add compute machines that use Red Hat Enterprise Linux as the operating system to an OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 cluster.
Prerequisites
- You installed the required packages and performed the necessary configuration on the machine that you run the playbook on.
- You prepared the RHEL hosts for installation.
Procedure
Perform the following steps on the machine that you prepared to run the playbook:
Create an Ansible inventory file that is named
/<path>/inventory/hoststhat defines your compute machine hosts and required variables:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the user name that runs the Ansible tasks on the remote compute machines.
- 2
- If you do not specify
rootfor theansible_user, you must setansible_becometoTrueand assign the user sudo permissions. - 3
- Specify the path and file name of the
kubeconfigfile for your cluster. - 4
- List each RHEL machine to add to your cluster. You must provide the fully-qualified domain name for each host. This name is the hostname that the cluster uses to access the machine, so set the correct public or private name to access the machine.
Navigate to the Ansible playbook directory:
cd /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible
$ cd /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansibleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook -i /<path>/inventory/hosts playbooks/scaleup.yml
$ ansible-playbook -i /<path>/inventory/hosts playbooks/scaleup.yml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
<path>, specify the path to the Ansible inventory file that you created.
7.1.6. Required parameters for the Ansible hosts file
You must define the following parameters in the Ansible hosts file before you add Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) compute machines to your cluster.
| Parameter | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
|
| The SSH user that allows SSH-based authentication without requiring a password. If you use SSH key-based authentication, then you must manage the key with an SSH agent. |
A user name on the system. The default value is |
|
|
If the values of |
|
|
|
Specifies a path and file name to a local directory that contains the | The path and name of the configuration file. |
7.1.7. Optional: Removing RHCOS compute machines from a cluster
After you add the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) compute machines to your cluster, you can optionally remove the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute machines to free up resources.
Prerequisites
- You have added RHEL compute machines to your cluster.
Procedure
View the list of machines and record the node names of the RHCOS compute machines:
oc get nodes -o wide
$ oc get nodes -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For each RHCOS compute machine, delete the node:
Mark the node as unschedulable by running the
oc adm cordoncommand:oc adm cordon <node_name>
$ oc adm cordon <node_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the node name of one of the RHCOS compute machines.
Drain all the pods from the node:
oc adm drain <node_name> --force --delete-emptydir-data --ignore-daemonsets
$ oc adm drain <node_name> --force --delete-emptydir-data --ignore-daemonsets1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the node name of the RHCOS compute machine that you isolated.
Delete the node:
oc delete nodes <node_name>
$ oc delete nodes <node_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the node name of the RHCOS compute machine that you drained.
Review the list of compute machines to ensure that only the RHEL nodes remain:
oc get nodes -o wide
$ oc get nodes -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Remove the RHCOS machines from the load balancer for your cluster’s compute machines. You can delete the virtual machines or reimage the physical hardware for the RHCOS compute machines.
7.2. Adding RHCOS compute machines to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster
You can add more Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute machines to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster on bare metal.
Before you add more compute machines to a cluster that you installed on bare metal infrastructure, you must create RHCOS machines for it to use. You can either use an ISO image or network PXE booting to create the machines.
7.2.1. Prerequisites
- You installed a cluster on bare metal.
- You have installation media and Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) images that you used to create your cluster. If you do not have these files, you must obtain them by following the instructions in the installation procedure.
7.2.2. Creating more RHCOS machines using an ISO image
You can create more Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute machines for your bare metal cluster by using an ISO image to create the machines.
Prerequisites
- Obtain the URL of the Ignition config file for the compute machines for your cluster. You uploaded this file to your HTTP server during installation.
Procedure
Use the ISO file to install RHCOS on more compute machines. Use the same method that you used when you created machines before you installed the cluster:
- Burn the ISO image to a disk and boot it directly.
- Use ISO redirection with a LOM interface.
Boot the RHCOS ISO image without specifying any options, or interrupting the live boot sequence. Wait for the installer to boot into a shell prompt in the RHCOS live environment.
NoteYou can interrupt the RHCOS installation boot process to add kernel arguments. However, for this ISO procedure you must use the
coreos-installercommand as outlined in the following steps, instead of adding kernel arguments.Run the
coreos-installercommand and specify the options that meet your installation requirements. At a minimum, you must specify the URL that points to the Ignition config file for the node type, and the device that you are installing to:sudo coreos-installer install --ignition-url=http://<HTTP_server>/<node_type>.ign <device> --ignition-hash=sha512-<digest>
$ sudo coreos-installer install --ignition-url=http://<HTTP_server>/<node_type>.ign <device> --ignition-hash=sha512-<digest>1 2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- You must run the
coreos-installercommand by usingsudo, because thecoreuser does not have the required root privileges to perform the installation. - 2
- The
--ignition-hashoption is required when the Ignition config file is obtained through an HTTP URL to validate the authenticity of the Ignition config file on the cluster node.<digest>is the Ignition config file SHA512 digest obtained in a preceding step.
NoteIf you want to provide your Ignition config files through an HTTPS server that uses TLS, you can add the internal certificate authority (CA) to the system trust store before running
coreos-installer.The following example initializes a bootstrap node installation to the
/dev/sdadevice. The Ignition config file for the bootstrap node is obtained from an HTTP web server with the IP address 192.168.1.2:sudo coreos-installer install --ignition-url=http://192.168.1.2:80/installation_directory/bootstrap.ign /dev/sda --ignition-hash=sha512-a5a2d43879223273c9b60af66b44202a1d1248fc01cf156c46d4a79f552b6bad47bc8cc78ddf0116e80c59d2ea9e32ba53bc807afbca581aa059311def2c3e3b
$ sudo coreos-installer install --ignition-url=http://192.168.1.2:80/installation_directory/bootstrap.ign /dev/sda --ignition-hash=sha512-a5a2d43879223273c9b60af66b44202a1d1248fc01cf156c46d4a79f552b6bad47bc8cc78ddf0116e80c59d2ea9e32ba53bc807afbca581aa059311def2c3e3bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Monitor the progress of the RHCOS installation on the console of the machine.
ImportantEnsure that the installation is successful on each node before commencing with the OpenShift Container Platform installation. Observing the installation process can also help to determine the cause of RHCOS installation issues that might arise.
- Continue to create more compute machines for your cluster.
7.2.3. Creating more RHCOS machines by PXE or iPXE booting
You can create more Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute machines for your bare metal cluster by using PXE or iPXE booting.
Prerequisites
- Obtain the URL of the Ignition config file for the compute machines for your cluster. You uploaded this file to your HTTP server during installation.
-
Obtain the URLs of the RHCOS ISO image, compressed metal BIOS,
kernel, andinitramfsfiles that you uploaded to your HTTP server during cluster installation. - You have access to the PXE booting infrastructure that you used to create the machines for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster during installation. The machines must boot from their local disks after RHCOS is installed on them.
-
If you use UEFI, you have access to the
grub.conffile that you modified during OpenShift Container Platform installation.
Procedure
Confirm that your PXE or iPXE installation for the RHCOS images is correct.
For PXE:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the location of the live
kernelfile that you uploaded to your HTTP server. - 2
- Specify locations of the RHCOS files that you uploaded to your HTTP server. The
initrdparameter value is the location of the liveinitramfsfile, thecoreos.inst.ignition_urlparameter value is the location of the worker Ignition config file, and thecoreos.live.rootfs_urlparameter value is the location of the liverootfsfile. Thecoreos.inst.ignition_urlandcoreos.live.rootfs_urlparameters only support HTTP and HTTPS.
This configuration does not enable serial console access on machines with a graphical console. To configure a different console, add one or more console= arguments to the APPEND line. For example, add console=tty0 console=ttyS0 to set the first PC serial port as the primary console and the graphical console as a secondary console. For more information, see How does one set up a serial terminal and/or console in Red Hat Enterprise Linux?.
For iPXE:
kernel http://<HTTP_server>/rhcos-<version>-live-kernel-<architecture> initrd=main coreos.inst.install_dev=/dev/sda coreos.inst.ignition_url=http://<HTTP_server>/worker.ign coreos.live.rootfs_url=http://<HTTP_server>/rhcos-<version>-live-rootfs.<architecture>.img initrd --name main http://<HTTP_server>/rhcos-<version>-live-initramfs.<architecture>.img
kernel http://<HTTP_server>/rhcos-<version>-live-kernel-<architecture> initrd=main coreos.inst.install_dev=/dev/sda coreos.inst.ignition_url=http://<HTTP_server>/worker.ign coreos.live.rootfs_url=http://<HTTP_server>/rhcos-<version>-live-rootfs.<architecture>.img1 initrd --name main http://<HTTP_server>/rhcos-<version>-live-initramfs.<architecture>.img2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify locations of the RHCOS files that you uploaded to your HTTP server. The
kernelparameter value is the location of thekernelfile, theinitrd=mainargument is needed for booting on UEFI systems, thecoreos.inst.ignition_urlparameter value is the location of the worker Ignition config file, and thecoreos.live.rootfs_urlparameter value is the location of the liverootfsfile. Thecoreos.inst.ignition_urlandcoreos.live.rootfs_urlparameters only support HTTP and HTTPS. - 2
- Specify the location of the
initramfsfile that you uploaded to your HTTP server.
This configuration does not enable serial console access on machines with a graphical console. To configure a different console, add one or more console= arguments to the kernel line. For example, add console=tty0 console=ttyS0 to set the first PC serial port as the primary console and the graphical console as a secondary console. For more information, see How does one set up a serial terminal and/or console in Red Hat Enterprise Linux?.
- Use the PXE or iPXE infrastructure to create the required compute machines for your cluster.
7.2.4. Approving the certificate signing requests for your machines
When you add machines to a cluster, two pending certificate signing requests (CSRs) are generated for each machine that you added. You must confirm that these CSRs are approved or, if necessary, approve them yourself. The client requests must be approved first, followed by the server requests.
Prerequisites
- You added machines to your cluster.
Procedure
Confirm that the cluster recognizes the machines:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master-0 Ready master 63m v1.24.0 master-1 Ready master 63m v1.24.0 master-2 Ready master 64m v1.24.0
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master-0 Ready master 63m v1.24.0 master-1 Ready master 63m v1.24.0 master-2 Ready master 64m v1.24.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output lists all of the machines that you created.
NoteThe preceding output might not include the compute nodes, also known as worker nodes, until some CSRs are approved.
Review the pending CSRs and ensure that you see the client requests with the
PendingorApprovedstatus for each machine that you added to the cluster:oc get csr
$ oc get csrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE REQUESTOR CONDITION csr-8b2br 15m system:serviceaccount:openshift-machine-config-operator:node-bootstrapper Pending csr-8vnps 15m system:serviceaccount:openshift-machine-config-operator:node-bootstrapper Pending ...
NAME AGE REQUESTOR CONDITION csr-8b2br 15m system:serviceaccount:openshift-machine-config-operator:node-bootstrapper Pending csr-8vnps 15m system:serviceaccount:openshift-machine-config-operator:node-bootstrapper Pending ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, two machines are joining the cluster. You might see more approved CSRs in the list.
If the CSRs were not approved, after all of the pending CSRs for the machines you added are in
Pendingstatus, approve the CSRs for your cluster machines:NoteBecause the CSRs rotate automatically, approve your CSRs within an hour of adding the machines to the cluster. If you do not approve them within an hour, the certificates will rotate, and more than two certificates will be present for each node. You must approve all of these certificates. After the client CSR is approved, the Kubelet creates a secondary CSR for the serving certificate, which requires manual approval. Then, subsequent serving certificate renewal requests are automatically approved by the
machine-approverif the Kubelet requests a new certificate with identical parameters.NoteFor clusters running on platforms that are not machine API enabled, such as bare metal and other user-provisioned infrastructure, you must implement a method of automatically approving the kubelet serving certificate requests (CSRs). If a request is not approved, then the
oc exec,oc rsh, andoc logscommands cannot succeed, because a serving certificate is required when the API server connects to the kubelet. Any operation that contacts the Kubelet endpoint requires this certificate approval to be in place. The method must watch for new CSRs, confirm that the CSR was submitted by thenode-bootstrapperservice account in thesystem:nodeorsystem:admingroups, and confirm the identity of the node.To approve them individually, run the following command for each valid CSR:
oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>
$ oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
<csr_name>is the name of a CSR from the list of current CSRs.
To approve all pending CSRs, run the following command:
oc get csr -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if not .status}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' | xargs --no-run-if-empty oc adm certificate approve$ oc get csr -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if not .status}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' | xargs --no-run-if-empty oc adm certificate approveCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteSome Operators might not become available until some CSRs are approved.
Now that your client requests are approved, you must review the server requests for each machine that you added to the cluster:
oc get csr
$ oc get csrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE REQUESTOR CONDITION csr-bfd72 5m26s system:node:ip-10-0-50-126.us-east-2.compute.internal Pending csr-c57lv 5m26s system:node:ip-10-0-95-157.us-east-2.compute.internal Pending ...
NAME AGE REQUESTOR CONDITION csr-bfd72 5m26s system:node:ip-10-0-50-126.us-east-2.compute.internal Pending csr-c57lv 5m26s system:node:ip-10-0-95-157.us-east-2.compute.internal Pending ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the remaining CSRs are not approved, and are in the
Pendingstatus, approve the CSRs for your cluster machines:To approve them individually, run the following command for each valid CSR:
oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>
$ oc adm certificate approve <csr_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
<csr_name>is the name of a CSR from the list of current CSRs.
To approve all pending CSRs, run the following command:
oc get csr -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if not .status}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' | xargs oc adm certificate approve$ oc get csr -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if not .status}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' | xargs oc adm certificate approveCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
After all client and server CSRs have been approved, the machines have the
Readystatus. Verify this by running the following command:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIt can take a few minutes after approval of the server CSRs for the machines to transition to the
Readystatus.
Additional information
- For more information on CSRs, see Certificate Signing Requests.
7.2.5. Adding a new RHCOS worker node with a custom /var partition in AWS
OpenShift Container Platform supports partitioning devices during installation by using machine configs that are processed during the bootstrap. However, if you use /var partitioning, the device name must be determined at installation and cannot be changed. You cannot add different instance types as nodes if they have a different device naming schema. For example, if you configured the /var partition with the default AWS device name for m4.large instances, dev/xvdb, you cannot directly add an AWS m5.large instance, as m5.large instances use a /dev/nvme1n1 device by default. The device might fail to partition due to the different naming schema.
The procedure in this section shows how to add a new Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) compute node with an instance that uses a different device name from what was configured at installation. You create a custom user data secret and configure a new machine set. These steps are specific to an AWS cluster. The principles apply to other cloud deployments also. However, the device naming schema is different for other deployments and should be determined on a per-case basis.
Procedure
On a command line, change to the
openshift-machine-apinamespace:oc project openshift-machine-api
$ oc project openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a new secret from the
worker-user-datasecret:Export the
userDatasection of the secret to a text file:oc get secret worker-user-data --template='{{index .data.userData | base64decode}}' | jq > userData.txt$ oc get secret worker-user-data --template='{{index .data.userData | base64decode}}' | jq > userData.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the text file to add the
storage,filesystems, andsystemdstanzas for the partitions you want to use for the new node. You can specify any Ignition configuration parameters as needed.NoteDo not change the values in the
ignitionstanza.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies an absolute path to the AWS block device.
- 2
- Specifies the size of the data partition in Mebibytes.
- 3
- Specifies the start of the partition in Mebibytes. When adding a data partition to the boot disk, a minimum value of 25000 MB (Mebibytes) is recommended. The root file system is automatically resized to fill all available space up to the specified offset. If no value is specified, or if the specified value is smaller than the recommended minimum, the resulting root file system will be too small, and future reinstalls of RHCOS might overwrite the beginning of the data partition.
- 4
- Specifies an absolute path to the
/varpartition. - 5
- Specifies the filesystem format.
- 6
- Specifies the mount-point of the filesystem while Ignition is running relative to where the root filesystem will be mounted. This is not necessarily the same as where it should be mounted in the real root, but it is encouraged to make it the same.
- 7
- Defines a systemd mount unit that mounts the
/dev/disk/by-partlabel/vardevice to the/varpartition.
Extract the
disableTemplatingsection from thework-user-datasecret to a text file:oc get secret worker-user-data --template='{{index .data.disableTemplating | base64decode}}' | jq > disableTemplating.txt$ oc get secret worker-user-data --template='{{index .data.disableTemplating | base64decode}}' | jq > disableTemplating.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the new user data secret file from the two text files. This user data secret passes the additional node partition information in the
userData.txtfile to the newly created node.oc create secret generic worker-user-data-x5 --from-file=userData=userData.txt --from-file=disableTemplating=disableTemplating.txt
$ oc create secret generic worker-user-data-x5 --from-file=userData=userData.txt --from-file=disableTemplating=disableTemplating.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a new machine set for the new node:
Create a new machine set YAML file, similar to the following, which is configured for AWS. Add the required partitions and the newly-created user data secret:
TipUse an existing machine set as a template and change the parameters as needed for the new node.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the machine set:
$ oc create -f <file-name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file-name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The machines might take a few moments to become available.
Verify that the new partition and nodes are created:
Verify that the machine set is created:
oc get machineset
$ oc get machinesetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE ci-ln-2675bt2-76ef8-bdgsc-worker-us-east-1a 1 1 1 1 124m ci-ln-2675bt2-76ef8-bdgsc-worker-us-east-1b 2 2 2 2 124m worker-us-east-2-nvme1n1 1 1 1 1 2m35s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE ci-ln-2675bt2-76ef8-bdgsc-worker-us-east-1a 1 1 1 1 124m ci-ln-2675bt2-76ef8-bdgsc-worker-us-east-1b 2 2 2 2 124m worker-us-east-2-nvme1n1 1 1 1 1 2m35s1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This is the new machine set.
Verify that the new node is created:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This is new new node.
Verify that the custom
/varpartition is created on the new node:oc debug node/<node-name> -- chroot /host lsblk
$ oc debug node/<node-name> -- chroot /host lsblkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc debug node/ip-10-0-217-135.ec2.internal -- chroot /host lsblk
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-217-135.ec2.internal -- chroot /host lsblkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
nvme1n1device is mounted to the/varpartition.
7.3. Deploying machine health checks
Understand and deploy machine health checks.
You can use the advanced machine management and scaling capabilities only in clusters where the Machine API is operational. Clusters with user-provisioned infrastructure require additional validation and configuration to use the Machine API.
Clusters with the infrastructure platform type none cannot use the Machine API. This limitation applies even if the compute machines that are attached to the cluster are installed on a platform that supports the feature. This parameter cannot be changed after installation.
To view the platform type for your cluster, run the following command:
oc get infrastructure cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.platform}'
$ oc get infrastructure cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.platform}'7.3.1. About machine health checks
Machine health checks automatically repair unhealthy machines in a particular machine pool.
To monitor machine health, create a resource to define the configuration for a controller. Set a condition to check, such as staying in the NotReady status for five minutes or displaying a permanent condition in the node-problem-detector, and a label for the set of machines to monitor.
You cannot apply a machine health check to a machine with the master role.
The controller that observes a MachineHealthCheck resource checks for the defined condition. If a machine fails the health check, the machine is automatically deleted and one is created to take its place. When a machine is deleted, you see a machine deleted event.
To limit disruptive impact of the machine deletion, the controller drains and deletes only one node at a time. If there are more unhealthy machines than the maxUnhealthy threshold allows for in the targeted pool of machines, remediation stops and therefore enables manual intervention.
Consider the timeouts carefully, accounting for workloads and requirements.
- Long timeouts can result in long periods of downtime for the workload on the unhealthy machine.
-
Too short timeouts can result in a remediation loop. For example, the timeout for checking the
NotReadystatus must be long enough to allow the machine to complete the startup process.
To stop the check, remove the resource.
7.3.1.1. Limitations when deploying machine health checks
There are limitations to consider before deploying a machine health check:
- Only machines owned by a machine set are remediated by a machine health check.
- Control plane machines are not currently supported and are not remediated if they are unhealthy.
- If the node for a machine is removed from the cluster, a machine health check considers the machine to be unhealthy and remediates it immediately.
-
If the corresponding node for a machine does not join the cluster after the
nodeStartupTimeout, the machine is remediated. -
A machine is remediated immediately if the
Machineresource phase isFailed.
7.3.2. Sample MachineHealthCheck resource
The MachineHealthCheck resource for all cloud-based installation types, and other than bare metal, resembles the following YAML file:
- 1
- Specify the name of the machine health check to deploy.
- 2 3
- Specify a label for the machine pool that you want to check.
- 4
- Specify the machine set to track in
<cluster_name>-<label>-<zone>format. For example,prod-node-us-east-1a. - 5 6
- Specify the timeout duration for a node condition. If a condition is met for the duration of the timeout, the machine will be remediated. Long timeouts can result in long periods of downtime for a workload on an unhealthy machine.
- 7
- Specify the amount of machines allowed to be concurrently remediated in the targeted pool. This can be set as a percentage or an integer. If the number of unhealthy machines exceeds the limit set by
maxUnhealthy, remediation is not performed. - 8
- Specify the timeout duration that a machine health check must wait for a node to join the cluster before a machine is determined to be unhealthy.
The matchLabels are examples only; you must map your machine groups based on your specific needs.
7.3.2.1. Short-circuiting machine health check remediation
Short circuiting ensures that machine health checks remediate machines only when the cluster is healthy. Short-circuiting is configured through the maxUnhealthy field in the MachineHealthCheck resource.
If the user defines a value for the maxUnhealthy field, before remediating any machines, the MachineHealthCheck compares the value of maxUnhealthy with the number of machines within its target pool that it has determined to be unhealthy. Remediation is not performed if the number of unhealthy machines exceeds the maxUnhealthy limit.
If maxUnhealthy is not set, the value defaults to 100% and the machines are remediated regardless of the state of the cluster.
The appropriate maxUnhealthy value depends on the scale of the cluster you deploy and how many machines the MachineHealthCheck covers. For example, you can use the maxUnhealthy value to cover multiple machine sets across multiple availability zones so that if you lose an entire zone, your maxUnhealthy setting prevents further remediation within the cluster. In global Azure regions that do not have multiple availability zones, you can use availability sets to ensure high availability.
The maxUnhealthy field can be set as either an integer or percentage. There are different remediation implementations depending on the maxUnhealthy value.
7.3.2.1.1. Setting maxUnhealthy by using an absolute value
If maxUnhealthy is set to 2:
- Remediation will be performed if 2 or fewer nodes are unhealthy
- Remediation will not be performed if 3 or more nodes are unhealthy
These values are independent of how many machines are being checked by the machine health check.
7.3.2.1.2. Setting maxUnhealthy by using percentages
If maxUnhealthy is set to 40% and there are 25 machines being checked:
- Remediation will be performed if 10 or fewer nodes are unhealthy
- Remediation will not be performed if 11 or more nodes are unhealthy
If maxUnhealthy is set to 40% and there are 6 machines being checked:
- Remediation will be performed if 2 or fewer nodes are unhealthy
- Remediation will not be performed if 3 or more nodes are unhealthy
The allowed number of machines is rounded down when the percentage of maxUnhealthy machines that are checked is not a whole number.
7.3.3. Creating a MachineHealthCheck resource
You can create a MachineHealthCheck resource for all MachineSets in your cluster. You should not create a MachineHealthCheck resource that targets control plane machines.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
occommand line interface.
Procedure
-
Create a
healthcheck.ymlfile that contains the definition of your machine health check. Apply the
healthcheck.ymlfile to your cluster:oc apply -f healthcheck.yml
$ oc apply -f healthcheck.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.4. Scaling a machine set manually
To add or remove an instance of a machine in a machine set, you can manually scale the machine set.
This guidance is relevant to fully automated, installer-provisioned infrastructure installations. Customized, user-provisioned infrastructure installations do not have machine sets.
Prerequisites
-
Install an OpenShift Container Platform cluster and the
occommand line. -
Log in to
ocas a user withcluster-adminpermission.
Procedure
View the machine sets that are in the cluster:
oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machinesets -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The machine sets are listed in the form of
<clusterid>-worker-<aws-region-az>.View the machines that are in the cluster:
oc get machine -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc get machine -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the annotation on the machine that you want to delete:
oc annotate machine/<machine_name> -n openshift-machine-api machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine="true"
$ oc annotate machine/<machine_name> -n openshift-machine-api machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-delete-machine="true"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Scale the machine set by running one of the following commands:
oc scale --replicas=2 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc scale --replicas=2 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Or:
oc edit machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc edit machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to scale the machine set:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can scale the machine set up or down. It takes several minutes for the new machines to be available.
ImportantBy default, the machine controller tries to drain the node that is backed by the machine until it succeeds. In some situations, such as with a misconfigured pod disruption budget, the drain operation might not be able to succeed. If the drain operation fails, the machine controller cannot proceed removing the machine.
You can skip draining the node by annotating
machine.openshift.io/exclude-node-drainingin a specific machine.
Verification
Verify the deletion of the intended machine:
oc get machines
$ oc get machinesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.5. Understanding the difference between machine sets and the machine config pool
MachineSet objects describe OpenShift Container Platform nodes with respect to the cloud or machine provider.
The MachineConfigPool object allows MachineConfigController components to define and provide the status of machines in the context of upgrades.
The MachineConfigPool object allows users to configure how upgrades are rolled out to the OpenShift Container Platform nodes in the machine config pool.
The NodeSelector object can be replaced with a reference to the MachineSet object.
7.4. Recommended node host practices
The OpenShift Container Platform node configuration file contains important options. For example, two parameters control the maximum number of pods that can be scheduled to a node: podsPerCore and maxPods.
When both options are in use, the lower of the two values limits the number of pods on a node. Exceeding these values can result in:
- Increased CPU utilization.
- Slow pod scheduling.
- Potential out-of-memory scenarios, depending on the amount of memory in the node.
- Exhausting the pool of IP addresses.
- Resource overcommitting, leading to poor user application performance.
In Kubernetes, a pod that is holding a single container actually uses two containers. The second container is used to set up networking prior to the actual container starting. Therefore, a system running 10 pods will actually have 20 containers running.
Disk IOPS throttling from the cloud provider might have an impact on CRI-O and kubelet. They might get overloaded when there are large number of I/O intensive pods running on the nodes. It is recommended that you monitor the disk I/O on the nodes and use volumes with sufficient throughput for the workload.
podsPerCore sets the number of pods the node can run based on the number of processor cores on the node. For example, if podsPerCore is set to 10 on a node with 4 processor cores, the maximum number of pods allowed on the node will be 40.
kubeletConfig: podsPerCore: 10
kubeletConfig:
podsPerCore: 10
Setting podsPerCore to 0 disables this limit. The default is 0. podsPerCore cannot exceed maxPods.
maxPods sets the number of pods the node can run to a fixed value, regardless of the properties of the node.
kubeletConfig:
maxPods: 250
kubeletConfig:
maxPods: 2507.4.1. Creating a KubeletConfig CRD to edit kubelet parameters
The kubelet configuration is currently serialized as an Ignition configuration, so it can be directly edited. However, there is also a new kubelet-config-controller added to the Machine Config Controller (MCC). This lets you use a KubeletConfig custom resource (CR) to edit the kubelet parameters.
As the fields in the kubeletConfig object are passed directly to the kubelet from upstream Kubernetes, the kubelet validates those values directly. Invalid values in the kubeletConfig object might cause cluster nodes to become unavailable. For valid values, see the Kubernetes documentation.
Consider the following guidance:
-
Create one
KubeletConfigCR for each machine config pool with all the config changes you want for that pool. If you are applying the same content to all of the pools, you need only oneKubeletConfigCR for all of the pools. -
Edit an existing
KubeletConfigCR to modify existing settings or add new settings, instead of creating a CR for each change. It is recommended that you create a CR only to modify a different machine config pool, or for changes that are intended to be temporary, so that you can revert the changes. -
As needed, create multiple
KubeletConfigCRs with a limit of 10 per cluster. For the firstKubeletConfigCR, the Machine Config Operator (MCO) creates a machine config appended withkubelet. With each subsequent CR, the controller creates anotherkubeletmachine config with a numeric suffix. For example, if you have akubeletmachine config with a-2suffix, the nextkubeletmachine config is appended with-3.
If you want to delete the machine configs, delete them in reverse order to avoid exceeding the limit. For example, you delete the kubelet-3 machine config before deleting the kubelet-2 machine config.
If you have a machine config with a kubelet-9 suffix, and you create another KubeletConfig CR, a new machine config is not created, even if there are fewer than 10 kubelet machine configs.
Example KubeletConfig CR
oc get kubeletconfig
$ oc get kubeletconfigNAME AGE set-max-pods 15m
NAME AGE
set-max-pods 15mExample showing a KubeletConfig machine config
oc get mc | grep kubelet
$ oc get mc | grep kubelet... 99-worker-generated-kubelet-1 b5c5119de007945b6fe6fb215db3b8e2ceb12511 3.2.0 26m ...
...
99-worker-generated-kubelet-1 b5c5119de007945b6fe6fb215db3b8e2ceb12511 3.2.0 26m
...The following procedure is an example to show how to configure the maximum number of pods per node on the worker nodes.
Prerequisites
Obtain the label associated with the static
MachineConfigPoolCR for the type of node you want to configure. Perform one of the following steps:View the machine config pool:
oc describe machineconfigpool <name>
$ oc describe machineconfigpool <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc describe machineconfigpool worker
$ oc describe machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If a label has been added it appears under
labels.
If the label is not present, add a key/value pair:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
View the available machine configuration objects that you can select:
oc get machineconfig
$ oc get machineconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, the two kubelet-related configs are
01-master-kubeletand01-worker-kubelet.Check the current value for the maximum pods per node:
oc describe node <node_name>
$ oc describe node <node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc describe node ci-ln-5grqprb-f76d1-ncnqq-worker-a-mdv94
$ oc describe node ci-ln-5grqprb-f76d1-ncnqq-worker-a-mdv94Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Look for
value: pods: <value>in theAllocatablestanza:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the maximum pods per node on the worker nodes by creating a custom resource file that contains the kubelet configuration:
ImportantKubelet configurations that target a specific machine config pool also affect any dependent pools. For example, creating a kubelet configuration for the pool containing worker nodes will also apply to any subset pools, including the pool containing infrastructure nodes. To avoid this, you must create a new machine config pool with a selection expression that only includes worker nodes, and have your kubelet configuration target this new pool.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe rate at which the kubelet talks to the API server depends on queries per second (QPS) and burst values. The default values,
50forkubeAPIQPSand100forkubeAPIBurst, are sufficient if there are limited pods running on each node. It is recommended to update the kubelet QPS and burst rates if there are enough CPU and memory resources on the node.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the machine config pool for workers with the label:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=set-max-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
KubeletConfigobject:oc create -f change-maxPods-cr.yaml
$ oc create -f change-maxPods-cr.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
KubeletConfigobject is created:oc get kubeletconfig
$ oc get kubeletconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE set-max-pods 15m
NAME AGE set-max-pods 15mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Depending on the number of worker nodes in the cluster, wait for the worker nodes to be rebooted one by one. For a cluster with 3 worker nodes, this could take about 10 to 15 minutes.
Verify that the changes are applied to the node:
Check on a worker node that the
maxPodsvalue changed:oc describe node <node_name>
$ oc describe node <node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Locate the
Allocatablestanza:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the
podsparameter should report the value you set in theKubeletConfigobject.
Verify the change in the
KubeletConfigobject:oc get kubeletconfigs set-max-pods -o yaml
$ oc get kubeletconfigs set-max-pods -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This should show a status of
Trueandtype:Success, as shown in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4.3. Control plane node sizing
The control plane node resource requirements depend on the number and type of nodes and objects in the cluster. The following control plane node size recommendations are based on the results of a control plane density focused testing, or Cluster-density. This test creates the following objects across a given number of namespaces:
- 1 image stream
- 1 build
-
5 deployments, with 2 pod replicas in a
sleepstate, mounting 4 secrets, 4 config maps, and 1 downward API volume each - 5 services, each one pointing to the TCP/8080 and TCP/8443 ports of one of the previous deployments
- 1 route pointing to the first of the previous services
- 10 secrets containing 2048 random string characters
- 10 config maps containing 2048 random string characters
| Number of worker nodes | Cluster-density (namespaces) | CPU cores | Memory (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 500 | 4 | 16 |
| 120 | 1000 | 8 | 32 |
| 252 | 4000 | 16 | 64 |
| 501 | 4000 | 16 | 96 |
On a large and dense cluster with three masters or control plane nodes, the CPU and memory usage will spike up when one of the nodes is stopped, rebooted or fails. The failures can be due to unexpected issues with power, network or underlying infrastructure in addition to intentional cases where the cluster is restarted after shutting it down to save costs. The remaining two control plane nodes must handle the load in order to be highly available which leads to increase in the resource usage. This is also expected during upgrades because the masters are cordoned, drained, and rebooted serially to apply the operating system updates, as well as the control plane Operators update. To avoid cascading failures, keep the overall CPU and memory resource usage on the control plane nodes to at most 60% of all available capacity to handle the resource usage spikes. Increase the CPU and memory on the control plane nodes accordingly to avoid potential downtime due to lack of resources.
The node sizing varies depending on the number of nodes and object counts in the cluster. It also depends on whether the objects are actively being created on the cluster. During object creation, the control plane is more active in terms of resource usage compared to when the objects are in the running phase.
Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM ) runs on the control plane nodes and it’s memory footprint depends on the number of namespaces and user installed operators that OLM needs to manage on the cluster. Control plane nodes need to be sized accordingly to avoid OOM kills. Following data points are based on the results from cluster maximums testing.
| Number of namespaces | OLM memory at idle state (GB) | OLM memory with 5 user operators installed (GB) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 0.823 | 1.7 |
| 1000 | 1.2 | 2.5 |
| 1500 | 1.7 | 3.2 |
| 2000 | 2 | 4.4 |
| 3000 | 2.7 | 5.6 |
| 4000 | 3.8 | 7.6 |
| 5000 | 4.2 | 9.02 |
| 6000 | 5.8 | 11.3 |
| 7000 | 6.6 | 12.9 |
| 8000 | 6.9 | 14.8 |
| 9000 | 8 | 17.7 |
| 10,000 | 9.9 | 21.6 |
You can modify the control plane node size in a running OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 cluster for the following configurations only:
- Clusters installed with a user-provisioned installation method.
- AWS clusters installed with an installer-provisioned infrastructure installation method.
For all other configurations, you must estimate your total node count and use the suggested control plane node size during installation.
The recommendations are based on the data points captured on OpenShift Container Platform clusters with OpenShift SDN as the network plugin.
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11, half of a CPU core (500 millicore) is now reserved by the system by default compared to OpenShift Container Platform 3.11 and previous versions. The sizes are determined taking that into consideration.
7.4.4. Setting up CPU Manager
Procedure
Optional: Label a node:
oc label node perf-node.example.com cpumanager=true
# oc label node perf-node.example.com cpumanager=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
MachineConfigPoolof the nodes where CPU Manager should be enabled. In this example, all workers have CPU Manager enabled:oc edit machineconfigpool worker
# oc edit machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a label to the worker machine config pool:
metadata: creationTimestamp: 2020-xx-xxx generation: 3 labels: custom-kubelet: cpumanager-enabledmetadata: creationTimestamp: 2020-xx-xxx generation: 3 labels: custom-kubelet: cpumanager-enabledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
KubeletConfig,cpumanager-kubeletconfig.yaml, custom resource (CR). Refer to the label created in the previous step to have the correct nodes updated with the new kubelet config. See themachineConfigPoolSelectorsection:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify a policy:
-
none. This policy explicitly enables the existing default CPU affinity scheme, providing no affinity beyond what the scheduler does automatically. This is the default policy. -
static. This policy allows containers in guaranteed pods with integer CPU requests. It also limits access to exclusive CPUs on the node. Ifstatic, you must use a lowercases.
-
- 2
- Optional. Specify the CPU Manager reconcile frequency. The default is
5s.
Create the dynamic kubelet config:
oc create -f cpumanager-kubeletconfig.yaml
# oc create -f cpumanager-kubeletconfig.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This adds the CPU Manager feature to the kubelet config and, if needed, the Machine Config Operator (MCO) reboots the node. To enable CPU Manager, a reboot is not needed.
Check for the merged kubelet config:
oc get machineconfig 99-worker-XXXXXX-XXXXX-XXXX-XXXXX-kubelet -o json | grep ownerReference -A7
# oc get machineconfig 99-worker-XXXXXX-XXXXX-XXXX-XXXXX-kubelet -o json | grep ownerReference -A7Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the worker for the updated
kubelet.conf:oc debug node/perf-node.example.com sh-4.2# cat /host/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf | grep cpuManager
# oc debug node/perf-node.example.com sh-4.2# cat /host/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf | grep cpuManagerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
cpuManagerPolicy: static cpuManagerReconcilePeriod: 5s
cpuManagerPolicy: static1 cpuManagerReconcilePeriod: 5s2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod that requests a core or multiple cores. Both limits and requests must have their CPU value set to a whole integer. That is the number of cores that will be dedicated to this pod:
cat cpumanager-pod.yaml
# cat cpumanager-pod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the pod:
oc create -f cpumanager-pod.yaml
# oc create -f cpumanager-pod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the pod is scheduled to the node that you labeled:
oc describe pod cpumanager
# oc describe pod cpumanagerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
cgroupsare set up correctly. Get the process ID (PID) of thepauseprocess:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pods of quality of service (QoS) tier
Guaranteedare placed within thekubepods.slice. Pods of other QoS tiers end up in childcgroupsofkubepods:cd /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-pod69c01f8e_6b74_11e9_ac0f_0a2b62178a22.slice/crio-b5437308f1ad1a7db0574c542bdf08563b865c0345c86e9585f8c0b0a655612c.scope for i in `ls cpuset.cpus tasks` ; do echo -n "$i "; cat $i ; done
# cd /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-pod69c01f8e_6b74_11e9_ac0f_0a2b62178a22.slice/crio-b5437308f1ad1a7db0574c542bdf08563b865c0345c86e9585f8c0b0a655612c.scope # for i in `ls cpuset.cpus tasks` ; do echo -n "$i "; cat $i ; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
cpuset.cpus 1 tasks 32706
cpuset.cpus 1 tasks 32706Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the allowed CPU list for the task:
grep ^Cpus_allowed_list /proc/32706/status
# grep ^Cpus_allowed_list /proc/32706/statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Cpus_allowed_list: 1
Cpus_allowed_list: 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that another pod (in this case, the pod in the
burstableQoS tier) on the system cannot run on the core allocated for theGuaranteedpod:cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-besteffort.slice/kubepods-besteffort-podc494a073_6b77_11e9_98c0_06bba5c387ea.slice/crio-c56982f57b75a2420947f0afc6cafe7534c5734efc34157525fa9abbf99e3849.scope/cpuset.cpus 0 oc describe node perf-node.example.com
# cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-besteffort.slice/kubepods-besteffort-podc494a073_6b77_11e9_98c0_06bba5c387ea.slice/crio-c56982f57b75a2420947f0afc6cafe7534c5734efc34157525fa9abbf99e3849.scope/cpuset.cpus 0 # oc describe node perf-node.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This VM has two CPU cores. The
system-reservedsetting reserves 500 millicores, meaning that half of one core is subtracted from the total capacity of the node to arrive at theNode Allocatableamount. You can see thatAllocatable CPUis 1500 millicores. This means you can run one of the CPU Manager pods since each will take one whole core. A whole core is equivalent to 1000 millicores. If you try to schedule a second pod, the system will accept the pod, but it will never be scheduled:NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cpumanager-6cqz7 1/1 Running 0 33m cpumanager-7qc2t 0/1 Pending 0 11s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cpumanager-6cqz7 1/1 Running 0 33m cpumanager-7qc2t 0/1 Pending 0 11sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.5. Huge pages
Understand and configure huge pages.
7.5.1. What huge pages do
Memory is managed in blocks known as pages. On most systems, a page is 4Ki. 1Mi of memory is equal to 256 pages; 1Gi of memory is 256,000 pages, and so on. CPUs have a built-in memory management unit that manages a list of these pages in hardware. The Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) is a small hardware cache of virtual-to-physical page mappings. If the virtual address passed in a hardware instruction can be found in the TLB, the mapping can be determined quickly. If not, a TLB miss occurs, and the system falls back to slower, software-based address translation, resulting in performance issues. Since the size of the TLB is fixed, the only way to reduce the chance of a TLB miss is to increase the page size.
A huge page is a memory page that is larger than 4Ki. On x86_64 architectures, there are two common huge page sizes: 2Mi and 1Gi. Sizes vary on other architectures. To use huge pages, code must be written so that applications are aware of them. Transparent Huge Pages (THP) attempt to automate the management of huge pages without application knowledge, but they have limitations. In particular, they are limited to 2Mi page sizes. THP can lead to performance degradation on nodes with high memory utilization or fragmentation due to defragmenting efforts of THP, which can lock memory pages. For this reason, some applications may be designed to (or recommend) usage of pre-allocated huge pages instead of THP.
7.5.2. How huge pages are consumed by apps
Nodes must pre-allocate huge pages in order for the node to report its huge page capacity. A node can only pre-allocate huge pages for a single size.
Huge pages can be consumed through container-level resource requirements using the resource name hugepages-<size>, where size is the most compact binary notation using integer values supported on a particular node. For example, if a node supports 2048KiB page sizes, it exposes a schedulable resource hugepages-2Mi. Unlike CPU or memory, huge pages do not support over-commitment.
- 1
- Specify the amount of memory for
hugepagesas the exact amount to be allocated. Do not specify this value as the amount of memory forhugepagesmultiplied by the size of the page. For example, given a huge page size of 2MB, if you want to use 100MB of huge-page-backed RAM for your application, then you would allocate 50 huge pages. OpenShift Container Platform handles the math for you. As in the above example, you can specify100MBdirectly.
Allocating huge pages of a specific size
Some platforms support multiple huge page sizes. To allocate huge pages of a specific size, precede the huge pages boot command parameters with a huge page size selection parameter hugepagesz=<size>. The <size> value must be specified in bytes with an optional scale suffix [kKmMgG]. The default huge page size can be defined with the default_hugepagesz=<size> boot parameter.
Huge page requirements
- Huge page requests must equal the limits. This is the default if limits are specified, but requests are not.
- Huge pages are isolated at a pod scope. Container isolation is planned in a future iteration.
-
EmptyDirvolumes backed by huge pages must not consume more huge page memory than the pod request. -
Applications that consume huge pages via
shmget()withSHM_HUGETLBmust run with a supplemental group that matches proc/sys/vm/hugetlb_shm_group.
7.5.3. Configuring huge pages
Nodes must pre-allocate huge pages used in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. There are two ways of reserving huge pages: at boot time and at run time. Reserving at boot time increases the possibility of success because the memory has not yet been significantly fragmented. The Node Tuning Operator currently supports boot time allocation of huge pages on specific nodes.
7.5.3.1. At boot time
Procedure
To minimize node reboots, the order of the steps below needs to be followed:
Label all nodes that need the same huge pages setting by a label.
oc label node <node_using_hugepages> node-role.kubernetes.io/worker-hp=
$ oc label node <node_using_hugepages> node-role.kubernetes.io/worker-hp=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a file with the following content and name it
hugepages-tuned-boottime.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Tuned
hugepagesobjectoc create -f hugepages-tuned-boottime.yaml
$ oc create -f hugepages-tuned-boottime.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a file with the following content and name it
hugepages-mcp.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the machine config pool:
oc create -f hugepages-mcp.yaml
$ oc create -f hugepages-mcp.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Given enough non-fragmented memory, all the nodes in the worker-hp machine config pool should now have 50 2Mi huge pages allocated.
oc get node <node_using_hugepages> -o jsonpath="{.status.allocatable.hugepages-2Mi}"
100Mi
$ oc get node <node_using_hugepages> -o jsonpath="{.status.allocatable.hugepages-2Mi}"
100MiThe TuneD bootloader plugin only supports Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) worker nodes.
7.6. Understanding device plugins
The device plugin provides a consistent and portable solution to consume hardware devices across clusters. The device plugin provides support for these devices through an extension mechanism, which makes these devices available to Containers, provides health checks of these devices, and securely shares them.
OpenShift Container Platform supports the device plugin API, but the device plugin Containers are supported by individual vendors.
A device plugin is a gRPC service running on the nodes (external to the kubelet) that is responsible for managing specific hardware resources. Any device plugin must support following remote procedure calls (RPCs):
Example device plugins
For easy device plugin reference implementation, there is a stub device plugin in the Device Manager code: vendor/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/kubelet/cm/deviceplugin/device_plugin_stub.go.
7.6.1. Methods for deploying a device plugin
- Daemon sets are the recommended approach for device plugin deployments.
- Upon start, the device plugin will try to create a UNIX domain socket at /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugin/ on the node to serve RPCs from Device Manager.
- Since device plugins must manage hardware resources, access to the host file system, as well as socket creation, they must be run in a privileged security context.
- More specific details regarding deployment steps can be found with each device plugin implementation.
7.6.2. Understanding the Device Manager
Device Manager provides a mechanism for advertising specialized node hardware resources with the help of plugins known as device plugins.
You can advertise specialized hardware without requiring any upstream code changes.
OpenShift Container Platform supports the device plugin API, but the device plugin Containers are supported by individual vendors.
Device Manager advertises devices as Extended Resources. User pods can consume devices, advertised by Device Manager, using the same Limit/Request mechanism, which is used for requesting any other Extended Resource.
Upon start, the device plugin registers itself with Device Manager invoking Register on the /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/kubelet.sock and starts a gRPC service at /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/<plugin>.sock for serving Device Manager requests.
Device Manager, while processing a new registration request, invokes ListAndWatch remote procedure call (RPC) at the device plugin service. In response, Device Manager gets a list of Device objects from the plugin over a gRPC stream. Device Manager will keep watching on the stream for new updates from the plugin. On the plugin side, the plugin will also keep the stream open and whenever there is a change in the state of any of the devices, a new device list is sent to the Device Manager over the same streaming connection.
While handling a new pod admission request, Kubelet passes requested Extended Resources to the Device Manager for device allocation. Device Manager checks in its database to verify if a corresponding plugin exists or not. If the plugin exists and there are free allocatable devices as well as per local cache, Allocate RPC is invoked at that particular device plugin.
Additionally, device plugins can also perform several other device-specific operations, such as driver installation, device initialization, and device resets. These functionalities vary from implementation to implementation.
7.6.3. Enabling Device Manager
Enable Device Manager to implement a device plugin to advertise specialized hardware without any upstream code changes.
Device Manager provides a mechanism for advertising specialized node hardware resources with the help of plugins known as device plugins.
Obtain the label associated with the static
MachineConfigPoolCRD for the type of node you want to configure by entering the following command. Perform one of the following steps:View the machine config:
oc describe machineconfig <name>
# oc describe machineconfig <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc describe machineconfig 00-worker
# oc describe machineconfig 00-workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name: 00-worker Namespace: Labels: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role=worker
Name: 00-worker Namespace: Labels: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role=worker1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Label required for the Device Manager.
Procedure
Create a custom resource (CR) for your configuration change.
Sample configuration for a Device Manager CR
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Device Manager:
oc create -f devicemgr.yaml
$ oc create -f devicemgr.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubeletconfig.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/devicemgr created
kubeletconfig.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/devicemgr createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that Device Manager was actually enabled by confirming that /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/kubelet.sock is created on the node. This is the UNIX domain socket on which the Device Manager gRPC server listens for new plugin registrations. This sock file is created when the Kubelet is started only if Device Manager is enabled.
7.7. Taints and tolerations
Understand and work with taints and tolerations.
7.7.1. Understanding taints and tolerations
A taint allows a node to refuse a pod to be scheduled unless that pod has a matching toleration.
You apply taints to a node through the Node specification (NodeSpec) and apply tolerations to a pod through the Pod specification (PodSpec). When you apply a taint a node, the scheduler cannot place a pod on that node unless the pod can tolerate the taint.
Example taint in a node specification
Example toleration in a Pod spec
Taints and tolerations consist of a key, value, and effect.
| Parameter | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
The | ||||||
|
|
The | ||||||
|
| The effect is one of the following:
| ||||||
|
|
|
If you add a
NoScheduletaint to a control plane node, the node must have thenode-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoScheduletaint, which is added by default.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
A toleration matches a taint:
If the
operatorparameter is set toEqual:-
the
keyparameters are the same; -
the
valueparameters are the same; -
the
effectparameters are the same.
-
the
If the
operatorparameter is set toExists:-
the
keyparameters are the same; -
the
effectparameters are the same.
-
the
The following taints are built into OpenShift Container Platform:
-
node.kubernetes.io/not-ready: The node is not ready. This corresponds to the node conditionReady=False. -
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable: The node is unreachable from the node controller. This corresponds to the node conditionReady=Unknown. -
node.kubernetes.io/memory-pressure: The node has memory pressure issues. This corresponds to the node conditionMemoryPressure=True. -
node.kubernetes.io/disk-pressure: The node has disk pressure issues. This corresponds to the node conditionDiskPressure=True. -
node.kubernetes.io/network-unavailable: The node network is unavailable. -
node.kubernetes.io/unschedulable: The node is unschedulable. -
node.cloudprovider.kubernetes.io/uninitialized: When the node controller is started with an external cloud provider, this taint is set on a node to mark it as unusable. After a controller from the cloud-controller-manager initializes this node, the kubelet removes this taint. node.kubernetes.io/pid-pressure: The node has pid pressure. This corresponds to the node conditionPIDPressure=True.ImportantOpenShift Container Platform does not set a default pid.available
evictionHard.
7.7.2. Adding taints and tolerations
You add tolerations to pods and taints to nodes to allow the node to control which pods should or should not be scheduled on them. For existing pods and nodes, you should add the toleration to the pod first, then add the taint to the node to avoid pods being removed from the node before you can add the toleration.
Procedure
Add a toleration to a pod by editing the
Podspec to include atolerationsstanza:Sample pod configuration file with an Equal operator
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Sample pod configuration file with an Exists operator
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
Existsoperator does not take avalue.
This example places a taint on
node1that has keykey1, valuevalue1, and taint effectNoExecute.Add a taint to a node by using the following command with the parameters described in the Taint and toleration components table:
oc adm taint nodes <node_name> <key>=<value>:<effect>
$ oc adm taint nodes <node_name> <key>=<value>:<effect>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc adm taint nodes node1 key1=value1:NoExecute
$ oc adm taint nodes node1 key1=value1:NoExecuteCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command places a taint on
node1that has keykey1, valuevalue1, and effectNoExecute.NoteIf you add a
NoScheduletaint to a control plane node, the node must have thenode-role.kubernetes.io/master=:NoScheduletaint, which is added by default.For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The tolerations on the pod match the taint on the node. A pod with either toleration can be scheduled onto
node1.
7.7.3. Adding taints and tolerations using a machine set
You can add taints to nodes using a machine set. All nodes associated with the MachineSet object are updated with the taint. Tolerations respond to taints added by a machine set in the same manner as taints added directly to the nodes.
Procedure
Add a toleration to a pod by editing the
Podspec to include atolerationsstanza:Sample pod configuration file with
EqualoperatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Sample pod configuration file with
ExistsoperatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the taint to the
MachineSetobject:Edit the
MachineSetYAML for the nodes you want to taint or you can create a newMachineSetobject:oc edit machineset <machineset>
$ oc edit machineset <machineset>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the taint to the
spec.template.specsection:Example taint in a machine set specification
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example places a taint that has the key
key1, valuevalue1, and taint effectNoExecuteon the nodes.Scale down the machine set to 0:
oc scale --replicas=0 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc scale --replicas=0 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to scale the machine set:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait for the machines to be removed.
Scale up the machine set as needed:
oc scale --replicas=2 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc scale --replicas=2 machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Or:
oc edit machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-api
$ oc edit machineset <machineset> -n openshift-machine-apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait for the machines to start. The taint is added to the nodes associated with the
MachineSetobject.
7.7.4. Binding a user to a node using taints and tolerations
If you want to dedicate a set of nodes for exclusive use by a particular set of users, add a toleration to their pods. Then, add a corresponding taint to those nodes. The pods with the tolerations are allowed to use the tainted nodes or any other nodes in the cluster.
If you want ensure the pods are scheduled to only those tainted nodes, also add a label to the same set of nodes and add a node affinity to the pods so that the pods can only be scheduled onto nodes with that label.
Procedure
To configure a node so that users can use only that node:
Add a corresponding taint to those nodes:
For example:
oc adm taint nodes node1 dedicated=groupName:NoSchedule
$ oc adm taint nodes node1 dedicated=groupName:NoScheduleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the taint:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add a toleration to the pods by writing a custom admission controller.
7.7.5. Controlling nodes with special hardware using taints and tolerations
In a cluster where a small subset of nodes have specialized hardware, you can use taints and tolerations to keep pods that do not need the specialized hardware off of those nodes, leaving the nodes for pods that do need the specialized hardware. You can also require pods that need specialized hardware to use specific nodes.
You can achieve this by adding a toleration to pods that need the special hardware and tainting the nodes that have the specialized hardware.
Procedure
To ensure nodes with specialized hardware are reserved for specific pods:
Add a toleration to pods that need the special hardware.
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Taint the nodes that have the specialized hardware using one of the following commands:
oc adm taint nodes <node-name> disktype=ssd:NoSchedule
$ oc adm taint nodes <node-name> disktype=ssd:NoScheduleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Or:
oc adm taint nodes <node-name> disktype=ssd:PreferNoSchedule
$ oc adm taint nodes <node-name> disktype=ssd:PreferNoScheduleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the taint:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.7.6. Removing taints and tolerations
You can remove taints from nodes and tolerations from pods as needed. You should add the toleration to the pod first, then add the taint to the node to avoid pods being removed from the node before you can add the toleration.
Procedure
To remove taints and tolerations:
To remove a taint from a node:
oc adm taint nodes <node-name> <key>-
$ oc adm taint nodes <node-name> <key>-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc adm taint nodes ip-10-0-132-248.ec2.internal key1-
$ oc adm taint nodes ip-10-0-132-248.ec2.internal key1-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
node/ip-10-0-132-248.ec2.internal untainted
node/ip-10-0-132-248.ec2.internal untaintedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove a toleration from a pod, edit the
Podspec to remove the toleration:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8. Topology Manager
Understand and work with Topology Manager.
7.8.1. Topology Manager policies
Topology Manager aligns Pod resources of all Quality of Service (QoS) classes by collecting topology hints from Hint Providers, such as CPU Manager and Device Manager, and using the collected hints to align the Pod resources.
Topology Manager supports four allocation policies, which you assign in the KubeletConfig custom resource (CR) named cpumanager-enabled:
nonepolicy- This is the default policy and does not perform any topology alignment.
best-effortpolicy-
For each container in a pod with the
best-efforttopology management policy, kubelet calls each Hint Provider to discover their resource availability. Using this information, the Topology Manager stores the preferred NUMA Node affinity for that container. If the affinity is not preferred, Topology Manager stores this and admits the pod to the node. restrictedpolicy-
For each container in a pod with the
restrictedtopology management policy, kubelet calls each Hint Provider to discover their resource availability. Using this information, the Topology Manager stores the preferred NUMA Node affinity for that container. If the affinity is not preferred, Topology Manager rejects this pod from the node, resulting in a pod in aTerminatedstate with a pod admission failure. single-numa-nodepolicy-
For each container in a pod with the
single-numa-nodetopology management policy, kubelet calls each Hint Provider to discover their resource availability. Using this information, the Topology Manager determines if a single NUMA Node affinity is possible. If it is, the pod is admitted to the node. If a single NUMA Node affinity is not possible, the Topology Manager rejects the pod from the node. This results in a pod in a Terminated state with a pod admission failure.
7.8.2. Setting up Topology Manager
To use Topology Manager, you must configure an allocation policy in the KubeletConfig custom resource (CR) named cpumanager-enabled. This file might exist if you have set up CPU Manager. If the file does not exist, you can create the file.
Prequisites
-
Configure the CPU Manager policy to be
static.
Procedure
To activate Topololgy Manager:
Configure the Topology Manager allocation policy in the custom resource.
oc edit KubeletConfig cpumanager-enabled
$ oc edit KubeletConfig cpumanager-enabledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.3. Pod interactions with Topology Manager policies
The example Pod specs below help illustrate pod interactions with Topology Manager.
The following pod runs in the BestEffort QoS class because no resource requests or limits are specified.
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
The next pod runs in the Burstable QoS class because requests are less than limits.
If the selected policy is anything other than none, Topology Manager would not consider either of these Pod specifications.
The last example pod below runs in the Guaranteed QoS class because requests are equal to limits.
Topology Manager would consider this pod. The Topology Manager would consult the hint providers, which are CPU Manager and Device Manager, to get topology hints for the pod.
Topology Manager will use this information to store the best topology for this container. In the case of this pod, CPU Manager and Device Manager will use this stored information at the resource allocation stage.
7.9. Resource requests and overcommitment
For each compute resource, a container may specify a resource request and limit. Scheduling decisions are made based on the request to ensure that a node has enough capacity available to meet the requested value. If a container specifies limits, but omits requests, the requests are defaulted to the limits. A container is not able to exceed the specified limit on the node.
The enforcement of limits is dependent upon the compute resource type. If a container makes no request or limit, the container is scheduled to a node with no resource guarantees. In practice, the container is able to consume as much of the specified resource as is available with the lowest local priority. In low resource situations, containers that specify no resource requests are given the lowest quality of service.
Scheduling is based on resources requested, while quota and hard limits refer to resource limits, which can be set higher than requested resources. The difference between request and limit determines the level of overcommit; for instance, if a container is given a memory request of 1Gi and a memory limit of 2Gi, it is scheduled based on the 1Gi request being available on the node, but could use up to 2Gi; so it is 200% overcommitted.
7.10. Cluster-level overcommit using the Cluster Resource Override Operator
The Cluster Resource Override Operator is an admission webhook that allows you to control the level of overcommit and manage container density across all the nodes in your cluster. The Operator controls how nodes in specific projects can exceed defined memory and CPU limits.
You must install the Cluster Resource Override Operator using the OpenShift Container Platform console or CLI as shown in the following sections. During the installation, you create a ClusterResourceOverride custom resource (CR), where you set the level of overcommit, as shown in the following example:
- 1
- The name must be
cluster. - 2
- Optional. If a container memory limit has been specified or defaulted, the memory request is overridden to this percentage of the limit, between 1-100. The default is 50.
- 3
- Optional. If a container CPU limit has been specified or defaulted, the CPU request is overridden to this percentage of the limit, between 1-100. The default is 25.
- 4
- Optional. If a container memory limit has been specified or defaulted, the CPU limit is overridden to a percentage of the memory limit, if specified. Scaling 1Gi of RAM at 100 percent is equal to 1 CPU core. This is processed prior to overriding the CPU request (if configured). The default is 200.
The Cluster Resource Override Operator overrides have no effect if limits have not been set on containers. Create a LimitRange object with default limits per individual project or configure limits in Pod specs for the overrides to apply.
When configured, overrides can be enabled per-project by applying the following label to the Namespace object for each project:
The Operator watches for the ClusterResourceOverride CR and ensures that the ClusterResourceOverride admission webhook is installed into the same namespace as the operator.
7.10.1. Installing the Cluster Resource Override Operator using the web console
You can use the OpenShift Container Platform web console to install the Cluster Resource Override Operator to help control overcommit in your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
The Cluster Resource Override Operator has no effect if limits have not been set on containers. You must specify default limits for a project using a
LimitRangeobject or configure limits inPodspecs for the overrides to apply.
Procedure
To install the Cluster Resource Override Operator using the OpenShift Container Platform web console:
In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, navigate to Home → Projects
- Click Create Project.
-
Specify
clusterresourceoverride-operatoras the name of the project. - Click Create.
Navigate to Operators → OperatorHub.
- Choose ClusterResourceOverride Operator from the list of available Operators and click Install.
- On the Install Operator page, make sure A specific Namespace on the cluster is selected for Installation Mode.
- Make sure clusterresourceoverride-operator is selected for Installed Namespace.
- Select an Update Channel and Approval Strategy.
- Click Install.
On the Installed Operators page, click ClusterResourceOverride.
- On the ClusterResourceOverride Operator details page, click Create ClusterResourceOverride.
On the Create ClusterResourceOverride page, click YAML view and edit the YAML template to set the overcommit values as needed:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name must be
cluster. - 2
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container memory limit, if used, between 1-100. The default is 50.
- 3
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container CPU limit, if used, between 1-100. The default is 25.
- 4
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container memory limit, if used. Scaling 1Gi of RAM at 100 percent is equal to 1 CPU core. This is processed prior to overriding the CPU request, if configured. The default is 200.
- Click Create.
Check the current state of the admission webhook by checking the status of the cluster custom resource:
- On the ClusterResourceOverride Operator page, click cluster.
On the ClusterResourceOverride Details page, click YAML. The
mutatingWebhookConfigurationRefsection appears when the webhook is called.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Reference to the
ClusterResourceOverrideadmission webhook.
7.10.2. Installing the Cluster Resource Override Operator using the CLI
You can use the OpenShift Container Platform CLI to install the Cluster Resource Override Operator to help control overcommit in your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
The Cluster Resource Override Operator has no effect if limits have not been set on containers. You must specify default limits for a project using a
LimitRangeobject or configure limits inPodspecs for the overrides to apply.
Procedure
To install the Cluster Resource Override Operator using the CLI:
Create a namespace for the Cluster Resource Override Operator:
Create a
Namespaceobject YAML file (for example,cro-namespace.yaml) for the Cluster Resource Override Operator:apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: clusterresourceoverride-operator
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: clusterresourceoverride-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the namespace:
oc create -f <file-name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file-name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc create -f cro-namespace.yaml
$ oc create -f cro-namespace.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create an Operator group:
Create an
OperatorGroupobject YAML file (for example, cro-og.yaml) for the Cluster Resource Override Operator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Operator Group:
oc create -f <file-name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file-name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc create -f cro-og.yaml
$ oc create -f cro-og.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a subscription:
Create a
Subscriptionobject YAML file (for example, cro-sub.yaml) for the Cluster Resource Override Operator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the subscription:
oc create -f <file-name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file-name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc create -f cro-sub.yaml
$ oc create -f cro-sub.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
ClusterResourceOverridecustom resource (CR) object in theclusterresourceoverride-operatornamespace:Change to the
clusterresourceoverride-operatornamespace.oc project clusterresourceoverride-operator
$ oc project clusterresourceoverride-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
ClusterResourceOverrideobject YAML file (for example, cro-cr.yaml) for the Cluster Resource Override Operator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name must be
cluster. - 2
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container memory limit, if used, between 1-100. The default is 50.
- 3
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container CPU limit, if used, between 1-100. The default is 25.
- 4
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container memory limit, if used. Scaling 1Gi of RAM at 100 percent is equal to 1 CPU core. This is processed prior to overriding the CPU request, if configured. The default is 200.
Create the
ClusterResourceOverrideobject:oc create -f <file-name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file-name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc create -f cro-cr.yaml
$ oc create -f cro-cr.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verify the current state of the admission webhook by checking the status of the cluster custom resource.
oc get clusterresourceoverride cluster -n clusterresourceoverride-operator -o yaml
$ oc get clusterresourceoverride cluster -n clusterresourceoverride-operator -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
mutatingWebhookConfigurationRefsection appears when the webhook is called.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Reference to the
ClusterResourceOverrideadmission webhook.
7.10.3. Configuring cluster-level overcommit
The Cluster Resource Override Operator requires a ClusterResourceOverride custom resource (CR) and a label for each project where you want the Operator to control overcommit.
Prerequisites
-
The Cluster Resource Override Operator has no effect if limits have not been set on containers. You must specify default limits for a project using a
LimitRangeobject or configure limits inPodspecs for the overrides to apply.
Procedure
To modify cluster-level overcommit:
Edit the
ClusterResourceOverrideCR:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container memory limit, if used, between 1-100. The default is 50.
- 2
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container CPU limit, if used, between 1-100. The default is 25.
- 3
- Optional. Specify the percentage to override the container memory limit, if used. Scaling 1Gi of RAM at 100 percent is equal to 1 CPU core. This is processed prior to overriding the CPU request, if configured. The default is 200.
Ensure the following label has been added to the Namespace object for each project where you want the Cluster Resource Override Operator to control overcommit:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Add this label to each project.
7.11. Node-level overcommit
You can use various ways to control overcommit on specific nodes, such as quality of service (QOS) guarantees, CPU limits, or reserve resources. You can also disable overcommit for specific nodes and specific projects.
7.11.1. Understanding compute resources and containers
The node-enforced behavior for compute resources is specific to the resource type.
7.11.1.1. Understanding container CPU requests
A container is guaranteed the amount of CPU it requests and is additionally able to consume excess CPU available on the node, up to any limit specified by the container. If multiple containers are attempting to use excess CPU, CPU time is distributed based on the amount of CPU requested by each container.
For example, if one container requested 500m of CPU time and another container requested 250m of CPU time, then any extra CPU time available on the node is distributed among the containers in a 2:1 ratio. If a container specified a limit, it will be throttled not to use more CPU than the specified limit. CPU requests are enforced using the CFS shares support in the Linux kernel. By default, CPU limits are enforced using the CFS quota support in the Linux kernel over a 100ms measuring interval, though this can be disabled.
7.11.1.2. Understanding container memory requests
A container is guaranteed the amount of memory it requests. A container can use more memory than requested, but once it exceeds its requested amount, it could be terminated in a low memory situation on the node. If a container uses less memory than requested, it will not be terminated unless system tasks or daemons need more memory than was accounted for in the node’s resource reservation. If a container specifies a limit on memory, it is immediately terminated if it exceeds the limit amount.
7.11.2. Understanding overcomitment and quality of service classes
A node is overcommitted when it has a pod scheduled that makes no request, or when the sum of limits across all pods on that node exceeds available machine capacity.
In an overcommitted environment, it is possible that the pods on the node will attempt to use more compute resource than is available at any given point in time. When this occurs, the node must give priority to one pod over another. The facility used to make this decision is referred to as a Quality of Service (QoS) Class.
A pod is designated as one of three QoS classes with decreasing order of priority:
| Priority | Class Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (highest) | Guaranteed | If limits and optionally requests are set (not equal to 0) for all resources and they are equal, then the pod is classified as Guaranteed. |
| 2 | Burstable | If requests and optionally limits are set (not equal to 0) for all resources, and they are not equal, then the pod is classified as Burstable. |
| 3 (lowest) | BestEffort | If requests and limits are not set for any of the resources, then the pod is classified as BestEffort. |
Memory is an incompressible resource, so in low memory situations, containers that have the lowest priority are terminated first:
- Guaranteed containers are considered top priority, and are guaranteed to only be terminated if they exceed their limits, or if the system is under memory pressure and there are no lower priority containers that can be evicted.
- Burstable containers under system memory pressure are more likely to be terminated once they exceed their requests and no other BestEffort containers exist.
- BestEffort containers are treated with the lowest priority. Processes in these containers are first to be terminated if the system runs out of memory.
7.11.2.1. Understanding how to reserve memory across quality of service tiers
You can use the qos-reserved parameter to specify a percentage of memory to be reserved by a pod in a particular QoS level. This feature attempts to reserve requested resources to exclude pods from lower OoS classes from using resources requested by pods in higher QoS classes.
OpenShift Container Platform uses the qos-reserved parameter as follows:
-
A value of
qos-reserved=memory=100%will prevent theBurstableandBestEffortQoS classes from consuming memory that was requested by a higher QoS class. This increases the risk of inducing OOM onBestEffortandBurstableworkloads in favor of increasing memory resource guarantees forGuaranteedandBurstableworkloads. -
A value of
qos-reserved=memory=50%will allow theBurstableandBestEffortQoS classes to consume half of the memory requested by a higher QoS class. -
A value of
qos-reserved=memory=0%will allow aBurstableandBestEffortQoS classes to consume up to the full node allocatable amount if available, but increases the risk that aGuaranteedworkload will not have access to requested memory. This condition effectively disables this feature.
7.11.3. Understanding swap memory and QOS
You can disable swap by default on your nodes to preserve quality of service (QOS) guarantees. Otherwise, physical resources on a node can oversubscribe, affecting the resource guarantees the Kubernetes scheduler makes during pod placement.
For example, if two guaranteed pods have reached their memory limit, each container could start using swap memory. Eventually, if there is not enough swap space, processes in the pods can be terminated due to the system being oversubscribed.
Failing to disable swap results in nodes not recognizing that they are experiencing MemoryPressure, resulting in pods not receiving the memory they made in their scheduling request. As a result, additional pods are placed on the node to further increase memory pressure, ultimately increasing your risk of experiencing a system out of memory (OOM) event.
If swap is enabled, any out-of-resource handling eviction thresholds for available memory will not work as expected. Take advantage of out-of-resource handling to allow pods to be evicted from a node when it is under memory pressure, and rescheduled on an alternative node that has no such pressure.
7.11.4. Understanding nodes overcommitment
In an overcommitted environment, it is important to properly configure your node to provide best system behavior.
When the node starts, it ensures that the kernel tunable flags for memory management are set properly. The kernel should never fail memory allocations unless it runs out of physical memory.
To ensure this behavior, OpenShift Container Platform configures the kernel to always overcommit memory by setting the vm.overcommit_memory parameter to 1, overriding the default operating system setting.
OpenShift Container Platform also configures the kernel not to panic when it runs out of memory by setting the vm.panic_on_oom parameter to 0. A setting of 0 instructs the kernel to call oom_killer in an Out of Memory (OOM) condition, which kills processes based on priority
You can view the current setting by running the following commands on your nodes:
sysctl -a |grep commit
$ sysctl -a |grep commitExample output
#... vm.overcommit_memory = 0 #...
#...
vm.overcommit_memory = 0
#...sysctl -a |grep panic
$ sysctl -a |grep panicExample output
#... vm.panic_on_oom = 0 #...
#...
vm.panic_on_oom = 0
#...The above flags should already be set on nodes, and no further action is required.
You can also perform the following configurations for each node:
- Disable or enforce CPU limits using CPU CFS quotas
- Reserve resources for system processes
- Reserve memory across quality of service tiers
7.11.5. Disabling or enforcing CPU limits using CPU CFS quotas
Nodes by default enforce specified CPU limits using the Completely Fair Scheduler (CFS) quota support in the Linux kernel.
If you disable CPU limit enforcement, it is important to understand the impact on your node:
- If a container has a CPU request, the request continues to be enforced by CFS shares in the Linux kernel.
- If a container does not have a CPU request, but does have a CPU limit, the CPU request defaults to the specified CPU limit, and is enforced by CFS shares in the Linux kernel.
- If a container has both a CPU request and limit, the CPU request is enforced by CFS shares in the Linux kernel, and the CPU limit has no impact on the node.
Prerequisites
Obtain the label associated with the static
MachineConfigPoolCRD for the type of node you want to configure by entering the following command:oc edit machineconfigpool <name>
$ oc edit machineconfigpool <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc edit machineconfigpool worker
$ oc edit machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The label appears under Labels.
TipIf the label is not present, add a key/value pair such as:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=small-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=small-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
Create a custom resource (CR) for your configuration change.
Sample configuration for a disabling CPU limits
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to create the CR:
oc create -f <file_name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.11.6. Reserving resources for system processes
To provide more reliable scheduling and minimize node resource overcommitment, each node can reserve a portion of its resources for use by system daemons that are required to run on your node for your cluster to function. In particular, it is recommended that you reserve resources for incompressible resources such as memory.
Procedure
To explicitly reserve resources for non-pod processes, allocate node resources by specifying resources available for scheduling. For more details, see Allocating Resources for Nodes.
7.11.7. Disabling overcommitment for a node
When enabled, overcommitment can be disabled on each node.
Procedure
To disable overcommitment in a node run the following command on that node:
sysctl -w vm.overcommit_memory=0
$ sysctl -w vm.overcommit_memory=07.12. Project-level limits
To help control overcommit, you can set per-project resource limit ranges, specifying memory and CPU limits and defaults for a project that overcommit cannot exceed.
For information on project-level resource limits, see Additional resources.
Alternatively, you can disable overcommitment for specific projects.
7.12.1. Disabling overcommitment for a project
When enabled, overcommitment can be disabled per-project. For example, you can allow infrastructure components to be configured independently of overcommitment.
Procedure
To disable overcommitment in a project:
Edit the namespace object to add the following annotation:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Setting this annotation to
falsedisables overcommit for this namespace.
7.13. Freeing node resources using garbage collection
Understand and use garbage collection.
7.13.1. Understanding how terminated containers are removed through garbage collection
Container garbage collection removes terminated containers by using eviction thresholds.
When eviction thresholds are set for garbage collection, the node tries to keep any container for any pod accessible from the API. If the pod has been deleted, the containers will be as well. Containers are preserved as long the pod is not deleted and the eviction threshold is not reached. If the node is under disk pressure, it will remove containers and their logs will no longer be accessible using oc logs.
- eviction-soft - A soft eviction threshold pairs an eviction threshold with a required administrator-specified grace period.
- eviction-hard - A hard eviction threshold has no grace period, and if observed, OpenShift Container Platform takes immediate action.
The following table lists the eviction thresholds:
| Node condition | Eviction signal | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MemoryPressure |
| The available memory on the node. |
| DiskPressure |
|
The available disk space or inodes on the node root file system, |
For evictionHard you must specify all of these parameters. If you do not specify all parameters, only the specified parameters are applied and the garbage collection will not function properly.
If a node is oscillating above and below a soft eviction threshold, but not exceeding its associated grace period, the corresponding node would constantly oscillate between true and false. As a consequence, the scheduler could make poor scheduling decisions.
To protect against this oscillation, use the eviction-pressure-transition-period flag to control how long OpenShift Container Platform must wait before transitioning out of a pressure condition. OpenShift Container Platform will not set an eviction threshold as being met for the specified pressure condition for the period specified before toggling the condition back to false.
7.13.2. Understanding how images are removed through garbage collection
Image garbage collection removes images that are not referenced by any running pods.
OpenShift Container Platform determines which images to remove from a node based on the disk usage that is reported by cAdvisor.
The policy for image garbage collection is based on two conditions:
- The percent of disk usage (expressed as an integer) which triggers image garbage collection. The default is 85.
- The percent of disk usage (expressed as an integer) to which image garbage collection attempts to free. Default is 80.
For image garbage collection, you can modify any of the following variables using a custom resource.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The minimum age for an unused image before the image is removed by garbage collection. The default is 2m. |
|
| The percent of disk usage, expressed as an integer, which triggers image garbage collection. The default is 85. |
|
| The percent of disk usage, expressed as an integer, to which image garbage collection attempts to free. The default is 80. |
Two lists of images are retrieved in each garbage collector run:
- A list of images currently running in at least one pod.
- A list of images available on a host.
As new containers are run, new images appear. All images are marked with a time stamp. If the image is running (the first list above) or is newly detected (the second list above), it is marked with the current time. The remaining images are already marked from the previous spins. All images are then sorted by the time stamp.
Once the collection starts, the oldest images get deleted first until the stopping criterion is met.
7.13.3. Configuring garbage collection for containers and images
As an administrator, you can configure how OpenShift Container Platform performs garbage collection by creating a kubeletConfig object for each machine config pool.
OpenShift Container Platform supports only one kubeletConfig object for each machine config pool.
You can configure any combination of the following:
- Soft eviction for containers
- Hard eviction for containers
- Eviction for images
Container garbage collection removes terminated containers. Image garbage collection removes images that are not referenced by any running pods.
Prerequisites
Obtain the label associated with the static
MachineConfigPoolCRD for the type of node you want to configure by entering the following command:oc edit machineconfigpool <name>
$ oc edit machineconfigpool <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc edit machineconfigpool worker
$ oc edit machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The label appears under Labels.
TipIf the label is not present, add a key/value pair such as:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=small-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=small-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
Create a custom resource (CR) for your configuration change.
ImportantIf there is one file system, or if
/var/lib/kubeletand/var/lib/containers/are in the same file system, the settings with the highest values trigger evictions, as those are met first. The file system triggers the eviction.Sample configuration for a container garbage collection CR:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Name for the object.
- 2
- Specify the label from the machine config pool.
- 3
- For container garbage collection: Type of eviction:
evictionSoftorevictionHard. - 4
- For container garbage collection: Eviction thresholds based on a specific eviction trigger signal.
- 5
- For container garbage collection: Grace periods for the soft eviction. This parameter does not apply to
eviction-hard. - 6
- For container garbage collection: Eviction thresholds based on a specific eviction trigger signal. For
evictionHardyou must specify all of these parameters. If you do not specify all parameters, only the specified parameters are applied and the garbage collection will not function properly. - 7
- For container garbage collection: The duration to wait before transitioning out of an eviction pressure condition.
- 8
- For image garbage collection: The minimum age for an unused image before the image is removed by garbage collection.
- 9
- For image garbage collection: The percent of disk usage (expressed as an integer) that triggers image garbage collection.
- 10
- For image garbage collection: The percent of disk usage (expressed as an integer) that image garbage collection attempts to free.
Run the following command to create the CR:
oc create -f <file_name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc create -f gc-container.yaml
$ oc create -f gc-container.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubeletconfig.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/gc-container created
kubeletconfig.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/gc-container createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that garbage collection is active by entering the following command. The Machine Config Pool you specified in the custom resource appears with
UPDATINGas 'true` until the change is fully implemented:oc get machineconfigpool
$ oc get machineconfigpoolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING master rendered-master-546383f80705bd5aeaba93 True False worker rendered-worker-b4c51bb33ccaae6fc4a6a5 False True
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING master rendered-master-546383f80705bd5aeaba93 True False worker rendered-worker-b4c51bb33ccaae6fc4a6a5 False TrueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.14. Using the Node Tuning Operator
Understand and use the Node Tuning Operator.
The Node Tuning Operator helps you manage node-level tuning by orchestrating the TuneD daemon and achieves low latency performance by using the Performance Profile controller. The majority of high-performance applications require some level of kernel tuning. The Node Tuning Operator provides a unified management interface to users of node-level sysctls and more flexibility to add custom tuning specified by user needs.
The Operator manages the containerized TuneD daemon for OpenShift Container Platform as a Kubernetes daemon set. It ensures the custom tuning specification is passed to all containerized TuneD daemons running in the cluster in the format that the daemons understand. The daemons run on all nodes in the cluster, one per node.
Node-level settings applied by the containerized TuneD daemon are rolled back on an event that triggers a profile change or when the containerized TuneD daemon is terminated gracefully by receiving and handling a termination signal.
The Node Tuning Operator uses the Performance Profile controller to implement automatic tuning to achieve low latency performance for OpenShift Container Platform applications. The cluster administrator configures a performance profile to define node-level settings such as the following:
- Updating the kernel to kernel-rt.
- Choosing CPUs for housekeeping.
- Choosing CPUs for running workloads.
The Node Tuning Operator is part of a standard OpenShift Container Platform installation in version 4.1 and later.
In earlier versions of OpenShift Container Platform, the Performance Addon Operator was used to implement automatic tuning to achieve low latency performance for OpenShift applications. In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 and later, this functionality is part of the Node Tuning Operator.
7.14.1. Accessing an example Node Tuning Operator specification
Use this process to access an example Node Tuning Operator specification.
Procedure
Run the following command to access an example Node Tuning Operator specification:
oc get tuned.tuned.openshift.io/default -o yaml -n openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operator
oc get tuned.tuned.openshift.io/default -o yaml -n openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The default CR is meant for delivering standard node-level tuning for the OpenShift Container Platform platform and it can only be modified to set the Operator Management state. Any other custom changes to the default CR will be overwritten by the Operator. For custom tuning, create your own Tuned CRs. Newly created CRs will be combined with the default CR and custom tuning applied to OpenShift Container Platform nodes based on node or pod labels and profile priorities.
While in certain situations the support for pod labels can be a convenient way of automatically delivering required tuning, this practice is discouraged and strongly advised against, especially in large-scale clusters. The default Tuned CR ships without pod label matching. If a custom profile is created with pod label matching, then the functionality will be enabled at that time. The pod label functionality will be deprecated in future versions of the Node Tuning Operator.
7.14.2. Custom tuning specification
The custom resource (CR) for the Operator has two major sections. The first section, profile:, is a list of TuneD profiles and their names. The second, recommend:, defines the profile selection logic.
Multiple custom tuning specifications can co-exist as multiple CRs in the Operator’s namespace. The existence of new CRs or the deletion of old CRs is detected by the Operator. All existing custom tuning specifications are merged and appropriate objects for the containerized TuneD daemons are updated.
Management state
The Operator Management state is set by adjusting the default Tuned CR. By default, the Operator is in the Managed state and the spec.managementState field is not present in the default Tuned CR. Valid values for the Operator Management state are as follows:
- Managed: the Operator will update its operands as configuration resources are updated
- Unmanaged: the Operator will ignore changes to the configuration resources
- Removed: the Operator will remove its operands and resources the Operator provisioned
Profile data
The profile: section lists TuneD profiles and their names.
Recommended profiles
The profile: selection logic is defined by the recommend: section of the CR. The recommend: section is a list of items to recommend the profiles based on a selection criteria.
recommend: <recommend-item-1> # ... <recommend-item-n>
recommend:
<recommend-item-1>
# ...
<recommend-item-n>The individual items of the list:
- 1
- Optional.
- 2
- A dictionary of key/value
MachineConfiglabels. The keys must be unique. - 3
- If omitted, profile match is assumed unless a profile with a higher priority matches first or
machineConfigLabelsis set. - 4
- An optional list.
- 5
- Profile ordering priority. Lower numbers mean higher priority (
0is the highest priority). - 6
- A TuneD profile to apply on a match. For example
tuned_profile_1. - 7
- Optional operand configuration.
- 8
- Turn debugging on or off for the TuneD daemon. Options are
truefor on orfalsefor off. The default isfalse. - 9
- Turn
reapply_sysctlfunctionality on or off for the TuneD daemon. Options aretruefor on andfalsefor off.
<match> is an optional list recursively defined as follows:
- label: <label_name>
value: <label_value>
type: <label_type>
<match>
- label: <label_name>
value: <label_value>
type: <label_type>
<match>
If <match> is not omitted, all nested <match> sections must also evaluate to true. Otherwise, false is assumed and the profile with the respective <match> section will not be applied or recommended. Therefore, the nesting (child <match> sections) works as logical AND operator. Conversely, if any item of the <match> list matches, the entire <match> list evaluates to true. Therefore, the list acts as logical OR operator.
If machineConfigLabels is defined, machine config pool based matching is turned on for the given recommend: list item. <mcLabels> specifies the labels for a machine config. The machine config is created automatically to apply host settings, such as kernel boot parameters, for the profile <tuned_profile_name>. This involves finding all machine config pools with machine config selector matching <mcLabels> and setting the profile <tuned_profile_name> on all nodes that are assigned the found machine config pools. To target nodes that have both master and worker roles, you must use the master role.
The list items match and machineConfigLabels are connected by the logical OR operator. The match item is evaluated first in a short-circuit manner. Therefore, if it evaluates to true, the machineConfigLabels item is not considered.
When using machine config pool based matching, it is advised to group nodes with the same hardware configuration into the same machine config pool. Not following this practice might result in TuneD operands calculating conflicting kernel parameters for two or more nodes sharing the same machine config pool.
Example: node or pod label based matching
The CR above is translated for the containerized TuneD daemon into its recommend.conf file based on the profile priorities. The profile with the highest priority (10) is openshift-control-plane-es and, therefore, it is considered first. The containerized TuneD daemon running on a given node looks to see if there is a pod running on the same node with the tuned.openshift.io/elasticsearch label set. If not, the entire <match> section evaluates as false. If there is such a pod with the label, in order for the <match> section to evaluate to true, the node label also needs to be node-role.kubernetes.io/master or node-role.kubernetes.io/infra.
If the labels for the profile with priority 10 matched, openshift-control-plane-es profile is applied and no other profile is considered. If the node/pod label combination did not match, the second highest priority profile (openshift-control-plane) is considered. This profile is applied if the containerized TuneD pod runs on a node with labels node-role.kubernetes.io/master or node-role.kubernetes.io/infra.
Finally, the profile openshift-node has the lowest priority of 30. It lacks the <match> section and, therefore, will always match. It acts as a profile catch-all to set openshift-node profile, if no other profile with higher priority matches on a given node.
Example: machine config pool based matching
To minimize node reboots, label the target nodes with a label the machine config pool’s node selector will match, then create the Tuned CR above and finally create the custom machine config pool itself.
Cloud provider-specific TuneD profiles
With this functionality, all Cloud provider-specific nodes can conveniently be assigned a TuneD profile specifically tailored to a given Cloud provider on a OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This can be accomplished without adding additional node labels or grouping nodes into machine config pools.
This functionality takes advantage of spec.providerID node object values in the form of <cloud-provider>://<cloud-provider-specific-id> and writes the file /var/lib/tuned/provider with the value <cloud-provider> in NTO operand containers. The content of this file is then used by TuneD to load provider-<cloud-provider> profile if such profile exists.
The openshift profile that both openshift-control-plane and openshift-node profiles inherit settings from is now updated to use this functionality through the use of conditional profile loading. Neither NTO nor TuneD currently ship any Cloud provider-specific profiles. However, it is possible to create a custom profile provider-<cloud-provider> that will be applied to all Cloud provider-specific cluster nodes.
Example GCE Cloud provider profile
Due to profile inheritance, any setting specified in the provider-<cloud-provider> profile will be overwritten by the openshift profile and its child profiles.
7.14.3. Default profiles set on a cluster
The following are the default profiles set on a cluster.
Starting with OpenShift Container Platform 4.9, all OpenShift TuneD profiles are shipped with the TuneD package. You can use the oc exec command to view the contents of these profiles:
oc exec $tuned_pod -n openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operator -- find /usr/lib/tuned/openshift{,-control-plane,-node} -name tuned.conf -exec grep -H ^ {} \;
$ oc exec $tuned_pod -n openshift-cluster-node-tuning-operator -- find /usr/lib/tuned/openshift{,-control-plane,-node} -name tuned.conf -exec grep -H ^ {} \;7.14.4. Supported TuneD daemon plugins
Excluding the [main] section, the following TuneD plugins are supported when using custom profiles defined in the profile: section of the Tuned CR:
- audio
- cpu
- disk
- eeepc_she
- modules
- mounts
- net
- scheduler
- scsi_host
- selinux
- sysctl
- sysfs
- usb
- video
- vm
- bootloader
There is some dynamic tuning functionality provided by some of these plugins that is not supported. The following TuneD plugins are currently not supported:
- script
- systemd
The TuneD bootloader plugin only supports Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) worker nodes.
Additional resources
7.15. Configuring the maximum number of pods per node
Two parameters control the maximum number of pods that can be scheduled to a node: podsPerCore and maxPods. If you use both options, the lower of the two limits the number of pods on a node.
For example, if podsPerCore is set to 10 on a node with 4 processor cores, the maximum number of pods allowed on the node will be 40.
Prerequisites
Obtain the label associated with the static
MachineConfigPoolCRD for the type of node you want to configure by entering the following command:oc edit machineconfigpool <name>
$ oc edit machineconfigpool <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc edit machineconfigpool worker
$ oc edit machineconfigpool workerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The label appears under Labels.
TipIf the label is not present, add a key/value pair such as:
oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=small-pods
$ oc label machineconfigpool worker custom-kubelet=small-podsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
Create a custom resource (CR) for your configuration change.
Sample configuration for a
max-podsCRCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteSetting
podsPerCoreto0disables this limit.In the above example, the default value for
podsPerCoreis10and the default value formaxPodsis250. This means that unless the node has 25 cores or more, by default,podsPerCorewill be the limiting factor.Run the following command to create the CR:
oc create -f <file_name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <file_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
List the
MachineConfigPoolCRDs to see if the change is applied. TheUPDATINGcolumn reportsTrueif the change is picked up by the Machine Config Controller:oc get machineconfigpools
$ oc get machineconfigpoolsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED master master-9cc2c72f205e103bb534 False False False worker worker-8cecd1236b33ee3f8a5e False True False
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED master master-9cc2c72f205e103bb534 False False False worker worker-8cecd1236b33ee3f8a5e False True FalseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Once the change is complete, the
UPDATEDcolumn reportsTrue.oc get machineconfigpools
$ oc get machineconfigpoolsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED master master-9cc2c72f205e103bb534 False True False worker worker-8cecd1236b33ee3f8a5e True False False
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED master master-9cc2c72f205e103bb534 False True False worker worker-8cecd1236b33ee3f8a5e True False FalseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 8. Postinstallation network configuration
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can further expand and customize your network to your requirements.
8.1. Cluster Network Operator configuration
The configuration for the cluster network is specified as part of the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration and stored in a custom resource (CR) object that is named cluster. The CR specifies the fields for the Network API in the operator.openshift.io API group.
The CNO configuration inherits the following fields during cluster installation from the Network API in the Network.config.openshift.io API group and these fields cannot be changed:
clusterNetwork- IP address pools from which pod IP addresses are allocated.
serviceNetwork- IP address pool for services.
defaultNetwork.type- Cluster network provider, such as OpenShift SDN or OVN-Kubernetes.
After cluster installation, you cannot modify the fields listed in the previous section.
8.2. Enabling the cluster-wide proxy
The Proxy object is used to manage the cluster-wide egress proxy. When a cluster is installed or upgraded without the proxy configured, a Proxy object is still generated but it will have a nil spec. For example:
A cluster administrator can configure the proxy for OpenShift Container Platform by modifying this cluster Proxy object.
Only the Proxy object named cluster is supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator permissions
-
OpenShift Container Platform
ocCLI tool installed
Procedure
Create a config map that contains any additional CA certificates required for proxying HTTPS connections.
NoteYou can skip this step if the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle.
Create a file called
user-ca-bundle.yamlwith the following contents, and provide the values of your PEM-encoded certificates:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the config map from this file:
oc create -f user-ca-bundle.yaml
$ oc create -f user-ca-bundle.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Use the
oc editcommand to modify theProxyobject:oc edit proxy/cluster
$ oc edit proxy/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the necessary fields for the proxy:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. - 2
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be either
httporhttps. Specify a URL for the proxy that supports the URL scheme. For example, most proxies will report an error if they are configured to usehttpsbut they only supporthttp. This failure message may not propagate to the logs and can appear to be a network connection failure instead. If using a proxy that listens forhttpsconnections from the cluster, you may need to configure the cluster to accept the CAs and certificates that the proxy uses. - 3
- A comma-separated list of destination domain names, domains, IP addresses or other network CIDRs to exclude proxying.
Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass proxy for all destinations. If you scale up workers that are not included in the network defined by thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidrfield from the installation configuration, you must add them to this list to prevent connection issues.This field is ignored if neither the
httpProxyorhttpsProxyfields are set. - 4
- One or more URLs external to the cluster to use to perform a readiness check before writing the
httpProxyandhttpsProxyvalues to status. - 5
- A reference to the config map in the
openshift-confignamespace that contains additional CA certificates required for proxying HTTPS connections. Note that the config map must already exist before referencing it here. This field is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle.
- Save the file to apply the changes.
8.3. Setting DNS to private
After you deploy a cluster, you can modify its DNS to use only a private zone.
Procedure
Review the
DNScustom resource for your cluster:oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the
specsection contains both a private and a public zone.Patch the
DNScustom resource to remove the public zone:oc patch dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge --patch='{"spec": {"publicZone": null}}' dns.config.openshift.io/cluster patched$ oc patch dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster --type=merge --patch='{"spec": {"publicZone": null}}' dns.config.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Because the Ingress Controller consults the
DNSdefinition when it createsIngressobjects, when you create or modifyIngressobjects, only private records are created.ImportantDNS records for the existing Ingress objects are not modified when you remove the public zone.
Optional: Review the
DNScustom resource for your cluster and confirm that the public zone was removed:oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get dnses.config.openshift.io/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.4. Configuring ingress cluster traffic
OpenShift Container Platform provides the following methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster:
- If you have HTTP/HTTPS, use an Ingress Controller.
- If you have a TLS-encrypted protocol other than HTTPS, such as TLS with the SNI header, use an Ingress Controller.
- Otherwise, use a load balancer, an external IP, or a node port.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Allows access to HTTP/HTTPS traffic and TLS-encrypted protocols other than HTTPS, such as TLS with the SNI header. | |
| Automatically assign an external IP by using a load balancer service | Allows traffic to non-standard ports through an IP address assigned from a pool. |
| Allows traffic to non-standard ports through a specific IP address. | |
| Expose a service on all nodes in the cluster. |
8.5. Configuring the node port service range
As a cluster administrator, you can expand the available node port range. If your cluster uses of a large number of node ports, you might need to increase the number of available ports.
The default port range is 30000-32767. You can never reduce the port range, even if you first expand it beyond the default range.
8.5.1. Prerequisites
-
Your cluster infrastructure must allow access to the ports that you specify within the expanded range. For example, if you expand the node port range to
30000-32900, the inclusive port range of32768-32900must be allowed by your firewall or packet filtering configuration.
8.5.1.1. Expanding the node port range
You can expand the node port range for the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To expand the node port range, enter the following command. Replace
<port>with the largest port number in the new range.oc patch network.config.openshift.io cluster --type=merge -p \ '{ "spec": { "serviceNodePortRange": "30000-<port>" } }'$ oc patch network.config.openshift.io cluster --type=merge -p \ '{ "spec": { "serviceNodePortRange": "30000-<port>" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to update the node port range:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the configuration is active, enter the following command. It can take several minutes for the update to apply.
oc get configmaps -n openshift-kube-apiserver config \ -o jsonpath="{.data['config\.yaml']}" | \ grep -Eo '"service-node-port-range":["[[:digit:]]+-[[:digit:]]+"]'$ oc get configmaps -n openshift-kube-apiserver config \ -o jsonpath="{.data['config\.yaml']}" | \ grep -Eo '"service-node-port-range":["[[:digit:]]+-[[:digit:]]+"]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
"service-node-port-range":["30000-33000"]
"service-node-port-range":["30000-33000"]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.6. Configuring IPsec encryption
With IPsec enabled, all network traffic between nodes on the OVN-Kubernetes Container Network Interface (CNI) cluster network travels through an encrypted tunnel.
IPsec is disabled by default.
8.6.1. Prerequisites
- Your cluster must use the OVN-Kubernetes cluster network provider.
8.6.1.1. Enabling IPsec encryption
As a cluster administrator, you can enable IPsec encryption after cluster installation.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. -
You have reduced the size of your cluster MTU by
46bytes to allow for the overhead of the IPsec ESP header.
Procedure
To enable IPsec encryption, enter the following command:
oc patch networks.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge \ -p '{"spec":{"defaultNetwork":{"ovnKubernetesConfig":{"ipsecConfig":{ }}}}}'$ oc patch networks.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge \ -p '{"spec":{"defaultNetwork":{"ovnKubernetesConfig":{"ipsecConfig":{ }}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.6.1.2. Verifying that IPsec is enabled
As a cluster administrator, you can verify that IPsec is enabled.
Verification
To find the names of the OVN-Kubernetes control plane pods, enter the following command:
oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep ovnkube-master
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep ovnkube-masterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that IPsec is enabled on your cluster:
oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -c nbdb rsh ovnkube-master-<XXXXX> \ ovn-nbctl --no-leader-only get nb_global . ipsec
$ oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -c nbdb rsh ovnkube-master-<XXXXX> \ ovn-nbctl --no-leader-only get nb_global . ipsecCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<XXXXX>- Specifies the random sequence of letters for a pod from the previous step.
Example output
true
trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.7. Configuring network policy
As a cluster administrator or project administrator, you can configure network policies for a project.
8.7.1. About network policy
In a cluster using a Kubernetes Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin that supports Kubernetes network policy, network isolation is controlled entirely by NetworkPolicy objects. In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11, OpenShift SDN supports using network policy in its default network isolation mode.
Network policy does not apply to the host network namespace. Pods with host networking enabled are unaffected by network policy rules. However, pods connecting to the host-networked pods might be affected by the network policy rules.
Network policies cannot block traffic from localhost or from their resident nodes.
By default, all pods in a project are accessible from other pods and network endpoints. To isolate one or more pods in a project, you can create NetworkPolicy objects in that project to indicate the allowed incoming connections. Project administrators can create and delete NetworkPolicy objects within their own project.
If a pod is matched by selectors in one or more NetworkPolicy objects, then the pod will accept only connections that are allowed by at least one of those NetworkPolicy objects. A pod that is not selected by any NetworkPolicy objects is fully accessible.
A network policy applies to only the TCP, UDP, ICMP, and SCTP protocols. Other protocols are not affected.
The following example NetworkPolicy objects demonstrate supporting different scenarios:
Deny all traffic:
To make a project deny by default, add a
NetworkPolicyobject that matches all pods but accepts no traffic:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Only allow connections from the OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Controller:
To make a project allow only connections from the OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Controller, add the following
NetworkPolicyobject.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Only accept connections from pods within a project:
To make pods accept connections from other pods in the same project, but reject all other connections from pods in other projects, add the following
NetworkPolicyobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Only allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic based on pod labels:
To enable only HTTP and HTTPS access to the pods with a specific label (
role=frontendin following example), add aNetworkPolicyobject similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Accept connections by using both namespace and pod selectors:
To match network traffic by combining namespace and pod selectors, you can use a
NetworkPolicyobject similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
NetworkPolicy objects are additive, which means you can combine multiple NetworkPolicy objects together to satisfy complex network requirements.
For example, for the NetworkPolicy objects defined in previous samples, you can define both allow-same-namespace and allow-http-and-https policies within the same project. Thus allowing the pods with the label role=frontend, to accept any connection allowed by each policy. That is, connections on any port from pods in the same namespace, and connections on ports 80 and 443 from pods in any namespace.
8.7.1.1. Using the allow-from-router network policy
Use the following NetworkPolicy to allow external traffic regardless of the router configuration:
- 1
policy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress:""label supports both OpenShift-SDN and OVN-Kubernetes.
8.7.1.2. Using the allow-from-hostnetwork network policy
Add the following allow-from-hostnetwork NetworkPolicy object to direct traffic from the host network pods:
8.7.2. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
8.7.3. Creating a network policy using the CLI
To define granular rules describing ingress or egress network traffic allowed for namespaces in your cluster, you can create a network policy.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a cluster network provider that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OpenShift SDN network provider withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy rule:
Create a
<policy_name>.yamlfile:touch <policy_name>.yaml
$ touch <policy_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the network policy file name.
Define a network policy in the file that you just created, such as in the following examples:
Deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Allow ingress from all pods in the same namespace
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To create the network policy object, enter the following command:
oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>
$ oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the network policy file name.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/default-deny created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/default-deny createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of creating a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
8.7.4. Configuring multitenant isolation by using network policy
You can configure your project to isolate it from pods and services in other project namespaces.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a cluster network provider that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OpenShift SDN network provider withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the following
NetworkPolicyobjects:A policy named
allow-from-openshift-ingress.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepolicy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress: ""is the preferred namespace selector label for OpenShift SDN. You can use thenetwork.openshift.io/policy-group: ingressnamespace selector label, but this is a legacy label.A policy named
allow-from-openshift-monitoring:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A policy named
allow-same-namespace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A policy named
allow-from-kube-apiserver-operator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more details, see New
kube-apiserver-operatorwebhook controller validating health of webhook.
Optional: To confirm that the network policies exist in your current project, enter the following command:
oc describe networkpolicy
$ oc describe networkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.7.5. Creating default network policies for a new project
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the new project template to automatically include NetworkPolicy objects when you create a new project.
8.7.6. Modifying the template for new projects
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the default project template so that new projects are created using your custom requirements.
To create your own custom project template:
Procedure
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. Generate the default project template:
oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yaml
$ oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Use a text editor to modify the generated
template.yamlfile by adding objects or modifying existing objects. The project template must be created in the
openshift-confignamespace. Load your modified template:oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-config
$ oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the project configuration resource using the web console or CLI.
Using the web console:
- Navigate to the Administration → Cluster Settings page.
- Click Configuration to view all configuration resources.
- Find the entry for Project and click Edit YAML.
Using the CLI:
Edit the
project.config.openshift.io/clusterresource:oc edit project.config.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit project.config.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Update the
specsection to include theprojectRequestTemplateandnameparameters, and set the name of your uploaded project template. The default name isproject-request.Project configuration resource with custom project template
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After you save your changes, create a new project to verify that your changes were successfully applied.
8.7.6.1. Adding network policies to the new project template
As a cluster administrator, you can add network policies to the default template for new projects. OpenShift Container Platform will automatically create all the NetworkPolicy objects specified in the template in the project.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a default CNI network provider that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OpenShift SDN network provider withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You must have created a custom default project template for new projects.
Procedure
Edit the default template for a new project by running the following command:
oc edit template <project_template> -n openshift-config
$ oc edit template <project_template> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<project_template>with the name of the default template that you configured for your cluster. The default template name isproject-request.In the template, add each
NetworkPolicyobject as an element to theobjectsparameter. Theobjectsparameter accepts a collection of one or more objects.In the following example, the
objectsparameter collection includes severalNetworkPolicyobjects.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Create a new project to confirm that your network policy objects are created successfully by running the following commands:
Create a new project:
oc new-project <project>
$ oc new-project <project>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<project>with the name for the project you are creating.
Confirm that the network policy objects in the new project template exist in the new project:
oc get networkpolicy NAME POD-SELECTOR AGE allow-from-openshift-ingress <none> 7s allow-from-same-namespace <none> 7s
$ oc get networkpolicy NAME POD-SELECTOR AGE allow-from-openshift-ingress <none> 7s allow-from-same-namespace <none> 7sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.8. Supported configurations
The following configurations are supported for the current release of Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh.
8.8.1. Supported platforms
The Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh Operator supports multiple versions of the ServiceMeshControlPlane resource. Version 2.4 Service Mesh control planes are supported on the following platform versions:
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform version 4.10 or later.
- Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated version 4.
- Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) version 4.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA).
8.8.2. Unsupported configurations
Explicitly unsupported cases include:
- OpenShift Online is not supported for Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh does not support the management of microservices outside the cluster where Service Mesh is running.
8.8.3. Supported network configurations
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh supports the following network configurations.
- OpenShift-SDN
- OVN-Kubernetes is available on all supported versions of OpenShift Container Platform.
- Third-Party Container Network Interface (CNI) plugins that have been certified on OpenShift Container Platform and passed Service Mesh conformance testing. See Certified OpenShift CNI Plug-ins for more information.
8.8.4. Supported configurations for Service Mesh
This release of Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh is only available on OpenShift Container Platform x86_64, IBM Z, and IBM Power.
- IBM Z is only supported on OpenShift Container Platform 4.10 and later.
- IBM Power is only supported on OpenShift Container Platform 4.10 and later.
- Configurations where all Service Mesh components are contained within a single OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Configurations that do not integrate external services such as virtual machines.
-
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh does not support
EnvoyFilterconfiguration except where explicitly documented.
8.8.5. Supported configurations for Kiali
- The Kiali console is only supported on the two most recent releases of the Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, or Apple Safari browsers.
-
The
openshiftauthentication strategy is the only supported authentication configuration when Kiali is deployed with Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh (OSSM). Theopenshiftstrategy controls access based on the individual’s role-based access control (RBAC) roles of the OpenShift Container Platform.
8.8.6. Supported configurations for Distributed Tracing
- Jaeger agent as a sidecar is the only supported configuration for Jaeger. Jaeger as a daemonset is not supported for multitenant installations or OpenShift Dedicated.
8.8.7. Supported WebAssembly module
- 3scale WebAssembly is the only provided WebAssembly module. You can create custom WebAssembly modules.
8.8.8. Operator overview
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh requires the following four Operators:
- OpenShift Elasticsearch - (Optional) Provides database storage for tracing and logging with the distributed tracing platform (Jaeger). It is based on the open source Elasticsearch project.
- Red Hat OpenShift distributed tracing platform (Jaeger) - Provides distributed tracing to monitor and troubleshoot transactions in complex distributed systems. It is based on the open source Jaeger project.
- Kiali Operator provided by Red Hat - Provides observability for your service mesh. You can view configurations, monitor traffic, and analyze traces in a single console. It is based on the open source Kiali project.
-
Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh - Allows you to connect, secure, control, and observe the microservices that comprise your applications. The Service Mesh Operator defines and monitors the
ServiceMeshControlPlaneresources that manage the deployment, updating, and deletion of the Service Mesh components. It is based on the open source Istio project.
Next steps
- Install Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh in your OpenShift Container Platform environment.
8.9. Optimizing routing
The OpenShift Container Platform HAProxy router can be scaled or configured to optimize performance.
8.9.1. Baseline Ingress Controller (router) performance
The OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Controller, or router, is the ingress point for ingress traffic for applications and services that are configured using routes and ingresses.
When evaluating a single HAProxy router performance in terms of HTTP requests handled per second, the performance varies depending on many factors. In particular:
- HTTP keep-alive/close mode
- Route type
- TLS session resumption client support
- Number of concurrent connections per target route
- Number of target routes
- Back end server page size
- Underlying infrastructure (network/SDN solution, CPU, and so on)
While performance in your specific environment will vary, Red Hat lab tests on a public cloud instance of size 4 vCPU/16GB RAM. A single HAProxy router handling 100 routes terminated by backends serving 1kB static pages is able to handle the following number of transactions per second.
In HTTP keep-alive mode scenarios:
| Encryption | LoadBalancerService | HostNetwork |
|---|---|---|
| none | 21515 | 29622 |
| edge | 16743 | 22913 |
| passthrough | 36786 | 53295 |
| re-encrypt | 21583 | 25198 |
In HTTP close (no keep-alive) scenarios:
| Encryption | LoadBalancerService | HostNetwork |
|---|---|---|
| none | 5719 | 8273 |
| edge | 2729 | 4069 |
| passthrough | 4121 | 5344 |
| re-encrypt | 2320 | 2941 |
The default Ingress Controller configuration was used with the spec.tuningOptions.threadCount field set to 4. Two different endpoint publishing strategies were tested: Load Balancer Service and Host Network. TLS session resumption was used for encrypted routes. With HTTP keep-alive, a single HAProxy router is capable of saturating a 1 Gbit NIC at page sizes as small as 8 kB.
When running on bare metal with modern processors, you can expect roughly twice the performance of the public cloud instance above. This overhead is introduced by the virtualization layer in place on public clouds and holds mostly true for private cloud-based virtualization as well. The following table is a guide to how many applications to use behind the router:
| Number of applications | Application type |
|---|---|
| 5-10 | static file/web server or caching proxy |
| 100-1000 | applications generating dynamic content |
In general, HAProxy can support routes for up to 1000 applications, depending on the technology in use. Ingress Controller performance might be limited by the capabilities and performance of the applications behind it, such as language or static versus dynamic content.
Ingress, or router, sharding should be used to serve more routes towards applications and help horizontally scale the routing tier.
8.10. Postinstallation RHOSP network configuration
You can configure some aspects of an OpenShift Container Platform on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) cluster after installation.
8.10.1. Configuring application access with floating IP addresses
After you install OpenShift Container Platform, configure Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) to allow application network traffic.
You do not need to perform this procedure if you provided values for platform.openstack.apiFloatingIP and platform.openstack.ingressFloatingIP in the install-config.yaml file, or os_api_fip and os_ingress_fip in the inventory.yaml playbook, during installation. The floating IP addresses are already set.
Prerequisites
- OpenShift Container Platform cluster must be installed
- Floating IP addresses are enabled as described in the OpenShift Container Platform on RHOSP installation documentation.
Procedure
After you install the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, attach a floating IP address to the ingress port:
Show the port:
openstack port show <cluster_name>-<cluster_ID>-ingress-port
$ openstack port show <cluster_name>-<cluster_ID>-ingress-portCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach the port to the IP address:
openstack floating ip set --port <ingress_port_ID> <apps_FIP>
$ openstack floating ip set --port <ingress_port_ID> <apps_FIP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a wildcard
Arecord for*apps.to your DNS file:*.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> IN A <apps_FIP>
*.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> IN A <apps_FIP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you do not control the DNS server but want to enable application access for non-production purposes, you can add these hostnames to /etc/hosts:
<apps_FIP> console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain> <apps_FIP> integrated-oauth-server-openshift-authentication.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain> <apps_FIP> oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain> <apps_FIP> prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain> <apps_FIP> <app name>.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain>
<apps_FIP> console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain>
<apps_FIP> integrated-oauth-server-openshift-authentication.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain>
<apps_FIP> oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain>
<apps_FIP> prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain>
<apps_FIP> <app name>.apps.<cluster name>.<base domain>8.10.2. Kuryr ports pools
A Kuryr ports pool maintains a number of ports on standby for pod creation.
Keeping ports on standby minimizes pod creation time. Without ports pools, Kuryr must explicitly request port creation or deletion whenever a pod is created or deleted.
The Neutron ports that Kuryr uses are created in subnets that are tied to namespaces. These pod ports are also added as subports to the primary port of OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes.
Because Kuryr keeps each namespace in a separate subnet, a separate ports pool is maintained for each namespace-worker pair.
Prior to installing a cluster, you can set the following parameters in the cluster-network-03-config.yml manifest file to configure ports pool behavior:
-
The
enablePortPoolsPrepopulationparameter controls pool prepopulation, which forces Kuryr to add Neutron ports to the pools when the first pod that is configured to use the dedicated network for pods is created in a namespace. The default value isfalse. -
The
poolMinPortsparameter is the minimum number of free ports that are kept in the pool. The default value is1. The
poolMaxPortsparameter is the maximum number of free ports that are kept in the pool. A value of0disables that upper bound. This is the default setting.If your OpenStack port quota is low, or you have a limited number of IP addresses on the pod network, consider setting this option to ensure that unneeded ports are deleted.
-
The
poolBatchPortsparameter defines the maximum number of Neutron ports that can be created at once. The default value is3.
8.10.3. Adjusting Kuryr ports pool settings in active deployments on RHOSP
You can use a custom resource (CR) to configure how Kuryr manages Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) Neutron ports to control the speed and efficiency of pod creation on a deployed cluster.
Procedure
From a command line, open the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) CR for editing:
oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the settings to meet your requirements. The following file is provided as an example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set
enablePortPoolsPrepopulationtotrueto make Kuryr create Neutron ports when the first pod that is configured to use the dedicated network for pods is created in a namespace. This setting raises the Neutron ports quota but can reduce the time that is required to spawn pods. The default value isfalse. - 2
- Kuryr creates new ports for a pool if the number of free ports in that pool is lower than the value of
poolMinPorts. The default value is1. - 3
poolBatchPortscontrols the number of new ports that are created if the number of free ports is lower than the value ofpoolMinPorts. The default value is3.- 4
- If the number of free ports in a pool is higher than the value of
poolMaxPorts, Kuryr deletes them until the number matches that value. Setting the value to0disables this upper bound, preventing pools from shrinking. The default value is0.
- Save your changes and quit the text editor to commit your changes.
Modifying these options on a running cluster forces the kuryr-controller and kuryr-cni pods to restart. As a result, the creation of new pods and services will be delayed.
8.10.4. Enabling OVS hardware offloading
For clusters that run on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), you can enable Open vSwitch (OVS) hardware offloading.
OVS is a multi-layer virtual switch that enables large-scale, multi-server network virtualization.
Prerequisites
- You installed a cluster on RHOSP that is configured for single-root input/output virtualization (SR-IOV).
- You installed the SR-IOV Network Operator on your cluster.
-
You created two
hw-offloadtype virtual function (VF) interfaces on your cluster.
Application layer gateway flows are broken in OpenShift Container Platform version 4.10, 4.11, and 4.12. Also, you cannot offload the application layer gateway flow for OpenShift Container Platform version 4.13.
Procedure
Create an
SriovNetworkNodePolicypolicy for the twohw-offloadtype VF interfaces that are on your cluster:The first virtual function interface
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The second virtual function interface
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionresources for the two interfaces:A
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionresource for the first interfaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionresource for the second interfaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the interfaces that you created with a pod. For example:
A pod that uses the two OVS offload interfaces
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.10.5. Attaching an OVS hardware offloading network
You can attach an Open vSwitch (OVS) hardware offloading network to your cluster.
Prerequisites
- Your cluster is installed and running.
- You provisioned an OVS hardware offloading network on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) to use with your cluster.
Procedure
Create a file named
network.yamlfrom the following template:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
pciBusIdSpecifies the device that is connected to the offloading network. If you do not have it, you can find this value by running the following command:
oc describe SriovNetworkNodeState -n openshift-sriov-network-operator
$ oc describe SriovNetworkNodeState -n openshift-sriov-network-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
From a command line, enter the following command to patch your cluster with the file:
oc apply -f network.yaml
$ oc apply -f network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 9. Postinstallation storage configuration
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can further expand and customize your cluster to your requirements, including storage configuration.
9.1. Dynamic provisioning
9.1.1. About dynamic provisioning
The StorageClass resource object describes and classifies storage that can be requested, as well as provides a means for passing parameters for dynamically provisioned storage on demand. StorageClass objects can also serve as a management mechanism for controlling different levels of storage and access to the storage. Cluster Administrators (cluster-admin) or Storage Administrators (storage-admin) define and create the StorageClass objects that users can request without needing any detailed knowledge about the underlying storage volume sources.
The OpenShift Container Platform persistent volume framework enables this functionality and allows administrators to provision a cluster with persistent storage. The framework also gives users a way to request those resources without having any knowledge of the underlying infrastructure.
Many storage types are available for use as persistent volumes in OpenShift Container Platform. While all of them can be statically provisioned by an administrator, some types of storage are created dynamically using the built-in provider and plugin APIs.
9.1.2. Available dynamic provisioning plugins
OpenShift Container Platform provides the following provisioner plugins, which have generic implementations for dynamic provisioning that use the cluster’s configured provider’s API to create new storage resources:
| Storage type | Provisioner plugin name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) Cinder |
| |
| RHOSP Manila Container Storage Interface (CSI) |
| Once installed, the OpenStack Manila CSI Driver Operator and ManilaDriver automatically create the required storage classes for all available Manila share types needed for dynamic provisioning. |
| AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS) |
|
For dynamic provisioning when using multiple clusters in different zones, tag each node with |
| Azure Disk |
| |
| Azure File |
|
The |
| GCE Persistent Disk (gcePD) |
| In multi-zone configurations, it is advisable to run one OpenShift Container Platform cluster per GCE project to avoid PVs from being created in zones where no node in the current cluster exists. |
|
|
Any chosen provisioner plugin also requires configuration for the relevant cloud, host, or third-party provider as per the relevant documentation.
9.2. Defining a storage class
StorageClass objects are currently a globally scoped object and must be created by cluster-admin or storage-admin users.
The Cluster Storage Operator might install a default storage class depending on the platform in use. This storage class is owned and controlled by the operator. It cannot be deleted or modified beyond defining annotations and labels. If different behavior is desired, you must define a custom storage class.
The following sections describe the basic definition for a StorageClass object and specific examples for each of the supported plugin types.
9.2.1. Basic StorageClass object definition
The following resource shows the parameters and default values that you use to configure a storage class. This example uses the AWS ElasticBlockStore (EBS) object definition.
Sample StorageClass definition
- 1 1
- (required) The API object type.
- 2
- (required) The current apiVersion.
- 3
- (required) The name of the storage class.
- 4
- (optional) Annotations for the storage class.
- 5
- (required) The type of provisioner associated with this storage class.
- 6
- (optional) The parameters required for the specific provisioner, this will change from plugin to plugin.
9.2.2. Storage class annotations
To set a storage class as the cluster-wide default, add the following annotation to your storage class metadata:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"For example:
This enables any persistent volume claim (PVC) that does not specify a specific storage class to automatically be provisioned through the default storage class. However, your cluster can have more than one storage class, but only one of them can be the default storage class.
The beta annotation storageclass.beta.kubernetes.io/is-default-class is still working; however, it will be removed in a future release.
To set a storage class description, add the following annotation to your storage class metadata:
kubernetes.io/description: My Storage Class Description
kubernetes.io/description: My Storage Class DescriptionFor example:
9.2.3. RHOSP Cinder object definition
cinder-storageclass.yaml
- 1
- Name of the storage class. The persistent volume claim uses this storage class for provisioning the associated persistent volumes.
- 2
- Volume type created in Cinder. Default is empty.
- 3
- Availability Zone. If not specified, volumes are generally round-robined across all active zones where the OpenShift Container Platform cluster has a node.
- 4
- File system that is created on dynamically provisioned volumes. This value is copied to the
fsTypefield of dynamically provisioned persistent volumes and the file system is created when the volume is mounted for the first time. The default value isext4.
9.2.4. AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS) object definition
aws-ebs-storageclass.yaml
- 1
- (required) Name of the storage class. The persistent volume claim uses this storage class for provisioning the associated persistent volumes.
- 2
- (required) Select from
io1,gp2,sc1,st1. The default isgp2. See the AWS documentation for valid Amazon Resource Name (ARN) values. - 3
- Optional: Only for io1 volumes. I/O operations per second per GiB. The AWS volume plugin multiplies this with the size of the requested volume to compute IOPS of the volume. The value cap is 20,000 IOPS, which is the maximum supported by AWS. See the AWS documentation for further details.
- 4
- Optional: Denotes whether to encrypt the EBS volume. Valid values are
trueorfalse. - 5
- Optional: The full ARN of the key to use when encrypting the volume. If none is supplied, but
encyptedis set totrue, then AWS generates a key. See the AWS documentation for a valid ARN value. - 6
- Optional: File system that is created on dynamically provisioned volumes. This value is copied to the
fsTypefield of dynamically provisioned persistent volumes and the file system is created when the volume is mounted for the first time. The default value isext4.
9.2.5. Azure Disk object definition
azure-advanced-disk-storageclass.yaml
- 1
- Name of the storage class. The persistent volume claim uses this storage class for provisioning the associated persistent volumes.
- 2
- Using
WaitForFirstConsumeris strongly recommended. This provisions the volume while allowing enough storage to schedule the pod on a free worker node from an available zone. - 3
- Possible values are
Shared(default),Managed, andDedicated.ImportantRed Hat only supports the use of
kind: Managedin the storage class.With
SharedandDedicated, Azure creates unmanaged disks, while OpenShift Container Platform creates a managed disk for machine OS (root) disks. But because Azure Disk does not allow the use of both managed and unmanaged disks on a node, unmanaged disks created withSharedorDedicatedcannot be attached to OpenShift Container Platform nodes. - 4
- Azure storage account SKU tier. Default is empty. Note that Premium VMs can attach both
Standard_LRSandPremium_LRSdisks, Standard VMs can only attachStandard_LRSdisks, Managed VMs can only attach managed disks, and unmanaged VMs can only attach unmanaged disks.-
If
kindis set toShared, Azure creates all unmanaged disks in a few shared storage accounts in the same resource group as the cluster. -
If
kindis set toManaged, Azure creates new managed disks. If
kindis set toDedicatedand astorageAccountis specified, Azure uses the specified storage account for the new unmanaged disk in the same resource group as the cluster. For this to work:- The specified storage account must be in the same region.
- Azure Cloud Provider must have write access to the storage account.
-
If
kindis set toDedicatedand astorageAccountis not specified, Azure creates a new dedicated storage account for the new unmanaged disk in the same resource group as the cluster.
-
If
9.2.6. Azure File object definition
The Azure File storage class uses secrets to store the Azure storage account name and the storage account key that are required to create an Azure Files share. These permissions are created as part of the following procedure.
Procedure
Define a
ClusterRoleobject that allows access to create and view secrets:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the cluster role to view and create secrets.
Add the cluster role to the service account:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user <persistent-volume-binder-role> system:serviceaccount:kube-system:persistent-volume-binder
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user <persistent-volume-binder-role> system:serviceaccount:kube-system:persistent-volume-binderCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Azure File
StorageClassobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Name of the storage class. The persistent volume claim uses this storage class for provisioning the associated persistent volumes.
- 2
- Location of the Azure storage account, such as
eastus. Default is empty, meaning that a new Azure storage account will be created in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s location. - 3
- SKU tier of the Azure storage account, such as
Standard_LRS. Default is empty, meaning that a new Azure storage account will be created with theStandard_LRSSKU. - 4
- Name of the Azure storage account. If a storage account is provided, then
skuNameandlocationare ignored. If no storage account is provided, then the storage class searches for any storage account that is associated with the resource group for any accounts that match the definedskuNameandlocation.
9.2.6.1. Considerations when using Azure File
The following file system features are not supported by the default Azure File storage class:
- Symlinks
- Hard links
- Extended attributes
- Sparse files
- Named pipes
Additionally, the owner user identifier (UID) of the Azure File mounted directory is different from the process UID of the container. The uid mount option can be specified in the StorageClass object to define a specific user identifier to use for the mounted directory.
The following StorageClass object demonstrates modifying the user and group identifier, along with enabling symlinks for the mounted directory.
9.2.7. GCE PersistentDisk (gcePD) object definition
gce-pd-storageclass.yaml
9.2.8. VMware vSphere object definition
vsphere-storageclass.yaml
- 1
- Name of the storage class. The persistent volume claim uses this storage class for provisioning the associated persistent volumes.
- 2
- For more information about using VMware vSphere with OpenShift Container Platform, see the VMware vSphere documentation.
- 3
diskformat:thin,zeroedthickandeagerzeroedthickare all valid disk formats. See vSphere docs for additional details regarding the disk format types. The default value isthin.
9.2.9. Red Hat Virtualization (RHV) object definition
OpenShift Container Platform creates a default object of type StorageClass named ovirt-csi-sc which is used for creating dynamically provisioned persistent volumes.
To create additional storage classes for different configurations, create and save a file with the StorageClass object described by the following sample YAML:
ovirt-storageclass.yaml
- 1
- Name of the storage class.
- 2
- Set to
falseif the storage class is the default storage class in the cluster. If set totrue, the existing default storage class must be edited and set tofalse. - 3
trueenables dynamic volume expansion,falseprevents it.trueis recommended.- 4
- Dynamically provisioned persistent volumes of this storage class are created with this reclaim policy. This default policy is
Delete. - 5
- Indicates how to provision and bind
PersistentVolumeClaims. When not set,VolumeBindingImmediateis used. This field is only applied by servers that enable theVolumeSchedulingfeature. - 6
- The RHV storage domain name to use.
- 7
- If
true, the disk is thin provisioned. Iffalse, the disk is preallocated. Thin provisioning is recommended. - 8
- Optional: File system type to be created. Possible values:
ext4(default) orxfs.
9.3. Changing the default storage class
Use the following process to change the default storage class. For example you have two defined storage classes, gp2 and standard, and you want to change the default storage class from gp2 to standard.
List the storage class:
oc get storageclass
$ oc get storageclassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE gp2 (default) kubernetes.io/aws-ebs standard kubernetes.io/aws-ebs
NAME TYPE gp2 (default) kubernetes.io/aws-ebs1 standard kubernetes.io/aws-ebsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
(default)denotes the default storage class.
Change the value of the
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-classannotation tofalsefor the default storage class:oc patch storageclass gp2 -p '{"metadata": {"annotations": {"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class": "false"}}}'$ oc patch storageclass gp2 -p '{"metadata": {"annotations": {"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class": "false"}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make another storage class the default by setting the
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-classannotation totrue:oc patch storageclass standard -p '{"metadata": {"annotations": {"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class": "true"}}}'$ oc patch storageclass standard -p '{"metadata": {"annotations": {"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class": "true"}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the changes:
oc get storageclass
$ oc get storageclassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE gp2 kubernetes.io/aws-ebs standard (default) kubernetes.io/aws-ebs
NAME TYPE gp2 kubernetes.io/aws-ebs standard (default) kubernetes.io/aws-ebsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.4. Optimizing storage
Optimizing storage helps to minimize storage use across all resources. By optimizing storage, administrators help ensure that existing storage resources are working in an efficient manner.
9.5. Available persistent storage options
Understand your persistent storage options so that you can optimize your OpenShift Container Platform environment.
| Storage type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Block |
| AWS EBS and VMware vSphere support dynamic persistent volume (PV) provisioning natively in OpenShift Container Platform. |
| File |
| RHEL NFS, NetApp NFS [1], and Vendor NFS |
| Object |
| AWS S3 |
- NetApp NFS supports dynamic PV provisioning when using the Trident plugin.
9.6. Recommended configurable storage technology
The following table summarizes the recommended and configurable storage technologies for the given OpenShift Container Platform cluster application.
| Storage type | Block | File | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
2 3 Prometheus is the underlying technology used for metrics. 4 This does not apply to physical disk, VM physical disk, VMDK, loopback over NFS, AWS EBS, and Azure Disk.
5 For metrics, using file storage with the 6 For logging, review the recommended storage solution in Configuring persistent storage for the log store section. Using NFS storage as a persistent volume or through NAS, such as Gluster, can corrupt the data. Hence, NFS is not supported for Elasticsearch storage and LokiStack log store in OpenShift Container Platform Logging. You must use one persistent volume type per log store. 7 Object storage is not consumed through OpenShift Container Platform’s PVs or PVCs. Apps must integrate with the object storage REST API. | |||
| ROX1 | Yes4 | Yes4 | Yes |
| RWX2 | No | Yes | Yes |
| Registry | Configurable | Configurable | Recommended |
| Scaled registry | Not configurable | Configurable | Recommended |
| Metrics3 | Recommended | Configurable5 | Not configurable |
| Elasticsearch Logging | Recommended | Configurable6 | Not supported6 |
| Loki Logging | Configurable | Not configurable | Recommended |
| Apps | Recommended | Recommended | Not configurable7 |
A scaled registry is an OpenShift image registry where two or more pod replicas are running.
9.6.1. Specific application storage recommendations
Testing shows issues with using the NFS server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) as storage backend for core services. This includes the OpenShift Container Registry and Quay, Prometheus for monitoring storage, and Elasticsearch for logging storage. Therefore, using RHEL NFS to back PVs used by core services is not recommended.
Other NFS implementations on the marketplace might not have these issues. Contact the individual NFS implementation vendor for more information on any testing that was possibly completed against these OpenShift Container Platform core components.
9.6.1.1. Registry
In a non-scaled/high-availability (HA) OpenShift image registry cluster deployment:
- The storage technology does not have to support RWX access mode.
- The storage technology must ensure read-after-write consistency.
- The preferred storage technology is object storage followed by block storage.
- File storage is not recommended for OpenShift image registry cluster deployment with production workloads.
9.6.1.2. Scaled registry
In a scaled/HA OpenShift image registry cluster deployment:
- The storage technology must support RWX access mode.
- The storage technology must ensure read-after-write consistency.
- The preferred storage technology is object storage.
- Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF), Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), Google Cloud Storage (GCS), Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, and OpenStack Swift are supported.
- Object storage should be S3 or Swift compliant.
- For non-cloud platforms, such as vSphere and bare metal installations, the only configurable technology is file storage.
- Block storage is not configurable.
9.6.1.3. Metrics
In an OpenShift Container Platform hosted metrics cluster deployment:
- The preferred storage technology is block storage.
- Object storage is not configurable.
It is not recommended to use file storage for a hosted metrics cluster deployment with production workloads.
9.6.1.4. Logging
In an OpenShift Container Platform hosted logging cluster deployment:
- The preferred storage technology is block storage.
- Object storage is not configurable.
9.6.1.5. Applications
Application use cases vary from application to application, as described in the following examples:
- Storage technologies that support dynamic PV provisioning have low mount time latencies, and are not tied to nodes to support a healthy cluster.
- Application developers are responsible for knowing and understanding the storage requirements for their application, and how it works with the provided storage to ensure that issues do not occur when an application scales or interacts with the storage layer.
9.6.2. Other specific application storage recommendations
It is not recommended to use RAID configurations on Write intensive workloads, such as etcd. If you are running etcd with a RAID configuration, you might be at risk of encountering performance issues with your workloads.
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) Cinder: RHOSP Cinder tends to be adept in ROX access mode use cases.
- Databases: Databases (RDBMSs, NoSQL DBs, etc.) tend to perform best with dedicated block storage.
- The etcd database must have enough storage and adequate performance capacity to enable a large cluster. Information about monitoring and benchmarking tools to establish ample storage and a high-performance environment is described in Recommended etcd practices.
9.7. Deploy Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation is a provider of agnostic persistent storage for OpenShift Container Platform supporting file, block, and object storage, either in-house or in hybrid clouds. As a Red Hat storage solution, Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation is completely integrated with OpenShift Container Platform for deployment, management, and monitoring.
| If you are looking for Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation information about… | See the following Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation documentation: |
|---|---|
| What’s new, known issues, notable bug fixes, and Technology Previews | |
| Supported workloads, layouts, hardware and software requirements, sizing and scaling recommendations | |
| Instructions on deploying OpenShift Data Foundation to use an external Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster | |
| Instructions on deploying OpenShift Data Foundation to local storage on bare metal infrastructure | Deploying OpenShift Data Foundation 4.9 using bare metal infrastructure |
| Instructions on deploying OpenShift Data Foundation on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform VMware vSphere clusters | |
| Instructions on deploying OpenShift Data Foundation using Amazon Web Services for local or cloud storage | Deploying OpenShift Data Foundation 4.9 using Amazon Web Services |
| Instructions on deploying and managing OpenShift Data Foundation on existing Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Google Cloud clusters | Deploying and managing OpenShift Data Foundation 4.9 using Google Cloud |
| Instructions on deploying and managing OpenShift Data Foundation on existing Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Azure clusters | Deploying and managing OpenShift Data Foundation 4.9 using Microsoft Azure |
| Instructions on deploying OpenShift Data Foundation to use local storage on IBM Power infrastructure | |
| Instructions on deploying OpenShift Data Foundation to use local storage on IBM Z infrastructure | |
| Allocating storage to core services and hosted applications in Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation, including snapshot and clone | |
| Managing storage resources across a hybrid cloud or multicloud environment using the Multicloud Object Gateway (NooBaa) | |
| Safely replacing storage devices for Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation | |
| Safely replacing a node in a Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation cluster | |
| Scaling operations in Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation | |
| Monitoring a Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation 4.9 cluster | |
| Resolve issues encountered during operations | |
| Migrating your OpenShift Container Platform cluster from version 3 to version 4 |
Chapter 10. Preparing for users
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can further expand and customize your cluster to your requirements, including taking steps to prepare for users.
10.1. Understanding identity provider configuration
The OpenShift Container Platform control plane includes a built-in OAuth server. Developers and administrators obtain OAuth access tokens to authenticate themselves to the API.
As an administrator, you can configure OAuth to specify an identity provider after you install your cluster.
10.1.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a custom resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
10.1.2. Supported identity providers
You can configure the following types of identity providers:
| Identity provider | Description |
|---|---|
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure an |
After you define an identity provider, you can use RBAC to define and apply permissions.
10.1.3. Identity provider parameters
The following parameters are common to all identity providers:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The provider name is prefixed to provider user names to form an identity name. |
|
| Defines how new identities are mapped to users when they log in. Enter one of the following values:
|
When adding or changing identity providers, you can map identities from the new provider to existing users by setting the mappingMethod parameter to add.
10.1.4. Sample identity provider CR
The following custom resource (CR) shows the parameters and default values that you use to configure an identity provider. This example uses the htpasswd identity provider.
Sample identity provider CR
10.2. Using RBAC to define and apply permissions
Understand and apply role-based access control.
10.2.1. RBAC overview
Role-based access control (RBAC) objects determine whether a user is allowed to perform a given action within a project.
Cluster administrators can use the cluster roles and bindings to control who has various access levels to the OpenShift Container Platform platform itself and all projects.
Developers can use local roles and bindings to control who has access to their projects. Note that authorization is a separate step from authentication, which is more about determining the identity of who is taking the action.
Authorization is managed using:
| Authorization object | Description |
|---|---|
| Rules |
Sets of permitted verbs on a set of objects. For example, whether a user or service account can |
| Roles | Collections of rules. You can associate, or bind, users and groups to multiple roles. |
| Bindings | Associations between users and/or groups with a role. |
There are two levels of RBAC roles and bindings that control authorization:
| RBAC level | Description |
|---|---|
| Cluster RBAC | Roles and bindings that are applicable across all projects. Cluster roles exist cluster-wide, and cluster role bindings can reference only cluster roles. |
| Local RBAC | Roles and bindings that are scoped to a given project. While local roles exist only in a single project, local role bindings can reference both cluster and local roles. |
A cluster role binding is a binding that exists at the cluster level. A role binding exists at the project level. The cluster role view must be bound to a user using a local role binding for that user to view the project. Create local roles only if a cluster role does not provide the set of permissions needed for a particular situation.
This two-level hierarchy allows reuse across multiple projects through the cluster roles while allowing customization inside of individual projects through local roles.
During evaluation, both the cluster role bindings and the local role bindings are used. For example:
- Cluster-wide "allow" rules are checked.
- Locally-bound "allow" rules are checked.
- Deny by default.
10.2.1.1. Default cluster roles
OpenShift Container Platform includes a set of default cluster roles that you can bind to users and groups cluster-wide or locally.
It is not recommended to manually modify the default cluster roles. Modifications to these system roles can prevent a cluster from functioning properly.
| Default cluster role | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A project manager. If used in a local binding, an |
|
| A user that can get basic information about projects and users. |
|
| A super-user that can perform any action in any project. When bound to a user with a local binding, they have full control over quota and every action on every resource in the project. |
|
| A user that can get basic cluster status information. |
|
| A user that can get or view most of the objects but cannot modify them. |
|
| A user that can modify most objects in a project but does not have the power to view or modify roles or bindings. |
|
| A user that can create their own projects. |
|
| A user who cannot make any modifications, but can see most objects in a project. They cannot view or modify roles or bindings. |
Be mindful of the difference between local and cluster bindings. For example, if you bind the cluster-admin role to a user by using a local role binding, it might appear that this user has the privileges of a cluster administrator. This is not the case. Binding the cluster-admin to a user in a project grants super administrator privileges for only that project to the user. That user has the permissions of the cluster role admin, plus a few additional permissions like the ability to edit rate limits, for that project. This binding can be confusing via the web console UI, which does not list cluster role bindings that are bound to true cluster administrators. However, it does list local role bindings that you can use to locally bind cluster-admin.
The relationships between cluster roles, local roles, cluster role bindings, local role bindings, users, groups and service accounts are illustrated below.
The get pods/exec, get pods/*, and get * rules grant execution privileges when they are applied to a role. Apply the principle of least privilege and assign only the minimal RBAC rights required for users and agents. For more information, see RBAC rules allow execution privileges.
10.2.1.2. Evaluating authorization
OpenShift Container Platform evaluates authorization by using:
- Identity
- The user name and list of groups that the user belongs to.
- Action
The action you perform. In most cases, this consists of:
- Project: The project you access. A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations that allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities.
-
Verb : The action itself:
get,list,create,update,delete,deletecollection, orwatch. - Resource name: The API endpoint that you access.
- Bindings
- The full list of bindings, the associations between users or groups with a role.
OpenShift Container Platform evaluates authorization by using the following steps:
- The identity and the project-scoped action is used to find all bindings that apply to the user or their groups.
- Bindings are used to locate all the roles that apply.
- Roles are used to find all the rules that apply.
- The action is checked against each rule to find a match.
- If no matching rule is found, the action is then denied by default.
Remember that users and groups can be associated with, or bound to, multiple roles at the same time.
Project administrators can use the CLI to view local roles and bindings, including a matrix of the verbs and resources each are associated with.
The cluster role bound to the project administrator is limited in a project through a local binding. It is not bound cluster-wide like the cluster roles granted to the cluster-admin or system:admin.
Cluster roles are roles defined at the cluster level but can be bound either at the cluster level or at the project level.
10.2.1.2.1. Cluster role aggregation
The default admin, edit, view, and cluster-reader cluster roles support cluster role aggregation, where the cluster rules for each role are dynamically updated as new rules are created. This feature is relevant only if you extend the Kubernetes API by creating custom resources.
10.2.2. Projects and namespaces
A Kubernetes namespace provides a mechanism to scope resources in a cluster. The Kubernetes documentation has more information on namespaces.
Namespaces provide a unique scope for:
- Named resources to avoid basic naming collisions.
- Delegated management authority to trusted users.
- The ability to limit community resource consumption.
Most objects in the system are scoped by namespace, but some are excepted and have no namespace, including nodes and users.
A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations and is the central vehicle by which access to resources for regular users is managed. A project allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities. Users must be given access to projects by administrators, or if allowed to create projects, automatically have access to their own projects.
Projects can have a separate name, displayName, and description.
-
The mandatory
nameis a unique identifier for the project and is most visible when using the CLI tools or API. The maximum name length is 63 characters. -
The optional
displayNameis how the project is displayed in the web console (defaults toname). -
The optional
descriptioncan be a more detailed description of the project and is also visible in the web console.
Each project scopes its own set of:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Pods, services, replication controllers, etc. |
|
| Rules for which users can or cannot perform actions on objects. |
|
| Quotas for each kind of object that can be limited. |
|
| Service accounts act automatically with designated access to objects in the project. |
Cluster administrators can create projects and delegate administrative rights for the project to any member of the user community. Cluster administrators can also allow developers to create their own projects.
Developers and administrators can interact with projects by using the CLI or the web console.
10.2.3. Default projects
OpenShift Container Platform comes with a number of default projects, and projects starting with openshift- are the most essential to users. These projects host master components that run as pods and other infrastructure components. The pods created in these namespaces that have a critical pod annotation are considered critical, and the have guaranteed admission by kubelet. Pods created for master components in these namespaces are already marked as critical.
You cannot assign an SCC to pods created in one of the default namespaces: default, kube-system, kube-public, openshift-node, openshift-infra, and openshift. You cannot use these namespaces for running pods or services.
10.2.4. Viewing cluster roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view cluster roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. - Obtain permission to view the cluster roles and bindings.
Users with the cluster-admin default cluster role bound cluster-wide can perform any action on any resource, including viewing cluster roles and bindings.
Procedure
To view the cluster roles and their associated rule sets:
oc describe clusterrole.rbac
$ oc describe clusterrole.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the current set of cluster role bindings, which shows the users and groups that are bound to various roles:
oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2.5. Viewing local roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view local roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. Obtain permission to view the local roles and bindings:
-
Users with the
cluster-admindefault cluster role bound cluster-wide can perform any action on any resource, including viewing local roles and bindings. -
Users with the
admindefault cluster role bound locally can view and manage roles and bindings in that project.
-
Users with the
Procedure
To view the current set of local role bindings, which show the users and groups that are bound to various roles for the current project:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the local role bindings for a different project, add the
-nflag to the command:oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe-project
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe-projectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2.6. Adding roles to users
You can use the oc adm administrator CLI to manage the roles and bindings.
Binding, or adding, a role to users or groups gives the user or group the access that is granted by the role. You can add and remove roles to and from users and groups using oc adm policy commands.
You can bind any of the default cluster roles to local users or groups in your project.
Procedure
Add a role to a user in a specific project:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, you can add the
adminrole to thealiceuser injoeproject by running:oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joe
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the role to the user:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the local role bindings and verify the addition in the output:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to view the local role bindings for the
joeproject:oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aliceuser has been added to theadminsRoleBinding.
10.2.7. Creating a local role
You can create a local role for a project and then bind it to a user.
Procedure
To create a local role for a project, run the following command:
oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>
$ oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role -
<resource>, the resources that the role applies to -
<project>, the project name
For example, to create a local role that allows a user to view pods in the
blueproject, run the following command:oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blue
$ oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To bind the new role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blue
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2.8. Creating a cluster role
You can create a cluster role.
Procedure
To create a cluster role, run the following command:
oc create clusterrole <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource>
$ oc create clusterrole <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role -
<resource>, the resources that the role applies to
For example, to create a cluster role that allows a user to view pods, run the following command:
oc create clusterrole podviewonly --verb=get --resource=pod
$ oc create clusterrole podviewonly --verb=get --resource=podCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
10.2.9. Local role binding commands
When you manage a user or group’s associated roles for local role bindings using the following operations, a project may be specified with the -n flag. If it is not specified, then the current project is used.
You can use the following commands for local RBAC management.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicates which users can perform an action on a resource. |
|
| Binds a specified role to specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified users and all of their roles in the current project. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified groups and all of their roles in the current project. |
10.2.10. Cluster role binding commands
You can also manage cluster role bindings using the following operations. The -n flag is not used for these operations because cluster role bindings use non-namespaced resources.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Binds a given role to specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
10.2.11. Creating a cluster admin
The cluster-admin role is required to perform administrator level tasks on the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, such as modifying cluster resources.
Prerequisites
- You must have created a user to define as the cluster admin.
Procedure
Define the user as a cluster admin:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user>
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.3. The kubeadmin user
OpenShift Container Platform creates a cluster administrator, kubeadmin, after the installation process completes.
This user has the cluster-admin role automatically applied and is treated as the root user for the cluster. The password is dynamically generated and unique to your OpenShift Container Platform environment. After installation completes the password is provided in the installation program’s output. For example:
INFO Install complete! INFO Run 'export KUBECONFIG=<your working directory>/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI. INFO The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p <provided>' succeeds (wait a few minutes). INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.demo1.openshift4-beta-abcorp.com INFO Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: <provided>
INFO Install complete!
INFO Run 'export KUBECONFIG=<your working directory>/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI.
INFO The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p <provided>' succeeds (wait a few minutes).
INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.demo1.openshift4-beta-abcorp.com
INFO Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: <provided>10.3.1. Removing the kubeadmin user
After you define an identity provider and create a new cluster-admin user, you can remove the kubeadmin to improve cluster security.
If you follow this procedure before another user is a cluster-admin, then OpenShift Container Platform must be reinstalled. It is not possible to undo this command.
Prerequisites
- You must have configured at least one identity provider.
-
You must have added the
cluster-adminrole to a user. - You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Remove the
kubeadminsecrets:oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-system
$ oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.4. Image configuration
Understand and configure image registry settings.
10.4.1. Image controller configuration parameters
The image.config.openshift.io/cluster resource holds cluster-wide information about how to handle images. The canonical, and only valid name is cluster. Its spec offers the following configuration parameters.
Parameters such as DisableScheduledImport, MaxImagesBulkImportedPerRepository, MaxScheduledImportsPerMinute, ScheduledImageImportMinimumIntervalSeconds, InternalRegistryHostname are not configurable.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Limits the container image registries from which normal users can import images. Set this list to the registries that you trust to contain valid images, and that you want applications to be able to import from. Users with permission to create images or Every element of this list contains a location of the registry specified by the registry domain name.
|
|
|
A reference to a config map containing additional CAs that should be trusted during
The namespace for this config map is |
|
|
Provides the hostnames for the default external image registry. The external hostname should be set only when the image registry is exposed externally. The first value is used in |
|
| Contains configuration that determines how the container runtime should treat individual registries when accessing images for builds and pods. For instance, whether or not to allow insecure access. It does not contain configuration for the internal cluster registry.
Either |
When the allowedRegistries parameter is defined, all registries, including registry.redhat.io and quay.io registries and the default OpenShift image registry, are blocked unless explicitly listed. When using the parameter, to prevent pod failure, add all registries including the registry.redhat.io and quay.io registries and the internalRegistryHostname to the allowedRegistries list, as they are required by payload images within your environment. For disconnected clusters, mirror registries should also be added.
The status field of the image.config.openshift.io/cluster resource holds observed values from the cluster.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Set by the Image Registry Operator, which controls the |
|
|
Set by the Image Registry Operator, provides the external hostnames for the image registry when it is exposed externally. The first value is used in |
10.4.2. Configuring image registry settings
You can configure image registry settings by editing the image.config.openshift.io/cluster custom resource (CR). When changes to the registry are applied to the image.config.openshift.io/cluster CR, the Machine Config Operator (MCO) performs the following sequential actions:
- Cordons the node
- Applies changes by restarting CRI-O
Uncordons the node
NoteThe MCO does not restart nodes when it detects changes.
Procedure
Edit the
image.config.openshift.io/clustercustom resource:oc edit image.config.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit image.config.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following is an example
image.config.openshift.io/clusterCR:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
Image: Holds cluster-wide information about how to handle images. The canonical, and only valid name iscluster.- 2
allowedRegistriesForImport: Limits the container image registries from which normal users may import images. Set this list to the registries that you trust to contain valid images, and that you want applications to be able to import from. Users with permission to create images orImageStreamMappingsfrom the API are not affected by this policy. Typically only cluster administrators have the appropriate permissions.- 3
additionalTrustedCA: A reference to a config map containing additional certificate authorities (CA) that are trusted during image stream import, pod image pull,openshift-image-registrypullthrough, and builds. The namespace for this config map isopenshift-config. The format of the config map is to use the registry hostname as the key, and the PEM certificate as the value, for each additional registry CA to trust.- 4
registrySources: Contains configuration that determines whether the container runtime allows or blocks individual registries when accessing images for builds and pods. Either theallowedRegistriesparameter or theblockedRegistriesparameter can be set, but not both. You can also define whether or not to allow access to insecure registries or registries that allow registries that use image short names. This example uses theallowedRegistriesparameter, which defines the registries that are allowed to be used. The insecure registryinsecure.comis also allowed. TheregistrySourcesparameter does not contain configuration for the internal cluster registry.
NoteWhen the
allowedRegistriesparameter is defined, all registries, including the registry.redhat.io and quay.io registries and the default OpenShift image registry, are blocked unless explicitly listed. If you use the parameter, to prevent pod failure, you must add theregistry.redhat.ioandquay.ioregistries and theinternalRegistryHostnameto theallowedRegistrieslist, as they are required by payload images within your environment. Do not add theregistry.redhat.ioandquay.ioregistries to theblockedRegistrieslist.When using the
allowedRegistries,blockedRegistries, orinsecureRegistriesparameter, you can specify an individual repository within a registry. For example:reg1.io/myrepo/myapp:latest.Insecure external registries should be avoided to reduce possible security risks.
To check that the changes are applied, list your nodes:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For more information on the allowed, blocked, and insecure registry parameters, see Configuring image registry settings.
10.4.2.1. Configuring additional trust stores for image registry access
The image.config.openshift.io/cluster custom resource can contain a reference to a config map that contains additional certificate authorities to be trusted during image registry access.
Prerequisites
- The certificate authorities (CA) must be PEM-encoded.
Procedure
You can create a config map in the openshift-config namespace and use its name in AdditionalTrustedCA in the image.config.openshift.io custom resource to provide additional CAs that should be trusted when contacting external registries.
The config map key is the hostname of a registry with the port for which this CA is to be trusted, and the PEM certificate content is the value, for each additional registry CA to trust.
Image registry CA config map example
- 1
- If the registry has the port, such as
registry-with-port.example.com:5000,:should be replaced with...
You can configure additional CAs with the following procedure.
To configure an additional CA:
oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=<external_registry_address>=ca.crt -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=<external_registry_address>=ca.crt -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc edit image.config.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit image.config.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow spec: additionalTrustedCA: name: registry-configspec: additionalTrustedCA: name: registry-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.4.2.2. Configuring image registry repository mirroring
Setting up container registry repository mirroring enables you to do the following:
- Configure your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to redirect requests to pull images from a repository on a source image registry and have it resolved by a repository on a mirrored image registry.
- Identify multiple mirrored repositories for each target repository, to make sure that if one mirror is down, another can be used.
The attributes of repository mirroring in OpenShift Container Platform include:
- Image pulls are resilient to registry downtimes.
- Clusters in disconnected environments can pull images from critical locations, such as quay.io, and have registries behind a company firewall provide the requested images.
- A particular order of registries is tried when an image pull request is made, with the permanent registry typically being the last one tried.
-
The mirror information you enter is added to the
/etc/containers/registries.conffile on every node in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. - When a node makes a request for an image from the source repository, it tries each mirrored repository in turn until it finds the requested content. If all mirrors fail, the cluster tries the source repository. If successful, the image is pulled to the node.
Setting up repository mirroring can be done in the following ways:
At OpenShift Container Platform installation:
By pulling container images needed by OpenShift Container Platform and then bringing those images behind your company’s firewall, you can install OpenShift Container Platform into a datacenter that is in a disconnected environment.
After OpenShift Container Platform installation:
Even if you don’t configure mirroring during OpenShift Container Platform installation, you can do so later using the
ImageContentSourcePolicyobject.
The following procedure provides a post-installation mirror configuration, where you create an ImageContentSourcePolicy object that identifies:
- The source of the container image repository you want to mirror.
- A separate entry for each mirror repository you want to offer the content requested from the source repository.
You can only configure global pull secrets for clusters that have an ImageContentSourcePolicy object. You cannot add a pull secret to a project.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Configure mirrored repositories, by either:
- Setting up a mirrored repository with Red Hat Quay, as described in Red Hat Quay Repository Mirroring. Using Red Hat Quay allows you to copy images from one repository to another and also automatically sync those repositories repeatedly over time.
Using a tool such as
skopeoto copy images manually from the source directory to the mirrored repository.For example, after installing the skopeo RPM package on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7 or RHEL 8 system, use the
skopeocommand as shown in this example:skopeo copy \ docker://registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6 \ docker://example.io/example/ubi-minimal
$ skopeo copy \ docker://registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6 \ docker://example.io/example/ubi-minimalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, you have a container image registry that is named
example.iowith an image repository namedexampleto which you want to copy theubi8/ubi-minimalimage fromregistry.access.redhat.com. After you create the registry, you can configure your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to redirect requests made of the source repository to the mirrored repository.
- Log in to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Create an
ImageContentSourcePolicyfile (for example,registryrepomirror.yaml), replacing the source and mirrors with your own registry and repository pairs and images:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Indicates the name of the image registry and repository.
- 2
- Indicates multiple mirror repositories for each target repository. If one mirror is down, the target repository can use another mirror.
- 3
- Indicates the registry and repository containing the content that is mirrored.
- 4
- You can configure a namespace inside a registry to use any image in that namespace. If you use a registry domain as a source, the
ImageContentSourcePolicyresource is applied to all repositories from the registry. - 5
- If you configure the registry name, the
ImageContentSourcePolicyresource is applied to all repositories from a source registry to a mirror registry. - 6
- Pulls the image
mirror.example.net/image@sha256:…. - 7
- Pulls the image
myimagein the source registry namespace from the mirrormirror.example.net/myimage@sha256:…. - 8
- Pulls the image
registry.example.com/example/myimagefrom the mirror registrymirror.example.net/registry-example-com/example/myimage@sha256:…. TheImageContentSourcePolicyresource is applied to all repositories from a source registry to a mirror registrymirror.example.net/registry-example-com.
Create the new
ImageContentSourcePolicyobject:oc create -f registryrepomirror.yaml
$ oc create -f registryrepomirror.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the
ImageContentSourcePolicyobject is created, the new settings are deployed to each node and the cluster starts using the mirrored repository for requests to the source repository.To check that the mirrored configuration settings, are applied, do the following on one of the nodes.
List your nodes:
oc get node
$ oc get nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
Imagecontentsourcepolicyresource does not restart the nodes.Start the debugging process to access the node:
oc debug node/ip-10-0-147-35.ec2.internal
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-147-35.ec2.internalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Starting pod/ip-10-0-147-35ec2internal-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host`
Starting pod/ip-10-0-147-35ec2internal-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host`Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change your root directory to
/host:chroot /host
sh-4.2# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the
/etc/containers/registries.conffile to make sure the changes were made:cat /etc/containers/registries.conf
sh-4.2# cat /etc/containers/registries.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pull an image digest to the node from the source and check if it is resolved by the mirror.
ImageContentSourcePolicyobjects support image digests only, not image tags.podman pull --log-level=debug registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6
sh-4.2# podman pull --log-level=debug registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Troubleshooting repository mirroring
If the repository mirroring procedure does not work as described, use the following information about how repository mirroring works to help troubleshoot the problem.
- The first working mirror is used to supply the pulled image.
- The main registry is only used if no other mirror works.
-
From the system context, the
Insecureflags are used as fallback. -
The format of the
/etc/containers/registries.conffile has changed recently. It is now version 2 and in TOML format.
10.5. Populating OperatorHub from mirrored Operator catalogs
If you mirrored Operator catalogs for use with disconnected clusters, you can populate OperatorHub with the Operators from your mirrored catalogs. You can use the generated manifests from the mirroring process to create the required ImageContentSourcePolicy and CatalogSource objects.
10.5.1. Prerequisites
10.5.2. Creating the ImageContentSourcePolicy object
After mirroring Operator catalog content to your mirror registry, create the required ImageContentSourcePolicy (ICSP) object. The ICSP object configures nodes to translate between the image references stored in Operator manifests and the mirrored registry.
Procedure
On a host with access to the disconnected cluster, create the ICSP by running the following command to specify the
imageContentSourcePolicy.yamlfile in your manifests directory:oc create -f <path/to/manifests/dir>/imageContentSourcePolicy.yaml
$ oc create -f <path/to/manifests/dir>/imageContentSourcePolicy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<path/to/manifests/dir>is the path to the manifests directory for your mirrored content.You can now create a
CatalogSourceobject to reference your mirrored index image and Operator content.
10.5.3. Adding a catalog source to a cluster
Adding a catalog source to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster enables the discovery and installation of Operators for users. Cluster administrators can create a CatalogSource object that references an index image. OperatorHub uses catalog sources to populate the user interface.
Alternatively, you can use the web console to manage catalog sources. From the Administration → Cluster Settings → Configuration → OperatorHub page, click the Sources tab, where you can create, update, delete, disable, and enable individual sources.
Prerequisites
- An index image built and pushed to a registry.
Procedure
Create a
CatalogSourceobject that references your index image. If you used theoc adm catalog mirrorcommand to mirror your catalog to a target registry, you can use the generatedcatalogSource.yamlfile in your manifests directory as a starting point.Modify the following to your specifications and save it as a
catalogSource.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If you mirrored content to local files before uploading to a registry, remove any backslash (
/) characters from themetadata.namefield to avoid an "invalid resource name" error when you create the object. - 2
- If you want the catalog source to be available globally to users in all namespaces, specify the
openshift-marketplacenamespace. Otherwise, you can specify a different namespace for the catalog to be scoped and available only for that namespace. - 3
- Specify your index image. If you specify a tag after the image name, for example
:v4.11, the catalog source pod uses an image pull policy ofAlways, meaning the pod always pulls the image prior to starting the container. If you specify a digest, for example@sha256:<id>, the image pull policy isIfNotPresent, meaning the pod pulls the image only if it does not already exist on the node. - 4
- Specify your name or an organization name publishing the catalog.
- 5
- Catalog sources can automatically check for new versions to keep up to date.
Use the file to create the
CatalogSourceobject:oc apply -f catalogSource.yaml
$ oc apply -f catalogSource.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verify the following resources are created successfully.
Check the pods:
oc get pods -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc get pods -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE my-operator-catalog-6njx6 1/1 Running 0 28s marketplace-operator-d9f549946-96sgr 1/1 Running 0 26h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE my-operator-catalog-6njx6 1/1 Running 0 28s marketplace-operator-d9f549946-96sgr 1/1 Running 0 26hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the catalog source:
oc get catalogsource -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc get catalogsource -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DISPLAY TYPE PUBLISHER AGE my-operator-catalog My Operator Catalog grpc 5s
NAME DISPLAY TYPE PUBLISHER AGE my-operator-catalog My Operator Catalog grpc 5sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the package manifest:
oc get packagemanifest -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc get packagemanifest -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CATALOG AGE jaeger-product My Operator Catalog 93s
NAME CATALOG AGE jaeger-product My Operator Catalog 93sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can now install the Operators from the OperatorHub page on your OpenShift Container Platform web console.
10.6. About Operator installation with OperatorHub
OperatorHub is a user interface for discovering Operators; it works in conjunction with Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM), which installs and manages Operators on a cluster.
As a cluster administrator, you can install an Operator from OperatorHub using the OpenShift Container Platform web console or CLI. Subscribing an Operator to one or more namespaces makes the Operator available to developers on your cluster.
During installation, you must determine the following initial settings for the Operator:
- Installation Mode
- Choose All namespaces on the cluster (default) to have the Operator installed on all namespaces or choose individual namespaces, if available, to only install the Operator on selected namespaces. This example chooses All namespaces… to make the Operator available to all users and projects.
- Update Channel
- If an Operator is available through multiple channels, you can choose which channel you want to subscribe to. For example, to deploy from the stable channel, if available, select it from the list.
- Approval Strategy
You can choose automatic or manual updates.
If you choose automatic updates for an installed Operator, when a new version of that Operator is available in the selected channel, Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) automatically upgrades the running instance of your Operator without human intervention.
If you select manual updates, when a newer version of an Operator is available, OLM creates an update request. As a cluster administrator, you must then manually approve that update request to have the Operator updated to the new version.
10.6.1. Installing from OperatorHub using the web console
You can install and subscribe to an Operator from OperatorHub using the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
Prerequisites
-
Access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions.
Procedure
- Navigate in the web console to the Operators → OperatorHub page.
Scroll or type a keyword into the Filter by keyword box to find the Operator you want. For example, type
jaegerto find the Jaeger Operator.You can also filter options by Infrastructure Features. For example, select Disconnected if you want to see Operators that work in disconnected environments, also known as restricted network environments.
Select the Operator to display additional information.
NoteChoosing a Community Operator warns that Red Hat does not certify Community Operators; you must acknowledge the warning before continuing.
- Read the information about the Operator and click Install.
On the Install Operator page:
Select one of the following:
-
All namespaces on the cluster (default) installs the Operator in the default
openshift-operatorsnamespace to watch and be made available to all namespaces in the cluster. This option is not always available. - A specific namespace on the cluster allows you to choose a specific, single namespace in which to install the Operator. The Operator will only watch and be made available for use in this single namespace.
-
All namespaces on the cluster (default) installs the Operator in the default
- Select an Update Channel (if more than one is available).
- Select Automatic or Manual approval strategy, as described earlier.
Click Install to make the Operator available to the selected namespaces on this OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you selected a Manual approval strategy, the upgrade status of the subscription remains Upgrading until you review and approve the install plan.
After approving on the Install Plan page, the subscription upgrade status moves to Up to date.
- If you selected an Automatic approval strategy, the upgrade status should resolve to Up to date without intervention.
After the upgrade status of the subscription is Up to date, select Operators → Installed Operators to verify that the cluster service version (CSV) of the installed Operator eventually shows up. The Status should ultimately resolve to InstallSucceeded in the relevant namespace.
NoteFor the All namespaces… installation mode, the status resolves to InstallSucceeded in the
openshift-operatorsnamespace, but the status is Copied if you check in other namespaces.If it does not:
-
Check the logs in any pods in the
openshift-operatorsproject (or other relevant namespace if A specific namespace… installation mode was selected) on the Workloads → Pods page that are reporting issues to troubleshoot further.
-
Check the logs in any pods in the
10.6.2. Installing from OperatorHub using the CLI
Instead of using the OpenShift Container Platform web console, you can install an Operator from OperatorHub using the CLI. Use the oc command to create or update a Subscription object.
Prerequisites
-
Access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions. -
Install the
occommand to your local system.
Procedure
View the list of Operators available to the cluster from OperatorHub:
oc get packagemanifests -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc get packagemanifests -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note the catalog for your desired Operator.
Inspect your desired Operator to verify its supported install modes and available channels:
oc describe packagemanifests <operator_name> -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc describe packagemanifests <operator_name> -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow An Operator group, defined by an
OperatorGroupobject, selects target namespaces in which to generate required RBAC access for all Operators in the same namespace as the Operator group.The namespace to which you subscribe the Operator must have an Operator group that matches the install mode of the Operator, either the
AllNamespacesorSingleNamespacemode. If the Operator you intend to install uses theAllNamespaces, then theopenshift-operatorsnamespace already has an appropriate Operator group in place.However, if the Operator uses the
SingleNamespacemode and you do not already have an appropriate Operator group in place, you must create one.NoteThe web console version of this procedure handles the creation of the
OperatorGroupandSubscriptionobjects automatically behind the scenes for you when choosingSingleNamespacemode.Create an
OperatorGroupobject YAML file, for exampleoperatorgroup.yaml:Example
OperatorGroupobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningOperator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) creates the following cluster roles for each Operator group:
-
<operatorgroup_name>-admin -
<operatorgroup_name>-edit -
<operatorgroup_name>-view
When you manually create an Operator group, you must specify a unique name that does not conflict with the existing cluster roles or other Operator groups on the cluster.
-
Create the
OperatorGroupobject:oc apply -f operatorgroup.yaml
$ oc apply -f operatorgroup.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
Subscriptionobject YAML file to subscribe a namespace to an Operator, for examplesub.yaml:Example
SubscriptionobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For default
AllNamespacesinstall mode usage, specify theopenshift-operatorsnamespace. Alternatively, you can specify a custom global namespace, if you have created one. Otherwise, specify the relevant single namespace forSingleNamespaceinstall mode usage. - 2
- Name of the channel to subscribe to.
- 3
- Name of the Operator to subscribe to.
- 4
- Name of the catalog source that provides the Operator.
- 5
- Namespace of the catalog source. Use
openshift-marketplacefor the default OperatorHub catalog sources. - 6
- The
envparameter defines a list of Environment Variables that must exist in all containers in the pod created by OLM. - 7
- The
envFromparameter defines a list of sources to populate Environment Variables in the container. - 8
- The
volumesparameter defines a list of Volumes that must exist on the pod created by OLM. - 9
- The
volumeMountsparameter defines a list of VolumeMounts that must exist in all containers in the pod created by OLM. If avolumeMountreferences avolumethat does not exist, OLM fails to deploy the Operator. - 10
- The
tolerationsparameter defines a list of Tolerations for the pod created by OLM. - 11
- The
resourcesparameter defines resource constraints for all the containers in the pod created by OLM. - 12
- The
nodeSelectorparameter defines aNodeSelectorfor the pod created by OLM.
Create the
Subscriptionobject:oc apply -f sub.yaml
$ oc apply -f sub.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow At this point, OLM is now aware of the selected Operator. A cluster service version (CSV) for the Operator should appear in the target namespace, and APIs provided by the Operator should be available for creation.
Chapter 11. Configuring alert notifications
In OpenShift Container Platform, an alert is fired when the conditions defined in an alerting rule are true. An alert provides a notification that a set of circumstances are apparent within a cluster. Firing alerts can be viewed in the Alerting UI in the OpenShift Container Platform web console by default. After an installation, you can configure OpenShift Container Platform to send alert notifications to external systems.
11.1. Sending notifications to external systems
In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11, firing alerts can be viewed in the Alerting UI. Alerts are not configured by default to be sent to any notification systems. You can configure OpenShift Container Platform to send alerts to the following receiver types:
- PagerDuty
- Webhook
- Slack
Routing alerts to receivers enables you to send timely notifications to the appropriate teams when failures occur. For example, critical alerts require immediate attention and are typically paged to an individual or a critical response team. Alerts that provide non-critical warning notifications might instead be routed to a ticketing system for non-immediate review.
Checking that alerting is operational by using the watchdog alert
OpenShift Container Platform monitoring includes a watchdog alert that fires continuously. Alertmanager repeatedly sends watchdog alert notifications to configured notification providers. The provider is usually configured to notify an administrator when it stops receiving the watchdog alert. This mechanism helps you quickly identify any communication issues between Alertmanager and the notification provider.
11.1.1. Configuring alert receivers
You can configure alert receivers to ensure that you learn about important issues with your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-admincluster role.
Procedure
In the Administrator perspective, navigate to Administration → Cluster Settings → Configuration → Alertmanager.
NoteAlternatively, you can navigate to the same page through the notification drawer. Select the bell icon at the top right of the OpenShift Container Platform web console and choose Configure in the AlertmanagerReceiverNotConfigured alert.
- Select Create Receiver in the Receivers section of the page.
- In the Create Receiver form, add a Receiver Name and choose a Receiver Type from the list.
Edit the receiver configuration:
For PagerDuty receivers:
- Choose an integration type and add a PagerDuty integration key.
- Add the URL of your PagerDuty installation.
- Select Show advanced configuration if you want to edit the client and incident details or the severity specification.
For webhook receivers:
- Add the endpoint to send HTTP POST requests to.
- Select Show advanced configuration if you want to edit the default option to send resolved alerts to the receiver.
For email receivers:
- Add the email address to send notifications to.
- Add SMTP configuration details, including the address to send notifications from, the smarthost and port number used for sending emails, the hostname of the SMTP server, and authentication details.
- Choose whether TLS is required.
- Select Show advanced configuration if you want to edit the default option not to send resolved alerts to the receiver or edit the body of email notifications configuration.
For Slack receivers:
- Add the URL of the Slack webhook.
- Add the Slack channel or user name to send notifications to.
- Select Show advanced configuration if you want to edit the default option not to send resolved alerts to the receiver or edit the icon and username configuration. You can also choose whether to find and link channel names and usernames.
By default, firing alerts with labels that match all of the selectors will be sent to the receiver. If you want label values for firing alerts to be matched exactly before they are sent to the receiver:
- Add routing label names and values in the Routing Labels section of the form.
- Select Regular Expression if want to use a regular expression.
- Select Add Label to add further routing labels.
- Select Create to create the receiver.
Chapter 12. Converting a connected cluster to a disconnected cluster
There might be some scenarios where you need to convert your OpenShift Container Platform cluster from a connected cluster to a disconnected cluster.
A disconnected cluster, also known as a restricted cluster, does not have an active connection to the internet. As such, you must mirror the contents of your registries and installation media. You can create this mirror registry on a host that can access both the internet and your closed network, or copy images to a device that you can move across network boundaries.
This topic describes the general process for converting an existing, connected cluster into a disconnected cluster.
12.1. About the mirror registry
You can mirror the images that are required for OpenShift Container Platform installation and subsequent product updates to a container mirror registry such as Red Hat Quay, JFrog Artifactory, Sonatype Nexus Repository, or Harbor. If you do not have access to a large-scale container registry, you can use the mirror registry for Red Hat OpenShift, a small-scale container registry included with OpenShift Container Platform subscriptions.
You can use any container registry that supports Docker v2-2, such as Red Hat Quay, the mirror registry for Red Hat OpenShift, Artifactory, Sonatype Nexus Repository, or Harbor. Regardless of your chosen registry, the procedure to mirror content from Red Hat hosted sites on the internet to an isolated image registry is the same. After you mirror the content, you configure each cluster to retrieve this content from your mirror registry.
The OpenShift image registry cannot be used as the target registry because it does not support pushing without a tag, which is required during the mirroring process.
If choosing a container registry that is not the mirror registry for Red Hat OpenShift, it must be reachable by every machine in the clusters that you provision. If the registry is unreachable, installation, updating, or normal operations such as workload relocation might fail. For that reason, you must run mirror registries in a highly available way, and the mirror registries must at least match the production availability of your OpenShift Container Platform clusters.
When you populate your mirror registry with OpenShift Container Platform images, you can follow two scenarios. If you have a host that can access both the internet and your mirror registry, but not your cluster nodes, you can directly mirror the content from that machine. This process is referred to as connected mirroring. If you have no such host, you must mirror the images to a file system and then bring that host or removable media into your restricted environment. This process is referred to as disconnected mirroring.
For mirrored registries, to view the source of pulled images, you must review the Trying to access log entry in the CRI-O logs. Other methods to view the image pull source, such as using the crictl images command on a node, show the non-mirrored image name, even though the image is pulled from the mirrored location.
Red Hat does not test third party registries with OpenShift Container Platform.
12.2. Prerequisites
-
The
occlient is installed. - A running cluster.
An installed mirror registry, which is a container image registry that supports Docker v2-2 in the location that will host the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, such as one of the following registries:
If you have an subscription to Red Hat Quay, see the documentation on deploying Red Hat Quay for proof-of-concept purposes or by using the Quay Operator.
- The mirror repository must be configured to share images. For example, a Red Hat Quay repository requires Organizations in order to share images.
- Access to the internet to obtain the necessary container images.
12.3. Preparing the cluster for mirroring
Before disconnecting your cluster, you must mirror, or copy, the images to a mirror registry that is reachable by every node in your disconnected cluster. In order to mirror the images, you must prepare your cluster by:
- Adding the mirror registry certificates to the list of trusted CAs on your host.
-
Creating a
.dockerconfigjsonfile that contains your image pull secret, which is from thecloud.openshift.comtoken.
Procedure
Configuring credentials that allow image mirroring:
Add the CA certificate for the mirror registry, in the simple PEM or DER file formats, to the list of trusted CAs. For example:
cp </path/to/cert.crt> /usr/share/pki/ca-trust-source/anchors/
$ cp </path/to/cert.crt> /usr/share/pki/ca-trust-source/anchors/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - where,
</path/to/cert.crt> - Specifies the path to the certificate on your local file system.
- where,
Update the CA trust. For example, in Linux:
update-ca-trust
$ update-ca-trustCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Extract the
.dockerconfigjsonfile from the global pull secret:oc extract secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --confirm --to=.
$ oc extract secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --confirm --to=.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
.dockerconfigjson
.dockerconfigjsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
.dockerconfigjsonfile to add your mirror registry and authentication credentials and save it as a new file:{"auths":{"<local_registry>": {"auth": "<credentials>","email": "you@example.com"}}},"<registry>:<port>/<namespace>/":{"auth":"<token>"}}}{"auths":{"<local_registry>": {"auth": "<credentials>","email": "you@example.com"}}},"<registry>:<port>/<namespace>/":{"auth":"<token>"}}}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<local_registry>- Specifies the registry domain name, and optionally the port, that your mirror registry uses to serve content.
auth- Specifies the base64-encoded user name and password for your mirror registry.
<registry>:<port>/<namespace>- Specifies the mirror registry details.
<token>Specifies the base64-encoded
username:passwordfor your mirror registry.For example:
{"auths":{"cloud.openshift.com":{"auth":"b3BlbnNoaWZ0Y3UjhGOVZPT0lOMEFaUjdPUzRGTA==","email":"user@example.com"}, "quay.io":{"auth":"b3BlbnNoaWZ0LXJlbGVhc2UtZGOVZPT0lOMEFaUGSTd4VGVGVUjdPUzRGTA==","email":"user@example.com"}, "registry.connect.redhat.com"{"auth":"NTE3MTMwNDB8dWhjLTFEZlN3VHkxOSTd4VGVGVU1MdTpleUpoYkdjaUailA==","email":"user@example.com"}, "registry.redhat.io":{"auth":"NTE3MTMwNDB8dWhjLTFEZlN3VH3BGSTd4VGVGVU1MdTpleUpoYkdjaU9fZw==","email":"user@example.com"}, "registry.svc.ci.openshift.org":{"auth":"dXNlcjpyWjAwWVFjSEJiT2RKVW1pSmg4dW92dGp1SXRxQ3RGN1pwajJhN1ZXeTRV"},"my-registry:5000/my-namespace/":{"auth":"dXNlcm5hbWU6cGFzc3dvcmQ="}}}$ {"auths":{"cloud.openshift.com":{"auth":"b3BlbnNoaWZ0Y3UjhGOVZPT0lOMEFaUjdPUzRGTA==","email":"user@example.com"}, "quay.io":{"auth":"b3BlbnNoaWZ0LXJlbGVhc2UtZGOVZPT0lOMEFaUGSTd4VGVGVUjdPUzRGTA==","email":"user@example.com"}, "registry.connect.redhat.com"{"auth":"NTE3MTMwNDB8dWhjLTFEZlN3VHkxOSTd4VGVGVU1MdTpleUpoYkdjaUailA==","email":"user@example.com"}, "registry.redhat.io":{"auth":"NTE3MTMwNDB8dWhjLTFEZlN3VH3BGSTd4VGVGVU1MdTpleUpoYkdjaU9fZw==","email":"user@example.com"}, "registry.svc.ci.openshift.org":{"auth":"dXNlcjpyWjAwWVFjSEJiT2RKVW1pSmg4dW92dGp1SXRxQ3RGN1pwajJhN1ZXeTRV"},"my-registry:5000/my-namespace/":{"auth":"dXNlcm5hbWU6cGFzc3dvcmQ="}}}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
12.4. Mirroring the images
After the cluster is properly configured, you can mirror the images from your external repositories to the mirror repository.
Procedure
Mirror the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) images:
oc adm catalog mirror registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v{product-version} <mirror_registry>:<port>/olm -a <reg_creds>$ oc adm catalog mirror registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v{product-version} <mirror_registry>:<port>/olm -a <reg_creds>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
product-version-
Specifies the tag that corresponds to the version of OpenShift Container Platform to install, such as
4.8. mirror_registry-
Specifies the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the target registry and namespace to mirror the Operator content to, where
<namespace>is any existing namespace on the registry. reg_creds-
Specifies the location of your modified
.dockerconfigjsonfile.
For example:
oc adm catalog mirror registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.8 mirror.registry.com:443/olm -a ./.dockerconfigjson --index-filter-by-os='.*'
$ oc adm catalog mirror registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.8 mirror.registry.com:443/olm -a ./.dockerconfigjson --index-filter-by-os='.*'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mirror the content for any other Red Hat-provided Operator:
oc adm catalog mirror <index_image> <mirror_registry>:<port>/<namespace> -a <reg_creds>
$ oc adm catalog mirror <index_image> <mirror_registry>:<port>/<namespace> -a <reg_creds>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
index_image- Specifies the index image for the catalog that you want to mirror.
mirror_registry-
Specifies the FQDN for the target registry and namespace to mirror the Operator content to, where
<namespace>is any existing namespace on the registry. reg_creds- Optional: Specifies the location of your registry credentials file, if required.
For example:
oc adm catalog mirror registry.redhat.io/redhat/community-operator-index:v4.8 mirror.registry.com:443/olm -a ./.dockerconfigjson --index-filter-by-os='.*'
$ oc adm catalog mirror registry.redhat.io/redhat/community-operator-index:v4.8 mirror.registry.com:443/olm -a ./.dockerconfigjson --index-filter-by-os='.*'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mirror the OpenShift Container Platform image repository:
oc adm release mirror -a .dockerconfigjson --from=quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:v<product-version>-<architecture> --to=<local_registry>/<local_repository> --to-release-image=<local_registry>/<local_repository>:v<product-version>-<architecture>
$ oc adm release mirror -a .dockerconfigjson --from=quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:v<product-version>-<architecture> --to=<local_registry>/<local_repository> --to-release-image=<local_registry>/<local_repository>:v<product-version>-<architecture>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
product-version-
Specifies the tag that corresponds to the version of OpenShift Container Platform to install, such as
4.8.15-x86_64. architecture-
Specifies the type of architecture for your server, such as
x86_64. local_registry- Specifies the registry domain name for your mirror repository.
local_repository-
Specifies the name of the repository to create in your registry, such as
ocp4/openshift4.
For example:
oc adm release mirror -a .dockerconfigjson --from=quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:4.8.15-x86_64 --to=mirror.registry.com:443/ocp/release --to-release-image=mirror.registry.com:443/ocp/release:4.8.15-x86_64
$ oc adm release mirror -a .dockerconfigjson --from=quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:4.8.15-x86_64 --to=mirror.registry.com:443/ocp/release --to-release-image=mirror.registry.com:443/ocp/release:4.8.15-x86_64Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mirror any other registries, as needed:
oc image mirror <online_registry>/my/image:latest <mirror_registry>
$ oc image mirror <online_registry>/my/image:latest <mirror_registry>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Additional information
- For more information about mirroring Operator catalogs, see Mirroring an Operator catalog.
-
For more information about the
oc adm catalog mirrorcommand, see the OpenShift CLI administrator command reference.
12.5. Configuring the cluster for the mirror registry
After creating and mirroring the images to the mirror registry, you must modify your cluster so that pods can pull images from the mirror registry.
You must:
- Add the mirror registry credentials to the global pull secret.
- Add the mirror registry server certificate to the cluster.
Create an
ImageContentSourcePolicycustom resource (ICSP), which associates the mirror registry with the source registry.Add mirror registry credential to the cluster global pull-secret:
oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=<pull_secret_location>
$ oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=<pull_secret_location>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Provide the path to the new pull secret file.
For example:
oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=.mirrorsecretconfigjson
$ oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=.mirrorsecretconfigjsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the CA-signed mirror registry server certificate to the nodes in the cluster:
Create a config map that includes the server certificate for the mirror registry
oc create configmap <config_map_name> --from-file=<mirror_address_host>..<port>=$path/ca.crt -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap <config_map_name> --from-file=<mirror_address_host>..<port>=$path/ca.crt -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
S oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=mirror.registry.com..443=/root/certs/ca-chain.cert.pem -n openshift-config
S oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=mirror.registry.com..443=/root/certs/ca-chain.cert.pem -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the config map to update the
image.config.openshift.io/clustercustom resource (CR). OpenShift Container Platform applies the changes to this CR to all nodes in the cluster:oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"<config_map_name>"}}}' --type=merge$ oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"<config_map_name>"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"registry-config"}}}' --type=merge$ oc patch image.config.openshift.io/cluster --patch '{"spec":{"additionalTrustedCA":{"name":"registry-config"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create an ICSP to redirect container pull requests from the online registries to the mirror registry:
Create the
ImageContentSourcePolicycustom resource:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the ICSP object:
oc create -f registryrepomirror.yaml
$ oc create -f registryrepomirror.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io/mirror-ocp created
imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io/mirror-ocp createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform applies the changes to this CR to all nodes in the cluster.
Verify that the credentials, CA, and ICSP for mirror registry were added:
Log into a node:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set
/hostas the root directory within the debug shell:chroot /host
sh-4.4# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the
config.jsonfile for the credentials:cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.json
sh-4.4# cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
{"auths":{"brew.registry.redhat.io":{"xx=="},"brewregistry.stage.redhat.io":{"auth":"xxx=="},"mirror.registry.com:443":{"auth":"xx="}}}{"auths":{"brew.registry.redhat.io":{"xx=="},"brewregistry.stage.redhat.io":{"auth":"xxx=="},"mirror.registry.com:443":{"auth":"xx="}}}1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Ensure that the mirror registry and credentials are present.
Change to the
certs.ddirectorycd /etc/docker/certs.d/
sh-4.4# cd /etc/docker/certs.d/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the certificates in the
certs.ddirectory:ls
sh-4.4# lsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc.cluster.local:5000 image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000 mirror.registry.com:443
image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc.cluster.local:5000 image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000 mirror.registry.com:4431 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Ensure that the mirror registry is in the list.
Check that the ICSP added the mirror registry to the
registries.conffile:cat /etc/containers/registries.conf
sh-4.4# cat /etc/containers/registries.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
registry.mirrorparameters indicate that the mirror registry is searched before the original registry.Exit the node.
exit
sh-4.4# exitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
12.6. Ensure applications continue to work
Before disconnecting the cluster from the network, ensure that your cluster is working as expected and all of your applications are working as expected.
Procedure
Use the following commands to check the status of your cluster:
Ensure your pods are running:
oc get pods --all-namespaces
$ oc get pods --all-namespacesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure your nodes are in the READY status:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
12.7. Disconnect the cluster from the network
After mirroring all the required repositories and configuring your cluster to work as a disconnected cluster, you can disconnect the cluster from the network.
The Insights Operator is degraded when the cluster loses its Internet connection. You can avoid this problem by temporarily disabling the Insights Operator until you can restore it.
12.8. Restoring a degraded Insights Operator
Disconnecting the cluster from the network necessarily causes the cluster to lose the Internet connection. The Insights Operator becomes degraded because it requires access to Red Hat Insights.
This topic describes how to recover from a degraded Insights Operator.
Procedure
Edit your
.dockerconfigjsonfile to remove thecloud.openshift.comentry, for example:"cloud.openshift.com":{"auth":"<hash>","email":"user@example.com"}"cloud.openshift.com":{"auth":"<hash>","email":"user@example.com"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file.
Update the cluster secret with the edited
.dockerconfigjsonfile:oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=./.dockerconfigjson
$ oc set data secret/pull-secret -n openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=./.dockerconfigjsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the Insights Operator is no longer degraded:
oc get co insights
$ oc get co insightsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE insights 4.5.41 True False False 3d
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE insights 4.5.41 True False False 3dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
12.9. Restoring the network
If you want to reconnect a disconnected cluster and pull images from online registries, delete the cluster’s ImageContentSourcePolicy (ICSP) objects. Without the ICSP, pull requests to external registries are no longer redirected to the mirror registry.
Procedure
View the ICSP objects in your cluster:
oc get imagecontentsourcepolicy
$ oc get imagecontentsourcepolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE mirror-ocp 6d20h ocp4-index-0 6d18h qe45-index-0 6d15h
NAME AGE mirror-ocp 6d20h ocp4-index-0 6d18h qe45-index-0 6d15hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete all the ICSP objects you created when disconnecting your cluster:
oc delete imagecontentsourcepolicy <icsp_name> <icsp_name> <icsp_name>
$ oc delete imagecontentsourcepolicy <icsp_name> <icsp_name> <icsp_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc delete imagecontentsourcepolicy mirror-ocp ocp4-index-0 qe45-index-0
$ oc delete imagecontentsourcepolicy mirror-ocp ocp4-index-0 qe45-index-0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io "mirror-ocp" deleted imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io "ocp4-index-0" deleted imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io "qe45-index-0" deleted
imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io "mirror-ocp" deleted imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io "ocp4-index-0" deleted imagecontentsourcepolicy.operator.openshift.io "qe45-index-0" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait for all the nodes to restart and return to the READY status and verify that the
registries.conffile is pointing to the original registries and not the mirror registries:Log into a node:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set
/hostas the root directory within the debug shell:chroot /host
sh-4.4# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Examine the
registries.conffile:cat /etc/containers/registries.conf
sh-4.4# cat /etc/containers/registries.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
unqualified-search-registries = ["registry.access.redhat.com", "docker.io"]
unqualified-search-registries = ["registry.access.redhat.com", "docker.io"]1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
registryandregistry.mirrorentries created by the ICSPs you deleted are removed.
Chapter 13. Cluster capabilities
Cluster administrators can use cluster capabilities to disable one or more optional components prior to installation. Cluster administrators can enable cluster capabilities at anytime after installation.
Cluster administrators cannot disable a cluster capability after it is enabled.
13.1. Optional cluster capabilities in OpenShift Container Platform 4.11
Optional cluster capabilities are components that can be disabled during the installation process. Cluster administrators can disable optional cluster capabilities to reduce the resources consumed by a cluster. Currently, cluster Operators provide a cluster capability’s features.
If you want to use the features provided by a disabled cluster capability, you can enable the capability after installation. After a cluster capability is enabled, it cannot be disabled.
13.1.1. Bare-metal capability
Purpose
The Cluster Baremetal Operator provides the features for the baremetal capability.
The Cluster Baremetal Operator (CBO) deploys all the components necessary to take a bare-metal server to a fully functioning worker node ready to run OpenShift Container Platform compute nodes. The CBO ensures that the metal3 deployment, which consists of the Bare Metal Operator (BMO) and Ironic containers, runs on one of the control plane nodes within the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. The CBO also listens for OpenShift Container Platform updates to resources that it watches and takes appropriate action.
The bare-metal capability is required for installer provisioned installation (IPI) deployments. Disabling the bare-metal capability can result in unexpected problems with IPI deployments.
It is recommended that cluster adminstrators only disable the bare-metal capability during user-provisioned installations (UPI) that do not have any BareMetalHost resources in the cluster.
If the bare-metal capability is disabled, the cluster cannot provision or manage bare-metal nodes. Only disable the capability if there are no BareMetalHost resources in your deployment.
13.1.2. OpenShift samples capability
Purpose
The Cluster Samples Operator provides the features for the openshift-samples capability.
The Cluster Samples Operator manages the sample image streams and templates stored in the openshift namespace.
On initial start up, the Operator creates the default samples configuration resource to initiate the creation of the image streams and templates. The configuration object is a cluster scoped object with the key cluster and type configs.samples.
The image streams are the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS)-based OpenShift Container Platform image streams pointing to images on registry.redhat.io. Similarly, the templates are those categorized as OpenShift Container Platform templates.
If you disable the samples capability, users cannot access the image streams, samples, and templates it provides. Depending on your deployment, you might want to disable this component if you do not need it.
13.1.3. Marketplace capability
Purpose
The Marketplace Operator provides the features for the marketplace capability.
The Marketplace Operator simplifies the process for bringing off-cluster Operators to your cluster by using a set of default Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) catalogs on the cluster. When the Marketplace Operator is installed, it creates the openshift-marketplace namespace. OLM ensures catalog sources installed in the openshift-marketplace namespace are available for all namespaces on the cluster.
If you disable the marketplace capability, the Marketplace Operator does not create the openshift-marketplace namespace. Catalog sources can still be configured and managed on the cluster manually, but OLM depends on the openshift-marketplace namespace in order to make catalogs available to all namespaces on the cluster. Users with elevated permissions to create namespaces prefixed with openshift-, such as system or cluster administrators, can manually create the openshift-marketplace namespace.
If you enable the marketplace capability, you can enable and disable individual catalogs by configuring the Marketplace Operator.
13.2. Viewing the cluster capabilities
As a cluster administrator, you can view the capabilities by using the clusterversion resource status.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
To view the status of the cluster capabilities, run the following command:
oc get clusterversion version -o jsonpath='{.spec.capabilities}{"\n"}{.status.capabilities}{"\n"}'$ oc get clusterversion version -o jsonpath='{.spec.capabilities}{"\n"}{.status.capabilities}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
{"additionalEnabledCapabilities":["openshift-samples"],"baselineCapabilitySet":"None"} {"enabledCapabilities":["openshift-samples"],"knownCapabilities":["baremetal","marketplace","openshift-samples"]}{"additionalEnabledCapabilities":["openshift-samples"],"baselineCapabilitySet":"None"} {"enabledCapabilities":["openshift-samples"],"knownCapabilities":["baremetal","marketplace","openshift-samples"]}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
13.3. Enabling the cluster capabilities by setting baseline capability set
As a cluster administrator, you can enable the capabilities by setting baselineCapabilitySet.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
To set the
baselineCapabilitySet, run the following command:oc patch clusterversion version --type merge -p '{"spec":{"capabilities":{"baselineCapabilitySet":"vCurrent"}}}'$ oc patch clusterversion version --type merge -p '{"spec":{"capabilities":{"baselineCapabilitySet":"vCurrent"}}}'1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
baselineCapabilitySetyou can specifyvCurrent,v4.11, orNone.
The following table describes the
baselineCapabilitySetvalues.Expand Table 13.1. Cluster capabilities baselineCapabilitySet values description Value Description vCurrentSpecify when you want to automatically add new capabilities as they become recommended.
v4.11Specify when you want the capabilities defined in OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 and not automatically enable capabilities, which might be introduced in later versions.
NoneSpecify when the other sets are too large, and you do not need any capabilities or want to fine-tune via
additionalEnabledCapabilities.
13.4. Enabling the cluster capabilities by setting additional enabled capabilities
As a cluster administrator, you can enable the cluster capabilities by setting additionalEnabledCapabilities.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
View the additional enabled capabilities by running the following command:
oc get clusterversion version -o jsonpath='{.spec.capabilities.additionalEnabledCapabilities}{"\n"}'$ oc get clusterversion version -o jsonpath='{.spec.capabilities.additionalEnabledCapabilities}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
["openshift-samples"]
["openshift-samples"]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To set the
additionalEnabledCapabilities, run the following command:oc patch clusterversion/version --type merge -p '{"spec":{"capabilities":{"additionalEnabledCapabilities":["openshift-samples", "marketplace"]}}}'$ oc patch clusterversion/version --type merge -p '{"spec":{"capabilities":{"additionalEnabledCapabilities":["openshift-samples", "marketplace"]}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
It is not possible to disable a capability which is already enabled in a cluster. The cluster version Operator (CVO) continues to reconcile the capability which is already enabled in the cluster.
If you try to disable a capability, then CVO shows the divergent spec:
oc get clusterversion version -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[?(@.type=="ImplicitlyEnabledCapabilities")]}{"\n"}'
$ oc get clusterversion version -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[?(@.type=="ImplicitlyEnabledCapabilities")]}{"\n"}'Example output
{"lastTransitionTime":"2022-07-22T03:14:35Z","message":"The following capabilities could not be disabled: openshift-samples","reason":"CapabilitiesImplicitlyEnabled","status":"True","type":"ImplicitlyEnabledCapabilities"}
{"lastTransitionTime":"2022-07-22T03:14:35Z","message":"The following capabilities could not be disabled: openshift-samples","reason":"CapabilitiesImplicitlyEnabled","status":"True","type":"ImplicitlyEnabledCapabilities"}
During the cluster upgrades, it is possible that a given capability could be implicitly enabled. If a resource was already running on the cluster before the upgrade, then any capabilities that is part of the resource will be enabled. For example, during a cluster upgrade, a resource that is already running on the cluster has been changed to be part of the marketplace capability by the system. Even if a cluster administrator does not explicitly enabled the marketplace capability, it is implicitly enabled by the system.
Chapter 14. Configuring additional devices in an IBM Z or LinuxONE environment
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can configure additional devices for your cluster in an IBM Z or LinuxONE environment, which is installed with z/VM. The following devices can be configured:
- Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) host
- FCP LUN
- DASD
- qeth
You can configure devices by adding udev rules using the Machine Config Operator (MCO) or you can configure devices manually.
The procedures described here apply only to z/VM installations. If you have installed your cluster with RHEL KVM on IBM Z or LinuxONE infrastructure, no additional configuration is needed inside the KVM guest after the devices were added to the KVM guests. However, both in z/VM and RHEL KVM environments the next steps to configure the Local Storage Operator and Kubernetes NMState Operator need to be applied.
14.1. Configuring additional devices using the Machine Config Operator (MCO)
Tasks in this section describe how to use features of the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to configure additional devices in an IBM Z or LinuxONE environment. Configuring devices with the MCO is persistent but only allows specific configurations for compute nodes. MCO does not allow control plane nodes to have different configurations.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
- The device must be available to the z/VM guest.
- The device is already attached.
-
The device is not included in the
cio_ignorelist, which can be set in the kernel parameters. You have created a
MachineConfigobject file with the following YAML:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.1.1. Configuring a Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) host
The following is an example of how to configure an FCP host adapter with N_Port Identifier Virtualization (NPIV) by adding a udev rule.
Procedure
Take the following sample udev rule
441-zfcp-host-0.0.8000.rules:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Convert the rule to Base64 encoded by running the following command:
base64 /path/to/file/
$ base64 /path/to/file/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the following MCO sample profile into a YAML file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.1.2. Configuring an FCP LUN
The following is an example of how to configure an FCP LUN by adding a udev rule. You can add new FCP LUNs or add additional paths to LUNs that are already configured with multipathing.
Procedure
Take the following sample udev rule
41-zfcp-lun-0.0.8000:0x500507680d760026:0x00bc000000000000.rules:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Convert the rule to Base64 encoded by running the following command:
base64 /path/to/file/
$ base64 /path/to/file/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the following MCO sample profile into a YAML file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.1.3. Configuring DASD
The following is an example of how to configure a DASD device by adding a udev rule.
Procedure
Take the following sample udev rule
41-dasd-eckd-0.0.4444.rules:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Convert the rule to Base64 encoded by running the following command:
base64 /path/to/file/
$ base64 /path/to/file/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the following MCO sample profile into a YAML file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.1.4. Configuring qeth
The following is an example of how to configure a qeth device by adding a udev rule.
Procedure
Take the following sample udev rule
41-qeth-0.0.1000.rules:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Convert the rule to Base64 encoded by running the following command:
base64 /path/to/file/
$ base64 /path/to/file/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the following MCO sample profile into a YAML file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.2. Configuring additional devices manually
Tasks in this section describe how to manually configure additional devices in an IBM Z or LinuxONE environment. This configuration method is persistent over node restarts but not OpenShift Container Platform native and you need to redo the steps if you replace the node.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
- The device must be available to the node.
- In a z/VM environment, the device must be attached to the z/VM guest.
Procedure
Connect to the node via SSH by running the following command:
ssh <user>@<node_ip_address>
$ ssh <user>@<node_ip_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also start a debug session to the node by running the following command:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To enable the devices with the
chzdevcommand, enter the following command:sudo chzdev -e 0.0.8000 sudo chzdev -e 1000-1002 sude chzdev -e 4444 sudo chzdev -e 0.0.8000:0x500507680d760026:0x00bc000000000000
$ sudo chzdev -e 0.0.8000 sudo chzdev -e 1000-1002 sude chzdev -e 4444 sudo chzdev -e 0.0.8000:0x500507680d760026:0x00bc000000000000Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.3. RoCE network Cards
RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) network cards do not need to be enabled and their interfaces can be configured with the Kubernetes NMState Operator whenever they are available in the node. For example, RoCE network cards are available if they are attached in a z/VM environment or passed through in a RHEL KVM environment.
14.4. Enabling multipathing for FCP LUNs
Tasks in this section describe how to manually configure additional devices in an IBM Z or LinuxONE environment. This configuration method is persistent over node restarts but not OpenShift Container Platform native and you need to redo the steps if you replace the node.
On IBM Z and LinuxONE, you can enable multipathing only if you configured your cluster for it during installation. For more information, see "Installing RHCOS and starting the OpenShift Container Platform bootstrap process" in Installing a cluster with z/VM on IBM Z and LinuxONE.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster as a user with administrative privileges.
- You have configured multiple paths to a LUN with either method explained above.
Procedure
Connect to the node via SSH by running the following command:
ssh <user>@<node_ip_address>
$ ssh <user>@<node_ip_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also start a debug session to the node by running the following command:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To enable multipathing, run the following command:
sudo /sbin/mpathconf --enable
$ sudo /sbin/mpathconf --enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To start the
multipathddaemon, run the following command:sudo multipath
$ sudo multipathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To format your multipath device with fdisk, run the following command:
sudo fdisk /dev/mapper/mpatha
$ sudo fdisk /dev/mapper/mpathaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that the devices have been grouped, run the following command:
sudo multipath -II
$ sudo multipath -IICopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Legal Notice
Copyright © Red Hat
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of the OpenJS Foundation.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.