Chapter 1. Monitoring overview
1.1. About OpenShift Container Platform monitoring
OpenShift Container Platform includes a preconfigured, preinstalled, and self-updating monitoring stack that provides monitoring for core platform components. You also have the option to enable monitoring for user-defined projects.
A cluster administrator can configure the monitoring stack with the supported configurations. OpenShift Container Platform delivers monitoring best practices out of the box.
A set of alerts are included by default that immediately notify cluster administrators about issues with a cluster. Default dashboards in the OpenShift Container Platform web console include visual representations of cluster metrics to help you to quickly understand the state of your cluster.
With the OpenShift Container Platform web console, you can view and manage metrics, alerts, and review monitoring dashboards. OpenShift Container Platform also provides access to third-party interfaces, such as Prometheus, Alertmanager, and Grafana.
After installing OpenShift Container Platform 4.9, cluster administrators can optionally enable monitoring for user-defined projects. By using this feature, cluster administrators, developers, and other users can specify how services and pods are monitored in their own projects. As a cluster administrator, you can find answers to common problems such as user metrics unavailability and Prometheus consuming a lot of disk space in troubleshooting monitoring issues.
1.2. Understanding the monitoring stack
The OpenShift Container Platform monitoring stack is based on the Prometheus open source project and its wider ecosystem. The monitoring stack includes the following:
-
Default platform monitoring components. A set of platform monitoring components are installed in the
openshift-monitoringproject by default during an OpenShift Container Platform installation. This provides monitoring for core OpenShift Container Platform components including Kubernetes services. The default monitoring stack also enables remote health monitoring for clusters. These components are illustrated in the Installed by default section in the following diagram. -
Components for monitoring user-defined projects. After optionally enabling monitoring for user-defined projects, additional monitoring components are installed in the
openshift-user-workload-monitoringproject. This provides monitoring for user-defined projects. These components are illustrated in the User section in the following diagram.
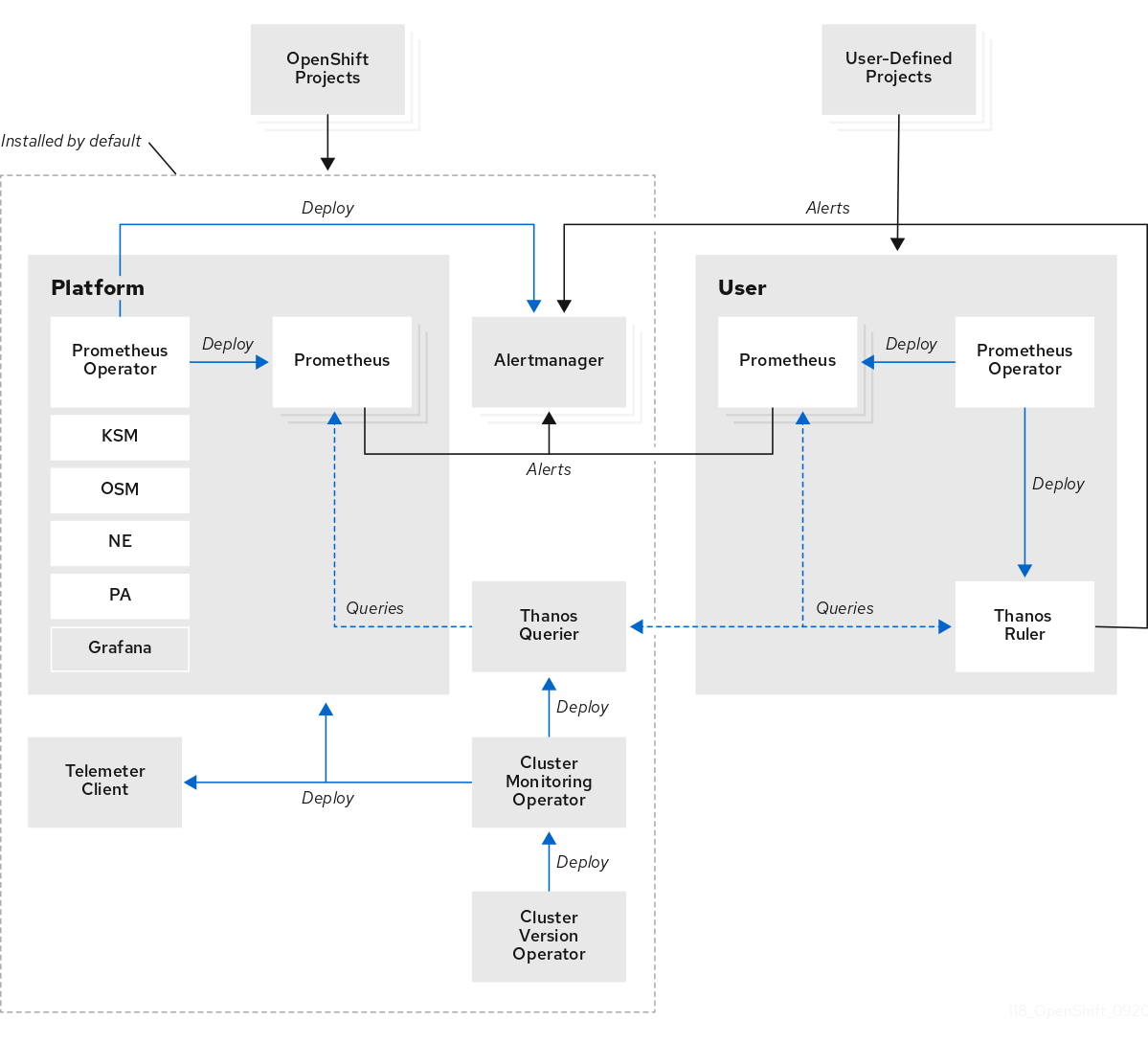
1.2.1. Default monitoring components
By default, the OpenShift Container Platform 4.9 monitoring stack includes these components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cluster Monitoring Operator | The Cluster Monitoring Operator (CMO) is a central component of the monitoring stack. It deploys, manages, and automatically updates Prometheus and Alertmanager instances, Thanos Querier, Telemeter Client, and metrics targets. The CMO is deployed by the Cluster Version Operator (CVO). |
| Prometheus Operator |
The Prometheus Operator (PO) in the |
| Prometheus | Prometheus is the monitoring system on which the OpenShift Container Platform monitoring stack is based. Prometheus is a time-series database and a rule evaluation engine for metrics. Prometheus sends alerts to Alertmanager for processing. |
| Prometheus Adapter |
The Prometheus Adapter (PA in the preceding diagram) translates Kubernetes node and pod queries for use in Prometheus. The resource metrics that are translated include CPU and memory utilization metrics. The Prometheus Adapter exposes the cluster resource metrics API for horizontal pod autoscaling. The Prometheus Adapter is also used by the |
| Alertmanager | The Alertmanager service handles alerts received from Prometheus. Alertmanager is also responsible for sending the alerts to external notification systems. |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
| Thanos Querier | Thanos Querier aggregates and optionally deduplicates core OpenShift Container Platform metrics and metrics for user-defined projects under a single, multi-tenant interface. |
| Grafana | The Grafana analytics platform provides dashboards for analyzing and visualizing the metrics. The Grafana instance that is provided with the monitoring stack, along with its dashboards, is read-only. |
| Telemeter Client | Telemeter Client sends a subsection of the data from platform Prometheus instances to Red Hat to facilitate Remote Health Monitoring for clusters. |
All of the components in the monitoring stack are monitored by the stack and are automatically updated when OpenShift Container Platform is updated.
1.2.2. Default monitoring targets
In addition to the components of the stack itself, the default monitoring stack monitors:
- CoreDNS
- Elasticsearch (if Logging is installed)
- etcd
- Fluentd (if Logging is installed)
- HAProxy
- Image registry
- Kubelets
- Kubernetes API server
- Kubernetes controller manager
- Kubernetes scheduler
- Metering (if Metering is installed)
- OpenShift API server
- OpenShift Controller Manager
- Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM)
Each OpenShift Container Platform component is responsible for its monitoring configuration. For problems with the monitoring of an OpenShift Container Platform component, open a Jira issue against that component, not against the general monitoring component.
Other OpenShift Container Platform framework components might be exposing metrics as well. For details, see their respective documentation.
1.2.3. Components for monitoring user-defined projects
OpenShift Container Platform 4.9 includes an optional enhancement to the monitoring stack that enables you to monitor services and pods in user-defined projects. This feature includes the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Prometheus Operator |
The Prometheus Operator (PO) in the |
| Prometheus | Prometheus is the monitoring system through which monitoring is provided for user-defined projects. Prometheus sends alerts to Alertmanager for processing. |
| Thanos Ruler | The Thanos Ruler is a rule evaluation engine for Prometheus that is deployed as a separate process. In OpenShift Container Platform 4.9, Thanos Ruler provides rule and alerting evaluation for the monitoring of user-defined projects. |
The components in the preceding table are deployed after monitoring is enabled for user-defined projects.
All of the components in the monitoring stack are monitored by the stack and are automatically updated when OpenShift Container Platform is updated.
1.2.4. Monitoring targets for user-defined projects
When monitoring is enabled for user-defined projects, you can monitor:
- Metrics provided through service endpoints in user-defined projects.
- Pods running in user-defined projects.
1.3. Glossary of common terms for OpenShift Container Platform monitoring
This glossary defines common terms that are used in OpenShift Container Platform architecture.
- Alertmanager
- Alertmanager handles alerts received from Prometheus. Alertmanager is also responsible for sending the alerts to external notification systems.
- Alerting rules
- Alerting rules contain a set of conditions that outline a particular state within a cluster. Alerts are triggered when those conditions are true. An alerting rule can be assigned a severity that defines how the alerts are routed.
- Cluster Monitoring Operator
- The Cluster Monitoring Operator (CMO) is a central component of the monitoring stack. It deploys and manages Prometheus instances such as, the Thanos Querier, the Telemeter Client, and metrics targets to ensure that they are up to date. The CMO is deployed by the Cluster Version Operator (CVO).
- Cluster Version Operator
- The Cluster Version Operator (CVO) manages the lifecycle of cluster Operators, many of which are installed in OpenShift Container Platform by default.
- config map
-
A config map provides a way to inject configuration data into pods. You can reference the data stored in a config map in a volume of type
ConfigMap. Applications running in a pod can use this data. - Container
- A container is a lightweight and executable image that includes software and all its dependencies. Containers virtualize the operating system. As a result, you can run containers anywhere from a data center to a public or private cloud as well as a developer’s laptop.
- custom resource (CR)
- A CR is an extension of the Kubernetes API. You can create custom resources.
- etcd
- etcd is the key-value store for OpenShift Container Platform, which stores the state of all resource objects.
- Fluentd
- Fluentd gathers logs from nodes and feeds them to Elasticsearch.
- Kubelets
- Runs on nodes and reads the container manifests. Ensures that the defined containers have started and are running.
- Kubernetes API server
- Kubernetes API server validates and configures data for the API objects.
- Kubernetes controller manager
- Kubernetes controller manager governs the state of the cluster.
- Kubernetes scheduler
- Kubernetes scheduler allocates pods to nodes.
- labels
- Labels are key-value pairs that you can use to organize and select subsets of objects such as a pod.
- Metering
- Metering is a general purpose data analysis tool that enables you to write reports to process data from different data sources.
- node
- A worker machine in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. A node is either a virtual machine (VM) or a physical machine.
- Operator
- The preferred method of packaging, deploying, and managing a Kubernetes application in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. An Operator takes human operational knowledge and encodes it into software that is packaged and shared with customers.
- Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM)
- OLM helps you install, update, and manage the lifecycle of Kubernetes native applications. OLM is an open source toolkit designed to manage Operators in an effective, automated, and scalable way.
- Persistent storage
- Stores the data even after the device is shut down. Kubernetes uses persistent volumes to store the application data.
- Persistent volume claim (PVC)
- You can use a PVC to mount a PersistentVolume into a Pod. You can access the storage without knowing the details of the cloud environment.
- pod
- The pod is the smallest logical unit in Kubernetes. A pod is comprised of one or more containers to run in a worker node.
- Prometheus
- Prometheus is the monitoring system on which the OpenShift Container Platform monitoring stack is based. Prometheus is a time-series database and a rule evaluation engine for metrics. Prometheus sends alerts to Alertmanager for processing.
- Prometheus adapter
- The Prometheus Adapter translates Kubernetes node and pod queries for use in Prometheus. The resource metrics that are translated include CPU and memory utilization. The Prometheus Adapter exposes the cluster resource metrics API for horizontal pod autoscaling.
- Prometheus Operator
-
The Prometheus Operator (PO) in the
openshift-monitoringproject creates, configures, and manages platform Prometheus and Alertmanager instances. It also automatically generates monitoring target configurations based on Kubernetes label queries. - Silences
- A silence can be applied to an alert to prevent notifications from being sent when the conditions for an alert are true. You can mute an alert after the initial notification, while you work on resolving the underlying issue.
- storage
- OpenShift Container Platform supports many types of storage, both for on-premise and cloud providers. You can manage container storage for persistent and non-persistent data in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Thanos Ruler
- The Thanos Ruler is a rule evaluation engine for Prometheus that is deployed as a separate process. In OpenShift Container Platform, Thanos Ruler provides rule and alerting evaluation for the monitoring of user-defined projects.
- web console
- A user interface (UI) to manage OpenShift Container Platform.