6.15. Other Virtual Machine Tasks
6.15.1. Enabling SAP Monitoring
Procedure 6.34. Enabling SAP Monitoring on Virtual Machines
- Click the Virtual Machines tab and select a virtual machine.
- Click .
- Click the Custom Properties tab.
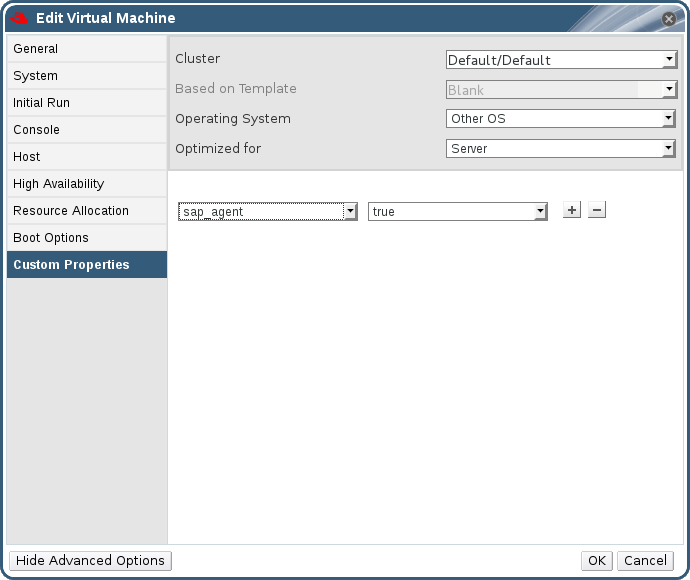
Figure 6.21. Enable SAP
- Select
sap_agentfrom the drop-down list. Ensure the secondary drop-down menu is set to True.If previous properties have been set, select the plus sign to add a new property rule and selectsap_agent. - Click .
6.15.2. Configuring Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4 and Higher Virtual Machines to use SPICE
Note
6.15.2.1. Installing and Configuring QXL Drivers
Procedure 6.35. Installing QXL Drivers
- Log in to a Red Hat Enterprise Linux virtual machine.
- Install the QXL drivers:
# yum install xorg-x11-drv-qxl
Procedure 6.36. Configuring QXL drivers in GNOME
- Click System.
- Click Administration.
- Click Display.
- Click the Hardware tab.
- Click Video Cards Configure.
- Select qxl and click OK.
- Restart X-Windows by logging out of the virtual machine and logging back in.
Procedure 6.37. Configuring QXL drivers on the command line:
- Back up
/etc/X11/xorg.conf:# cp /etc/X11/xorg.conf /etc/X11/xorg.conf.$$.backup
- Make the following change to the Device section of
/etc/X11/xorg.conf:Section "Device" Identifier "Videocard0" Driver "qxl" Endsection
6.15.2.2. Configuring a Virtual Machine's Tablet and Mouse to use SPICE
/etc/X11/xorg.conf file to enable SPICE for your virtual machine's tablet devices.
Procedure 6.38. Configuring a Virtual Machine's Tablet and Mouse to use SPICE
- Verify that the tablet device is available on your guest:
# /sbin/lsusb -v | grep 'QEMU USB Tablet'
If there is no output from the command, do not continue configuring the tablet. - Back up
/etc/X11/xorg.conf:# cp /etc/X11/xorg.conf /etc/X11/xorg.conf.$$.backup
- Make the following changes to
/etc/X11/xorg.conf:Section "ServerLayout" Identifier "single head configuration" Screen 0 "Screen0" 0 0 InputDevice "Keyboard0" "CoreKeyboard" InputDevice "Tablet" "SendCoreEvents" InputDevice "Mouse" "CorePointer" EndSection Section "InputDevice" Identifier "Mouse" Driver "void" #Option "Device" "/dev/input/mice" #Option "Emulate3Buttons" "yes" EndSection Section "InputDevice" Identifier "Tablet" Driver "evdev" Option "Device" "/dev/input/event2" Option "CorePointer" "true" EndSection
- Log out and log back into the virtual machine to restart X-Windows.
6.15.3. KVM virtual machine timing management
pvclock provides a stable source of timing for KVM guests that support it.
- Clocks can fall out of synchronization with the actual time which invalidates sessions and affects networks.
- Virtual machines with slower clocks may have issues migrating.
Important
ntpd service and add it to the default startup sequence:
- For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
# service ntpd start # chkconfig ntpd on
- For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
# systemctl start ntpd.service # systemctl enable ntpd.service
ntpd service should minimize the affects of clock skew in all cases.
Your CPU has a constant Time Stamp Counter if the constant_tsc flag is present. To determine if your CPU has the constant_tsc flag run the following command:
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep constant_tsc
constant_tsc bit. If no output is given follow the instructions below.
Systems without constant time stamp counters require additional configuration. Power management features interfere with accurate time keeping and must be disabled for virtual machines to accurately keep time with KVM.
Important
constant_tsc bit, disable all power management features (BZ#513138). Each system has several timers it uses to keep time. The TSC is not stable on the host, which is sometimes caused by cpufreq changes, deep C state, or migration to a host with a faster TSC. Deep C sleep states can stop the TSC. To prevent the kernel using deep C states append "processor.max_cstate=1" to the kernel boot options in the grub.conf file on the host:
term Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server (2.6.18-159.el5)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-159.el5 ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 rhgb quiet processor.max_cstate=1cpufreq (only necessary on hosts without the constant_tsc) by editing the /etc/sysconfig/cpuspeed configuration file and change the MIN_SPEED and MAX_SPEED variables to the highest frequency available. Valid limits can be found in the /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/cpufreq/scaling_available_frequencies files.
engine-config tool to receive alerts when hosts drift out of sync.
You can use the engine-config tool to configure alerts when your hosts drift out of sync.
EnableHostTimeDrift and HostTimeDriftInSec. EnableHostTimeDrift, with a default value of false, can be enabled to receive alert notifications of host time drift. The HostTimeDriftInSec parameter is used to set the maximum allowable drift before alerts start being sent.
For certain Red Hat Enterprise Linux virtual machines, additional kernel parameters are required. These parameters can be set by appending them to the end of the /kernel line in the /boot/grub/grub.conf file of the virtual machine.
Note
ktune package
ktune package provides an interactive Bourne shell script, fix_clock_drift.sh. When run as the superuser, this script inspects various system parameters to determine if the virtual machine on which it is run is susceptible to clock drift under load. If so, it then creates a new grub.conf.kvm file in the /boot/grub/ directory. This file contains a kernel boot line with additional kernel parameters that allow the kernel to account for and prevent significant clock drift on the KVM virtual machine. After running fix_clock_drift.sh as the superuser, and once the script has created the grub.conf.kvm file, then the virtual machine's current grub.conf file should be backed up manually by the system administrator, the new grub.conf.kvm file should be manually inspected to ensure that it is identical to grub.conf with the exception of the additional boot line parameters, the grub.conf.kvm file should finally be renamed grub.conf, and the virtual machine should be rebooted.
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux | Additional virtual machine kernel parameters |
|---|---|
| 5.4 AMD64/Intel 64 with the paravirtualized clock | Additional parameters are not required |
| 5.4 AMD64/Intel 64 without the paravirtualized clock | notsc lpj=n |
| 5.4 x86 with the paravirtualized clock | Additional parameters are not required |
| 5.4 x86 without the paravirtualized clock | clocksource=acpi_pm lpj=n |
| 5.3 AMD64/Intel 64 | notsc |
| 5.3 x86 | clocksource=acpi_pm |
| 4.8 AMD64/Intel 64 | notsc |
| 4.8 x86 | clock=pmtmr |
| 3.9 AMD64/Intel 64 | Additional parameters are not required |
| 3.9 x86 | Additional parameters are not required |