Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
A.2. Strategies for Disk Repartitioning
- Unpartitioned free space is available
- An unused partition is available
- Free space in an actively used partition is available
Note
A.2.1. Using Unpartitioned Free Space
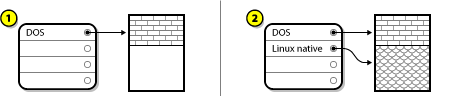
Figure A.8. Disk Drive with Unpartitioned Free Space
A.2.2. Using Space from an Unused Partition
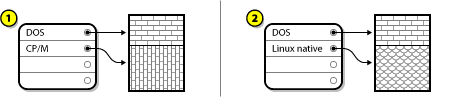
Figure A.9. Disk Drive with an Unused Partition
A.2.3. Using Free Space from an Active Partition
- Destructive Repartitioning
- In this case, the single large partition is deleted and several smaller ones are created instead. Any data held in the original partition is destroyed. This means that making a complete backup is necessary. It is highly recommended to make two backups, use verification (if available in your backup software), and try to read data from the backup before deleting the partition.
Warning
If an operating system was installed on that partition, it must be reinstalled if you want to use that system as well. Be aware that some computers sold with pre-installed operating systems might not include the installation media to reinstall the original operating system. You should check whether this applies to your system is before you destroy your original partition and its operating system installation.After creating a smaller partition for your existing operating system, you can reinstall software, restore your data, and start your Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation.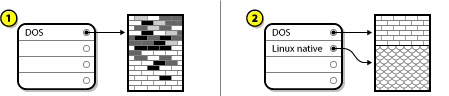
Figure A.10. Disk Drive Being Destructively Repartitioned
In the above example, 1 represents before and 2 represents after.Warning
Any data previously present in the original partition is lost. - Non-Destructive Repartitioning
- With non-destructive repartitioning you execute a program that makes a big partition smaller without losing any of the files stored in that partition. This method is usually reliable, but can be very time-consuming on large drives.While the process of non-destructive repartitioning is rather straightforward, there are three steps involved:
- Compress and backup existing data
- Resize the existing partition
- Create new partition(s)
A.2.3.1. Compress Existing Data
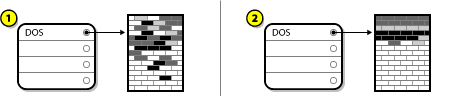
Figure A.11. Disk Drive Being Compressed
A.2.3.2. Resize the Existing Partition
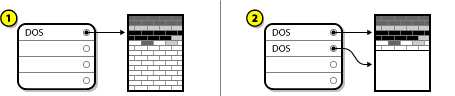
Figure A.12. Disk Drive with Partition Resized
A.2.3.3. Create new partitions
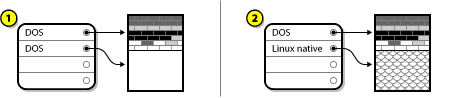
Figure A.13. Disk Drive with Final Partition Configuration