Chapter 6. Creating a private cluster on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS
For Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS workloads that do not require public internet access, you can create a private cluster.
6.1. Creating a private Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster using the ROSA CLI
You can create a private cluster with multiple availability zones (Multi-AZ) on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS using the ROSA command-line interface (CLI), rosa.
Creating a cluster with hosted control planes can take around 10 minutes.
Prerequisites
- You have available AWS service quotas.
- You have enabled the Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS in the AWS Console.
- You have installed and configured the latest version of the ROSA CLI on your installation host.
Procedure
Create a VPC with at least one private subnet. Ensure that your machine’s classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) matches your virtual private cloud’s CIDR. For more information, see Requirements for using your own VPC and VPC Validation.
ImportantIf you use a firewall, you must configure it so that ROSA can access the sites that required to function.
For more information, see the "AWS PrivateLink firewall prerequisites" section.
Create the account-wide IAM roles by running the following command:
rosa create account-roles --hosted-cp
$ rosa create account-roles --hosted-cpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the OIDC configuration by running the following command:
rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yes
$ rosa create oidc-config --mode=auto --yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the OIDC configuration ID because you need it to create the Operator roles.
Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Operator roles by running the following command:
rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix <operator_roles_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$<account_roles_prefix>:role/$<account_roles_prefix>-HCP-ROSA-Installer-Role
$ rosa create operator-roles --hosted-cp --prefix <operator_roles_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> --installer-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$<account_roles_prefix>:role/$<account_roles_prefix>-HCP-ROSA-Installer-RoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a private Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster by running the following command:
rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster-name> --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator_role_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> [--machine-cidr=<VPC CIDR>/16] --subnet-ids=<private-subnet-id1>[,<private-subnet-id2>,<private-subnet-id3>]
$ rosa create cluster --private --cluster-name=<cluster-name> --sts --mode=auto --hosted-cp --operator-roles-prefix <operator_role_prefix> --oidc-config-id <oidc_config_id> [--machine-cidr=<VPC CIDR>/16] --subnet-ids=<private-subnet-id1>[,<private-subnet-id2>,<private-subnet-id3>]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the following command to check the status of your cluster. During cluster creation, the
Statefield from the output will transition frompendingtoinstalling, and finally, toready.rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>
$ rosa describe cluster --cluster=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf installation fails or the
Statefield does not change toreadyafter 10 minutes, see the "Troubleshooting Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS installations" documentation in the Additional resources section.Enter the following command to follow the OpenShift installer logs to track the progress of your cluster:
rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2. Adding additional AWS security groups to the AWS PrivateLink endpoint
With Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS clusters, the AWS PrivateLink endpoint exposed in the host’s Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) has a security group that limits access to requests that originate from within the cluster’s Machine CIDR range. You must create and attach another security group to the PrivateLink endpoint to grant API access to entities outside of the VPC through VPC peering, transit gateways, or other network connectivity.
Adding additional AWS security groups to the AWS PrivateLink endpoint is only supported on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS version 4.17.2 and later.
Prerequisites
- Your corporate network or other VPC has connectivity.
- You have permission to create and attach security groups within the VPC.
Procedure
Set your cluster name as an environmental variable by running the following command:
export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster_name>
$ export CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the variable exists by running the following command:
echo $CLUSTER_NAME
$ echo $CLUSTER_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
hcp-private
hcp-privateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the VPC endpoint (VPCE) ID and VPC ID by running the following command:
read -r VPCE_ID VPC_ID <<< $(aws ec2 describe-vpc-endpoints --filters "Name=tag:api.openshift.com/id,Values=$(rosa describe cluster -c ${CLUSTER_NAME} -o yaml | grep '^id: ' | cut -d' ' -f2)" --query 'VpcEndpoints[].[VpcEndpointId,VpcId]' --output text)$ read -r VPCE_ID VPC_ID <<< $(aws ec2 describe-vpc-endpoints --filters "Name=tag:api.openshift.com/id,Values=$(rosa describe cluster -c ${CLUSTER_NAME} -o yaml | grep '^id: ' | cut -d' ' -f2)" --query 'VpcEndpoints[].[VpcEndpointId,VpcId]' --output text)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningModifying or removing the default AWS PrivateLink endpoint security group is not supported and might result in unexpected behavior.
Create an additional security group by running the following command:
export SG_ID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group --description "Granting API access to ${CLUSTER_NAME} from outside of VPC" --group-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-api-sg" --vpc-id $VPC_ID --output text)$ export SG_ID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group --description "Granting API access to ${CLUSTER_NAME} from outside of VPC" --group-name "${CLUSTER_NAME}-api-sg" --vpc-id $VPC_ID --output text)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add an inbound (ingress) rule to the security group by running the following command:
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id $SG_ID --ip-permissions FromPort=443,ToPort=443,IpProtocol=tcp,IpRanges=[{CidrIp=<cidr-to-allow>}]$ aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id $SG_ID --ip-permissions FromPort=443,ToPort=443,IpProtocol=tcp,IpRanges=[{CidrIp=<cidr-to-allow>}]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the new security group to the VPCE by running the following command:
aws ec2 modify-vpc-endpoint --vpc-endpoint-id $VPCE_ID --add-security-group-ids $SG_ID
$ aws ec2 modify-vpc-endpoint --vpc-endpoint-id $VPCE_ID --add-security-group-ids $SG_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can now access the API of your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS private cluster from the specified CIDR block.
6.3. Additional principals on your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
You can allow AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles as additional principals to connect to your cluster’s private API server endpoint.
You can access your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster’s API Server endpoint from either the public internet or the interface endpoint that was created within the VPC private subnets. By default, you can privately access your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API Server by using the -kube-system-kube-controller-manager Operator role. To be able to access Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API server from another account directly without using the primary account where cluster is installed, you must include cross-account IAM roles as additional principals. This feature allows you to simplify your network architecture and reduce data transfer costs by avoiding peering or attaching cross-account VPCs to cluster’s VPC.
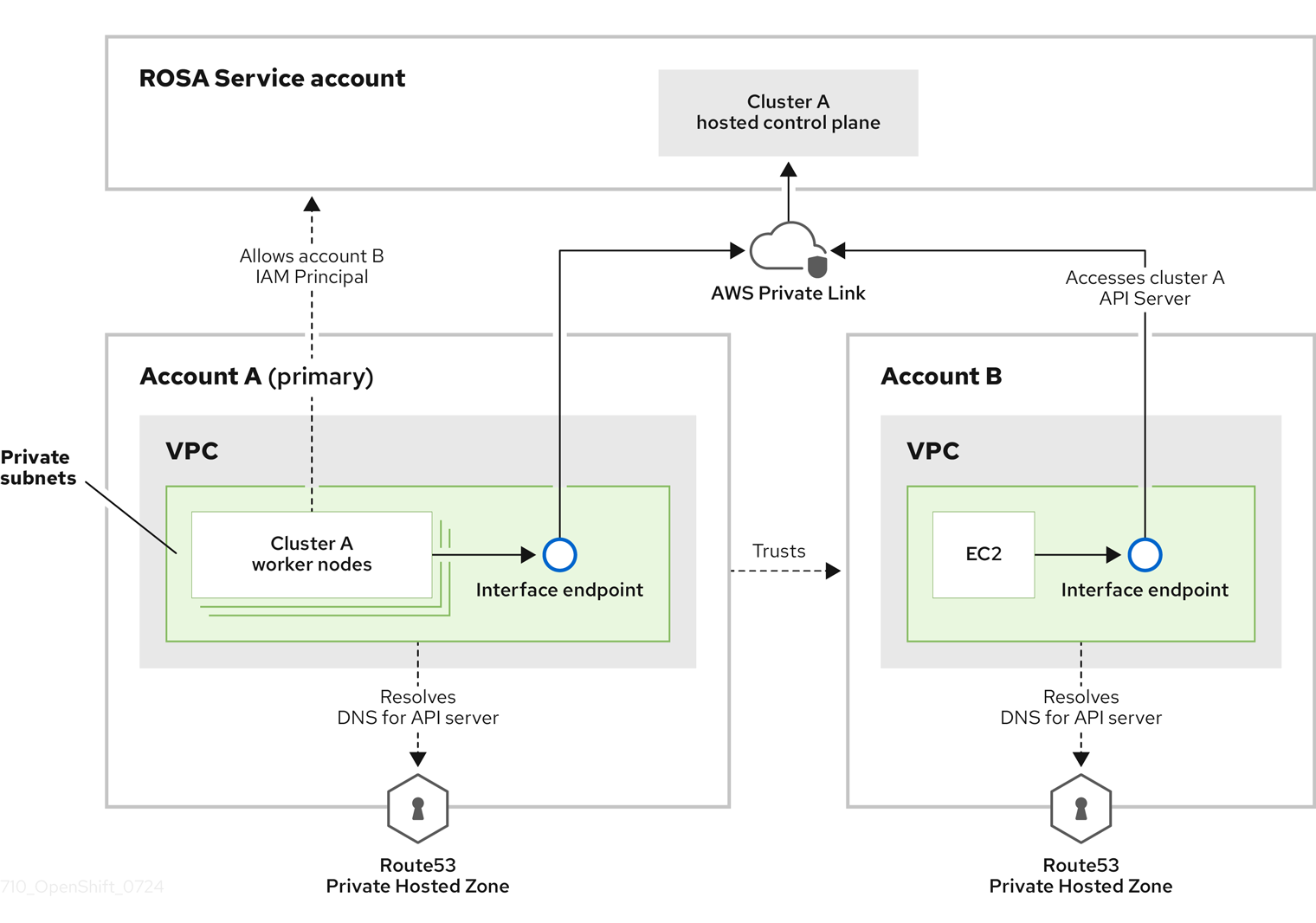
In this diagram, the cluster creating account is designated as Account A. This account designates that another account, Account B, should have access to the API server.
After you have configured additional allowed principals, you must create the interface VPC endpoint in the VPC from where you want to access the cross-account Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API server. Then, create a private hosted zone in Route53 to route calls made to cross-account Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS API server to pass through the created VPC endpoint.
6.3.1. Adding additional principals while creating your Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
Use the --additional-allowed-principals argument to permit access through other roles.
Procedure
Add the
--additional-allowed-principalsargument to therosa create clustercommand, similar to the following:rosa create cluster [...] --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>
$ rosa create cluster [...] --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can use
arn:aws:iam::account_id:role/role_nameto approve a specific role.When the cluster creation command runs, you receive a summary of your cluster with the
--additional-allowed-principalsspecified:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.2. Adding additional principals to your existing Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS cluster
You can add additional principals to your cluster by using the command-line interface (CLI).
Procedure
Run the following command to edit your cluster and add an additional principal who can access this cluster’s endpoint:
rosa edit cluster -c <cluster_name> --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>
$ rosa edit cluster -c <cluster_name> --additional-allowed-principals <arn_string>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can use
arn:aws:iam::account_id:role/role_nameto approve a specific role.
Next steps
- Configure an identity provider.