第5章 Migrating virtual machine instances between Compute nodes
You sometimes need to migrate instances from one Compute node to another Compute node in the overcloud, to perform maintenance, rebalance the workload, or replace a failed or failing node.
- Compute node maintenance
- If you need to temporarily take a Compute node out of service, for instance, to perform hardware maintenance or repair, kernel upgrades and software updates, you can migrate instances running on the Compute node to another Compute node.
- Failing Compute node
- If a Compute node is about to fail and you need to service it or replace it, you can migrate instances from the failing Compute node to a healthy Compute node.
- Failed Compute nodes
- If a Compute node has already failed, you can evacuate the instances. You can rebuild instances from the original image on another Compute node, using the same name, UUID, network addresses, and any other allocated resources the instance had before the Compute node failed.
- Workload rebalancing
- You can migrate one or more instances to another Compute node to rebalance the workload. For example, you can consolidate instances on a Compute node to conserve power, migrate instances to a Compute node that is physically closer to other networked resources to reduce latency, or distribute instances across Compute nodes to avoid hot spots and increase resiliency.
Director configures all Compute nodes to provide secure migration. All Compute nodes also require a shared SSH key to provide the users of each host with access to other Compute nodes during the migration process. Director creates this key using the OS::TripleO::Services::NovaCompute composable service. This composable service is one of the main services included on all Compute roles by default. For more information, see Composable Services and Custom Roles in the Advanced Overcloud Customization guide.
If you have a functioning Compute node, and you want to make a copy of an instance for backup purposes, or to copy the instance to a different environment, follow the procedure in Importing virtual machines into the overcloud in the Director Installation and Usage guide.
5.1. Migration types
Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) supports the following types of migration.
Cold migration
Cold migration, or non-live migration, involves shutting down a running instance before migrating it from the source Compute node to the destination Compute node.
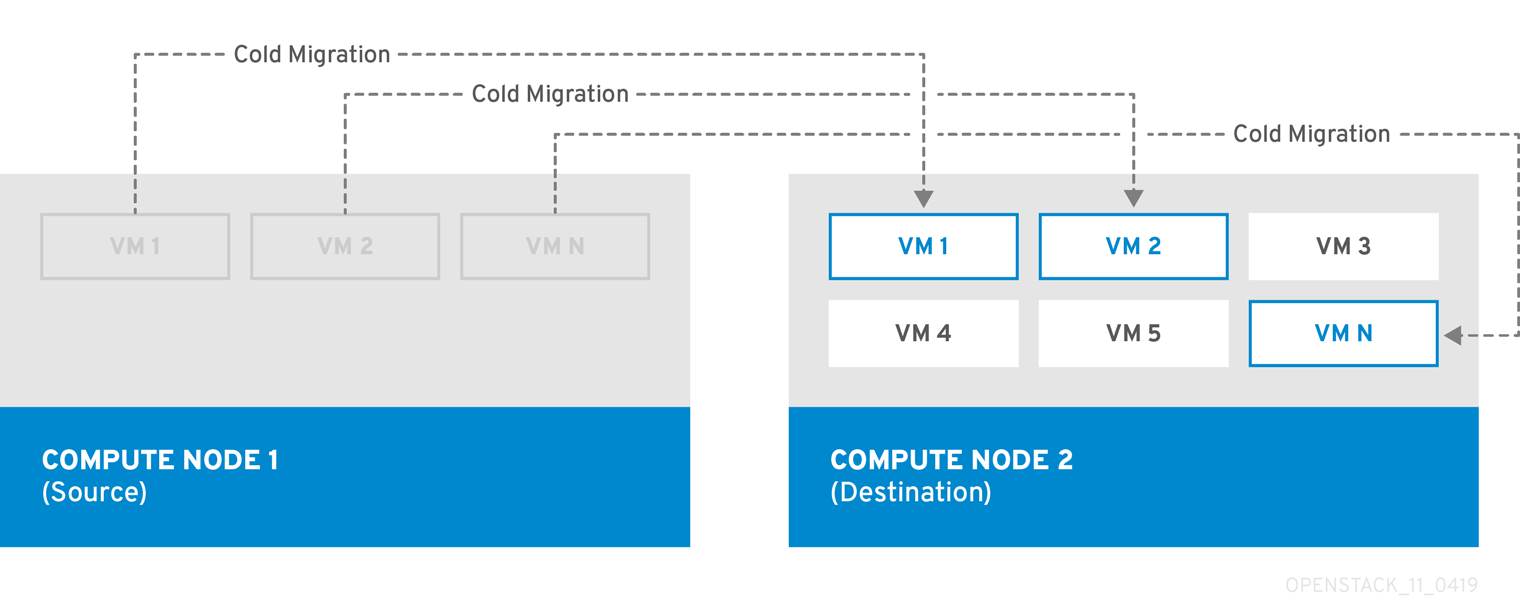
Cold migration involves some downtime for the instance. The migrated instance maintains access to the same volumes and IP addresses.
Cold migration requires that both the source and destination Compute nodes are running.
Live migration
Live migration involves moving the instance from the source Compute node to the destination Compute node without shutting it down, and while maintaining state consistency.
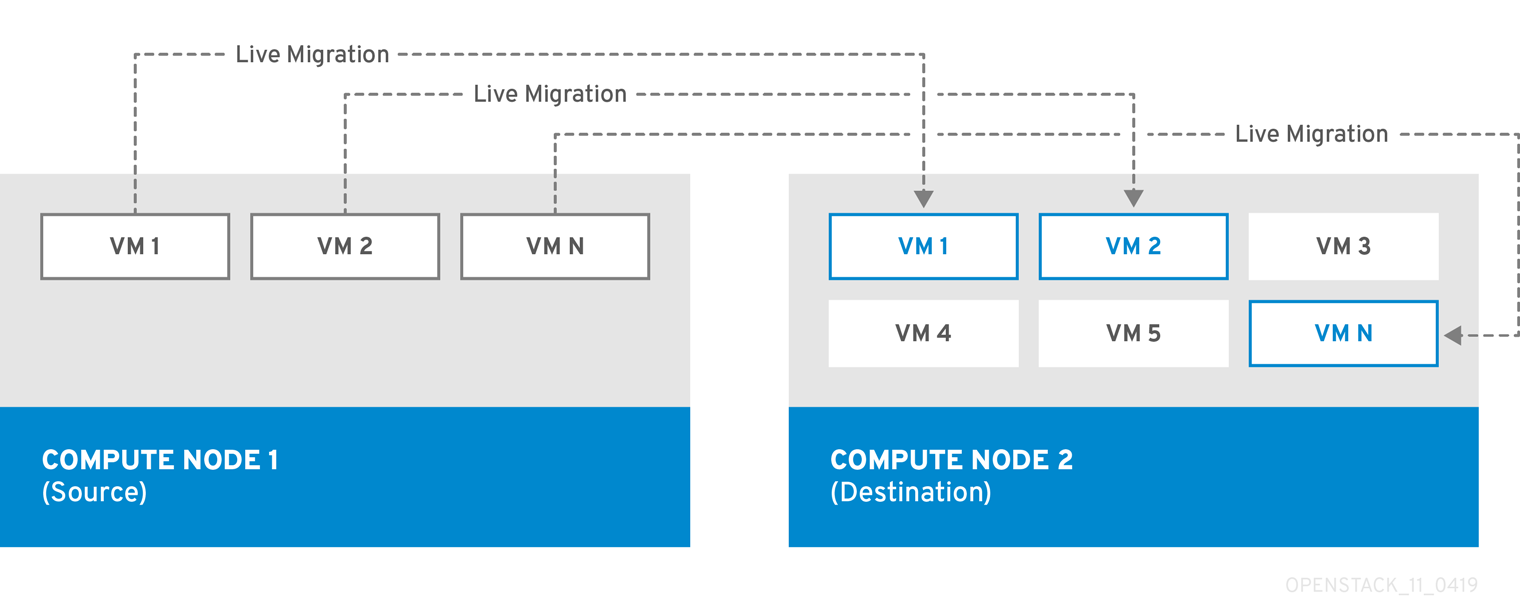
Live migrating an instance involves little or no perceptible downtime. In some cases, instances cannot use live migration. For more information, see Migration Constraints.
Live migration requires that both the source and destination Compute nodes are running.
Evacuation
If you need to migrate instances because the source Compute node has already failed, you can evacuate the instances.