Networking
Configuring and managing cluster networking
Abstract
Chapter 1. About networking
Red Hat OpenShift Networking is an ecosystem of features, plugins and advanced networking capabilities that extend Kubernetes networking with the advanced networking-related features that your cluster needs to manage its network traffic for one or multiple hybrid clusters. This ecosystem of networking capabilities integrates ingress, egress, load balancing, high-performance throughput, security, inter- and intra-cluster traffic management and provides role-based observability tooling to reduce its natural complexities.
The following list highlights some of the most commonly used Red Hat OpenShift Networking features available on your cluster:
Primary cluster network provided by either of the following Container Network Interface (CNI) plugins:
- OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, the default plugin
- OpenShift SDN network plugin
- Certified 3rd-party alternative primary network plugins
- Cluster Network Operator for network plugin management
- Ingress Operator for TLS encrypted web traffic
- DNS Operator for name assignment
- MetalLB Operator for traffic load balancing on bare metal clusters
- IP failover support for high-availability
- Additional hardware network support through multiple CNI plugins, including for macvlan, ipvlan, and SR-IOV hardware networks
- IPv4, IPv6, and dual stack addressing
- Hybrid Linux-Windows host clusters for Windows-based workloads
- Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh for discovery, load balancing, service-to-service authentication, failure recovery, metrics, and monitoring of services
- Single-node OpenShift
- Network Observability Operator for network debugging and insights
- Submariner for inter-cluster networking
- Red Hat Service Interconnect for layer 7 inter-cluster networking
Chapter 2. Understanding networking
Cluster Administrators have several options for exposing applications that run inside a cluster to external traffic and securing network connections:
- Service types, such as node ports or load balancers
-
API resources, such as
IngressandRoute
By default, Kubernetes allocates each pod an internal IP address for applications running within the pod. Pods and their containers can network, but clients outside the cluster do not have networking access. When you expose your application to external traffic, giving each pod its own IP address means that pods can be treated like physical hosts or virtual machines in terms of port allocation, networking, naming, service discovery, load balancing, application configuration, and migration.
Some cloud platforms offer metadata APIs that listen on the 169.254.169.254 IP address, a link-local IP address in the IPv4 169.254.0.0/16 CIDR block.
This CIDR block is not reachable from the pod network. Pods that need access to these IP addresses must be given host network access by setting the spec.hostNetwork field in the pod spec to true.
If you allow a pod host network access, you grant the pod privileged access to the underlying network infrastructure.
2.1. OpenShift Container Platform DNS
If you are running multiple services, such as front-end and back-end services for use with multiple pods, environment variables are created for user names, service IPs, and more so the front-end pods can communicate with the back-end services. If the service is deleted and recreated, a new IP address can be assigned to the service, and requires the front-end pods to be recreated to pick up the updated values for the service IP environment variable. Additionally, the back-end service must be created before any of the front-end pods to ensure that the service IP is generated properly, and that it can be provided to the front-end pods as an environment variable.
For this reason, OpenShift Container Platform has a built-in DNS so that the services can be reached by the service DNS as well as the service IP/port.
2.2. OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Operator
When you create your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, pods and services running on the cluster are each allocated their own IP addresses. The IP addresses are accessible to other pods and services running nearby but are not accessible to outside clients. The Ingress Operator implements the IngressController API and is the component responsible for enabling external access to OpenShift Container Platform cluster services.
The Ingress Operator makes it possible for external clients to access your service by deploying and managing one or more HAProxy-based Ingress Controllers to handle routing. You can use the Ingress Operator to route traffic by specifying OpenShift Container Platform Route and Kubernetes Ingress resources. Configurations within the Ingress Controller, such as the ability to define endpointPublishingStrategy type and internal load balancing, provide ways to publish Ingress Controller endpoints.
2.2.1. Comparing routes and Ingress
The Kubernetes Ingress resource in OpenShift Container Platform implements the Ingress Controller with a shared router service that runs as a pod inside the cluster. The most common way to manage Ingress traffic is with the Ingress Controller. You can scale and replicate this pod like any other regular pod. This router service is based on HAProxy, which is an open source load balancer solution.
The OpenShift Container Platform route provides Ingress traffic to services in the cluster. Routes provide advanced features that might not be supported by standard Kubernetes Ingress Controllers, such as TLS re-encryption, TLS passthrough, and split traffic for blue-green deployments.
Ingress traffic accesses services in the cluster through a route. Routes and Ingress are the main resources for handling Ingress traffic. Ingress provides features similar to a route, such as accepting external requests and delegating them based on the route. However, with Ingress you can only allow certain types of connections: HTTP/2, HTTPS and server name identification (SNI), and TLS with certificate. In OpenShift Container Platform, routes are generated to meet the conditions specified by the Ingress resource.
2.3. Glossary of common terms for OpenShift Container Platform networking
This glossary defines common terms that are used in the networking content.
- authentication
- To control access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster, a cluster administrator can configure user authentication and ensure only approved users access the cluster. To interact with an OpenShift Container Platform cluster, you must authenticate to the OpenShift Container Platform API. You can authenticate by providing an OAuth access token or an X.509 client certificate in your requests to the OpenShift Container Platform API.
- AWS Load Balancer Operator
-
The AWS Load Balancer (ALB) Operator deploys and manages an instance of the
aws-load-balancer-controller. - Cluster Network Operator
- The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) deploys and manages the cluster network components in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This includes deployment of the Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin selected for the cluster during installation.
- config map
-
A config map provides a way to inject configuration data into pods. You can reference the data stored in a config map in a volume of type
ConfigMap. Applications running in a pod can use this data. - custom resource (CR)
- A CR is extension of the Kubernetes API. You can create custom resources.
- DNS
- Cluster DNS is a DNS server which serves DNS records for Kubernetes services. Containers started by Kubernetes automatically include this DNS server in their DNS searches.
- DNS Operator
- The DNS Operator deploys and manages CoreDNS to provide a name resolution service to pods. This enables DNS-based Kubernetes Service discovery in OpenShift Container Platform.
- deployment
- A Kubernetes resource object that maintains the life cycle of an application.
- domain
- Domain is a DNS name serviced by the Ingress Controller.
- egress
- The process of data sharing externally through a network’s outbound traffic from a pod.
- External DNS Operator
- The External DNS Operator deploys and manages ExternalDNS to provide the name resolution for services and routes from the external DNS provider to OpenShift Container Platform.
- HTTP-based route
- An HTTP-based route is an unsecured route that uses the basic HTTP routing protocol and exposes a service on an unsecured application port.
- Ingress
- The Kubernetes Ingress resource in OpenShift Container Platform implements the Ingress Controller with a shared router service that runs as a pod inside the cluster.
- Ingress Controller
- The Ingress Operator manages Ingress Controllers. Using an Ingress Controller is the most common way to allow external access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- installer-provisioned infrastructure
- The installation program deploys and configures the infrastructure that the cluster runs on.
- kubelet
- A primary node agent that runs on each node in the cluster to ensure that containers are running in a pod.
- Kubernetes NMState Operator
- The Kubernetes NMState Operator provides a Kubernetes API for performing state-driven network configuration across the OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s nodes with NMState.
- kube-proxy
- Kube-proxy is a proxy service which runs on each node and helps in making services available to the external host. It helps in forwarding the request to correct containers and is capable of performing primitive load balancing.
- load balancers
- OpenShift Container Platform uses load balancers for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster.
- MetalLB Operator
-
As a cluster administrator, you can add the MetalLB Operator to your cluster so that when a service of type
LoadBalanceris added to the cluster, MetalLB can add an external IP address for the service. - multicast
- With IP multicast, data is broadcast to many IP addresses simultaneously.
- namespaces
- A namespace isolates specific system resources that are visible to all processes. Inside a namespace, only processes that are members of that namespace can see those resources.
- networking
- Network information of a OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- node
- A worker machine in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. A node is either a virtual machine (VM) or a physical machine.
- OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Operator
-
The Ingress Operator implements the
IngressControllerAPI and is the component responsible for enabling external access to OpenShift Container Platform services. - pod
- One or more containers with shared resources, such as volume and IP addresses, running in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. A pod is the smallest compute unit defined, deployed, and managed.
- PTP Operator
-
The PTP Operator creates and manages the
linuxptpservices. - route
- The OpenShift Container Platform route provides Ingress traffic to services in the cluster. Routes provide advanced features that might not be supported by standard Kubernetes Ingress Controllers, such as TLS re-encryption, TLS passthrough, and split traffic for blue-green deployments.
- scaling
- Increasing or decreasing the resource capacity.
- service
- Exposes a running application on a set of pods.
- Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Network Operator
- The Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Network Operator manages the SR-IOV network devices and network attachments in your cluster.
- software-defined networking (SDN)
- OpenShift Container Platform uses a software-defined networking (SDN) approach to provide a unified cluster network that enables communication between pods across the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)
- SCTP is a reliable message based protocol that runs on top of an IP network.
- taint
- Taints and tolerations ensure that pods are scheduled onto appropriate nodes. You can apply one or more taints on a node.
- toleration
- You can apply tolerations to pods. Tolerations allow the scheduler to schedule pods with matching taints.
- web console
- A user interface (UI) to manage OpenShift Container Platform.
Chapter 3. Accessing hosts
Learn how to create a bastion host to access OpenShift Container Platform instances and access the control plane nodes with secure shell (SSH) access.
3.1. Accessing hosts on Amazon Web Services in an installer-provisioned infrastructure cluster
The OpenShift Container Platform installer does not create any public IP addresses for any of the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances that it provisions for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. To be able to SSH to your OpenShift Container Platform hosts, you must follow this procedure.
Procedure
-
Create a security group that allows SSH access into the virtual private cloud (VPC) created by the
openshift-installcommand. - Create an Amazon EC2 instance on one of the public subnets the installer created.
Associate a public IP address with the Amazon EC2 instance that you created.
Unlike with the OpenShift Container Platform installation, you should associate the Amazon EC2 instance you created with an SSH keypair. It does not matter what operating system you choose for this instance, as it will simply serve as an SSH bastion to bridge the internet into your OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s VPC. The Amazon Machine Image (AMI) you use does matter. With Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS), for example, you can provide keys via Ignition, like the installer does.
After you provisioned your Amazon EC2 instance and can SSH into it, you must add the SSH key that you associated with your OpenShift Container Platform installation. This key can be different from the key for the bastion instance, but does not have to be.
NoteDirect SSH access is only recommended for disaster recovery. When the Kubernetes API is responsive, run privileged pods instead.
-
Run
oc get nodes, inspect the output, and choose one of the nodes that is a master. The hostname looks similar toip-10-0-1-163.ec2.internal. From the bastion SSH host you manually deployed into Amazon EC2, SSH into that control plane host. Ensure that you use the same SSH key you specified during the installation:
ssh -i <ssh-key-path> core@<master-hostname>
$ ssh -i <ssh-key-path> core@<master-hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 4. Networking Operators overview
OpenShift Container Platform supports multiple types of networking Operators. You can manage the cluster networking using these networking Operators.
4.1. Cluster Network Operator
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) deploys and manages the cluster network components in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This includes deployment of the Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin selected for the cluster during installation. For more information, see Cluster Network Operator in OpenShift Container Platform.
4.2. DNS Operator
The DNS Operator deploys and manages CoreDNS to provide a name resolution service to pods. This enables DNS-based Kubernetes Service discovery in OpenShift Container Platform. For more information, see DNS Operator in OpenShift Container Platform.
4.3. Ingress Operator
When you create your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, pods and services running on the cluster are each allocated IP addresses. The IP addresses are accessible to other pods and services running nearby but are not accessible to external clients. The Ingress Operator implements the Ingress Controller API and is responsible for enabling external access to OpenShift Container Platform cluster services. For more information, see Ingress Operator in OpenShift Container Platform.
4.4. External DNS Operator
The External DNS Operator deploys and manages ExternalDNS to provide the name resolution for services and routes from the external DNS provider to OpenShift Container Platform. For more information, see Understanding the External DNS Operator.
4.5. Ingress Node Firewall Operator
The Ingress Node Firewall Operator uses an extended Berkley Packet Filter (eBPF) and eXpress Data Path (XDP) plugin to process node firewall rules, update statistics and generate events for dropped traffic. The operator manages ingress node firewall resources, verifies firewall configuration, does not allow incorrectly configured rules that can prevent cluster access, and loads ingress node firewall XDP programs to the selected interfaces in the rule’s object(s). For more information, see Understanding the Ingress Node Firewall Operator
4.6. Network Observability Operator
The Network Observability Operator is an optional Operator that allows cluster administrators to observe the network traffic for OpenShift Container Platform clusters. The Network Observability Operator uses the eBPF technology to create network flows. The network flows are then enriched with OpenShift Container Platform information and stored in Loki. You can view and analyze the stored network flows information in the OpenShift Container Platform console for further insight and troubleshooting. For more information, see About Network Observability Operator.
Chapter 5. Cluster Network Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
You can use the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) to deploy and manage cluster network components on an OpenShift Container Platform cluster, including the Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin selected for the cluster during installation.
5.1. Cluster Network Operator
The Cluster Network Operator implements the network API from the operator.openshift.io API group. The Operator deploys the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, or the network provider plugin that you selected during cluster installation, by using a daemon set.
Procedure
The Cluster Network Operator is deployed during installation as a Kubernetes Deployment.
Run the following command to view the Deployment status:
oc get -n openshift-network-operator deployment/network-operator
$ oc get -n openshift-network-operator deployment/network-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE network-operator 1/1 1 1 56m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE network-operator 1/1 1 1 56mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to view the state of the Cluster Network Operator:
oc get clusteroperator/network
$ oc get clusteroperator/networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE network 4.5.4 True False False 50m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE network 4.5.4 True False False 50mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following fields provide information about the status of the operator:
AVAILABLE,PROGRESSING, andDEGRADED. TheAVAILABLEfield isTruewhen the Cluster Network Operator reports an available status condition.
5.2. Viewing the cluster network configuration
Every new OpenShift Container Platform installation has a network.config object named cluster.
Procedure
Use the
oc describecommand to view the cluster network configuration:oc describe network.config/cluster
$ oc describe network.config/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.3. Viewing Cluster Network Operator status
You can inspect the status and view the details of the Cluster Network Operator using the oc describe command.
Procedure
Run the following command to view the status of the Cluster Network Operator:
oc describe clusteroperators/network
$ oc describe clusteroperators/networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.4. Viewing Cluster Network Operator logs
You can view Cluster Network Operator logs by using the oc logs command.
Procedure
Run the following command to view the logs of the Cluster Network Operator:
oc logs --namespace=openshift-network-operator deployment/network-operator
$ oc logs --namespace=openshift-network-operator deployment/network-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.5. Cluster Network Operator configuration
The configuration for the cluster network is specified as part of the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration and stored in a custom resource (CR) object that is named cluster. The CR specifies the fields for the Network API in the operator.openshift.io API group.
The CNO configuration inherits the following fields during cluster installation from the Network API in the Network.config.openshift.io API group and these fields cannot be changed:
clusterNetwork- IP address pools from which pod IP addresses are allocated.
serviceNetwork- IP address pool for services.
defaultNetwork.type- Cluster network plugin, such as OpenShift SDN or OVN-Kubernetes.
After cluster installation, you cannot modify the fields listed in the previous section.
You can specify the cluster network plugin configuration for your cluster by setting the fields for the defaultNetwork object in the CNO object named cluster.
5.5.1. Cluster Network Operator configuration object
The fields for the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) are described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The name of the CNO object. This name is always |
|
|
| A list specifying the blocks of IP addresses from which pod IP addresses are allocated and the subnet prefix length assigned to each individual node in the cluster. For example:
This value is ready-only and inherited from the |
|
|
| A block of IP addresses for services. The OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes network plugins support only a single IP address block for the service network. For example: spec: serviceNetwork: - 172.30.0.0/14
This value is ready-only and inherited from the |
|
|
| Configures the network plugin for the cluster network. |
|
|
| The fields for this object specify the kube-proxy configuration. If you are using the OVN-Kubernetes cluster network plugin, the kube-proxy configuration has no effect. |
For a cluster that needs to deploy objects across multiple networks, ensure that you specify the same value for the clusterNetwork.hostPrefix parameter for each network type that is defined in the install-config.yaml file. Setting a different value for each clusterNetwork.hostPrefix parameter can impact the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, where the plugin cannot effectively route object traffic among different nodes.
defaultNetwork object configuration
The values for the defaultNetwork object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Either Note OpenShift Container Platform uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin by default. |
|
|
| This object is only valid for the OpenShift SDN network plugin. |
|
|
| This object is only valid for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. |
Configuration for the OpenShift SDN network plugin
The following table describes the configuration fields for the OpenShift SDN network plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The network isolation mode for OpenShift SDN. |
|
|
| The maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the VXLAN overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically. |
|
|
|
The port to use for all VXLAN packets. The default value is |
You can only change the configuration for your cluster network plugin during cluster installation.
Example OpenShift SDN configuration
Configuration for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
The following table describes the configuration fields for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically. |
|
|
| The UDP port for the Geneve overlay network. |
|
|
| If the field is present, IPsec is enabled for the cluster. |
|
|
| Specify a configuration object for customizing network policy audit logging. If unset, the defaults audit log settings are used. |
|
|
| Optional: Specify a configuration object for customizing how egress traffic is sent to the node gateway. Note While migrating egress traffic, you can expect some disruption to workloads and service traffic until the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) successfully rolls out the changes. |
|
|
If your existing network infrastructure overlaps with the This field cannot be changed after installation. |
The default value is |
|
|
If your existing network infrastructure overlaps with the This field cannot be changed after installation. |
The default value is |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| integer |
The maximum number of messages to generate every second per node. The default value is |
|
| integer |
The maximum size for the audit log in bytes. The default value is |
|
| integer | The maximum number of log files that are retained. |
|
| string | One of the following additional audit log targets:
|
|
| string |
The syslog facility, such as |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Set this field to
This field has an interaction with the Open vSwitch hardware offloading feature. If you set this field to |
You can only change the configuration for your cluster network plugin during cluster installation, except for the gatewayConfig field that can be changed at runtime as a postinstallation activity.
Example OVN-Kubernetes configuration with IPSec enabled
kubeProxyConfig object configuration
The values for the kubeProxyConfig object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The refresh period for Note
Because of performance improvements introduced in OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 and greater, adjusting the |
|
|
|
The minimum duration before refreshing kubeProxyConfig:
proxyArguments:
iptables-min-sync-period:
- 0s
|
5.5.2. Cluster Network Operator example configuration
A complete CNO configuration is specified in the following example:
Example Cluster Network Operator object
Chapter 6. DNS Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
The DNS Operator deploys and manages CoreDNS to provide a name resolution service to pods, enabling DNS-based Kubernetes Service discovery in OpenShift Container Platform.
6.1. DNS Operator
The DNS Operator implements the dns API from the operator.openshift.io API group. The Operator deploys CoreDNS using a daemon set, creates a service for the daemon set, and configures the kubelet to instruct pods to use the CoreDNS service IP address for name resolution.
Procedure
The DNS Operator is deployed during installation with a Deployment object.
Use the
oc getcommand to view the deployment status:oc get -n openshift-dns-operator deployment/dns-operator
$ oc get -n openshift-dns-operator deployment/dns-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE dns-operator 1/1 1 1 23h
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE dns-operator 1/1 1 1 23hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
oc getcommand to view the state of the DNS Operator:oc get clusteroperator/dns
$ oc get clusteroperator/dnsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE dns 4.1.0-0.11 True False False 92m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE dns 4.1.0-0.11 True False False 92mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow AVAILABLE,PROGRESSINGandDEGRADEDprovide information about the status of the operator.AVAILABLEisTruewhen at least 1 pod from the CoreDNS daemon set reports anAvailablestatus condition.
6.2. Changing the DNS Operator managementState
DNS manages the CoreDNS component to provide a name resolution service for pods and services in the cluster. The managementState of the DNS Operator is set to Managed by default, which means that the DNS Operator is actively managing its resources. You can change it to Unmanaged, which means the DNS Operator is not managing its resources.
The following are use cases for changing the DNS Operator managementState:
-
You are a developer and want to test a configuration change to see if it fixes an issue in CoreDNS. You can stop the DNS Operator from overwriting the fix by setting the
managementStatetoUnmanaged. -
You are a cluster administrator and have reported an issue with CoreDNS, but need to apply a workaround until the issue is fixed. You can set the
managementStatefield of the DNS Operator toUnmanagedto apply the workaround.
Procedure
Change
managementStateDNS Operator:oc patch dns.operator.openshift.io default --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"managementState":"Unmanaged"}}'oc patch dns.operator.openshift.io default --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"managementState":"Unmanaged"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3. Controlling DNS pod placement
The DNS Operator has two daemon sets: one for CoreDNS and one for managing the /etc/hosts file. The daemon set for /etc/hosts must run on every node host to add an entry for the cluster image registry to support pulling images. Security policies can prohibit communication between pairs of nodes, which prevents the daemon set for CoreDNS from running on every node.
As a cluster administrator, you can use a custom node selector to configure the daemon set for CoreDNS to run or not run on certain nodes.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the
ocCLI. -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To prevent communication between certain nodes, configure the
spec.nodePlacement.nodeSelectorAPI field:Modify the DNS Operator object named
default:oc edit dns.operator/default
$ oc edit dns.operator/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify a node selector that includes only control plane nodes in the
spec.nodePlacement.nodeSelectorAPI field:spec: nodePlacement: nodeSelector: node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""spec: nodePlacement: nodeSelector: node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To allow the daemon set for CoreDNS to run on nodes, configure a taint and toleration:
Modify the DNS Operator object named
default:oc edit dns.operator/default
$ oc edit dns.operator/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify a taint key and a toleration for the taint:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If the taint is
dns-only, it can be tolerated indefinitely. You can omittolerationSeconds.
6.4. View the default DNS
Every new OpenShift Container Platform installation has a dns.operator named default.
Procedure
Use the
oc describecommand to view the defaultdns:oc describe dns.operator/default
$ oc describe dns.operator/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To find the service CIDR of your cluster, use the
oc getcommand:oc get networks.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{$.status.serviceNetwork}'$ oc get networks.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{$.status.serviceNetwork}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Example output
[172.30.0.0/16]
[172.30.0.0/16]6.5. Using DNS forwarding
You can use DNS forwarding to override the default forwarding configuration in the /etc/resolv.conf file in the following ways:
- Specify name servers for every zone. If the forwarded zone is the Ingress domain managed by OpenShift Container Platform, then the upstream name server must be authorized for the domain.
- Provide a list of upstream DNS servers.
- Change the default forwarding policy.
A DNS forwarding configuration for the default domain can have both the default servers specified in the /etc/resolv.conf file and the upstream DNS servers.
Procedure
Modify the DNS Operator object named
default:oc edit dns.operator/default
$ oc edit dns.operator/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you issue the previous command, the Operator creates and updates the config map named
dns-defaultwith additional server configuration blocks based onServer. If none of the servers have a zone that matches the query, then name resolution falls back to the upstream DNS servers.Configuring DNS forwarding
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Must comply with the
rfc6335service name syntax. - 2
- Must conform to the definition of a subdomain in the
rfc1123service name syntax. The cluster domain,cluster.local, is an invalid subdomain for thezonesfield. - 3
- Defines the policy to select upstream resolvers. Default value is
Random. You can also use the valuesRoundRobin, andSequential. - 4
- A maximum of 15
upstreamsis allowed perforwardPlugin. - 5
- Optional. You can use it to override the default policy and forward DNS resolution to the specified DNS resolvers (upstream resolvers) for the default domain. If you do not provide any upstream resolvers, the DNS name queries go to the servers in
/etc/resolv.conf. - 6
- Determines the order in which upstream servers are selected for querying. You can specify one of these values:
Random,RoundRobin, orSequential. The default value isSequential. - 7
- Optional. You can use it to provide upstream resolvers.
- 8
- You can specify two types of
upstreams-SystemResolvConfandNetwork.SystemResolvConfconfigures the upstream to use/etc/resolv.confandNetworkdefines aNetworkresolver. You can specify one or both. - 9
- If the specified type is
Network, you must provide an IP address. Theaddressfield must be a valid IPv4 or IPv6 address. - 10
- If the specified type is
Network, you can optionally provide a port. Theportfield must have a value between1and65535. If you do not specify a port for the upstream, by default port 853 is tried.
Optional: When working in a highly regulated environment, you might need the ability to secure DNS traffic when forwarding requests to upstream resolvers so that you can ensure additional DNS traffic and data privacy. Cluster administrators can configure transport layer security (TLS) for forwarded DNS queries.
Configuring DNS forwarding with TLS
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Must comply with the
rfc6335service name syntax. - 2
- Must conform to the definition of a subdomain in the
rfc1123service name syntax. The cluster domain,cluster.local, is an invalid subdomain for thezonesfield. The cluster domain,cluster.local, is an invalidsubdomainforzones. - 3
- When configuring TLS for forwarded DNS queries, set the
transportfield to have the valueTLS. By default, CoreDNS caches forwarded connections for 10 seconds. CoreDNS will hold a TCP connection open for those 10 seconds if no request is issued. With large clusters, ensure that your DNS server is aware that it might get many new connections to hold open because you can initiate a connection per node. Set up your DNS hierarchy accordingly to avoid performance issues. - 4
- When configuring TLS for forwarded DNS queries, this is a mandatory server name used as part of the server name indication (SNI) to validate the upstream TLS server certificate.
- 5
- Defines the policy to select upstream resolvers. Default value is
Random. You can also use the valuesRoundRobin, andSequential. - 6
- Required. You can use it to provide upstream resolvers. A maximum of 15
upstreamsentries are allowed perforwardPluginentry. - 7
- Optional. You can use it to override the default policy and forward DNS resolution to the specified DNS resolvers (upstream resolvers) for the default domain. If you do not provide any upstream resolvers, the DNS name queries go to the servers in
/etc/resolv.conf. - 8
Networktype indicates that this upstream resolver should handle forwarded requests separately from the upstream resolvers listed in/etc/resolv.conf. Only theNetworktype is allowed when using TLS and you must provide an IP address.- 9
- The
addressfield must be a valid IPv4 or IPv6 address. - 10
- You can optionally provide a port. The
portmust have a value between1and65535. If you do not specify a port for the upstream, by default port 853 is tried.
NoteIf
serversis undefined or invalid, the config map only contains the default server.
Verification
View the config map:
oc get configmap/dns-default -n openshift-dns -o yaml
$ oc get configmap/dns-default -n openshift-dns -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample DNS ConfigMap based on previous sample DNS
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Changes to the
forwardPlugintriggers a rolling update of the CoreDNS daemon set.
6.6. DNS Operator status
You can inspect the status and view the details of the DNS Operator using the oc describe command.
Procedure
View the status of the DNS Operator:
oc describe clusteroperators/dns
$ oc describe clusteroperators/dns6.7. DNS Operator logs
You can view DNS Operator logs by using the oc logs command.
Procedure
View the logs of the DNS Operator:
oc logs -n openshift-dns-operator deployment/dns-operator -c dns-operator
$ oc logs -n openshift-dns-operator deployment/dns-operator -c dns-operator6.8. Setting the CoreDNS log level
You can configure the CoreDNS log level to determine the amount of detail in logged error messages. The valid values for CoreDNS log level are Normal, Debug, and Trace. The default logLevel is Normal.
The errors plugin is always enabled. The following logLevel settings report different error responses:
-
logLevel:Normalenables the "errors" class:log . { class error }. -
logLevel:Debugenables the "denial" class:log . { class denial error }. -
logLevel:Traceenables the "all" class:log . { class all }.
Procedure
To set
logLeveltoDebug, enter the following command:oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"logLevel":"Debug"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"logLevel":"Debug"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To set
logLeveltoTrace, enter the following command:oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"logLevel":"Trace"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"logLevel":"Trace"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To ensure the desired log level was set, check the config map:
oc get configmap/dns-default -n openshift-dns -o yaml
$ oc get configmap/dns-default -n openshift-dns -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.9. Viewing the CoreDNS logs
You can view CoreDNS logs by using the oc logs command.
Procedure
View the logs of a specific CoreDNS pod by entering the following command:
oc -n openshift-dns logs -c dns <core_dns_pod_name>
$ oc -n openshift-dns logs -c dns <core_dns_pod_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Follow the logs of all CoreDNS pods by entering the following command:
oc -n openshift-dns logs -c dns -l dns.operator.openshift.io/daemonset-dns=default -f --max-log-requests=<number>
$ oc -n openshift-dns logs -c dns -l dns.operator.openshift.io/daemonset-dns=default -f --max-log-requests=<number>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the number of DNS pods to stream logs from. The maximum is 6.
6.10. Setting the CoreDNS Operator log level
Cluster administrators can configure the Operator log level to more quickly track down OpenShift DNS issues. The valid values for operatorLogLevel are Normal, Debug, and Trace. Trace has the most detailed information. The default operatorlogLevel is Normal. There are seven logging levels for issues: Trace, Debug, Info, Warning, Error, Fatal and Panic. After the logging level is set, log entries with that severity or anything above it will be logged.
-
operatorLogLevel: "Normal"setslogrus.SetLogLevel("Info"). -
operatorLogLevel: "Debug"setslogrus.SetLogLevel("Debug"). -
operatorLogLevel: "Trace"setslogrus.SetLogLevel("Trace").
Procedure
To set
operatorLogLeveltoDebug, enter the following command:oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"operatorLogLevel":"Debug"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"operatorLogLevel":"Debug"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To set
operatorLogLeveltoTrace, enter the following command:oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"operatorLogLevel":"Trace"}}' --type=merge$ oc patch dnses.operator.openshift.io/default -p '{"spec":{"operatorLogLevel":"Trace"}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.11. Tuning the CoreDNS cache
You can configure the maximum duration of both successful or unsuccessful caching, also known as positive or negative caching respectively, done by CoreDNS. Tuning the duration of caching of DNS query responses can reduce the load for any upstream DNS resolvers.
Procedure
Edit the DNS Operator object named
defaultby running the following command:oc edit dns.operator.openshift.io/default
$ oc edit dns.operator.openshift.io/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the time-to-live (TTL) caching values:
Configuring DNS caching
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The string value
1his converted to its respective number of seconds by CoreDNS. If this field is omitted, the value is assumed to be0sand the cluster uses the internal default value of900sas a fallback. - 2
- The string value can be a combination of units such as
0.5h10mand is converted to its respective number of seconds by CoreDNS. If this field is omitted, the value is assumed to be0sand the cluster uses the internal default value of30sas a fallback.
WarningSetting TTL fields to low values could lead to an increased load on the cluster, any upstream resolvers, or both.
Chapter 7. Ingress Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
7.1. OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Operator
When you create your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, pods and services running on the cluster are each allocated their own IP addresses. The IP addresses are accessible to other pods and services running nearby but are not accessible to outside clients. The Ingress Operator implements the IngressController API and is the component responsible for enabling external access to OpenShift Container Platform cluster services.
The Ingress Operator makes it possible for external clients to access your service by deploying and managing one or more HAProxy-based Ingress Controllers to handle routing. You can use the Ingress Operator to route traffic by specifying OpenShift Container Platform Route and Kubernetes Ingress resources. Configurations within the Ingress Controller, such as the ability to define endpointPublishingStrategy type and internal load balancing, provide ways to publish Ingress Controller endpoints.
7.2. The Ingress configuration asset
The installation program generates an asset with an Ingress resource in the config.openshift.io API group, cluster-ingress-02-config.yml.
YAML Definition of the Ingress resource
The installation program stores this asset in the cluster-ingress-02-config.yml file in the manifests/ directory. This Ingress resource defines the cluster-wide configuration for Ingress. This Ingress configuration is used as follows:
- The Ingress Operator uses the domain from the cluster Ingress configuration as the domain for the default Ingress Controller.
-
The OpenShift API Server Operator uses the domain from the cluster Ingress configuration. This domain is also used when generating a default host for a
Routeresource that does not specify an explicit host.
7.3. Ingress Controller configuration parameters
The IngressController custom resource (CR) includes optional configuration parameters that you can configure to meet specific needs for your organization.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The
If empty, the default value is |
|
|
|
|
|
For cloud environments, use the
On Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure you can configure the following
If not set, the default value is based on
For most platforms, the
For non-cloud environments, such as a bare-metal platform, use the
If you do not set a value in one of these fields, the default value is based on binding ports specified in the
If you need to update the
|
|
|
The
The secret must contain the following keys and data: *
If not set, a wildcard certificate is automatically generated and used. The certificate is valid for the Ingress Controller The in-use certificate, whether generated or user-specified, is automatically integrated with OpenShift Container Platform built-in OAuth server. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If not set, the defaults values are used. Note
The |
|
|
If not set, the default value is based on the
When using the
The minimum TLS version for Ingress Controllers is Note
Ciphers and the minimum TLS version of the configured security profile are reflected in the Important
The Ingress Operator converts the TLS |
|
|
The
The |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By setting the
By default, the policy is set to
By setting These adjustments are only applied to cleartext, edge-terminated, and re-encrypt routes, and only when using HTTP/1.
For request headers, these adjustments are applied only for routes that have the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For any cookie that you want to capture, the following parameters must be in your
For example: httpCaptureCookies:
- matchType: Exact
maxLength: 128
name: MYCOOKIE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The
|
|
|
The
These connections come from load balancer health probes or web browser speculative connections (preconnect) and can be safely ignored. However, these requests can be caused by network errors, so setting this field to |
7.3.1. Ingress Controller TLS security profiles
TLS security profiles provide a way for servers to regulate which ciphers a connecting client can use when connecting to the server.
7.3.1.1. Understanding TLS security profiles
You can use a TLS (Transport Layer Security) security profile to define which TLS ciphers are required by various OpenShift Container Platform components. The OpenShift Container Platform TLS security profiles are based on Mozilla recommended configurations.
You can specify one of the following TLS security profiles for each component:
| Profile | Description |
|---|---|
|
| This profile is intended for use with legacy clients or libraries. The profile is based on the Old backward compatibility recommended configuration.
The Note For the Ingress Controller, the minimum TLS version is converted from 1.0 to 1.1. |
|
| This profile is the default TLS security profile for the Ingress Controller, kubelet, and control plane. The profile is based on the Intermediate compatibility recommended configuration.
The Note This profile is the recommended configuration for the majority of clients. |
|
| This profile is intended for use with modern clients that have no need for backwards compatibility. This profile is based on the Modern compatibility recommended configuration.
The |
|
| This profile allows you to define the TLS version and ciphers to use. Warning
Use caution when using a |
When using one of the predefined profile types, the effective profile configuration is subject to change between releases. For example, given a specification to use the Intermediate profile deployed on release X.Y.Z, an upgrade to release X.Y.Z+1 might cause a new profile configuration to be applied, resulting in a rollout.
7.3.1.2. Configuring the TLS security profile for the Ingress Controller
To configure a TLS security profile for an Ingress Controller, edit the IngressController custom resource (CR) to specify a predefined or custom TLS security profile. If a TLS security profile is not configured, the default value is based on the TLS security profile set for the API server.
Sample IngressController CR that configures the Old TLS security profile
The TLS security profile defines the minimum TLS version and the TLS ciphers for TLS connections for Ingress Controllers.
You can see the ciphers and the minimum TLS version of the configured TLS security profile in the IngressController custom resource (CR) under Status.Tls Profile and the configured TLS security profile under Spec.Tls Security Profile. For the Custom TLS security profile, the specific ciphers and minimum TLS version are listed under both parameters.
The HAProxy Ingress Controller image supports TLS 1.3 and the Modern profile.
The Ingress Operator also converts the TLS 1.0 of an Old or Custom profile to 1.1.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Edit the
IngressControllerCR in theopenshift-ingress-operatorproject to configure the TLS security profile:oc edit IngressController default -n openshift-ingress-operator
$ oc edit IngressController default -n openshift-ingress-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
spec.tlsSecurityProfilefield:Sample
IngressControllerCR for aCustomprofileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file to apply the changes.
Verification
Verify that the profile is set in the
IngressControllerCR:oc describe IngressController default -n openshift-ingress-operator
$ oc describe IngressController default -n openshift-ingress-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.1.3. Configuring mutual TLS authentication
You can configure the Ingress Controller to enable mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication by setting a spec.clientTLS value. The clientTLS value configures the Ingress Controller to verify client certificates. This configuration includes setting a clientCA value, which is a reference to a config map. The config map contains the PEM-encoded CA certificate bundle that is used to verify a client’s certificate. Optionally, you can also configure a list of certificate subject filters.
If the clientCA value specifies an X509v3 certificate revocation list (CRL) distribution point, the Ingress Operator downloads and manages a CRL config map based on the HTTP URI X509v3 CRL Distribution Point specified in each provided certificate. The Ingress Controller uses this config map during mTLS/TLS negotiation. Requests that do not provide valid certificates are rejected.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - You have a PEM-encoded CA certificate bundle.
If your CA bundle references a CRL distribution point, you must have also included the end-entity or leaf certificate to the client CA bundle. This certificate must have included an HTTP URI under
CRL Distribution Points, as described in RFC 5280. For example:Issuer: C=US, O=Example Inc, CN=Example Global G2 TLS RSA SHA256 2020 CA1 Subject: SOME SIGNED CERT X509v3 CRL Distribution Points: Full Name: URI:http://crl.example.com/example.crlIssuer: C=US, O=Example Inc, CN=Example Global G2 TLS RSA SHA256 2020 CA1 Subject: SOME SIGNED CERT X509v3 CRL Distribution Points: Full Name: URI:http://crl.example.com/example.crlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
In the
openshift-confignamespace, create a config map from your CA bundle:oc create configmap \ router-ca-certs-default \ --from-file=ca-bundle.pem=client-ca.crt \ -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap \ router-ca-certs-default \ --from-file=ca-bundle.pem=client-ca.crt \1 -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The config map data key must be
ca-bundle.pem, and the data value must be a CA certificate in PEM format.
Edit the
IngressControllerresource in theopenshift-ingress-operatorproject:oc edit IngressController default -n openshift-ingress-operator
$ oc edit IngressController default -n openshift-ingress-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
spec.clientTLSfield and subfields to configure mutual TLS:Sample
IngressControllerCR for aclientTLSprofile that specifies filtering patternsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Optional, get the Distinguished Name (DN) for
allowedSubjectPatternsby entering the following command.
openssl x509 -in custom-cert.pem -noout -subject subject= /CN=example.com/ST=NC/C=US/O=Security/OU=OpenShift
$ openssl x509 -in custom-cert.pem -noout -subject
subject= /CN=example.com/ST=NC/C=US/O=Security/OU=OpenShift7.4. View the default Ingress Controller
The Ingress Operator is a core feature of OpenShift Container Platform and is enabled out of the box.
Every new OpenShift Container Platform installation has an ingresscontroller named default. It can be supplemented with additional Ingress Controllers. If the default ingresscontroller is deleted, the Ingress Operator will automatically recreate it within a minute.
Procedure
View the default Ingress Controller:
oc describe --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default
$ oc describe --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.5. View Ingress Operator status
You can view and inspect the status of your Ingress Operator.
Procedure
View your Ingress Operator status:
oc describe clusteroperators/ingress
$ oc describe clusteroperators/ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.6. View Ingress Controller logs
You can view your Ingress Controller logs.
Procedure
View your Ingress Controller logs:
oc logs --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator deployments/ingress-operator -c <container_name>
$ oc logs --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator deployments/ingress-operator -c <container_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.7. View Ingress Controller status
Your can view the status of a particular Ingress Controller.
Procedure
View the status of an Ingress Controller:
oc describe --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/<name>
$ oc describe --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/<name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8. Configuring the Ingress Controller
7.8.1. Setting a custom default certificate
As an administrator, you can configure an Ingress Controller to use a custom certificate by creating a Secret resource and editing the IngressController custom resource (CR).
Prerequisites
- You must have a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded files, where the certificate is signed by a trusted certificate authority or by a private trusted certificate authority that you configured in a custom PKI.
Your certificate meets the following requirements:
- The certificate is valid for the ingress domain.
-
The certificate uses the
subjectAltNameextension to specify a wildcard domain, such as*.apps.ocp4.example.com.
You must have an
IngressControllerCR. You may use the default one:oc --namespace openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers
$ oc --namespace openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE default 10m
NAME AGE default 10mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you have intermediate certificates, they must be included in the tls.crt file of the secret containing a custom default certificate. Order matters when specifying a certificate; list your intermediate certificate(s) after any server certificate(s).
Procedure
The following assumes that the custom certificate and key pair are in the tls.crt and tls.key files in the current working directory. Substitute the actual path names for tls.crt and tls.key. You also may substitute another name for custom-certs-default when creating the Secret resource and referencing it in the IngressController CR.
This action will cause the Ingress Controller to be redeployed, using a rolling deployment strategy.
Create a Secret resource containing the custom certificate in the
openshift-ingressnamespace using thetls.crtandtls.keyfiles.oc --namespace openshift-ingress create secret tls custom-certs-default --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key
$ oc --namespace openshift-ingress create secret tls custom-certs-default --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.keyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the IngressController CR to reference the new certificate secret:
oc patch --type=merge --namespace openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default \ --patch '{"spec":{"defaultCertificate":{"name":"custom-certs-default"}}}'$ oc patch --type=merge --namespace openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default \ --patch '{"spec":{"defaultCertificate":{"name":"custom-certs-default"}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the update was effective:
echo Q |\ openssl s_client -connect console-openshift-console.apps.<domain>:443 -showcerts 2>/dev/null |\ openssl x509 -noout -subject -issuer -enddate
$ echo Q |\ openssl s_client -connect console-openshift-console.apps.<domain>:443 -showcerts 2>/dev/null |\ openssl x509 -noout -subject -issuer -enddateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<domain>- Specifies the base domain name for your cluster.
Example output
subject=C = US, ST = NC, L = Raleigh, O = RH, OU = OCP4, CN = *.apps.example.com issuer=C = US, ST = NC, L = Raleigh, O = RH, OU = OCP4, CN = example.com notAfter=May 10 08:32:45 2022 GM
subject=C = US, ST = NC, L = Raleigh, O = RH, OU = OCP4, CN = *.apps.example.com issuer=C = US, ST = NC, L = Raleigh, O = RH, OU = OCP4, CN = example.com notAfter=May 10 08:32:45 2022 GMCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to set a custom default certificate:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The certificate secret name should match the value used to update the CR.
Once the IngressController CR has been modified, the Ingress Operator updates the Ingress Controller’s deployment to use the custom certificate.
7.8.2. Removing a custom default certificate
As an administrator, you can remove a custom certificate that you configured an Ingress Controller to use.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You previously configured a custom default certificate for the Ingress Controller.
Procedure
To remove the custom certificate and restore the certificate that ships with OpenShift Container Platform, enter the following command:
oc patch -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default \ --type json -p $'- op: remove\n path: /spec/defaultCertificate'
$ oc patch -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default \ --type json -p $'- op: remove\n path: /spec/defaultCertificate'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow There can be a delay while the cluster reconciles the new certificate configuration.
Verification
To confirm that the original cluster certificate is restored, enter the following command:
echo Q | \ openssl s_client -connect console-openshift-console.apps.<domain>:443 -showcerts 2>/dev/null | \ openssl x509 -noout -subject -issuer -enddate
$ echo Q | \ openssl s_client -connect console-openshift-console.apps.<domain>:443 -showcerts 2>/dev/null | \ openssl x509 -noout -subject -issuer -enddateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<domain>- Specifies the base domain name for your cluster.
Example output
subject=CN = *.apps.<domain> issuer=CN = ingress-operator@1620633373 notAfter=May 10 10:44:36 2023 GMT
subject=CN = *.apps.<domain> issuer=CN = ingress-operator@1620633373 notAfter=May 10 10:44:36 2023 GMTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.3. Autoscaling an Ingress Controller
You can automatically scale an Ingress Controller to dynamically meet routing performance or availability requirements, such as the requirement to increase throughput.
The following procedure provides an example for scaling up the default Ingress Controller.
Prerequisites
-
You have the OpenShift CLI (
oc) installed. -
You have access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. You installed the Custom Metrics Autoscaler Operator and an associated KEDA Controller.
-
You can install the Operator by using OperatorHub on the web console. After you install the Operator, you can create an instance of
KedaController.
-
You can install the Operator by using OperatorHub on the web console. After you install the Operator, you can create an instance of
Procedure
Create a service account to authenticate with Thanos by running the following command:
oc create -n openshift-ingress-operator serviceaccount thanos && oc describe -n openshift-ingress-operator serviceaccount thanos
$ oc create -n openshift-ingress-operator serviceaccount thanos && oc describe -n openshift-ingress-operator serviceaccount thanosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Manually create the service account secret token with the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define a
TriggerAuthenticationobject within theopenshift-ingress-operatornamespace by using the service account’s token.Define the
secretvariable that contains the secret by running the following command:secret=$(oc get secret -n openshift-ingress-operator | grep thanos-token | head -n 1 | awk '{ print $1 }')$ secret=$(oc get secret -n openshift-ingress-operator | grep thanos-token | head -n 1 | awk '{ print $1 }')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
TriggerAuthenticationobject and pass the value of thesecretvariable to theTOKENparameter:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create and apply a role for reading metrics from Thanos:
Create a new role,
thanos-metrics-reader.yaml, that reads metrics from pods and nodes:thanos-metrics-reader.yaml
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the new role by running the following command:
oc apply -f thanos-metrics-reader.yaml
$ oc apply -f thanos-metrics-reader.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Add the new role to the service account by entering the following commands:
oc adm policy -n openshift-ingress-operator add-role-to-user thanos-metrics-reader -z thanos --role-namespace=openshift-ingress-operator
$ oc adm policy -n openshift-ingress-operator add-role-to-user thanos-metrics-reader -z thanos --role-namespace=openshift-ingress-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc adm policy -n openshift-ingress-operator add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-monitoring-view -z thanos
$ oc adm policy -n openshift-ingress-operator add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-monitoring-view -z thanosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe argument
add-cluster-role-to-useris only required if you use cross-namespace queries. The following step uses a query from thekube-metricsnamespace which requires this argument.Create a new
ScaledObjectYAML file,ingress-autoscaler.yaml, that targets the default Ingress Controller deployment:Example
ScaledObjectdefinitionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The custom resource that you are targeting. In this case, the Ingress Controller.
- 2
- Optional: The maximum number of replicas. If you omit this field, the default maximum is set to 100 replicas.
- 3
- The Thanos service endpoint in the
openshift-monitoringnamespace. - 4
- The Ingress Operator namespace.
- 5
- This expression evaluates to however many worker nodes are present in the deployed cluster.
ImportantIf you are using cross-namespace queries, you must target port 9091 and not port 9092 in the
serverAddressfield. You also must have elevated privileges to read metrics from this port.Apply the custom resource definition by running the following command:
oc apply -f ingress-autoscaler.yaml
$ oc apply -f ingress-autoscaler.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the default Ingress Controller is scaled out to match the value returned by the
kube-state-metricsquery by running the following commands:Use the
grepcommand to search the Ingress Controller YAML file for replicas:oc get -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default -o yaml | grep replicas:
$ oc get -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default -o yaml | grep replicas:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
replicas: 3
replicas: 3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the pods in the
openshift-ingressproject:oc get pods -n openshift-ingress
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE router-default-7b5df44ff-l9pmm 2/2 Running 0 17h router-default-7b5df44ff-s5sl5 2/2 Running 0 3d22h router-default-7b5df44ff-wwsth 2/2 Running 0 66s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE router-default-7b5df44ff-l9pmm 2/2 Running 0 17h router-default-7b5df44ff-s5sl5 2/2 Running 0 3d22h router-default-7b5df44ff-wwsth 2/2 Running 0 66sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.4. Scaling an Ingress Controller
Manually scale an Ingress Controller to meeting routing performance or availability requirements such as the requirement to increase throughput. oc commands are used to scale the IngressController resource. The following procedure provides an example for scaling up the default IngressController.
Scaling is not an immediate action, as it takes time to create the desired number of replicas.
Procedure
View the current number of available replicas for the default
IngressController:oc get -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default -o jsonpath='{$.status.availableReplicas}'$ oc get -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default -o jsonpath='{$.status.availableReplicas}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
2
2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Scale the default
IngressControllerto the desired number of replicas using theoc patchcommand. The following example scales the defaultIngressControllerto 3 replicas:oc patch -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"replicas": 3}}' --type=merge$ oc patch -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"replicas": 3}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io/default patched
ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io/default patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the default
IngressControllerscaled to the number of replicas that you specified:oc get -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default -o jsonpath='{$.status.availableReplicas}'$ oc get -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default -o jsonpath='{$.status.availableReplicas}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
3
3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to scale an Ingress Controller to three replicas:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If you need a different amount of replicas, change the
replicasvalue.
7.8.5. Configuring Ingress access logging
You can configure the Ingress Controller to enable access logs. If you have clusters that do not receive much traffic, then you can log to a sidecar. If you have high traffic clusters, to avoid exceeding the capacity of the logging stack or to integrate with a logging infrastructure outside of OpenShift Container Platform, you can forward logs to a custom syslog endpoint. You can also specify the format for access logs.
Container logging is useful to enable access logs on low-traffic clusters when there is no existing Syslog logging infrastructure, or for short-term use while diagnosing problems with the Ingress Controller.
Syslog is needed for high-traffic clusters where access logs could exceed the OpenShift Logging stack’s capacity, or for environments where any logging solution needs to integrate with an existing Syslog logging infrastructure. The Syslog use-cases can overlap.
Prerequisites
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Configure Ingress access logging to a sidecar.
To configure Ingress access logging, you must specify a destination using
spec.logging.access.destination. To specify logging to a sidecar container, you must specifyContainerspec.logging.access.destination.type. The following example is an Ingress Controller definition that logs to aContainerdestination:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When you configure the Ingress Controller to log to a sidecar, the operator creates a container named
logsinside the Ingress Controller Pod:oc -n openshift-ingress logs deployment.apps/router-default -c logs
$ oc -n openshift-ingress logs deployment.apps/router-default -c logsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
2020-05-11T19:11:50.135710+00:00 router-default-57dfc6cd95-bpmk6 router-default-57dfc6cd95-bpmk6 haproxy[108]: 174.19.21.82:39654 [11/May/2020:19:11:50.133] public be_http:hello-openshift:hello-openshift/pod:hello-openshift:hello-openshift:10.128.2.12:8080 0/0/1/0/1 200 142 - - --NI 1/1/0/0/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1"
2020-05-11T19:11:50.135710+00:00 router-default-57dfc6cd95-bpmk6 router-default-57dfc6cd95-bpmk6 haproxy[108]: 174.19.21.82:39654 [11/May/2020:19:11:50.133] public be_http:hello-openshift:hello-openshift/pod:hello-openshift:hello-openshift:10.128.2.12:8080 0/0/1/0/1 200 142 - - --NI 1/1/0/0/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure Ingress access logging to a Syslog endpoint.
To configure Ingress access logging, you must specify a destination using
spec.logging.access.destination. To specify logging to a Syslog endpoint destination, you must specifySyslogforspec.logging.access.destination.type. If the destination type isSyslog, you must also specify a destination endpoint usingspec.logging.access.destination.syslog.endpointand you can specify a facility usingspec.logging.access.destination.syslog.facility. The following example is an Ingress Controller definition that logs to aSyslogdestination:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe
syslogdestination port must be UDP.
Configure Ingress access logging with a specific log format.
You can specify
spec.logging.access.httpLogFormatto customize the log format. The following example is an Ingress Controller definition that logs to asyslogendpoint with IP address 1.2.3.4 and port 10514:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Disable Ingress access logging.
To disable Ingress access logging, leave
spec.loggingorspec.logging.accessempty:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.6. Setting Ingress Controller thread count
A cluster administrator can set the thread count to increase the amount of incoming connections a cluster can handle. You can patch an existing Ingress Controller to increase the amount of threads.
Prerequisites
- The following assumes that you already created an Ingress Controller.
Procedure
Update the Ingress Controller to increase the number of threads:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"tuningOptions": {"threadCount": 8}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"tuningOptions": {"threadCount": 8}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you have a node that is capable of running large amounts of resources, you can configure
spec.nodePlacement.nodeSelectorwith labels that match the capacity of the intended node, and configurespec.tuningOptions.threadCountto an appropriately high value.
7.8.7. Configuring an Ingress Controller to use an internal load balancer
When creating an Ingress Controller on cloud platforms, the Ingress Controller is published by a public cloud load balancer by default. As an administrator, you can create an Ingress Controller that uses an internal cloud load balancer.
If your cloud provider is Microsoft Azure, you must have at least one public load balancer that points to your nodes. If you do not, all of your nodes will lose egress connectivity to the internet.
If you want to change the scope for an IngressController, you can change the .spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.scope parameter after the custom resource (CR) is created.
Figure 7.1. Diagram of LoadBalancer
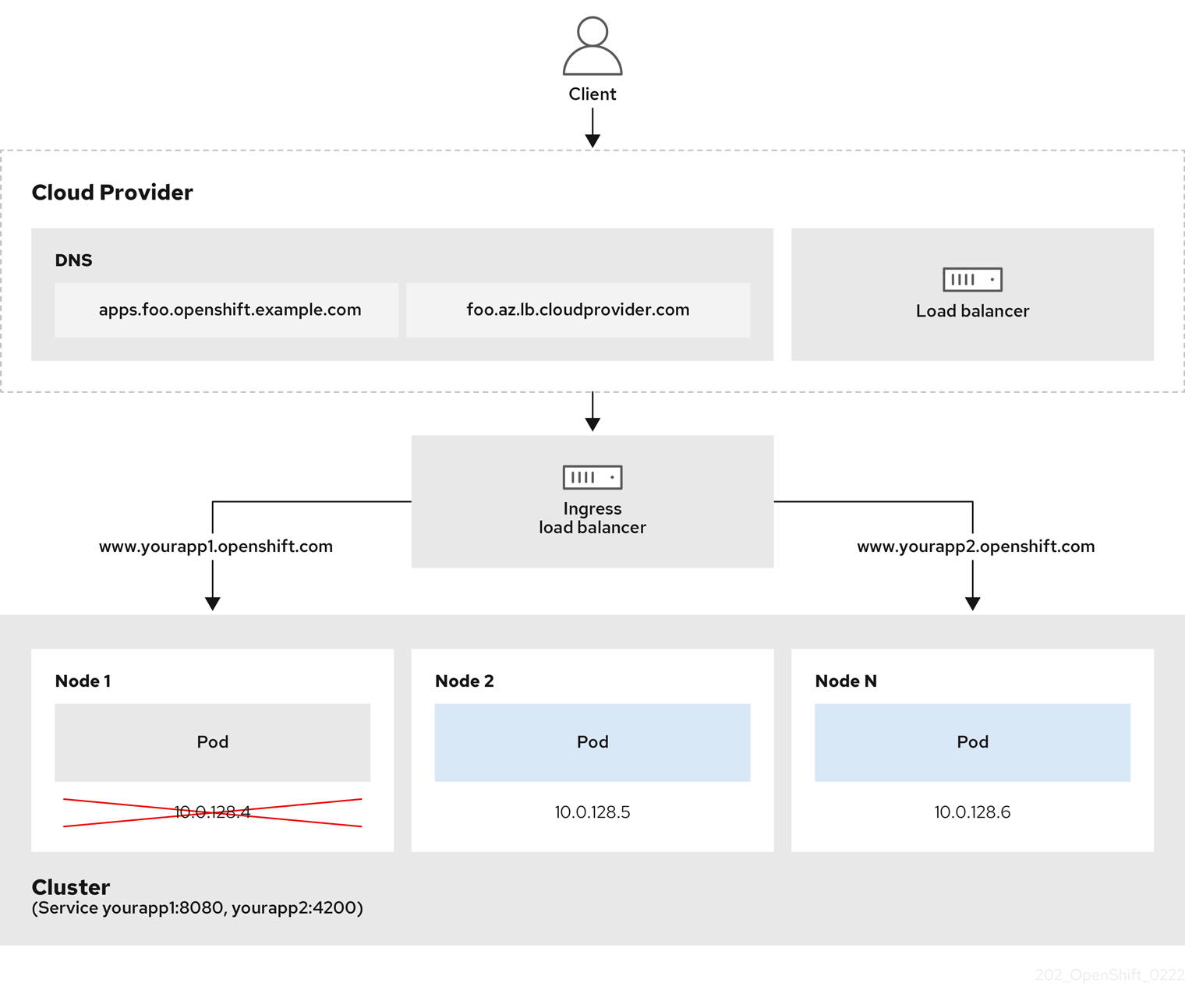
The preceding graphic shows the following concepts pertaining to OpenShift Container Platform Ingress LoadBalancerService endpoint publishing strategy:
- You can load balance externally, using the cloud provider load balancer, or internally, using the OpenShift Ingress Controller Load Balancer.
- You can use the single IP address of the load balancer and more familiar ports, such as 8080 and 4200 as shown on the cluster depicted in the graphic.
- Traffic from the external load balancer is directed at the pods, and managed by the load balancer, as depicted in the instance of a down node. See the Kubernetes Services documentation for implementation details.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an
IngressControllercustom resource (CR) in a file named<name>-ingress-controller.yaml, such as in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Ingress Controller defined in the previous step by running the following command:
oc create -f <name>-ingress-controller.yaml
$ oc create -f <name>-ingress-controller.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<name>with the name of theIngressControllerobject.
Optional: Confirm that the Ingress Controller was created by running the following command:
oc --all-namespaces=true get ingresscontrollers
$ oc --all-namespaces=true get ingresscontrollersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.8. Configuring global access for an Ingress Controller on Google Cloud
An Ingress Controller created on Google Cloud with an internal load balancer generates an internal IP address for the service. A cluster administrator can specify the global access option, which enables clients in any region within the same VPC network and compute region as the load balancer, to reach the workloads running on your cluster.
For more information, see the Google Cloud documentation for global access.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on Google Cloud infrastructure.
- You configured an Ingress Controller to use an internal load balancer.
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Configure the Ingress Controller resource to allow global access.
NoteYou can also create an Ingress Controller and specify the global access option.
Configure the Ingress Controller resource:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator edit ingresscontroller/default
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator edit ingresscontroller/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the YAML file:
Sample
clientAccessconfiguration toGlobalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set
gcp.clientAccesstoGlobal.
- Save the file to apply the changes.
Run the following command to verify that the service allows global access:
oc -n openshift-ingress edit svc/router-default -o yaml
$ oc -n openshift-ingress edit svc/router-default -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows that global access is enabled for Google Cloud with the annotation,
networking.gke.io/internal-load-balancer-allow-global-access.
7.8.9. Setting the Ingress Controller health check interval
A cluster administrator can set the health check interval to define how long the router waits between two consecutive health checks. This value is applied globally as a default for all routes. The default value is 5 seconds.
Prerequisites
- The following assumes that you already created an Ingress Controller.
Procedure
Update the Ingress Controller to change the interval between back end health checks:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"tuningOptions": {"healthCheckInterval": "8s"}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"tuningOptions": {"healthCheckInterval": "8s"}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteTo override the
healthCheckIntervalfor a single route, use the route annotationrouter.openshift.io/haproxy.health.check.interval
7.8.10. Configuring the default Ingress Controller for your cluster to be internal
You can configure the default Ingress Controller for your cluster to be internal by deleting and recreating it.
If your cloud provider is Microsoft Azure, you must have at least one public load balancer that points to your nodes. If you do not, all of your nodes will lose egress connectivity to the internet.
If you want to change the scope for an IngressController, you can change the .spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.scope parameter after the custom resource (CR) is created.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Configure the
defaultIngress Controller for your cluster to be internal by deleting and recreating it.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.11. Configuring the route admission policy
Administrators and application developers can run applications in multiple namespaces with the same domain name. This is for organizations where multiple teams develop microservices that are exposed on the same hostname.
Allowing claims across namespaces should only be enabled for clusters with trust between namespaces, otherwise a malicious user could take over a hostname. For this reason, the default admission policy disallows hostname claims across namespaces.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator privileges.
Procedure
Edit the
.spec.routeAdmissionfield of theingresscontrollerresource variable using the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"routeAdmission":{"namespaceOwnership":"InterNamespaceAllowed"}}}' --type=merge$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"routeAdmission":{"namespaceOwnership":"InterNamespaceAllowed"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample Ingress Controller configuration
spec: routeAdmission: namespaceOwnership: InterNamespaceAllowed ...spec: routeAdmission: namespaceOwnership: InterNamespaceAllowed ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to configure the route admission policy:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.12. Using wildcard routes
The HAProxy Ingress Controller has support for wildcard routes. The Ingress Operator uses wildcardPolicy to configure the ROUTER_ALLOW_WILDCARD_ROUTES environment variable of the Ingress Controller.
The default behavior of the Ingress Controller is to admit routes with a wildcard policy of None, which is backwards compatible with existing IngressController resources.
Procedure
Configure the wildcard policy.
Use the following command to edit the
IngressControllerresource:oc edit IngressController
$ oc edit IngressControllerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Under
spec, set thewildcardPolicyfield toWildcardsDisallowedorWildcardsAllowed:spec: routeAdmission: wildcardPolicy: WildcardsDisallowed # or WildcardsAllowedspec: routeAdmission: wildcardPolicy: WildcardsDisallowed # or WildcardsAllowedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.13. Using X-Forwarded headers
You configure the HAProxy Ingress Controller to specify a policy for how to handle HTTP headers including Forwarded and X-Forwarded-For. The Ingress Operator uses the HTTPHeaders field to configure the ROUTER_SET_FORWARDED_HEADERS environment variable of the Ingress Controller.
Procedure
Configure the
HTTPHeadersfield for the Ingress Controller.Use the following command to edit the
IngressControllerresource:oc edit IngressController
$ oc edit IngressControllerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Under
spec, set theHTTPHeaderspolicy field toAppend,Replace,IfNone, orNever:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Example use cases
As a cluster administrator, you can:
Configure an external proxy that injects the
X-Forwarded-Forheader into each request before forwarding it to an Ingress Controller.To configure the Ingress Controller to pass the header through unmodified, you specify the
neverpolicy. The Ingress Controller then never sets the headers, and applications receive only the headers that the external proxy provides.Configure the Ingress Controller to pass the
X-Forwarded-Forheader that your external proxy sets on external cluster requests through unmodified.To configure the Ingress Controller to set the
X-Forwarded-Forheader on internal cluster requests, which do not go through the external proxy, specify theif-nonepolicy. If an HTTP request already has the header set through the external proxy, then the Ingress Controller preserves it. If the header is absent because the request did not come through the proxy, then the Ingress Controller adds the header.
As an application developer, you can:
Configure an application-specific external proxy that injects the
X-Forwarded-Forheader.To configure an Ingress Controller to pass the header through unmodified for an application’s Route, without affecting the policy for other Routes, add an annotation
haproxy.router.openshift.io/set-forwarded-headers: if-noneorhaproxy.router.openshift.io/set-forwarded-headers: neveron the Route for the application.NoteYou can set the
haproxy.router.openshift.io/set-forwarded-headersannotation on a per route basis, independent from the globally set value for the Ingress Controller.
7.8.14. Enabling HTTP/2 Ingress connectivity
You can enable transparent end-to-end HTTP/2 connectivity in HAProxy. It allows application owners to make use of HTTP/2 protocol capabilities, including single connection, header compression, binary streams, and more.
You can enable HTTP/2 connectivity for an individual Ingress Controller or for the entire cluster.
To enable the use of HTTP/2 for the connection from the client to HAProxy, a route must specify a custom certificate. A route that uses the default certificate cannot use HTTP/2. This restriction is necessary to avoid problems from connection coalescing, where the client re-uses a connection for different routes that use the same certificate.
The connection from HAProxy to the application pod can use HTTP/2 only for re-encrypt routes and not for edge-terminated or insecure routes. This restriction is because HAProxy uses Application-Level Protocol Negotiation (ALPN), which is a TLS extension, to negotiate the use of HTTP/2 with the back-end. The implication is that end-to-end HTTP/2 is possible with passthrough and re-encrypt and not with insecure or edge-terminated routes.
Using WebSockets with a re-encrypt route and with HTTP/2 enabled on an Ingress Controller requires WebSocket support over HTTP/2. WebSockets over HTTP/2 is a feature of HAProxy 2.4, which is unsupported in OpenShift Container Platform at this time.
For non-passthrough routes, the Ingress Controller negotiates its connection to the application independently of the connection from the client. This means a client may connect to the Ingress Controller and negotiate HTTP/1.1, and the Ingress Controller may then connect to the application, negotiate HTTP/2, and forward the request from the client HTTP/1.1 connection using the HTTP/2 connection to the application. This poses a problem if the client subsequently tries to upgrade its connection from HTTP/1.1 to the WebSocket protocol, because the Ingress Controller cannot forward WebSocket to HTTP/2 and cannot upgrade its HTTP/2 connection to WebSocket. Consequently, if you have an application that is intended to accept WebSocket connections, it must not allow negotiating the HTTP/2 protocol or else clients will fail to upgrade to the WebSocket protocol.
Procedure
Enable HTTP/2 on a single Ingress Controller.
To enable HTTP/2 on an Ingress Controller, enter the
oc annotatecommand:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator annotate ingresscontrollers/<ingresscontroller_name> ingress.operator.openshift.io/default-enable-http2=true
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator annotate ingresscontrollers/<ingresscontroller_name> ingress.operator.openshift.io/default-enable-http2=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<ingresscontroller_name>with the name of the Ingress Controller to annotate.
Enable HTTP/2 on the entire cluster.
To enable HTTP/2 for the entire cluster, enter the
oc annotatecommand:oc annotate ingresses.config/cluster ingress.operator.openshift.io/default-enable-http2=true
$ oc annotate ingresses.config/cluster ingress.operator.openshift.io/default-enable-http2=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the annotation:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.15. Configuring the PROXY protocol for an Ingress Controller
A cluster administrator can configure the PROXY protocol when an Ingress Controller uses either the HostNetwork or NodePortService endpoint publishing strategy types. The PROXY protocol enables the load balancer to preserve the original client addresses for connections that the Ingress Controller receives. The original client addresses are useful for logging, filtering, and injecting HTTP headers. In the default configuration, the connections that the Ingress Controller receives only contain the source address that is associated with the load balancer.
This feature is not supported in cloud deployments. This restriction is because when OpenShift Container Platform runs in a cloud platform, and an IngressController specifies that a service load balancer should be used, the Ingress Operator configures the load balancer service and enables the PROXY protocol based on the platform requirement for preserving source addresses.
You must configure both OpenShift Container Platform and the external load balancer to either use the PROXY protocol or to use TCP.
The PROXY protocol is unsupported for the default Ingress Controller with installer-provisioned clusters on non-cloud platforms that use a Keepalived Ingress VIP.
Prerequisites
- You created an Ingress Controller.
Procedure
Edit the Ingress Controller resource:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator edit ingresscontroller/default
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator edit ingresscontroller/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the PROXY configuration:
If your Ingress Controller uses the hostNetwork endpoint publishing strategy type, set the
spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.hostNetwork.protocolsubfield toPROXY:Sample
hostNetworkconfiguration toPROXYspec: endpointPublishingStrategy: hostNetwork: protocol: PROXY type: HostNetworkspec: endpointPublishingStrategy: hostNetwork: protocol: PROXY type: HostNetworkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If your Ingress Controller uses the NodePortService endpoint publishing strategy type, set the
spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.nodePort.protocolsubfield toPROXY:Sample
nodePortconfiguration toPROXYspec: endpointPublishingStrategy: nodePort: protocol: PROXY type: NodePortServicespec: endpointPublishingStrategy: nodePort: protocol: PROXY type: NodePortServiceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.16. Specifying an alternative cluster domain using the appsDomain option
As a cluster administrator, you can specify an alternative to the default cluster domain for user-created routes by configuring the appsDomain field. The appsDomain field is an optional domain for OpenShift Container Platform to use instead of the default, which is specified in the domain field. If you specify an alternative domain, it overrides the default cluster domain for the purpose of determining the default host for a new route.
For example, you can use the DNS domain for your company as the default domain for routes and ingresses for applications running on your cluster.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
-
You installed the
occommand-line interface.
Procedure
Configure the
appsDomainfield by specifying an alternative default domain for user-created routes.Edit the ingress
clusterresource:oc edit ingresses.config/cluster -o yaml
$ oc edit ingresses.config/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the YAML file:
Sample
appsDomainconfiguration totest.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verify that an existing route contains the domain name specified in the
appsDomainfield by exposing the route and verifying the route domain change:NoteWait for the
openshift-apiserverfinish rolling updates before exposing the route.Expose the route:
oc expose service hello-openshift route.route.openshift.io/hello-openshift exposed
$ oc expose service hello-openshift route.route.openshift.io/hello-openshift exposedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
oc get routes NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD hello-openshift hello_openshift-<my_project>.test.example.com hello-openshift 8080-tcp None
$ oc get routes NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD hello-openshift hello_openshift-<my_project>.test.example.com hello-openshift 8080-tcp NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.17. Converting HTTP header case
HAProxy lowercases HTTP header names by default; for example, changing Host: xyz.com to host: xyz.com. If legacy applications are sensitive to the capitalization of HTTP header names, use the Ingress Controller spec.httpHeaders.headerNameCaseAdjustments API field for a solution to accommodate legacy applications until they can be fixed.
OpenShift Container Platform includes HAProxy 2.2. If you want to update to this version of the web-based load balancer, ensure that you add the spec.httpHeaders.headerNameCaseAdjustments section to your cluster’s configuration file.
As a cluster administrator, you can convert the HTTP header case by entering the oc patch command or by setting the HeaderNameCaseAdjustments field in the Ingress Controller YAML file.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Capitalize an HTTP header by using the
oc patchcommand.Change the HTTP header from
hosttoHostby running the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/default --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"httpHeaders":{"headerNameCaseAdjustments":["Host"]}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/default --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"httpHeaders":{"headerNameCaseAdjustments":["Host"]}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
Routeresource YAML file so that the annotation can be applied to the application.Example of a route named
my-applicationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set
haproxy.router.openshift.io/h1-adjust-caseso that the Ingress Controller can adjust thehostrequest header as specified.
Specify adjustments by configuring the
HeaderNameCaseAdjustmentsfield in the Ingress Controller YAML configuration file.The following example Ingress Controller YAML file adjusts the
hostheader toHostfor HTTP/1 requests to appropriately annotated routes:Example Ingress Controller YAML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example route enables HTTP response header name case adjustments by using the
haproxy.router.openshift.io/h1-adjust-caseannotation:Example route YAML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set
haproxy.router.openshift.io/h1-adjust-caseto true.
7.8.18. Using router compression
You configure the HAProxy Ingress Controller to specify router compression globally for specific MIME types. You can use the mimeTypes variable to define the formats of MIME types to which compression is applied. The types are: application, image, message, multipart, text, video, or a custom type prefaced by "X-". To see the full notation for MIME types and subtypes, see RFC1341.
Memory allocated for compression can affect the max connections. Additionally, compression of large buffers can cause latency, like heavy regex or long lists of regex.
Not all MIME types benefit from compression, but HAProxy still uses resources to try to compress if instructed to. Generally, text formats, such as html, css, and js, formats benefit from compression, but formats that are already compressed, such as image, audio, and video, benefit little in exchange for the time and resources spent on compression.
Procedure
Configure the
httpCompressionfield for the Ingress Controller.Use the following command to edit the
IngressControllerresource:oc edit -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/default
$ oc edit -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontrollers/defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Under
spec, set thehttpCompressionpolicy field tomimeTypesand specify a list of MIME types that should have compression applied:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.19. Exposing router metrics
You can expose the HAProxy router metrics by default in Prometheus format on the default stats port, 1936. The external metrics collection and aggregation systems such as Prometheus can access the HAProxy router metrics. You can view the HAProxy router metrics in a browser in the HTML and comma separated values (CSV) format.
Prerequisites
- You configured your firewall to access the default stats port, 1936.
Procedure
Get the router pod name by running the following command:
oc get pods -n openshift-ingress
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE router-default-76bfffb66c-46qwp 1/1 Running 0 11h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE router-default-76bfffb66c-46qwp 1/1 Running 0 11hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the router’s username and password, which the router pod stores in the
/var/lib/haproxy/conf/metrics-auth/statsUsernameand/var/lib/haproxy/conf/metrics-auth/statsPasswordfiles:Get the username by running the following command:
oc rsh <router_pod_name> cat metrics-auth/statsUsername
$ oc rsh <router_pod_name> cat metrics-auth/statsUsernameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the password by running the following command:
oc rsh <router_pod_name> cat metrics-auth/statsPassword
$ oc rsh <router_pod_name> cat metrics-auth/statsPasswordCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Get the router IP and metrics certificates by running the following command:
oc describe pod <router_pod>
$ oc describe pod <router_pod>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the raw statistics in Prometheus format by running the following command:
curl -u <user>:<password> http://<router_IP>:<stats_port>/metrics
$ curl -u <user>:<password> http://<router_IP>:<stats_port>/metricsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Access the metrics securely by running the following command:
curl -u user:password https://<router_IP>:<stats_port>/metrics -k
$ curl -u user:password https://<router_IP>:<stats_port>/metrics -kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Access the default stats port, 1936, by running the following command:
curl -u <user>:<password> http://<router_IP>:<stats_port>/metrics
$ curl -u <user>:<password> http://<router_IP>:<stats_port>/metricsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 7.1. Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the stats window by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://<user>:<password>@<router_IP>:<stats_port>
http://<user>:<password>@<router_IP>:<stats_port>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Get the stats in CSV format by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://<user>:<password>@<router_ip>:1936/metrics;csv
http://<user>:<password>@<router_ip>:1936/metrics;csvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.20. Customizing HAProxy error code response pages
As a cluster administrator, you can specify a custom error code response page for either 503, 404, or both error pages. The HAProxy router serves a 503 error page when the application pod is not running or a 404 error page when the requested URL does not exist. For example, if you customize the 503 error code response page, then the page is served when the application pod is not running, and the default 404 error code HTTP response page is served by the HAProxy router for an incorrect route or a non-existing route.
Custom error code response pages are specified in a config map then patched to the Ingress Controller. The config map keys have two available file names as follows: error-page-503.http and error-page-404.http.
Custom HTTP error code response pages must follow the HAProxy HTTP error page configuration guidelines. Here is an example of the default OpenShift Container Platform HAProxy router http 503 error code response page. You can use the default content as a template for creating your own custom page.
By default, the HAProxy router serves only a 503 error page when the application is not running or when the route is incorrect or non-existent. This default behavior is the same as the behavior on OpenShift Container Platform 4.8 and earlier. If a config map for the customization of an HTTP error code response is not provided, and you are using a custom HTTP error code response page, the router serves a default 404 or 503 error code response page.
If you use the OpenShift Container Platform default 503 error code page as a template for your customizations, the headers in the file require an editor that can use CRLF line endings.
Procedure
Create a config map named
my-custom-error-code-pagesin theopenshift-confignamespace:oc -n openshift-config create configmap my-custom-error-code-pages \ --from-file=error-page-503.http \ --from-file=error-page-404.http
$ oc -n openshift-config create configmap my-custom-error-code-pages \ --from-file=error-page-503.http \ --from-file=error-page-404.httpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantIf you do not specify the correct format for the custom error code response page, a router pod outage occurs. To resolve this outage, you must delete or correct the config map and delete the affected router pods so they can be recreated with the correct information.
Patch the Ingress Controller to reference the
my-custom-error-code-pagesconfig map by name:oc patch -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"httpErrorCodePages":{"name":"my-custom-error-code-pages"}}}' --type=merge$ oc patch -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"httpErrorCodePages":{"name":"my-custom-error-code-pages"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Ingress Operator copies the
my-custom-error-code-pagesconfig map from theopenshift-confignamespace to theopenshift-ingressnamespace. The Operator names the config map according to the pattern,<your_ingresscontroller_name>-errorpages, in theopenshift-ingressnamespace.Display the copy:
oc get cm default-errorpages -n openshift-ingress
$ oc get cm default-errorpages -n openshift-ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DATA AGE default-errorpages 2 25s
NAME DATA AGE default-errorpages 2 25s1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The example config map name is
default-errorpagesbecause thedefaultIngress Controller custom resource (CR) was patched.
Confirm that the config map containing the custom error response page mounts on the router volume where the config map key is the filename that has the custom HTTP error code response:
For 503 custom HTTP custom error code response:
oc -n openshift-ingress rsh <router_pod> cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/error_code_pages/error-page-503.http
$ oc -n openshift-ingress rsh <router_pod> cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/error_code_pages/error-page-503.httpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For 404 custom HTTP custom error code response:
oc -n openshift-ingress rsh <router_pod> cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/error_code_pages/error-page-404.http
$ oc -n openshift-ingress rsh <router_pod> cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/error_code_pages/error-page-404.httpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify your custom error code HTTP response:
Create a test project and application:
oc new-project test-ingress
$ oc new-project test-ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc new-app django-psql-example
$ oc new-app django-psql-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For 503 custom http error code response:
- Stop all the pods for the application.
Run the following curl command or visit the route hostname in the browser:
curl -vk <route_hostname>
$ curl -vk <route_hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For 404 custom http error code response:
- Visit a non-existent route or an incorrect route.
Run the following curl command or visit the route hostname in the browser:
curl -vk <route_hostname>
$ curl -vk <route_hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check if the
errorfileattribute is properly in thehaproxy.configfile:oc -n openshift-ingress rsh <router> cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config | grep errorfile
$ oc -n openshift-ingress rsh <router> cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config | grep errorfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.21. Setting the Ingress Controller maximum connections
A cluster administrator can set the maximum number of simultaneous connections for OpenShift router deployments. You can patch an existing Ingress Controller to increase the maximum number of connections.
Prerequisites
- The following assumes that you already created an Ingress Controller
Procedure
Update the Ingress Controller to change the maximum number of connections for HAProxy:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"tuningOptions": {"maxConnections": 7500}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"tuningOptions": {"maxConnections": 7500}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningIf you set the
spec.tuningOptions.maxConnectionsvalue greater than the current operating system limit, the HAProxy process will not start. See the table in the "Ingress Controller configuration parameters" section for more information about this parameter.
Chapter 8. Ingress Node Firewall Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
The Ingress Node Firewall Operator provides a stateless, eBPF-based firewall for managing node-level ingress traffic in OpenShift Container Platform.
8.1. Ingress Node Firewall Operator
The Ingress Node Firewall Operator provides ingress firewall rules at a node level by deploying the daemon set to nodes you specify and manage in the firewall configurations. To deploy the daemon set, you create an IngressNodeFirewallConfig custom resource (CR). The Operator applies the IngressNodeFirewallConfig CR to create ingress node firewall daemon set daemon, which run on all nodes that match the nodeSelector.
You configure rules of the IngressNodeFirewall CR and apply them to clusters using the nodeSelector and setting values to "true".
The Ingress Node Firewall Operator supports only stateless firewall rules.
The maximum transmission units (MTU) parameter is 4Kb (kilobytes) in OpenShift Container Platform 4.13.
Network interface controllers (NICs) that do not support native XDP drivers will run at a lower performance.
Ingress Node Firewall Operator is not supported on Amazon Web Services (AWS) with the default OpenShift installation or on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA). For more information on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS support and ingress, see Ingress Operator in Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
8.2. Installing the Ingress Node Firewall Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can install the Ingress Node Firewall Operator by using the OpenShift Container Platform CLI or the web console.
8.2.1. Installing the Ingress Node Firewall Operator using the CLI
As a cluster administrator, you can install the Operator using the CLI.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have an account with administrator privileges.
Procedure
To create the
openshift-ingress-node-firewallnamespace, enter the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create an
OperatorGroupCR, enter the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Subscribe to the Ingress Node Firewall Operator.
To create a
SubscriptionCR for the Ingress Node Firewall Operator, enter the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To verify that the Operator is installed, enter the following command:
oc get ip -n openshift-ingress-node-firewall
$ oc get ip -n openshift-ingress-node-firewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED install-5cvnz ingress-node-firewall.4.13.0-202211122336 Automatic true
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED install-5cvnz ingress-node-firewall.4.13.0-202211122336 Automatic trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify the version of the Operator, enter the following command:
oc get csv -n openshift-ingress-node-firewall
$ oc get csv -n openshift-ingress-node-firewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE ingress-node-firewall.4.13.0-202211122336 Ingress Node Firewall Operator 4.13.0-202211122336 ingress-node-firewall.4.13.0-202211102047 Succeeded
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE ingress-node-firewall.4.13.0-202211122336 Ingress Node Firewall Operator 4.13.0-202211122336 ingress-node-firewall.4.13.0-202211102047 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.2.2. Installing the Ingress Node Firewall Operator using the web console
As a cluster administrator, you can install the Operator using the web console.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have an account with administrator privileges.
Procedure
Install the Ingress Node Firewall Operator:
- In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, click Operators → OperatorHub.
- Select Ingress Node Firewall Operator from the list of available Operators, and then click Install.
- On the Install Operator page, under Installed Namespace, select Operator recommended Namespace.
- Click Install.
Verify that the Ingress Node Firewall Operator is installed successfully:
- Navigate to the Operators → Installed Operators page.
Ensure that Ingress Node Firewall Operator is listed in the openshift-ingress-node-firewall project with a Status of InstallSucceeded.
NoteDuring installation an Operator might display a Failed status. If the installation later succeeds with an InstallSucceeded message, you can ignore the Failed message.
If the Operator does not have a Status of InstallSucceeded, troubleshoot using the following steps:
- Inspect the Operator Subscriptions and Install Plans tabs for any failures or errors under Status.
-
Navigate to the Workloads → Pods page and check the logs for pods in the
openshift-ingress-node-firewallproject. Check the namespace of the YAML file. If the annotation is missing, you can add the annotation
workload.openshift.io/allowed=managementto the Operator namespace with the following command:oc annotate ns/openshift-ingress-node-firewall workload.openshift.io/allowed=management
$ oc annotate ns/openshift-ingress-node-firewall workload.openshift.io/allowed=managementCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFor single-node OpenShift clusters, the
openshift-ingress-node-firewallnamespace requires theworkload.openshift.io/allowed=managementannotation.
8.3. Deploying Ingress Node Firewall Operator
Prerequisite
- The Ingress Node Firewall Operator is installed.
Procedure
To deploy the Ingress Node Firewall Operator, create a IngressNodeFirewallConfig custom resource that will deploy the Operator’s daemon set. You can deploy one or multiple IngressNodeFirewall CRDs to nodes by applying firewall rules.
-
Create the
IngressNodeFirewallConfiginside theopenshift-ingress-node-firewallnamespace namedingressnodefirewallconfig. Run the following command to deploy Ingress Node Firewall Operator rules:
oc apply -f rule.yaml
$ oc apply -f rule.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3.1. Ingress Node Firewall configuration object
The fields for the Ingress Node Firewall configuration object are described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The name of the CR object. The name of the firewall rules object must be |
|
|
|
Namespace for the Ingress Firewall Operator CR object. The |
|
|
| A node selection constraint used to target nodes through specified node labels. For example: spec:
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""
Note
One label used in |
The Operator consumes the CR and creates an ingress node firewall daemon set on all the nodes that match the nodeSelector.
Ingress Node Firewall Operator example configuration
A complete Ingress Node Firewall Configuration is specified in the following example:
Example Ingress Node Firewall Configuration object
The Operator consumes the CR and creates an ingress node firewall daemon set on all the nodes that match the nodeSelector.
8.3.2. Ingress Node Firewall rules object
The fields for the Ingress Node Firewall rules object are described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The name of the CR object. |
|
|
|
The fields for this object specify the interfaces to apply the firewall rules to. For example, |
|
|
|
You can use |
|
|
|
|
8.3.2.1. Ingress object configuration
The values for the ingress object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Allows you to set the CIDR block. You can configure multiple CIDRs from different address families. Note
Different CIDRs allow you to use the same order rule. In the case that there are multiple |
|
|
|
Ingress firewall
Set Note Ingress firewall rules are verified using a verification webhook that blocks any invalid configuration. The verification webhook prevents you from blocking any critical cluster services such as the API server or SSH. |
8.3.2.2. Ingress Node Firewall rules object example
A complete Ingress Node Firewall configuration is specified in the following example:
Example Ingress Node Firewall configuration
- 1
- A <label_name> and a <label_value> must exist on the node and must match the
nodeselectorlabel and value applied to the nodes you want theingressfirewallconfigCR to run on. The <label_value> can betrueorfalse. By usingnodeSelectorlabels, you can target separate groups of nodes to apply different rules to using theingressfirewallconfigCR.
8.3.2.3. Zero trust Ingress Node Firewall rules object example
Zero trust Ingress Node Firewall rules can provide additional security to multi-interface clusters. For example, you can use zero trust Ingress Node Firewall rules to drop all traffic on a specific interface except for SSH.
A complete configuration of a zero trust Ingress Node Firewall rule set is specified in the following example:
Users need to add all ports their application will use to their allowlist in the following case to ensure proper functionality.
Example zero trust Ingress Node Firewall rules
8.4. Viewing Ingress Node Firewall Operator rules
Procedure
Run the following command to view all current rules :
oc get ingressnodefirewall
$ oc get ingressnodefirewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Choose one of the returned
<resource>names and run the following command to view the rules or configs:oc get <resource> <name> -o yaml
$ oc get <resource> <name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.5. Troubleshooting the Ingress Node Firewall Operator
Run the following command to list installed Ingress Node Firewall custom resource definitions (CRD):
oc get crds | grep ingressnodefirewall
$ oc get crds | grep ingressnodefirewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE ingressnodefirewallconfigs.ingressnodefirewall.openshift.io 2022-08-25T10:03:01Z ingressnodefirewallnodestates.ingressnodefirewall.openshift.io 2022-08-25T10:03:00Z ingressnodefirewalls.ingressnodefirewall.openshift.io 2022-08-25T10:03:00Z
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE ingressnodefirewallconfigs.ingressnodefirewall.openshift.io 2022-08-25T10:03:01Z ingressnodefirewallnodestates.ingressnodefirewall.openshift.io 2022-08-25T10:03:00Z ingressnodefirewalls.ingressnodefirewall.openshift.io 2022-08-25T10:03:00ZCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to view the state of the Ingress Node Firewall Operator:
oc get pods -n openshift-ingress-node-firewall
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ingress-node-firewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ingress-node-firewall-controller-manager 2/2 Running 0 5d21h ingress-node-firewall-daemon-pqx56 3/3 Running 0 5d21h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ingress-node-firewall-controller-manager 2/2 Running 0 5d21h ingress-node-firewall-daemon-pqx56 3/3 Running 0 5d21hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following fields provide information about the status of the Operator:
READY,STATUS,AGE, andRESTARTS. TheSTATUSfield isRunningwhen the Ingress Node Firewall Operator is deploying a daemon set to the assigned nodes.Run the following command to collect all ingress firewall node pods' logs:
oc adm must-gather – gather_ingress_node_firewall
$ oc adm must-gather – gather_ingress_node_firewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The logs are available in the sos node’s report containing eBPF
bpftooloutputs at/sos_commands/ebpf. These reports include lookup tables used or updated as the ingress firewall XDP handles packet processing, updates statistics, and emits events.
Chapter 9. Configuring an Ingress Controller for manual DNS Management
As a cluster administrator, when you create an Ingress Controller, the Operator manages the DNS records automatically. This has some limitations when the required DNS zone is different from the cluster DNS zone or when the DNS zone is hosted outside the cloud provider.
As a cluster administrator, you can configure an Ingress Controller to stop automatic DNS management and start manual DNS management. Set dnsManagementPolicy to specify when it should be automatically or manually managed.
When you change an Ingress Controller from Managed to Unmanaged DNS management policy, the Operator does not clean up the previous wildcard DNS record provisioned on the cloud. When you change an Ingress Controller from Unmanaged to Managed DNS management policy, the Operator attempts to create the DNS record on the cloud provider if it does not exist or updates the DNS record if it already exists.
When you set dnsManagementPolicy to unmanaged, you have to manually manage the lifecycle of the wildcard DNS record on the cloud provider.
9.1. Managed DNS management policy
The Managed DNS management policy for Ingress Controllers ensures that the lifecycle of the wildcard DNS record on the cloud provider is automatically managed by the Operator.
9.2. Unmanaged DNS management policy
The Unmanaged DNS management policy for Ingress Controllers ensures that the lifecycle of the wildcard DNS record on the cloud provider is not automatically managed, instead it becomes the responsibility of the cluster administrator.
On the AWS cloud platform, if the domain on the Ingress Controller does not match with dnsConfig.Spec.BaseDomain then the DNS management policy is automatically set to Unmanaged.
9.3. Creating a custom Ingress Controller with the Unmanaged DNS management policy
As a cluster administrator, you can create a new custom Ingress Controller with the Unmanaged DNS management policy.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a custom resource (CR) file named
sample-ingress.yamlcontaining the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the
<name>with a name for theIngressControllerobject. - 2
- Specify the
domainbased on the DNS record that was created as a prerequisite. - 3
- Specify the
scopeasExternalto expose the load balancer externally. - 4
dnsManagementPolicyindicates if the Ingress Controller is managing the lifecycle of the wildcard DNS record associated with the load balancer. The valid values areManagedandUnmanaged. The default value isManaged.
Save the file to apply the changes.
oc apply -f <name>.yaml
oc apply -f <name>.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.4. Modifying an existing Ingress Controller
As a cluster administrator, you can modify an existing Ingress Controller to manually manage the DNS record lifecycle.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Modify the chosen
IngressControllerto setdnsManagementPolicy:SCOPE=$(oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontroller <name> -o=jsonpath="{.status.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.scope}") oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/<name> --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"dnsManagementPolicy":"Unmanaged", "scope":"${SCOPE}"}}}}'SCOPE=$(oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontroller <name> -o=jsonpath="{.status.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.scope}") oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/<name> --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"dnsManagementPolicy":"Unmanaged", "scope":"${SCOPE}"}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optional: You can delete the associated DNS record in the cloud provider.
Chapter 10. Verifying connectivity to an endpoint
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) runs a controller, the connectivity check controller, that performs a connection health check between resources within your cluster. By reviewing the results of the health checks, you can diagnose connection problems or eliminate network connectivity as the cause of an issue that you are investigating.
10.1. Connection health checks that are performed
To verify that cluster resources are reachable, a TCP connection is made to each of the following cluster API services:
- Kubernetes API server service
- Kubernetes API server endpoints
- OpenShift API server service
- OpenShift API server endpoints
- Load balancers
To verify that services and service endpoints are reachable on every node in the cluster, a TCP connection is made to each of the following targets:
- Health check target service
- Health check target endpoints
10.2. Implementation of connection health checks
The connectivity check controller orchestrates connection verification checks in your cluster. The results for the connection tests are stored in PodNetworkConnectivity objects in the openshift-network-diagnostics namespace. Connection tests are performed every minute in parallel.
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) deploys several resources to the cluster to send and receive connectivity health checks:
- Health check source
-
This program deploys in a single pod replica set managed by a
Deploymentobject. The program consumesPodNetworkConnectivityobjects and connects to thespec.targetEndpointspecified in each object. - Health check target
- A pod deployed as part of a daemon set on every node in the cluster. The pod listens for inbound health checks. The presence of this pod on every node allows for the testing of connectivity to each node.
You can configure the nodes which network connectivity sources and targets run on with a node selector. Additionally, you can specify permissible tolerations for source and target pods. The configuration is defined in the singleton cluster custom resource of the Network API in the config.openshift.io/v1 API group.
Pod scheduling occurs after you have updated the configuration. Therefore, you must apply node labels that you intend to use in your selectors before updating the configuration. Labels applied after updating your network connectivity check pod placement are ignored.
Refer to the default configuration in the following YAML:
Default configuration for connectivity source and target pods
- 1 1
- Specifies the network diagnostics configuration. If a value is not specified or an empty object is specified, and
spec.disableNetworkDiagnostics=trueis set in thenetwork.operator.openshift.iocustom resource namedcluster, network diagnostics are disabled. If set, this value overridesspec.disableNetworkDiagnostics=true. - 2
- Specifies the diagnostics mode. The value can be the empty string,
All, orDisabled. The empty string is equivalent to specifyingAll. - 3
- Optional: Specifies a selector for connectivity check source pods. You can use the
nodeSelectorandtolerationsfields to further specify thesourceNodepods. These are optional for both source and target pods. You can omit them, use both, or use only one of them. - 4
- Optional: Specifies a selector for connectivity check target pods. You can use the
nodeSelectorandtolerationsfields to further specify thetargetNodepods. These are optional for both source and target pods. You can omit them, use both, or use only one of them.
10.3. PodNetworkConnectivityCheck object fields
The PodNetworkConnectivityCheck object fields are described in the following tables.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The name of the object in the following format:
|
|
|
|
The namespace that the object is associated with. This value is always |
|
|
|
The name of the pod where the connection check originates, such as |
|
|
|
The target of the connection check, such as |
|
|
| Configuration for the TLS certificate to use. |
|
|
| The name of the TLS certificate used, if any. The default value is an empty string. |
|
|
| An object representing the condition of the connection test and logs of recent connection successes and failures. |
|
|
| The latest status of the connection check and any previous statuses. |
|
|
| Connection test logs from unsuccessful attempts. |
|
|
| Connect test logs covering the time periods of any outages. |
|
|
| Connection test logs from successful attempts. |
The following table describes the fields for objects in the status.conditions array:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The time that the condition of the connection transitioned from one status to another. |
|
|
| The details about last transition in a human readable format. |
|
|
| The last status of the transition in a machine readable format. |
|
|
| The status of the condition. |
|
|
| The type of the condition. |
The following table describes the fields for objects in the status.conditions array:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The timestamp from when the connection failure is resolved. |
|
|
| Connection log entries, including the log entry related to the successful end of the outage. |
|
|
| A summary of outage details in a human readable format. |
|
|
| The timestamp from when the connection failure is first detected. |
|
|
| Connection log entries, including the original failure. |
10.3.1. Connection log fields
The fields for a connection log entry are described in the following table. The object is used in the following fields:
-
status.failures[] -
status.successes[] -
status.outages[].startLogs[] -
status.outages[].endLogs[]
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Records the duration of the action. |
|
|
| Provides the status in a human readable format. |
|
|
|
Provides the reason for status in a machine readable format. The value is one of |
|
|
| Indicates if the log entry is a success or failure. |
|
|
| The start time of connection check. |
10.4. Verifying network connectivity for an endpoint
As a cluster administrator, you can verify the connectivity of an endpoint, such as an API server, load balancer, service, or pod.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
To list the current
PodNetworkConnectivityCheckobjects, enter the following command:oc get podnetworkconnectivitycheck -n openshift-network-diagnostics
$ oc get podnetworkconnectivitycheck -n openshift-network-diagnosticsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the connection test logs:
- From the output of the previous command, identify the endpoint that you want to review the connectivity logs for.
View the object by entering the following command:
oc get podnetworkconnectivitycheck <name> \ -n openshift-network-diagnostics -o yaml
$ oc get podnetworkconnectivitycheck <name> \ -n openshift-network-diagnostics -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<name>specifies the name of thePodNetworkConnectivityCheckobject.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 11. Changing the MTU for the cluster network
As a cluster administrator, you can change the MTU for the cluster network after cluster installation. This change is disruptive as cluster nodes must be rebooted to finalize the MTU change. You can change the MTU only for clusters using the OVN-Kubernetes or OpenShift SDN network plugins.
11.1. About the cluster MTU
During installation the maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the cluster network is detected automatically based on the MTU of the primary network interface of nodes in the cluster. You do not normally need to override the detected MTU.
You might want to change the MTU of the cluster network for several reasons:
- The MTU detected during cluster installation is not correct for your infrastructure
- Your cluster infrastructure now requires a different MTU, such as from the addition of nodes that need a different MTU for optimal performance
You can change the cluster MTU for only the OVN-Kubernetes and OpenShift SDN cluster network plugins.
11.1.1. Service interruption considerations
When you initiate an MTU change on your cluster the following effects might impact service availability:
- At least two rolling reboots are required to complete the migration to a new MTU. During this time, some nodes are not available as they restart.
- Specific applications deployed to the cluster with shorter timeout intervals than the absolute TCP timeout interval might experience disruption during the MTU change.
11.1.2. MTU value selection
When planning your MTU migration there are two related but distinct MTU values to consider.
- Hardware MTU: This MTU value is set based on the specifics of your network infrastructure.
Cluster network MTU: This MTU value is always less than your hardware MTU to account for the cluster network overlay overhead. The specific overhead is determined by your network plugin:
-
OVN-Kubernetes:
100bytes -
OpenShift SDN:
50bytes
-
OVN-Kubernetes:
If your cluster requires different MTU values for different nodes, you must subtract the overhead value for your network plugin from the lowest MTU value that is used by any node in your cluster. For example, if some nodes in your cluster have an MTU of 9001, and some have an MTU of 1500, you must set this value to 1400.
To avoid selecting an MTU value that is not acceptable by a node, verify the maximum MTU value (maxmtu) that is accepted by the network interface by using the ip -d link command.
11.1.3. How the migration process works
The following table summarizes the migration process by segmenting between the user-initiated steps in the process and the actions that the migration performs in response.
| User-initiated steps | OpenShift Container Platform activity |
|---|---|
| Set the following values in the Cluster Network Operator configuration:
| Cluster Network Operator (CNO): Confirms that each field is set to a valid value.
If the values provided are valid, the CNO writes out a new temporary configuration with the MTU for the cluster network set to the value of the Machine Config Operator (MCO): Performs a rolling reboot of each node in the cluster. |
| Reconfigure the MTU of the primary network interface for the nodes on the cluster. You can use a variety of methods to accomplish this, including:
| N/A |
|
Set the | Machine Config Operator (MCO): Performs a rolling reboot of each node in the cluster with the new MTU configuration. |
11.2. Changing the cluster MTU
As a cluster administrator, you can change the maximum transmission unit (MTU) for your cluster. The migration is disruptive and nodes in your cluster might be temporarily unavailable as the MTU update rolls out.
The following procedure describes how to change the cluster MTU by using either machine configs, DHCP, or an ISO. If you use the DHCP or ISO approach, you must refer to configuration artifacts that you kept after installing your cluster to complete the procedure.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. You identified the target MTU for your cluster. The correct MTU varies depending on the network plugin that your cluster uses:
-
OVN-Kubernetes: The cluster MTU must be set to
100less than the lowest hardware MTU value in your cluster. -
OpenShift SDN: The cluster MTU must be set to
50less than the lowest hardware MTU value in your cluster.
-
OVN-Kubernetes: The cluster MTU must be set to
- If your nodes are physical machines, ensure that the cluster network and the connected network switches support jumbo frames.
- If your nodes are virtual machines (VMs), ensure that the hypervisor and the connected network switches support jumbo frames.
Procedure
To increase or decrease the MTU for the cluster network complete the following procedure.
To obtain the current MTU for the cluster network, enter the following command:
oc describe network.config cluster
$ oc describe network.config clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Prepare your configuration for the hardware MTU:
If your hardware MTU is specified with DHCP, update your DHCP configuration such as with the following dnsmasq configuration:
dhcp-option-force=26,<mtu>
dhcp-option-force=26,<mtu>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<mtu>- Specifies the hardware MTU for the DHCP server to advertise.
- If your hardware MTU is specified with a kernel command line with PXE, update that configuration accordingly.
If your hardware MTU is specified in a NetworkManager connection configuration, complete the following steps. This approach is the default for OpenShift Container Platform if you do not explicitly specify your network configuration with DHCP, a kernel command line, or some other method. Your cluster nodes must all use the same underlying network configuration for the following procedure to work unmodified.
Find the primary network interface:
If you are using the OpenShift SDN network plugin, enter the following command:
oc debug node/<node_name> -- chroot /host ip route list match 0.0.0.0/0 | awk '{print $5 }'$ oc debug node/<node_name> -- chroot /host ip route list match 0.0.0.0/0 | awk '{print $5 }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<node_name>- Specifies the name of a node in your cluster.
If you are using the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, enter the following command:
oc debug node/<node_name> -- chroot /host nmcli -g connection.interface-name c show ovs-if-phys0
$ oc debug node/<node_name> -- chroot /host nmcli -g connection.interface-name c show ovs-if-phys0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<node_name>- Specifies the name of a node in your cluster.
Create the following NetworkManager configuration in the
<interface>-mtu.conffile:Example NetworkManager connection configuration
[connection-<interface>-mtu] match-device=interface-name:<interface> ethernet.mtu=<mtu>
[connection-<interface>-mtu] match-device=interface-name:<interface> ethernet.mtu=<mtu>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<mtu>- Specifies the new hardware MTU value.
<interface>- Specifies the primary network interface name.
Create two
MachineConfigobjects, one for the control plane nodes and another for the worker nodes in your cluster:Create the following Butane config in the
control-plane-interface.bufile:NoteThe Butane version you specify in the config file should match the OpenShift Container Platform version and always ends in
0. For example,4.13.0. See "Creating machine configs with Butane" for information about Butane.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the following Butane config in the
worker-interface.bufile:NoteThe Butane version you specify in the config file should match the OpenShift Container Platform version and always ends in
0. For example,4.13.0. See "Creating machine configs with Butane" for information about Butane.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create
MachineConfigobjects from the Butane configs by running the following command:for manifest in control-plane-interface worker-interface; do butane --files-dir . $manifest.bu > $manifest.yaml done$ for manifest in control-plane-interface worker-interface; do butane --files-dir . $manifest.bu > $manifest.yaml doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To begin the MTU migration, specify the migration configuration by entering the following command. The Machine Config Operator performs a rolling reboot of the nodes in the cluster in preparation for the MTU change.
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": { "mtu": { "network": { "from": <overlay_from>, "to": <overlay_to> } , "machine": { "to" : <machine_to> } } } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": { "mtu": { "network": { "from": <overlay_from>, "to": <overlay_to> } , "machine": { "to" : <machine_to> } } } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<overlay_from>- Specifies the current cluster network MTU value.
<overlay_to>-
Specifies the target MTU for the cluster network. This value is set relative to the value for
<machine_to>and for OVN-Kubernetes must be100less and for OpenShift SDN must be50less. <machine_to>- Specifies the MTU for the primary network interface on the underlying host network.
Example that increases the cluster MTU
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": { "mtu": { "network": { "from": 1400, "to": 9000 } , "machine": { "to" : 9100} } } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": { "mtu": { "network": { "from": 1400, "to": 9000 } , "machine": { "to" : 9100} } } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow As the MCO updates machines in each machine config pool, it reboots each node one by one. You must wait until all the nodes are updated. Check the machine config pool status by entering the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successfully updated node has the following status:
UPDATED=true,UPDATING=false,DEGRADED=false.NoteBy default, the MCO updates one machine per pool at a time, causing the total time the migration takes to increase with the size of the cluster.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the following statements are true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStart
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<config_name>is the name of the machine config from themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.The machine config must include the following update to the systemd configuration:
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/mtu-migration.sh
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/mtu-migration.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Update the underlying network interface MTU value:
If you are specifying the new MTU with a NetworkManager connection configuration, enter the following command. The MachineConfig Operator automatically performs a rolling reboot of the nodes in your cluster.
for manifest in control-plane-interface worker-interface; do oc create -f $manifest.yaml done$ for manifest in control-plane-interface worker-interface; do oc create -f $manifest.yaml doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If you are specifying the new MTU with a DHCP server option or a kernel command line and PXE, make the necessary changes for your infrastructure.
As the MCO updates machines in each machine config pool, it reboots each node one by one. You must wait until all the nodes are updated. Check the machine config pool status by entering the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successfully updated node has the following status:
UPDATED=true,UPDATING=false,DEGRADED=false.NoteBy default, the MCO updates one machine per pool at a time, causing the total time the migration takes to increase with the size of the cluster.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the following statements are true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep path:
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep path:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<config_name>is the name of the machine config from themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.If the machine config is successfully deployed, the previous output contains the
/etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/99-<interface>-mtu.conffile path and theExecStart=/usr/local/bin/mtu-migration.shline.
To finalize the MTU migration, enter one of the following commands:
If you are using the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": null, "defaultNetwork":{ "ovnKubernetesConfig": { "mtu": <mtu> }}}}'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": null, "defaultNetwork":{ "ovnKubernetesConfig": { "mtu": <mtu> }}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<mtu>-
Specifies the new cluster network MTU that you specified with
<overlay_to>.
If you are using the OpenShift SDN network plugin:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": null, "defaultNetwork":{ "openshiftSDNConfig": { "mtu": <mtu> }}}}'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch \ '{"spec": { "migration": null, "defaultNetwork":{ "openshiftSDNConfig": { "mtu": <mtu> }}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<mtu>-
Specifies the new cluster network MTU that you specified with
<overlay_to>.
After finalizing the MTU migration, each MCP node is rebooted one by one. You must wait until all the nodes are updated. Check the machine config pool status by entering the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successfully updated node has the following status:
UPDATED=true,UPDATING=false,DEGRADED=false.
Verification
You can verify that a node in your cluster uses an MTU that you specified in the previous procedure.
To get the current MTU for the cluster network, enter the following command:
oc describe network.config cluster
$ oc describe network.config clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the current MTU for the primary network interface of a node.
To list the nodes in your cluster, enter the following command:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To obtain the current MTU setting for the primary network interface on a node, enter the following command:
oc debug node/<node> -- chroot /host ip address show <interface>
$ oc debug node/<node> -- chroot /host ip address show <interface>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<node>- Specifies a node from the output from the previous step.
<interface>- Specifies the primary network interface name for the node.
Example output
ens3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 8051
ens3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 8051Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 12. Configuring the node port service range
During cluster installation, you can configure the node port range to meet the requirements of your cluster. After cluster installation, only a cluster administrator can expand the range as a postinstallation task. If your cluster uses a large number of node ports, consider increasing the available port range according to the requirements of your cluster.
If you do not set a node port range during cluster installation, the default range of 30000-32768 applies to your cluster. In this situation, you can expand the range on either side, but you must preserve 30000-32768 within your new port range.
Red Hat has not performed testing outside the default port range of 30000-32768. For ranges outside the default port range, ensure that you test to verify the expanding node port range does not impact your cluster. In particular, ensure that there is:
- No overlap with any ports already in use by host processes
- No overlap with any ports already in use by pods that are configured with host networking
If you expanded the range and a port allocation issue occurs, create a new cluster and set the required range for it.
If you expand the node port range and OpenShift CLI (oc) stops working because of a port conflict with the OpenShift Container Platform API server, you must create a new cluster.
12.1. Expanding the node port range
You can expand the node port range for your cluster. After you install your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, you cannot shrink the node port range on either side of the currently configured range.
Red Hat has not performed testing outside the default port range of 30000-32768. For ranges outside the default port range, ensure that you test to verify that expanding your node port range does not impact your cluster. If you expanded the range and a port allocation issue occurs, create a new cluster and set the required range for it.
Prerequisites
-
Installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Logged in to the cluster as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. -
You ensured that your cluster infrastructure allows access to the ports that exist in the extended range. For example, if you expand the node port range to
30000-32900, your firewall or packet filtering configuration must allow the inclusive port range of30000-32900.
Procedure
To expand the range for the
serviceNodePortRangeparameter in thenetwork.config.openshift.ioobject that your cluster uses to manage traffic for pods, enter the following command:oc patch network.config.openshift.io cluster --type=merge -p \ '{ "spec": { "serviceNodePortRange": "<port_range>" } }'$ oc patch network.config.openshift.io cluster --type=merge -p \ '{ "spec": { "serviceNodePortRange": "<port_range>" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<port_range>-
specifies your expanded range, such as
30000-32900.
TipYou can also apply the following YAML to update the node port range:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To confirm that the updated configuration is active, enter the following command. The update can take several minutes to apply.
oc get configmaps -n openshift-kube-apiserver config \ -o jsonpath="{.data['config\.yaml']}" | \ grep -Eo '"service-node-port-range":["[[:digit:]]+-[[:digit:]]+"]'$ oc get configmaps -n openshift-kube-apiserver config \ -o jsonpath="{.data['config\.yaml']}" | \ grep -Eo '"service-node-port-range":["[[:digit:]]+-[[:digit:]]+"]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
"service-node-port-range":["30000-32900"]
"service-node-port-range":["30000-32900"]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 13. Configuring the cluster network range
As a cluster administrator, you can expand the cluster network range after cluster installation. You might want to expand the cluster network range if you need more IP addresses for additional nodes.
For example, if you deployed a cluster and specified 10.128.0.0/19 as the cluster network range and a host prefix of 23, you are limited to 16 nodes. You can expand that to 510 nodes by changing the CIDR mask on a cluster to /14.
When expanding the cluster network address range, your cluster must use the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. Other network plugins are not supported.
The following limitations apply when modifying the cluster network IP address range:
- The CIDR mask size specified must always be smaller than the currently configured CIDR mask size, because you can only increase IP space by adding more nodes to an installed cluster
- The host prefix cannot be modified
- Pods that are configured with an overridden default gateway must be recreated after the cluster network expands
13.1. Expanding the cluster network IP address range
You can expand the IP address range for the cluster network. Because this change requires rolling out a new Operator configuration across the cluster, it can take up to 30 minutes to take effect.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Ensure that the cluster uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
Procedure
To obtain the cluster network range and host prefix for your cluster, enter the following command:
oc get network.operator.openshift.io \ -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.clusterNetwork}"$ oc get network.operator.openshift.io \ -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.clusterNetwork}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
[{"cidr":"10.217.0.0/22","hostPrefix":23}][{"cidr":"10.217.0.0/22","hostPrefix":23}]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To expand the cluster network IP address range, enter the following command. Use the CIDR IP address range and host prefix returned from the output of the previous command.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<network>-
Specifies the network part of the
cidrfield that you obtained from the previous step. You cannot change this value. <cidr>-
Specifies the network prefix length. For example,
14. Change this value to a smaller number than the value from the output in the previous step to expand the cluster network range. <prefix>-
Specifies the current host prefix for your cluster. This value must be the same value for the
hostPrefixfield that you obtained from the previous step.
Example command
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the configuration is active, enter the following command. It can take up to 30 minutes for this change to take effect.
oc get network.operator.openshift.io \ -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.clusterNetwork}"$ oc get network.operator.openshift.io \ -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.clusterNetwork}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
[{"cidr":"10.217.0.0/14","hostPrefix":23}][{"cidr":"10.217.0.0/14","hostPrefix":23}]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 14. Configuring IP failover
This topic describes configuring IP failover for pods and services on your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
IP failover uses Keepalived to host a set of externally accessible Virtual IP (VIP) addresses on a set of hosts. Each VIP address is only serviced by a single host at a time. Keepalived uses the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) to determine which host, from the set of hosts, services which VIP. If a host becomes unavailable, or if the service that Keepalived is watching does not respond, the VIP is switched to another host from the set. This means a VIP is always serviced as long as a host is available.
Every VIP in the set is serviced by a node selected from the set. If a single node is available, the VIPs are served. There is no way to explicitly distribute the VIPs over the nodes, so there can be nodes with no VIPs and other nodes with many VIPs. If there is only one node, all VIPs are on it.
The administrator must ensure that all of the VIP addresses meet the following requirements:
- Accessible on the configured hosts from outside the cluster.
- Not used for any other purpose within the cluster.
Keepalived on each node determines whether the needed service is running. If it is, VIPs are supported and Keepalived participates in the negotiation to determine which node serves the VIP. For a node to participate, the service must be listening on the watch port on a VIP or the check must be disabled.
Each VIP in the set might be served by a different node.
IP failover monitors a port on each VIP to determine whether the port is reachable on the node. If the port is not reachable, the VIP is not assigned to the node. If the port is set to 0, this check is suppressed. The check script does the needed testing.
When a node running Keepalived passes the check script, the VIP on that node can enter the master state based on its priority and the priority of the current master and as determined by the preemption strategy.
A cluster administrator can provide a script through the OPENSHIFT_HA_NOTIFY_SCRIPT variable, and this script is called whenever the state of the VIP on the node changes. Keepalived uses the master state when it is servicing the VIP, the backup state when another node is servicing the VIP, or in the fault state when the check script fails. The notify script is called with the new state whenever the state changes.
You can create an IP failover deployment configuration on OpenShift Container Platform. The IP failover deployment configuration specifies the set of VIP addresses, and the set of nodes on which to service them. A cluster can have multiple IP failover deployment configurations, with each managing its own set of unique VIP addresses. Each node in the IP failover configuration runs an IP failover pod, and this pod runs Keepalived.
When using VIPs to access a pod with host networking, the application pod runs on all nodes that are running the IP failover pods. This enables any of the IP failover nodes to become the master and service the VIPs when needed. If application pods are not running on all nodes with IP failover, either some IP failover nodes never service the VIPs or some application pods never receive any traffic. Use the same selector and replication count, for both IP failover and the application pods, to avoid this mismatch.
While using VIPs to access a service, any of the nodes can be in the IP failover set of nodes, since the service is reachable on all nodes, no matter where the application pod is running. Any of the IP failover nodes can become master at any time. The service can either use external IPs and a service port or it can use a NodePort. Setting up a NodePort is a privileged operation.
When using external IPs in the service definition, the VIPs are set to the external IPs, and the IP failover monitoring port is set to the service port. When using a node port, the port is open on every node in the cluster, and the service load-balances traffic from whatever node currently services the VIP. In this case, the IP failover monitoring port is set to the NodePort in the service definition.
Even though a service VIP is highly available, performance can still be affected. Keepalived makes sure that each of the VIPs is serviced by some node in the configuration, and several VIPs can end up on the same node even when other nodes have none. Strategies that externally load-balance across a set of VIPs can be thwarted when IP failover puts multiple VIPs on the same node.
When you use ExternalIP, you can set up IP failover to have the same VIP range as the ExternalIP range. You can also disable the monitoring port. In this case, all of the VIPs appear on same node in the cluster. Any user can set up a service with an ExternalIP and make it highly available.
There are a maximum of 254 VIPs in the cluster.
14.1. IP failover environment variables
The following table contains the variables used to configure IP failover.
| Variable Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IP failover pod tries to open a TCP connection to this port on each Virtual IP (VIP). If connection is established, the service is considered to be running. If this port is set to |
|
|
The interface name that IP failover uses to send Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) traffic. The default value is
If your cluster uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, set this value to | |
|
|
|
The number of replicas to create. This must match |
|
|
The list of IP address ranges to replicate. This must be provided. For example, | |
|
|
|
The offset value used to set the virtual router IDs. Using different offset values allows multiple IP failover configurations to exist within the same cluster. The default offset is |
|
|
The number of groups to create for VRRP. If not set, a group is created for each virtual IP range specified with the | |
|
| INPUT |
The name of the iptables chain, to automatically add an |
|
| The full path name in the pod file system of a script that is periodically run to verify the application is operating. | |
|
|
| The period, in seconds, that the check script is run. |
|
| The full path name in the pod file system of a script that is run whenever the state changes. | |
|
|
|
The strategy for handling a new higher priority host. The |
14.2. Configuring IP failover in your cluster
As a cluster administrator, you can configure IP failover on an entire cluster, or on a subset of nodes, as defined by the label selector. You can also configure multiple IP failover deployments in your cluster, where each one is independent of the others.
The IP failover deployment ensures that a failover pod runs on each of the nodes matching the constraints or the label used.
This pod runs Keepalived, which can monitor an endpoint and use Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) to fail over the virtual IP (VIP) from one node to another if the first node cannot reach the service or endpoint.
For production use, set a selector that selects at least two nodes, and set replicas equal to the number of selected nodes.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in to the cluster as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You created a pull secret.
Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) only:
- You installed an RHOSP client (RHCOS documentation) on the target environment.
-
You also downloaded the RHOSP
openrc.shrc file (RHCOS documentation).
Procedure
Create an IP failover service account:
oc create sa ipfailover
$ oc create sa ipfailoverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update security context constraints (SCC) for
hostNetwork:oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged -z ipfailover
$ oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged -z ipfailoverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc adm policy add-scc-to-user hostnetwork -z ipfailover
$ oc adm policy add-scc-to-user hostnetwork -z ipfailoverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) only: Complete the following steps to make a failover VIP address reachable on RHOSP ports.
Use the RHOSP CLI to show the default RHOSP API and VIP addresses in the
allowed_address_pairsparameter of your RHOSP cluster:openstack port show <cluster_name> -c allowed_address_pairs
$ openstack port show <cluster_name> -c allowed_address_pairsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Output example
*Field* *Value* allowed_address_pairs ip_address='192.168.0.5', mac_address='fa:16:3e:31:f9:cb' ip_address='192.168.0.7', mac_address='fa:16:3e:31:f9:cb'*Field* *Value* allowed_address_pairs ip_address='192.168.0.5', mac_address='fa:16:3e:31:f9:cb' ip_address='192.168.0.7', mac_address='fa:16:3e:31:f9:cb'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set a different VIP address for the IP failover deployment and make the address reachable on RHOSP ports by entering the following command in the RHOSP CLI. Do not set any default RHOSP API and VIP addresses as the failover VIP address for the IP failover deployment.
Example of adding the
1.1.1.1failover IP address as an allowed address on RHOSP ports.openstack port set <cluster_name> --allowed-address ip-address=1.1.1.1,mac-address=fa:fa:16:3e:31:f9:cb
$ openstack port set <cluster_name> --allowed-address ip-address=1.1.1.1,mac-address=fa:fa:16:3e:31:f9:cbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a deployment YAML file to configure IP failover for your deployment. See "Example deployment YAML for IP failover configuration" in a later step.
Specify the following specification in the IP failover deployment so that you pass the failover VIP address to the
OPENSHIFT_HA_VIRTUAL_IPSenvironment variable:Example of adding the
1.1.1.1VIP address toOPENSHIFT_HA_VIRTUAL_IPSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a deployment YAML file to configure IP failover.
NoteFor Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), you do not need to re-create the deployment YAML file. You already created this file as part of the earlier instructions.
Example deployment YAML for IP failover configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the IP failover deployment.
- 2
- The list of IP address ranges to replicate. This must be provided. For example,
1.2.3.4-6,1.2.3.9. - 3
- The number of groups to create for VRRP. If not set, a group is created for each virtual IP range specified with the
OPENSHIFT_HA_VIP_GROUPSvariable. - 4
- The interface name that IP failover uses to send VRRP traffic. By default,
eth0is used. - 5
- The IP failover pod tries to open a TCP connection to this port on each VIP. If connection is established, the service is considered to be running. If this port is set to
0, the test always passes. The default value is80. - 6
- The offset value used to set the virtual router IDs. Using different offset values allows multiple IP failover configurations to exist within the same cluster. The default offset is
0, and the allowed range is0through255. - 7
- The number of replicas to create. This must match
spec.replicasvalue in IP failover deployment configuration. The default value is2. - 8
- The name of the
iptableschain to automatically add aniptablesrule to allow the VRRP traffic on. If the value is not set, aniptablesrule is not added. If the chain does not exist, it is not created, and Keepalived operates in unicast mode. The default isINPUT. - 9
- The full path name in the pod file system of a script that is run whenever the state changes.
- 10
- The full path name in the pod file system of a script that is periodically run to verify the application is operating.
- 11
- The strategy for handling a new higher priority host. The default value is
preempt_delay 300, which causes a Keepalived instance to take over a VIP after 5 minutes if a lower-priority master is holding the VIP. - 12
- The period, in seconds, that the check script is run. The default value is
2. - 13
- Create the pull secret before creating the deployment, otherwise you will get an error when creating the deployment.
14.3. Configuring check and notify scripts
Keepalived monitors the health of the application by periodically running an optional user-supplied check script. For example, the script can test a web server by issuing a request and verifying the response. As cluster administrator, you can provide an optional notify script, which is called whenever the state changes.
The check and notify scripts run in the IP failover pod and use the pod file system, not the host file system. However, the IP failover pod makes the host file system available under the /hosts mount path. When configuring a check or notify script, you must provide the full path to the script. The recommended approach for providing the scripts is to use a ConfigMap object.
The full path names of the check and notify scripts are added to the Keepalived configuration file, _/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf, which is loaded every time Keepalived starts. The scripts can be added to the pod with a ConfigMap object as described in the following methods.
Check script
When a check script is not provided, a simple default script is run that tests the TCP connection. This default test is suppressed when the monitor port is 0.
Each IP failover pod manages a Keepalived daemon that manages one or more virtual IP (VIP) addresses on the node where the pod is running. The Keepalived daemon keeps the state of each VIP for that node. A particular VIP on a particular node might be in master, backup, or fault state.
If the check script returns non-zero, the node enters the backup state, and any VIPs it holds are reassigned.
Notify script
Keepalived passes the following three parameters to the notify script:
-
$1-grouporinstance -
$2- Name of thegrouporinstance -
$3- The new state:master,backup, orfault
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the desired script and create a
ConfigMapobject to hold it. The script has no input arguments and must return0forOKand1forfail.The check script,
mycheckscript.sh:#!/bin/bash # Whatever tests are needed # E.g., send request and verify response exit 0#!/bin/bash # Whatever tests are needed # E.g., send request and verify response exit 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
ConfigMapobject :oc create configmap mycustomcheck --from-file=mycheckscript.sh
$ oc create configmap mycustomcheck --from-file=mycheckscript.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the script to the pod. The
defaultModefor the mountedConfigMapobject files must able to run by usingoccommands or by editing the deployment configuration. A value of0755,493decimal, is typical:oc set env deploy/ipfailover-keepalived \ OPENSHIFT_HA_CHECK_SCRIPT=/etc/keepalive/mycheckscript.sh$ oc set env deploy/ipfailover-keepalived \ OPENSHIFT_HA_CHECK_SCRIPT=/etc/keepalive/mycheckscript.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc set volume deploy/ipfailover-keepalived --add --overwrite \ --name=config-volume \ --mount-path=/etc/keepalive \ --source='{"configMap": { "name": "mycustomcheck", "defaultMode": 493}}'$ oc set volume deploy/ipfailover-keepalived --add --overwrite \ --name=config-volume \ --mount-path=/etc/keepalive \ --source='{"configMap": { "name": "mycustomcheck", "defaultMode": 493}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe
oc set envcommand is whitespace sensitive. There must be no whitespace on either side of the=sign.TipYou can alternatively edit the
ipfailover-keepaliveddeployment configuration:oc edit deploy ipfailover-keepalived
$ oc edit deploy ipfailover-keepalivedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In the
spec.container.envfield, add theOPENSHIFT_HA_CHECK_SCRIPTenvironment variable to point to the mounted script file. - 2
- Add the
spec.container.volumeMountsfield to create the mount point. - 3
- Add a new
spec.volumesfield to mention the config map. - 4
- This sets run permission on the files. When read back, it is displayed in decimal,
493.
Save the changes and exit the editor. This restarts
ipfailover-keepalived.
14.4. Configuring VRRP preemption
When a Virtual IP (VIP) on a node leaves the fault state by passing the check script, the VIP on the node enters the backup state if it has lower priority than the VIP on the node that is currently in the master state. The nopreempt strategy does not move master from the lower priority VIP on the host to the higher priority VIP on the host. With preempt_delay 300, the default, Keepalived waits the specified 300 seconds and moves master to the higher priority VIP on the host.
Procedure
To specify preemption enter
oc edit deploy ipfailover-keepalivedto edit the router deployment configuration:oc edit deploy ipfailover-keepalived
$ oc edit deploy ipfailover-keepalivedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set the
OPENSHIFT_HA_PREEMPTIONvalue:-
preempt_delay 300: Keepalived waits the specified 300 seconds and movesmasterto the higher priority VIP on the host. This is the default value. -
nopreempt: does not movemasterfrom the lower priority VIP on the host to the higher priority VIP on the host.
-
14.5. Deploying multiple IP failover instances
Each IP failover pod managed by the IP failover deployment configuration, 1 pod per node or replica, runs a Keepalived daemon. As more IP failover deployment configurations are configured, more pods are created and more daemons join into the common Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) negotiation. This negotiation is done by all the Keepalived daemons and it determines which nodes service which virtual IPs (VIP).
Internally, Keepalived assigns a unique vrrp-id to each VIP. The negotiation uses this set of vrrp-ids, when a decision is made, the VIP corresponding to the winning vrrp-id is serviced on the winning node.
Therefore, for every VIP defined in the IP failover deployment configuration, the IP failover pod must assign a corresponding vrrp-id. This is done by starting at OPENSHIFT_HA_VRRP_ID_OFFSET and sequentially assigning the vrrp-ids to the list of VIPs. The vrrp-ids can have values in the range 1..255.
When there are multiple IP failover deployment configurations, you must specify OPENSHIFT_HA_VRRP_ID_OFFSET so that there is room to increase the number of VIPs in the deployment configuration and none of the vrrp-id ranges overlap.
14.6. Configuring IP failover for more than 254 addresses
IP failover management is limited to 254 groups of Virtual IP (VIP) addresses. By default OpenShift Container Platform assigns one IP address to each group. You can use the OPENSHIFT_HA_VIP_GROUPS variable to change this so multiple IP addresses are in each group and define the number of VIP groups available for each Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) instance when configuring IP failover.
Grouping VIPs creates a wider range of allocation of VIPs per VRRP in the case of VRRP failover events, and is useful when all hosts in the cluster have access to a service locally. For example, when a service is being exposed with an ExternalIP.
As a rule for failover, do not limit services, such as the router, to one specific host. Instead, services should be replicated to each host so that in the case of IP failover, the services do not have to be recreated on the new host.
If you are using OpenShift Container Platform health checks, the nature of IP failover and groups means that all instances in the group are not checked. For that reason, the Kubernetes health checks must be used to ensure that services are live.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To change the number of IP addresses assigned to each group, change the value for the
OPENSHIFT_HA_VIP_GROUPSvariable, for example:Example
DeploymentYAML for IP failover configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If
OPENSHIFT_HA_VIP_GROUPSis set to3in an environment with seven VIPs, it creates three groups, assigning three VIPs to the first group, and two VIPs to the two remaining groups.
If the number of groups set by OPENSHIFT_HA_VIP_GROUPS is fewer than the number of IP addresses set to fail over, the group contains more than one IP address, and all of the addresses move as a single unit.
14.7. High availability For ExternalIP
In non-cloud clusters, IP failover and ExternalIP to a service can be combined. The result is high availability services for users that create services using ExternalIP.
The approach is to specify an spec.ExternalIP.autoAssignCIDRs range of the cluster network configuration, and then use the same range in creating the IP failover configuration.
Because IP failover can support up to a maximum of 255 VIPs for the entire cluster, the spec.ExternalIP.autoAssignCIDRs must be /24 or smaller.
14.8. Removing IP failover
When IP failover is initially configured, the worker nodes in the cluster are modified with an iptables rule that explicitly allows multicast packets on 224.0.0.18 for Keepalived. Because of the change to the nodes, removing IP failover requires running a job to remove the iptables rule and removing the virtual IP addresses used by Keepalived.
Procedure
Optional: Identify and delete any check and notify scripts that are stored as config maps:
Identify whether any pods for IP failover use a config map as a volume:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Namespace: default Pod: keepalived-worker-59df45db9c-2x9mn Volumes that use config maps: volume: config-volume configMap: mycustomcheck
Namespace: default Pod: keepalived-worker-59df45db9c-2x9mn Volumes that use config maps: volume: config-volume configMap: mycustomcheckCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the preceding step provided the names of config maps that are used as volumes, delete the config maps:
oc delete configmap <configmap_name>
$ oc delete configmap <configmap_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Identify an existing deployment for IP failover:
oc get deployment -l ipfailover
$ oc get deployment -l ipfailoverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE default ipfailover 2/2 2 2 105d
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE default ipfailover 2/2 2 2 105dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the deployment:
oc delete deployment <ipfailover_deployment_name>
$ oc delete deployment <ipfailover_deployment_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the
ipfailoverservice account:oc delete sa ipfailover
$ oc delete sa ipfailoverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run a job that removes the IP tables rule that was added when IP failover was initially configured:
Create a file such as
remove-ipfailover-job.yamlwith contents that are similar to the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the job:
oc create -f remove-ipfailover-job.yaml
$ oc create -f remove-ipfailover-job.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
job.batch/remove-ipfailover-2h8dm created
job.batch/remove-ipfailover-2h8dm createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Confirm that the job removed the initial configuration for IP failover.
oc logs job/remove-ipfailover-2h8dm
$ oc logs job/remove-ipfailover-2h8dmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
remove-failover.sh: OpenShift IP Failover service terminating. - Removing ip_vs module ... - Cleaning up ... - Releasing VIPs (interface eth0) ...
remove-failover.sh: OpenShift IP Failover service terminating. - Removing ip_vs module ... - Cleaning up ... - Releasing VIPs (interface eth0) ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 15. Configuring interface-level network sysctls
In Linux, sysctl allows an administrator to modify kernel parameters at runtime. You can modify interface-level network sysctls using the tuning Container Network Interface (CNI) meta plugin. The tuning CNI meta plugin operates in a chain with a main CNI plugin as illustrated.

The main CNI plugin assigns the interface and passes this to the tuning CNI meta plugin at runtime. You can change some sysctls and several interface attributes (promiscuous mode, all-multicast mode, MTU, and MAC address) in the network namespace by using the tuning CNI meta plugin. In the tuning CNI meta plugin configuration, the interface name is represented by the IFNAME token, and is replaced with the actual name of the interface at runtime.
In OpenShift Container Platform, the tuning CNI meta plugin only supports changing interface-level network sysctls.
15.1. Configuring the tuning CNI
The following procedure configures the tuning CNI to change the interface-level network net.ipv4.conf.IFNAME.accept_redirects sysctl. This example enables accepting and sending ICMP-redirected packets.
Procedure
Create a network attachment definition, such as
tuning-example.yaml, with the following content:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the name for the additional network attachment to create. The name must be unique within the specified namespace.
- 2
- Specifies the namespace that the object is associated with.
- 3
- Specifies the CNI specification version.
- 4
- Specifies the name for the configuration. It is recommended to match the configuration name to the name value of the network attachment definition.
- 5
- Specifies the name of the main CNI plugin to configure.
- 6
- Specifies the name of the CNI meta plugin.
- 7
- Specifies the sysctl to set.
An example yaml file is shown here:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the yaml by running the following command:
oc apply -f tuning-example.yaml
$ oc apply -f tuning-example.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkattachmentdefinition.k8.cni.cncf.io/tuningnad created
networkattachmentdefinition.k8.cni.cncf.io/tuningnad createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod such as
examplepod.yamlwith the network attachment definition similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the name of the configured
NetworkAttachmentDefinition. - 2
runAsUsercontrols which user ID the container is run with.- 3
runAsGroupcontrols which primary group ID the containers is run with.- 4
allowPrivilegeEscalationdetermines if a pod can request to allow privilege escalation. If unspecified, it defaults to true. This boolean directly controls whether theno_new_privsflag gets set on the container process.- 5
capabilitiespermit privileged actions without giving full root access. This policy ensures all capabilities are dropped from the pod.- 6
runAsNonRoot: truerequires that the container will run with a user with any UID other than 0.- 7
RuntimeDefaultenables the default seccomp profile for a pod or container workload.
Apply the yaml by running the following command:
oc apply -f examplepod.yaml
$ oc apply -f examplepod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the pod is created by running the following command:
oc get pod
$ oc get podCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tunepod 1/1 Running 0 47s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tunepod 1/1 Running 0 47sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in to the pod by running the following command:
oc rsh tunepod
$ oc rsh tunepodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the values of the configured sysctl flags. For example, find the value
net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirectsby running the following command:sysctl net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirects
sh-4.4# sysctl net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirectsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirects = 1
net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirects = 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 16. Using the Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)
As a cluster administrator, you can use the Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) on a bare-metal cluster.
16.1. Support for SCTP on OpenShift Container Platform
As a cluster administrator, you can enable SCTP on the hosts in the cluster. On Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS), the SCTP module is disabled by default.
SCTP is a reliable message based protocol that runs on top of an IP network.
When enabled, you can use SCTP as a protocol with pods, services, and network policy. A Service object must be defined with the type parameter set to either the ClusterIP or NodePort value.
16.1.1. Example configurations using SCTP protocol
You can configure a pod or service to use SCTP by setting the protocol parameter to the SCTP value in the pod or service object.
In the following example, a pod is configured to use SCTP:
In the following example, a service is configured to use SCTP:
In the following example, a NetworkPolicy object is configured to apply to SCTP network traffic on port 80 from any pods with a specific label:
16.2. Enabling Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)
As a cluster administrator, you can load and enable the blacklisted SCTP kernel module on worker nodes in your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a file named
load-sctp-module.yamlthat contains the following YAML definition:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the
MachineConfigobject, enter the following command:oc create -f load-sctp-module.yaml
$ oc create -f load-sctp-module.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To watch the status of the nodes while the MachineConfig Operator applies the configuration change, enter the following command. When the status of a node transitions to
Ready, the configuration update is applied.oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.3. Verifying Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is enabled
You can verify that SCTP is working on a cluster by creating a pod with an application that listens for SCTP traffic, associating it with a service, and then connecting to the exposed service.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the internet from the cluster to install the
ncpackage. -
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a pod starts an SCTP listener:
Create a file named
sctp-server.yamlthat defines a pod with the following YAML:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the pod by entering the following command:
oc create -f sctp-server.yaml
$ oc create -f sctp-server.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a service for the SCTP listener pod.
Create a file named
sctp-service.yamlthat defines a service with the following YAML:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the service, enter the following command:
oc create -f sctp-service.yaml
$ oc create -f sctp-service.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a pod for the SCTP client.
Create a file named
sctp-client.yamlwith the following YAML:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the
Podobject, enter the following command:oc apply -f sctp-client.yaml
$ oc apply -f sctp-client.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Run an SCTP listener on the server.
To connect to the server pod, enter the following command:
oc rsh sctpserver
$ oc rsh sctpserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To start the SCTP listener, enter the following command:
nc -l 30102 --sctp
$ nc -l 30102 --sctpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Connect to the SCTP listener on the server.
- Open a new terminal window or tab in your terminal program.
Obtain the IP address of the
sctpserviceservice. Enter the following command:oc get services sctpservice -o go-template='{{.spec.clusterIP}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc get services sctpservice -o go-template='{{.spec.clusterIP}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To connect to the client pod, enter the following command:
oc rsh sctpclient
$ oc rsh sctpclientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To start the SCTP client, enter the following command. Replace
<cluster_IP>with the cluster IP address of thesctpserviceservice.nc <cluster_IP> 30102 --sctp
# nc <cluster_IP> 30102 --sctpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 17. Using Precision Time Protocol (PTP) hardware
You can configure linuxptp services and use PTP-capable hardware in OpenShift Container Platform cluster nodes.
17.1. About PTP hardware
You can use the OpenShift Container Platform console or OpenShift CLI (oc) to install PTP by deploying the PTP Operator. The PTP Operator creates and manages the linuxptp services and provides the following features:
- Discovery of the PTP-capable devices in the cluster.
-
Management of the configuration of
linuxptpservices. -
Notification of PTP clock events that negatively affect the performance and reliability of your application with the PTP Operator
cloud-event-proxysidecar.
The PTP Operator works with PTP-capable devices on clusters provisioned only on bare-metal infrastructure.
17.2. About PTP
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is used to synchronize clocks in a network. When used in conjunction with hardware support, PTP is capable of sub-microsecond accuracy, and is more accurate than Network Time Protocol (NTP).
17.2.1. Elements of a PTP domain
PTP is used to synchronize multiple nodes connected in a network, with clocks for each node. The clocks synchronized by PTP are organized in a source-destination hierarchy. The hierarchy is created and updated automatically by the best master clock (BMC) algorithm, which runs on every clock. Destination clocks are synchronized to source clocks, and destination clocks can themselves be the source for other downstream clocks. The three primary types of PTP clocks are described below.
- Grandmaster clock
- The grandmaster clock provides standard time information to other clocks across the network and ensures accurate and stable synchronisation. It writes time stamps and responds to time requests from other clocks. Grandmaster clocks synchronize to a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) time source. The Grandmaster clock is the authoritative source of time in the network and is responsible for providing time synchronization to all other devices.
- Ordinary clock
- The ordinary clock has a single port connection that can play the role of source or destination clock, depending on its position in the network. The ordinary clock can read and write time stamps.
- Boundary clock
- The boundary clock has ports in two or more communication paths and can be a source and a destination to other destination clocks at the same time. The boundary clock works as a destination clock upstream. The destination clock receives the timing message, adjusts for delay, and then creates a new source time signal to pass down the network. The boundary clock produces a new timing packet that is still correctly synced with the source clock and can reduce the number of connected devices reporting directly to the source clock.
17.2.2. Advantages of PTP over NTP
One of the main advantages that PTP has over NTP is the hardware support present in various network interface controllers (NIC) and network switches. The specialized hardware allows PTP to account for delays in message transfer and improves the accuracy of time synchronization. To achieve the best possible accuracy, it is recommended that all networking components between PTP clocks are PTP hardware enabled.
Hardware-based PTP provides optimal accuracy, since the NIC can time stamp the PTP packets at the exact moment they are sent and received. Compare this to software-based PTP, which requires additional processing of the PTP packets by the operating system.
Before enabling PTP, ensure that NTP is disabled for the required nodes. You can disable the chrony time service (chronyd) using a MachineConfig custom resource. For more information, see Disabling chrony time service.
17.2.3. Using PTP with dual NIC hardware
OpenShift Container Platform supports single and dual NIC hardware for precision PTP timing in the cluster.
For 5G telco networks that deliver mid-band spectrum coverage, each virtual distributed unit (vDU) requires connections to 6 radio units (RUs). To make these connections, each vDU host requires 2 NICs configured as boundary clocks.
Dual NIC hardware allows you to connect each NIC to the same upstream leader clock with separate ptp4l instances for each NIC feeding the downstream clocks.
17.3. Overview of linuxptp in OpenShift Container Platform nodes
OpenShift Container Platform uses PTP and linuxptp for high precision system timing in bare-metal infrastructure. The linuxptp package includes the ts2phc, pmc, ptp4l, and phc2sys programs for system clock synchronization.
- ts2phc
ts2phcsynchronizes the PTP hardware clock (PHC) across PTP devices with a high degree of precision.ts2phcis used in grandmaster clock configurations. It receives the precision timing signal a high precision clock source such as Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). GNSS provides an accurate and reliable source of synchronized time for use in large distributed networks. GNSS clocks typically provide time information with a precision of a few nanoseconds.The
ts2phcsystem daemon sends timing information from the grandmaster clock to other PTP devices in the network by reading time information from the grandmaster clock and converting it to PHC format. PHC time is used by other devices in the network to synchronize their clocks with the grandmaster clock.- pmc
-
pmcimplements a PTP management client (pmc) according to IEEE standard 1588.1588.pmcprovides basic management access for theptp4lsystem daemon.pmcreads from standard input and sends the output over the selected transport, printing any replies it receives. - ptp4l
ptp4limplements the PTP boundary clock and ordinary clock and runs as a system daemon.ptp4ldoes the following:- Synchronizes the PHC to the source clock with hardware time stamping
- Synchronizes the system clock to the source clock with software time stamping
- phc2sys
-
phc2syssynchronizes the system clock to the PHC on the network interface controller (NIC). Thephc2syssystem daemon continuously monitors the PHC for timing information. When it detects a timing error, the PHC corrects the system clock.
17.4. Installing the PTP Operator using the CLI
As a cluster administrator, you can install the Operator by using the CLI.
Prerequisites
- A cluster installed on bare-metal hardware with nodes that have hardware that supports PTP.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a namespace for the PTP Operator.
Save the following YAML in the
ptp-namespace.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
NamespaceCR:oc create -f ptp-namespace.yaml
$ oc create -f ptp-namespace.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create an Operator group for the PTP Operator.
Save the following YAML in the
ptp-operatorgroup.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
OperatorGroupCR:oc create -f ptp-operatorgroup.yaml
$ oc create -f ptp-operatorgroup.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Subscribe to the PTP Operator.
Save the following YAML in the
ptp-sub.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
SubscriptionCR:oc create -f ptp-sub.yaml
$ oc create -f ptp-sub.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To verify that the Operator is installed, enter the following command:
oc get csv -n openshift-ptp -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phase
$ oc get csv -n openshift-ptp -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phaseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name Phase 4.13.0-202301261535 Succeeded
Name Phase 4.13.0-202301261535 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.5. Installing the PTP Operator using the web console
As a cluster administrator, you can install the PTP Operator using the web console.
You have to create the namespace and Operator group as mentioned in the previous section.
Procedure
Install the PTP Operator using the OpenShift Container Platform web console:
- In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, click Operators → OperatorHub.
- Choose PTP Operator from the list of available Operators, and then click Install.
- On the Install Operator page, under A specific namespace on the cluster select openshift-ptp. Then, click Install.
Optional: Verify that the PTP Operator installed successfully:
- Switch to the Operators → Installed Operators page.
Ensure that PTP Operator is listed in the openshift-ptp project with a Status of InstallSucceeded.
NoteDuring installation an Operator might display a Failed status. If the installation later succeeds with an InstallSucceeded message, you can ignore the Failed message.
If the Operator does not appear as installed, to troubleshoot further:
- Go to the Operators → Installed Operators page and inspect the Operator Subscriptions and Install Plans tabs for any failure or errors under Status.
-
Go to the Workloads → Pods page and check the logs for pods in the
openshift-ptpproject.
17.6. Configuring PTP devices
The PTP Operator adds the NodePtpDevice.ptp.openshift.io custom resource definition (CRD) to OpenShift Container Platform.
When installed, the PTP Operator searches your cluster for PTP-capable network devices on each node. It creates and updates a NodePtpDevice custom resource (CR) object for each node that provides a compatible PTP-capable network device.
17.6.1. Discovering PTP-capable network devices in your cluster
Identify PTP-capable network devices that exist in your cluster so that you can configure them
Prerequisties
- You installed the PTP Operator.
Procedure
To return a complete list of PTP capable network devices in your cluster, run the following command:
oc get NodePtpDevice -n openshift-ptp -o yaml
$ oc get NodePtpDevice -n openshift-ptp -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6.2. Configuring linuxptp services as a grandmaster clock
You can configure the linuxptp services (ptp4l, phc2sys, ts2phc) as a grandmaster clock (T-GM) by creating a PtpConfig custom resource (CR) that configures the host NIC.
The ts2phc utility allows you to synchronize the system clock with the PTP grandmaster clock so that the node can stream precision clock signal to downstream PTP ordinary clocks and boundary clocks.
Use the following example PtpConfig CR as the basis to configure linuxptp services as the grandmaster clock for your particular hardware and environment. This example CR does not configure PTP fast events. To configure PTP fast events, set appropriate values for ptp4lOpts, ptp4lConf, and ptpClockThreshold. ptpClockThreshold is used only when events are enabled. See "Configuring the PTP fast event notifications publisher" for more information.
Prerequisites
- For T-GM clocks in production environments, install an Intel E810 Westport Channel NIC in the bare-metal cluster host.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Create the
PtpConfigresource. For example:Depending on your requirements, use one of the following T-GM configurations for your deployment. Save the YAML in the
grandmaster-clock-ptp-config.yamlfile:Example 17.1. Example PTP grandmaster clock configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe example PTP grandmaster clock configuration is for test purposes only and is not intended for production.
Example 17.2. PTP grandmaster clock configuration for E810 NIC
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the CR by running the following command:
oc create -f grandmaster-clock-ptp-config.yaml
$ oc create -f grandmaster-clock-ptp-config.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Check that the
PtpConfigprofile is applied to the node.Get the list of pods in the
openshift-ptpnamespace by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-74m2g 3/3 Running 3 4d15h 10.16.230.7 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-5f4f48d7c-x7zkf 1/1 Running 1 4d15h 10.128.1.145 compute-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-74m2g 3/3 Running 3 4d15h 10.16.230.7 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-5f4f48d7c-x7zkf 1/1 Running 1 4d15h 10.128.1.145 compute-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the profile is correct. Examine the logs of the
linuxptpdaemon that corresponds to the node you specified in thePtpConfigprofile. Run the following command:oc logs linuxptp-daemon-74m2g -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-container
$ oc logs linuxptp-daemon-74m2g -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-containerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6.2.1. Grandmaster clock PtpConfig configuration reference
The following reference information describes the configuration options for the PtpConfig custom resource (CR) that configures the linuxptp services (ptp4l, phc2sys, ts2phc) as a grandmaster clock.
| PtpConfig CR field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specify an array of
The plugin mechanism allows the PTP Operator to do automated hardware configuration. For the Intel Westport Channel NIC, when |
|
|
Specify system configuration options for the |
|
|
Specify the required configuration to start |
|
| Specify the maximum amount of time to wait for the transmit (TX) timestamp from the sender before discarding the data. |
|
| Specify the JBOD boundary clock time delay value. This value is used to correct the time values that are passed between the network time devices. |
|
|
Specify system config options for the Note
Ensure that the network interface listed here is configured as grandmaster and is referenced as required in the |
|
|
Configure the scheduling policy for |
|
|
Set an integer value from 1-65 to configure FIFO priority for |
|
|
Optional. If |
|
|
Sets the configuration for the
|
|
|
Set options for the |
|
|
Specify an array of one or more |
|
|
Specify the |
|
|
Specify the |
|
|
Specify |
|
|
Set |
|
|
Set |
17.6.3. Configuring linuxptp services as an ordinary clock
You can configure linuxptp services (ptp4l, phc2sys) as ordinary clock by creating a PtpConfig custom resource (CR) object.
Use the following example PtpConfig CR as the basis to configure linuxptp services as an ordinary clock for your particular hardware and environment. This example CR does not configure PTP fast events. To configure PTP fast events, set appropriate values for ptp4lOpts, ptp4lConf, and ptpClockThreshold. ptpClockThreshold is required only when events are enabled. See "Configuring the PTP fast event notifications publisher" for more information.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Create the following
PtpConfigCR, and then save the YAML in theordinary-clock-ptp-config.yamlfile.Example PTP ordinary clock configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expand Table 17.2. PTP ordinary clock CR configuration options Custom resource field Description nameThe name of the
PtpConfigCR.profileSpecify an array of one or more
profileobjects. Each profile must be uniquely named.interfaceSpecify the network interface to be used by the
ptp4lservice, for exampleens787f1.ptp4lOptsSpecify system config options for the
ptp4lservice, for example-2to select the IEEE 802.3 network transport. The options should not include the network interface name-i <interface>and service config file-f /etc/ptp4l.confbecause the network interface name and the service config file are automatically appended. Append--summary_interval -4to use PTP fast events with this interface.phc2sysOptsSpecify system config options for the
phc2sysservice. If this field is empty, the PTP Operator does not start thephc2sysservice. For Intel Columbiaville 800 Series NICs, setphc2sysOptsoptions to-a -r -m -n 24 -N 8 -R 16.-mprints messages tostdout. Thelinuxptp-daemonDaemonSetparses the logs and generates Prometheus metrics.ptp4lConfSpecify a string that contains the configuration to replace the default
/etc/ptp4l.conffile. To use the default configuration, leave the field empty.tx_timestamp_timeoutFor Intel Columbiaville 800 Series NICs, set
tx_timestamp_timeoutto50.boundary_clock_jbodFor Intel Columbiaville 800 Series NICs, set
boundary_clock_jbodto0.ptpSchedulingPolicyScheduling policy for
ptp4landphc2sysprocesses. Default value isSCHED_OTHER. UseSCHED_FIFOon systems that support FIFO scheduling.ptpSchedulingPriorityInteger value from 1-65 used to set FIFO priority for
ptp4landphc2sysprocesses whenptpSchedulingPolicyis set toSCHED_FIFO. TheptpSchedulingPriorityfield is not used whenptpSchedulingPolicyis set toSCHED_OTHER.ptpClockThresholdOptional. If
ptpClockThresholdis not present, default values are used for theptpClockThresholdfields.ptpClockThresholdconfigures how long after the PTP master clock is disconnected before PTP events are triggered.holdOverTimeoutis the time value in seconds before the PTP clock event state changes toFREERUNwhen the PTP master clock is disconnected. ThemaxOffsetThresholdandminOffsetThresholdsettings configure offset values in nanoseconds that compare against the values forCLOCK_REALTIME(phc2sys) or master offset (ptp4l). When theptp4lorphc2sysoffset value is outside this range, the PTP clock state is set toFREERUN. When the offset value is within this range, the PTP clock state is set toLOCKED.recommendSpecify an array of one or more
recommendobjects that define rules on how theprofileshould be applied to nodes..recommend.profileSpecify the
.recommend.profileobject name defined in theprofilesection..recommend.prioritySet
.recommend.priorityto0for ordinary clock..recommend.matchSpecify
.recommend.matchrules withnodeLabelornodeNamevalues..recommend.match.nodeLabelSet
nodeLabelwith thekeyof thenode.Labelsfield from the node object by using theoc get nodes --show-labelscommand. For example,node-role.kubernetes.io/worker..recommend.match.nodeNameSet
nodeNamewith the value of thenode.Namefield from the node object by using theoc get nodescommand. For example,compute-1.example.com.Create the
PtpConfigCR by running the following command:oc create -f ordinary-clock-ptp-config.yaml
$ oc create -f ordinary-clock-ptp-config.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Check that the
PtpConfigprofile is applied to the node.Get the list of pods in the
openshift-ptpnamespace by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-tdspf 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-657bbb64c8-2f8sj 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-tdspf 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-657bbb64c8-2f8sj 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the profile is correct. Examine the logs of the
linuxptpdaemon that corresponds to the node you specified in thePtpConfigprofile. Run the following command:oc logs linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-container
$ oc logs linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-containerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6.4. Configuring linuxptp services as a boundary clock
You can configure the linuxptp services (ptp4l, phc2sys) as boundary clock by creating a PtpConfig custom resource (CR) object.
Use the following example PtpConfig CR as the basis to configure linuxptp services as the boundary clock for your particular hardware and environment. This example CR does not configure PTP fast events. To configure PTP fast events, set appropriate values for ptp4lOpts, ptp4lConf, and ptpClockThreshold. ptpClockThreshold is used only when events are enabled. See "Configuring the PTP fast event notifications publisher" for more information.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Create the following
PtpConfigCR, and then save the YAML in theboundary-clock-ptp-config.yamlfile.Example PTP boundary clock configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expand Table 17.3. PTP boundary clock CR configuration options Custom resource field Description nameThe name of the
PtpConfigCR.profileSpecify an array of one or more
profileobjects.nameSpecify the name of a profile object which uniquely identifies a profile object.
ptp4lOptsSpecify system config options for the
ptp4lservice. The options should not include the network interface name-i <interface>and service config file-f /etc/ptp4l.confbecause the network interface name and the service config file are automatically appended.ptp4lConfSpecify the required configuration to start
ptp4las boundary clock. For example,ens1f0synchronizes from a grandmaster clock andens1f3synchronizes connected devices.<interface_1>The interface that receives the synchronization clock.
<interface_2>The interface that sends the synchronization clock.
tx_timestamp_timeoutFor Intel Columbiaville 800 Series NICs, set
tx_timestamp_timeoutto50.boundary_clock_jbodFor Intel Columbiaville 800 Series NICs, ensure
boundary_clock_jbodis set to0. For Intel Fortville X710 Series NICs, ensureboundary_clock_jbodis set to1.phc2sysOptsSpecify system config options for the
phc2sysservice. If this field is empty, the PTP Operator does not start thephc2sysservice.ptpSchedulingPolicyScheduling policy for ptp4l and phc2sys processes. Default value is
SCHED_OTHER. UseSCHED_FIFOon systems that support FIFO scheduling.ptpSchedulingPriorityInteger value from 1-65 used to set FIFO priority for
ptp4landphc2sysprocesses whenptpSchedulingPolicyis set toSCHED_FIFO. TheptpSchedulingPriorityfield is not used whenptpSchedulingPolicyis set toSCHED_OTHER.ptpClockThresholdOptional. If
ptpClockThresholdis not present, default values are used for theptpClockThresholdfields.ptpClockThresholdconfigures how long after the PTP master clock is disconnected before PTP events are triggered.holdOverTimeoutis the time value in seconds before the PTP clock event state changes toFREERUNwhen the PTP master clock is disconnected. ThemaxOffsetThresholdandminOffsetThresholdsettings configure offset values in nanoseconds that compare against the values forCLOCK_REALTIME(phc2sys) or master offset (ptp4l). When theptp4lorphc2sysoffset value is outside this range, the PTP clock state is set toFREERUN. When the offset value is within this range, the PTP clock state is set toLOCKED.recommendSpecify an array of one or more
recommendobjects that define rules on how theprofileshould be applied to nodes..recommend.profileSpecify the
.recommend.profileobject name defined in theprofilesection..recommend.prioritySpecify the
prioritywith an integer value between0and99. A larger number gets lower priority, so a priority of99is lower than a priority of10. If a node can be matched with multiple profiles according to rules defined in thematchfield, the profile with the higher priority is applied to that node..recommend.matchSpecify
.recommend.matchrules withnodeLabelornodeNamevalues..recommend.match.nodeLabelSet
nodeLabelwith thekeyof thenode.Labelsfield from the node object by using theoc get nodes --show-labelscommand. For example,node-role.kubernetes.io/worker..recommend.match.nodeNameSet
nodeNamewith the value of thenode.Namefield from the node object by using theoc get nodescommand. For example,compute-1.example.com.Create the CR by running the following command:
oc create -f boundary-clock-ptp-config.yaml
$ oc create -f boundary-clock-ptp-config.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Check that the
PtpConfigprofile is applied to the node.Get the list of pods in the
openshift-ptpnamespace by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-tdspf 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-657bbb64c8-2f8sj 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-tdspf 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-657bbb64c8-2f8sj 1/1 Running 0 43m 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the profile is correct. Examine the logs of the
linuxptpdaemon that corresponds to the node you specified in thePtpConfigprofile. Run the following command:oc logs linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-container
$ oc logs linuxptp-daemon-4xkbb -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-containerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6.5. Configuring linuxptp services as boundary clocks for dual NIC hardware
You can configure the linuxptp services (ptp4l, phc2sys) as boundary clocks for dual-NIC hardware by creating a PtpConfig custom resource (CR) object for each NIC.
Dual NIC hardware allows you to connect each NIC to the same upstream leader clock with separate ptp4l instances for each NIC feeding the downstream clocks.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Create two separate
PtpConfigCRs, one for each NIC, using the reference CR in "Configuring linuxptp services as a boundary clock" as the basis for each CR. For example:Create
boundary-clock-ptp-config-nic1.yaml, specifying values forphc2sysOpts:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the required interfaces to start
ptp4las a boundary clock. For example,ens5f0synchronizes from a grandmaster clock andens5f1synchronizes connected devices. - 2
- Required
phc2sysOptsvalues.-mprints messages tostdout. Thelinuxptp-daemonDaemonSetparses the logs and generates Prometheus metrics.
Create
boundary-clock-ptp-config-nic2.yaml, removing thephc2sysOptsfield altogether to disable thephc2sysservice for the second NIC:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the required interfaces to start
ptp4las a boundary clock on the second NIC.
NoteYou must completely remove the
phc2sysOptsfield from the secondPtpConfigCR to disable thephc2sysservice on the second NIC.
Create the dual NIC
PtpConfigCRs by running the following commands:Create the CR that configures PTP for the first NIC:
oc create -f boundary-clock-ptp-config-nic1.yaml
$ oc create -f boundary-clock-ptp-config-nic1.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the CR that configures PTP for the second NIC:
oc create -f boundary-clock-ptp-config-nic2.yaml
$ oc create -f boundary-clock-ptp-config-nic2.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Check that the PTP Operator has applied the
PtpConfigCRs for both NICs. Examine the logs for thelinuxptpdaemon corresponding to the node that has the dual NIC hardware installed. For example, run the following command:oc logs linuxptp-daemon-cvgr6 -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-container
$ oc logs linuxptp-daemon-cvgr6 -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-containerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ptp4l[80828.335]: [ptp4l.1.config] master offset 5 s2 freq -5727 path delay 519 ptp4l[80828.343]: [ptp4l.0.config] master offset -5 s2 freq -10607 path delay 533 phc2sys[80828.390]: [ptp4l.0.config] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 1 s2 freq -87239 delay 539
ptp4l[80828.335]: [ptp4l.1.config] master offset 5 s2 freq -5727 path delay 519 ptp4l[80828.343]: [ptp4l.0.config] master offset -5 s2 freq -10607 path delay 533 phc2sys[80828.390]: [ptp4l.0.config] CLOCK_REALTIME phc offset 1 s2 freq -87239 delay 539Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6.6. Intel Columbiaville E800 series NIC as PTP ordinary clock reference
The following table describes the changes that you must make to the reference PTP configuration in order to use Intel Columbiaville E800 series NICs as ordinary clocks. Make the changes in a PtpConfig custom resource (CR) that you apply to the cluster.
| PTP configuration | Recommended setting |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For phc2sysOpts, -m prints messages to stdout. The linuxptp-daemon DaemonSet parses the logs and generates Prometheus metrics.
17.6.7. Configuring FIFO priority scheduling for PTP hardware
In telco or other deployment configurations that require low latency performance, PTP daemon threads run in a constrained CPU footprint alongside the rest of the infrastructure components. By default, PTP threads run with the SCHED_OTHER policy. Under high load, these threads might not get the scheduling latency they require for error-free operation.
To mitigate against potential scheduling latency errors, you can configure the PTP Operator linuxptp services to allow threads to run with a SCHED_FIFO policy. If SCHED_FIFO is set for a PtpConfig CR, then ptp4l and phc2sys will run in the parent container under chrt with a priority set by the ptpSchedulingPriority field of the PtpConfig CR.
Setting ptpSchedulingPolicy is optional, and is only required if you are experiencing latency errors.
Procedure
Edit the
PtpConfigCR profile:oc edit PtpConfig -n openshift-ptp
$ oc edit PtpConfig -n openshift-ptpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change the
ptpSchedulingPolicyandptpSchedulingPriorityfields:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Save and exit to apply the changes to the
PtpConfigCR.
Verification
Get the name of the
linuxptp-daemonpod and corresponding node where thePtpConfigCR has been applied:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-gmv2n 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-lgm55 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-3r4dcvf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 1d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-gmv2n 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-lgm55 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-3r4dcvf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 1d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the
ptp4lprocess is running with the updatedchrtFIFO priority:oc -n openshift-ptp logs linuxptp-daemon-lgm55 -c linuxptp-daemon-container|grep chrt
$ oc -n openshift-ptp logs linuxptp-daemon-lgm55 -c linuxptp-daemon-container|grep chrtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
I1216 19:24:57.091872 1600715 daemon.go:285] /bin/chrt -f 65 /usr/sbin/ptp4l -f /var/run/ptp4l.0.config -2 --summary_interval -4 -m
I1216 19:24:57.091872 1600715 daemon.go:285] /bin/chrt -f 65 /usr/sbin/ptp4l -f /var/run/ptp4l.0.config -2 --summary_interval -4 -mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6.8. Configuring log filtering for linuxptp services
The linuxptp daemon generates logs that you can use for debugging purposes. In telco or other deployment configurations that feature a limited storage capacity, these logs can add to the storage demand.
To reduce the number log messages, you can configure the PtpConfig custom resource (CR) to exclude log messages that report the master offset value. The master offset log message reports the difference between the current node’s clock and the master clock in nanoseconds.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Edit the
PtpConfigCR:oc edit PtpConfig -n openshift-ptp
$ oc edit PtpConfig -n openshift-ptpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In
spec.profile, add theptpSettings.logReducespecification and set the value totrue:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFor debugging purposes, you can revert this specification to
Falseto include the master offset messages.-
Save and exit to apply the changes to the
PtpConfigCR.
Verification
Get the name of the
linuxptp-daemonpod and corresponding node where thePtpConfigCR has been applied:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-gmv2n 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-lgm55 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-3r4dcvf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 1d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-gmv2n 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-lgm55 3/3 Running 0 1d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-3r4dcvf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 1d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that master offset messages are excluded from the logs by running the following command:
oc -n openshift-ptp logs <linux_daemon_container> -c linuxptp-daemon-container | grep "master offset"
$ oc -n openshift-ptp logs <linux_daemon_container> -c linuxptp-daemon-container | grep "master offset"1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- <linux_daemon_container> is the name of the
linuxptp-daemonpod, for examplelinuxptp-daemon-gmv2n.
When you configure the
logReducespecification, this command does not report any instances ofmaster offsetin the logs of thelinuxptpdaemon.
17.7. Troubleshooting common PTP Operator issues
Troubleshoot common problems with the PTP Operator by performing the following steps.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the PTP Operator on a bare-metal cluster with hosts that support PTP.
Procedure
Check the Operator and operands are successfully deployed in the cluster for the configured nodes.
oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-lmvgn 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-qhfg7 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-6b8dcbf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 5d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-lmvgn 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-qhfg7 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-6b8dcbf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 5d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen the PTP fast event bus is enabled, the number of ready
linuxptp-daemonpods is3/3. If the PTP fast event bus is not enabled,2/2is displayed.Check that supported hardware is found in the cluster.
oc -n openshift-ptp get nodeptpdevices.ptp.openshift.io
$ oc -n openshift-ptp get nodeptpdevices.ptp.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the available PTP network interfaces for a node:
oc -n openshift-ptp get nodeptpdevices.ptp.openshift.io <node_name> -o yaml
$ oc -n openshift-ptp get nodeptpdevices.ptp.openshift.io <node_name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- <node_name>
Specifies the node you want to query, for example,
compute-0.example.com.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Check that the PTP interface is successfully synchronized to the primary clock by accessing the
linuxptp-daemonpod for the corresponding node.Get the name of the
linuxptp-daemonpod and corresponding node you want to troubleshoot by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wide
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptp -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-lmvgn 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-qhfg7 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-6b8dcbf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 5d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.com
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE linuxptp-daemon-lmvgn 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.24 compute-0.example.com linuxptp-daemon-qhfg7 3/3 Running 0 4d17h 10.1.196.25 compute-1.example.com ptp-operator-6b8dcbf7f4-zndk7 1/1 Running 0 5d7h 10.129.0.61 control-plane-1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remote shell into the required
linuxptp-daemoncontainer:oc rsh -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-container <linux_daemon_container>
$ oc rsh -n openshift-ptp -c linuxptp-daemon-container <linux_daemon_container>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- <linux_daemon_container>
-
is the container you want to diagnose, for example
linuxptp-daemon-lmvgn.
In the remote shell connection to the
linuxptp-daemoncontainer, use the PTP Management Client (pmc) tool to diagnose the network interface. Run the followingpmccommand to check the sync status of the PTP device, for exampleptp4l.pmc -u -f /var/run/ptp4l.0.config -b 0 'GET PORT_DATA_SET'
# pmc -u -f /var/run/ptp4l.0.config -b 0 'GET PORT_DATA_SET'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output when the node is successfully synced to the primary clock
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.7.1. Collecting Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Operator data
You can use the oc adm must-gather CLI command to collect information about your cluster, including features and objects associated with Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Operator.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have installed the PTP Operator.
Procedure
To collect PTP Operator data with
must-gather, you must specify the PTP Operatormust-gatherimage.oc adm must-gather --image=registry.redhat.io/openshift4/ptp-must-gather-rhel8:v4.13
$ oc adm must-gather --image=registry.redhat.io/openshift4/ptp-must-gather-rhel8:v4.13Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.8. PTP hardware fast event notifications framework
Cloud native applications such as virtual RAN (vRAN) require access to notifications about hardware timing events that are critical to the functioning of the overall network. PTP clock synchronization errors can negatively affect the performance and reliability of your low-latency application, for example, a vRAN application running in a distributed unit (DU).
17.8.1. About PTP and clock synchronization error events
Loss of PTP synchronization is a critical error for a RAN network. If synchronization is lost on a node, the radio might be shut down and the network Over the Air (OTA) traffic might be shifted to another node in the wireless network. Fast event notifications mitigate against workload errors by allowing cluster nodes to communicate PTP clock sync status to the vRAN application running in the DU.
Event notifications are available to vRAN applications running on the same DU node. A publish-subscribe REST API passes events notifications to the messaging bus. Publish-subscribe messaging, or pub-sub messaging, is an asynchronous service-to-service communication architecture where any message published to a topic is immediately received by all of the subscribers to the topic.
The PTP Operator generates fast event notifications for every PTP-capable network interface. You can access the events by using a cloud-event-proxy sidecar container over an HTTP or Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) message bus.
PTP fast event notifications are available for network interfaces configured to use PTP ordinary clocks or PTP boundary clocks.
HTTP transport is the default transport for PTP and bare-metal events. Use HTTP transport instead of AMQP for PTP and bare-metal events where possible. AMQ Interconnect is EOL from 30 June 2024. Extended life cycle support (ELS) for AMQ Interconnect ends 29 November 2029. For more information see, Red Hat AMQ Interconnect support status.
17.8.2. About the PTP fast event notifications framework
Use the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) fast event notifications framework to subscribe cluster applications to PTP events that the bare-metal cluster node generates.
The fast events notifications framework uses a REST API for communication. The REST API is based on the O-RAN O-Cloud Notification API Specification for Event Consumers 3.0 that is available from O-RAN ALLIANCE Specifications.
The framework consists of a publisher, subscriber, and an AMQ or HTTP messaging protocol to handle communications between the publisher and subscriber applications. Applications run the cloud-event-proxy container in a sidecar pattern to subscribe to PTP events. The cloud-event-proxy sidecar container can access the same resources as the primary application container without using any of the resources of the primary application and with no significant latency.
HTTP transport is the default transport for PTP and bare-metal events. Use HTTP transport instead of AMQP for PTP and bare-metal events where possible. AMQ Interconnect is EOL from 30 June 2024. Extended life cycle support (ELS) for AMQ Interconnect ends 29 November 2029. For more information see, Red Hat AMQ Interconnect support status.
Figure 17.1. Overview of PTP fast events
-
 Event is generated on the cluster host
Event is generated on the cluster host -
linuxptp-daemonin the PTP Operator-managed pod runs as a KubernetesDaemonSetand manages the variouslinuxptpprocesses (ptp4l,phc2sys, and optionally for grandmaster clocks,ts2phc). Thelinuxptp-daemonpasses the event to the UNIX domain socket. -
 Event is passed to the cloud-event-proxy sidecar
Event is passed to the cloud-event-proxy sidecar -
The PTP plugin reads the event from the UNIX domain socket and passes it to the
cloud-event-proxysidecar in the PTP Operator-managed pod.cloud-event-proxydelivers the event from the Kubernetes infrastructure to Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs) with low latency. -
 Event is persisted
Event is persisted -
The
cloud-event-proxysidecar in the PTP Operator-managed pod processes the event and publishes the cloud-native event by using a REST API. -
 Message is transported
Message is transported -
The message transporter transports the event to the
cloud-event-proxysidecar in the application pod over HTTP or AMQP 1.0 QPID. -
 Event is available from the REST API
Event is available from the REST API -
The
cloud-event-proxysidecar in the Application pod processes the event and makes it available by using the REST API. -
 Consumer application requests a subscription and receives the subscribed event
Consumer application requests a subscription and receives the subscribed event -
The consumer application sends an API request to the
cloud-event-proxysidecar in the application pod to create a PTP events subscription. Thecloud-event-proxysidecar creates an AMQ or HTTP messaging listener protocol for the resource specified in the subscription.
The cloud-event-proxy sidecar in the application pod receives the event from the PTP Operator-managed pod, unwraps the cloud events object to retrieve the data, and posts the event to the consumer application. The consumer application listens to the address specified in the resource qualifier and receives and processes the PTP event.
17.8.3. Configuring the PTP fast event notifications publisher
To start using PTP fast event notifications for a network interface in your cluster, you must enable the fast event publisher in the PTP Operator PtpOperatorConfig custom resource (CR) and configure ptpClockThreshold values in a PtpConfig CR that you create.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (
oc). -
You have logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have installed the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Modify the default PTP Operator config to enable PTP fast events.
Save the following YAML in the
ptp-operatorconfig.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set
enableEventPublishertotrueto enable PTP fast event notifications.
NoteIn OpenShift Container Platform 4.13 or later, you do not need to set the
spec.ptpEventConfig.transportHostfield in thePtpOperatorConfigresource when you use HTTP transport for PTP events. SettransportHostonly when you use AMQP transport for PTP events.Update the
PtpOperatorConfigCR:oc apply -f ptp-operatorconfig.yaml
$ oc apply -f ptp-operatorconfig.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
PtpConfigcustom resource (CR) for the PTP enabled interface, and set the required values forptpClockThresholdandptp4lOpts. The following YAML illustrates the required values that you must set in thePtpConfigCR:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Append
--summary_interval -4to use PTP fast events. - 2
- Required
phc2sysOptsvalues.-mprints messages tostdout. Thelinuxptp-daemonDaemonSetparses the logs and generates Prometheus metrics. - 3
- Specify a string that contains the configuration to replace the default
/etc/ptp4l.conffile. To use the default configuration, leave the field empty. - 4
- Optional. If the
ptpClockThresholdstanza is not present, default values are used for theptpClockThresholdfields. The stanza shows defaultptpClockThresholdvalues. TheptpClockThresholdvalues configure how long after the PTP master clock is disconnected before PTP events are triggered.holdOverTimeoutis the time value in seconds before the PTP clock event state changes toFREERUNwhen the PTP master clock is disconnected. ThemaxOffsetThresholdandminOffsetThresholdsettings configure offset values in nanoseconds that compare against the values forCLOCK_REALTIME(phc2sys) or master offset (ptp4l). When theptp4lorphc2sysoffset value is outside this range, the PTP clock state is set toFREERUN. When the offset value is within this range, the PTP clock state is set toLOCKED.
17.8.4. Migrating consumer applications to use HTTP transport for PTP or bare-metal events
If you have previously deployed PTP or bare-metal events consumer applications, you need to update the applications to use HTTP message transport.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have updated the PTP Operator or Bare Metal Event Relay to version 4.13+ which uses HTTP transport by default.
Procedure
Update your events consumer application to use HTTP transport. Set the
http-event-publishersvariable for the cloud event sidecar deployment.For example, in a cluster with PTP events configured, the following YAML snippet illustrates a cloud event sidecar deployment:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The PTP Operator automatically resolves
NODE_NAMEto the host that is generating the PTP events. For example,compute-1.example.com.
In a cluster with bare-metal events configured, set the
http-event-publishersfield tohw-event-publisher-service.openshift-bare-metal-events.svc.cluster.local:9043in the cloud event sidecar deployment CR.Deploy the
consumer-events-subscription-serviceservice alongside the events consumer application. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.8.5. Installing the AMQ messaging bus
To pass PTP fast event notifications between publisher and subscriber on a node, you can install and configure an AMQ messaging bus to run locally on the node. To use AMQ messaging, you must install the AMQ Interconnect Operator.
HTTP transport is the default transport for PTP and bare-metal events. Use HTTP transport instead of AMQP for PTP and bare-metal events where possible. AMQ Interconnect is EOL from 30 June 2024. Extended life cycle support (ELS) for AMQ Interconnect ends 29 November 2029. For more information see, Red Hat AMQ Interconnect support status.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
-
Install the AMQ Interconnect Operator to its own
amq-interconnectnamespace. See Adding the Red Hat Integration - AMQ Interconnect Operator.
Verification
Check that the AMQ Interconnect Operator is available and the required pods are running:
oc get pods -n amq-interconnect
$ oc get pods -n amq-interconnectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE amq-interconnect-645db76c76-k8ghs 1/1 Running 0 23h interconnect-operator-5cb5fc7cc-4v7qm 1/1 Running 0 23h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE amq-interconnect-645db76c76-k8ghs 1/1 Running 0 23h interconnect-operator-5cb5fc7cc-4v7qm 1/1 Running 0 23hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the required
linuxptp-daemonPTP event producer pods are running in theopenshift-ptpnamespace.oc get pods -n openshift-ptp
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE linuxptp-daemon-2t78p 3/3 Running 0 12h linuxptp-daemon-k8n88 3/3 Running 0 12h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE linuxptp-daemon-2t78p 3/3 Running 0 12h linuxptp-daemon-k8n88 3/3 Running 0 12hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.8.6. Subscribing DU applications to PTP events REST API reference
Use the PTP event notifications REST API to subscribe a distributed unit (DU) application to the PTP events that are generated on the parent node.
Subscribe applications to PTP events by using the resource address /cluster/node/<node_name>/ptp, where <node_name> is the cluster node running the DU application.
Deploy your cloud-event-consumer DU application container and cloud-event-proxy sidecar container in a separate DU application pod. The cloud-event-consumer DU application subscribes to the cloud-event-proxy container in the application pod.
Use the following API endpoints to subscribe the cloud-event-consumer DU application to PTP events posted by the cloud-event-proxy container at http://localhost:8089/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/ in the DU application pod:
/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions-
POST: Creates a new subscription -
GET: Retrieves a list of subscriptions -
DELETE: Deletes all subscriptions
-
/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions/<subscription_id>-
GET: Returns details for the specified subscription ID -
DELETE: Deletes the subscription associated with the specified subscription ID
-
/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/health-
GET: Returns the health status ofocloudNotificationsAPI
-
api/ocloudNotifications/v1/publishers-
GET: Returns an array ofos-clock-sync-state,ptp-clock-class-change, andlock-statemessages for the cluster node
-
/api/ocloudnotifications/v1/{resource_address}/CurrentState-
GET: Returns the current state of one the following event types:os-clock-sync-state,ptp-clock-class-change, orlock-stateevents
-
9089 is the default port for the cloud-event-consumer container deployed in the application pod. You can configure a different port for your DU application as required.
17.8.6.1. api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions
HTTP method
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions
Description
Returns a list of subscriptions. If subscriptions exist, a 200 OK status code is returned along with the list of subscriptions.
Example API response
HTTP method
POST api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions
Description
Creates a new subscription. If a subscription is successfully created, or if it already exists, a 201 Created status code is returned.
| Parameter | Type |
|---|---|
| subscription | data |
Example payload
{
"uriLocation": "http://localhost:8089/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions",
"resource": "/cluster/node/compute-1.example.com/ptp"
}
{
"uriLocation": "http://localhost:8089/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions",
"resource": "/cluster/node/compute-1.example.com/ptp"
}HTTP method
DELETE api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions
Description
Deletes all subscriptions.
Example API response
{
"status": "deleted all subscriptions"
}
{
"status": "deleted all subscriptions"
}17.8.6.2. api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions/{subscription_id}
HTTP method
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions/{subscription_id}
Description
Returns details for the subscription with ID subscription_id.
| Parameter | Type |
|---|---|
|
| string |
Example API response
HTTP method
DELETE api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions/{subscription_id}
Description
Deletes the subscription with ID subscription_id.
| Parameter | Type |
|---|---|
|
| string |
Example API response
{
"status": "OK"
}
{
"status": "OK"
}17.8.6.3. api/ocloudNotifications/v1/health
HTTP method
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/health/
Description
Returns the health status for the ocloudNotifications REST API.
Example API response
OK
OK17.8.6.4. api/ocloudNotifications/v1/publishers
HTTP method
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/publishers
Description
Returns an array of os-clock-sync-state, ptp-clock-class-change, and lock-state details for the cluster node. The system generates notifications when the relevant equipment state changes.
-
os-clock-sync-statenotifications describe the host operating system clock synchronization state. Can be inLOCKEDorFREERUNstate. -
ptp-clock-class-changenotifications describe the current state of the PTP clock class. -
lock-statenotifications describe the current status of the PTP equipment lock state. Can be inLOCKED,HOLDOVERorFREERUNstate.
Example API response
You can find os-clock-sync-state, ptp-clock-class-change and lock-state events in the logs for the cloud-event-proxy container. For example:
oc logs -f linuxptp-daemon-cvgr6 -n openshift-ptp -c cloud-event-proxy
$ oc logs -f linuxptp-daemon-cvgr6 -n openshift-ptp -c cloud-event-proxyExample os-clock-sync-state event
Example ptp-clock-class-change event
Example lock-state event
17.8.6.5. api/ocloudNotifications/v1/{resource_address}/CurrentState
HTTP method
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/lock-state/CurrentState
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/sync-status/os-clock-sync-state/CurrentState
GET api/ocloudNotifications/v1/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/ptp-clock-class-change/CurrentState
Description
Configure the CurrentState API endpoint to return the current state of the os-clock-sync-state, ptp-clock-class-change, or lock-state events for the cluster node.
-
os-clock-sync-statenotifications describe the host operating system clock synchronization state. Can be inLOCKEDorFREERUNstate. -
ptp-clock-class-changenotifications describe the current state of the PTP clock class. -
lock-statenotifications describe the current status of the PTP equipment lock state. Can be inLOCKED,HOLDOVERorFREERUNstate.
| Parameter | Type |
|---|---|
|
| string |
Example lock-state API response
Example os-clock-sync-state API response
Example ptp-clock-class-change API response
17.8.7. Monitoring PTP fast event metrics
You can monitor PTP fast events metrics from cluster nodes where the linuxptp-daemon is running. You can also monitor PTP fast event metrics in the OpenShift Container Platform web console by using the preconfigured and self-updating Prometheus monitoring stack.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI
oc. -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install and configure the PTP Operator on a node with PTP-capable hardware.
Procedure
Check for exposed PTP metrics on any node where the
linuxptp-daemonis running. For example, run the following command:curl http://<node_name>:9091/metrics
$ curl http://<node_name>:9091/metricsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To view the PTP event in the OpenShift Container Platform web console, copy the name of the PTP metric you want to query, for example,
openshift_ptp_offset_ns. - In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, click Observe → Metrics.
- Paste the PTP metric name into the Expression field, and click Run queries.
Chapter 18. Developing Precision Time Protocol events consumer applications
When developing consumer applications that make use of Precision Time Protocol (PTP) events on a bare-metal cluster node, you need to deploy your consumer application and a cloud-event-proxy container in a separate application pod. The cloud-event-proxy container receives the events from the PTP Operator pod and passes it to the consumer application. The consumer application subscribes to the events posted in the cloud-event-proxy container by using a REST API.
For more information about deploying PTP events applications, see About the PTP fast event notifications framework.
The following information provides general guidance for developing consumer applications that use PTP events. A complete events consumer application example is outside the scope of this information.
18.1. PTP events consumer application reference
PTP event consumer applications require the following features:
-
A web service running with a
POSThandler to receive the cloud native PTP events JSON payload -
A
createSubscriptionfunction to subscribe to the PTP events producer -
A
getCurrentStatefunction to poll the current state of the PTP events producer
The following example Go snippets illustrate these requirements:
Example PTP events consumer server function in Go
Example PTP events createSubscription function in Go
- 1
- Replace
<node_name>with the FQDN of the node that is generating the PTP events. For example,compute-1.example.com.
Example PTP events consumer getCurrentState function in Go
18.2. Reference cloud-event-proxy deployment and service CRs
Use the following example cloud-event-proxy deployment and subscriber service CRs as a reference when deploying your PTP events consumer application.
HTTP transport is the default transport for PTP and bare-metal events. Use HTTP transport instead of AMQP for PTP and bare-metal events where possible. AMQ Interconnect is EOL from 30 June 2024. Extended life cycle support (ELS) for AMQ Interconnect ends 29 November 2029. For more information see, Red Hat AMQ Interconnect support status.
Reference cloud-event-proxy deployment with HTTP transport
Reference cloud-event-proxy deployment with AMQ transport
Reference cloud-event-proxy subscriber service
18.3. PTP events available from the cloud-event-proxy sidecar REST API
PTP events consumer applications can poll the PTP events producer for the following PTP timing events.
| Resource URI | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Describes the current status of the PTP equipment lock state. Can be in |
|
|
Describes the host operating system clock synchronization state. Can be in |
|
| Describes the current state of the PTP clock class. |
18.4. Subscribing the consumer application to PTP events
Before the PTP events consumer application can poll for events, you need to subscribe the application to the event producer.
18.4.1. Subscribing to PTP lock-state events
To create a subscription for PTP lock-state events, send a POST action to the cloud event API at http://localhost:8081/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions with the following payload:
{
"endpointUri": "http://localhost:8989/event",
"resource": "/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/lock-state",
}
{
"endpointUri": "http://localhost:8989/event",
"resource": "/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/lock-state",
}Example response
18.4.2. Subscribing to PTP os-clock-sync-state events
To create a subscription for PTP os-clock-sync-state events, send a POST action to the cloud event API at http://localhost:8081/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions with the following payload:
{
"endpointUri": "http://localhost:8989/event",
"resource": "/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/sync-status/os-clock-sync-state",
}
{
"endpointUri": "http://localhost:8989/event",
"resource": "/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/sync-status/os-clock-sync-state",
}Example response
18.4.3. Subscribing to PTP ptp-clock-class-change events
To create a subscription for PTP ptp-clock-class-change events, send a POST action to the cloud event API at http://localhost:8081/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/subscriptions with the following payload:
{
"endpointUri": "http://localhost:8989/event",
"resource": "/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/ptp-clock-class-change",
}
{
"endpointUri": "http://localhost:8989/event",
"resource": "/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/ptp-clock-class-change",
}Example response
18.5. Getting the current PTP clock status
To get the current PTP status for the node, send a GET action to one of the following event REST APIs:
-
http://localhost:8081/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/lock-state/CurrentState -
http://localhost:8081/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/sync-status/os-clock-sync-state/CurrentState -
http://localhost:8081/api/ocloudNotifications/v1/cluster/node/<node_name>/sync/ptp-status/ptp-clock-class-change/CurrentState
The response is a cloud native event JSON object. For example:
Example lock-state API response
18.6. Verifying that the PTP events consumer application is receiving events
Verify that the cloud-event-proxy container in the application pod is receiving PTP events.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have installed and configured the PTP Operator.
Procedure
Get the list of active
linuxptp-daemonpods. Run the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ptp
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ptpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE linuxptp-daemon-2t78p 3/3 Running 0 8h linuxptp-daemon-k8n88 3/3 Running 0 8h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE linuxptp-daemon-2t78p 3/3 Running 0 8h linuxptp-daemon-k8n88 3/3 Running 0 8hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Access the metrics for the required consumer-side
cloud-event-proxycontainer by running the following command:oc exec -it <linuxptp-daemon> -n openshift-ptp -c cloud-event-proxy -- curl 127.0.0.1:9091/metrics
$ oc exec -it <linuxptp-daemon> -n openshift-ptp -c cloud-event-proxy -- curl 127.0.0.1:9091/metricsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- <linuxptp-daemon>
Specifies the pod you want to query, for example,
linuxptp-daemon-2t78p.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 19. External DNS Operator
19.1. External DNS Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
The External DNS Operator deploys and manages ExternalDNS to provide the name resolution for services and routes from the external DNS provider to OpenShift Container Platform.
19.1.1. External DNS Operator
The External DNS Operator implements the External DNS API from the olm.openshift.io API group. The External DNS Operator updates services, routes, and external DNS providers.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the
yqCLI tool.
Procedure
You can deploy the External DNS Operator on demand from the OperatorHub. Deploying the External DNS Operator creates a Subscription object.
Check the name of an install plan by running the following command:
oc -n external-dns-operator get sub external-dns-operator -o yaml | yq '.status.installplan.name'
$ oc -n external-dns-operator get sub external-dns-operator -o yaml | yq '.status.installplan.name'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
install-zcvlr
install-zcvlrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check if the status of an install plan is
Completeby running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator get ip <install_plan_name> -o yaml | yq '.status.phase'
$ oc -n external-dns-operator get ip <install_plan_name> -o yaml | yq '.status.phase'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Complete
CompleteCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the status of the
external-dns-operatordeployment by running the following command:oc get -n external-dns-operator deployment/external-dns-operator
$ oc get -n external-dns-operator deployment/external-dns-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE external-dns-operator 1/1 1 1 23h
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE external-dns-operator 1/1 1 1 23hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.1.2. External DNS Operator logs
You can view External DNS Operator logs by using the oc logs command.
Procedure
View the logs of the External DNS Operator by running the following command:
oc logs -n external-dns-operator deployment/external-dns-operator -c external-dns-operator
$ oc logs -n external-dns-operator deployment/external-dns-operator -c external-dns-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.1.2.1. External DNS Operator domain name limitations
The External DNS Operator uses the TXT registry which adds the prefix for TXT records. This reduces the maximum length of the domain name for TXT records. A DNS record cannot be present without a corresponding TXT record, so the domain name of the DNS record must follow the same limit as the TXT records. For example, a DNS record of <domain_name_from_source> results in a TXT record of external-dns-<record_type>-<domain_name_from_source>.
The domain name of the DNS records generated by the External DNS Operator has the following limitations:
| Record type | Number of characters |
|---|---|
| CNAME | 44 |
| Wildcard CNAME records on AzureDNS | 42 |
| A | 48 |
| Wildcard A records on AzureDNS | 46 |
The following error appears in the External DNS Operator logs if the generated domain name exceeds any of the domain name limitations:
time="2022-09-02T08:53:57Z" level=error msg="Failure in zone test.example.io. [Id: /hostedzone/Z06988883Q0H0RL6UMXXX]" time="2022-09-02T08:53:57Z" level=error msg="InvalidChangeBatch: [FATAL problem: DomainLabelTooLong (Domain label is too long) encountered with 'external-dns-a-hello-openshift-aaaaaaaaaa-bbbbbbbbbb-ccccccc']\n\tstatus code: 400, request id: e54dfd5a-06c6-47b0-bcb9-a4f7c3a4e0c6"
time="2022-09-02T08:53:57Z" level=error msg="Failure in zone test.example.io. [Id: /hostedzone/Z06988883Q0H0RL6UMXXX]"
time="2022-09-02T08:53:57Z" level=error msg="InvalidChangeBatch: [FATAL problem: DomainLabelTooLong (Domain label is too long) encountered with 'external-dns-a-hello-openshift-aaaaaaaaaa-bbbbbbbbbb-ccccccc']\n\tstatus code: 400, request id: e54dfd5a-06c6-47b0-bcb9-a4f7c3a4e0c6"19.2. Installing External DNS Operator on cloud providers
You can install the External DNS Operator on cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
19.2.1. Installing the External DNS Operator with OperatorHub
You can install the External DNS Operator by using the OpenShift Container Platform OperatorHub.
Procedure
- Click Operators → OperatorHub in the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
- Click External DNS Operator. You can use the Filter by keyword text box or the filter list to search for External DNS Operator from the list of Operators.
-
Select the
external-dns-operatornamespace. - On the External DNS Operator page, click Install.
On the Install Operator page, ensure that you selected the following options:
- Update the channel as stable-v1.
- Installation mode as A specific name on the cluster.
-
Installed namespace as
external-dns-operator. If namespaceexternal-dns-operatordoes not exist, it gets created during the Operator installation. - Select Approval Strategy as Automatic or Manual. Approval Strategy is set to Automatic by default.
- Click Install.
If you select Automatic updates, the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) automatically upgrades the running instance of your Operator without any intervention.
If you select Manual updates, the OLM creates an update request. As a cluster administrator, you must then manually approve that update request to have the Operator updated to the new version.
Verification
Verify that the External DNS Operator shows the Status as Succeeded on the Installed Operators dashboard.
19.2.2. Installing the External DNS Operator by using the CLI
You can install the External DNS Operator by using the CLI.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console as a user with
cluster-adminpermissions. -
You are logged into the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a
Namespaceobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
Namespaceobject:Example
namespace.yamlfileapiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: external-dns-operator
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: external-dns-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
Namespaceobject by running the following command:oc apply -f namespace.yaml
$ oc apply -f namespace.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create an
OperatorGroupobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
OperatorGroupobject:Example
operatorgroup.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
OperatorGroupobject by running the following command:oc apply -f operatorgroup.yaml
$ oc apply -f operatorgroup.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
Subscriptionobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
Subscriptionobject:Example
subscription.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
Subscriptionobject by running the following command:oc apply -f subscription.yaml
$ oc apply -f subscription.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Get the name of the install plan from the subscription by running the following command:
oc -n external-dns-operator \ get subscription external-dns-operator \ --template='{{.status.installplan.name}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc -n external-dns-operator \ get subscription external-dns-operator \ --template='{{.status.installplan.name}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the status of the install plan is
Completeby running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator \ get ip <install_plan_name> \ --template='{{.status.phase}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc -n external-dns-operator \ get ip <install_plan_name> \ --template='{{.status.phase}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the status of the
external-dns-operatorpod isRunningby running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator get pod
$ oc -n external-dns-operator get podCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE external-dns-operator-5584585fd7-5lwqm 2/2 Running 0 11m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE external-dns-operator-5584585fd7-5lwqm 2/2 Running 0 11mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the catalog source of the subscription is
redhat-operatorsby running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator get subscription
$ oc -n external-dns-operator get subscriptionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME PACKAGE SOURCE CHANNEL external-dns-operator external-dns-operator redhat-operators stable-v1
NAME PACKAGE SOURCE CHANNEL external-dns-operator external-dns-operator redhat-operators stable-v1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the
external-dns-operatorversion by running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator get csv
$ oc -n external-dns-operator get csvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE external-dns-operator.v<1.y.z> ExternalDNS Operator <1.y.z> Succeeded
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE external-dns-operator.v<1.y.z> ExternalDNS Operator <1.y.z> SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.3. External DNS Operator configuration parameters
The External DNS Operator includes the following configuration parameters.
19.3.1. External DNS Operator configuration parameters
The External DNS Operator includes the following configuration parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Enables the type of a cloud provider. |
|
|
Enables you to specify DNS zones by their domains. If you do not specify zones, the zones: - "myzoneid"
|
|
|
Enables you to specify AWS zones by their domains. If you do not specify domains, the
|
|
|
Enables you to specify the source for the DNS records,
|
19.4. Creating DNS records on AWS
You can create DNS records on AWS and AWS GovCloud by using External DNS Operator.
19.4.1. Creating DNS records on an public hosted zone for AWS by using Red Hat External DNS Operator
You can create DNS records on a public hosted zone for AWS by using the Red Hat External DNS Operator. You can use the same instructions to create DNS records on a hosted zone for AWS GovCloud.
Procedure
Check the user. The user must have access to the
kube-systemnamespace. If you don’t have the credentials, as you can fetch the credentials from thekube-systemnamespace to use the cloud provider client:oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
system:admin
system:adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Fetch the values from aws-creds secret present in
kube-systemnamespace.export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(oc get secrets aws-creds -n kube-system --template={{.data.aws_access_key_id}} | base64 -d) export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(oc get secrets aws-creds -n kube-system --template={{.data.aws_secret_access_key}} | base64 -d)$ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(oc get secrets aws-creds -n kube-system --template={{.data.aws_access_key_id}} | base64 -d) $ export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(oc get secrets aws-creds -n kube-system --template={{.data.aws_secret_access_key}} | base64 -d)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the routes to check the domain:
oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep console
$ oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support downloads http edge/Redirect None
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support downloads http edge/Redirect NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the list of dns zones to find the one which corresponds to the previously found route’s domain:
aws route53 list-hosted-zones | grep testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support
$ aws route53 list-hosted-zones | grep testextdnsoperator.apacshift.supportCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
HOSTEDZONES terraform /hostedzone/Z02355203TNN1XXXX1J6O testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support. 5
HOSTEDZONES terraform /hostedzone/Z02355203TNN1XXXX1J6O testextdnsoperator.apacshift.support. 5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create
ExternalDNSresource forroutesource:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Defines the name of external DNS resource.
- 2
- By default all hosted zones are selected as potential targets. You can include a hosted zone that you need.
- 3
- The matching of the target zone’s domain has to be exact (as opposed to regular expression match).
- 4
- Specify the exact domain of the zone you want to update. The hostname of the routes must be subdomains of the specified domain.
- 5
- Defines the
AWS Route53DNS provider. - 6
- Defines options for the source of DNS records.
- 7
- Defines OpenShift
routeresource as the source for the DNS records which gets created in the previously specified DNS provider. - 8
- If the source is
OpenShiftRoute, then you can pass the OpenShift Ingress Controller name. External DNS Operator selects the canonical hostname of that router as the target while creating CNAME record.
Check the records created for OCP routes using the following command:
aws route53 list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id Z02355203TNN1XXXX1J6O --query "ResourceRecordSets[?Type == 'CNAME']" | grep console
$ aws route53 list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id Z02355203TNN1XXXX1J6O --query "ResourceRecordSets[?Type == 'CNAME']" | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.5. Creating DNS records on Azure
You can create DNS records on Azure by using the External DNS Operator.
Using the External DNS Operator on a {entra-first}-enabled cluster or a cluster that runs in Microsoft Azure Government (MAG) regions is not supported.
19.5.1. Creating DNS records on an Azure public DNS zone
You can create DNS records on a public DNS zone for Azure by using the External DNS Operator.
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
-
The
adminuser must have access to thekube-systemnamespace.
Procedure
Fetch the credentials from the
kube-systemnamespace to use the cloud provider client by running the following command:CLIENT_ID=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_client_id}} | base64 -d) CLIENT_SECRET=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_client_secret}} | base64 -d) RESOURCE_GROUP=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_resourcegroup}} | base64 -d) SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_subscription_id}} | base64 -d) TENANT_ID=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_tenant_id}} | base64 -d)$ CLIENT_ID=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_client_id}} | base64 -d) $ CLIENT_SECRET=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_client_secret}} | base64 -d) $ RESOURCE_GROUP=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_resourcegroup}} | base64 -d) $ SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_subscription_id}} | base64 -d) $ TENANT_ID=$(oc get secrets azure-credentials -n kube-system --template={{.data.azure_tenant_id}} | base64 -d)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in to Azure by running the following command:
az login --service-principal -u "${CLIENT_ID}" -p "${CLIENT_SECRET}" --tenant "${TENANT_ID}"$ az login --service-principal -u "${CLIENT_ID}" -p "${CLIENT_SECRET}" --tenant "${TENANT_ID}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get a list of routes by running the following command:
oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep console
$ oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.test.azure.example.com console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.test.azure.example.com downloads http edge/Redirect None
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.test.azure.example.com console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.test.azure.example.com downloads http edge/Redirect NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get a list of DNS zones by running the following command:
az network dns zone list --resource-group "${RESOURCE_GROUP}"$ az network dns zone list --resource-group "${RESOURCE_GROUP}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file, for example,
external-dns-sample-azure.yaml, that defines theExternalDNSobject:Example
external-dns-sample-azure.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the External DNS name.
- 2
- Defines the zone ID.
- 3
- Defines the provider type.
- 4
- You can define options for the source of DNS records.
- 5
- If the source type is
OpenShiftRoute, you can pass the OpenShift Ingress Controller name. External DNS selects the canonical hostname of that router as the target while creating CNAME record. - 6
- Defines the
routeresource as the source for the Azure DNS records.
Check the DNS records created for OpenShift Container Platform routes by running the following command:
az network dns record-set list -g "${RESOURCE_GROUP}" -z test.azure.example.com | grep console$ az network dns record-set list -g "${RESOURCE_GROUP}" -z test.azure.example.com | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteTo create records on private hosted zones on private Azure DNS, you need to specify the private zone under the
zonesfield which populates the provider type toazure-private-dnsin theExternalDNScontainer arguments.
19.6. Creating DNS records on Google Cloud
You can create DNS records on Google Cloud by using the External DNS Operator.
Using the External DNS Operator on a cluster with Google Cloud Workload Identity enabled is not supported. For more information about the Google Cloud Workload Identity, see Using manual mode with Google Cloud Workload Identity.
19.6.1. Creating DNS records on a public managed zone for Google Cloud
You can create DNS records on a public managed zone for Google Cloud by using the External DNS Operator.
Prerequisites
- You must have administrator privileges.
Procedure
Copy the
gcp-credentialssecret in theencoded-gcloud.jsonfile by running the following command:oc get secret gcp-credentials -n kube-system --template='{{$v := index .data "service_account.json"}}{{$v}}' | base64 -d - > decoded-gcloud.json$ oc get secret gcp-credentials -n kube-system --template='{{$v := index .data "service_account.json"}}{{$v}}' | base64 -d - > decoded-gcloud.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Export your Google credentials by running the following command:
export GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS=decoded-gcloud.json
$ export GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS=decoded-gcloud.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Activate your account by using the following command:
gcloud auth activate-service-account <client_email as per decoded-gcloud.json> --key-file=decoded-gcloud.json
$ gcloud auth activate-service-account <client_email as per decoded-gcloud.json> --key-file=decoded-gcloud.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set your project by running the following command:
gcloud config set project <project_id as per decoded-gcloud.json>
$ gcloud config set project <project_id as per decoded-gcloud.json>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get a list of routes by running the following command:
oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep console
$ oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.test.gcp.example.com console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.test.gcp.example.com downloads http edge/Redirect None
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.test.gcp.example.com console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.test.gcp.example.com downloads http edge/Redirect NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get a list of managed zones by running the following command:
gcloud dns managed-zones list | grep test.gcp.example.com
$ gcloud dns managed-zones list | grep test.gcp.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
qe-cvs4g-private-zone test.gcp.example.com
qe-cvs4g-private-zone test.gcp.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file, for example,
external-dns-sample-gcp.yaml, that defines theExternalDNSobject:Example
external-dns-sample-gcp.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the External DNS name.
- 2
- By default, all hosted zones are selected as potential targets. You can include your hosted zone.
- 3
- The domain of the target must match the string defined by the
namekey. - 4
- Specify the exact domain of the zone you want to update. The hostname of the routes must be subdomains of the specified domain.
- 5
- Defines the provider type.
- 6
- You can define options for the source of DNS records.
- 7
- If the source type is
OpenShiftRoute, you can pass the OpenShift Ingress Controller name. External DNS selects the canonical hostname of that router as the target while creating CNAME record. - 8
- Defines the
routeresource as the source for Google Cloud DNS records.
Check the DNS records created for OpenShift Container Platform routes by running the following command:
gcloud dns record-sets list --zone=qe-cvs4g-private-zone | grep console
$ gcloud dns record-sets list --zone=qe-cvs4g-private-zone | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.7. Creating DNS records on Infoblox
You can create DNS records on Infoblox by using the External DNS Operator.
19.7.1. Creating DNS records on a public DNS zone on Infoblox
You can create DNS records on a public DNS zone on Infoblox by using the External DNS Operator.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have access to the Infoblox UI.
Procedure
Create a
secretobject with Infoblox credentials by running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator create secret generic infoblox-credentials --from-literal=EXTERNAL_DNS_INFOBLOX_WAPI_USERNAME=<infoblox_username> --from-literal=EXTERNAL_DNS_INFOBLOX_WAPI_PASSWORD=<infoblox_password>
$ oc -n external-dns-operator create secret generic infoblox-credentials --from-literal=EXTERNAL_DNS_INFOBLOX_WAPI_USERNAME=<infoblox_username> --from-literal=EXTERNAL_DNS_INFOBLOX_WAPI_PASSWORD=<infoblox_password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get a list of routes by running the following command:
oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep console
$ oc get routes --all-namespaces | grep consoleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example Output
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.test.example.com console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.test.example.com downloads http edge/Redirect None
openshift-console console console-openshift-console.apps.test.example.com console https reencrypt/Redirect None openshift-console downloads downloads-openshift-console.apps.test.example.com downloads http edge/Redirect NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file, for example,
external-dns-sample-infoblox.yaml, that defines theExternalDNSobject:Example
external-dns-sample-infoblox.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the External DNS name.
- 2
- Defines the provider type.
- 3
- You can define options for the source of DNS records.
- 4
- If the source type is
OpenShiftRoute, you can pass the OpenShift Ingress Controller name. External DNS selects the canonical hostname of that router as the target while creating CNAME record.
Create the
ExternalDNSresource on Infoblox by running the following command:oc create -f external-dns-sample-infoblox.yaml
$ oc create -f external-dns-sample-infoblox.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the Infoblox UI, check the DNS records created for
consoleroutes:- Click Data Management → DNS → Zones.
- Select the zone name.
19.8. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy on the External DNS Operator
After configuring the cluster-wide proxy, the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) triggers automatic updates to all of the deployed Operators with the new contents of the HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY, and NO_PROXY environment variables.
19.8.1. Trusting the certificate authority of the cluster-wide proxy
You can configure the External DNS Operator to trust the certificate authority of the cluster-wide proxy.
Procedure
Create the config map to contain the CA bundle in the
external-dns-operatornamespace by running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator create configmap trusted-ca
$ oc -n external-dns-operator create configmap trusted-caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To inject the trusted CA bundle into the config map, add the
config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=truelabel to the config map by running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator label cm trusted-ca config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=true
$ oc -n external-dns-operator label cm trusted-ca config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the subscription of the External DNS Operator by running the following command:
oc -n external-dns-operator patch subscription external-dns-operator --type='json' -p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/config", "value":{"env":[{"name":"TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME","value":"trusted-ca"}]}}]'$ oc -n external-dns-operator patch subscription external-dns-operator --type='json' -p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/config", "value":{"env":[{"name":"TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME","value":"trusted-ca"}]}}]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
After the deployment of the External DNS Operator is completed, verify that the trusted CA environment variable is added to the
external-dns-operatordeployment by running the following command:oc -n external-dns-operator exec deploy/external-dns-operator -c external-dns-operator -- printenv TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME
$ oc -n external-dns-operator exec deploy/external-dns-operator -c external-dns-operator -- printenv TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
trusted-ca
trusted-caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 20. Network policy
20.1. About network policy
As a developer, you can define network policies that restrict traffic to pods in your cluster.
20.1.1. About network policy
In a cluster using a network plugin that supports Kubernetes network policy, network isolation is controlled entirely by NetworkPolicy objects. In OpenShift Container Platform 4.13, OpenShift SDN supports using network policy in its default network isolation mode.
- A network policy does not apply to the host network namespace. Pods with host networking enabled are unaffected by network policy rules. However, pods connecting to the host-networked pods might be affected by the network policy rules.
-
Using the
namespaceSelectorfield without thepodSelectorfield set to{}will not includehostNetworkpods. You must use thepodSelectorset to{}with thenamespaceSelectorfield in order to targethostNetworkpods when creating network policies. - Network policies cannot block traffic from localhost or from their resident nodes.
By default, all pods in a project are accessible from other pods and network endpoints. To isolate one or more pods in a project, you can create NetworkPolicy objects in that project to indicate the allowed incoming connections. Project administrators can create and delete NetworkPolicy objects within their own project.
If a pod is matched by selectors in one or more NetworkPolicy objects, then the pod will accept only connections that are allowed by at least one of those NetworkPolicy objects. A pod that is not selected by any NetworkPolicy objects is fully accessible.
A network policy applies to only the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), and Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) protocols. Other protocols are not affected.
The following example NetworkPolicy objects demonstrate supporting different scenarios:
Deny all traffic:
To make a project deny by default, add a
NetworkPolicyobject that matches all pods but accepts no traffic:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Only allow connections from the OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Controller:
To make a project allow only connections from the OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Controller, add the following
NetworkPolicyobject.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Only accept connections from pods within a project:
ImportantTo allow ingress connections from
hostNetworkpods in the same namespace, you need to apply theallow-from-hostnetworkpolicy together with theallow-same-namespacepolicy.To make pods accept connections from other pods in the same project, but reject all other connections from pods in other projects, add the following
NetworkPolicyobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Only allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic based on pod labels:
To enable only HTTP and HTTPS access to the pods with a specific label (
role=frontendin following example), add aNetworkPolicyobject similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Accept connections by using both namespace and pod selectors:
To match network traffic by combining namespace and pod selectors, you can use a
NetworkPolicyobject similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
NetworkPolicy objects are additive, which means you can combine multiple NetworkPolicy objects together to satisfy complex network requirements.
For example, for the NetworkPolicy objects defined in previous samples, you can define both allow-same-namespace and allow-http-and-https policies within the same project. Thus allowing the pods with the label role=frontend, to accept any connection allowed by each policy. That is, connections on any port from pods in the same namespace, and connections on ports 80 and 443 from pods in any namespace.
20.1.1.1. Using the allow-from-router network policy
Use the following NetworkPolicy to allow external traffic regardless of the router configuration:
- 1
policy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress:""label supports both OpenShift-SDN and OVN-Kubernetes.
20.1.1.2. Using the allow-from-hostnetwork network policy
Add the following allow-from-hostnetwork NetworkPolicy object to direct traffic from the host network pods.
20.1.2. Optimizations for network policy with OpenShift SDN
Use a network policy to isolate pods that are differentiated from one another by labels within a namespace.
It is inefficient to apply NetworkPolicy objects to large numbers of individual pods in a single namespace. Pod labels do not exist at the IP address level, so a network policy generates a separate Open vSwitch (OVS) flow rule for every possible link between every pod selected with a podSelector.
For example, if the spec podSelector and the ingress podSelector within a NetworkPolicy object each match 200 pods, then 40,000 (200*200) OVS flow rules are generated. This might slow down a node.
When designing your network policy, refer to the following guidelines:
Reduce the number of OVS flow rules by using namespaces to contain groups of pods that need to be isolated.
NetworkPolicyobjects that select a whole namespace, by using thenamespaceSelectoror an emptypodSelector, generate only a single OVS flow rule that matches the VXLAN virtual network ID (VNID) of the namespace.- Keep the pods that do not need to be isolated in their original namespace, and move the pods that require isolation into one or more different namespaces.
- Create additional targeted cross-namespace network policies to allow the specific traffic that you do want to allow from the isolated pods.
20.1.3. Optimizations for network policy with OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
When designing your network policy, refer to the following guidelines:
-
For network policies with the same
spec.podSelectorspec, it is more efficient to use one network policy with multipleingressoregressrules, than multiple network policies with subsets ofingressoregressrules. Every
ingressoregressrule based on thepodSelectorornamespaceSelectorspec generates the number of OVS flows proportional tonumber of pods selected by network policy + number of pods selected by ingress or egress rule. Therefore, it is preferable to use thepodSelectorornamespaceSelectorspec that can select as many pods as you need in one rule, instead of creating individual rules for every pod.For example, the following policy contains two rules:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following policy expresses those same two rules as one:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The same guideline applies to the
spec.podSelectorspec. If you have the sameingressoregressrules for different network policies, it might be more efficient to create one network policy with a commonspec.podSelectorspec. For example, the following two policies have different rules:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following network policy expresses those same two rules as one:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can apply this optimization when only multiple selectors are expressed as one. In cases where selectors are based on different labels, it may not be possible to apply this optimization. In those cases, consider applying some new labels for network policy optimization specifically.
20.1.3.1. NetworkPolicy CR and external IPs in OVN-Kubernetes
In OVN-Kubernetes, the NetworkPolicy custom resource (CR) enforces strict isolation rules. If a service is exposed using an external IP, a network policy can block access from other namespaces unless explicitly configured to allow traffic.
To allow access to external IPs across namespaces, create a NetworkPolicy CR that explicitly permits ingress from the required namespaces and ensures traffic is allowed to the designated service ports. Without allowing traffic to the required ports, access might still be restricted.
Example output
where:
<policy_name>- Specifies your name for the policy.
<my_namespace>- Specifies the name of the namespace where the policy is deployed.
For more details, see "About network policy".
20.1.4. Next steps
20.2. Creating a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can create a network policy for a namespace.
20.2.1. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
20.2.2. Creating a network policy using the CLI
To define granular rules describing ingress or egress network traffic allowed for namespaces in your cluster, you can create a network policy.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy rule:
Create a
<policy_name>.yamlfile:touch <policy_name>.yaml
$ touch <policy_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the network policy file name.
Define a network policy in the file that you just created, such as in the following examples:
Deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces
This is a fundamental policy, blocking all cross-pod networking other than cross-pod traffic allowed by the configuration of other Network Policies.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Allow ingress from all pods in the same namespace
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Allow ingress traffic to one pod from a particular namespace
This policy allows traffic to pods labelled
pod-afrom pods running innamespace-y.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To create the network policy object, enter the following command:
oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>
$ oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the network policy file name.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of creating a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
20.2.3. Creating a default deny all network policy
This is a fundamental policy, blocking all cross-pod networking other than network traffic allowed by the configuration of other deployed network policies. This procedure enforces a default deny-by-default policy.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create the following YAML that defines a
deny-by-defaultpolicy to deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces. Save the YAML in thedeny-by-default.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f deny-by-default.yaml
$ oc apply -f deny-by-default.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.2.4. Creating a network policy to allow traffic from external clients
With the deny-by-default policy in place you can proceed to configure a policy that allows traffic from external clients to a pod with the label app=web.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows external service from the public Internet directly or by using a Load Balancer to access the pod. Traffic is only allowed to a pod with the label app=web.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from the public Internet directly or by using a load balancer to access the pod. Save the YAML in the
web-allow-external.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-external.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-external.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-external created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-external createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This policy allows traffic from all resources, including external traffic as illustrated in the following diagram:
20.2.5. Creating a network policy allowing traffic to an application from all namespaces
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows traffic from all pods in all namespaces to a particular application.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in all namespaces to a particular application. Save the YAML in the
web-allow-all-namespaces.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, if you omit specifying a
namespaceSelectorit does not select any namespaces, which means the policy allows traffic only from the namespace the network policy is deployed to.Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-all-namespaces.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-all-namespaces.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-all-namespaces created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-all-namespaces createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in thesecondarynamespace and to start a shell:oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=secondary --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=secondary --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is allowed:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.2.6. Creating a network policy allowing traffic to an application from a namespace
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows traffic to a pod with the label app=web from a particular namespace. You might want to do this to:
- Restrict traffic to a production database only to namespaces where production workloads are deployed.
- Enable monitoring tools deployed to a particular namespace to scrape metrics from the current namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in a particular namespaces with a label
purpose=production. Save the YAML in theweb-allow-prod.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-prod created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/web-allow-prod createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to create the
prodnamespace:oc create namespace prod
$ oc create namespace prodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to label the
prodnamespace:oc label namespace/prod purpose=production
$ oc label namespace/prod purpose=productionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to create the
devnamespace:oc create namespace dev
$ oc create namespace devCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to label the
devnamespace:oc label namespace/dev purpose=testing
$ oc label namespace/dev purpose=testingCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in thedevnamespace and to start a shell:oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=dev --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=dev --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is blocked:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
wget: download timed out
wget: download timed outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in theprodnamespace and start a shell:oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is allowed:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.3. Viewing a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can view a network policy for a namespace.
20.3.1. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
20.3.2. Viewing network policies using the CLI
You can examine the network policies in a namespace.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can view any network policy in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the network policy exists.
Procedure
List network policies in a namespace:
To view network policy objects defined in a namespace, enter the following command:
oc get networkpolicy
$ oc get networkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To examine a specific network policy, enter the following command:
oc describe networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc describe networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy to inspect.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
For example:
oc describe networkpolicy allow-same-namespace
$ oc describe networkpolicy allow-same-namespaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Output for
oc describecommandCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of viewing a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
20.4. Editing a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can edit an existing network policy for a namespace.
20.4.1. Editing a network policy
You can edit a network policy in a namespace.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can edit a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the network policy exists.
Procedure
Optional: To list the network policy objects in a namespace, enter the following command:
oc get networkpolicy
$ oc get networkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Edit the network policy object.
If you saved the network policy definition in a file, edit the file and make any necessary changes, and then enter the following command.
oc apply -n <namespace> -f <policy_file>.yaml
$ oc apply -n <namespace> -f <policy_file>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
<policy_file>- Specifies the name of the file containing the network policy.
If you need to update the network policy object directly, enter the following command:
oc edit networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc edit networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Confirm that the network policy object is updated.
oc describe networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc describe networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of editing a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from the policy in the web console through the Actions menu.
20.4.2. Example NetworkPolicy object
The following annotates an example NetworkPolicy object:
- 1
- The name of the NetworkPolicy object.
- 2
- A selector that describes the pods to which the policy applies. The policy object can only select pods in the project that defines the NetworkPolicy object.
- 3
- A selector that matches the pods from which the policy object allows ingress traffic. The selector matches pods in the same namespace as the NetworkPolicy.
- 4
- A list of one or more destination ports on which to accept traffic.
20.5. Deleting a network policy
As a user with the admin role, you can delete a network policy from a namespace.
20.5.1. Deleting a network policy using the CLI
You can delete a network policy in a namespace.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can delete any network policy in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the network policy exists.
Procedure
To delete a network policy object, enter the following command:
oc delete networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc delete networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/default-deny deleted
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/default-deny deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of deleting a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from the policy in the web console through the Actions menu.
20.6. Defining a default network policy for projects
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the new project template to automatically include network policies when you create a new project. If you do not yet have a customized template for new projects, you must first create one.
20.6.1. Modifying the template for new projects
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the default project template so that new projects are created using your custom requirements.
To create your own custom project template:
Procedure
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. Generate the default project template:
oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yaml
$ oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Use a text editor to modify the generated
template.yamlfile by adding objects or modifying existing objects. The project template must be created in the
openshift-confignamespace. Load your modified template:oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-config
$ oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the project configuration resource using the web console or CLI.
Using the web console:
- Navigate to the Administration → Cluster Settings page.
- Click Configuration to view all configuration resources.
- Find the entry for Project and click Edit YAML.
Using the CLI:
Edit the
project.config.openshift.io/clusterresource:oc edit project.config.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit project.config.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Update the
specsection to include theprojectRequestTemplateandnameparameters, and set the name of your uploaded project template. The default name isproject-request.Project configuration resource with custom project template
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After you save your changes, create a new project to verify that your changes were successfully applied.
20.6.2. Adding network policies to the new project template
As a cluster administrator, you can add network policies to the default template for new projects. OpenShift Container Platform will automatically create all the NetworkPolicy objects specified in the template in the project.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a default CNI network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You must have created a custom default project template for new projects.
Procedure
Edit the default template for a new project by running the following command:
oc edit template <project_template> -n openshift-config
$ oc edit template <project_template> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<project_template>with the name of the default template that you configured for your cluster. The default template name isproject-request.In the template, add each
NetworkPolicyobject as an element to theobjectsparameter. Theobjectsparameter accepts a collection of one or more objects.In the following example, the
objectsparameter collection includes severalNetworkPolicyobjects.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Create a new project to confirm that your network policy objects are created successfully by running the following commands:
Create a new project:
oc new-project <project>
$ oc new-project <project>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<project>with the name for the project you are creating.
Confirm that the network policy objects in the new project template exist in the new project:
oc get networkpolicy NAME POD-SELECTOR AGE allow-from-openshift-ingress <none> 7s allow-from-same-namespace <none> 7s
$ oc get networkpolicy NAME POD-SELECTOR AGE allow-from-openshift-ingress <none> 7s allow-from-same-namespace <none> 7sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.7. Configuring multitenant isolation with network policy
As a cluster administrator, you can configure your network policies to provide multitenant network isolation.
If you are using the OpenShift SDN network plugin, configuring network policies as described in this section provides network isolation similar to multitenant mode but with network policy mode set.
20.7.1. Configuring multitenant isolation by using network policy
You can configure your project to isolate it from pods and services in other project namespaces.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the following
NetworkPolicyobjects:A policy named
allow-from-openshift-ingress.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepolicy-group.network.openshift.io/ingress: ""is the preferred namespace selector label for OpenShift SDN. You can use thenetwork.openshift.io/policy-group: ingressnamespace selector label, but this is a legacy label.A policy named
allow-from-openshift-monitoring:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A policy named
allow-same-namespace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A policy named
allow-from-kube-apiserver-operator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more details, see New
kube-apiserver-operatorwebhook controller validating health of webhook.
Optional: To confirm that the network policies exist in your current project, enter the following command:
oc describe networkpolicy
$ oc describe networkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.7.2. Next steps
Chapter 21. CIDR range definitions
You must specify non-overlapping ranges for the following CIDR ranges.
Machine CIDR ranges cannot be changed after creating your cluster.
OVN-Kubernetes, the default network provider in OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 to 4.13, uses the following IP address ranges internally: 100.64.0.0/16, 169.254.169.0/29, fd98::/64 and fd69::/125. If your cluster uses OVN-Kubernetes, do not include any IP address ranges in any other CIDR definitions in your cluster.
21.1. Machine CIDR
In the Machine classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) field, you must specify the IP address range for machines or cluster nodes.
The default is 10.0.0.0/16. This range must not conflict with any connected networks.
21.2. Service CIDR
In the Service CIDR field, you must specify the IP address range for services. The range must be large enough to accommodate your workload. The address block must not overlap with any external service accessed from within the cluster. The default is 172.30.0.0/16.
21.3. Pod CIDR
In the pod CIDR field, you must specify the IP address range for pods.
The pod CIDR is the same as the clusterNetwork CIDR and the cluster CIDR. The range must be large enough to accommodate your workload. The address block must not overlap with any external service accessed from within the cluster. The default is 10.128.0.0/14. You can expand the range after cluster installation.
21.4. Host Prefix
In the Host Prefix field, you must specify the subnet prefix length assigned to pods scheduled to individual machines. The host prefix determines the pod IP address pool for each machine.
For example, if the host prefix is set to /23, each machine is assigned a /23 subnet from the pod CIDR address range. The default is /23, allowing 510 cluster nodes, and 510 pod IP addresses per node.
Chapter 22. AWS Load Balancer Operator
22.1. AWS Load Balancer Operator release notes
The AWS Load Balancer (ALB) Operator deploys and manages an instance of the AWSLoadBalancerController resource.
The AWS Load Balancer (ALB) Operator is only supported on the x86_64 architecture.
These release notes track the development of the AWS Load Balancer Operator in OpenShift Container Platform.
For an overview of the AWS Load Balancer Operator, see AWS Load Balancer Operator in OpenShift Container Platform.
AWS Load Balancer Operator currently does not support AWS GovCloud.
22.1.1. AWS Load Balancer Operator 1.0.0
The AWS Load Balancer Operator is now generally available with this release. The AWS Load Balancer Operator version 1.0.0 supports the AWS Load Balancer Controller version 2.4.4.
The following advisory is available for the AWS Load Balancer Operator version 1.0.0:
22.1.1.1. Notable changes
-
This release uses the new
v1API version.
22.1.1.2. Bug fixes
- Previously, the controller provisioned by the AWS Load Balancer Operator did not properly use the configuration for the cluster-wide proxy. These settings are now applied appropriately to the controller. (OCPBUGS-4052, OCPBUGS-5295)
22.1.2. Earlier versions
The two earliest versions of the AWS Load Balancer Operator are available as a Technology Preview. These versions should not be used in a production cluster. For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
The following advisory is available for the AWS Load Balancer Operator version 0.2.0:
The following advisory is available for the AWS Load Balancer Operator version 0.0.1:
22.2. AWS Load Balancer Operator in OpenShift Container Platform
The AWS Load Balancer Operator deploys and manages the AWS Load Balancer Controller. You can install the AWS Load Balancer Operator from OperatorHub by using OpenShift Container Platform web console or CLI.
22.2.1. AWS Load Balancer Operator considerations
Review the following limitations before installing and using the AWS Load Balancer Operator:
- The IP traffic mode only works on AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS). The AWS Load Balancer Operator disables the IP traffic mode for the AWS Load Balancer Controller. As a result of disabling the IP traffic mode, the AWS Load Balancer Controller cannot use the pod readiness gate.
-
The AWS Load Balancer Operator adds command-line flags such as
--disable-ingress-class-annotationand--disable-ingress-group-name-annotationto the AWS Load Balancer Controller. Therefore, the AWS Load Balancer Operator does not allow using thekubernetes.io/ingress.classandalb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.nameannotations in theIngressresource. -
You have configured the AWS Load Balancer Operator so that the SVC type is
NodePort(notLoadBalancerorClusterIP).
22.2.2. AWS Load Balancer Operator
The AWS Load Balancer Operator can tag the public subnets if the kubernetes.io/role/elb tag is missing. Also, the AWS Load Balancer Operator detects the following information from the underlying AWS cloud:
- The ID of the virtual private cloud (VPC) on which the cluster hosting the Operator is deployed in.
- Public and private subnets of the discovered VPC.
The AWS Load Balancer Operator supports the Kubernetes service resource of type LoadBalancer by using Network Load Balancer (NLB) with the instance target type only.
Prerequisites
- You must have the AWS credentials secret. The credentials are used to provide subnet tagging and VPC discovery.
Procedure
You can deploy the AWS Load Balancer Operator on demand from OperatorHub, by creating a
Subscriptionobject by running the following command:oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get sub aws-load-balancer-operator --template='{{.status.installplan.name}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get sub aws-load-balancer-operator --template='{{.status.installplan.name}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
install-zlfbt
install-zlfbtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check if the status of an install plan is
Completeby running the following command:oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get ip <install_plan_name> --template='{{.status.phase}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get ip <install_plan_name> --template='{{.status.phase}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Complete
CompleteCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the status of the
aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-managerdeployment by running the following command:oc get -n aws-load-balancer-operator deployment/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager
$ oc get -n aws-load-balancer-operator deployment/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-managerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager 1/1 1 1 23h
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager 1/1 1 1 23hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.2.3. AWS Load Balancer Operator logs
You can view the AWS Load Balancer Operator logs by using the oc logs command.
Procedure
View the logs of the AWS Load Balancer Operator by running the following command:
oc logs -n aws-load-balancer-operator deployment/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager -c manager
$ oc logs -n aws-load-balancer-operator deployment/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager -c managerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.3. Installing the AWS Load Balancer Operator
The AWS Load Balancer Operator deploys and manages the AWS Load Balancer Controller. You can install the AWS Load Balancer Operator from the OperatorHub by using OpenShift Container Platform web console or CLI.
22.3.1. Installing the AWS Load Balancer Operator by using the web console
You can install the AWS Load Balancer Operator by using the web console.
Prerequisites
-
You have logged in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console as a user with
cluster-adminpermissions. - Your cluster is configured with AWS as the platform type and cloud provider.
- If you are using a security token service (STS) or user-provisioned infrastructure, follow the related preparation steps. For example, if you are using AWS Security Token Service, see "Preparing for the AWS Load Balancer Operator on a cluster using the AWS Security Token Service (STS)".
Procedure
- Navigate to Operators → OperatorHub in the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
- Select the AWS Load Balancer Operator. You can use the Filter by keyword text box or use the filter list to search for the AWS Load Balancer Operator from the list of Operators.
-
Select the
aws-load-balancer-operatornamespace. On the Install Operator page, select the following options:
- Update the channel as stable-v1.
- Installation mode as All namespaces on the cluster (default).
-
Installed Namespace as
aws-load-balancer-operator. If theaws-load-balancer-operatornamespace does not exist, it gets created during the Operator installation. - Select Update approval as Automatic or Manual. By default, the Update approval is set to Automatic. If you select automatic updates, the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) automatically upgrades the running instance of your Operator without any intervention. If you select manual updates, the OLM creates an update request. As a cluster administrator, you must then manually approve that update request to update the Operator updated to the new version.
- Click Install.
Verification
- Verify that the AWS Load Balancer Operator shows the Status as Succeeded on the Installed Operators dashboard.
22.3.2. Installing the AWS Load Balancer Operator by using the CLI
You can install the AWS Load Balancer Operator by using the CLI.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console as a user with
cluster-adminpermissions. - Your cluster is configured with AWS as the platform type and cloud provider.
-
You are logged into the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a
Namespaceobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
Namespaceobject:Example
namespace.yamlfileapiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: aws-load-balancer-operator
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: aws-load-balancer-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
Namespaceobject by running the following command:oc apply -f namespace.yaml
$ oc apply -f namespace.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
CredentialsRequestobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
CredentialsRequestobject:Example
credentialsrequest.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
CredentialsRequestobject by running the following command:oc apply -f credentialsrequest.yaml
$ oc apply -f credentialsrequest.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create an
OperatorGroupobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
OperatorGroupobject:Example
operatorgroup.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
OperatorGroupobject by running the following command:oc apply -f operatorgroup.yaml
$ oc apply -f operatorgroup.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
Subscriptionobject:Create a YAML file that defines the
Subscriptionobject:Example
subscription.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
Subscriptionobject by running the following command:oc apply -f subscription.yaml
$ oc apply -f subscription.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Get the name of the install plan from the subscription:
oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator \ get subscription aws-load-balancer-operator \ --template='{{.status.installplan.name}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator \ get subscription aws-load-balancer-operator \ --template='{{.status.installplan.name}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the status of the install plan:
oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator \ get ip <install_plan_name> \ --template='{{.status.phase}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator \ get ip <install_plan_name> \ --template='{{.status.phase}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output must be
Complete.
22.4. Preparing for the AWS Load Balancer Operator on a cluster using the AWS Security Token Service
You can install the AWS Load Balancer Operator on a cluster that uses STS. Follow these steps to prepare your cluster before installing the Operator.
The AWS Load Balancer Operator relies on the CredentialsRequest object to bootstrap the Operator and the AWS Load Balancer Controller. The AWS Load Balancer Operator waits until the required secrets are created and available. The Cloud Credential Operator does not provision the secrets automatically in the STS cluster. You must set the credentials secrets manually by using the ccoctl binary.
If you do not want to provision credential secret by using the Cloud Credential Operator, you can configure the AWSLoadBalancerController instance on the STS cluster by specifying the credential secret in the AWS load Balancer Controller custom resource (CR).
22.4.1. Bootstrapping AWS Load Balancer Operator on Security Token Service cluster
Prerequisites
-
You must extract and prepare the
ccoctlbinary.
Procedure
Create the
aws-load-balancer-operatornamespace by running the following command:oc create namespace aws-load-balancer-operator
$ oc create namespace aws-load-balancer-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download the
CredentialsRequestcustom resource (CR) of the AWS Load Balancer Operator, and create a directory to store it by running the following command:curl --create-dirs -o <path-to-credrequests-dir>/cr.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/aws-load-balancer-operator/main/hack/operator-credentials-request.yaml
$ curl --create-dirs -o <path-to-credrequests-dir>/cr.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/aws-load-balancer-operator/main/hack/operator-credentials-request.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
ccoctltool to processCredentialsRequestobjects of the AWS Load Balancer Operator, by running the following command:ccoctl aws create-iam-roles \ --name <name> --region=<aws_region> \ --credentials-requests-dir=<path-to-credrequests-dir> \ --identity-provider-arn <oidc-arn>$ ccoctl aws create-iam-roles \ --name <name> --region=<aws_region> \ --credentials-requests-dir=<path-to-credrequests-dir> \ --identity-provider-arn <oidc-arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the secrets generated in the manifests directory of your cluster by running the following command:
ls manifests/*-credentials.yaml | xargs -I{} oc apply -f {}$ ls manifests/*-credentials.yaml | xargs -I{} oc apply -f {}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the credentials secret of the AWS Load Balancer Operator is created by running the following command:
oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get secret aws-load-balancer-operator --template='{{index .data "credentials"}}' | base64 -d$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get secret aws-load-balancer-operator --template='{{index .data "credentials"}}' | base64 -dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
[default] sts_regional_endpoints = regional role_arn = arn:aws:iam::999999999999:role/aws-load-balancer-operator-aws-load-balancer-operator web_identity_token_file = /var/run/secrets/openshift/serviceaccount/token
[default] sts_regional_endpoints = regional role_arn = arn:aws:iam::999999999999:role/aws-load-balancer-operator-aws-load-balancer-operator web_identity_token_file = /var/run/secrets/openshift/serviceaccount/tokenCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.4.2. Configuring AWS Load Balancer Operator on Security Token Service cluster by using managed CredentialsRequest objects
Prerequisites
-
You must extract and prepare the
ccoctlbinary.
Procedure
The AWS Load Balancer Operator creates the
CredentialsRequestobject in theopenshift-cloud-credential-operatornamespace for eachAWSLoadBalancerControllercustom resource (CR). You can extract and save the createdCredentialsRequestobject in a directory by running the following command:oc get credentialsrequest -n openshift-cloud-credential-operator \ aws-load-balancer-controller-<cr-name> -o yaml > <path-to-credrequests-dir>/cr.yaml$ oc get credentialsrequest -n openshift-cloud-credential-operator \ aws-load-balancer-controller-<cr-name> -o yaml > <path-to-credrequests-dir>/cr.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aws-load-balancer-controller-<cr-name>parameter specifies the credential request name created by the AWS Load Balancer Operator. Thecr-namespecifies the name of the AWS Load Balancer Controller instance.
Use the
ccoctltool to process allCredentialsRequestobjects in thecredrequestsdirectory by running the following command:ccoctl aws create-iam-roles \ --name <name> --region=<aws_region> \ --credentials-requests-dir=<path-to-credrequests-dir> \ --identity-provider-arn <oidc-arn>$ ccoctl aws create-iam-roles \ --name <name> --region=<aws_region> \ --credentials-requests-dir=<path-to-credrequests-dir> \ --identity-provider-arn <oidc-arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the secrets generated in manifests directory to your cluster, by running the following command:
ls manifests/*-credentials.yaml | xargs -I{} oc apply -f {}$ ls manifests/*-credentials.yaml | xargs -I{} oc apply -f {}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
aws-load-balancer-controllerpod is created:oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE aws-load-balancer-controller-cluster-9b766d6-gg82c 1/1 Running 0 137m aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager-b55ff68cc-85jzg 2/2 Running 0 3h26m
$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE aws-load-balancer-controller-cluster-9b766d6-gg82c 1/1 Running 0 137m aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager-b55ff68cc-85jzg 2/2 Running 0 3h26mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.4.3. Configuring the AWS Load Balancer Operator on Security Token Service cluster by using specific credentials
You can specify the credential secret by using the spec.credentials field in the AWS Load Balancer Controller custom resource (CR). You can use the predefined CredentialsRequest object of the controller to know which roles are required.
Prerequisites
-
You must extract and prepare the
ccoctlbinary.
Procedure
Download the CredentialsRequest custom resource (CR) of the AWS Load Balancer Controller, and create a directory to store it by running the following command:
curl --create-dirs -o <path-to-credrequests-dir>/cr.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/aws-load-balancer-operator/main/hack/controller/controller-credentials-request.yaml
$ curl --create-dirs -o <path-to-credrequests-dir>/cr.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/aws-load-balancer-operator/main/hack/controller/controller-credentials-request.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
ccoctltool to process theCredentialsRequestobject of the controller:ccoctl aws create-iam-roles \ --name <name> --region=<aws_region> \ --credentials-requests-dir=<path-to-credrequests-dir> \ --identity-provider-arn <oidc-arn>$ ccoctl aws create-iam-roles \ --name <name> --region=<aws_region> \ --credentials-requests-dir=<path-to-credrequests-dir> \ --identity-provider-arn <oidc-arn>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the secrets to your cluster:
ls manifests/*-credentials.yaml | xargs -I{} oc apply -f {}$ ls manifests/*-credentials.yaml | xargs -I{} oc apply -f {}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the credentials secret has been created for use by the controller:
oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get secret aws-load-balancer-controller-manual-cluster --template='{{index .data "credentials"}}' | base64 -d$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator get secret aws-load-balancer-controller-manual-cluster --template='{{index .data "credentials"}}' | base64 -dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
[default] sts_regional_endpoints = regional role_arn = arn:aws:iam::999999999999:role/aws-load-balancer-operator-aws-load-balancer-controller web_identity_token_file = /var/run/secrets/openshift/serviceaccount/token[default] sts_regional_endpoints = regional role_arn = arn:aws:iam::999999999999:role/aws-load-balancer-operator-aws-load-balancer-controller web_identity_token_file = /var/run/secrets/openshift/serviceaccount/tokenCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerresource YAML file, for example,sample-aws-lb-manual-creds.yaml, as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.5. Creating an instance of the AWS Load Balancer Controller
After installing the AWS Load Balancer Operator, you can create the AWS Load Balancer Controller.
22.5.1. Creating the AWS Load Balancer Controller
You can install only a single instance of the AWSLoadBalancerController object in a cluster. You can create the AWS Load Balancer Controller by using CLI. The AWS Load Balancer Operator reconciles only the cluster named resource.
Prerequisites
-
You have created the
echoservernamespace. -
You have access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a YAML file that defines the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerobject:Example
sample-aws-lb.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Defines the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerobject. - 2
- Defines the AWS Load Balancer Controller name. This instance name gets added as a suffix to all related resources.
- 3
- Configures the subnet tagging method for the AWS Load Balancer Controller. The following values are valid:
-
Auto: The AWS Load Balancer Operator determines the subnets that belong to the cluster and tags them appropriately. The Operator cannot determine the role correctly if the internal subnet tags are not present on internal subnet. -
Manual: You manually tag the subnets that belong to the cluster with the appropriate role tags. Use this option if you installed your cluster on user-provided infrastructure.
-
- 4
- Defines the tags used by the AWS Load Balancer Controller when it provisions AWS resources.
- 5
- Defines the ingress class name. The default value is
alb. - 6
- Specifies the number of replicas of the AWS Load Balancer Controller.
- 7
- Specifies annotations as an add-on for the AWS Load Balancer Controller.
- 8
- Enables the
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/wafv2-acl-arnannotation.
Create the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerobject by running the following command:oc create -f sample-aws-lb.yaml
$ oc create -f sample-aws-lb.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file that defines the
Deploymentresource:Example
sample-aws-lb.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file that defines the
Serviceresource:Example
service-albo.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a YAML file that defines the
Ingressresource:Example
ingress-albo.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Save the status of the
Ingressresource in theHOSTvariable by running the following command:HOST=$(oc get ingress -n echoserver echoserver --template='{{(index .status.loadBalancer.ingress 0).hostname}}')$ HOST=$(oc get ingress -n echoserver echoserver --template='{{(index .status.loadBalancer.ingress 0).hostname}}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the status of the
Ingressresource by running the following command:curl $HOST
$ curl $HOSTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.6. Serving multiple ingress resources through a single AWS Load Balancer
You can route the traffic to different services that are part of a single domain through a single AWS Load Balancer. Each Ingress resource provides different endpoints of the domain.
22.6.1. Creating multiple ingress resources through a single AWS Load Balancer
You can route the traffic to multiple ingress resources through a single AWS Load Balancer by using the CLI.
Prerequisites
-
You have an access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create an
IngressClassParamsresource YAML file, for example,sample-single-lb-params.yaml, as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
IngressClassParamsresource by running the following command:oc create -f sample-single-lb-params.yaml
$ oc create -f sample-single-lb-params.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
IngressClassresource YAML file, for example,sample-single-lb-class.yaml, as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Defines the API group and version of the
IngressClassresource. - 2
- Specifies the ingress class name.
- 3
- Defines the controller name. The
ingress.k8s.aws/albvalue denotes that all ingress resources of this class should be managed by the AWS Load Balancer Controller. - 4
- Defines the API group of the
IngressClassParamsresource. - 5
- Defines the resource type of the
IngressClassParamsresource. - 6
- Defines the
IngressClassParamsresource name.
Create the
IngressClassresource by running the following command:oc create -f sample-single-lb-class.yaml
$ oc create -f sample-single-lb-class.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerresource YAML file, for example,sample-single-lb.yaml, as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Defines the name of the
IngressClassresource.
Create the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerresource by running the following command:oc create -f sample-single-lb.yaml
$ oc create -f sample-single-lb.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
Ingressresource YAML file, for example,sample-multiple-ingress.yaml, as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the ingress name.
- 2
- Indicates the load balancer to provision in the public subnet to access the internet.
- 3
- Specifies the order in which the rules from the multiple ingress resources are matched when the request is received at the load balancer.
- 4
- Indicates that the load balancer will target OpenShift Container Platform nodes to reach the service.
- 5
- Specifies the ingress class that belongs to this ingress.
- 6
- Defines a domain name used for request routing.
- 7
- Defines the path that must route to the service.
- 8
- Defines the service name that serves the endpoint configured in the
Ingressresource. - 9
- Defines the port on the service that serves the endpoint.
Create the
Ingressresource by running the following command:oc create -f sample-multiple-ingress.yaml
$ oc create -f sample-multiple-ingress.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.7. Adding TLS termination
You can add TLS termination on the AWS Load Balancer.
22.7.1. Adding TLS termination on the AWS Load Balancer
You can route the traffic for the domain to pods of a service and add TLS termination on the AWS Load Balancer.
Prerequisites
-
You have an access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a YAML file that defines the
AWSLoadBalancerControllerresource:Example
add-tls-termination-albc.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Defines the ingress class name. If the ingress class is not present in your cluster the AWS Load Balancer Controller creates one. The AWS Load Balancer Controller reconciles the additional ingress class values if
spec.controlleris set toingress.k8s.aws/alb.
Create a YAML file that defines the
Ingressresource:Example
add-tls-termination-ingress.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the ingress name.
- 2
- The controller provisions the load balancer for ingress in a public subnet to access the load balancer over the internet.
- 3
- The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the certificate that you attach to the load balancer.
- 4
- Defines the ingress class name.
- 5
- Defines the domain for traffic routing.
- 6
- Defines the service for traffic routing.
22.8. Configuring cluster-wide proxy
You can configure the cluster-wide proxy in the AWS Load Balancer Operator. After configuring the cluster-wide proxy, Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) automatically updates all the deployments of the Operators with the environment variables such as HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY, and NO_PROXY. These variables are populated to the managed controller by the AWS Load Balancer Operator.
22.8.1. Trusting the certificate authority of the cluster-wide proxy
Create the config map to contain the certificate authority (CA) bundle in the
aws-load-balancer-operatornamespace by running the following command:oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator create configmap trusted-ca
$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator create configmap trusted-caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To inject the trusted CA bundle into the config map, add the
config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=truelabel to the config map by running the following command:oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator label cm trusted-ca config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=true
$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator label cm trusted-ca config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the AWS Load Balancer Operator subscription to access the config map in the AWS Load Balancer Operator deployment by running the following command:
oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator patch subscription aws-load-balancer-operator --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"config":{"env":[{"name":"TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME","value":"trusted-ca"}],"volumes":[{"name":"trusted-ca","configMap":{"name":"trusted-ca"}}],"volumeMounts":[{"name":"trusted-ca","mountPath":"/etc/pki/tls/certs/albo-tls-ca-bundle.crt","subPath":"ca-bundle.crt"}]}}}'$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator patch subscription aws-load-balancer-operator --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"config":{"env":[{"name":"TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME","value":"trusted-ca"}],"volumes":[{"name":"trusted-ca","configMap":{"name":"trusted-ca"}}],"volumeMounts":[{"name":"trusted-ca","mountPath":"/etc/pki/tls/certs/albo-tls-ca-bundle.crt","subPath":"ca-bundle.crt"}]}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the AWS Load Balancer Operator is deployed, verify that the CA bundle is added to the
aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-managerdeployment by running the following command:oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator exec deploy/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager -c manager -- bash -c "ls -l /etc/pki/tls/certs/albo-tls-ca-bundle.crt; printenv TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME"
$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator exec deploy/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager -c manager -- bash -c "ls -l /etc/pki/tls/certs/albo-tls-ca-bundle.crt; printenv TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP_NAME"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
-rw-r--r--. 1 root 1000690000 5875 Jan 11 12:25 /etc/pki/tls/certs/albo-tls-ca-bundle.crt trusted-ca
-rw-r--r--. 1 root 1000690000 5875 Jan 11 12:25 /etc/pki/tls/certs/albo-tls-ca-bundle.crt trusted-caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Restart deployment of the AWS Load Balancer Operator every time the config map changes by running the following command:
oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator rollout restart deployment/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-manager
$ oc -n aws-load-balancer-operator rollout restart deployment/aws-load-balancer-operator-controller-managerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 23. Multiple networks
23.1. Understanding multiple networks
In Kubernetes, container networking is delegated to networking plugins that implement the Container Network Interface (CNI).
OpenShift Container Platform uses the Multus CNI plugin to allow chaining of CNI plugins. During cluster installation, you configure your default pod network. The default network handles all ordinary network traffic for the cluster. You can define an additional network based on the available CNI plugins and attach one or more of these networks to your pods. You can define more than one additional network for your cluster, depending on your needs. This gives you flexibility when you configure pods that deliver network functionality, such as switching or routing.
23.1.1. Usage scenarios for an additional network
You can use an additional network in situations where network isolation is needed, including data plane and control plane separation. Isolating network traffic is useful for the following performance and security reasons:
- Performance
- You can send traffic on two different planes to manage how much traffic is along each plane.
- Security
- You can send sensitive traffic onto a network plane that is managed specifically for security considerations, and you can separate private data that must not be shared between tenants or customers.
All of the pods in the cluster still use the cluster-wide default network to maintain connectivity across the cluster. Every pod has an eth0 interface that is attached to the cluster-wide pod network. You can view the interfaces for a pod by using the oc exec -it <pod_name> -- ip a command. If you add additional network interfaces that use Multus CNI, they are named net1, net2, …, netN.
To attach additional network interfaces to a pod, you must create configurations that define how the interfaces are attached. You specify each interface by using a NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource (CR). A CNI configuration inside each of these CRs defines how that interface is created.
23.1.2. Additional networks in OpenShift Container Platform
OpenShift Container Platform provides the following CNI plugins for creating additional networks in your cluster:
- bridge: Configure a bridge-based additional network to allow pods on the same host to communicate with each other and the host.
- host-device: Configure a host-device additional network to allow pods access to a physical Ethernet network device on the host system.
- ipvlan: Configure an ipvlan-based additional network to allow pods on a host to communicate with other hosts and pods on those hosts, similar to a macvlan-based additional network. Unlike a macvlan-based additional network, each pod shares the same MAC address as the parent physical network interface.
- vlan: Configure a vlan-based additional network to allow VLAN-based network isolation and connectivity for pods.
- macvlan: Configure a macvlan-based additional network to allow pods on a host to communicate with other hosts and pods on those hosts by using a physical network interface. Each pod that is attached to a macvlan-based additional network is provided a unique MAC address.
- SR-IOV: Configure an SR-IOV based additional network to allow pods to attach to a virtual function (VF) interface on SR-IOV capable hardware on the host system.
23.2. Configuring an additional network
As a cluster administrator, you can configure an additional network for your cluster. The following network types are supported:
23.2.1. Approaches to managing an additional network
You can manage the lifecycle of an additional network in OpenShift Container Platform by using one of two approaches: modifying the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration or applying a YAML manifest. Each approach is mutually exclusive and you can only use one approach for managing an additional network at a time. For either approach, the additional network is managed by a Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin that you configure. The two different approaches are summarized here:
-
Modifying the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration: Configuring additional networks through CNO is only possible for cluster administrators. The CNO automatically creates and manages the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject. By using this approach, you can defineNetworkAttachmentDefinitionobjects at install time through configuration of theinstall-config. -
Applying a YAML manifest: You can manage the additional network directly by creating an
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject. Compared to modifying the CNO configuration, this approach gives you more granular control and flexibility when it comes to configuration.
When deploying OpenShift Container Platform nodes with multiple network interfaces on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) with OVN Kubernetes, DNS configuration of the secondary interface might take precedence over the DNS configuration of the primary interface. In this case, remove the DNS nameservers for the subnet ID that is attached to the secondary interface:
openstack subnet set --dns-nameserver 0.0.0.0 <subnet_id>
$ openstack subnet set --dns-nameserver 0.0.0.0 <subnet_id>23.2.2. IP address assignment for additional networks
For additional networks, IP addresses can be assigned using an IP Address Management (IPAM) CNI plugin, which supports various assignment methods, including Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and static assignment.
The DHCP IPAM CNI plugin responsible for dynamic assignment of IP addresses operates with two distinct components:
- CNI Plugin: Responsible for integrating with the Kubernetes networking stack to request and release IP addresses.
- DHCP IPAM CNI Daemon: A listener for DHCP events that coordinates with existing DHCP servers in the environment to handle IP address assignment requests. This daemon is not a DHCP server itself.
For networks requiring type: dhcp in their IPAM configuration, ensure the following:
- A DHCP server is available and running in the environment. The DHCP server is external to the cluster and is expected to be part of the customer’s existing network infrastructure.
- The DHCP server is appropriately configured to serve IP addresses to the nodes.
In cases where a DHCP server is unavailable in the environment, it is recommended to use the Whereabouts IPAM CNI plugin instead. The Whereabouts CNI provides similar IP address management capabilities without the need for an external DHCP server.
Use the Whereabouts CNI plugin when there is no external DHCP server or where static IP address management is preferred. The Whereabouts plugin includes a reconciler daemon to manage stale IP address allocations.
A DHCP lease must be periodically renewed throughout the container’s lifetime, so a separate daemon, the DHCP IPAM CNI Daemon, is required. To deploy the DHCP IPAM CNI daemon, modify the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration to trigger the deployment of this daemon as part of the additional network setup.
23.2.3. Configuration for an additional network attachment
An additional network is configured by using the NetworkAttachmentDefinition API in the k8s.cni.cncf.io API group.
Do not store any sensitive information or a secret in the NetworkAttachmentDefinition object because this information is accessible by the project administration user.
The configuration for the API is described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| The name for the additional network. |
|
|
| The namespace that the object is associated with. |
|
|
| The CNI plugin configuration in JSON format. |
23.2.3.1. Configuration of an additional network through the Cluster Network Operator
The configuration for an additional network attachment is specified as part of the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration.
The following YAML describes the configuration parameters for managing an additional network with the CNO:
Cluster Network Operator configuration
- 1
- An array of one or more additional network configurations.
- 2
- The name for the additional network attachment that you are creating. The name must be unique within the specified
namespace. - 3
- The namespace to create the network attachment in. If you do not specify a value then the
defaultnamespace is used.ImportantTo prevent namespace issues for the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, do not name your additional network attachment
default, because this namespace is reserved for thedefaultadditional network attachment. - 4
- A CNI plugin configuration in JSON format.
23.2.3.2. Configuration of an additional network from a YAML manifest
The configuration for an additional network is specified from a YAML configuration file, such as in the following example:
23.2.4. Configurations for additional network types
The specific configuration fields for additional networks is described in the following sections.
23.2.4.1. Configuration for a bridge additional network
The following object describes the configuration parameters for the bridge CNI plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The CNI specification version. The |
|
|
|
The value for the |
|
|
|
The name of the CNI plugin to configure: |
|
|
| The configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specify the name of the virtual bridge to use. If the bridge interface does not exist on the host, it is created. The default value is |
|
|
|
Optional: Set to |
|
|
|
Optional: Set to |
|
|
|
Optional: Set to |
|
|
|
Optional: Set to |
|
|
|
Optional: Set to |
|
|
|
Optional: Set to |
|
|
| Optional: Specify a virtual LAN (VLAN) tag as an integer value. By default, no VLAN tag is assigned. |
|
|
|
Optional: Indicates whether the default vlan must be preserved on the |
|
|
| Optional: Set the maximum transmission unit (MTU) to the specified value. The default value is automatically set by the kernel. |
|
|
|
Optional: Enables duplicate address detection for the container side |
|
|
|
Optional: Enables mac spoof check, limiting the traffic originating from the container to the mac address of the interface. The default value is |
The VLAN parameter configures the VLAN tag on the host end of the veth and also enables the vlan_filtering feature on the bridge interface.
To configure uplink for a L2 network you need to allow the vlan on the uplink interface by using the following command:
bridge vlan add vid VLAN_ID dev DEV
$ bridge vlan add vid VLAN_ID dev DEV23.2.4.1.1. bridge configuration example
The following example configures an additional network named bridge-net:
23.2.4.2. Configuration for a host device additional network
Specify your network device by setting only one of the following parameters: device,hwaddr, kernelpath, or pciBusID.
The following object describes the configuration parameters for the host-device CNI plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The CNI specification version. The |
|
|
|
The value for the |
|
|
|
The name of the CNI plugin to configure: |
|
|
|
Optional: The name of the device, such as |
|
|
| Optional: The device hardware MAC address. |
|
|
|
Optional: The Linux kernel device path, such as |
|
|
|
Optional: The PCI address of the network device, such as |
23.2.4.2.1. host-device configuration example
The following example configures an additional network named hostdev-net:
23.2.4.3. Configuration for an VLAN additional network
The following object describes the configuration parameters for the VLAN CNI plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The CNI specification version. The |
|
|
|
The value for the |
|
|
|
The name of the CNI plugin to configure: |
|
|
|
The Ethernet interface to associate with the network attachment. If a |
|
|
| Set the id of the vlan. |
|
|
| The configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition. |
|
|
| Optional: Set the maximum transmission unit (MTU) to the specified value. The default value is automatically set by the kernel. |
|
|
| Optional: DNS information to return, for example, a priority-ordered list of DNS nameservers. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies if the master interface is in the container network namespace or the main network namespace. |
23.2.4.3.1. vlan configuration example
The following example configures an additional network named vlan-net:
23.2.4.4. Configuration for an IPVLAN additional network
The following object describes the configuration parameters for the IPVLAN CNI plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The CNI specification version. The |
|
|
|
The value for the |
|
|
|
The name of the CNI plugin to configure: |
|
|
| The configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition. This is required unless the plugin is chained. |
|
|
|
Optional: The operating mode for the virtual network. The value must be |
|
|
|
Optional: The Ethernet interface to associate with the network attachment. If a |
|
|
| Optional: Set the maximum transmission unit (MTU) to the specified value. The default value is automatically set by the kernel. |
-
The
ipvlanobject does not allow virtual interfaces to communicate with themasterinterface. Therefore the container will not be able to reach the host by using theipvlaninterface. Be sure that the container joins a network that provides connectivity to the host, such as a network supporting the Precision Time Protocol (PTP). -
A single
masterinterface cannot simultaneously be configured to use bothmacvlanandipvlan. -
For IP allocation schemes that cannot be interface agnostic, the
ipvlanplugin can be chained with an earlier plugin that handles this logic. If themasteris omitted, then the previous result must contain a single interface name for theipvlanplugin to enslave. Ifipamis omitted, then the previous result is used to configure theipvlaninterface.
23.2.4.4.1. ipvlan configuration example
The following example configures an additional network named ipvlan-net:
23.2.4.5. Configuration for a MACVLAN additional network
The following object describes the configuration parameters for the MAC Virtual LAN (MACVLAN) Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The CNI specification version. The |
|
|
|
The value for the |
|
|
|
The name of the CNI plugin to configure: |
|
|
| The configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition. |
|
|
|
Optional: Configures traffic visibility on the virtual network. Must be either |
|
|
| Optional: The host network interface to associate with the newly created macvlan interface. If a value is not specified, then the default route interface is used. |
|
|
| Optional: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) to the specified value. The default value is automatically set by the kernel. |
If you specify the master key for the plugin configuration, use a different physical network interface than the one that is associated with your primary network plugin to avoid possible conflicts.
23.2.4.5.1. MACVLAN configuration example
The following example configures an additional network named macvlan-net:
23.2.4.6. Configuration for an OVN-Kubernetes additional network
The Red Hat OpenShift Networking OVN-Kubernetes network plugin allows the configuration of secondary network interfaces for pods. To configure secondary network interfaces, you must define the configurations in the NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource definition (CRD).
Configuration for an OVN-Kubernetes additional network is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
Pod and multi-network policy creation might remain in a pending state until the OVN-Kubernetes control plane agent in the nodes processes the associated network-attachment-definition CR.
The following sections provide example configurations for each of the topologies that OVN-Kubernetes currently allows for secondary networks.
Networks names must be unique. For example, creating multiple NetworkAttachmentDefinition CRDs with different configurations that reference the same network is unsupported.
23.2.4.6.1. OVN-Kubernetes network plugin JSON configuration table
The following table describes the configuration parameters for the OVN-Kubernetes CNI network plugin:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The CNI specification version. The required value is |
|
|
|
The name of the network. These networks are not namespaced. For example, you can have a network named |
|
|
|
The name of the CNI plugin to configure. The required value is |
|
|
|
The topological configuration for the network. The required value is |
|
|
| The subnet to use for the network across the cluster.
For |
|
|
|
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) to the specified value. The default value, |
|
|
|
The metadata |
|
|
| A comma-separated list of CIDRs and IPs. IPs are removed from the assignable IP pool, and are never passed to the pods. When omitted, the logical switch implementing the network only provides layer 2 communication, and users must configure IPs for the pods. Port security only prevents MAC spoofing. |
23.2.4.6.2. Configuration for a switched topology
The switched (layer 2) topology networks interconnect the workloads through a cluster-wide logical switch. This configuration can be used for IPv6 and dual-stack deployments.
Layer 2 switched topology networks only allow for the transfer of data packets between pods within a cluster.
The following NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource definition (CRD) YAML describes the fields needed to configure a switched secondary network.
23.2.4.6.3. Configuring pods for additional networks
You must specify the secondary network attachments through the k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks annotation.
The following example provisions a pod with two secondary attachments, one for each of the attachment configurations presented in this guide.
23.2.4.6.4. Configuring pods with a static IP address
The following example provisions a pod with a static IP address.
- You can only specify the IP address for a pod’s secondary network attachment for layer 2 attachments.
- Specifying a static IP address for the pod is only possible when the attachment configuration does not feature subnets.
23.2.5. Configuration of IP address assignment for an additional network
The IP address management (IPAM) Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin provides IP addresses for other CNI plugins.
You can use the following IP address assignment types:
- Static assignment.
- Dynamic assignment through a DHCP server. The DHCP server you specify must be reachable from the additional network.
- Dynamic assignment through the Whereabouts IPAM CNI plugin.
23.2.5.1. Static IP address assignment configuration
The following table describes the configuration for static IP address assignment:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
|
|
| An array of objects specifying IP addresses to assign to the virtual interface. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses are supported. |
|
|
| An array of objects specifying routes to configure inside the pod. |
|
|
| Optional: An array of objects specifying the DNS configuration. |
The addresses array requires objects with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
An IP address and network prefix that you specify. For example, if you specify |
|
|
| The default gateway to route egress network traffic to. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IP address range in CIDR format, such as |
|
|
| The gateway where network traffic is routed. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| An array of one or more IP addresses for to send DNS queries to. |
|
|
|
The default domain to append to a hostname. For example, if the domain is set to |
|
|
|
An array of domain names to append to an unqualified hostname, such as |
Static IP address assignment configuration example
23.2.5.2. Dynamic IP address (DHCP) assignment configuration
The following JSON describes the configuration for dynamic IP address address assignment with DHCP.
A pod obtains its original DHCP lease when it is created. The lease must be periodically renewed by a minimal DHCP server deployment running on the cluster.
To trigger the deployment of the DHCP server, you must create a shim network attachment by editing the Cluster Network Operator configuration, as in the following example:
Example shim network attachment definition
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
Dynamic IP address (DHCP) assignment configuration example
{
"ipam": {
"type": "dhcp"
}
}
{
"ipam": {
"type": "dhcp"
}
}23.2.5.3. Dynamic IP address assignment configuration with Whereabouts
The Whereabouts CNI plugin allows the dynamic assignment of an IP address to an additional network without the use of a DHCP server.
The following table describes the configuration for dynamic IP address assignment with Whereabouts:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
|
|
| An IP address and range in CIDR notation. IP addresses are assigned from within this range of addresses. |
|
|
| Optional: A list of zero or more IP addresses and ranges in CIDR notation. IP addresses within an excluded address range are not assigned. |
Dynamic IP address assignment configuration example that uses Whereabouts
23.2.5.4. Creating a whereabouts-reconciler daemon set
The Whereabouts reconciler is responsible for managing dynamic IP address assignments for the pods within a cluster by using the Whereabouts IP Address Management (IPAM) solution. It ensures that each pod gets a unique IP address from the specified IP address range. It also handles IP address releases when pods are deleted or scaled down.
You can also use a NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource (CR) for dynamic IP address assignment.
The whereabouts-reconciler daemon set is automatically created when you configure an additional network through the Cluster Network Operator. It is not automatically created when you configure an additional network from a YAML manifest.
To trigger the deployment of the whereabouts-reconciler daemon set, you must manually create a whereabouts-shim network attachment by editing the Cluster Network Operator custom resource (CR) file.
Use the following procedure to deploy the whereabouts-reconciler daemon set.
Procedure
Edit the
Network.operator.openshift.iocustom resource (CR) by running the following command:oc edit network.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit network.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Include the
additionalNetworkssection shown in this example YAML extract within thespecdefinition of the custom resource (CR):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file and exit the text editor.
Verify that the
whereabouts-reconcilerdaemon set deployed successfully by running the following command:oc get all -n openshift-multus | grep whereabouts-reconciler
$ oc get all -n openshift-multus | grep whereabouts-reconcilerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.2.5.5. Configuring the Whereabouts IP reconciler schedule
The Whereabouts IPAM CNI plugin runs the IP reconciler daily. This process cleans up any stranded IP allocations that might result in exhausting IPs and therefore prevent new pods from getting an IP allocated to them.
Use this procedure to change the frequency at which the IP reconciler runs.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have deployed the
whereabouts-reconcilerdaemon set, and thewhereabouts-reconcilerpods are up and running.
Procedure
Run the following command to create a
ConfigMapobject namedwhereabouts-configin theopenshift-multusnamespace with a specific cron expression for the IP reconciler:oc create configmap whereabouts-config -n openshift-multus --from-literal=reconciler_cron_expression="*/15 * * * *"
$ oc create configmap whereabouts-config -n openshift-multus --from-literal=reconciler_cron_expression="*/15 * * * *"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This cron expression indicates the IP reconciler runs every 15 minutes. Adjust the expression based on your specific requirements.
NoteThe
whereabouts-reconcilerdaemon set can only consume a cron expression pattern that includes five asterisks. The sixth, which is used to denote seconds, is currently not supported.Retrieve information about resources related to the
whereabouts-reconcilerdaemon set and pods within theopenshift-multusnamespace by running the following command:oc get all -n openshift-multus | grep whereabouts-reconciler
$ oc get all -n openshift-multus | grep whereabouts-reconcilerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to verify that the
whereabouts-reconcilerpod runs the IP reconciler with the configured interval:oc -n openshift-multus logs whereabouts-reconciler-2p7hw
$ oc -n openshift-multus logs whereabouts-reconciler-2p7hwCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.2.6. Creating an additional network attachment with the Cluster Network Operator
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) manages additional network definitions. When you specify an additional network to create, the CNO creates the NetworkAttachmentDefinition object automatically.
Do not edit the NetworkAttachmentDefinition objects that the Cluster Network Operator manages. Doing so might disrupt network traffic on your additional network.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Optional: Create the namespace for the additional networks:
oc create namespace <namespace_name>
$ oc create namespace <namespace_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To edit the CNO configuration, enter the following command:
oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the CR that you are creating by adding the configuration for the additional network that you are creating, as in the following example CR.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save your changes and quit the text editor to commit your changes.
Verification
Confirm that the CNO created the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject by running the following command. There might be a delay before the CNO creates the object.oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>
$ oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Specifies the namespace for the network attachment that you added to the CNO configuration.
Example output
NAME AGE test-network-1 14m
NAME AGE test-network-1 14mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.2.7. Creating an additional network attachment by applying a YAML manifest
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a YAML file with your additional network configuration, such as in the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the additional network, enter the following command:
oc apply -f <file>.yaml
$ oc apply -f <file>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<file>- Specifies the name of the file contained the YAML manifest.
23.3. About virtual routing and forwarding
23.3.1. About virtual routing and forwarding
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) devices combined with IP rules provide the ability to create virtual routing and forwarding domains. VRF reduces the number of permissions needed by CNF, and provides increased visibility of the network topology of secondary networks. VRF is used to provide multi-tenancy functionality, for example, where each tenant has its own unique routing tables and requires different default gateways.
Processes can bind a socket to the VRF device. Packets through the binded socket use the routing table associated with the VRF device. An important feature of VRF is that it impacts only OSI model layer 3 traffic and above so L2 tools, such as LLDP, are not affected. This allows higher priority IP rules such as policy based routing to take precedence over the VRF device rules directing specific traffic.
23.3.1.1. Benefits of secondary networks for pods for telecommunications operators
In telecommunications use cases, each CNF can potentially be connected to multiple different networks sharing the same address space. These secondary networks can potentially conflict with the cluster’s main network CIDR. Using the CNI VRF plugin, network functions can be connected to different customers' infrastructure using the same IP address, keeping different customers isolated. IP addresses are overlapped with OpenShift Container Platform IP space. The CNI VRF plugin also reduces the number of permissions needed by CNF and increases the visibility of network topologies of secondary networks.
23.4. Configuring multi-network policy
As a cluster administrator, you can configure multi-network for additional networks. You can specify multi-network policy for SR-IOV and macvlan additional networks. Macvlan additional networks are fully supported. Other types of additional networks, such as ipvlan, are not supported.
Support for configuring multi-network policies for SR-IOV additional networks is a Technology Preview feature and is only supported with kernel network interface cards (NICs). SR-IOV is not supported for Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) applications.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
Configured network policies are ignored in IPv6 networks.
23.4.1. Differences between multi-network policy and network policy
Although the MultiNetworkPolicy API implements the NetworkPolicy API, there are several important differences:
You must use the
MultiNetworkPolicyAPI:apiVersion: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1beta1 kind: MultiNetworkPolicy
apiVersion: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1beta1 kind: MultiNetworkPolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
You must use the
multi-networkpolicyresource name when using the CLI to interact with multi-network policies. For example, you can view a multi-network policy object with theoc get multi-networkpolicy <name>command where<name>is the name of a multi-network policy. You can use the
k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/policy-forannotation on aMultiNetworkPolicyobject to point to aNetworkAttachmentDefinition(NAD) custom resource (CR). The NAD CR defines the network to which the policy applies.Example multi-network policy that includes the
k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/policy-forannotationapiVersion: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1beta1 kind: MultiNetworkPolicy metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/policy-for:<namespace_name>/<network_name>apiVersion: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1beta1 kind: MultiNetworkPolicy metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/policy-for:<namespace_name>/<network_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace_name>- Specifies the namespace name.
<network_name>- Specifies the name of a network attachment definition.
23.4.2. Enabling multi-network policy for the cluster
As a cluster administrator, you can enable multi-network policy support on your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the
multinetwork-enable-patch.yamlfile with the following YAML:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the cluster to enable multi-network policy:
oc patch network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch-file=multinetwork-enable-patch.yaml
$ oc patch network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge --patch-file=multinetwork-enable-patch.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.4.3. Working with multi-network policy
As a cluster administrator, you can create, edit, view, and delete multi-network policies.
23.4.3.1. Prerequisites
- You have enabled multi-network policy support for your cluster.
23.4.3.2. Creating a multi-network policy using the CLI
To define granular rules describing ingress or egress network traffic allowed for namespaces in your cluster, you can create a multi-network policy.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the multi-network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy rule:
Create a
<policy_name>.yamlfile:touch <policy_name>.yaml
$ touch <policy_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the multi-network policy file name.
Define a multi-network policy in the file that you just created, such as in the following examples:
Deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces
This is a fundamental policy, blocking all cross-pod networking other than cross-pod traffic allowed by the configuration of other Network Policies.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<network_name>- Specifies the name of a network attachment definition.
Allow ingress from all pods in the same namespace
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<network_name>- Specifies the name of a network attachment definition.
Allow ingress traffic to one pod from a particular namespace
This policy allows traffic to pods labelled
pod-afrom pods running innamespace-y.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<network_name>- Specifies the name of a network attachment definition.
Restrict traffic to a service
This policy when applied ensures every pod with both labels
app=bookstoreandrole=apican only be accessed by pods with labelapp=bookstore. In this example the application could be a REST API server, marked with labelsapp=bookstoreandrole=api.This example addresses the following use cases:
- Restricting the traffic to a service to only the other microservices that need to use it.
Restricting the connections to a database to only permit the application using it.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<network_name>- Specifies the name of a network attachment definition.
To create the multi-network policy object, enter the following command:
oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>
$ oc apply -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the multi-network policy file name.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/deny-by-default created
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/deny-by-default createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of creating a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
23.4.3.3. Editing a multi-network policy
You can edit a multi-network policy in a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the multi-network policy exists.
Procedure
Optional: To list the multi-network policy objects in a namespace, enter the following command:
oc get multi-networkpolicy
$ oc get multi-networkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Edit the multi-network policy object.
If you saved the multi-network policy definition in a file, edit the file and make any necessary changes, and then enter the following command.
oc apply -n <namespace> -f <policy_file>.yaml
$ oc apply -n <namespace> -f <policy_file>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
<policy_file>- Specifies the name of the file containing the network policy.
If you need to update the multi-network policy object directly, enter the following command:
oc edit multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc edit multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Confirm that the multi-network policy object is updated.
oc describe multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc describe multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the multi-network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of editing a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from the policy in the web console through the Actions menu.
23.4.3.4. Viewing multi-network policies using the CLI
You can examine the multi-network policies in a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the multi-network policy exists.
Procedure
List multi-network policies in a namespace:
To view multi-network policy objects defined in a namespace, enter the following command:
oc get multi-networkpolicy
$ oc get multi-networkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To examine a specific multi-network policy, enter the following command:
oc describe multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc describe multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the multi-network policy to inspect.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of viewing a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from a form in the web console.
23.4.3.5. Deleting a multi-network policy using the CLI
You can delete a multi-network policy in a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace where the multi-network policy exists.
Procedure
To delete a multi-network policy object, enter the following command:
oc delete multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc delete multi-networkpolicy <policy_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<policy_name>- Specifies the name of the multi-network policy.
<namespace>- Optional: Specifies the namespace if the object is defined in a different namespace than the current namespace.
Example output
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/default-deny deleted
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/default-deny deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you log in to the web console with cluster-admin privileges, you have a choice of deleting a network policy in any namespace in the cluster directly in YAML or from the policy in the web console through the Actions menu.
23.4.3.6. Creating a default deny all multi-network policy
This is a fundamental policy, blocking all cross-pod networking other than network traffic allowed by the configuration of other deployed network policies. This procedure enforces a default deny-by-default policy.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the multi-network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create the following YAML that defines a
deny-by-defaultpolicy to deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces. Save the YAML in thedeny-by-default.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
namespace: defaultdeploys this policy to thedefaultnamespace.- 2
network_name: specifies the name of a network attachment definition.- 3
podSelector:is empty, this means it matches all the pods. Therefore, the policy applies to all pods in the default namespace.- 4
- There are no
ingressrules specified. This causes incoming traffic to be dropped to all pods.
Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f deny-by-default.yaml
$ oc apply -f deny-by-default.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/deny-by-default created
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/deny-by-default createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.4.3.7. Creating a multi-network policy to allow traffic from external clients
With the deny-by-default policy in place you can proceed to configure a policy that allows traffic from external clients to a pod with the label app=web.
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows external service from the public Internet directly or by using a Load Balancer to access the pod. Traffic is only allowed to a pod with the label app=web.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the multi-network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from the public Internet directly or by using a load balancer to access the pod. Save the YAML in the
web-allow-external.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-external.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-external.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/web-allow-external created
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/web-allow-external createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This policy allows traffic from all resources, including external traffic as illustrated in the following diagram:

23.4.3.8. Creating a multi-network policy allowing traffic to an application from all namespaces
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows traffic from all pods in all namespaces to a particular application.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the multi-network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in all namespaces to a particular application. Save the YAML in the
web-allow-all-namespaces.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, if you omit specifying a
namespaceSelectorit does not select any namespaces, which means the policy allows traffic only from the namespace the network policy is deployed to.Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-all-namespaces.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-all-namespaces.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/web-allow-all-namespaces created
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/web-allow-all-namespaces createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in thesecondarynamespace and to start a shell:oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=secondary --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=secondary --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is allowed:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.4.3.9. Creating a multi-network policy allowing traffic to an application from a namespace
If you log in with a user with the cluster-admin role, then you can create a network policy in any namespace in the cluster.
Follow this procedure to configure a policy that allows traffic to a pod with the label app=web from a particular namespace. You might want to do this to:
- Restrict traffic to a production database only to namespaces where production workloads are deployed.
- Enable monitoring tools deployed to a particular namespace to scrape metrics from the current namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Your cluster uses a network plugin that supports
NetworkPolicyobjects, such as the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin or the OpenShift SDN network plugin withmode: NetworkPolicyset. This mode is the default for OpenShift SDN. -
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You are working in the namespace that the multi-network policy applies to.
Procedure
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in a particular namespaces with a label
purpose=production. Save the YAML in theweb-allow-prod.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/web-allow-prod created
multinetworkpolicy.k8s.cni.cncf.io/web-allow-prod createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to create the
prodnamespace:oc create namespace prod
$ oc create namespace prodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to label the
prodnamespace:oc label namespace/prod purpose=production
$ oc label namespace/prod purpose=productionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to create the
devnamespace:oc create namespace dev
$ oc create namespace devCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to label the
devnamespace:oc label namespace/dev purpose=testing
$ oc label namespace/dev purpose=testingCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in thedevnamespace and to start a shell:oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=dev --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=dev --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is blocked:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
wget: download timed out
wget: download timed outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in theprodnamespace and start a shell:oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-$RANDOM --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command in the shell and observe that the request is allowed:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
# wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.5. Attaching a pod to an additional network
As a cluster user you can attach a pod to an additional network.
23.5.1. Adding a pod to an additional network
You can add a pod to an additional network. The pod continues to send normal cluster-related network traffic over the default network.
When a pod is created additional networks are attached to it. However, if a pod already exists, you cannot attach additional networks to it.
The pod must be in the same namespace as the additional network.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Log in to the cluster.
Procedure
Add an annotation to the
Podobject. Only one of the following annotation formats can be used:To attach an additional network without any customization, add an annotation with the following format. Replace
<network>with the name of the additional network to associate with the pod:metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: <network>[,<network>,...]metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: <network>[,<network>,...]1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- To specify more than one additional network, separate each network with a comma. Do not include whitespace between the comma. If you specify the same additional network multiple times, that pod will have multiple network interfaces attached to that network.
To attach an additional network with customizations, add an annotation with the following format:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To create the pod, enter the following command. Replace
<name>with the name of the pod.oc create -f <name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To Confirm that the annotation exists in the
PodCR, enter the following command, replacing<name>with the name of the pod.oc get pod <name> -o yaml
$ oc get pod <name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example, the
example-podpod is attached to thenet1additional network:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/network-statusparameter is a JSON array of objects. Each object describes the status of an additional network attached to the pod. The annotation value is stored as a plain text value.
23.5.1.1. Specifying pod-specific addressing and routing options
When attaching a pod to an additional network, you may want to specify further properties about that network in a particular pod. This allows you to change some aspects of routing, as well as specify static IP addresses and MAC addresses. To accomplish this, you can use the JSON formatted annotations.
Prerequisites
- The pod must be in the same namespace as the additional network.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster.
Procedure
To add a pod to an additional network while specifying addressing and/or routing options, complete the following steps:
Edit the
Podresource definition. If you are editing an existingPodresource, run the following command to edit its definition in the default editor. Replace<name>with the name of thePodresource to edit.oc edit pod <name>
$ oc edit pod <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the
Podresource definition, add thek8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networksparameter to the podmetadatamapping. Thek8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networksaccepts a JSON string of a list of objects that reference the name ofNetworkAttachmentDefinitioncustom resource (CR) names in addition to specifying additional properties.metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: '[<network>[,<network>,...]]'metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: '[<network>[,<network>,...]]'1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<network>with a JSON object as shown in the following examples. The single quotes are required.
In the following example the annotation specifies which network attachment will have the default route, using the
default-routeparameter.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
namekey is the name of the additional network to associate with the pod. - 2
- The
default-routekey specifies a value of a gateway for traffic to be routed over if no other routing entry is present in the routing table. If more than onedefault-routekey is specified, this will cause the pod to fail to become active.
The default route will cause any traffic that is not specified in other routes to be routed to the gateway.
Setting the default route to an interface other than the default network interface for OpenShift Container Platform may cause traffic that is anticipated for pod-to-pod traffic to be routed over another interface.
To verify the routing properties of a pod, the oc command may be used to execute the ip command within a pod.
oc exec -it <pod_name> -- ip route
$ oc exec -it <pod_name> -- ip route
You may also reference the pod’s k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/network-status to see which additional network has been assigned the default route, by the presence of the default-route key in the JSON-formatted list of objects.
To set a static IP address or MAC address for a pod you can use the JSON formatted annotations. This requires you create networks that specifically allow for this functionality. This can be specified in a rawCNIConfig for the CNO.
Edit the CNO CR by running the following command:
oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The following YAML describes the configuration parameters for the CNO:
Cluster Network Operator YAML configuration
- 1
- Specify a name for the additional network attachment that you are creating. The name must be unique within the specified
namespace. - 2
- Specify the namespace to create the network attachment in. If you do not specify a value, then the
defaultnamespace is used. - 3
- Specify the CNI plugin configuration in JSON format, which is based on the following template.
The following object describes the configuration parameters for utilizing static MAC address and IP address using the macvlan CNI plugin:
macvlan CNI plugin JSON configuration object using static IP and MAC address
- 1
- Specifies the name for the additional network attachment to create. The name must be unique within the specified
namespace. - 2
- Specifies an array of CNI plugin configurations. The first object specifies a macvlan plugin configuration and the second object specifies a tuning plugin configuration.
- 3
- Specifies that a request is made to enable the static IP address functionality of the CNI plugin runtime configuration capabilities.
- 4
- Specifies the interface that the macvlan plugin uses.
- 5
- Specifies that a request is made to enable the static MAC address functionality of a CNI plugin.
The above network attachment can be referenced in a JSON formatted annotation, along with keys to specify which static IP and MAC address will be assigned to a given pod.
Edit the pod with:
oc edit pod <name>
$ oc edit pod <name>macvlan CNI plugin JSON configuration object using static IP and MAC address
Static IP addresses and MAC addresses do not have to be used at the same time, you may use them individually, or together.
To verify the IP address and MAC properties of a pod with additional networks, use the oc command to execute the ip command within a pod.
oc exec -it <pod_name> -- ip a
$ oc exec -it <pod_name> -- ip a23.6. Removing a pod from an additional network
As a cluster user you can remove a pod from an additional network.
23.6.1. Removing a pod from an additional network
You can remove a pod from an additional network only by deleting the pod.
Prerequisites
- An additional network is attached to the pod.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Log in to the cluster.
Procedure
To delete the pod, enter the following command:
oc delete pod <name> -n <namespace>
$ oc delete pod <name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
<name>is the name of the pod. -
<namespace>is the namespace that contains the pod.
-
23.7. Editing an additional network
As a cluster administrator you can modify the configuration for an existing additional network.
23.7.1. Modifying an additional network attachment definition
As a cluster administrator, you can make changes to an existing additional network. Any existing pods attached to the additional network will not be updated.
Prerequisites
- You have configured an additional network for your cluster.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To edit an additional network for your cluster, complete the following steps:
Run the following command to edit the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) CR in your default text editor:
oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
In the
additionalNetworkscollection, update the additional network with your changes. - Save your changes and quit the text editor to commit your changes.
Optional: Confirm that the CNO updated the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject by running the following command. Replace<network-name>with the name of the additional network to display. There might be a delay before the CNO updates theNetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject to reflect your changes.oc get network-attachment-definitions <network-name> -o yaml
$ oc get network-attachment-definitions <network-name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the following console output displays a
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject that is namednet1:oc get network-attachment-definitions net1 -o go-template='{{printf "%s\n" .spec.config}}' { "cniVersion": "0.3.1", "type": "macvlan", "master": "ens5", "mode": "bridge", "ipam": {"type":"static","routes":[{"dst":"0.0.0.0/0","gw":"10.128.2.1"}],"addresses":[{"address":"10.128.2.100/23","gateway":"10.128.2.1"}],"dns":{"nameservers":["172.30.0.10"],"domain":"us-west-2.compute.internal","search":["us-west-2.compute.internal"]}} }$ oc get network-attachment-definitions net1 -o go-template='{{printf "%s\n" .spec.config}}' { "cniVersion": "0.3.1", "type": "macvlan", "master": "ens5", "mode": "bridge", "ipam": {"type":"static","routes":[{"dst":"0.0.0.0/0","gw":"10.128.2.1"}],"addresses":[{"address":"10.128.2.100/23","gateway":"10.128.2.1"}],"dns":{"nameservers":["172.30.0.10"],"domain":"us-west-2.compute.internal","search":["us-west-2.compute.internal"]}} }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.8. Removing an additional network
As a cluster administrator you can remove an additional network attachment.
23.8.1. Removing an additional network attachment definition
As a cluster administrator, you can remove an additional network from your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. The additional network is not removed from any pods it is attached to.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To remove an additional network from your cluster, complete the following steps:
Edit the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) in your default text editor by running the following command:
oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit networks.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the CR by removing the configuration from the
additionalNetworkscollection for the network attachment definition you are removing.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If you are removing the configuration mapping for the only additional network attachment definition in the
additionalNetworkscollection, you must specify an empty collection.
- Save your changes and quit the text editor to commit your changes.
Optional: Confirm that the additional network CR was deleted by running the following command:
oc get network-attachment-definition --all-namespaces
$ oc get network-attachment-definition --all-namespacesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
23.9. Assigning a secondary network to a VRF
As a cluster administrator, you can configure an additional network for a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) domain by using the CNI VRF plugin. The virtual network that this plugin creates is associated with the physical interface that you specify.
Using a secondary network with a VRF instance has the following advantages:
- Workload isolation
- Isolate workload traffic by configuring a VRF instance for the additional network.
- Improved security
- Enable improved security through isolated network paths in the VRF domain.
- Multi-tenancy support
- Support multi-tenancy through network segmentation with a unique routing table in the VRF domain for each tenant.
Applications that use VRFs must bind to a specific device. The common usage is to use the SO_BINDTODEVICE option for a socket. The SO_BINDTODEVICE option binds the socket to the device that is specified in the passed interface name, for example, eth1. To use the SO_BINDTODEVICE option, the application must have CAP_NET_RAW capabilities.
Using a VRF through the ip vrf exec command is not supported in OpenShift Container Platform pods. To use VRF, bind applications directly to the VRF interface.
23.9.1. Creating an additional network attachment with the CNI VRF plugin
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) manages additional network definitions. When you specify an additional network to create, the CNO creates the NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource (CR) automatically.
Do not edit the NetworkAttachmentDefinition CRs that the Cluster Network Operator manages. Doing so might disrupt network traffic on your additional network.
To create an additional network attachment with the CNI VRF plugin, perform the following procedure.
Prerequisites
- Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (oc).
- Log in to the OpenShift cluster as a user with cluster-admin privileges.
Procedure
Create the
Networkcustom resource (CR) for the additional network attachment and insert therawCNIConfigconfiguration for the additional network, as in the following example CR. Save the YAML as the fileadditional-network-attachment.yaml.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
pluginsmust be a list. The first item in the list must be the secondary network underpinning the VRF network. The second item in the list is the VRF plugin configuration.- 2
typemust be set tovrf.- 3
vrfnameis the name of the VRF that the interface is assigned to. If it does not exist in the pod, it is created.- 4
- Optional.
tableis the routing table ID. By default, thetableidparameter is used. If it is not specified, the CNI assigns a free routing table ID to the VRF.
NoteVRF functions correctly only when the resource is of type
netdevice.Create the
Networkresource:oc create -f additional-network-attachment.yaml
$ oc create -f additional-network-attachment.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the CNO created the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionCR by running the following command. Replace<namespace>with the namespace that you specified when configuring the network attachment, for example,additional-network-1.oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>
$ oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE additional-network-1 14m
NAME AGE additional-network-1 14mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThere might be a delay before the CNO creates the CR.
Verification
Create a pod and assign it to the additional network with the VRF instance:
Create a YAML file that defines the
Podresource:Example
pod-additional-net.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the name of the additional network with the VRF instance.
Create the
Podresource by running the following command:oc create -f pod-additional-net.yaml
$ oc create -f pod-additional-net.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
pod/test-pod created
pod/test-pod createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verify that the pod network attachment is connected to the VRF additional network. Start a remote session with the pod and run the following command:
ip vrf show
$ ip vrf showCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name Table ----------------------- vrf-1 1001
Name Table ----------------------- vrf-1 1001Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the VRF interface is the controller for the additional interface:
ip link
$ ip linkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
5: net1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master red state UP mode
5: net1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master red state UP modeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 24. Hardware networks
24.1. About Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) hardware networks
The Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) specification is a standard for a type of PCI device assignment that can share a single device with multiple pods.
SR-IOV can segment a compliant network device, recognized on the host node as a physical function (PF), into multiple virtual functions (VFs). The VF is used like any other network device. The SR-IOV network device driver for the device determines how the VF is exposed in the container:
-
netdevicedriver: A regular kernel network device in thenetnsof the container -
vfio-pcidriver: A character device mounted in the container
You can use SR-IOV network devices with additional networks on your OpenShift Container Platform cluster installed on bare metal or Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) infrastructure for applications that require high bandwidth or low latency.
You can configure multi-network policies for SR-IOV networks. The support for this is technology preview and SR-IOV additional networks are only supported with kernel NICs. They are not supported for Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) applications.
Creating multi-network policies on SR-IOV networks might not deliver the same performance to applications compared to SR-IOV networks without a multi-network policy configured.
Multi-network policies for SR-IOV network is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
You can enable SR-IOV on a node by using the following command:
oc label node <node_name> feature.node.kubernetes.io/network-sriov.capable="true"
$ oc label node <node_name> feature.node.kubernetes.io/network-sriov.capable="true"24.1.1. Components that manage SR-IOV network devices
The SR-IOV Network Operator creates and manages the components of the SR-IOV stack. It performs the following functions:
- Orchestrates discovery and management of SR-IOV network devices
-
Generates
NetworkAttachmentDefinitioncustom resources for the SR-IOV Container Network Interface (CNI) - Creates and updates the configuration of the SR-IOV network device plugin
-
Creates node specific
SriovNetworkNodeStatecustom resources -
Updates the
spec.interfacesfield in eachSriovNetworkNodeStatecustom resource
The Operator provisions the following components:
- SR-IOV network configuration daemon
- A daemon set that is deployed on worker nodes when the SR-IOV Network Operator starts. The daemon is responsible for discovering and initializing SR-IOV network devices in the cluster.
- SR-IOV Network Operator webhook
- A dynamic admission controller webhook that validates the Operator custom resource and sets appropriate default values for unset fields.
- SR-IOV Network resources injector
-
A dynamic admission controller webhook that provides functionality for patching Kubernetes pod specifications with requests and limits for custom network resources such as SR-IOV VFs. The SR-IOV network resources injector adds the
resourcefield to only the first container in a pod automatically. - SR-IOV network device plugin
- A device plugin that discovers, advertises, and allocates SR-IOV network virtual function (VF) resources. Device plugins are used in Kubernetes to enable the use of limited resources, typically in physical devices. Device plugins give the Kubernetes scheduler awareness of resource availability, so that the scheduler can schedule pods on nodes with sufficient resources.
- SR-IOV CNI plugin
- A CNI plugin that attaches VF interfaces allocated from the SR-IOV network device plugin directly into a pod.
- SR-IOV InfiniBand CNI plugin
- A CNI plugin that attaches InfiniBand (IB) VF interfaces allocated from the SR-IOV network device plugin directly into a pod.
The SR-IOV Network resources injector and SR-IOV Network Operator webhook are enabled by default and can be disabled by editing the default SriovOperatorConfig CR. Use caution when disabling the SR-IOV Network Operator Admission Controller webhook. You can disable the webhook under specific circumstances, such as troubleshooting, or if you want to use unsupported devices.
24.1.1.1. Supported platforms
The SR-IOV Network Operator is supported on the following platforms:
- Bare metal
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)
24.1.1.2. Supported devices
OpenShift Container Platform supports the following network interface controllers:
| Manufacturer | Model | Vendor ID | Device ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broadcom | BCM57414 | 14e4 | 16d7 |
| Broadcom | BCM57508 | 14e4 | 1750 |
| Broadcom | BCM57504 | 14e4 | 1751 |
| Intel | X710 | 8086 | 1572 |
| Intel | XL710 | 8086 | 1583 |
| Intel | X710 Base T | 8086 | 15ff |
| Intel | XXV710 | 8086 | 158b |
| Intel | E810-CQDA2 | 8086 | 1592 |
| Intel | E810-2CQDA2 | 8086 | 1592 |
| Intel | E810-XXVDA2 | 8086 | 159b |
| Intel | E810-XXVDA4 | 8086 | 1593 |
| Intel | E810-XXVDA4T | 8086 | 1593 |
| Mellanox | MT27700 Family [ConnectX‑4] | 15b3 | 1013 |
| Mellanox | MT27710 Family [ConnectX‑4 Lx] | 15b3 | 1015 |
| Mellanox | MT27800 Family [ConnectX‑5] | 15b3 | 1017 |
| Mellanox | MT28880 Family [ConnectX‑5 Ex] | 15b3 | 1019 |
| Mellanox | MT28908 Family [ConnectX‑6] | 15b3 | 101b |
| Mellanox | MT2892 Family [ConnectX‑6 Dx] | 15b3 | 101d |
| Mellanox | MT2894 Family [ConnectX‑6 Lx] | 15b3 | 101f |
| Mellanox | MT42822 BlueField‑2 in ConnectX‑6 NIC mode | 15b3 | a2d6 |
| Pensando [1] | DSC-25 dual-port 25G distributed services card for ionic driver | 0x1dd8 | 0x1002 |
| Pensando [1] | DSC-100 dual-port 100G distributed services card for ionic driver | 0x1dd8 | 0x1003 |
| Silicom | STS Family | 8086 | 1591 |
- OpenShift SR-IOV is supported, but you must set a static, Virtual Function (VF) media access control (MAC) address using the SR-IOV CNI config file when using SR-IOV.
For the most up-to-date list of supported cards and compatible OpenShift Container Platform versions available, see Openshift Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) and PTP hardware networks Support Matrix.
24.1.1.3. Automated discovery of SR-IOV network devices
The SR-IOV Network Operator searches your cluster for SR-IOV capable network devices on worker nodes. The Operator creates and updates a SriovNetworkNodeState custom resource (CR) for each worker node that provides a compatible SR-IOV network device.
The CR is assigned the same name as the worker node. The status.interfaces list provides information about the network devices on a node.
Do not modify a SriovNetworkNodeState object. The Operator creates and manages these resources automatically.
24.1.1.3.1. Example SriovNetworkNodeState object
The following YAML is an example of a SriovNetworkNodeState object created by the SR-IOV Network Operator:
An SriovNetworkNodeState object
24.1.1.4. Example use of a virtual function in a pod
You can run a remote direct memory access (RDMA) or a Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) application in a pod with SR-IOV VF attached.
This example shows a pod using a virtual function (VF) in RDMA mode:
Pod spec that uses RDMA mode
The following example shows a pod with a VF in DPDK mode:
Pod spec that uses DPDK mode
24.1.1.5. DPDK library for use with container applications
An optional library, app-netutil, provides several API methods for gathering network information about a pod from within a container running within that pod.
This library can assist with integrating SR-IOV virtual functions (VFs) in Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) mode into the container. The library provides both a Golang API and a C API.
Currently there are three API methods implemented:
GetCPUInfo()- This function determines which CPUs are available to the container and returns the list.
GetHugepages()-
This function determines the amount of huge page memory requested in the
Podspec for each container and returns the values. GetInterfaces()- This function determines the set of interfaces in the container and returns the list. The return value includes the interface type and type-specific data for each interface.
The repository for the library includes a sample Dockerfile to build a container image, dpdk-app-centos. The container image can run one of the following DPDK sample applications, depending on an environment variable in the pod specification: l2fwd, l3wd or testpmd. The container image provides an example of integrating the app-netutil library into the container image itself. The library can also integrate into an init container. The init container can collect the required data and pass the data to an existing DPDK workload.
24.1.1.6. Huge pages resource injection for Downward API
When a pod specification includes a resource request or limit for huge pages, the Network Resources Injector automatically adds Downward API fields to the pod specification to provide the huge pages information to the container.
The Network Resources Injector adds a volume that is named podnetinfo and is mounted at /etc/podnetinfo for each container in the pod. The volume uses the Downward API and includes a file for huge pages requests and limits. The file naming convention is as follows:
-
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_1G_request_<container-name> -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_1G_limit_<container-name> -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_2M_request_<container-name> -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_2M_limit_<container-name>
The paths specified in the previous list are compatible with the app-netutil library. By default, the library is configured to search for resource information in the /etc/podnetinfo directory. If you choose to specify the Downward API path items yourself manually, the app-netutil library searches for the following paths in addition to the paths in the previous list.
-
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_request -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_limit -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_1G_request -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_1G_limit -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_2M_request -
/etc/podnetinfo/hugepages_2M_limit
As with the paths that the Network Resources Injector can create, the paths in the preceding list can optionally end with a _<container-name> suffix.
24.1.3. Next steps
24.2. Installing the SR-IOV Network Operator
You can install the Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Network Operator on your cluster to manage SR-IOV network devices and network attachments.
24.2.1. Installing SR-IOV Network Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can install the SR-IOV Network Operator by using the OpenShift Container Platform CLI or the web console.
24.2.1.1. CLI: Installing the SR-IOV Network Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can install the Operator using the CLI.
Prerequisites
- A cluster installed on bare-metal hardware with nodes that have hardware that supports SR-IOV.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
An account with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To create the
openshift-sriov-network-operatornamespace, enter the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create an OperatorGroup CR, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Subscribe to the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Run the following command to get the OpenShift Container Platform major and minor version. It is required for the
channelvalue in the next step.OC_VERSION=$(oc version -o yaml | grep openshiftVersion | \ grep -o '[0-9]*[.][0-9]*' | head -1)$ OC_VERSION=$(oc version -o yaml | grep openshiftVersion | \ grep -o '[0-9]*[.][0-9]*' | head -1)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a Subscription CR for the SR-IOV Network Operator, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To verify that the Operator is installed, enter the following command:
oc get csv -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phase
$ oc get csv -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phaseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name Phase sriov-network-operator.4.13.0-202310121402 Succeeded
Name Phase sriov-network-operator.4.13.0-202310121402 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.2.1.2. Web console: Installing the SR-IOV Network Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can install the Operator using the web console.
Prerequisites
- A cluster installed on bare-metal hardware with nodes that have hardware that supports SR-IOV.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
An account with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Install the SR-IOV Network Operator:
- In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, click Operators → OperatorHub.
- Select SR-IOV Network Operator from the list of available Operators, and then click Install.
- On the Install Operator page, under Installed Namespace, select Operator recommended Namespace.
- Click Install.
Verify that the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed successfully:
- Navigate to the Operators → Installed Operators page.
Ensure that SR-IOV Network Operator is listed in the openshift-sriov-network-operator project with a Status of InstallSucceeded.
NoteDuring installation an Operator might display a Failed status. If the installation later succeeds with an InstallSucceeded message, you can ignore the Failed message.
If the Operator does not appear as installed, to troubleshoot further:
- Inspect the Operator Subscriptions and Install Plans tabs for any failure or errors under Status.
-
Navigate to the Workloads → Pods page and check the logs for pods in the
openshift-sriov-network-operatorproject. Check the namespace of the YAML file. If the annotation is missing, you can add the annotation
workload.openshift.io/allowed=managementto the Operator namespace with the following command:oc annotate ns/openshift-sriov-network-operator workload.openshift.io/allowed=management
$ oc annotate ns/openshift-sriov-network-operator workload.openshift.io/allowed=managementCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFor single-node OpenShift clusters, the annotation
workload.openshift.io/allowed=managementis required for the namespace.
24.2.2. Next steps
- Optional: Configuring the SR-IOV Network Operator
24.3. Configuring the SR-IOV Network Operator
The Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Network Operator manages the SR-IOV network devices and network attachments in your cluster.
24.3.1. Configuring the SR-IOV Network Operator
Modifying the SR-IOV Network Operator configuration is not normally necessary. The default configuration is recommended for most use cases. Complete the steps to modify the relevant configuration only if the default behavior of the Operator is not compatible with your use case.
The SR-IOV Network Operator adds the SriovOperatorConfig.sriovnetwork.openshift.io CustomResourceDefinition resource. The Operator automatically creates a SriovOperatorConfig custom resource (CR) named default in the openshift-sriov-network-operator namespace.
The default CR contains the SR-IOV Network Operator configuration for your cluster. To change the Operator configuration, you must modify this CR.
24.3.1.1. SR-IOV Network Operator config custom resource
The fields for the sriovoperatorconfig custom resource are described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Specifies the name of the SR-IOV Network Operator instance. The default value is |
|
|
|
Specifies the namespace of the SR-IOV Network Operator instance. The default value is |
|
|
| Specifies the node selection to control scheduling the SR-IOV Network Config Daemon on selected nodes. By default, this field is not set and the Operator deploys the SR-IOV Network Config daemon set on worker nodes. |
|
|
|
Specifies whether to disable the node draining process or enable the node draining process when you apply a new policy to configure the NIC on a node. Setting this field to
For single-node clusters, set this field to |
|
|
|
Specifies whether to enable or disable the Network Resources Injector daemon set. By default, this field is set to |
|
|
| Specifies whether to enable or disable the Operator Admission Controller webhook daemon set. |
|
|
|
Specifies the log verbosity level of the Operator. By default, this field is set to |
24.3.1.2. About the Network Resources Injector
The Network Resources Injector is a Kubernetes Dynamic Admission Controller application. It provides the following capabilities:
- Mutation of resource requests and limits in a pod specification to add an SR-IOV resource name according to an SR-IOV network attachment definition annotation.
-
Mutation of a pod specification with a Downward API volume to expose pod annotations, labels, and huge pages requests and limits. Containers that run in the pod can access the exposed information as files under the
/etc/podnetinfopath.
By default, the Network Resources Injector is enabled by the SR-IOV Network Operator and runs as a daemon set on all control plane nodes. The following is an example of Network Resources Injector pods running in a cluster with three control plane nodes:
oc get pods -n openshift-sriov-network-operator
$ oc get pods -n openshift-sriov-network-operatorExample output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE network-resources-injector-5cz5p 1/1 Running 0 10m network-resources-injector-dwqpx 1/1 Running 0 10m network-resources-injector-lktz5 1/1 Running 0 10m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
network-resources-injector-5cz5p 1/1 Running 0 10m
network-resources-injector-dwqpx 1/1 Running 0 10m
network-resources-injector-lktz5 1/1 Running 0 10m24.3.1.3. About the SR-IOV Network Operator admission controller webhook
The SR-IOV Network Operator Admission Controller webhook is a Kubernetes Dynamic Admission Controller application. It provides the following capabilities:
-
Validation of the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyCR when it is created or updated. -
Mutation of the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyCR by setting the default value for thepriorityanddeviceTypefields when the CR is created or updated.
By default the SR-IOV Network Operator Admission Controller webhook is enabled by the Operator and runs as a daemon set on all control plane nodes.
Use caution when disabling the SR-IOV Network Operator Admission Controller webhook. You can disable the webhook under specific circumstances, such as troubleshooting, or if you want to use unsupported devices. For information about configuring unsupported devices, see Configuring the SR-IOV Network Operator to use an unsupported NIC.
The following is an example of the Operator Admission Controller webhook pods running in a cluster with three control plane nodes:
oc get pods -n openshift-sriov-network-operator
$ oc get pods -n openshift-sriov-network-operatorExample output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE operator-webhook-9jkw6 1/1 Running 0 16m operator-webhook-kbr5p 1/1 Running 0 16m operator-webhook-rpfrl 1/1 Running 0 16m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
operator-webhook-9jkw6 1/1 Running 0 16m
operator-webhook-kbr5p 1/1 Running 0 16m
operator-webhook-rpfrl 1/1 Running 0 16m24.3.1.4. About custom node selectors
The SR-IOV Network Config daemon discovers and configures the SR-IOV network devices on cluster nodes. By default, it is deployed to all the worker nodes in the cluster. You can use node labels to specify on which nodes the SR-IOV Network Config daemon runs.
24.3.1.5. Disabling or enabling the Network Resources Injector
To disable or enable the Network Resources Injector, which is enabled by default, complete the following procedure.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You must have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Procedure
Set the
enableInjectorfield. Replace<value>withfalseto disable the feature ortrueto enable the feature.oc patch sriovoperatorconfig default \ --type=merge -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ --patch '{ "spec": { "enableInjector": <value> } }'$ oc patch sriovoperatorconfig default \ --type=merge -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ --patch '{ "spec": { "enableInjector": <value> } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to update the Operator:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.3.1.6. Disabling or enabling the SR-IOV Network Operator admission controller webhook
To disable or enable the admission controller webhook, which is enabled by default, complete the following procedure.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You must have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Procedure
Set the
enableOperatorWebhookfield. Replace<value>withfalseto disable the feature ortrueto enable it:oc patch sriovoperatorconfig default --type=merge \ -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ --patch '{ "spec": { "enableOperatorWebhook": <value> } }'$ oc patch sriovoperatorconfig default --type=merge \ -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ --patch '{ "spec": { "enableOperatorWebhook": <value> } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to update the Operator:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.3.1.7. Configuring a custom NodeSelector for the SR-IOV Network Config daemon
The SR-IOV Network Config daemon discovers and configures the SR-IOV network devices on cluster nodes. By default, it is deployed to all the worker nodes in the cluster. You can use node labels to specify on which nodes the SR-IOV Network Config daemon runs.
To specify the nodes where the SR-IOV Network Config daemon is deployed, complete the following procedure.
When you update the configDaemonNodeSelector field, the SR-IOV Network Config daemon is recreated on each selected node. While the daemon is recreated, cluster users are unable to apply any new SR-IOV Network node policy or create new SR-IOV pods.
Procedure
To update the node selector for the operator, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<node_label>with a label to apply as in the following example:"node-role.kubernetes.io/worker": "".TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to update the Operator:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.3.1.8. Configuring the SR-IOV Network Operator for single node installations
By default, the SR-IOV Network Operator drains workloads from a node before every policy change. The Operator performs this action to ensure that there no workloads using the virtual functions before the reconfiguration.
For installations on a single node, there are no other nodes to receive the workloads. As a result, the Operator must be configured not to drain the workloads from the single node.
After performing the following procedure to disable draining workloads, you must remove any workload that uses an SR-IOV network interface before you change any SR-IOV network node policy.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You must have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Procedure
To set the
disableDrainfield totrue, enter the following command:oc patch sriovoperatorconfig default --type=merge \ -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ --patch '{ "spec": { "disableDrain": true } }'$ oc patch sriovoperatorconfig default --type=merge \ -n openshift-sriov-network-operator \ --patch '{ "spec": { "disableDrain": true } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to update the Operator:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.3.1.9. Deploying the SR-IOV Operator for hosted control planes
Hosted control planes is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
After you configure and deploy your hosting service cluster, you can create a subscription to the SR-IOV Operator on a hosted cluster. The SR-IOV pod runs on worker machines rather than the control plane.
Prerequisites
You must configure and deploy the hosted cluster on AWS. For more information, see Configuring the hosting cluster on AWS (Technology Preview).
Procedure
Create a namespace and an Operator group:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a subscription to the SR-IOV Operator:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that the SR-IOV Operator is ready, run the following command and view the resulting output:
oc get csv -n openshift-sriov-network-operator
$ oc get csv -n openshift-sriov-network-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE sriov-network-operator.4.13.0-202211021237 SR-IOV Network Operator 4.13.0-202211021237 sriov-network-operator.4.13.0-202210290517 Succeeded
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE sriov-network-operator.4.13.0-202211021237 SR-IOV Network Operator 4.13.0-202211021237 sriov-network-operator.4.13.0-202210290517 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the SR-IOV pods are deployed, run the following command:
oc get pods -n openshift-sriov-network-operator
$ oc get pods -n openshift-sriov-network-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.3.2. Next steps
24.4. Configuring an SR-IOV network device
You can configure a Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) device in your cluster.
24.4.1. SR-IOV network node configuration object
You specify the SR-IOV network device configuration for a node by creating an SR-IOV network node policy. The API object for the policy is part of the sriovnetwork.openshift.io API group.
The following YAML describes an SR-IOV network node policy:
- 1
- The name for the custom resource object.
- 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed.
- 3
- The resource name of the SR-IOV network device plugin. You can create multiple SR-IOV network node policies for a resource name.
When specifying a name, be sure to use the accepted syntax expression
^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+$in theresourceName. - 4
- The node selector specifies the nodes to configure. Only SR-IOV network devices on the selected nodes are configured. The SR-IOV Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin and device plugin are deployed on selected nodes only.Important
The SR-IOV Network Operator applies node network configuration policies to nodes in sequence. Before applying node network configuration policies, the SR-IOV Network Operator checks if the machine config pool (MCP) for a node is in an unhealthy state such as
DegradedorUpdating. If a node is in an unhealthy MCP, the process of applying node network configuration policies to all targeted nodes in the cluster pauses until the MCP returns to a healthy state.To avoid a node in an unhealthy MCP from blocking the application of node network configuration policies to other nodes, including nodes in other MCPs, you must create a separate node network configuration policy for each MCP.
- 5
- Optional: The priority is an integer value between
0and99. A smaller value receives higher priority. For example, a priority of10is a higher priority than99. The default value is99. - 6
- Optional: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the virtual function. The maximum MTU value can vary for different network interface controller (NIC) models.Important
If you want to create virtual function on the default network interface, ensure that the MTU is set to a value that matches the cluster MTU.
- 7
- Optional: Set
needVhostNettotrueto mount the/dev/vhost-netdevice in the pod. Use the mounted/dev/vhost-netdevice with Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) to forward traffic to the kernel network stack. - 8
- The number of the virtual functions (VF) to create for the SR-IOV physical network device. For an Intel network interface controller (NIC), the number of VFs cannot be larger than the total VFs supported by the device. For a Mellanox NIC, the number of VFs cannot be larger than
127. - 9
- The NIC selector identifies the device for the Operator to configure. You do not have to specify values for all the parameters. It is recommended to identify the network device with enough precision to avoid selecting a device unintentionally.
If you specify
rootDevices, you must also specify a value forvendor,deviceID, orpfNames. If you specify bothpfNamesandrootDevicesat the same time, ensure that they refer to the same device. If you specify a value fornetFilter, then you do not need to specify any other parameter because a network ID is unique. - 10
- Optional: The vendor hexadecimal code of the SR-IOV network device. The only allowed values are
8086and15b3. - 11
- Optional: The device hexadecimal code of the SR-IOV network device. For example,
101bis the device ID for a Mellanox ConnectX-6 device. - 12
- Optional: An array of one or more physical function (PF) names for the device.
- 13
- Optional: An array of one or more PCI bus addresses for the PF of the device. Provide the address in the following format:
0000:02:00.1. - 14
- Optional: The platform-specific network filter. The only supported platform is Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP). Acceptable values use the following format:
openstack/NetworkID:xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx. Replacexxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxwith the value from the/var/config/openstack/latest/network_data.jsonmetadata file. - 15
- Optional: The driver type for the virtual functions. The only allowed values are
netdeviceandvfio-pci. The default value isnetdevice.For a Mellanox NIC to work in DPDK mode on bare metal nodes, use the
netdevicedriver type and setisRdmatotrue. - 16
- Optional: Configures whether to enable remote direct memory access (RDMA) mode. The default value is
false.If the
isRdmaparameter is set totrue, you can continue to use the RDMA-enabled VF as a normal network device. A device can be used in either mode.Set
isRdmatotrueand additionally setneedVhostNettotrueto configure a Mellanox NIC for use with Fast Datapath DPDK applications.NoteYou cannot set the
isRdmaparameter totruefor intel NICs. - 17
- Optional: The link type for the VFs. The default value is
ethfor Ethernet. Change this value to 'ib' for InfiniBand.When
linkTypeis set toib,isRdmais automatically set totrueby the SR-IOV Network Operator webhook. WhenlinkTypeis set toib,deviceTypeshould not be set tovfio-pci.Do not set linkType to 'eth' for SriovNetworkNodePolicy, because this can lead to an incorrect number of available devices reported by the device plugin.
- 18
- Optional: The NIC device mode. The only allowed values are
legacyorswitchdev.When
eSwitchModeis set tolegacy, the default SR-IOV behavior is enabled.When
eSwitchModeis set toswitchdev, hardware offloading is enabled. - 19
- Optional: To exclude advertising an SR-IOV network resource’s NUMA node to the Topology Manager, set the value to
true. The default value isfalse.
24.4.1.1. SR-IOV network node configuration examples
The following example describes the configuration for an InfiniBand device:
Example configuration for an InfiniBand device
The following example describes the configuration for an SR-IOV network device in a RHOSP virtual machine:
Example configuration for an SR-IOV device in a virtual machine
24.4.1.2. Virtual function (VF) partitioning for SR-IOV devices
In some cases, you might want to split virtual functions (VFs) from the same physical function (PF) into multiple resource pools. For example, you might want some of the VFs to load with the default driver and the remaining VFs load with the vfio-pci driver. In such a deployment, the pfNames selector in your SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource (CR) can be used to specify a range of VFs for a pool using the following format: <pfname>#<first_vf>-<last_vf>.
For example, the following YAML shows the selector for an interface named netpf0 with VF 2 through 7:
pfNames: ["netpf0#2-7"]
pfNames: ["netpf0#2-7"]-
netpf0is the PF interface name. -
2is the first VF index (0-based) that is included in the range. -
7is the last VF index (0-based) that is included in the range.
You can select VFs from the same PF by using different policy CRs if the following requirements are met:
-
The
numVfsvalue must be identical for policies that select the same PF. -
The VF index must be in the range of
0to<numVfs>-1. For example, if you have a policy withnumVfsset to8, then the<first_vf>value must not be smaller than0, and the<last_vf>must not be larger than7. - The VFs ranges in different policies must not overlap.
-
The
<first_vf>must not be larger than the<last_vf>.
The following example illustrates NIC partitioning for an SR-IOV device.
The policy policy-net-1 defines a resource pool net-1 that contains the VF 0 of PF netpf0 with the default VF driver. The policy policy-net-1-dpdk defines a resource pool net-1-dpdk that contains the VF 8 to 15 of PF netpf0 with the vfio VF driver.
Policy policy-net-1:
Policy policy-net-1-dpdk:
Verifying that the interface is successfully partitioned
Confirm that the interface partitioned to virtual functions (VFs) for the SR-IOV device by running the following command.
ip link show <interface>
$ ip link show <interface> - 1
- Replace
<interface>with the interface that you specified when partitioning to VFs for the SR-IOV device, for example,ens3f1.
Example output
24.4.2. Configuring SR-IOV network devices
The SR-IOV Network Operator adds the SriovNetworkNodePolicy.sriovnetwork.openshift.io CustomResourceDefinition to OpenShift Container Platform. You can configure an SR-IOV network device by creating a SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource (CR).
When applying the configuration specified in a SriovNetworkNodePolicy object, the SR-IOV Operator might drain the nodes, and in some cases, reboot nodes.
It might take several minutes for a configuration change to apply.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - You have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
- You have enough available nodes in your cluster to handle the evicted workload from drained nodes.
- You have not selected any control plane nodes for SR-IOV network device configuration.
Procedure
-
Create an
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject, and then save the YAML in the<name>-sriov-node-network.yamlfile. Replace<name>with the name for this configuration. -
Optional: Label the SR-IOV capable cluster nodes with
SriovNetworkNodePolicy.Spec.NodeSelectorif they are not already labeled. For more information about labeling nodes, see "Understanding how to update labels on nodes". Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject:oc create -f <name>-sriov-node-network.yaml
$ oc create -f <name>-sriov-node-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<name>specifies the name for this configuration.After applying the configuration update, all the pods in
sriov-network-operatornamespace transition to theRunningstatus.To verify that the SR-IOV network device is configured, enter the following command. Replace
<node_name>with the name of a node with the SR-IOV network device that you just configured.oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.syncStatus}'$ oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.syncStatus}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.4.3. Troubleshooting SR-IOV configuration
After following the procedure to configure an SR-IOV network device, the following sections address some error conditions.
To display the state of nodes, run the following command:
oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name>
$ oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name>
where: <node_name> specifies the name of a node with an SR-IOV network device.
Error output: Cannot allocate memory
"lastSyncError": "write /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:3b:00.1/sriov_numvfs: cannot allocate memory"
"lastSyncError": "write /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:3b:00.1/sriov_numvfs: cannot allocate memory"When a node indicates that it cannot allocate memory, check the following items:
- Confirm that global SR-IOV settings are enabled in the BIOS for the node.
- Confirm that VT-d is enabled in the BIOS for the node.
24.4.4. Assigning an SR-IOV network to a VRF
As a cluster administrator, you can assign an SR-IOV network interface to your VRF domain by using the CNI VRF plugin.
To do this, add the VRF configuration to the optional metaPlugins parameter of the SriovNetwork resource.
Applications that use VRFs need to bind to a specific device. The common usage is to use the SO_BINDTODEVICE option for a socket. SO_BINDTODEVICE binds the socket to a device that is specified in the passed interface name, for example, eth1. To use SO_BINDTODEVICE, the application must have CAP_NET_RAW capabilities.
Using a VRF through the ip vrf exec command is not supported in OpenShift Container Platform pods. To use VRF, bind applications directly to the VRF interface.
24.4.4.1. Creating an additional SR-IOV network attachment with the CNI VRF plugin
The SR-IOV Network Operator manages additional network definitions. When you specify an additional SR-IOV network to create, the SR-IOV Network Operator creates the NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource (CR) automatically.
Do not edit NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resources that the SR-IOV Network Operator manages. Doing so might disrupt network traffic on your additional network.
To create an additional SR-IOV network attachment with the CNI VRF plugin, perform the following procedure.
Prerequisites
- Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (oc).
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform cluster as a user with cluster-admin privileges.
Procedure
Create the
SriovNetworkcustom resource (CR) for the additional SR-IOV network attachment and insert themetaPluginsconfiguration, as in the following example CR. Save the YAML as the filesriov-network-attachment.yaml.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
SriovNetworkresource:oc create -f sriov-network-attachment.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-network-attachment.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verifying that the NetworkAttachmentDefinition CR is successfully created
Confirm that the SR-IOV Network Operator created the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionCR by running the following command.oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>
$ oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<namespace>with the namespace that you specified when configuring the network attachment, for example,additional-sriov-network-1.
Example output
NAME AGE additional-sriov-network-1 14m
NAME AGE additional-sriov-network-1 14mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThere might be a delay before the SR-IOV Network Operator creates the CR.
Verifying that the additional SR-IOV network attachment is successful
To verify that the VRF CNI is correctly configured and the additional SR-IOV network attachment is attached, do the following:
- Create an SR-IOV network that uses the VRF CNI.
- Assign the network to a pod.
Verify that the pod network attachment is connected to the SR-IOV additional network. Remote shell into the pod and run the following command:
ip vrf show
$ ip vrf showCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name Table ----------------------- red 10
Name Table ----------------------- red 10Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm the VRF interface is master of the secondary interface:
ip link
$ ip linkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
... 5: net1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master red state UP mode ...
... 5: net1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master red state UP mode ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.4.5. Exclude the SR-IOV network topology for NUMA-aware scheduling
You can exclude advertising the Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) node for the SR-IOV network to the Topology Manager for more flexible SR-IOV network deployments during NUMA-aware pod scheduling.
In some scenarios, it is a priority to maximize CPU and memory resources for a pod on a single NUMA node. By not providing a hint to the Topology Manager about the NUMA node for the pod’s SR-IOV network resource, the Topology Manager can deploy the SR-IOV network resource and the pod CPU and memory resources to different NUMA nodes. This can add to network latency because of the data transfer between NUMA nodes. However, it is acceptable in scenarios when workloads require optimal CPU and memory performance.
For example, consider a compute node, compute-1, that features two NUMA nodes: numa0 and numa1. The SR-IOV-enabled NIC is present on numa0. The CPUs available for pod scheduling are present on numa1 only. By setting the excludeTopology specification to true, the Topology Manager can assign CPU and memory resources for the pod to numa1 and can assign the SR-IOV network resource for the same pod to numa0. This is only possible when you set the excludeTopology specification to true. Otherwise, the Topology Manager attempts to place all resources on the same NUMA node.
24.4.5.1. Excluding the SR-IOV network topology for NUMA-aware scheduling
To exclude advertising the SR-IOV network resource’s Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) node to the Topology Manager, you can configure the excludeTopology specification in the SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource. Use this configuration for more flexible SR-IOV network deployments during NUMA-aware pod scheduling.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have configured the CPU Manager policy to
static. For more information about CPU Manager, see the Additional resources section. -
You have configured the Topology Manager policy to
single-numa-node. - You have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Procedure
Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyCR:Save the following YAML in the
sriov-network-node-policy.yamlfile, replacing values in the YAML to match your environment:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The resource name of the SR-IOV network device plugin. This YAML uses a sample
resourceNamevalue. - 2
- Identify the device for the Operator to configure by using the NIC selector.
- 3
- To exclude advertising the NUMA node for the SR-IOV network resource to the Topology Manager, set the value to
true. The default value isfalse.
NoteIf multiple
SriovNetworkNodePolicyresources target the same SR-IOV network resource, theSriovNetworkNodePolicyresources must have the same value as theexcludeTopologyspecification. Otherwise, the conflicting policy is rejected.Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyresource by running the following command:oc create -f sriov-network-node-policy.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-network-node-policy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
sriovnetworknodepolicy.sriovnetwork.openshift.io/policy-for-numa-0 created
sriovnetworknodepolicy.sriovnetwork.openshift.io/policy-for-numa-0 createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create the
SriovNetworkCR:Save the following YAML in the
sriov-network.yamlfile, replacing values in the YAML to match your environment:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
sriov-numa-0-networkwith the name for the SR-IOV network resource. - 2
- Specify the resource name for the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyCR from the previous step. This YAML uses a sampleresourceNamevalue. - 3
- Enter the namespace for your SR-IOV network resource.
- 4
- Enter the IP address management configuration for the SR-IOV network.
Create the
SriovNetworkresource by running the following command:oc create -f sriov-network.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
sriovnetwork.sriovnetwork.openshift.io/sriov-numa-0-network created
sriovnetwork.sriovnetwork.openshift.io/sriov-numa-0-network createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a pod and assign the SR-IOV network resource from the previous step:
Save the following YAML in the
sriov-network-pod.yamlfile, replacing values in the YAML to match your environment:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This is the name of the
SriovNetworkresource that uses theSriovNetworkNodePolicyresource.
Create the
Podresource by running the following command:oc create -f sriov-network-pod.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-network-pod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
pod/example-pod created
pod/example-pod createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify the status of the pod by running the following command, replacing
<pod_name>with the name of the pod:oc get pod <pod_name>
$ oc get pod <pod_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE test-deployment-sriov-76cbbf4756-k9v72 1/1 Running 0 45h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE test-deployment-sriov-76cbbf4756-k9v72 1/1 Running 0 45hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open a debug session with the target pod to verify that the SR-IOV network resources are deployed to a different node than the memory and CPU resources.
Open a debug session with the pod by running the following command, replacing <pod_name> with the target pod name.
oc debug pod/<pod_name>
$ oc debug pod/<pod_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set
/hostas the root directory within the debug shell. The debug pod mounts the root file system from the host in/hostwithin the pod. By changing the root directory to/host, you can run binaries from the host file system:chroot /host
$ chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View information about the CPU allocation by running the following commands:
lscpu | grep NUMA
$ lscpu | grep NUMACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NUMA node(s): 2 NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,... NUMA node1 CPU(s): 1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,...
NUMA node(s): 2 NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,... NUMA node1 CPU(s): 1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow cat /proc/self/status | grep Cpus
$ cat /proc/self/status | grep CpusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Cpus_allowed: aa Cpus_allowed_list: 1,3,5,7
Cpus_allowed: aa Cpus_allowed_list: 1,3,5,7Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow cat /sys/class/net/net1/device/numa_node
$ cat /sys/class/net/net1/device/numa_nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
0
0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, CPUs 1,3,5, and 7 are allocated to
NUMA node1but the SR-IOV network resource can use the NIC inNUMA node0.
If the excludeTopology specification is set to True, it is possible that the required resources exist in the same NUMA node.
24.4.6. Next steps
24.5. Configuring an SR-IOV Ethernet network attachment
You can configure an Ethernet network attachment for an Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) device in the cluster.
24.5.1. Ethernet device configuration object
You can configure an Ethernet network device by defining an SriovNetwork object.
The following YAML describes an SriovNetwork object:
- 1
- A name for the object. The SR-IOV Network Operator creates a
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject with same name. - 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed.
- 3
- The value for the
spec.resourceNameparameter from theSriovNetworkNodePolicyobject that defines the SR-IOV hardware for this additional network. - 4
- The target namespace for the
SriovNetworkobject. Only pods in the target namespace can attach to the additional network. - 5
- Optional: A Virtual LAN (VLAN) ID for the additional network. The integer value must be from
0to4095. The default value is0. - 6
- Optional: The spoof check mode of the VF. The allowed values are the strings
"on"and"off".ImportantYou must enclose the value you specify in quotes or the object is rejected by the SR-IOV Network Operator.
- 7
- A configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition.
- 8
- Optional: The link state of virtual function (VF). Allowed value are
enable,disableandauto. - 9
- Optional: A maximum transmission rate, in Mbps, for the VF.
- 10
- Optional: A minimum transmission rate, in Mbps, for the VF. This value must be less than or equal to the maximum transmission rate.Note
Intel NICs do not support the
minTxRateparameter. For more information, see BZ#1772847. - 11
- Optional: An IEEE 802.1p priority level for the VF. The default value is
0. - 12
- Optional: The trust mode of the VF. The allowed values are the strings
"on"and"off".ImportantYou must enclose the value that you specify in quotes, or the SR-IOV Network Operator rejects the object.
- 13
- Optional: The capabilities to configure for this additional network. You can specify
"{ "ips": true }"to enable IP address support or"{ "mac": true }"to enable MAC address support.
24.5.1.1. Configuration of IP address assignment for an additional network
The IP address management (IPAM) Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin provides IP addresses for other CNI plugins.
You can use the following IP address assignment types:
- Static assignment.
- Dynamic assignment through a DHCP server. The DHCP server you specify must be reachable from the additional network.
- Dynamic assignment through the Whereabouts IPAM CNI plugin.
24.5.1.1.1. Static IP address assignment configuration
The following table describes the configuration for static IP address assignment:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
|
|
| An array of objects specifying IP addresses to assign to the virtual interface. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses are supported. |
|
|
| An array of objects specifying routes to configure inside the pod. |
|
|
| Optional: An array of objects specifying the DNS configuration. |
The addresses array requires objects with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
An IP address and network prefix that you specify. For example, if you specify |
|
|
| The default gateway to route egress network traffic to. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IP address range in CIDR format, such as |
|
|
| The gateway where network traffic is routed. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| An array of one or more IP addresses for to send DNS queries to. |
|
|
|
The default domain to append to a hostname. For example, if the domain is set to |
|
|
|
An array of domain names to append to an unqualified hostname, such as |
Static IP address assignment configuration example
24.5.1.1.2. Dynamic IP address (DHCP) assignment configuration
The following JSON describes the configuration for dynamic IP address address assignment with DHCP.
A pod obtains its original DHCP lease when it is created. The lease must be periodically renewed by a minimal DHCP server deployment running on the cluster.
The SR-IOV Network Operator does not create a DHCP server deployment; The Cluster Network Operator is responsible for creating the minimal DHCP server deployment.
To trigger the deployment of the DHCP server, you must create a shim network attachment by editing the Cluster Network Operator configuration, as in the following example:
Example shim network attachment definition
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
Dynamic IP address (DHCP) assignment configuration example
{
"ipam": {
"type": "dhcp"
}
}
{
"ipam": {
"type": "dhcp"
}
}24.5.1.1.3. Dynamic IP address assignment configuration with Whereabouts
The Whereabouts CNI plugin allows the dynamic assignment of an IP address to an additional network without the use of a DHCP server.
The following table describes the configuration for dynamic IP address assignment with Whereabouts:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
|
|
| An IP address and range in CIDR notation. IP addresses are assigned from within this range of addresses. |
|
|
| Optional: A list of zero or more IP addresses and ranges in CIDR notation. IP addresses within an excluded address range are not assigned. |
Dynamic IP address assignment configuration example that uses Whereabouts
24.5.2. Configuring SR-IOV additional network
You can configure an additional network that uses SR-IOV hardware by creating an SriovNetwork object. When you create an SriovNetwork object, the SR-IOV Network Operator automatically creates a NetworkAttachmentDefinition object.
Do not modify or delete an SriovNetwork object if it is attached to any pods in a running state.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a
SriovNetworkobject, and then save the YAML in the<name>.yamlfile, where<name>is a name for this additional network. The object specification might resemble the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the object, enter the following command:
oc create -f <name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<name>specifies the name of the additional network.Optional: To confirm that the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject that is associated with theSriovNetworkobject that you created in the previous step exists, enter the following command. Replace<namespace>with the networkNamespace you specified in theSriovNetworkobject.oc get net-attach-def -n <namespace>
$ oc get net-attach-def -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.5.3. Next steps
24.6. Configuring an SR-IOV InfiniBand network attachment
You can configure an InfiniBand (IB) network attachment for an Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) device in the cluster.
24.6.1. InfiniBand device configuration object
You can configure an InfiniBand (IB) network device by defining an SriovIBNetwork object.
The following YAML describes an SriovIBNetwork object:
- 1
- A name for the object. The SR-IOV Network Operator creates a
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject with same name. - 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Operator is installed.
- 3
- The value for the
spec.resourceNameparameter from theSriovNetworkNodePolicyobject that defines the SR-IOV hardware for this additional network. - 4
- The target namespace for the
SriovIBNetworkobject. Only pods in the target namespace can attach to the network device. - 5
- Optional: A configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition.
- 6
- Optional: The link state of virtual function (VF). Allowed values are
enable,disableandauto. - 7
- Optional: The capabilities to configure for this network. You can specify
"{ "ips": true }"to enable IP address support or"{ "infinibandGUID": true }"to enable IB Global Unique Identifier (GUID) support.
24.6.1.1. Configuration of IP address assignment for an additional network
The IP address management (IPAM) Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin provides IP addresses for other CNI plugins.
You can use the following IP address assignment types:
- Static assignment.
- Dynamic assignment through a DHCP server. The DHCP server you specify must be reachable from the additional network.
- Dynamic assignment through the Whereabouts IPAM CNI plugin.
24.6.1.1.1. Static IP address assignment configuration
The following table describes the configuration for static IP address assignment:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
|
|
| An array of objects specifying IP addresses to assign to the virtual interface. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses are supported. |
|
|
| An array of objects specifying routes to configure inside the pod. |
|
|
| Optional: An array of objects specifying the DNS configuration. |
The addresses array requires objects with the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
An IP address and network prefix that you specify. For example, if you specify |
|
|
| The default gateway to route egress network traffic to. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IP address range in CIDR format, such as |
|
|
| The gateway where network traffic is routed. |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| An array of one or more IP addresses for to send DNS queries to. |
|
|
|
The default domain to append to a hostname. For example, if the domain is set to |
|
|
|
An array of domain names to append to an unqualified hostname, such as |
Static IP address assignment configuration example
24.6.1.1.2. Dynamic IP address (DHCP) assignment configuration
The following JSON describes the configuration for dynamic IP address address assignment with DHCP.
A pod obtains its original DHCP lease when it is created. The lease must be periodically renewed by a minimal DHCP server deployment running on the cluster.
To trigger the deployment of the DHCP server, you must create a shim network attachment by editing the Cluster Network Operator configuration, as in the following example:
Example shim network attachment definition
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
Dynamic IP address (DHCP) assignment configuration example
{
"ipam": {
"type": "dhcp"
}
}
{
"ipam": {
"type": "dhcp"
}
}24.6.1.1.3. Dynamic IP address assignment configuration with Whereabouts
The Whereabouts CNI plugin allows the dynamic assignment of an IP address to an additional network without the use of a DHCP server.
The following table describes the configuration for dynamic IP address assignment with Whereabouts:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The IPAM address type. The value |
|
|
| An IP address and range in CIDR notation. IP addresses are assigned from within this range of addresses. |
|
|
| Optional: A list of zero or more IP addresses and ranges in CIDR notation. IP addresses within an excluded address range are not assigned. |
Dynamic IP address assignment configuration example that uses Whereabouts
24.6.2. Configuring SR-IOV additional network
You can configure an additional network that uses SR-IOV hardware by creating an SriovIBNetwork object. When you create an SriovIBNetwork object, the SR-IOV Network Operator automatically creates a NetworkAttachmentDefinition object.
Do not modify or delete an SriovIBNetwork object if it is attached to any pods in a running state.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a
SriovIBNetworkobject, and then save the YAML in the<name>.yamlfile, where<name>is a name for this additional network. The object specification might resemble the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the object, enter the following command:
oc create -f <name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<name>specifies the name of the additional network.Optional: To confirm that the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionobject that is associated with theSriovIBNetworkobject that you created in the previous step exists, enter the following command. Replace<namespace>with the networkNamespace you specified in theSriovIBNetworkobject.oc get net-attach-def -n <namespace>
$ oc get net-attach-def -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.6.3. Next steps
24.7. Adding a pod to an SR-IOV additional network
You can add a pod to an existing Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) network.
24.7.1. Runtime configuration for a network attachment
When attaching a pod to an additional network, you can specify a runtime configuration to make specific customizations for the pod. For example, you can request a specific MAC hardware address.
You specify the runtime configuration by setting an annotation in the pod specification. The annotation key is k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks, and it accepts a JSON object that describes the runtime configuration.
24.7.1.1. Runtime configuration for an Ethernet-based SR-IOV attachment
The following JSON describes the runtime configuration options for an Ethernet-based SR-IOV network attachment.
- 1
- The name of the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR.
- 2
- Optional: The MAC address for the SR-IOV device that is allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "mac": true }in theSriovNetworkobject. - 3
- Optional: IP addresses for the SR-IOV device that is allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are supported. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "ips": true }in theSriovNetworkobject.
Example runtime configuration
24.7.1.2. Runtime configuration for an InfiniBand-based SR-IOV attachment
The following JSON describes the runtime configuration options for an InfiniBand-based SR-IOV network attachment.
- 1
- The name of the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR.
- 2
- The InfiniBand GUID for the SR-IOV device. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "infinibandGUID": true }in theSriovIBNetworkobject. - 3
- The IP addresses for the SR-IOV device that is allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are supported. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "ips": true }in theSriovIBNetworkobject.
Example runtime configuration
24.7.2. Adding a pod to an additional network
You can add a pod to an additional network. The pod continues to send normal cluster-related network traffic over the default network.
When a pod is created additional networks are attached to it. However, if a pod already exists, you cannot attach additional networks to it.
The pod must be in the same namespace as the additional network.
The SR-IOV Network Resource Injector adds the resource field to the first container in a pod automatically.
If you are using an Intel network interface controller (NIC) in Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) mode, only the first container in your pod is configured to access the NIC. Your SR-IOV additional network is configured for DPDK mode if the deviceType is set to vfio-pci in the SriovNetworkNodePolicy object.
You can work around this issue by either ensuring that the container that needs access to the NIC is the first container defined in the Pod object or by disabling the Network Resource Injector. For more information, see BZ#1990953.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Log in to the cluster.
- Install the SR-IOV Operator.
-
Create either an
SriovNetworkobject or anSriovIBNetworkobject to attach the pod to.
Procedure
Add an annotation to the
Podobject. Only one of the following annotation formats can be used:To attach an additional network without any customization, add an annotation with the following format. Replace
<network>with the name of the additional network to associate with the pod:metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: <network>[,<network>,...]metadata: annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: <network>[,<network>,...]1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- To specify more than one additional network, separate each network with a comma. Do not include whitespace between the comma. If you specify the same additional network multiple times, that pod will have multiple network interfaces attached to that network.
To attach an additional network with customizations, add an annotation with the following format:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To create the pod, enter the following command. Replace
<name>with the name of the pod.oc create -f <name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To Confirm that the annotation exists in the
PodCR, enter the following command, replacing<name>with the name of the pod.oc get pod <name> -o yaml
$ oc get pod <name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example, the
example-podpod is attached to thenet1additional network:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/network-statusparameter is a JSON array of objects. Each object describes the status of an additional network attached to the pod. The annotation value is stored as a plain text value.
24.7.3. Creating a non-uniform memory access (NUMA) aligned SR-IOV pod
You can create a NUMA aligned SR-IOV pod by restricting SR-IOV and the CPU resources allocated from the same NUMA node with restricted or single-numa-node Topology Manager polices.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have configured the CPU Manager policy to
static. For more information on CPU Manager, see the "Additional resources" section. You have configured the Topology Manager policy to
single-numa-node.NoteWhen
single-numa-nodeis unable to satisfy the request, you can configure the Topology Manager policy torestricted. For more flexible SR-IOV network resource scheduling, see Excluding SR-IOV network topology during NUMA-aware scheduling in the Additional resources section.
Procedure
Create the following SR-IOV pod spec, and then save the YAML in the
<name>-sriov-pod.yamlfile. Replace<name>with a name for this pod.The following example shows an SR-IOV pod spec:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<name>with the name of the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. - 2
- Replace
<image>with the name of thesample-podimage. - 3
- To create the SR-IOV pod with guaranteed QoS, set
memory limitsequal tomemory requests. - 4
- To create the SR-IOV pod with guaranteed QoS, set
cpu limitsequals tocpu requests.
Create the sample SR-IOV pod by running the following command:
oc create -f <filename>
$ oc create -f <filename>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<filename>with the name of the file you created in the previous step.
Confirm that the
sample-podis configured with guaranteed QoS.oc describe pod sample-pod
$ oc describe pod sample-podCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the
sample-podis allocated with exclusive CPUs.oc exec sample-pod -- cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/cpuset.cpus
$ oc exec sample-pod -- cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/cpuset.cpusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the SR-IOV device and CPUs that are allocated for the
sample-podare on the same NUMA node.oc exec sample-pod -- cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/cpuset.cpus
$ oc exec sample-pod -- cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/cpuset.cpusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.7.4. A test pod template for clusters that use SR-IOV on OpenStack
The following testpmd pod demonstrates container creation with huge pages, reserved CPUs, and the SR-IOV port.
An example testpmd pod
- 1
- This example assumes that the name of the performance profile is
cnf-performance profile.
24.8. Configuring interface-level network sysctl settings for SR-IOV networks
As a cluster administrator, you can modify interface-level network sysctls using the tuning Container Network Interface (CNI) meta plugin for a pod connected to a SR-IOV network device.
24.8.1. Labeling nodes with an SR-IOV enabled NIC
If you want to enable SR-IOV on only SR-IOV capable nodes there are a couple of ways to do this:
-
Install the Node Feature Discovery (NFD) Operator. NFD detects the presence of SR-IOV enabled NICs and labels the nodes with
node.alpha.kubernetes-incubator.io/nfd-network-sriov.capable = true. Examine the
SriovNetworkNodeStateCR for each node. Theinterfacesstanza includes a list of all of the SR-IOV devices discovered by the SR-IOV Network Operator on the worker node. Label each node withfeature.node.kubernetes.io/network-sriov.capable: "true"by using the following command:$ oc label node <node_name> feature.node.kubernetes.io/network-sriov.capable="true"
$ oc label node <node_name> feature.node.kubernetes.io/network-sriov.capable="true"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can label the nodes with whatever name you want.
24.8.2. Setting one sysctl flag
You can set interface-level network sysctl settings for a pod connected to a SR-IOV network device.
In this example, net.ipv4.conf.IFNAME.accept_redirects is set to 1 on the created virtual interfaces.
The sysctl-tuning-test is a namespace used in this example.
Use the following command to create the
sysctl-tuning-testnamespace:oc create namespace sysctl-tuning-test
$ oc create namespace sysctl-tuning-testCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.8.2.1. Setting one sysctl flag on nodes with SR-IOV network devices
The SR-IOV Network Operator adds the SriovNetworkNodePolicy.sriovnetwork.openshift.io custom resource definition (CRD) to OpenShift Container Platform. You can configure an SR-IOV network device by creating a SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource (CR).
When applying the configuration specified in a SriovNetworkNodePolicy object, the SR-IOV Operator might drain and reboot the nodes.
It can take several minutes for a configuration change to apply.
Follow this procedure to create a SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource (CR).
Procedure
Create an
SriovNetworkNodePolicycustom resource (CR). For example, save the following YAML as the filepolicyoneflag-sriov-node-network.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name for the custom resource object.
- 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed.
- 3
- The resource name of the SR-IOV network device plugin. You can create multiple SR-IOV network node policies for a resource name.
- 4
- The node selector specifies the nodes to configure. Only SR-IOV network devices on the selected nodes are configured. The SR-IOV Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin and device plugin are deployed on selected nodes only.
- 5
- Optional: The priority is an integer value between
0and99. A smaller value receives higher priority. For example, a priority of10is a higher priority than99. The default value is99. - 6
- The number of the virtual functions (VFs) to create for the SR-IOV physical network device. For an Intel network interface controller (NIC), the number of VFs cannot be larger than the total VFs supported by the device. For a Mellanox NIC, the number of VFs cannot be larger than
127. - 7
- The NIC selector identifies the device for the Operator to configure. You do not have to specify values for all the parameters. It is recommended to identify the network device with enough precision to avoid selecting a device unintentionally. If you specify
rootDevices, you must also specify a value forvendor,deviceID, orpfNames. If you specify bothpfNamesandrootDevicesat the same time, ensure that they refer to the same device. If you specify a value fornetFilter, then you do not need to specify any other parameter because a network ID is unique. - 8
- Optional: An array of one or more physical function (PF) names for the device.
- 9
- Optional: The driver type for the virtual functions. The only allowed value is
netdevice. For a Mellanox NIC to work in DPDK mode on bare metal nodes, setisRdmatotrue. - 10
- Optional: Configures whether to enable remote direct memory access (RDMA) mode. The default value is
false. If theisRdmaparameter is set totrue, you can continue to use the RDMA-enabled VF as a normal network device. A device can be used in either mode. SetisRdmatotrueand additionally setneedVhostNettotrueto configure a Mellanox NIC for use with Fast Datapath DPDK applications.
NoteThe
vfio-pcidriver type is not supported.Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject:oc create -f policyoneflag-sriov-node-network.yaml
$ oc create -f policyoneflag-sriov-node-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After applying the configuration update, all the pods in
sriov-network-operatornamespace change to theRunningstatus.To verify that the SR-IOV network device is configured, enter the following command. Replace
<node_name>with the name of a node with the SR-IOV network device that you just configured.oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.syncStatus}'$ oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.syncStatus}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Succeeded
SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.8.2.2. Configuring sysctl on a SR-IOV network
You can set interface specific sysctl settings on virtual interfaces created by SR-IOV by adding the tuning configuration to the optional metaPlugins parameter of the SriovNetwork resource.
The SR-IOV Network Operator manages additional network definitions. When you specify an additional SR-IOV network to create, the SR-IOV Network Operator creates the NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resource (CR) automatically.
Do not edit NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resources that the SR-IOV Network Operator manages. Doing so might disrupt network traffic on your additional network.
To change the interface-level network net.ipv4.conf.IFNAME.accept_redirects sysctl settings, create an additional SR-IOV network with the Container Network Interface (CNI) tuning plugin.
Prerequisites
- Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (oc).
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform cluster as a user with cluster-admin privileges.
Procedure
Create the
SriovNetworkcustom resource (CR) for the additional SR-IOV network attachment and insert themetaPluginsconfiguration, as in the following example CR. Save the YAML as the filesriov-network-interface-sysctl.yaml.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- A name for the object. The SR-IOV Network Operator creates a NetworkAttachmentDefinition object with same name.
- 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed.
- 3
- The value for the
spec.resourceNameparameter from theSriovNetworkNodePolicyobject that defines the SR-IOV hardware for this additional network. - 4
- The target namespace for the
SriovNetworkobject. Only pods in the target namespace can attach to the additional network. - 5
- A configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition.
- 6
- Optional: Set capabilities for the additional network. You can specify
"{ "ips": true }"to enable IP address support or"{ "mac": true }"to enable MAC address support. - 7
- Optional: The metaPlugins parameter is used to add additional capabilities to the device. In this use case set the
typefield totuning. Specify the interface-level networksysctlyou want to set in thesysctlfield.
Create the
SriovNetworkresource:oc create -f sriov-network-interface-sysctl.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-network-interface-sysctl.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verifying that the NetworkAttachmentDefinition CR is successfully created
Confirm that the SR-IOV Network Operator created the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionCR by running the following command:oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>
$ oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<namespace>with the value fornetworkNamespacethat you specified in theSriovNetworkobject. For example,sysctl-tuning-test.
Example output
NAME AGE onevalidflag 14m
NAME AGE onevalidflag 14mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThere might be a delay before the SR-IOV Network Operator creates the CR.
Verifying that the additional SR-IOV network attachment is successful
To verify that the tuning CNI is correctly configured and the additional SR-IOV network attachment is attached, do the following:
Create a
PodCR. Save the following YAML as the fileexamplepod.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR.
- 2
- Optional: The MAC address for the SR-IOV device that is allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "mac": true }in the SriovNetwork object. - 3
- Optional: IP addresses for the SR-IOV device that are allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are supported. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "ips": true }in theSriovNetworkobject.
Create the
PodCR:oc apply -f examplepod.yaml
$ oc apply -f examplepod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the pod is created by running the following command:
oc get pod -n sysctl-tuning-test
$ oc get pod -n sysctl-tuning-testCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tunepod 1/1 Running 0 47s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tunepod 1/1 Running 0 47sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in to the pod by running the following command:
oc rsh -n sysctl-tuning-test tunepod
$ oc rsh -n sysctl-tuning-test tunepodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the values of the configured sysctl flag. Find the value
net.ipv4.conf.IFNAME.accept_redirectsby running the following command::sysctl net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirects
$ sysctl net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirectsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirects = 1
net.ipv4.conf.net1.accept_redirects = 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.8.3. Configuring sysctl settings for pods associated with bonded SR-IOV interface flag
You can set interface-level network sysctl settings for a pod connected to a bonded SR-IOV network device.
In this example, the specific network interface-level sysctl settings that can be configured are set on the bonded interface.
The sysctl-tuning-test is a namespace used in this example.
Use the following command to create the
sysctl-tuning-testnamespace:oc create namespace sysctl-tuning-test
$ oc create namespace sysctl-tuning-testCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.8.3.1. Setting all sysctl flag on nodes with bonded SR-IOV network devices
The SR-IOV Network Operator adds the SriovNetworkNodePolicy.sriovnetwork.openshift.io custom resource definition (CRD) to OpenShift Container Platform. You can configure an SR-IOV network device by creating a SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource (CR).
When applying the configuration specified in a SriovNetworkNodePolicy object, the SR-IOV Operator might drain the nodes, and in some cases, reboot nodes.
It might take several minutes for a configuration change to apply.
Follow this procedure to create a SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resource (CR).
Procedure
Create an
SriovNetworkNodePolicycustom resource (CR). Save the following YAML as the filepolicyallflags-sriov-node-network.yaml. Replacepolicyallflagswith the name for the configuration.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name for the custom resource object.
- 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed.
- 3
- The resource name of the SR-IOV network device plugin. You can create multiple SR-IOV network node policies for a resource name.
- 4
- The node selector specifies the nodes to configure. Only SR-IOV network devices on the selected nodes are configured. The SR-IOV Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin and device plugin are deployed on selected nodes only.
- 5
- Optional: The priority is an integer value between
0and99. A smaller value receives higher priority. For example, a priority of10is a higher priority than99. The default value is99. - 6
- The number of virtual functions (VFs) to create for the SR-IOV physical network device. For an Intel network interface controller (NIC), the number of VFs cannot be larger than the total VFs supported by the device. For a Mellanox NIC, the number of VFs cannot be larger than
127. - 7
- The NIC selector identifies the device for the Operator to configure. You do not have to specify values for all the parameters. It is recommended to identify the network device with enough precision to avoid selecting a device unintentionally. If you specify
rootDevices, you must also specify a value forvendor,deviceID, orpfNames. If you specify bothpfNamesandrootDevicesat the same time, ensure that they refer to the same device. If you specify a value fornetFilter, then you do not need to specify any other parameter because a network ID is unique. - 8
- Optional: An array of one or more physical function (PF) names for the device.
- 9
- Optional: The driver type for the virtual functions. The only allowed value is
netdevice. For a Mellanox NIC to work in DPDK mode on bare metal nodes, setisRdmatotrue. - 10
- Optional: Configures whether to enable remote direct memory access (RDMA) mode. The default value is
false. If theisRdmaparameter is set totrue, you can continue to use the RDMA-enabled VF as a normal network device. A device can be used in either mode. SetisRdmatotrueand additionally setneedVhostNettotrueto configure a Mellanox NIC for use with Fast Datapath DPDK applications.
NoteThe
vfio-pcidriver type is not supported.Create the SriovNetworkNodePolicy object:
oc create -f policyallflags-sriov-node-network.yaml
$ oc create -f policyallflags-sriov-node-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After applying the configuration update, all the pods in sriov-network-operator namespace change to the
Runningstatus.To verify that the SR-IOV network device is configured, enter the following command. Replace
<node_name>with the name of a node with the SR-IOV network device that you just configured.oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.syncStatus}'$ oc get sriovnetworknodestates -n openshift-sriov-network-operator <node_name> -o jsonpath='{.status.syncStatus}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Succeeded
SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.8.3.2. Configuring sysctl on a bonded SR-IOV network
You can set interface specific sysctl settings on a bonded interface created from two SR-IOV interfaces. Do this by adding the tuning configuration to the optional Plugins parameter of the bond network attachment definition.
Do not edit NetworkAttachmentDefinition custom resources that the SR-IOV Network Operator manages. Doing so might disrupt network traffic on your additional network.
To change specific interface-level network sysctl settings create the SriovNetwork custom resource (CR) with the Container Network Interface (CNI) tuning plugin by using the following procedure.
Prerequisites
- Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (oc).
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform cluster as a user with cluster-admin privileges.
Procedure
Create the
SriovNetworkcustom resource (CR) for the bonded interface as in the following example CR. Save the YAML as the filesriov-network-attachment.yaml.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- A name for the object. The SR-IOV Network Operator creates a NetworkAttachmentDefinition object with same name.
- 2
- The namespace where the SR-IOV Network Operator is installed.
- 3
- The value for the
spec.resourceNameparameter from theSriovNetworkNodePolicyobject that defines the SR-IOV hardware for this additional network. - 4
- The target namespace for the
SriovNetworkobject. Only pods in the target namespace can attach to the additional network. - 5
- Optional: The capabilities to configure for this additional network. You can specify
"{ "ips": true }"to enable IP address support or"{ "mac": true }"to enable MAC address support.
Create the
SriovNetworkresource:oc create -f sriov-network-attachment.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-network-attachment.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a bond network attachment definition as in the following example CR. Save the YAML as the file
sriov-bond-network-interface.yaml.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The type is
bond. - 2
- The
modeattribute specifies the bonding mode. The bonding modes supported are:-
balance-rr- 0 -
active-backup- 1 balance-xor- 2For
balance-rrorbalance-xormodes, you must set thetrustmode toonfor the SR-IOV virtual function.
-
- 3
- The
failoverattribute is mandatory for active-backup mode. - 4
- The
linksInContainer=trueflag informs the Bond CNI that the required interfaces are to be found inside the container. By default, Bond CNI looks for these interfaces on the host which does not work for integration with SRIOV and Multus. - 5
- The
linkssection defines which interfaces will be used to create the bond. By default, Multus names the attached interfaces as: "net", plus a consecutive number, starting with one. - 6
- A configuration object for the IPAM CNI plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition. In this pod example IP addresses are configured manually, so in this case,
ipamis set to static. - 7
- Add additional capabilities to the device. For example, set the
typefield totuning. Specify the interface-level networksysctlyou want to set in the sysctl field. This example sets all interface-level networksysctlsettings that can be set.
Create the bond network attachment resource:
oc create -f sriov-bond-network-interface.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-bond-network-interface.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verifying that the NetworkAttachmentDefinition CR is successfully created
Confirm that the SR-IOV Network Operator created the
NetworkAttachmentDefinitionCR by running the following command:oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>
$ oc get network-attachment-definitions -n <namespace>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<namespace>with the networkNamespace that you specified when configuring the network attachment, for example,sysctl-tuning-test.
Example output
NAME AGE bond-sysctl-network 22m allvalidflags 47m
NAME AGE bond-sysctl-network 22m allvalidflags 47mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThere might be a delay before the SR-IOV Network Operator creates the CR.
Verifying that the additional SR-IOV network resource is successful
To verify that the tuning CNI is correctly configured and the additional SR-IOV network attachment is attached, do the following:
Create a
PodCR. For example, save the following YAML as the fileexamplepod.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR.
- 2
- Optional: The MAC address for the SR-IOV device that is allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "mac": true }in the SriovNetwork object. - 3
- Optional: IP addresses for the SR-IOV device that are allocated from the resource type defined in the SR-IOV network attachment definition CR. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are supported. To use this feature, you also must specify
{ "ips": true }in theSriovNetworkobject.
Apply the YAML:
oc apply -f examplepod.yaml
$ oc apply -f examplepod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the pod is created by running the following command:
oc get pod -n sysctl-tuning-test
$ oc get pod -n sysctl-tuning-testCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tunepod 1/1 Running 0 47s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tunepod 1/1 Running 0 47sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in to the pod by running the following command:
oc rsh -n sysctl-tuning-test tunepod
$ oc rsh -n sysctl-tuning-test tunepodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the values of the configured
sysctlflag. Find the valuenet.ipv6.neigh.IFNAME.base_reachable_time_msby running the following command::sysctl net.ipv6.neigh.bond0.base_reachable_time_ms
$ sysctl net.ipv6.neigh.bond0.base_reachable_time_msCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
net.ipv6.neigh.bond0.base_reachable_time_ms = 20000
net.ipv6.neigh.bond0.base_reachable_time_ms = 20000Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.9. Using high performance multicast
You can use multicast on your Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) hardware network.
24.9.1. High performance multicast
The OpenShift SDN network plugin supports multicast between pods on the default network. This is best used for low-bandwidth coordination or service discovery, and not high-bandwidth applications. For applications such as streaming media, like Internet Protocol television (IPTV) and multipoint videoconferencing, you can utilize Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) hardware to provide near-native performance.
When using additional SR-IOV interfaces for multicast:
- Multicast packages must be sent or received by a pod through the additional SR-IOV interface.
- The physical network which connects the SR-IOV interfaces decides the multicast routing and topology, which is not controlled by OpenShift Container Platform.
24.9.2. Configuring an SR-IOV interface for multicast
The follow procedure creates an example SR-IOV interface for multicast.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
SriovNetworkobject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod with multicast application:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
NET_ADMINcapability is required only if your application needs to assign the multicast IP address to the SR-IOV interface. Otherwise, it can be omitted.
24.10. Using DPDK and RDMA
The containerized Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) application is supported on OpenShift Container Platform. You can use Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) network hardware with the Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) and with remote direct memory access (RDMA).
For information on supported devices, refer to Supported devices.
24.10.1. Using a virtual function in DPDK mode with an Intel NIC
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Install the SR-IOV Network Operator.
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the following
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject, and then save the YAML in theintel-dpdk-node-policy.yamlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the driver type for the virtual functions to
vfio-pci.
NoteSee the
Configuring SR-IOV network devicessection for a detailed explanation on each option inSriovNetworkNodePolicy.When applying the configuration specified in a
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject, the SR-IOV Operator may drain the nodes, and in some cases, reboot nodes. It may take several minutes for a configuration change to apply. Ensure that there are enough available nodes in your cluster to handle the evicted workload beforehand.After the configuration update is applied, all the pods in
openshift-sriov-network-operatornamespace will change to aRunningstatus.Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject by running the following command:oc create -f intel-dpdk-node-policy.yaml
$ oc create -f intel-dpdk-node-policy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the following
SriovNetworkobject, and then save the YAML in theintel-dpdk-network.yamlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify a configuration object for the ipam CNI plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition.
NoteSee the "Configuring SR-IOV additional network" section for a detailed explanation on each option in
SriovNetwork.An optional library, app-netutil, provides several API methods for gathering network information about a container’s parent pod.
Create the
SriovNetworkobject by running the following command:oc create -f intel-dpdk-network.yaml
$ oc create -f intel-dpdk-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the following
Podspec, and then save the YAML in theintel-dpdk-pod.yamlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the same
target_namespacewhere theSriovNetworkobjectintel-dpdk-networkis created. If you would like to create the pod in a different namespace, changetarget_namespacein both thePodspec and theSriovNetworkobject. - 2
- Specify the DPDK image which includes your application and the DPDK library used by application.
- 3
- Specify additional capabilities required by the application inside the container for hugepage allocation, system resource allocation, and network interface access.
- 4
- Mount a hugepage volume to the DPDK pod under
/mnt/huge. The hugepage volume is backed by the emptyDir volume type with the medium beingHugepages. - 5
- Optional: Specify the number of DPDK devices allocated to DPDK pod. This resource request and limit, if not explicitly specified, will be automatically added by the SR-IOV network resource injector. The SR-IOV network resource injector is an admission controller component managed by the SR-IOV Operator. It is enabled by default and can be disabled by setting
enableInjectoroption tofalsein the defaultSriovOperatorConfigCR. - 6
- Specify the number of CPUs. The DPDK pod usually requires exclusive CPUs to be allocated from the kubelet. This is achieved by setting CPU Manager policy to
staticand creating a pod withGuaranteedQoS. - 7
- Specify hugepage size
hugepages-1Giorhugepages-2Miand the quantity of hugepages that will be allocated to the DPDK pod. Configure2Miand1Gihugepages separately. Configuring1Gihugepage requires adding kernel arguments to Nodes. For example, adding kernel argumentsdefault_hugepagesz=1GB,hugepagesz=1Gandhugepages=16will result in16*1Gihugepages be allocated during system boot.
Create the DPDK pod by running the following command:
oc create -f intel-dpdk-pod.yaml
$ oc create -f intel-dpdk-pod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.10.2. Using a virtual function in DPDK mode with a Mellanox NIC
You can create a network node policy and create a Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) pod using a virtual function in DPDK mode with a Mellanox NIC.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have installed the Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Network Operator.
-
You have logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Save the following
SriovNetworkNodePolicyYAML configuration to anmlx-dpdk-node-policy.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the device hex code of the SR-IOV network device.
- 2
- Specify the driver type for the virtual functions to
netdevice. A Mellanox SR-IOV Virtual Function (VF) can work in DPDK mode without using thevfio-pcidevice type. The VF device appears as a kernel network interface inside a container. - 3
- Enable Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) mode. This is required for Mellanox cards to work in DPDK mode.
NoteSee Configuring an SR-IOV network device for a detailed explanation of each option in the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject.When applying the configuration specified in an
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject, the SR-IOV Operator might drain the nodes, and in some cases, reboot nodes. It might take several minutes for a configuration change to apply. Ensure that there are enough available nodes in your cluster to handle the evicted workload beforehand.After the configuration update is applied, all the pods in the
openshift-sriov-network-operatornamespace will change to aRunningstatus.Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject by running the following command:oc create -f mlx-dpdk-node-policy.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-dpdk-node-policy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the following
SriovNetworkYAML configuration to anmlx-dpdk-network.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify a configuration object for the IP Address Management (IPAM) Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition.
NoteSee Configuring an SR-IOV network device for a detailed explanation on each option in the
SriovNetworkobject.The
app-netutiloption library provides several API methods for gathering network information about the parent pod of a container.Create the
SriovNetworkobject by running the following command:oc create -f mlx-dpdk-network.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-dpdk-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the following
PodYAML configuration to anmlx-dpdk-pod.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the same
target_namespacewhereSriovNetworkobjectmlx-dpdk-networkis created. To create the pod in a different namespace, changetarget_namespacein both thePodspec andSriovNetworkobject. - 2
- Specify the DPDK image which includes your application and the DPDK library used by the application.
- 3
- Specify additional capabilities required by the application inside the container for hugepage allocation, system resource allocation, and network interface access.
- 4
- Mount the hugepage volume to the DPDK pod under
/mnt/huge. The hugepage volume is backed by theemptyDirvolume type with the medium beingHugepages. - 5
- Optional: Specify the number of DPDK devices allocated for the DPDK pod. If not explicitly specified, this resource request and limit is automatically added by the SR-IOV network resource injector. The SR-IOV network resource injector is an admission controller component managed by SR-IOV Operator. It is enabled by default and can be disabled by setting the
enableInjectoroption tofalsein the defaultSriovOperatorConfigCR. - 6
- Specify the number of CPUs. The DPDK pod usually requires that exclusive CPUs be allocated from the kubelet. To do this, set the CPU Manager policy to
staticand create a pod withGuaranteedQuality of Service (QoS). - 7
- Specify hugepage size
hugepages-1Giorhugepages-2Miand the quantity of hugepages that will be allocated to the DPDK pod. Configure2Miand1Gihugepages separately. Configuring1Gihugepages requires adding kernel arguments to Nodes.
Create the DPDK pod by running the following command:
oc create -f mlx-dpdk-pod.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-dpdk-pod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.10.3. Overview of achieving a specific DPDK line rate
To achieve a specific Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) line rate, deploy a Node Tuning Operator and configure Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV). You must also tune the DPDK settings for the following resources:
- Isolated CPUs
- Hugepages
- The topology scheduler
In previous versions of OpenShift Container Platform, the Performance Addon Operator was used to implement automatic tuning to achieve low latency performance for OpenShift Container Platform applications. In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 and later, this functionality is part of the Node Tuning Operator.
DPDK test environment
The following diagram shows the components of a traffic-testing environment:
- Traffic generator: An application that can generate high-volume packet traffic.
- SR-IOV-supporting NIC: A network interface card compatible with SR-IOV. The card runs a number of virtual functions on a physical interface.
- Physical Function (PF): A PCI Express (PCIe) function of a network adapter that supports the SR-IOV interface.
- Virtual Function (VF): A lightweight PCIe function on a network adapter that supports SR-IOV. The VF is associated with the PCIe PF on the network adapter. The VF represents a virtualized instance of the network adapter.
- Switch: A network switch. Nodes can also be connected back-to-back.
-
testpmd: An example application included with DPDK. Thetestpmdapplication can be used to test the DPDK in a packet-forwarding mode. Thetestpmdapplication is also an example of how to build a fully-fledged application using the DPDK Software Development Kit (SDK). - worker 0 and worker 1: OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
24.10.4. Using SR-IOV and the Node Tuning Operator to achieve a DPDK line rate
You can use the Node Tuning Operator to configure isolated CPUs, hugepages, and a topology scheduler. You can then use the Node Tuning Operator with Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) to achieve a specific Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) line rate.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
-
You have logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. You have deployed a standalone Node Tuning Operator.
NoteIn previous versions of OpenShift Container Platform, the Performance Addon Operator was used to implement automatic tuning to achieve low latency performance for OpenShift applications. In OpenShift Container Platform 4.11 and later, this functionality is part of the Node Tuning Operator.
Procedure
Create a
PerformanceProfileobject based on the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- If hyperthreading is enabled on the system, allocate the relevant symbolic links to the
isolatedandreservedCPU groups. If the system contains multiple non-uniform memory access nodes (NUMAs), allocate CPUs from both NUMAs to both groups. You can also use the Performance Profile Creator for this task. For more information, see Creating a performance profile. - 2
- You can also specify a list of devices that will have their queues set to the reserved CPU count. For more information, see Reducing NIC queues using the Node Tuning Operator.
- 3
- Allocate the number and size of hugepages needed. You can specify the NUMA configuration for the hugepages. By default, the system allocates an even number to every NUMA node on the system. If needed, you can request the use of a realtime kernel for the nodes. See Provisioning a worker with real-time capabilities for more information.
-
Save the
yamlfile asmlx-dpdk-perfprofile-policy.yaml. Apply the performance profile using the following command:
oc create -f mlx-dpdk-perfprofile-policy.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-dpdk-perfprofile-policy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.10.4.1. Example SR-IOV Network Operator for virtual functions
You can use the Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Network Operator to allocate and configure Virtual Functions (VFs) from SR-IOV-supporting Physical Function NICs on the nodes.
For more information on deploying the Operator, see Installing the SR-IOV Network Operator. For more information on configuring an SR-IOV network device, see Configuring an SR-IOV network device.
There are some differences between running Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) workloads on Intel VFs and Mellanox VFs. This section provides object configuration examples for both VF types. The following is an example of an sriovNetworkNodePolicy object used to run DPDK applications on Intel NICs:
The following is an example of an sriovNetworkNodePolicy object for Mellanox NICs:
24.10.4.2. Example SR-IOV network operator
The following is an example definition of an sriovNetwork object. In this case, Intel and Mellanox configurations are identical:
- 1
- You can use a different IP Address Management (IPAM) implementation, such as Whereabouts. For more information, see Dynamic IP address assignment configuration with Whereabouts.
- 2
- You must request the
networkNamespacewhere the network attachment definition will be created. You must create thesriovNetworkCR under theopenshift-sriov-network-operatornamespace. - 3
- The
resourceNamevalue must match that of theresourceNamecreated under thesriovNetworkNodePolicy.
24.10.4.3. Example DPDK base workload
The following is an example of a Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) container:
- 1
- Request the SR-IOV networks you need. Resources for the devices will be injected automatically.
- 2
- Disable the CPU and IRQ load balancing base. See Disabling interrupt processing for individual pods for more information.
- 3
- Set the
runtimeClasstoperformance-performance. Do not set theruntimeClasstoHostNetworkorprivileged. - 4
- Request an equal number of resources for requests and limits to start the pod with
GuaranteedQuality of Service (QoS).
Do not start the pod with SLEEP and then exec into the pod to start the testpmd or the DPDK workload. This can add additional interrupts as the exec process is not pinned to any CPU.
24.10.4.4. Example testpmd script
The following is an example script for running testpmd:
This example uses two different sriovNetwork CRs. The environment variable contains the Virtual Function (VF) PCI address that was allocated for the pod. If you use the same network in the pod definition, you must split the pciAddress. It is important to configure the correct MAC addresses of the traffic generator. This example uses custom MAC addresses.
24.10.5. Using a virtual function in RDMA mode with a Mellanox NIC
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is the only supported mode when using RDMA on OpenShift Container Platform.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Install the SR-IOV Network Operator.
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the following
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject, and then save the YAML in themlx-rdma-node-policy.yamlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteSee the
Configuring SR-IOV network devicessection for a detailed explanation on each option inSriovNetworkNodePolicy.When applying the configuration specified in a
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject, the SR-IOV Operator may drain the nodes, and in some cases, reboot nodes. It may take several minutes for a configuration change to apply. Ensure that there are enough available nodes in your cluster to handle the evicted workload beforehand.After the configuration update is applied, all the pods in the
openshift-sriov-network-operatornamespace will change to aRunningstatus.Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject by running the following command:oc create -f mlx-rdma-node-policy.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-rdma-node-policy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the following
SriovNetworkobject, and then save the YAML in themlx-rdma-network.yamlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify a configuration object for the ipam CNI plugin as a YAML block scalar. The plugin manages IP address assignment for the attachment definition.
NoteSee the "Configuring SR-IOV additional network" section for a detailed explanation on each option in
SriovNetwork.An optional library, app-netutil, provides several API methods for gathering network information about a container’s parent pod.
Create the
SriovNetworkNodePolicyobject by running the following command:oc create -f mlx-rdma-network.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-rdma-network.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the following
Podspec, and then save the YAML in themlx-rdma-pod.yamlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the same
target_namespacewhereSriovNetworkobjectmlx-rdma-networkis created. If you would like to create the pod in a different namespace, changetarget_namespacein bothPodspec andSriovNetworkobject. - 2
- Specify the RDMA image which includes your application and RDMA library used by application.
- 3
- Specify additional capabilities required by the application inside the container for hugepage allocation, system resource allocation, and network interface access.
- 4
- Mount the hugepage volume to RDMA pod under
/mnt/huge. The hugepage volume is backed by the emptyDir volume type with the medium beingHugepages. - 5
- Specify number of CPUs. The RDMA pod usually requires exclusive CPUs be allocated from the kubelet. This is achieved by setting CPU Manager policy to
staticand create pod withGuaranteedQoS. - 6
- Specify hugepage size
hugepages-1Giorhugepages-2Miand the quantity of hugepages that will be allocated to the RDMA pod. Configure2Miand1Gihugepages separately. Configuring1Gihugepage requires adding kernel arguments to Nodes.
Create the RDMA pod by running the following command:
oc create -f mlx-rdma-pod.yaml
$ oc create -f mlx-rdma-pod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.10.6. A test pod template for clusters that use OVS-DPDK on OpenStack
The following testpmd pod demonstrates container creation with huge pages, reserved CPUs, and the SR-IOV port.
An example testpmd pod
24.10.7. A test pod template for clusters that use OVS hardware offloading on OpenStack
The following testpmd pod demonstrates Open vSwitch (OVS) hardware offloading on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP).
An example testpmd pod
- 1
- If your performance profile is not named
cnf-performance profile, replace that string with the correct performance profile name.
24.11. Using pod-level bonding
Bonding at the pod level is vital to enable workloads inside pods that require high availability and more throughput. With pod-level bonding, you can create a bond interface from multiple single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) virtual function interfaces in a kernel mode interface. The SR-IOV virtual functions are passed into the pod and attached to a kernel driver.
One scenario where pod level bonding is required is creating a bond interface from multiple SR-IOV virtual functions on different physical functions. Creating a bond interface from two different physical functions on the host can be used to achieve high availability and throughput at pod level.
For guidance on tasks such as creating a SR-IOV network, network policies, network attachment definitions and pods, see Configuring an SR-IOV network device.
24.11.1. Configuring a bond interface from two SR-IOV interfaces
Bonding enables multiple network interfaces to be aggregated into a single logical "bonded" interface. Bond Container Network Interface (Bond-CNI) brings bond capability into containers.
Bond-CNI can be created using Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) virtual functions and placing them in the container network namespace.
OpenShift Container Platform only supports Bond-CNI using SR-IOV virtual functions. The SR-IOV Network Operator provides the SR-IOV CNI plugin needed to manage the virtual functions. Other CNIs or types of interfaces are not supported.
Prerequisites
- The SR-IOV Network Operator must be installed and configured to obtain virtual functions in a container.
- To configure SR-IOV interfaces, an SR-IOV network and policy must be created for each interface.
- The SR-IOV Network Operator creates a network attachment definition for each SR-IOV interface, based on the SR-IOV network and policy defined.
-
The
linkStateis set to the default valueautofor the SR-IOV virtual function.
24.11.1.1. Creating a bond network attachment definition
Now that the SR-IOV virtual functions are available, you can create a bond network attachment definition.
- 1
- The cni-type is always set to
bond. - 2
- The
modeattribute specifies the bonding mode.NoteThe bonding modes supported are:
-
balance-rr- 0 -
active-backup- 1 -
balance-xor- 2
For
balance-rrorbalance-xormodes, you must set thetrustmode toonfor the SR-IOV virtual function. -
- 3
- The
failoverattribute is mandatory for active-backup mode and must be set to 1. - 4
- The
linksInContainer=trueflag informs the Bond CNI that the required interfaces are to be found inside the container. By default, Bond CNI looks for these interfaces on the host which does not work for integration with SRIOV and Multus. - 5
- The
linkssection defines which interfaces will be used to create the bond. By default, Multus names the attached interfaces as: "net", plus a consecutive number, starting with one.
24.11.1.2. Creating a pod using a bond interface
Test the setup by creating a pod with a YAML file named for example
podbonding.yamlwith content similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Note the network annotation: it contains two SR-IOV network attachments, and one bond network attachment. The bond attachment uses the two SR-IOV interfaces as bonded port interfaces.
Apply the yaml by running the following command:
oc apply -f podbonding.yaml
$ oc apply -f podbonding.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Inspect the pod interfaces with the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf no interface names are configured in the pod annotation, interface names are assigned automatically as
net<n>, with<n>starting at1.Optional: If you want to set a specific interface name for example
bond0, edit thek8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networksannotation and setbond0as the interface name as follows:annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: demo/sriovnet1, demo/sriovnet2, demo/bond-net1@bond0annotations: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: demo/sriovnet1, demo/sriovnet2, demo/bond-net1@bond0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.12. Configuring hardware offloading
As a cluster administrator, you can configure hardware offloading on compatible nodes to increase data processing performance and reduce load on host CPUs.
24.12.1. About hardware offloading
Open vSwitch hardware offloading is a method of processing network tasks by diverting them away from the CPU and offloading them to a dedicated processor on a network interface controller. As a result, clusters can benefit from faster data transfer speeds, reduced CPU workloads, and lower computing costs.
The key element for this feature is a modern class of network interface controllers known as SmartNICs. A SmartNIC is a network interface controller that is able to handle computationally-heavy network processing tasks. In the same way that a dedicated graphics card can improve graphics performance, a SmartNIC can improve network performance. In each case, a dedicated processor improves performance for a specific type of processing task.
In OpenShift Container Platform, you can configure hardware offloading for bare metal nodes that have a compatible SmartNIC. Hardware offloading is configured and enabled by the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Hardware offloading is not compatible with all workloads or application types. Only the following two communication types are supported:
- pod-to-pod
- pod-to-service, where the service is a ClusterIP service backed by a regular pod
In all cases, hardware offloading takes place only when those pods and services are assigned to nodes that have a compatible SmartNIC. Suppose, for example, that a pod on a node with hardware offloading tries to communicate with a service on a regular node. On the regular node, all the processing takes place in the kernel, so the overall performance of the pod-to-service communication is limited to the maximum performance of that regular node. Hardware offloading is not compatible with DPDK applications.
Enabling hardware offloading on a node, but not configuring pods to use, it can result in decreased throughput performance for pod traffic. You cannot configure hardware offloading for pods that are managed by OpenShift Container Platform.
24.12.2. Supported devices
Hardware offloading is supported on the following network interface controllers:
| Manufacturer | Model | Vendor ID | Device ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mellanox | MT27800 Family [ConnectX‑5] | 15b3 | 1017 |
| Mellanox | MT28880 Family [ConnectX‑5 Ex] | 15b3 | 1019 |
| Mellanox | MT2892 Family [ConnectX‑6 Dx] | 15b3 | 101d |
| Mellanox | MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] | 15b3 | 101f |
| Mellanox | MT42822 BlueField-2 in ConnectX-6 NIC mode | 15b3 | a2d6 |
24.12.3. Prerequisites
- Your cluster has at least one bare metal machine with a network interface controller that is supported for hardware offloading.
- You installed the SR-IOV Network Operator.
- Your cluster uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
-
In your OVN-Kubernetes network plugin configuration, the
gatewayConfig.routingViaHostfield is set tofalse.
24.12.4. Setting the SR-IOV Network Operator into systemd mode
To support hardware offloading, you must first set the SR-IOV Network Operator into systemd mode.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a
SriovOperatorConfigcustom resource (CR) to deploy all the SR-IOV Operator components:Create a file named
sriovOperatorConfig.yamlthat contains the following YAML:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the resource by running the following command:
oc apply -f sriovOperatorConfig.yaml
$ oc apply -f sriovOperatorConfig.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.12.5. Configuring a machine config pool for hardware offloading
To enable hardware offloading, you now create a dedicated machine config pool and configure it to work with the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Prerequisites
-
SR-IOV Network Operator installed and set into
systemdmode.
Procedure
Create a machine config pool for machines you want to use hardware offloading on.
Create a file, such as
mcp-offloading.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the machine config pool:
oc create -f mcp-offloading.yaml
$ oc create -f mcp-offloading.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Add nodes to the machine config pool. Label each node with the node role label of your pool:
oc label node worker-2 node-role.kubernetes.io/mcp-offloading=""
$ oc label node worker-2 node-role.kubernetes.io/mcp-offloading=""Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To verify that the new pool is created, run the following command:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add this machine config pool to the
SriovNetworkPoolConfigcustom resource:Create a file, such as
sriov-pool-config.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of your machine config pool for hardware offloading.
Apply the configuration:
oc create -f <SriovNetworkPoolConfig_name>.yaml
$ oc create -f <SriovNetworkPoolConfig_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you apply the configuration specified in a
SriovNetworkPoolConfigobject, the SR-IOV Operator drains and restarts the nodes in the machine config pool.It might take several minutes for a configuration changes to apply.
24.12.6. Configuring the SR-IOV network node policy
You can create an SR-IOV network device configuration for a node by creating an SR-IOV network node policy. To enable hardware offloading, you must define the .spec.eSwitchMode field with the value "switchdev".
The following procedure creates an SR-IOV interface for a network interface controller with hardware offloading.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a file, such as
sriov-node-policy.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> The name for the custom resource object. <.> Required. Hardware offloading is not supported with
vfio-pci. <.> Required.Apply the configuration for the policy:
oc create -f sriov-node-policy.yaml
$ oc create -f sriov-node-policy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you apply the configuration specified in a
SriovNetworkPoolConfigobject, the SR-IOV Operator drains and restarts the nodes in the machine config pool.It might take several minutes for a configuration change to apply.
24.12.6.1. An example SR-IOV network node policy for OpenStack
The following example describes an SR-IOV interface for a network interface controller (NIC) with hardware offloading on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP).
An SR-IOV interface for a NIC with hardware offloading on RHOSP
24.12.7. Creating a network attachment definition
After you define the machine config pool and the SR-IOV network node policy, you can create a network attachment definition for the network interface card you specified.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a file, such as
net-attach-def.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> The name for your network attachment definition. <.> The namespace for your network attachment definition. <.> This is the value of the
spec.resourceNamefield you specified in theSriovNetworkNodePolicyobject.Apply the configuration for the network attachment definition:
oc create -f net-attach-def.yaml
$ oc create -f net-attach-def.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Run the following command to see whether the new definition is present:
oc get net-attach-def -A
$ oc get net-attach-def -ACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAMESPACE NAME AGE net-attach-def net-attach-def 43h
NAMESPACE NAME AGE net-attach-def net-attach-def 43hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
24.12.8. Adding the network attachment definition to your pods
After you create the machine config pool, the SriovNetworkPoolConfig and SriovNetworkNodePolicy custom resources, and the network attachment definition, you can apply these configurations to your pods by adding the network attachment definition to your pod specifications.
Procedure
In the pod specification, add the
.metadata.annotations.k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networksfield and specify the network attachment definition you created for hardware offloading:.... metadata: annotations: v1.multus-cni.io/default-network: net-attach-def/net-attach-def <.>.... metadata: annotations: v1.multus-cni.io/default-network: net-attach-def/net-attach-def <.>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> The value must be the name and namespace of the network attachment definition you created for hardware offloading.
24.13. Switching Bluefield-2 from DPU to NIC
You can switch the Bluefield-2 network device from data processing unit (DPU) mode to network interface controller (NIC) mode.
24.13.1. Switching Bluefield-2 from DPU mode to NIC mode
Use the following procedure to switch Bluefield-2 from data processing units (DPU) mode to network interface controller (NIC) mode.
Currently, only switching Bluefield-2 from DPU to NIC mode is supported. Switching from NIC mode to DPU mode is unsupported.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the SR-IOV Network Operator. For more information, see "Installing SR-IOV Network Operator".
- You have updated Bluefield-2 to the latest firmware. For more information, see Firmware for NVIDIA BlueField-2.
Procedure
Add the following labels to each of your worker nodes by entering the following commands:
oc label node <example_node_name_one> node-role.kubernetes.io/sriov=
$ oc label node <example_node_name_one> node-role.kubernetes.io/sriov=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc label node <example_node_name_two> node-role.kubernetes.io/sriov=
$ oc label node <example_node_name_two> node-role.kubernetes.io/sriov=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a machine config pool for the SR-IOV Network Operator, for example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the following
machineconfig.yamlfile to the worker nodes:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Optional: The PCI address of a specific card can optionally be specified, for example
ExecStart=/bin/bash -c '/etc/default/switch_in_sriov_config_daemon.sh nic 0000:5e:00.0 || echo done'. By default, the first device is selected. If there is more than one device, you must specify which PCI address to be used. The PCI address must be the same on all nodes that are switching Bluefield-2 from DPU mode to NIC mode.
- Wait for the worker nodes to restart. After restarting, the Bluefield-2 network device on the worker nodes is switched into NIC mode.
- Optional: You might need to restart the host hardware because most recent Bluefield-2 firmware releases require a hardware restart to switch into NIC mode.
24.14. Uninstalling the SR-IOV Network Operator
To uninstall the SR-IOV Network Operator, you must delete any running SR-IOV workloads, uninstall the Operator, and delete the webhooks that the Operator used.
24.14.1. Uninstalling the SR-IOV Network Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can uninstall the SR-IOV Network Operator.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions. - You have the SR-IOV Network Operator installed.
Procedure
Delete all SR-IOV custom resources (CRs):
oc delete sriovnetwork -n openshift-sriov-network-operator --all
$ oc delete sriovnetwork -n openshift-sriov-network-operator --allCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete sriovnetworknodepolicy -n openshift-sriov-network-operator --all
$ oc delete sriovnetworknodepolicy -n openshift-sriov-network-operator --allCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete sriovibnetwork -n openshift-sriov-network-operator --all
$ oc delete sriovibnetwork -n openshift-sriov-network-operator --allCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Follow the instructions in the "Deleting Operators from a cluster" section to remove the SR-IOV Network Operator from your cluster.
Delete the SR-IOV custom resource definitions that remain in the cluster after the SR-IOV Network Operator is uninstalled:
oc delete crd sriovibnetworks.sriovnetwork.openshift.io
$ oc delete crd sriovibnetworks.sriovnetwork.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd sriovnetworknodepolicies.sriovnetwork.openshift.io
$ oc delete crd sriovnetworknodepolicies.sriovnetwork.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd sriovnetworknodestates.sriovnetwork.openshift.io
$ oc delete crd sriovnetworknodestates.sriovnetwork.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd sriovnetworkpoolconfigs.sriovnetwork.openshift.io
$ oc delete crd sriovnetworkpoolconfigs.sriovnetwork.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd sriovnetworks.sriovnetwork.openshift.io
$ oc delete crd sriovnetworks.sriovnetwork.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd sriovoperatorconfigs.sriovnetwork.openshift.io
$ oc delete crd sriovoperatorconfigs.sriovnetwork.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the SR-IOV webhooks:
oc delete mutatingwebhookconfigurations network-resources-injector-config
$ oc delete mutatingwebhookconfigurations network-resources-injector-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete MutatingWebhookConfiguration sriov-operator-webhook-config
$ oc delete MutatingWebhookConfiguration sriov-operator-webhook-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete ValidatingWebhookConfiguration sriov-operator-webhook-config
$ oc delete ValidatingWebhookConfiguration sriov-operator-webhook-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the SR-IOV Network Operator namespace:
oc delete namespace openshift-sriov-network-operator
$ oc delete namespace openshift-sriov-network-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 25. OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
25.1. About the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
The OpenShift Container Platform cluster uses a virtualized network for pod and service networks.
Part of Red Hat OpenShift Networking, the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is the default network provider for OpenShift Container Platform. OVN-Kubernetes is based on Open Virtual Network (OVN) and provides an overlay-based networking implementation.
For a cloud controller manager (CCM) with the --cloud-provider=external option set to cloud-provider-vsphere, a known issue exists for a cluster that operates in a networking environment with multiple subnets.
When you upgrade your cluster from OpenShift Container Platform 4.12 to OpenShift Container Platform 4.13, the CCM selects a wrong node IP address and this operation generates an error message in the namespaces/openshift-cloud-controller-manager/pods/vsphere-cloud-controller-manager logs. The error message indicates a mismatch with the node IP address and the vsphere-cloud-controller-manager pod IP address in your cluster.
The known issue might not impact the cluster upgrade operation, but you can set the correct IP address in both the nodeNetworking.external.networkSubnetCidr and the nodeNetworking.internal.networkSubnetCidr parameters for the nodeNetworking object that your cluster uses for its networking requirements.
A cluster that uses the OVN-Kubernetes plugin also runs Open vSwitch (OVS) on each node. OVN configures OVS on each node to implement the declared network configuration.
OVN-Kubernetes is the default networking solution for OpenShift Container Platform and single-node OpenShift deployments.
OVN-Kubernetes, which arose from the OVS project, uses many of the same constructs, such as open flow rules, to determine how packets travel through the network. For more information, see the Open Virtual Network website.
OVN-Kubernetes is a series of daemons for OVS that translate virtual network configurations into OpenFlow rules. OpenFlow is a protocol for communicating with network switches and routers, providing a means for remotely controlling the flow of network traffic on a network device, allowing network administrators to configure, manage, and monitor the flow of network traffic.
OVN-Kubernetes provides more of the advanced functionality not available with OpenFlow. OVN supports distributed virtual routing, distributed logical switches, access control, DHCP and DNS. OVN implements distributed virtual routing within logic flows which equate to open flows. So for example if you have a pod that sends out a DHCP request on the network, it sends out that broadcast looking for DHCP address there will be a logic flow rule that matches that packet, and it responds giving it a gateway, a DNS server an IP address and so on.
OVN-Kubernetes runs a daemon on each node. There are daemon sets for the databases and for the OVN controller that run on every node. The OVN controller programs the Open vSwitch daemon on the nodes to support the network provider features; egress IPs, firewalls, routers, hybrid networking, IPSEC encryption, IPv6, network policy, network policy logs, hardware offloading and multicast.
25.1.1. OVN-Kubernetes purpose
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is an open-source, fully-featured Kubernetes CNI plugin that uses Open Virtual Network (OVN) to manage network traffic flows. OVN is a community developed, vendor-agnostic network virtualization solution. The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin:
- Uses OVN (Open Virtual Network) to manage network traffic flows. OVN is a community developed, vendor-agnostic network virtualization solution.
- Implements Kubernetes network policy support, including ingress and egress rules.
- Uses the Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) protocol rather than VXLAN to create an overlay network between nodes.
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin provides the following advantages over OpenShift SDN.
- Full support for IPv6 single-stack and IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack networking on supported platforms
- Support for hybrid clusters with both Linux and Microsoft Windows workloads
- Optional IPsec encryption of intra-cluster communications
- Offload of network data processing from host CPU to compatible network cards and data processing units (DPUs)
25.1.2. Supported network plugin feature matrix
Red Hat OpenShift Networking offers two options for the network plugin, OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes, for the network plugin. The following table summarizes the current feature support for both network plugins:
| Feature | OpenShift SDN | OVN-Kubernetes |
|---|---|---|
| Egress IPs | Supported | Supported |
| Egress firewall | Supported | Supported [1] |
| Egress router | Supported | Supported [2] |
| Hybrid networking | Not supported | Supported |
| IPsec encryption for intra-cluster communication | Not supported | Supported |
| IPv4 single-stack | Supported | Supported |
| IPv6 single-stack | Not supported | Supported [3] |
| IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack | Not Supported | Supported [4] |
| IPv6/IPv4 dual-stack | Not supported | Supported [5] |
| Kubernetes network policy | Supported | Supported |
| Kubernetes network policy logs | Not supported | Supported |
| Hardware offloading | Not supported | Supported |
| Multicast | Supported | Supported |
- Egress firewall is also known as egress network policy in OpenShift SDN. This is not the same as network policy egress.
- Egress router for OVN-Kubernetes supports only redirect mode.
- IPv6 single-stack networking on a bare-metal platform.
- IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack networking on bare-metal, VMware vSphere (installer-provisioned infrastructure installations only), IBM Power®, and IBM Z® platforms. On VMware vSphere, dual-stack networking limitations exist.
- IPv6/IPv4 dual-stack networking on bare-metal and IBM Power® platforms.
25.1.3. OVN-Kubernetes IPv6 and dual-stack limitations
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin has the following limitations:
For clusters configured for dual-stack networking, both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic must use the same network interface as the default gateway. If this requirement is not met, pods on the host in the
ovnkube-nodedaemon set enter theCrashLoopBackOffstate. If you display a pod with a command such asoc get pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node -o yaml, thestatusfield contains more than one message about the default gateway, as shown in the following output:I1006 16:09:50.985852 60651 helper_linux.go:73] Found default gateway interface br-ex 192.168.127.1 I1006 16:09:50.985923 60651 helper_linux.go:73] Found default gateway interface ens4 fe80::5054:ff:febe:bcd4 F1006 16:09:50.985939 60651 ovnkube.go:130] multiple gateway interfaces detected: br-ex ens4
I1006 16:09:50.985852 60651 helper_linux.go:73] Found default gateway interface br-ex 192.168.127.1 I1006 16:09:50.985923 60651 helper_linux.go:73] Found default gateway interface ens4 fe80::5054:ff:febe:bcd4 F1006 16:09:50.985939 60651 ovnkube.go:130] multiple gateway interfaces detected: br-ex ens4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The only resolution is to reconfigure the host networking so that both IP families use the same network interface for the default gateway.
For clusters configured for dual-stack networking, both the IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables must contain the default gateway. If this requirement is not met, pods on the host in the
ovnkube-nodedaemon set enter theCrashLoopBackOffstate. If you display a pod with a command such asoc get pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node -o yaml, thestatusfield contains more than one message about the default gateway, as shown in the following output:I0512 19:07:17.589083 108432 helper_linux.go:74] Found default gateway interface br-ex 192.168.123.1 F0512 19:07:17.589141 108432 ovnkube.go:133] failed to get default gateway interface
I0512 19:07:17.589083 108432 helper_linux.go:74] Found default gateway interface br-ex 192.168.123.1 F0512 19:07:17.589141 108432 ovnkube.go:133] failed to get default gateway interfaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The only resolution is to reconfigure the host networking so that both IP families contain the default gateway.
25.1.4. Session affinity
Session affinity is a feature that applies to Kubernetes Service objects. You can use session affinity if you want to ensure that each time you connect to a <service_VIP>:<Port>, the traffic is always load balanced to the same back end. For more information, including how to set session affinity based on a client’s IP address, see Session affinity.
Stickiness timeout for session affinity
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin for OpenShift Container Platform calculates the stickiness timeout for a session from a client based on the last packet. For example, if you run a curl command 10 times, the sticky session timer starts from the tenth packet not the first. As a result, if the client is continuously contacting the service, then the session never times out. The timeout starts when the service has not received a packet for the amount of time set by the timeoutSeconds parameter.
25.2. OVN-Kubernetes architecture
25.2.1. Introduction to OVN-Kubernetes architecture
The following diagram shows the OVN-Kubernetes architecture.
Figure 25.1. OVK-Kubernetes architecture

The key components are:
- Cloud Management System (CMS) - A platform specific client for OVN that provides a CMS specific plugin for OVN integration. The plugin translates the cloud management system’s concept of the logical network configuration, stored in the CMS configuration database in a CMS-specific format, into an intermediate representation understood by OVN.
-
OVN Northbound database (
nbdb) - Stores the logical network configuration passed by the CMS plugin. -
OVN Southbound database (
sbdb) - Stores the physical and logical network configuration state for OpenVswitch (OVS) system on each node, including tables that bind them. -
ovn-northd - This is the intermediary client between
nbdbandsbdb. It translates the logical network configuration in terms of conventional network concepts, taken from thenbdb, into logical data path flows in thesbdbbelow it. The container name isnorthdand it runs in theovnkube-masterpods. -
ovn-controller - This is the OVN agent that interacts with OVS and hypervisors, for any information or update that is needed for
sbdb. Theovn-controllerreads logical flows from thesbdb, translates them intoOpenFlowflows and sends them to the node’s OVS daemon. The container name isovn-controllerand it runs in theovnkube-nodepods.
The OVN northbound database has the logical network configuration passed down to it by the cloud management system (CMS). The OVN northbound Database contains the current desired state of the network, presented as a collection of logical ports, logical switches, logical routers, and more. The ovn-northd (northd container) connects to the OVN northbound database and the OVN southbound database. It translates the logical network configuration in terms of conventional network concepts, taken from the OVN northbound Database, into logical data path flows in the OVN southbound database.
The OVN southbound database has physical and logical representations of the network and binding tables that link them together. Every node in the cluster is represented in the southbound database, and you can see the ports that are connected to it. It also contains all the logic flows, the logic flows are shared with the ovn-controller process that runs on each node and the ovn-controller turns those into OpenFlow rules to program Open vSwitch.
The Kubernetes control plane nodes each contain an ovnkube-master pod which hosts containers for the OVN northbound and southbound databases. All OVN northbound databases form a Raft cluster and all southbound databases form a separate Raft cluster. At any given time a single ovnkube-master is the leader and the other ovnkube-master pods are followers.
25.2.2. Listing all resources in the OVN-Kubernetes project
Finding the resources and containers that run in the OVN-Kubernetes project is important to help you understand the OVN-Kubernetes networking implementation.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
The OpenShift CLI (
oc) installed.
Procedure
Run the following command to get all resources, endpoints, and
ConfigMapsin the OVN-Kubernetes project:oc get all,ep,cm -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get all,ep,cm -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow There are three
ovnkube-mastersthat run on the control plane nodes, and two daemon sets used to deploy theovnkube-masterandovnkube-nodepods. There is oneovnkube-nodepod for each node in the cluster. Theovnkube-configConfigMaphas the OpenShift Container Platform OVN-Kubernetes configurations started by online-master andovnkube-node.List all the containers in the
ovnkube-masterpods by running the following command:oc get pods ovnkube-master-9g7zt \ -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[*].name}' -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes$ oc get pods ovnkube-master-9g7zt \ -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[*].name}' -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
northd nbdb kube-rbac-proxy sbdb ovnkube-master ovn-dbchecker
northd nbdb kube-rbac-proxy sbdb ovnkube-master ovn-dbcheckerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
ovnkube-masterpod is made up of several containers. It is responsible for hosting the northbound database (nbdbcontainer), the southbound database (sbdbcontainer), watching for cluster events for pods, egressIP, namespaces, services, endpoints, egress firewall, and network policy and writing them to the northbound database (ovnkube-masterpod), as well as managing pod subnet allocation to nodes.List all the containers in the
ovnkube-nodepods by running the following command:oc get pods ovnkube-node-jg52r \ -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[*].name}' -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes$ oc get pods ovnkube-node-jg52r \ -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[*].name}' -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
ovn-controller ovn-acl-logging kube-rbac-proxy kube-rbac-proxy-ovn-metrics ovnkube-node
ovn-controller ovn-acl-logging kube-rbac-proxy kube-rbac-proxy-ovn-metrics ovnkube-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
ovnkube-nodepod has a container (ovn-controller) that resides on each OpenShift Container Platform node. Each node’sovn-controllerconnects the OVN northbound to the OVN southbound database to learn about the OVN configuration. Theovn-controllerconnects southbound toovs-vswitchdas an OpenFlow controller, for control over network traffic, and to the localovsdb-serverto allow it to monitor and control Open vSwitch configuration.List the currently elected OVN-Kubernetes master leader by running the following command:
oc get lease -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get lease -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
NAME HOLDER AGE ovn-kubernetes-master ci-ln-gz990pb-72292-rthz2-master-2 50m
NAME HOLDER AGE ovn-kubernetes-master ci-ln-gz990pb-72292-rthz2-master-2 50mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.2.3. Listing the OVN-Kubernetes northbound database contents
To understand logic flow rules you need to examine the northbound database and understand what objects are there to see how they are translated into logic flow rules. The up to date information is present on the OVN Raft leader and this procedure describes how to find the Raft leader and subsequently query it to list the OVN northbound database contents.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
The OpenShift CLI (
oc) installed.
Procedure
Find the OVN Raft leader for the northbound database.
NoteThe Raft leader stores the most up to date information.
List the pods by running the following command:
oc get po -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get po -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Choose one of the master pods at random and run the following command:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes ovnkube-master-7j97q \ -- /usr/bin/ovn-appctl -t /var/run/ovn/ovnnb_db.ctl \ --timeout=3 cluster/status OVN_Northbound
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes ovnkube-master-7j97q \ -- /usr/bin/ovn-appctl -t /var/run/ovn/ovnnb_db.ctl \ --timeout=3 cluster/status OVN_NorthboundCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the
ovnkube-masterpod running on IP Address10.0.242.240using the following command:oc get po -o wide -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep 10.0.242.240 | grep -v ovnkube-node
$ oc get po -o wide -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep 10.0.242.240 | grep -v ovnkube-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ovnkube-master-gt4ms 6/6 Running 1 (143m ago) 150m 10.0.242.240 ip-10-0-242-240.ec2.internal <none> <none>
ovnkube-master-gt4ms 6/6 Running 1 (143m ago) 150m 10.0.242.240 ip-10-0-242-240.ec2.internal <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
ovnkube-master-gt4mspod runs on IP Address 10.0.242.240.
Run the following command to show all the objects in the northbound database:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl show
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl showCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output is too long to list here. The list includes the NAT rules, logical switches, load balancers and so on.
Run the following command to display the options available with the command
ovn-nbctl:oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-mk6p6 \ -c northd ovn-nbctl --help
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-mk6p6 \ -c northd ovn-nbctl --helpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can narrow down and focus on specific components by using some of the following commands:
Run the following command to show the list of logical routers:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl lr-list
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl lr-listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFrom this output you can see there is router on each node plus an
ovn_cluster_router.Run the following command to show the list of logical switches:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl ls-list
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl ls-listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFrom this output you can see there is an ext switch for each node plus switches with the node name itself and a join switch.
Run the following command to show the list of load balancers:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl lb-list
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-gt4ms \ -c northd -- ovn-nbctl lb-listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFrom this truncated output you can see there are many OVN-Kubernetes load balancers. Load balancers in OVN-Kubernetes are representations of services.
25.2.4. Command-line arguments for ovn-nbctl to examine northbound database contents
The following table describes the command-line arguments that can be used with ovn-nbctl to examine the contents of the northbound database.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
|
| An overview of the northbound database contents. |
|
| Show the details associated with the specified switch or router. |
|
| Show the logical routers. |
|
|
Using the router information from |
|
| Show network address translation details for the specified router. |
|
| Show the logical switches |
|
|
Using the switch information from |
|
| Get the type for the logical port. |
|
| Show the load balancers. |
25.2.5. Listing the OVN-Kubernetes southbound database contents
Logic flow rules are stored in the southbound database that is a representation of your infrastructure. The up to date information is present on the OVN Raft leader and this procedure describes how to find the Raft leader and query it to list the OVN southbound database contents.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
The OpenShift CLI (
oc) installed.
Procedure
Find the OVN Raft leader for the southbound database.
NoteThe Raft leader stores the most up to date information.
List the pods by running the following command:
oc get po -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get po -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Choose one of the master pods at random and run the following command to find the OVN southbound Raft leader:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes ovnkube-master-7j97q \ -- /usr/bin/ovn-appctl -t /var/run/ovn/ovnsb_db.ctl \ --timeout=3 cluster/status OVN_Southbound
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes ovnkube-master-7j97q \ -- /usr/bin/ovn-appctl -t /var/run/ovn/ovnsb_db.ctl \ --timeout=3 cluster/status OVN_SouthboundCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the
ovnkube-masterpod running on IP Address10.0.163.212using the following command:oc get po -o wide -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep 10.0.163.212 | grep -v ovnkube-node
$ oc get po -o wide -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes | grep 10.0.163.212 | grep -v ovnkube-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ovnkube-master-mk6p6 6/6 Running 0 136m 10.0.163.212 ip-10-0-163-212.ec2.internal <none> <none>
ovnkube-master-mk6p6 6/6 Running 0 136m 10.0.163.212 ip-10-0-163-212.ec2.internal <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
ovnkube-master-mk6p6pod runs on IP Address 10.0.163.212.
Run the following command to show all the information stored in the southbound database:
oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-mk6p6 \ -c northd -- ovn-sbctl show
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-mk6p6 \ -c northd -- ovn-sbctl showCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This detailed output shows the chassis and the ports that are attached to the chassis which in this case are all of the router ports and anything that runs like host networking. Any pods communicate out to the wider network using source network address translation (SNAT). Their IP address is translated into the IP address of the node that the pod is running on and then sent out into the network.
In addition to the chassis information the southbound database has all the logic flows and those logic flows are then sent to the
ovn-controllerrunning on each of the nodes. Theovn-controllertranslates the logic flows into open flow rules and ultimately programsOpenvSwitchso that your pods can then follow open flow rules and make it out of the network.Run the following command to display the options available with the command
ovn-sbctl:oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-mk6p6 \ -c northd -- ovn-sbctl --help
$ oc exec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -it ovnkube-master-mk6p6 \ -c northd -- ovn-sbctl --helpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.2.6. Command-line arguments for ovn-sbctl to examine southbound database contents
The following table describes the command-line arguments that can be used with ovn-sbctl to examine the contents of the southbound database.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Overview of the southbound database contents. |
|
| List the contents of southbound database for a the specified port . |
|
| List the logical flows. |
25.2.7. OVN-Kubernetes logical architecture
OVN is a network virtualization solution. It creates logical switches and routers. These switches and routers are interconnected to create any network topologies. When you run ovnkube-trace with the log level set to 2 or 5 the OVN-Kubernetes logical components are exposed. The following diagram shows how the routers and switches are connected in OpenShift Container Platform.
Figure 25.2. OVN-Kubernetes router and switch components
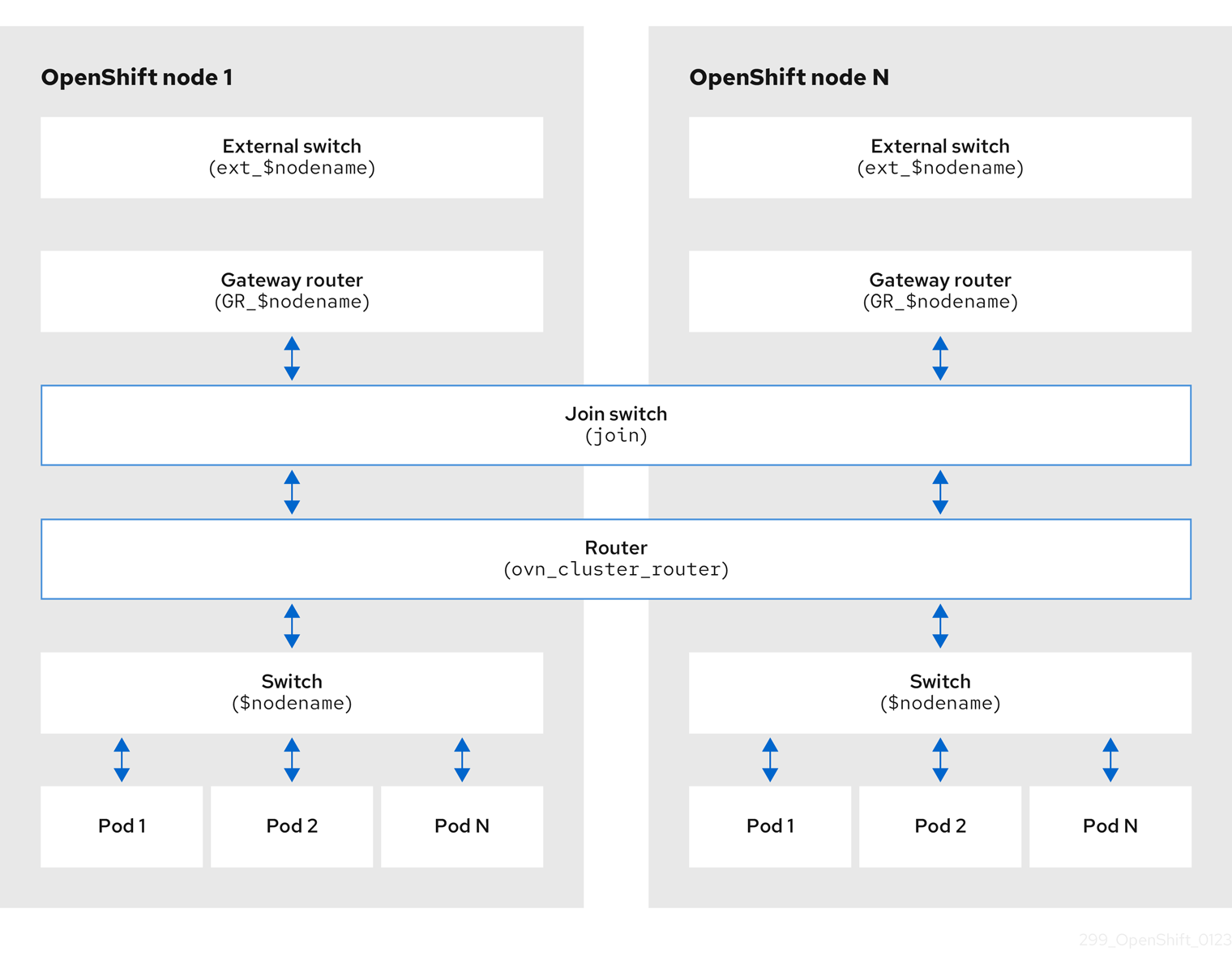
The key components involved in packet processing are:
- Gateway routers
-
Gateway routers sometimes called L3 gateway routers, are typically used between the distributed routers and the physical network. Gateway routers including their logical patch ports are bound to a physical location (not distributed), or chassis. The patch ports on this router are known as l3gateway ports in the ovn-southbound database (
ovn-sbdb). - Distributed logical routers
- Distributed logical routers and the logical switches behind them, to which virtual machines and containers attach, effectively reside on each hypervisor.
- Join local switch
- Join local switches are used to connect the distributed router and gateway routers. It reduces the number of IP addresses needed on the distributed router.
- Logical switches with patch ports
- Logical switches with patch ports are used to virtualize the network stack. They connect remote logical ports through tunnels.
- Logical switches with localnet ports
- Logical switches with localnet ports are used to connect OVN to the physical network. They connect remote logical ports by bridging the packets to directly connected physical L2 segments using localnet ports.
- Patch ports
- Patch ports represent connectivity between logical switches and logical routers and between peer logical routers. A single connection has a pair of patch ports at each such point of connectivity, one on each side.
- l3gateway ports
-
l3gateway ports are the port binding entries in the
ovn-sbdbfor logical patch ports used in the gateway routers. They are called l3gateway ports rather than patch ports just to portray the fact that these ports are bound to a chassis just like the gateway router itself. - localnet ports
-
localnet ports are present on the bridged logical switches that allows a connection to a locally accessible network from each
ovn-controllerinstance. This helps model the direct connectivity to the physical network from the logical switches. A logical switch can only have a single localnet port attached to it.
25.2.7.1. Installing network-tools on local host
Install network-tools on your local host to make a collection of tools available for debugging OpenShift Container Platform cluster network issues.
Procedure
Clone the
network-toolsrepository onto your workstation with the following command:git clone git@github.com:openshift/network-tools.git
$ git clone git@github.com:openshift/network-tools.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change into the directory for the repository you just cloned:
cd network-tools
$ cd network-toolsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: List all available commands:
./debug-scripts/network-tools -h
$ ./debug-scripts/network-tools -hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.2.7.2. Running network-tools
Get information about the logical switches and routers by running network-tools.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. -
You have installed
network-toolson local host.
Procedure
List the routers by running the following command:
./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command ovn-nbctl lr-list
$ ./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command ovn-nbctl lr-listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the localnet ports by running the following command:
./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command \ ovn-sbctl find Port_Binding type=localnet
$ ./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command \ ovn-sbctl find Port_Binding type=localnetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the
l3gatewayports by running the following command:./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command \ ovn-sbctl find Port_Binding type=l3gateway
$ ./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command \ ovn-sbctl find Port_Binding type=l3gatewayCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the patch ports by running the following command:
./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command \ ovn-sbctl find Port_Binding type=patch
$ ./debug-scripts/network-tools ovn-db-run-command \ ovn-sbctl find Port_Binding type=patchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.3. Troubleshooting OVN-Kubernetes
OVN-Kubernetes has many sources of built-in health checks and logs.
25.3.1. Monitoring OVN-Kubernetes health by using readiness probes
The ovnkube-master and ovnkube-node pods have containers configured with readiness probes.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster with
cluster-adminprivileges. -
You have installed
jq.
Procedure
Review the details of the
ovnkube-masterreadiness probe by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master \ -o json | jq '.items[0].spec.containers[] | .name,.readinessProbe'
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master \ -o json | jq '.items[0].spec.containers[] | .name,.readinessProbe'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The readiness probe for the northbound and southbound database containers in the
ovnkube-masterpod checks for the health of the Raft cluster hosting the databases.Review the details of the
ovnkube-nodereadiness probe by running the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master \ -o json | jq '.items[0].spec.containers[] | .name,.readinessProbe'
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master \ -o json | jq '.items[0].spec.containers[] | .name,.readinessProbe'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
ovnkube-nodecontainer in theovnkube-nodepod has a readiness probe to verify the presence of the ovn-kubernetes CNI configuration file, the absence of which would indicate that the pod is not running or is not ready to accept requests to configure pods.Show all events including the probe failures, for the namespace by using the following command:
oc get events -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get events -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Show the events for just this pod:
oc describe pod ovnkube-master-tp2z8 -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc describe pod ovnkube-master-tp2z8 -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Show the messages and statuses from the cluster network operator:
oc get co/network -o json | jq '.status.conditions[]'
$ oc get co/network -o json | jq '.status.conditions[]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Show the
readystatus of each container inovnkube-masterpods by running the following script:for p in $(oc get pods --selector app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ -o jsonpath='{range.items[*]}{" "}{.metadata.name}'); do echo === $p ===; \ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes $p -o json | jq '.status.containerStatuses[] | .name, .ready'; \ done$ for p in $(oc get pods --selector app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ -o jsonpath='{range.items[*]}{" "}{.metadata.name}'); do echo === $p ===; \ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes $p -o json | jq '.status.containerStatuses[] | .name, .ready'; \ doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe expectation is all container statuses are reporting as
true. Failure of a readiness probe sets the status tofalse.
25.3.2. Viewing OVN-Kubernetes alerts in the console
The Alerting UI provides detailed information about alerts and their governing alerting rules and silences.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the cluster as a developer or as a user with view permissions for the project that you are viewing metrics for.
Procedure (UI)
- In the Administrator perspective, select Observe → Alerting. The three main pages in the Alerting UI in this perspective are the Alerts, Silences, and Alerting Rules pages.
- View the rules for OVN-Kubernetes alerts by selecting Observe → Alerting → Alerting Rules.
25.3.3. Viewing OVN-Kubernetes alerts in the CLI
You can get information about alerts and their governing alerting rules and silences from the command line.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
The OpenShift CLI (
oc) installed. -
You have installed
jq.
Procedure
View active or firing alerts by running the following commands.
Set the alert manager route environment variable by running the following command:
ALERT_MANAGER=$(oc get route alertmanager-main -n openshift-monitoring \ -o jsonpath='{@.spec.host}')$ ALERT_MANAGER=$(oc get route alertmanager-main -n openshift-monitoring \ -o jsonpath='{@.spec.host}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Issue a
curlrequest to the alert manager route API with the correct authorization details requesting specific fields by running the following command:curl -s -k -H "Authorization: Bearer \ $(oc create token prometheus-k8s -n openshift-monitoring)" \ https://$ALERT_MANAGER/api/v1/alerts \ | jq '.data[] | "\(.labels.severity) \(.labels.alertname) \(.labels.pod) \(.labels.container) \(.labels.endpoint) \(.labels.instance)"'
$ curl -s -k -H "Authorization: Bearer \ $(oc create token prometheus-k8s -n openshift-monitoring)" \ https://$ALERT_MANAGER/api/v1/alerts \ | jq '.data[] | "\(.labels.severity) \(.labels.alertname) \(.labels.pod) \(.labels.container) \(.labels.endpoint) \(.labels.instance)"'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
View alerting rules by running the following command:
oc -n openshift-monitoring exec -c prometheus prometheus-k8s-0 -- curl -s 'http://localhost:9090/api/v1/rules' | jq '.data.groups[].rules[] | select(((.name|contains("ovn")) or (.name|contains("OVN")) or (.name|contains("Ovn")) or (.name|contains("North")) or (.name|contains("South"))) and .type=="alerting")'$ oc -n openshift-monitoring exec -c prometheus prometheus-k8s-0 -- curl -s 'http://localhost:9090/api/v1/rules' | jq '.data.groups[].rules[] | select(((.name|contains("ovn")) or (.name|contains("OVN")) or (.name|contains("Ovn")) or (.name|contains("North")) or (.name|contains("South"))) and .type=="alerting")'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.3.4. Viewing the OVN-Kubernetes logs using the CLI
You can view the logs for each of the pods in the ovnkube-master and ovnkube-node pods using the OpenShift CLI (oc).
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
Access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have installed
jq.
Procedure
View the log for a specific pod:
oc logs -f <pod_name> -c <container_name> -n <namespace>
$ oc logs -f <pod_name> -c <container_name> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
-f- Optional: Specifies that the output follows what is being written into the logs.
<pod_name>- Specifies the name of the pod.
<container_name>- Optional: Specifies the name of a container. When a pod has more than one container, you must specify the container name.
<namespace>- Specify the namespace the pod is running in.
For example:
oc logs ovnkube-master-7h4q7 -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc logs ovnkube-master-7h4q7 -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc logs -f ovnkube-master-7h4q7 -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -c ovn-dbchecker
$ oc logs -f ovnkube-master-7h4q7 -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -c ovn-dbcheckerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The contents of log files are printed out.
Examine the most recent entries in all the containers in the
ovnkube-masterpods:for p in $(oc get pods --selector app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ -o jsonpath='{range.items[*]}{" "}{.metadata.name}'); \ do echo === $p ===; for container in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes $p \ -o json | jq -r '.status.containerStatuses[] | .name');do echo ---$container---; \ oc logs -c $container $p -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes --tail=5; done; done$ for p in $(oc get pods --selector app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ -o jsonpath='{range.items[*]}{" "}{.metadata.name}'); \ do echo === $p ===; for container in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes $p \ -o json | jq -r '.status.containerStatuses[] | .name');do echo ---$container---; \ oc logs -c $container $p -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes --tail=5; done; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the last 5 lines of every log in every container in an
ovnkube-masterpod using the following command:oc logs -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes --all-containers --tail 5
$ oc logs -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes --all-containers --tail 5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.3.5. Viewing the OVN-Kubernetes logs using the web console
You can view the logs for each of the pods in the ovnkube-master and ovnkube-node pods in the web console.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
- In the OpenShift Container Platform console, navigate to Workloads → Pods or navigate to the pod through the resource you want to investigate.
-
Select the
openshift-ovn-kubernetesproject from the drop-down menu. - Click the name of the pod you want to investigate.
-
Click Logs. By default for the
ovnkube-masterthe logs associated with thenorthdcontainer are displayed. - Use the down-down menu to select logs for each container in turn.
25.3.5.1. Changing the OVN-Kubernetes log levels
The default log level for OVN-Kubernetes is 2. To debug OVN-Kubernetes set the log level to 5. Follow this procedure to increase the log level of the OVN-Kubernetes to help you debug an issue.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have access to the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
Procedure
Run the following command to get detailed information for all pods in the OVN-Kubernetes project:
oc get po -o wide -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get po -o wide -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
ConfigMapfile similar to the following example and use a filename such asenv-overrides.yaml:Example
ConfigMapfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the
ConfigMapfile by using the following command:oc apply -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -f env-overrides.yaml
$ oc apply -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -f env-overrides.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
configmap/env-overrides.yaml created
configmap/env-overrides.yaml createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the
ovnkubepods to apply the new log level by using the following commands:oc delete pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ --field-selector spec.nodeName=ip-10-0-217-114.ec2.internal -l app=ovnkube-node
$ oc delete pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ --field-selector spec.nodeName=ip-10-0-217-114.ec2.internal -l app=ovnkube-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ --field-selector spec.nodeName=ip-10-0-209-180.ec2.internal -l app=ovnkube-node
$ oc delete pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes \ --field-selector spec.nodeName=ip-10-0-209-180.ec2.internal -l app=ovnkube-nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master
$ oc delete pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-masterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.3.6. Checking the OVN-Kubernetes pod network connectivity
The connectivity check controller, in OpenShift Container Platform 4.10 and later, orchestrates connection verification checks in your cluster. These include Kubernetes API, OpenShift API and individual nodes. The results for the connection tests are stored in PodNetworkConnectivity objects in the openshift-network-diagnostics namespace. Connection tests are performed every minute in parallel.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed
jq.
Procedure
To list the current
PodNetworkConnectivityCheckobjects, enter the following command:oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics
$ oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnosticsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the most recent success for each connection object by using the following command:
oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics \ -o json | jq '.items[]| .spec.targetEndpoint,.status.successes[0]'
$ oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics \ -o json | jq '.items[]| .spec.targetEndpoint,.status.successes[0]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the most recent failures for each connection object by using the following command:
oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics \ -o json | jq '.items[]| .spec.targetEndpoint,.status.failures[0]'
$ oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics \ -o json | jq '.items[]| .spec.targetEndpoint,.status.failures[0]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the most recent outages for each connection object by using the following command:
oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics \ -o json | jq '.items[]| .spec.targetEndpoint,.status.outages[0]'
$ oc get podnetworkconnectivitychecks -n openshift-network-diagnostics \ -o json | jq '.items[]| .spec.targetEndpoint,.status.outages[0]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The connectivity check controller also logs metrics from these checks into Prometheus.
View all the metrics by running the following command:
oc exec prometheus-k8s-0 -n openshift-monitoring -- \ promtool query instant http://localhost:9090 \ '{component="openshift-network-diagnostics"}'$ oc exec prometheus-k8s-0 -n openshift-monitoring -- \ promtool query instant http://localhost:9090 \ '{component="openshift-network-diagnostics"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the latency between the source pod and the openshift api service for the last 5 minutes:
oc exec prometheus-k8s-0 -n openshift-monitoring -- \ promtool query instant http://localhost:9090 \ '{component="openshift-network-diagnostics"}'$ oc exec prometheus-k8s-0 -n openshift-monitoring -- \ promtool query instant http://localhost:9090 \ '{component="openshift-network-diagnostics"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.4. Tracing Openflow with ovnkube-trace
OVN and OVS traffic flows can be simulated in a single utility called ovnkube-trace. The ovnkube-trace utility runs ovn-trace, ovs-appctl ofproto/trace and ovn-detrace and correlates that information in a single output.
You can execute the ovnkube-trace binary from a dedicated container. For releases after OpenShift Container Platform 4.7, you can also copy the binary to a local host and execute it from that host.
The binaries in the Quay images do not currently work for Dual IP stack or IPv6 only environments. For those environments, you must build from source.
25.4.1. Installing the ovnkube-trace on local host
The ovnkube-trace tool traces packet simulations for arbitrary UDP or TCP traffic between points in an OVN-Kubernetes driven OpenShift Container Platform cluster. Copy the ovnkube-trace binary to your local host making it available to run against the cluster.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a pod variable by using the following command:
POD=$(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master -o name | head -1 | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}')$ POD=$(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-master -o name | head -1 | awk -F '/' '{print $NF}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command on your local host to copy the binary from the
ovnkube-masterpods:oc cp -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes $POD:/usr/bin/ovnkube-trace ovnkube-trace
$ oc cp -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes $POD:/usr/bin/ovnkube-trace ovnkube-traceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make
ovnkube-traceexecutable by running the following command:chmod +x ovnkube-trace
$ chmod +x ovnkube-traceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the options available with
ovnkube-traceby running the following command:./ovnkube-trace -help
$ ./ovnkube-trace -helpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command-line arguments supported are familiar Kubernetes constructs, such as namespaces, pods, services so you do not need to find the MAC address, the IP address of the destination nodes, or the ICMP type.
The log levels are:
- 0 (minimal output)
- 2 (more verbose output showing results of trace commands)
- 5 (debug output)
25.4.2. Running ovnkube-trace
Run ovn-trace to simulate packet forwarding within an OVN logical network.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. -
You have installed
ovnkube-traceon local host
Example: Testing that DNS resolution works from a deployed pod
This example illustrates how to test the DNS resolution from a deployed pod to the core DNS pod that runs in the cluster.
Procedure
Start a web service in the default namespace by entering the following command:
oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the pods running in the
openshift-dnsnamespace:oc get pods -n openshift-dns
oc get pods -n openshift-dnsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following
ovn-kube-tracecommand to verify DNS resolution is working:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The ouput indicates success from the deployed pod to the DNS port and also indicates that it is successful going back in the other direction. So you know bi-directional traffic is supported on UDP port 53 if my web pod wants to do dns resolution from core DNS.
If for example that did not work and you wanted to get the ovn-trace, the ovs-appctl ofproto/trace and ovn-detrace, and more debug type information increase the log level to 2 and run the command again as follows:
The output from this increased log level is too much to list here. In a failure situation the output of this command shows which flow is dropping that traffic. For example an egress or ingress network policy may be configured on the cluster that does not allow that traffic.
Example: Verifying by using debug output a configured default deny
This example illustrates how to identify by using the debug output that an ingress default deny policy blocks traffic.
Procedure
Create the following YAML that defines a
deny-by-defaultpolicy to deny ingress from all pods in all namespaces. Save the YAML in thedeny-by-default.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f deny-by-default.yaml
$ oc apply -f deny-by-default.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-by-default createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start a web service in the
defaultnamespace by entering the following command:oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80
$ oc run web --namespace=default --image=nginx --labels="app=web" --expose --port=80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to create the
prodnamespace:oc create namespace prod
$ oc create namespace prodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to label the
prodnamespace:oc label namespace/prod purpose=production
$ oc label namespace/prod purpose=productionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to deploy an
alpineimage in theprodnamespace and start a shell:oc run test-6459 --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- sh
$ oc run test-6459 --namespace=prod --rm -i -t --image=alpine -- shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Open another terminal session.
In this new terminal session run
ovn-traceto verify the failure in communication between the source podtest-6459running in namespaceprodand destination pod running in thedefaultnamespace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
I0116 14:20:47.380775 50822 ovs.go:90] Maximum command line arguments set to: 191102 ovn-trace source pod to destination pod indicates failure from test-6459 to web
I0116 14:20:47.380775 50822 ovs.go:90] Maximum command line arguments set to: 191102 ovn-trace source pod to destination pod indicates failure from test-6459 to webCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Increase the log level to 2 to expose the reason for the failure by running the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Ingress traffic is blocked due to the default deny policy being in place
Create a policy that allows traffic from all pods in a particular namespaces with a label
purpose=production. Save the YAML in theweb-allow-prod.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy by entering the following command:
oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yaml
$ oc apply -f web-allow-prod.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run
ovnkube-traceto verify that traffic is now allowed by entering the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the open shell run the following command:
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.default
wget -qO- --timeout=2 http://web.defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.5. Migrating from the OpenShift SDN network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can migrate to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin from the OpenShift SDN network plugin.
You can use the offline migration method for migrating from the OpenShift SDN network plugin to the OVN-Kubernetes plugin. The offline migration method is a manual process that includes some downtime.
25.5.1. Migration to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
Migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is a manual process that includes some downtime during which your cluster is unreachable.
Before you migrate your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to use the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, update your cluster to the latest z-stream release so that all the latest bug fixes apply to your cluster.
Although a rollback procedure is provided, the migration is intended to be a one-way process.
A migration to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is supported on the following platforms:
- Bare metal hardware
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud
- IBM Cloud®
- Microsoft Azure
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)
- Red Hat Virtualization (RHV)
- {vmw-first}
Migrating to or from the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is not supported for managed OpenShift cloud services such as Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated, Azure Red Hat OpenShift(ARO), and Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA).
Migrating from OpenShift SDN network plugin to OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is not supported on Nutanix.
25.5.1.1. Considerations for migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
If you have more than 150 nodes in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, then open a support case for consultation on your migration to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
The subnets assigned to nodes and the IP addresses assigned to individual pods are not preserved during the migration.
While the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin implements many of the capabilities present in the OpenShift SDN network plugin, the configuration is not the same.
If your cluster uses any of the following OpenShift SDN network plugin capabilities, you must manually configure the same capability in the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin:
- Namespace isolation
- Egress router pods
-
If your cluster or surrounding network uses any part of the
100.64.0.0/16address range, you must choose another unused IP range by specifying thev4InternalSubnetspec under thespec.defaultNetwork.ovnKubernetesConfigobject definition. OVN-Kubernetes uses the IP range100.64.0.0/16internally by default. -
If your
openshift-sdncluster with Precision Time Protocol (PTP) uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for hardware time stamping and you migrate to the OVN-Kubernetes plugin, the hardware time stamping cannot be applied to primary interface devices, such as an Open vSwitch (OVS) bridge. As a result, UDP version 4 configurations cannot work with abr-exinterface.
The following sections highlight the differences in configuration between the aforementioned capabilities in OVN-Kubernetes and OpenShift SDN network plugins.
Primary network interface
The OpenShift SDN plugin allows application of the NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy (NNCP) custom resource (CR) to the primary interface on a node. The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin does not have this capability.
If you have an NNCP applied to the primary interface, you must delete the NNCP before migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. Deleting the NNCP does not remove the configuration from the primary interface, but with OVN-Kubernetes, the Kubernetes NMState cannot manage this configuration. Instead, the configure-ovs.sh shell script manages the primary interface and the configuration attached to this interface.
Namespace isolation
OVN-Kubernetes supports only the network policy isolation mode.
For a cluster using OpenShift SDN that is configured in either the multitenant or subnet isolation mode, you can still migrate to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. Note that after the migration operation, multitenant isolation mode is dropped, so you must manually configure network policies to achieve the same level of project-level isolation for pods and services.
Egress IP addresses
OpenShift SDN supports two different Egress IP modes:
- In the automatically assigned approach, an egress IP address range is assigned to a node.
- In the manually assigned approach, a list of one or more egress IP addresses is assigned to a node.
The migration process supports migrating Egress IP configurations that use the automatically assigned mode.
The differences in configuring an egress IP address between OVN-Kubernetes and OpenShift SDN is described in the following table:
| OVN-Kubernetes | OpenShift SDN |
|---|---|
|
|
For more information on using egress IP addresses in OVN-Kubernetes, see "Configuring an egress IP address".
Egress network policies
The difference in configuring an egress network policy, also known as an egress firewall, between OVN-Kubernetes and OpenShift SDN is described in the following table:
| OVN-Kubernetes | OpenShift SDN |
|---|---|
|
|
Because the name of an EgressFirewall object can only be set to default, after the migration all migrated EgressNetworkPolicy objects are named default, regardless of what the name was under OpenShift SDN.
If you subsequently rollback to OpenShift SDN, all EgressNetworkPolicy objects are named default as the prior name is lost.
For more information on using an egress firewall in OVN-Kubernetes, see "Configuring an egress firewall for a project".
Egress router pods
OVN-Kubernetes supports egress router pods in redirect mode. OVN-Kubernetes does not support egress router pods in HTTP proxy mode or DNS proxy mode.
When you deploy an egress router with the Cluster Network Operator, you cannot specify a node selector to control which node is used to host the egress router pod.
Multicast
The difference between enabling multicast traffic on OVN-Kubernetes and OpenShift SDN is described in the following table:
| OVN-Kubernetes | OpenShift SDN |
|---|---|
|
|
For more information on using multicast in OVN-Kubernetes, see "Enabling multicast for a project".
Network policies
OVN-Kubernetes fully supports the Kubernetes NetworkPolicy API in the networking.k8s.io/v1 API group. No changes are necessary in your network policies when migrating from OpenShift SDN.
25.5.1.2. How the migration process works
The following table summarizes the migration process by segmenting between the user-initiated steps in the process and the actions that the migration performs in response.
| User-initiated steps | Migration activity |
|---|---|
|
Set the |
|
|
Update the |
|
| Reboot each node in the cluster. |
|
If a rollback to OpenShift SDN is required, the following table describes the process.
You must wait until the migration process from OpenShift SDN to OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is successful before initiating a rollback.
| User-initiated steps | Migration activity |
|---|---|
| Suspend the MCO to ensure that it does not interrupt the migration. | The MCO stops. |
|
Set the |
|
|
Update the |
|
| Reboot each node in the cluster. |
|
| Enable the MCO after all nodes in the cluster reboot. |
|
25.5.1.3. Using an Ansible playbook to migrate to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can use an Ansible collection, network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk, to migrate from the OpenShift SDN Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin to the OVN-Kubernetes plugin for your cluster. The Ansible collection includes the following playbooks:
-
playbooks/playbook-migration.yml: Includes playbooks that execute in a sequence where each playbook represents a step in the migration process. -
playbooks/playbook-rollback.yml: Includes playbooks that execute in a sequence where each playbook represents a step in the rollback process.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the
python3package, minimum version 3.10. -
You installed the
jmespathandjqpackages. - You logged in to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and opened the Ansible Automation Platform web console.
-
You created a security group rule that allows User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets on port
6081for all nodes on all cloud platforms. If you do not do this task, your cluster might fail to schedule pods. Check if your cluster uses static routes or routing policies in the host network.
-
If true, a later procedure step requires that you set the
routingViaHostparameter totrueand theipForwardingparameter toGlobalin thegatewayConfigsection of theplaybooks/playbook-migration.ymlfile.
-
If true, a later procedure step requires that you set the
-
If the OpenShift-SDN plugin uses the
100.64.0.0/16and100.88.0.0/16address ranges, you patched the address ranges. For more information, see "Patching OVN-Kubernetes address ranges" in the Additional resources section.
Procedure
Install the
ansible-corepackage, minimum version 2.15. The following example command shows how to install theansible-corepackage on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL):sudo dnf install -y ansible-core
$ sudo dnf install -y ansible-coreCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an
ansible.cfgfile and add information similar to the following example to the file. Ensure that file exists in the same directory as where theansible-galaxycommands and the playbooks run.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the Ansible Automation Platform web console, go to the Connect to Hub page and complete the following steps:
- In the Offline token section of the page, click the Load token button.
- After the token loads, click the Copy to clipboard icon.
-
Open the
ansible.cfgfile and paste the API token in thetoken=parameter. The API token is required for authenticating against the server URL specified in theansible.cfgfile.
Install the
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkAnsible collection by entering the followingansible-galaxycommand:ansible-galaxy collection install network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk
$ ansible-galaxy collection install network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkAnsible collection is installed on your system:ansible-galaxy collection list | grep network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk
$ ansible-galaxy collection list | grep network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk 1.0.2
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk 1.0.2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkAnsible collection is saved in the default path of~/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/network/offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk/.Configure migration features in the
playbooks/playbook-migration.ymlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow migration_interface_name-
If you use an
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy(NNCP) resource on a primary interface, specify the interface name in themigration-playbook.ymlfile so that the NNCP resource gets deleted on the primary interface during the migration process. migration_disable_auto_migration-
Disables the auto-migration of OpenShift SDN CNI plug-in features to the OVN-Kubernetes plugin. If you disable auto-migration of features, you must also set the
migration_egress_ip,migration_egress_firewall, andmigration_multicastparameters tofalse. If you need to enable auto-migration of features, set the parameter tofalse. migration_routing_via_host-
Set to
trueto configure local gateway mode orfalseto configure shared gateway mode for nodes in your cluster. The default value isfalse. In local gateway mode, traffic is routed through the host network stack. In shared gateway mode, traffic is not routed through the host network stack. migration_ip_forwarding-
If you configured local gateway mode, set IP forwarding to
Globalif you need the host network of the node to act as a router for traffic not related to OVN-Kubernetes. migration_cidr-
Specifies a Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) IP address block for your cluster. You cannot use any CIDR block that overlaps the
100.64.0.0/16CIDR block, because the OVN-Kubernetes network provider uses this block internally. migration_prefix- Ensure that you specify a prefix value, which is the slice of the CIDR block apportioned to each node in your cluster.
migration_mtu- Optional parameter that sets a specific maximum transmission unit (MTU) to your cluster network after the migration process.
migration_geneve_port-
Optional parameter that sets a Geneve port for OVN-Kubernetes. The default port is
6081. migration_ipv4_subnet-
Optional parameter that sets an IPv4 address range for internal use by OVN-Kubernetes. The default value for the parameter is
100.64.0.0/16.
To run the
playbooks/playbook-migration.ymlfile, enter the following command:ansible-playbook -v playbooks/playbook-migration.yml
$ ansible-playbook -v playbooks/playbook-migration.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.5.2. Migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can change the network plugin for your cluster to OVN-Kubernetes. During the migration, you must reboot every node in your cluster.
While performing the migration, your cluster is unavailable and workloads might be interrupted. Perform the migration only when an interruption in service is acceptable.
Prerequisites
- You have a cluster configured with the OpenShift SDN CNI network plugin in the network policy isolation mode.
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - You have a recent backup of the etcd database.
- You can manually reboot each node.
- You checked that your cluster is in a known good state without any errors.
-
You created a security group rule that allows User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets on port
6081for all nodes on all cloud platforms.
Procedure
To backup the configuration for the cluster network, enter the following command:
oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster -o yaml > cluster-openshift-sdn.yaml
$ oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster -o yaml > cluster-openshift-sdn.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
OVN_SDN_MIGRATION_TIMEOUTenvironment variable is set and is equal to0sby running the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the configuration from the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration object by running the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{"spec":{"migration":null}}'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{"spec":{"migration":null}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy(NNCP) custom resource (CR) that defines the primary network interface for the OpenShift SDN network plugin by completing the following steps:Check that the existing NNCP CR bonded the primary interface to your cluster by entering the following command:
oc get nncp
$ oc get nncpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS REASON bondmaster0 Available SuccessfullyConfigured
NAME STATUS REASON bondmaster0 Available SuccessfullyConfiguredCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Network Manager stores the connection profile for the bonded primary interface in the
/etc/NetworkManager/system-connectionssystem path.Remove the NNCP from your cluster:
oc delete nncp <nncp_manifest_filename>
$ oc delete nncp <nncp_manifest_filename>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To prepare all the nodes for the migration, set the
migrationfield on the CNO configuration object by running the following command:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis step does not deploy OVN-Kubernetes immediately. Instead, specifying the
migrationfield triggers the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to apply new machine configs to all the nodes in the cluster in preparation for the OVN-Kubernetes deployment.Check that the reboot is finished by running the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that all cluster Operators are available by running the following command:
oc get co
$ oc get coCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively: You can disable automatic migration of several OpenShift SDN capabilities to the OVN-Kubernetes equivalents:
- Egress IPs
- Egress firewall
- Multicast
To disable automatic migration of the configuration for any of the previously noted OpenShift SDN features, specify the following keys:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
bool: Specifies whether to enable migration of the feature. The default istrue.
Optional: You can customize the following settings for OVN-Kubernetes to meet your network infrastructure requirements:
Maximum transmission unit (MTU). Consider the following before customizing the MTU for this optional step:
- If you use the default MTU, and you want to keep the default MTU during migration, this step can be ignored.
- If you used a custom MTU, and you want to keep the custom MTU during migration, you must declare the custom MTU value in this step.
This step does not work if you want to change the MTU value during migration. Instead, you must first follow the instructions for "Changing the cluster MTU". You can then keep the custom MTU value by performing this procedure and declaring the custom MTU value in this step.
NoteOpenShift-SDN and OVN-Kubernetes have different overlay overhead. MTU values should be selected by following the guidelines found on the "MTU value selection" page.
- Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) overlay network port
- OVN-Kubernetes IPv4 internal subnet
To customize either of the previously noted settings, enter and customize the following command. If you do not need to change the default value, omit the key from the patch.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
mtu-
The MTU for the Geneve overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically, but if the nodes in your cluster do not all use the same MTU, then you must set this explicitly to
100less than the smallest node MTU value. port-
The UDP port for the Geneve overlay network. If a value is not specified, the default is
6081. The port cannot be the same as the VXLAN port that is used by OpenShift SDN. The default value for the VXLAN port is4789. ipv4_subnet-
An IPv4 address range for internal use by OVN-Kubernetes. You must ensure that the IP address range does not overlap with any other subnet used by your OpenShift Container Platform installation. The IP address range must be larger than the maximum number of nodes that can be added to the cluster. The default value is
100.64.0.0/16.
Example patch command to update
mtufieldCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow As the MCO updates machines in each machine config pool, it reboots each node one by one. You must wait until all the nodes are updated. Check the machine config pool status by entering the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successfully updated node has the following status:
UPDATED=true,UPDATING=false,DEGRADED=false.NoteBy default, the MCO updates one machine per pool at a time, causing the total time the migration takes to increase with the size of the cluster.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the following statements are true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStart
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<config_name>is the name of the machine config from themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.The machine config must include the following update to the systemd configuration:
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/configure-ovs.sh OVNKubernetes
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/configure-ovs.sh OVNKubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If a node is stuck in the
NotReadystate, investigate the machine config daemon pod logs and resolve any errors.To list the pods, enter the following command:
oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The names for the config daemon pods are in the following format:
machine-config-daemon-<seq>. The<seq>value is a random five character alphanumeric sequence.Display the pod log for the first machine config daemon pod shown in the previous output by enter the following command:
oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
podis the name of a machine config daemon pod.- Resolve any errors in the logs shown by the output from the previous command.
To start the migration, configure the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin by using one of the following commands:
To specify the network provider without changing the cluster network IP address block, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='merge' --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } }'$ oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='merge' --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To specify a different cluster network IP address block, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
cidris a CIDR block andprefixis the slice of the CIDR block apportioned to each node in your cluster. You cannot use any CIDR block that overlaps with the100.64.0.0/16CIDR block because the OVN-Kubernetes network provider uses this block internally.ImportantYou cannot change the service network address block during the migration.
Verify that the Multus daemon set rollout is complete before continuing with subsequent steps:
oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multus
$ oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the Multus pods is in the form of
multus-<xxxxx>where<xxxxx>is a random sequence of letters. It might take several moments for the pods to restart.Example output
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled out
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To complete changing the network plugin, reboot each node in your cluster. You can reboot the nodes in your cluster with either of the following approaches:
ImportantThe following scripts reboot all of the nodes in the cluster at the same time. This can cause your cluster to be unstable. Another option is to reboot your nodes manually one at a time. Rebooting nodes one-by-one causes considerable downtime in a cluster with many nodes.
Cluster Operators will not work correctly before you reboot the nodes.
With the
oc rshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow With the
sshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following. The script assumes that you have configured sudo to not prompt for a password.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Confirm that the migration succeeded:
To confirm that the network plugin is OVN-Kubernetes, enter the following command. The value of
status.networkTypemust beOVNKubernetes.oc get network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'$ oc get network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the cluster nodes are in the
Readystate, enter the following command:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that your pods are not in an error state, enter the following command:
oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'$ oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If pods on a node are in an error state, reboot that node.
To confirm that all of the cluster Operators are not in an abnormal state, enter the following command:
oc get co
$ oc get coCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The status of every cluster Operator must be the following:
AVAILABLE="True",PROGRESSING="False",DEGRADED="False". If a cluster Operator is not available or degraded, check the logs for the cluster Operator for more information.
Complete the following steps only if the migration succeeds and your cluster is in a good state:
To remove the migration configuration from the CNO configuration object, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove custom configuration for the OpenShift SDN network provider, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "openshiftSDNConfig": null } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "openshiftSDNConfig": null } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the OpenShift SDN network provider namespace, enter the following command:
oc delete namespace openshift-sdn
$ oc delete namespace openshift-sdnCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After a successful migration operation, remove the
network.openshift.io/network-type-migration-annotation from thenetwork.configcustom resource by entering the following command:oc annotate network.config cluster network.openshift.io/network-type-migration-
$ oc annotate network.config cluster network.openshift.io/network-type-migration-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Next steps
- Optional: After cluster migration, you can convert your IPv4 single-stack cluster to a dual-network cluster network that supports IPv4 and IPv6 address families. For more information, see "Converting to IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack networking".
25.5.4. Understanding changes to external IP behavior in OVN-Kubernetes
When migrating from OpenShift SDN to OVN-Kubernetes (OVN-K), services that use external IPs might become inaccessible across namespaces due to network policy enforcement.
In OpenShift SDN, external IPs were accessible across namespaces by default. However, in OVN-K, network policies strictly enforce multitenant isolation, preventing access to services exposed via external IPs from other namespaces.
To ensure access, consider the following alternatives:
- Use an ingress or route: Instead of exposing services by using external IPs, configure an ingress or route to allow external access while maintaining security controls.
-
Adjust the
NetworkPolicycustom resource (CR): Modify aNetworkPolicyCR to explicitly allow access from required namespaces and ensure that traffic is allowed to the designated service ports. Without explicitly allowing traffic to the required ports, access might still be blocked, even if the namespace is allowed. -
Use a
LoadBalancerservice: If applicable, deploy aLoadBalancerservice instead of relying on external IPs. For more information about configuring see "NetworkPolicy and external IPs in OVN-Kubernetes".
25.6. Rolling back to the OpenShift SDN network provider
As a cluster administrator, you can rollback to the OpenShift SDN from the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin only after the migration to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is completed and successful.
25.6.1. Migrating to the OpenShift SDN network plugin
Cluster administrators can roll back to the OpenShift SDN Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin by using the offline migration method. During the migration you must manually reboot every node in your cluster. With the offline migration method, there is some downtime, during which your cluster is unreachable.
You must wait until the migration process from OpenShift SDN to OVN-Kubernetes network plugin is successful before initiating a rollback.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - A cluster installed on infrastructure configured with the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
- A recent backup of the etcd database is available.
- A reboot can be triggered manually for each node.
- The cluster is in a known good state, without any errors.
Procedure
Stop all of the machine configuration pools managed by the Machine Config Operator (MCO):
Stop the
masterconfiguration pool by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": true } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": true } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop the
workermachine configuration pool by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec":{ "paused": true } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec":{ "paused": true } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To prepare for the migration, set the migration field to
nullby entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the migration status is empty for the
Network.config.openshift.ioobject by entering the following command in your CLI. Empty command output indicates that the object is not in a migration operation.oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration}'$ oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the patch to the
Network.operator.openshift.ioobject to set the network plugin back to OpenShift SDN by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantIf you applied the patch to the
Network.config.openshift.ioobject before the patch operation finalizes on theNetwork.operator.openshift.ioobject, the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) enters into a degradation state and this causes a slight delay until the CNO recovers from the degraded state.Confirm that the migration status of the network plugin for the
Network.config.openshift.io clusterobject isOpenShiftSDNby entering the following command in your CLI:oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration.networkType}'$ oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration.networkType}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the patch to the
Network.config.openshift.ioobject to set the network plugin back to OpenShift SDN by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } }'$ oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Disable automatic migration of several OVN-Kubernetes capabilities to the OpenShift SDN equivalents:
- Egress IPs
- Egress firewall
- Multicast
To disable automatic migration of the configuration for any of the previously noted OpenShift SDN features, specify the following keys:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
bool: Specifies whether to enable migration of the feature. The default istrue.Optional: You can customize the following settings for OpenShift SDN to meet your network infrastructure requirements:
- Maximum transmission unit (MTU)
- VXLAN port
To customize either or both of the previously noted settings, customize and enter the following command in your CLI. If you do not need to change the default value, omit the key from the patch.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow mtu-
The MTU for the VXLAN overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically, but if the nodes in your cluster do not all use the same MTU, then you must set this explicitly to
50less than the smallest node MTU value. port-
The UDP port for the VXLAN overlay network. If a value is not specified, the default is
4789. The port cannot be the same as the Geneve port that is used by OVN-Kubernetes. The default value for the Geneve port is6081.
Example patch command
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reboot each node in your cluster. You can reboot the nodes in your cluster with either of the following approaches:
With the
oc rshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow With the
sshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following. The script assumes that you have configured sudo to not prompt for a password.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Wait until the Multus daemon set rollout completes. Run the following command to see your rollout status:
oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multus
$ oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the Multus pods is in the form of
multus-<xxxxx>where<xxxxx>is a random sequence of letters. It might take several moments for the pods to restart.Example output
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled out
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the nodes in your cluster have rebooted and the multus pods are rolled out, start all of the machine configuration pools by running the following commands::
Start the master configuration pool:
oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the worker configuration pool:
oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
As the MCO updates machines in each config pool, it reboots each node.
By default the MCO updates a single machine per pool at a time, so the time that the migration requires to complete grows with the size of the cluster.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the following statements are true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<config_name>is the name of the machine config from themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.
Confirm that the migration succeeded:
To confirm that the network plugin is OpenShift SDN, enter the following command in your CLI. The value of
status.networkTypemust beOpenShiftSDN.oc get Network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'$ oc get Network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the cluster nodes are in the
Readystate, enter the following command in your CLI:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If a node is stuck in the
NotReadystate, investigate the machine config daemon pod logs and resolve any errors.To list the pods, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The names for the config daemon pods are in the following format:
machine-config-daemon-<seq>. The<seq>value is a random five character alphanumeric sequence.To display the pod log for each machine config daemon pod shown in the previous output, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
podis the name of a machine config daemon pod.- Resolve any errors in the logs shown by the output from the previous command.
To confirm that your pods are not in an error state, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'$ oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If pods on a node are in an error state, reboot that node.
Complete the following steps only if the migration succeeds and your cluster is in a good state:
To remove the migration configuration from the Cluster Network Operator configuration object, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the OVN-Kubernetes configuration, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "ovnKubernetesConfig":null } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "ovnKubernetesConfig":null } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the OVN-Kubernetes network provider namespace, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc delete namespace openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc delete namespace openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.6.2. Using an Ansible playbook to roll back to the OpenShift SDN network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can use the playbooks/playbook-rollback.yml from the network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk Ansible collection to roll back from the OVN-Kubernetes plugin to the OpenShift SDN Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the
python3package, minimum version 3.10. -
You installed the
jmespathandjqpackages. - You logged in to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and opened the Ansible Automation Platform web console.
-
You created a security group rule that allows User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets on port
6081for all nodes on all cloud platforms. If you do not do this task, your cluster might fail to schedule pods.
Procedure
Install the
ansible-corepackage, minimum version 2.15. The following example command shows how to install theansible-corepackage on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL):sudo dnf install -y ansible-core
$ sudo dnf install -y ansible-coreCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an
ansible.cfgfile and add information similar to the following example to the file. Ensure that file exists in the same directory as where theansible-galaxycommands and the playbooks run.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the Ansible Automation Platform web console, go to the Connect to Hub page and complete the following steps:
- In the Offline token section of the page, click the Load token button.
- After the token loads, click the Copy to clipboard icon.
-
Open the
ansible.cfgfile and paste the API token in thetoken=parameter. The API token is required for authenticating against the server URL specified in theansible.cfgfile.
Install the
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkAnsible collection by entering the followingansible-galaxycommand:ansible-galaxy collection install network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk
$ ansible-galaxy collection install network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkAnsible collection is installed on your system:ansible-galaxy collection list | grep network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk
$ ansible-galaxy collection list | grep network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk 1.0.2
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk 1.0.2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
network.offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnkAnsible collection is saved in the default path of~/.ansible/collections/ansible_collections/network/offline_migration_sdn_to_ovnk/.Configure rollback features in the
playbooks/playbook-migration.ymlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow rollback_disable_auto_migration-
Disables the auto-migration of OVN-Kubernetes plug-in features to the OpenShift SDN CNI plug-in. If you disable auto-migration of features, you must also set the
rollback_egress_ip,rollback_egress_firewall, androllback_multicastparameters tofalse. If you need to enable auto-migration of features, set the parameter tofalse. rollback_mtu- Optional parameter that sets a specific maximum transmission unit (MTU) to your cluster network after the migration process.
rollback_vxlanPort-
Optional parameter that sets a VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) port for use by OpenShift SDN CNI plug-in. The default value for the parameter is
4790.
To run the
playbooks/playbook-rollback.ymlfile, enter the following command:ansible-playbook -v playbooks/playbook-rollback.yml
$ ansible-playbook -v playbooks/playbook-rollback.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.7. Migrating from the Kuryr network plugin to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
Migration from Kuryr to OVN-Kubernetes is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
As the administrator of a cluster that runs on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), you can migrate to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin from the Kuryr SDN network plugin.
To learn more about OVN-Kubernetes, read About the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
25.7.1. Migration to the OVN-Kubernetes network provider
You can manually migrate a cluster that runs on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) to the OVN-Kubernetes network provider.
Migration to OVN-Kubernetes is a one-way process. During migration, your cluster will be unreachable for a brief time.
25.7.1.1. Considerations when migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network provider
Kubernetes namespaces are kept by Kuryr in separate RHOSP networking service (Neutron) subnets. Those subnets and the IP addresses that are assigned to individual pods are not preserved during the migration.
25.7.1.2. How the migration process works
The following table summarizes the migration process by relating the steps that you perform with the actions that your cluster and Operators take.
| User-initiated steps | Migration activity |
|---|---|
|
Set the |
|
|
Update the |
|
| Reboot each node in the cluster. |
|
| Clean up remaining resources Kuryr controlled. |
|
25.7.2. Migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can change the network plugin for your cluster to OVN-Kubernetes.
During the migration, you must reboot every node in your cluster. Your cluster is unavailable and workloads might be interrupted. Perform the migration only if an interruption in service is acceptable.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - You have a recent backup of the etcd database is available.
- You can manually reboot each node.
- The cluster you plan to migrate is in a known good state, without any errors.
- You installed the Python interpreter.
-
You installed the
openstacksdkpython package. -
You installed the
openstackCLI tool. - You have access to the underlying RHOSP cloud.
Procedure
Back up the configuration for the cluster network by running the following command:
oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster -o yaml > cluster-kuryr.yaml
$ oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster -o yaml > cluster-kuryr.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To set the
CLUSTERIDvariable, run the following command:CLUSTERID=$(oc get infrastructure.config.openshift.io cluster -o=jsonpath='{.status.infrastructureName}')$ CLUSTERID=$(oc get infrastructure.config.openshift.io cluster -o=jsonpath='{.status.infrastructureName}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To prepare all the nodes for the migration, set the
migrationfield on the Cluster Network Operator configuration object by running the following command:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis step does not deploy OVN-Kubernetes immediately. Specifying the
migrationfield triggers the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to apply new machine configs to all the nodes in the cluster. This prepares the cluster for the OVN-Kubernetes deployment.Optional: Customize the following settings for OVN-Kubernetes for your network infrastructure requirements:
- Maximum transmission unit (MTU)
- Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) overlay network port
- OVN-Kubernetes IPv4 internal subnet
- OVN-Kubernetes IPv6 internal subnet
To customize these settings, enter and customize the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
mtu-
Specifies the MTU for the Geneve overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically, but if the nodes in your cluster do not all use the same MTU, then you must set this explicitly to
100less than the smallest node MTU value. port-
Specifies the UDP port for the Geneve overlay network. If a value is not specified, the default is
6081. The port cannot be the same as the VXLAN port that is used by Kuryr. The default value for the VXLAN port is4789. ipv4_subnet-
Specifies an IPv4 address range for internal use by OVN-Kubernetes. You must ensure that the IP address range does not overlap with any other subnet used by your OpenShift Container Platform installation. The IP address range must be larger than the maximum number of nodes that can be added to the cluster. The default value is
100.64.0.0/16. ipv6_subnet-
Specifies an IPv6 address range for internal use by OVN-Kubernetes. You must ensure that the IP address range does not overlap with any other subnet used by your OpenShift Container Platform installation. The IP address range must be larger than the maximum number of nodes that can be added to the cluster. The default value is
fd98::/48.
If you do not need to change the default value, omit the key from the patch.
Example patch command to update
mtufieldCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the machine config pool status by entering the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow While the MCO updates machines in each machine config pool, it reboots each node one by one. You must wait until all the nodes are updated before continuing.
A successfully updated node has the following status:
UPDATED=true,UPDATING=false,DEGRADED=false.NoteBy default, the MCO updates one machine per pool at a time. Large clusters take more time to migrate than small clusters.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b1 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b2 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the output from the previous step. The following statements must be true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStart
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- <config_name>
Specifies the name of the machine config from the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.The machine config must include the following update to the systemd configuration:
Example output
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/configure-ovs.sh OVNKubernetes
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/configure-ovs.sh OVNKubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If a node is stuck in the
NotReadystate, investigate the machine config daemon pod logs and resolve any errors:To list the pods, enter the following command:
oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The names for the config daemon pods are in the following format:
machine-config-daemon-<seq>. The<seq>value is a random five character alphanumeric sequence.Display the pod log for the first machine config daemon pod shown in the previous output by enter the following command:
oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- <pod>
- Specifies the name of a machine config daemon pod.
- Resolve any errors in the logs shown by the output from the previous command.
To start the migration, configure the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin by using one of the following commands:
To specify the network provider without changing the cluster network IP address block, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='merge' --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } }'$ oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='merge' --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To specify a different cluster network IP address block, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
- <cidr>
- Specifies a CIDR block.
- <prefix>
Specifies a slice of the CIDR block that is apportioned to each node in your cluster.
ImportantYou cannot change the service network address block during the migration.
You cannot use any CIDR block that overlaps with the
100.64.0.0/16CIDR block because the OVN-Kubernetes network provider uses this block internally.
Verify that the Multus daemon set rollout is complete by entering the following command:
oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multus
$ oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the Multus pods is in the form of
multus-<xxxxx>, where<xxxxx>is a random sequence of letters. It might take several moments for the pods to restart.Example output
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled out
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To complete the migration, reboot each node in your cluster. For example, you can use a bash script similar to the following example. The script assumes that you can connect to each host by using
sshand that you have configuredsudoto not prompt for a password:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf SSH access is not available, you can use the
openstackcommand:for name in $(openstack server list --name ${CLUSTERID}\* -f value -c Name); do openstack server reboot $name; done$ for name in $(openstack server list --name ${CLUSTERID}\* -f value -c Name); do openstack server reboot $name; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, you might be able to reboot each node through the management portal for your infrastructure provider. Otherwise, contact the appropriate authority to either gain access to the virtual machines through SSH or the management portal and OpenStack client.
Verification
Confirm that the migration succeeded, and then remove the migration resources:
To confirm that the network plugin is OVN-Kubernetes, enter the following command.
oc get network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'$ oc get network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The value of
status.networkTypemust beOVNKubernetes.To confirm that the cluster nodes are in the
Readystate, enter the following command:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that your pods are not in an error state, enter the following command:
oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'$ oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If pods on a node are in an error state, reboot that node.
To confirm that all of the cluster Operators are not in an abnormal state, enter the following command:
oc get co
$ oc get coCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The status of every cluster Operator must be the following:
AVAILABLE="True",PROGRESSING="False",DEGRADED="False". If a cluster Operator is not available or degraded, check the logs for the cluster Operator for more information.ImportantDo not proceed if any of the previous verification steps indicate errors. You might encounter pods that have a
Terminatingstate due to finalizers that are removed during clean up. They are not an error indication.
If the migration completed and your cluster is in a good state, remove the migration configuration from the CNO configuration object by entering the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.7.3. Cleaning up resources after migration
After migration from the Kuryr network plugin to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, you must clean up the resources that Kuryr created previously.
The clean up process relies on a Python virtual environment to ensure that the package versions that you use support tags for Octavia objects. You do not need a virtual environment if you are certain that your environment uses at minimum: * openstacksdk version 0.54.0 * python-openstackclient version 5.5.0 * python-octaviaclient version 2.3.0
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift Container Platform CLI (
oc). - You installed a Python interpreter.
-
You installed the
openstacksdkPython package. -
You installed the
openstackCLI. - You have access to the underlying RHOSP cloud.
-
You can access the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Create a clean-up Python virtual environment:
Create a temporary directory for your environment. For example:
python3 -m venv /tmp/venv
$ python3 -m venv /tmp/venvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The virtual environment located in
/tmp/venvdirectory is used in all clean up examples.Enter the virtual environment. For example:
source /tmp/venv/bin/activate
$ source /tmp/venv/bin/activateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Upgrade the
pipcommand in the virtual environment by running the following command:(venv) $ pip install pip --upgrade
(venv) $ pip install pip --upgradeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Install the required Python packages by running the following command:
(venv) $ pip install openstacksdk==0.54.0 python-openstackclient==5.5.0 python-octaviaclient==2.3.0
(venv) $ pip install openstacksdk==0.54.0 python-openstackclient==5.5.0 python-octaviaclient==2.3.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
In your terminal, set variables to cluster and Kuryr identifiers by running the following commands:
Set the cluster ID:
(venv) $ CLUSTERID=$(oc get infrastructure.config.openshift.io cluster -o=jsonpath='{.status.infrastructureName}')(venv) $ CLUSTERID=$(oc get infrastructure.config.openshift.io cluster -o=jsonpath='{.status.infrastructureName}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the cluster tag:
(venv) $ CLUSTERTAG="openshiftClusterID=${CLUSTERID}"(venv) $ CLUSTERTAG="openshiftClusterID=${CLUSTERID}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the router ID:
(venv) $ ROUTERID=$(oc get kuryrnetwork -A --no-headers -o custom-columns=":status.routerId"|head -n 1)
(venv) $ ROUTERID=$(oc get kuryrnetwork -A --no-headers -o custom-columns=":status.routerId"|head -n 1)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a Bash function that removes finalizers from specified resources by running the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The function takes two parameters: the first parameter is name of the resource, and the second parameter is the finalizer to remove. The named resource is removed from the cluster and its definition is replaced with copied data, excluding the specified finalizer.
To remove Kuryr finalizers from services, enter the following command:
(venv) $ REMFIN services kuryr.openstack.org/service-finalizer
(venv) $ REMFIN services kuryr.openstack.org/service-finalizerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the Kuryr
service-subnet-gateway-ipservice, enter the following command:(venv) $ if $(oc get -n openshift-kuryr service service-subnet-gateway-ip &>/dev/null); then oc -n openshift-kuryr delete service service-subnet-gateway-ip fi(venv) $ if $(oc get -n openshift-kuryr service service-subnet-gateway-ip &>/dev/null); then oc -n openshift-kuryr delete service service-subnet-gateway-ip fiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove all tagged RHOSP load balancers from Octavia, enter the following command:
(venv) $ for lb in $(openstack loadbalancer list --tags $CLUSTERTAG -f value -c id); do openstack loadbalancer delete --cascade $lb done(venv) $ for lb in $(openstack loadbalancer list --tags $CLUSTERTAG -f value -c id); do openstack loadbalancer delete --cascade $lb doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove Kuryr finalizers from all
KuryrLoadBalancerCRs, enter the following command:(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrloadbalancers.openstack.org kuryr.openstack.org/kuryrloadbalancer-finalizers
(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrloadbalancers.openstack.org kuryr.openstack.org/kuryrloadbalancer-finalizersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the
openshift-kuryrnamespace, enter the following command:(venv) $ oc delete namespace openshift-kuryr
(venv) $ oc delete namespace openshift-kuryrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the Kuryr service subnet from the router, enter the following command:
(venv) $ openstack router remove subnet $ROUTERID ${CLUSTERID}-kuryr-service-subnet(venv) $ openstack router remove subnet $ROUTERID ${CLUSTERID}-kuryr-service-subnetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the Kuryr service network, enter the following command:
(venv) $ openstack network delete ${CLUSTERID}-kuryr-service-network(venv) $ openstack network delete ${CLUSTERID}-kuryr-service-networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove Kuryr finalizers from all pods, enter the following command:
(venv) $ REMFIN pods kuryr.openstack.org/pod-finalizer
(venv) $ REMFIN pods kuryr.openstack.org/pod-finalizerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove Kuryr finalizers from all
KuryrPortCRs, enter the following command:(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrports.openstack.org kuryr.openstack.org/kuryrport-finalizer
(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrports.openstack.org kuryr.openstack.org/kuryrport-finalizerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command deletes the
KuryrPortCRs.To remove Kuryr finalizers from network policies, enter the following command:
(venv) $ REMFIN networkpolicy kuryr.openstack.org/networkpolicy-finalizer
(venv) $ REMFIN networkpolicy kuryr.openstack.org/networkpolicy-finalizerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove Kuryr finalizers from remaining network policies, enter the following command:
(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrnetworkpolicies.openstack.org kuryr.openstack.org/networkpolicy-finalizer
(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrnetworkpolicies.openstack.org kuryr.openstack.org/networkpolicy-finalizerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove subports that Kuryr created from trunks, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To retrieve all networks and subnets from
KuryrNetworkCRs and remove ports, router interfaces and the network itself, enter the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the Kuryr security group, enter the following command:
(venv) $ openstack security group delete ${CLUSTERID}-kuryr-pods-security-group(venv) $ openstack security group delete ${CLUSTERID}-kuryr-pods-security-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove all tagged subnet pools, enter the following command:
(venv) $ for subnetpool in $(openstack subnet pool list --tags $CLUSTERTAG -f value -c ID); do openstack subnet pool delete $subnetpool done(venv) $ for subnetpool in $(openstack subnet pool list --tags $CLUSTERTAG -f value -c ID); do openstack subnet pool delete $subnetpool doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check that all of the networks based on
KuryrNetworkCRs were removed, enter the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the command returns any existing networks, intestigate and remove them before you continue.
To remove security groups that are related to network policy, enter the following command:
(venv) $ for sgid in $(openstack security group list -f value -c ID -c Description | grep 'Kuryr-Kubernetes Network Policy' | cut -f 1 -d ' '); do openstack security group delete $sgid done(venv) $ for sgid in $(openstack security group list -f value -c ID -c Description | grep 'Kuryr-Kubernetes Network Policy' | cut -f 1 -d ' '); do openstack security group delete $sgid doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove finalizers from
KuryrNetworkCRs, enter the following command:(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrnetworks.openstack.org kuryrnetwork.finalizers.kuryr.openstack.org
(venv) $ REMFIN kuryrnetworks.openstack.org kuryrnetwork.finalizers.kuryr.openstack.orgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the Kuryr router, enter the following command:
(venv) $ if $(python3 -c "import sys; import openstack; n = openstack.connect().network; r = n.get_router('$ROUTERID'); sys.exit(0) if r.description != 'Created By OpenShift Installer' else sys.exit(1)"); then openstack router delete $ROUTERID fi(venv) $ if $(python3 -c "import sys; import openstack; n = openstack.connect().network; r = n.get_router('$ROUTERID'); sys.exit(0) if r.description != 'Created By OpenShift Installer' else sys.exit(1)"); then openstack router delete $ROUTERID fiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.8. Converting to IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack networking
As a cluster administrator, you can convert your IPv4 single-stack cluster to a dual-network cluster network that supports IPv4 and IPv6 address families. After converting to dual-stack, all newly created pods are dual-stack enabled.
A dual-stack network is supported on clusters provisioned on bare metal, VMware vSphere, IBM Power, IBM Z infrastructure, and single node OpenShift clusters.
While using dual-stack networking, you cannot use IPv4-mapped IPv6 addresses, such as ::FFFF:198.51.100.1, where IPv6 is required.
25.8.1. Converting to a dual-stack cluster network
As a cluster administrator, you can convert your single-stack cluster network to a dual-stack cluster network.
After converting to dual-stack networking only newly created pods are assigned IPv6 addresses. Any pods created before the conversion must be recreated to receive an IPv6 address.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Your cluster uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
- The cluster nodes have IPv6 addresses.
- You have configured an IPv6-enabled router based on your infrastructure.
Procedure
To specify IPv6 address blocks for the cluster and service networks, create a file containing the following YAML:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify an object with the
cidrandhostPrefixparameters. The host prefix must be64or greater. The IPv6 Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) prefix must be large enough to accommodate the specified host prefix. - 1 2
- Specify an IPv6 CIDR with a prefix of
112. Kubernetes uses only the lowest 16 bits. For a prefix of112, IP addresses are assigned from112to128bits.
To patch the cluster network configuration, enter the following command:
oc patch network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='json' --patch-file <file>.yaml
$ oc patch network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='json' --patch-file <file>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
fileSpecifies the name of the file you created in the previous step.
Example output
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.config.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Complete the following step to verify that the cluster network recognizes the IPv6 address blocks that you specified in the previous procedure.
Display the network configuration:
oc describe network
$ oc describe networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.8.2. Converting to a single-stack cluster network
As a cluster administrator, you can convert your dual-stack cluster network to a single-stack cluster network.
If you originally converted your IPv4 single-stack cluster network to a dual-stack cluster, you can convert only back to the IPv4 single-stack cluster and not an IPv6 single-stack cluster network. The same restriction applies for converting back to an IPv6 single-stack cluster network.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Your cluster uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
- The cluster nodes have IPv6 addresses.
- You have enabled dual-stack networking.
Procedure
Edit the
networks.config.openshift.iocustom resource (CR) by running the following command:oc edit networks.config.openshift.io
$ oc edit networks.config.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Remove the IPv4 or IPv6 configuration that you added to the
cidrand thehostPrefixparameters from completing the "Converting to a dual-stack cluster network " procedure steps.
25.9. Logging for egress firewall and network policy rules
As a cluster administrator, you can configure audit logging for your cluster and enable logging for one or more namespaces. OpenShift Container Platform produces audit logs for both egress firewalls and network policies.
Audit logging is available for only the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
25.9.1. Audit logging
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin uses Open Virtual Network (OVN) ACLs to manage egress firewalls and network policies. Audit logging exposes allow and deny ACL events.
You can configure the destination for audit logs, such as a syslog server or a UNIX domain socket. Regardless of any additional configuration, an audit log is always saved to /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log on each OVN-Kubernetes pod in the cluster.
You can enable audit logging for each namespace by annotating each namespace configuration with a k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging section. In the k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging section, you must specify allow, deny, or both values to enable audit logging for a namespace.
A network policy does not support setting the Pass action set as a rule.
The ACL-logging implementation logs access control list (ACL) events for a network. You can view these logs to analyze any potential security issues.
Example namespace annotation
To view the default ACL logging configuration values, see the policyAuditConfig object in the cluster-network-03-config.yml file. If required, you can change the ACL logging configuration values for log file parameters in this file.
The logging message format is compatible with syslog as defined by RFC5424. The syslog facility is configurable and defaults to local0. The following example shows key parameters and their values outputted in a log message:
Example logging message that outputs parameters and their values
<timestamp>|<message_serial>|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|<severity>|name="<acl_name>", verdict="<verdict>", severity="<severity>", direction="<direction>": <flow>
<timestamp>|<message_serial>|acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)|<severity>|name="<acl_name>", verdict="<verdict>", severity="<severity>", direction="<direction>": <flow>Where:
-
<timestamp>states the time and date for the creation of a log message. -
<message_serial>lists the serial number for a log message. -
acl_log(ovn_pinctrl0)is a literal string that prints the location of the log message in the OVN-Kubernetes plugin. -
<severity>sets the severity level for a log message. If you enable audit logging that supportsallowanddenytasks then two severity levels show in the log message output. -
<name>states the name of the ACL-logging implementation in the OVN Network Bridging Database (nbdb) that was created by the network policy. -
<verdict>can be eitherallowordrop. -
<direction>can be eitherto-lportorfrom-lportto indicate that the policy was applied to traffic going to or away from a pod. -
<flow>shows packet information in a format equivalent to theOpenFlowprotocol. This parameter comprises Open vSwitch (OVS) fields.
The following example shows OVS fields that the flow parameter uses to extract packet information from system memory:
Example of OVS fields used by the flow parameter to extract packet information
<proto>,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=<src_mac>,dl_dst=<source_mac>,nw_src=<source_ip>,nw_dst=<target_ip>,nw_tos=<tos_dscp>,nw_ecn=<tos_ecn>,nw_ttl=<ip_ttl>,nw_frag=<fragment>,tp_src=<tcp_src_port>,tp_dst=<tcp_dst_port>,tcp_flags=<tcp_flags>
<proto>,vlan_tci=0x0000,dl_src=<src_mac>,dl_dst=<source_mac>,nw_src=<source_ip>,nw_dst=<target_ip>,nw_tos=<tos_dscp>,nw_ecn=<tos_ecn>,nw_ttl=<ip_ttl>,nw_frag=<fragment>,tp_src=<tcp_src_port>,tp_dst=<tcp_dst_port>,tcp_flags=<tcp_flags>Where:
-
<proto>states the protocol. Valid values aretcpandudp. -
vlan_tci=0x0000states the VLAN header as0because a VLAN ID is not set for internal pod network traffic. -
<src_mac>specifies the source for the Media Access Control (MAC) address. -
<source_mac>specifies the destination for the MAC address. -
<source_ip>lists the source IP address -
<target_ip>lists the target IP address. -
<tos_dscp>states Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) values to classify and prioritize certain network traffic over other traffic. -
<tos_ecn>states Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) values that indicate any congested traffic in your network. -
<ip_ttl>states the Time To Live (TTP) information for an packet. -
<fragment>specifies what type of IP fragments or IP non-fragments to match. -
<tcp_src_port>shows the source for the port for TCP and UDP protocols. -
<tcp_dst_port>lists the destination port for TCP and UDP protocols. -
<tcp_flags>supports numerous flags such asSYN,ACK,PSHand so on. If you need to set multiple values then each value is separated by a vertical bar (|). The UDP protocol does not support this parameter.
For more information about the previous field descriptions, go to the OVS manual page for ovs-fields.
Example ACL deny log entry for a network policy
The following table describes namespace annotation values:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Blocks namespace access to any traffic that matches an ACL rule with the |
|
|
Permits namespace access to any traffic that matches an ACL rule with the |
|
|
A |
25.9.2. Audit configuration
The configuration for audit logging is specified as part of the OVN-Kubernetes cluster network provider configuration. The following YAML illustrates the default values for the audit logging:
Audit logging configuration
The following table describes the configuration fields for audit logging.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| integer |
The maximum number of messages to generate every second per node. The default value is |
|
| integer |
The maximum size for the audit log in bytes. The default value is |
|
| integer | The maximum number of log files that are retained. |
|
| string | One of the following additional audit log targets:
|
|
| string |
The syslog facility, such as |
25.9.3. Configuring egress firewall and network policy auditing for a cluster
As a cluster administrator, you can customize audit logging for your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To customize the audit logging configuration, enter the following command:
oc edit network.operator.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit network.operator.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively customize and apply the following YAML to configure audit logging:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To create a namespace with network policies complete the following steps:
Create a namespace for verification:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
namespace/verify-audit-logging created
namespace/verify-audit-logging createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create network policies for the namespace:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-all created networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/allow-from-same-namespace created
networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/deny-all created networkpolicy.networking.k8s.io/allow-from-same-namespace createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a pod for source traffic in the
defaultnamespace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create two pods in the
verify-audit-loggingnamespace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
pod/client created pod/server created
pod/client created pod/server createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To generate traffic and produce network policy audit log entries, complete the following steps:
Obtain the IP address for pod named
serverin theverify-audit-loggingnamespace:POD_IP=$(oc get pods server -n verify-audit-logging -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')$ POD_IP=$(oc get pods server -n verify-audit-logging -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ping the IP address from the previous command from the pod named
clientin thedefaultnamespace and confirm that all packets are dropped:oc exec -it client -n default -- /bin/ping -c 2 $POD_IP
$ oc exec -it client -n default -- /bin/ping -c 2 $POD_IPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
PING 10.128.2.55 (10.128.2.55) 56(84) bytes of data. --- 10.128.2.55 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2041ms
PING 10.128.2.55 (10.128.2.55) 56(84) bytes of data. --- 10.128.2.55 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2041msCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ping the IP address saved in the
POD_IPshell environment variable from the pod namedclientin theverify-audit-loggingnamespace and confirm that all packets are allowed:oc exec -it client -n verify-audit-logging -- /bin/ping -c 2 $POD_IP
$ oc exec -it client -n verify-audit-logging -- /bin/ping -c 2 $POD_IPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Display the latest entries in the network policy audit log:
for pod in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node --no-headers=true | awk '{ print $1 }') ; do oc exec -it $pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -- tail -4 /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log done$ for pod in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node --no-headers=true | awk '{ print $1 }') ; do oc exec -it $pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -- tail -4 /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.9.4. Enabling egress firewall and network policy audit logging for a namespace
As a cluster administrator, you can enable audit logging for a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To enable audit logging for a namespace, enter the following command:
oc annotate namespace <namespace> \ k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging='{ "deny": "alert", "allow": "notice" }'$ oc annotate namespace <namespace> \ k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging='{ "deny": "alert", "allow": "notice" }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Specifies the name of the namespace.
TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to enable audit logging:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
namespace/verify-audit-logging annotated
namespace/verify-audit-logging annotatedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Display the latest entries in the audit log:
for pod in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node --no-headers=true | awk '{ print $1 }') ; do oc exec -it $pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -- tail -4 /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log done$ for pod in $(oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l app=ovnkube-node --no-headers=true | awk '{ print $1 }') ; do oc exec -it $pod -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -- tail -4 /var/log/ovn/acl-audit-log.log doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.9.5. Disabling egress firewall and network policy audit logging for a namespace
As a cluster administrator, you can disable audit logging for a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To disable audit logging for a namespace, enter the following command:
oc annotate --overwrite namespace <namespace> k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging-
$ oc annotate --overwrite namespace <namespace> k8s.ovn.org/acl-logging-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<namespace>- Specifies the name of the namespace.
TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to disable audit logging:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
namespace/verify-audit-logging annotated
namespace/verify-audit-logging annotatedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.10. Configuring IPsec encryption
With IPsec enabled, all pod-to-pod network traffic between nodes on the OVN-Kubernetes cluster network is encrypted with IPsec Transport mode.
IPsec is disabled by default. It can be enabled either during or after installing the cluster. For information about cluster installation, see OpenShift Container Platform installation overview. If you need to enable IPsec after cluster installation, you must first resize your cluster MTU to account for the overhead of the IPsec ESP IP header.
The following support limitations exist for IPsec on a OpenShift Container Platform cluster:
- You must disable IPsec before updating to OpenShift Container Platform 4.15. After disabling IPsec, you must also delete the associated IPsec daemonsets. There is a known issue that can cause interruptions in pod-to-pod communication if you update without disabling IPsec. (OCPBUGS-43323)
The following documentation describes how to enable and disable IPSec after cluster installation.
25.10.1. Prerequisites
-
You have decreased the size of the cluster MTU by
46bytes to allow for the additional overhead of the IPsec ESP header. For more information on resizing the MTU that your cluster uses, see Changing the MTU for the cluster network.
25.10.2. Types of network traffic flows encrypted by IPsec
With IPsec enabled, only the following network traffic flows between pods are encrypted:
- Traffic between pods on different nodes on the cluster network
- Traffic from a pod on the host network to a pod on the cluster network
The following traffic flows are not encrypted:
- Traffic between pods on the same node on the cluster network
- Traffic between pods on the host network
- Traffic from a pod on the cluster network to a pod on the host network
The encrypted and unencrypted flows are illustrated in the following diagram:
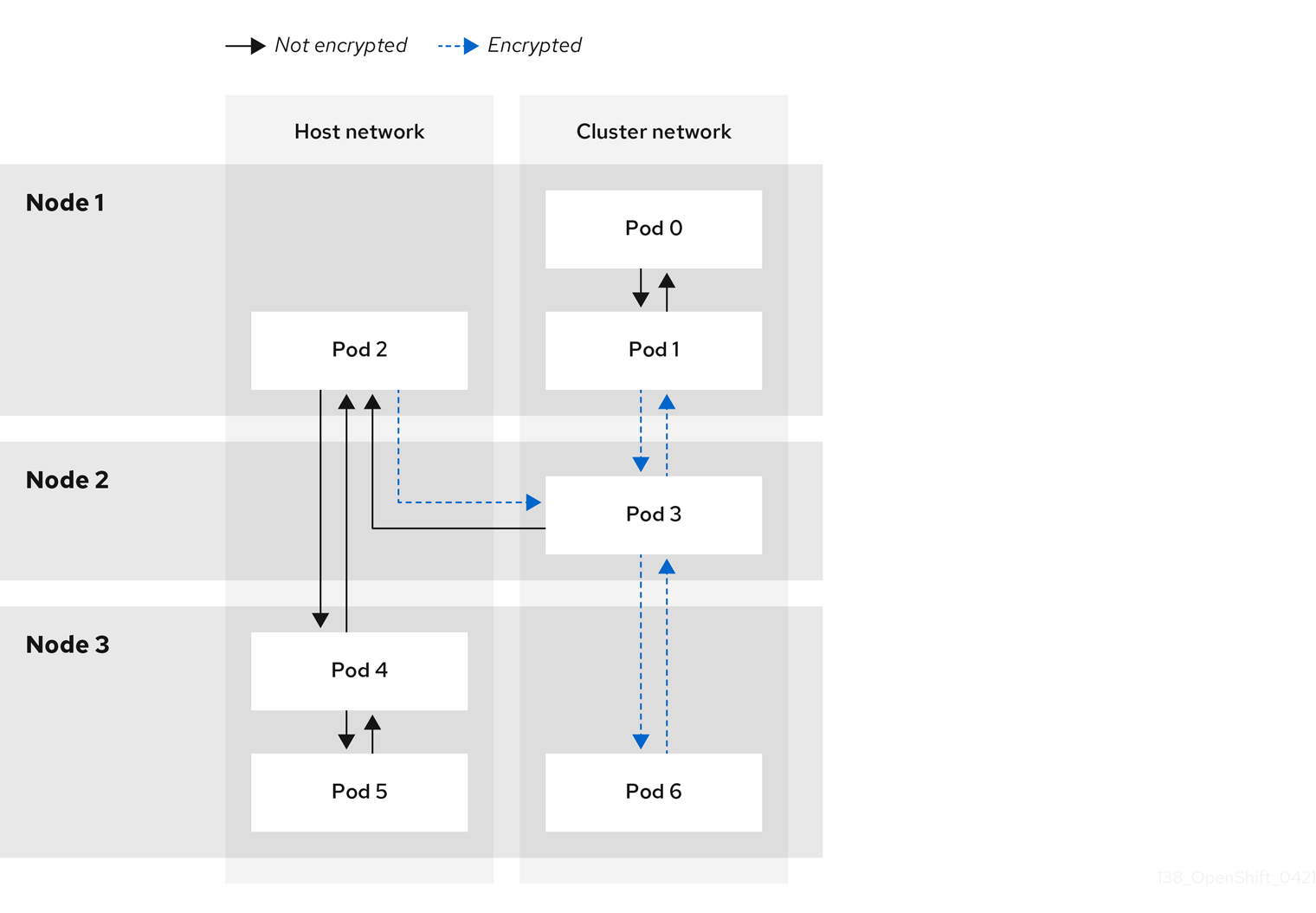
25.10.2.1. Network connectivity requirements when IPsec is enabled
You must configure the network connectivity between machines to allow OpenShift Container Platform cluster components to communicate. Each machine must be able to resolve the hostnames of all other machines in the cluster.
| Protocol | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UDP |
| IPsec IKE packets |
|
| IPsec NAT-T packets | |
| ESP | N/A | IPsec Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) |
25.10.3. Encryption protocol and IPsec mode
The encrypt cipher used is AES-GCM-16-256. The integrity check value (ICV) is 16 bytes. The key length is 256 bits.
The IPsec mode used is Transport mode, a mode that encrypts end-to-end communication by adding an Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP) header to the IP header of the original packet and encrypts the packet data. OpenShift Container Platform does not currently use or support IPsec Tunnel mode for pod-to-pod communication.
25.10.4. Security certificate generation and rotation
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) generates a self-signed X.509 certificate authority (CA) that is used by IPsec for encryption. Certificate signing requests (CSRs) from each node are automatically fulfilled by the CNO.
The CA is valid for 10 years. The individual node certificates are valid for 5 years and are automatically rotated after 4 1/2 years elapse.
25.10.5. Enabling IPsec encryption
As a cluster administrator, you can enable IPsec encryption after cluster installation.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. -
You have reduced the size of your cluster maximum transmission unit (MTU) by
46bytes to allow for the overhead of the IPsec ESP header.
Procedure
To enable IPsec encryption, enter the following command:
oc patch networks.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge \ -p '{"spec":{"defaultNetwork":{"ovnKubernetesConfig":{"ipsecConfig":{ }}}}}'$ oc patch networks.operator.openshift.io cluster --type=merge \ -p '{"spec":{"defaultNetwork":{"ovnKubernetesConfig":{"ipsecConfig":{ }}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To find the names of the OVN-Kubernetes control plane pods, enter the following command:
oc get pods -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc get pods -l app=ovnkube-master -n openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ovnkube-master-fvtnh 6/6 Running 0 122m ovnkube-master-hsgmm 6/6 Running 0 122m ovnkube-master-qcmdc 6/6 Running 0 122m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ovnkube-master-fvtnh 6/6 Running 0 122m ovnkube-master-hsgmm 6/6 Running 0 122m ovnkube-master-qcmdc 6/6 Running 0 122mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that IPsec is enabled on your cluster by entering the following command. The command output must state
trueto indicate that the node has IPsec enabled.oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes rsh ovnkube-master-<pod_number_sequence> \ ovn-nbctl --no-leader-only get nb_global . ipsec
$ oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes rsh ovnkube-master-<pod_number_sequence> \1 ovn-nbctl --no-leader-only get nb_global . ipsecCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<pod_number_sequence>with the random sequence of letters,fvtnh, for a data plane pod from the previous step.
25.10.6. Disabling IPsec encryption
As a cluster administrator, you can disable IPsec encryption only if you enabled IPsec after cluster installation.
After disabling IPsec, you must delete the associated IPsec daemonsets pods. If you do not delete these pods, you might experience issues with your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
To disable IPsec encryption, enter the following command:
oc patch networks.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=json \ -p='[{"op":"remove", "path":"/spec/defaultNetwork/ovnKubernetesConfig/ipsecConfig"}]'$ oc patch networks.operator.openshift.io/cluster --type=json \ -p='[{"op":"remove", "path":"/spec/defaultNetwork/ovnKubernetesConfig/ipsecConfig"}]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To find the name of the OVN-Kubernetes data plane pod that exists on the
masternode in your cluster, enter the following command:oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l=app=ovnkube-master
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l=app=ovnkube-masterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
ovnkube-master-5xqbf 8/8 Running 0 28m ...
ovnkube-master-5xqbf 8/8 Running 0 28m ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
masternode in your cluster has IPsec disabled by entering the following command. The command output must statefalseto indicate that the node has IPsec disabled.oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -c nbdb rsh ovnkube-master-<pod_number_sequence> \ ovn-nbctl --no-leader-only get nb_global . ipsec
$ oc -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -c nbdb rsh ovnkube-master-<pod_number_sequence> \1 ovn-nbctl --no-leader-only get nb_global . ipsecCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<pod_number_sequence>with the random sequence of letters, such as5xqbf, for the data plane pod from the previous step.
To remove the IPsec
ovn-ipsecdaemonset pod from theopenshift-ovn-kubernetesnamespace on the node, enter the following command:oc delete daemonset ovn-ipsec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc delete daemonset ovn-ipsec -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
ovn-ipsecdaemonset configures IPsec connections for east-west traffic on the node.
Verify that the
ovn-ipsecdaemonset pod was removed from the all nodes in your cluster by entering the following command. If the command output does not list the pod, the removal operation is successful.oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l=app=ovn-ipsec
$ oc get pods -n openshift-ovn-kubernetes -l=app=ovn-ipsecCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou might need to re-run the command for deleting the pod because sometimes the initial command attempt might not delete the pod.
-
Optional: You can increase the size of your cluster MTU by
46bytes because there is no longer any overhead from the IPsec ESP header in IP packets.
25.10.7. Additional resources
25.11. Configuring an egress firewall for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can create an egress firewall for a project that restricts egress traffic leaving your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
25.11.1. How an egress firewall works in a project
As a cluster administrator, you can use an egress firewall to limit the external hosts that some or all pods can access from within the cluster. An egress firewall supports the following scenarios:
- A pod can only connect to internal hosts and cannot start connections to the public internet.
- A pod can only connect to the public internet and cannot start connections to internal hosts that are outside the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- A pod cannot reach specified internal subnets or hosts outside the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- A pod can connect to only specific external hosts.
For example, you can allow one project access to a specified IP range but deny the same access to a different project. Or you can restrict application developers from updating from Python pip mirrors, and force updates to come only from approved sources.
Egress firewall does not apply to the host network namespace. Egress firewall rules do not impact any pods that have host networking enabled.
You configure an egress firewall policy by creating an EgressFirewall custom resource (CR) object. The egress firewall matches network traffic that meets any of the following criteria:
- An IP address range in CIDR format
- A DNS name that resolves to an IP address
- A port number
- A protocol that is one of the following protocols: TCP, UDP, and SCTP
If your egress firewall includes a deny rule for 0.0.0.0/0, the rule blocks access to your OpenShift Container Platform API servers. You must either add allow rules for each IP address or use the nodeSelector type allow rule in your egress policy rules to connect to API servers.
The following example illustrates the order of the egress firewall rules necessary to ensure API server access:
To find the IP address for your API servers, run oc get ep kubernetes -n default.
For more information, see BZ#1988324.
Egress firewall rules do not apply to traffic that goes through routers. Any user with permission to create a Route CR object can bypass egress firewall policy rules by creating a route that points to a forbidden destination.
25.11.1.1. Limitations of an egress firewall
An egress firewall has the following limitations:
- No project can have more than one EgressFirewall object.
- A maximum of one EgressFirewall object with a maximum of 8,000 rules can be defined per project.
-
If you use the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin and you configured
falsefor theroutingViaHostparameter in theNetworkcustom resource for your cluster, egress firewall rules impact the return ingress replies. If the egress firewall rules drop the ingress reply destination IP, the traffic is dropped.
Violating any of these restrictions results in a broken egress firewall for the project. As a result, all external network traffic drops, which can cause security risks for your organization.
You can create an Egress Firewall resource in the kube-node-lease, kube-public, kube-system, openshift and openshift- projects.
25.11.1.2. Matching order for egress firewall policy rules
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin evaluates egress firewall policy rules based on the first-to-last order of how you defined the rules. The first rule that matches an egress connection from a pod applies. The plugin ignores any subsequent rules for that connection.
25.11.1.3. Domain Name Server (DNS) resolution
If you use DNS names in any of your egress firewall policy rules, proper resolution of the domain names is subject to the following restrictions:
- Domain name updates are polled based on a time-to-live (TTL) duration. By default, the duration is 30 minutes. When the egress firewall controller queries the local name servers for a domain name, if the response includes a TTL and the TTL is less than 30 minutes, the controller sets the duration for that DNS name to the returned value. Each DNS name is queried after the TTL for the DNS record expires.
- The pod must resolve the domain from the same local name servers when necessary. Otherwise the IP addresses for the domain known by the egress firewall controller and the pod can be different. If the IP addresses for a hostname differ, consistent enforcement of the egress firewall does not apply.
- Because the egress firewall controller and pods asynchronously poll the same local name server, the pod might obtain the updated IP address before the egress controller does, which causes a race condition. Due to this current limitation, domain name usage in EgressFirewall objects is only recommended for domains with infrequent IP address changes.
Using DNS names in your egress firewall policy does not affect local DNS resolution through CoreDNS.
If your egress firewall policy uses domain names, and an external DNS server handles DNS resolution for an affected pod, you must include egress firewall rules that allow access to the IP addresses of your DNS server.
25.11.2. EgressFirewall custom resource (CR) object
You can define one or more rules for an egress firewall. A rule is either an Allow rule or a Deny rule, with a specification for the traffic that the rule applies to.
The following YAML describes an EgressFirewall CR object:
EgressFirewall object
25.11.2.1. EgressFirewall rules
The following YAML describes an egress firewall rule object. The user can select either an IP address range in CIDR format, a domain name, or use the nodeSelector to allow or deny egress traffic. The egress stanza expects an array of one or more objects.
Egress policy rule stanza
- 1
- The type of rule. The value must be either
AlloworDeny. - 2
- A stanza describing an egress traffic match rule that specifies the
cidrSelectorfield or thednsNamefield. You cannot use both fields in the same rule. - 3
- An IP address range in CIDR format.
- 4
- A DNS domain name.
- 5
- Labels are key/value pairs that the user defines. Labels are attached to objects, such as pods. The
nodeSelectorallows for one or more node labels to be selected and attached to pods. - 6
- Optional: A stanza describing a collection of network ports and protocols for the rule.
Ports stanza
ports: - port: <port> protocol: <protocol>
ports:
- port: <port>
protocol: <protocol> 25.11.2.2. Example EgressFirewall CR objects
The following example defines several egress firewall policy rules:
- 1
- A collection of egress firewall policy rule objects.
The following example defines a policy rule that denies traffic to the host at the 172.16.1.1/32 IP address, if the traffic is using either the TCP protocol and destination port 80 or any protocol and destination port 443.
25.11.2.3. Example nodeSelector for EgressFirewall
As a cluster administrator, you can allow or deny egress traffic to nodes in your cluster by specifying a label using nodeSelector. Labels can be applied to one or more nodes. The following is an example with the region=east label:
Instead of adding manual rules per node IP address, use node selectors to create a label that allows pods behind an egress firewall to access host network pods.
25.11.3. Creating an egress firewall policy object
As a cluster administrator, you can create an egress firewall policy object for a project.
If the project already has an EgressFirewall object defined, you must edit the existing policy to make changes to the egress firewall rules.
Prerequisites
- A cluster that uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Create a policy rule:
-
Create a
<policy_name>.yamlfile where<policy_name>describes the egress policy rules. - In the file you created, define an egress policy object.
-
Create a
Enter the following command to create the policy object. Replace
<policy_name>with the name of the policy and<project>with the project that the rule applies to.oc create -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <project>
$ oc create -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example, a new EgressFirewall object is created in a project named
project1:oc create -f default.yaml -n project1
$ oc create -f default.yaml -n project1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
egressfirewall.k8s.ovn.org/v1 created
egressfirewall.k8s.ovn.org/v1 createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Optional: Save the
<policy_name>.yamlfile so that you can make changes later.
25.12. Viewing an egress firewall for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can list the names of any existing egress firewalls and view the traffic rules for a specific egress firewall.
25.12.1. Viewing an EgressFirewall object
You can view an EgressFirewall object in your cluster.
Prerequisites
- A cluster using the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift Command-line Interface (CLI), commonly known as
oc. - You must log in to the cluster.
Procedure
Optional: To view the names of the EgressFirewall objects defined in your cluster, enter the following command:
oc get egressfirewall --all-namespaces
$ oc get egressfirewall --all-namespacesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To inspect a policy, enter the following command. Replace
<policy_name>with the name of the policy to inspect.oc describe egressfirewall <policy_name>
$ oc describe egressfirewall <policy_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.13. Editing an egress firewall for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can modify network traffic rules for an existing egress firewall.
25.13.1. Editing an EgressFirewall object
As a cluster administrator, you can update the egress firewall for a project.
Prerequisites
- A cluster using the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Find the name of the EgressFirewall object for the project. Replace
<project>with the name of the project.oc get -n <project> egressfirewall
$ oc get -n <project> egressfirewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: If you did not save a copy of the EgressFirewall object when you created the egress network firewall, enter the following command to create a copy.
oc get -n <project> egressfirewall <name> -o yaml > <filename>.yaml
$ oc get -n <project> egressfirewall <name> -o yaml > <filename>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<project>with the name of the project. Replace<name>with the name of the object. Replace<filename>with the name of the file to save the YAML to.After making changes to the policy rules, enter the following command to replace the EgressFirewall object. Replace
<filename>with the name of the file containing the updated EgressFirewall object.oc replace -f <filename>.yaml
$ oc replace -f <filename>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.14. Removing an egress firewall from a project
As a cluster administrator, you can remove an egress firewall from a project to remove all restrictions on network traffic from the project that leaves the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
25.14.1. Removing an EgressFirewall object
As a cluster administrator, you can remove an egress firewall from a project.
Prerequisites
- A cluster using the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Find the name of the EgressFirewall object for the project. Replace
<project>with the name of the project.oc get -n <project> egressfirewall
$ oc get -n <project> egressfirewallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the following command to delete the EgressFirewall object. Replace
<project>with the name of the project and<name>with the name of the object.oc delete -n <project> egressfirewall <name>
$ oc delete -n <project> egressfirewall <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.15. Configuring an egress IP address
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the OVN-Kubernetes Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin to assign one or more egress IP addresses to a namespace, or to specific pods in a namespace.
In an installer-provisioned infrastructure cluster, do not assign egress IP addresses to the infrastructure node that already hosts the ingress VIP. For more information, see the Red Hat Knowledgebase solution POD from the egress IP enabled namespace cannot access OCP route in an IPI cluster when the egress IP is assigned to the infra node that already hosts the ingress VIP.
25.15.1. Egress IP address architectural design and implementation
By using the OpenShift Container Platform egress IP address functionality, you can ensure that the traffic from one or more pods in one or more namespaces has a consistent source IP address for services outside the cluster network.
For example, you might have a pod that periodically queries a database that is hosted on a server outside of your cluster. To enforce access requirements for the server, a packet filtering device is configured to allow traffic only from specific IP addresses. To ensure that you can reliably allow access to the server from only that specific pod, you can configure a specific egress IP address for the pod that makes the requests to the server.
An egress IP address assigned to a namespace is different from an egress router, which is used to send traffic to specific destinations.
In some cluster configurations, application pods and ingress router pods run on the same node. If you configure an egress IP address for an application project in this scenario, the IP address is not used when you send a request to a route from the application project.
Egress IP addresses must not be configured in any Linux network configuration files, such as ifcfg-eth0.
25.15.1.1. Platform support
The Egress IP address feature that runs on a primary host network is supported on the following platforms:
| Platform | Supported |
|---|---|
| Bare metal | Yes |
| VMware vSphere | Yes |
| Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) | Yes |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Yes |
| Google Cloud | Yes |
| Microsoft Azure | Yes |
| IBM Z and IBM® LinuxONE | Yes |
| IBM Z and IBM® LinuxONE for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) KVM | Yes |
| IBM Power | Yes |
The Egress IP address feature that runs on secondary host networks is supported on the following platform:
| Platform | Supported |
|---|---|
| Bare metal | Yes |
The assignment of egress IP addresses to control plane nodes with the EgressIP feature is not supported on a cluster provisioned on Amazon Web Services (AWS). (BZ#2039656)
25.15.1.2. Public cloud platform considerations
Typically, public cloud providers place a limit on egress IPs. This means that there is a constraint on the absolute number of assignable IP addresses per node for clusters provisioned on public cloud infrastructure. The maximum number of assignable IP addresses per node, or the IP capacity, can be described in the following formula:
IP capacity = public cloud default capacity - sum(current IP assignments)
IP capacity = public cloud default capacity - sum(current IP assignments)While the Egress IPs capability manages the IP address capacity per node, it is important to plan for this constraint in your deployments. For example, if a public cloud provider limits IP address capacity to 10 IP addresses per node, and you have 8 nodes, the total number of assignable IP addresses is only 80. To achieve a higher IP address capacity, you would need to allocate additional nodes. For example, if you needed 150 assignable IP addresses, you would need to allocate 7 additional nodes.
To confirm the IP capacity and subnets for any node in your public cloud environment, you can enter the oc get node <node_name> -o yaml command. The cloud.network.openshift.io/egress-ipconfig annotation includes capacity and subnet information for the node.
The annotation value is an array with a single object with fields that provide the following information for the primary network interface:
-
interface: Specifies the interface ID on AWS and Azure and the interface name on Google Cloud. -
ifaddr: Specifies the subnet mask for one or both IP address families. -
capacity: Specifies the IP address capacity for the node. On AWS, the IP address capacity is provided per IP address family. On Azure and Google Cloud, the IP address capacity includes both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Automatic attachment and detachment of egress IP addresses for traffic between nodes are available. This allows for traffic from many pods in namespaces to have a consistent source IP address to locations outside of the cluster. This also supports OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes, which is the default networking plugin in Red Hat OpenShift Networking in OpenShift Container Platform 4.13.
When an RHOSP cluster administrator assigns a floating IP to the reservation port, OpenShift Container Platform cannot delete the reservation port. The CloudPrivateIPConfig object cannot perform delete and move operations until an RHOSP cluster administrator unassigns the floating IP from the reservation port.
The following examples illustrate the annotation from nodes on several public cloud providers. The annotations are indented for readability.
Example cloud.network.openshift.io/egress-ipconfig annotation on AWS
Example cloud.network.openshift.io/egress-ipconfig annotation on Google Cloud
The following sections describe the IP address capacity for supported public cloud environments for use in your capacity calculation.
25.15.1.2.1. Amazon Web Services (AWS) IP address capacity limits
On AWS, constraints on IP address assignments depend on the instance type configured. For more information, see IP addresses per network interface per instance type
25.15.1.2.2. Google Cloud IP address capacity limits
On Google Cloud, the networking model implements additional node IP addresses through IP address aliasing, rather than IP address assignments. However, IP address capacity maps directly to IP aliasing capacity.
The following capacity limits exist for IP aliasing assignment:
- Per node, the maximum number of IP aliases, both IPv4 and IPv6, is 100.
- Per VPC, the maximum number of IP aliases is unspecified, but OpenShift Container Platform scalability testing reveals the maximum to be approximately 15,000.
For more information, see Per instance quotas and Alias IP ranges overview.
25.15.1.2.3. Microsoft Azure IP address capacity limits
On Azure, the following capacity limits exist for IP address assignment:
- Per NIC, the maximum number of assignable IP addresses, for both IPv4 and IPv6, is 256.
- Per virtual network, the maximum number of assigned IP addresses cannot exceed 65,536.
For more information, see Networking limits.
25.15.1.3. Assignment of egress IPs to pods
To assign one or more egress IPs to a namespace or specific pods in a namespace, the following conditions must be satisfied:
-
At least one node in your cluster must have the
k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable: ""label. -
An
EgressIPobject exists that defines one or more egress IP addresses to use as the source IP address for traffic leaving the cluster from pods in a namespace.
If you create EgressIP objects prior to labeling any nodes in your cluster for egress IP assignment, OpenShift Container Platform might assign every egress IP address to the first node with the k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable: "" label.
To ensure that egress IP addresses are widely distributed across nodes in the cluster, always apply the label to the nodes you intent to host the egress IP addresses before creating any EgressIP objects.
25.15.1.4. Assignment of egress IPs to nodes
When creating an EgressIP object, the following conditions apply to nodes that are labeled with the k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable: "" label:
- An egress IP address is never assigned to more than one node at a time.
- An egress IP address is equally balanced between available nodes that can host the egress IP address.
If the
spec.EgressIPsarray in anEgressIPobject specifies more than one IP address, the following conditions apply:- No node will ever host more than one of the specified IP addresses.
- Traffic is balanced roughly equally between the specified IP addresses for a given namespace.
- If a node becomes unavailable, any egress IP addresses assigned to it are automatically reassigned, subject to the previously described conditions.
When a pod matches the selector for multiple EgressIP objects, there is no guarantee which of the egress IP addresses that are specified in the EgressIP objects is assigned as the egress IP address for the pod.
Additionally, if an EgressIP object specifies multiple egress IP addresses, there is no guarantee which of the egress IP addresses might be used. For example, if a pod matches a selector for an EgressIP object with two egress IP addresses, 10.10.20.1 and 10.10.20.2, either might be used for each TCP connection or UDP conversation.
25.15.1.5. Architectural diagram of an egress IP address configuration
The following diagram depicts an egress IP address configuration. The diagram describes four pods in two different namespaces running on three nodes in a cluster. The nodes are assigned IP addresses from the 192.168.126.0/18 CIDR block on the host network.
Both Node 1 and Node 3 are labeled with k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable: "" and thus available for the assignment of egress IP addresses.
The dashed lines in the diagram depict the traffic flow from pod1, pod2, and pod3 traveling through the pod network to egress the cluster from Node 1 and Node 3. When an external service receives traffic from any of the pods selected by the example EgressIP object, the source IP address is either 192.168.126.10 or 192.168.126.102. The traffic is balanced roughly equally between these two nodes.
The following resources from the diagram are illustrated in detail:
NamespaceobjectsThe namespaces are defined in the following manifest:
Namespace objects
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow EgressIPobjectThe following
EgressIPobject describes a configuration that selects all pods in any namespace with theenvlabel set toprod. The egress IP addresses for the selected pods are192.168.126.10and192.168.126.102.EgressIPobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For the configuration in the previous example, OpenShift Container Platform assigns both egress IP addresses to the available nodes. The
statusfield reflects whether and where the egress IP addresses are assigned.
25.15.2. EgressIP object
The following YAML describes the API for the EgressIP object. The scope of the object is cluster-wide; it is not created in a namespace.
EgressIP selected pods cannot serve as backends for services with externalTrafficPolicy set to Local. If you try this configuration, service ingress traffic that targets the pods gets incorrectly rerouted to the egress node that hosts the EgressIP. This situation negatively impacts the handling of incoming service traffic and causes connections to drop. This leads to unavailable and non-functional services.
- 1
- The name for the
EgressIPsobject. - 2
- An array of one or more IP addresses.
- 3
- One or more selectors for the namespaces to associate the egress IP addresses with.
- 4
- Optional: One or more selectors for pods in the specified namespaces to associate egress IP addresses with. Applying these selectors allows for the selection of a subset of pods within a namespace.
The following YAML describes the stanza for the namespace selector:
Namespace selector stanza
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
<label_name>: <label_value>
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
<label_name>: <label_value>- 1
- One or more matching rules for namespaces. If more than one match rule is provided, all matching namespaces are selected.
The following YAML describes the optional stanza for the pod selector:
Pod selector stanza
podSelector:
matchLabels:
<label_name>: <label_value>
podSelector:
matchLabels:
<label_name>: <label_value>- 1
- Optional: One or more matching rules for pods in the namespaces that match the specified
namespaceSelectorrules. If specified, only pods that match are selected. Others pods in the namespace are not selected.
In the following example, the EgressIP object associates the 192.168.126.11 and 192.168.126.102 egress IP addresses with pods that have the app label set to web and are in the namespaces that have the env label set to prod:
Example EgressIP object
In the following example, the EgressIP object associates the 192.168.127.30 and 192.168.127.40 egress IP addresses with any pods that do not have the environment label set to development:
Example EgressIP object
25.15.3. The egressIPConfig object
As a feature of egress IP, the reachabilityTotalTimeoutSeconds parameter configures the EgressIP node reachability check total timeout in seconds. If the EgressIP node cannot be reached within this timeout, the node is declared down.
You can set a value for the reachabilityTotalTimeoutSeconds in the configuration file for the egressIPConfig object. Setting a large value might cause the EgressIP implementation to react slowly to node changes. The implementation reacts slowly for EgressIP nodes that have an issue and are unreachable.
If you omit the reachabilityTotalTimeoutSeconds parameter from the egressIPConfig object, the platform chooses a reasonable default value, which is subject to change over time. The current default is 1 second. A value of 0 disables the reachability check for the EgressIP node.
The following egressIPConfig object describes changing the reachabilityTotalTimeoutSeconds from the default 1 second probes to 5 second probes:
- 1
- The
egressIPConfigholds the configurations for the options of theEgressIPobject. By changing these configurations, you can extend theEgressIPobject. - 2
- The value for
reachabilityTotalTimeoutSecondsaccepts integer values from0to60. A value of0disables the reachability check of the egressIP node. Setting a value from1to60corresponds to the timeout in seconds for a probe to send the reachability check to the node.
25.15.4. Labeling a node to host egress IP addresses
You can apply the k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable="" label to a node in your cluster so that OpenShift Container Platform can assign one or more egress IP addresses to the node.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
To label a node so that it can host one or more egress IP addresses, enter the following command:
oc label nodes <node_name> k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable=""
$ oc label nodes <node_name> k8s.ovn.org/egress-assignable=""1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the node to label.
TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the label to a node:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.15.5. Next steps
25.16. Assigning an egress IP address
As a cluster administrator, you can assign an egress IP address for traffic leaving the cluster from a namespace or from specific pods in a namespace.
25.16.1. Assigning an egress IP address to a namespace
You can assign one or more egress IP addresses to a namespace or to specific pods in a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
- Configure at least one node to host an egress IP address.
Procedure
Create an
EgressIPobject:-
Create a
<egressips_name>.yamlfile where<egressips_name>is the name of the object. In the file that you created, define an
EgressIPobject, as in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Create a
To create the object, enter the following command.
oc apply -f <egressips_name>.yaml
$ oc apply -f <egressips_name>.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<egressips_name>with the name of the object.
Example output
egressips.k8s.ovn.org/<egressips_name> created
egressips.k8s.ovn.org/<egressips_name> createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Optional: Store the
<egressips_name>.yamlfile so that you can make changes later. Add labels to the namespace that requires egress IP addresses. To add a label to the namespace of an
EgressIPobject defined in step 1, run the following command:oc label ns <namespace> env=qa
$ oc label ns <namespace> env=qa1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<namespace>with the namespace that requires egress IP addresses.
Verification
To show all egress IPs that are in use in your cluster, enter the following command:
oc get egressip -o yaml
$ oc get egressip -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe command
oc get egressiponly returns one egress IP address regardless of how many are configured. This is not a bug and is a limitation of Kubernetes. As a workaround, you can pass in the-o yamlor-o jsonflags to return all egress IPs addresses in use.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.17. Considerations for the use of an egress router pod
25.17.1. About an egress router pod
The OpenShift Container Platform egress router pod redirects traffic to a specified remote server from a private source IP address that is not used for any other purpose. An egress router pod can send network traffic to servers that are set up to allow access only from specific IP addresses.
The egress router pod is not intended for every outgoing connection. Creating large numbers of egress router pods can exceed the limits of your network hardware. For example, creating an egress router pod for every project or application could exceed the number of local MAC addresses that the network interface can handle before reverting to filtering MAC addresses in software.
The egress router image is not compatible with Amazon AWS, Azure Cloud, or any other cloud platform that does not support layer 2 manipulations due to their incompatibility with macvlan traffic.
25.17.1.1. Egress router modes
In redirect mode, an egress router pod configures iptables rules to redirect traffic from its own IP address to one or more destination IP addresses. Client pods that need to use the reserved source IP address must be configured to access the service for the egress router rather than connecting directly to the destination IP. You can access the destination service and port from the application pod by using the curl command. For example:
curl <router_service_IP> <port>
$ curl <router_service_IP> <port>The egress router CNI plugin supports redirect mode only. This is a difference with the egress router implementation that you can deploy with OpenShift SDN. Unlike the egress router for OpenShift SDN, the egress router CNI plugin does not support HTTP proxy mode or DNS proxy mode.
25.17.1.2. Egress router pod implementation
The egress router implementation uses the egress router Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin. The plugin adds a secondary network interface to a pod.
An egress router is a pod that has two network interfaces. For example, the pod can have eth0 and net1 network interfaces. The eth0 interface is on the cluster network and the pod continues to use the interface for ordinary cluster-related network traffic. The net1 interface is on a secondary network and has an IP address and gateway for that network. Other pods in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster can access the egress router service and the service enables the pods to access external services. The egress router acts as a bridge between pods and an external system.
Traffic that leaves the egress router exits through a node, but the packets have the MAC address of the net1 interface from the egress router pod.
When you add an egress router custom resource, the Cluster Network Operator creates the following objects:
-
The network attachment definition for the
net1secondary network interface of the pod. - A deployment for the egress router.
If you delete an egress router custom resource, the Operator deletes the two objects in the preceding list that are associated with the egress router.
25.17.1.3. Deployment considerations
An egress router pod adds an additional IP address and MAC address to the primary network interface of the node. As a result, you might need to configure your hypervisor or cloud provider to allow the additional address.
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)
If you deploy OpenShift Container Platform on RHOSP, you must allow traffic from the IP and MAC addresses of the egress router pod on your OpenStack environment. If you do not allow the traffic, then communication will fail:
openstack port set --allowed-address \ ip_address=<ip_address>,mac_address=<mac_address> <neutron_port_uuid>
$ openstack port set --allowed-address \ ip_address=<ip_address>,mac_address=<mac_address> <neutron_port_uuid>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Red Hat Virtualization (RHV)
- If you are using RHV, you must select No Network Filter for the Virtual network interface controller (vNIC).
- VMware vSphere
- If you are using VMware vSphere, see the VMware documentation for securing vSphere standard switches. View and change VMware vSphere default settings by selecting the host virtual switch from the vSphere Web Client.
Specifically, ensure that the following are enabled:
25.17.1.4. Failover configuration
To avoid downtime, the Cluster Network Operator deploys the egress router pod as a deployment resource. The deployment name is egress-router-cni-deployment. The pod that corresponds to the deployment has a label of app=egress-router-cni.
To create a new service for the deployment, use the oc expose deployment/egress-router-cni-deployment --port <port_number> command or create a file like the following example:
25.18. Deploying an egress router pod in redirect mode
As a cluster administrator, you can deploy an egress router pod to redirect traffic to specified destination IP addresses from a reserved source IP address.
The egress router implementation uses the egress router Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin.
25.18.1. Egress router custom resource
Define the configuration for an egress router pod in an egress router custom resource. The following YAML describes the fields for the configuration of an egress router in redirect mode:
<.> Optional: The namespace field specifies the namespace to create the egress router in. If you do not specify a value in the file or on the command line, the default namespace is used.
<.> The addresses field specifies the IP addresses to configure on the secondary network interface.
<.> The ip field specifies the reserved source IP address and netmask from the physical network that the node is on to use with egress router pod. Use CIDR notation to specify the IP address and netmask.
<.> The gateway field specifies the IP address of the network gateway.
<.> Optional: The redirectRules field specifies a combination of egress destination IP address, egress router port, and protocol. Incoming connections to the egress router on the specified port and protocol are routed to the destination IP address.
<.> Optional: The targetPort field specifies the network port on the destination IP address. If this field is not specified, traffic is routed to the same network port that it arrived on.
<.> The protocol field supports TCP, UDP, or SCTP.
<.> Optional: The fallbackIP field specifies a destination IP address. If you do not specify any redirect rules, the egress router sends all traffic to this fallback IP address. If you specify redirect rules, any connections to network ports that are not defined in the rules are sent by the egress router to this fallback IP address. If you do not specify this field, the egress router rejects connections to network ports that are not defined in the rules.
Example egress router specification
25.18.2. Deploying an egress router in redirect mode
You can deploy an egress router to redirect traffic from its own reserved source IP address to one or more destination IP addresses.
After you add an egress router, the client pods that need to use the reserved source IP address must be modified to connect to the egress router rather than connecting directly to the destination IP.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
- Create an egress router definition.
To ensure that other pods can find the IP address of the egress router pod, create a service that uses the egress router, as in the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> Specify the label for the egress router. The value shown is added by the Cluster Network Operator and is not configurable.
After you create the service, your pods can connect to the service. The egress router pod redirects traffic to the corresponding port on the destination IP address. The connections originate from the reserved source IP address.
Verification
To verify that the Cluster Network Operator started the egress router, complete the following procedure:
View the network attachment definition that the Operator created for the egress router:
oc get network-attachment-definition egress-router-cni-nad
$ oc get network-attachment-definition egress-router-cni-nadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the network attachment definition is not configurable.
Example output
NAME AGE egress-router-cni-nad 18m
NAME AGE egress-router-cni-nad 18mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the deployment for the egress router pod:
oc get deployment egress-router-cni-deployment
$ oc get deployment egress-router-cni-deploymentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the deployment is not configurable.
Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE egress-router-cni-deployment 1/1 1 1 18m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE egress-router-cni-deployment 1/1 1 1 18mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the status of the egress router pod:
oc get pods -l app=egress-router-cni
$ oc get pods -l app=egress-router-cniCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE egress-router-cni-deployment-575465c75c-qkq6m 1/1 Running 0 18m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE egress-router-cni-deployment-575465c75c-qkq6m 1/1 Running 0 18mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - View the logs and the routing table for the egress router pod.
Get the node name for the egress router pod:
POD_NODENAME=$(oc get pod -l app=egress-router-cni -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.nodeName}")$ POD_NODENAME=$(oc get pod -l app=egress-router-cni -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.nodeName}")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter into a debug session on the target node. This step instantiates a debug pod called
<node_name>-debug:oc debug node/$POD_NODENAME
$ oc debug node/$POD_NODENAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set
/hostas the root directory within the debug shell. The debug pod mounts the root file system of the host in/hostwithin the pod. By changing the root directory to/host, you can run binaries from the executable paths of the host:chroot /host
# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From within the
chrootenvironment console, display the egress router logs:cat /tmp/egress-router-log
# cat /tmp/egress-router-logCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The logging file location and logging level are not configurable when you start the egress router by creating an
EgressRouterobject as described in this procedure.From within the
chrootenvironment console, get the container ID:crictl ps --name egress-router-cni-pod | awk '{print $1}'# crictl ps --name egress-router-cni-pod | awk '{print $1}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
CONTAINER bac9fae69ddb6
CONTAINER bac9fae69ddb6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Determine the process ID of the container. In this example, the container ID is
bac9fae69ddb6:crictl inspect -o yaml bac9fae69ddb6 | grep 'pid:' | awk '{print $2}'# crictl inspect -o yaml bac9fae69ddb6 | grep 'pid:' | awk '{print $2}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
68857
68857Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the network namespace of the container:
nsenter -n -t 68857
# nsenter -n -t 68857Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the routing table:
ip route
# ip routeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example output, the
net1network interface is the default route. Traffic for the cluster network uses theeth0network interface. Traffic for the192.168.12.0/24network uses thenet1network interface and originates from the reserved source IP address192.168.12.99. The pod routes all other traffic to the gateway at IP address192.168.12.1. Routing for the service network is not shown.Example output
default via 192.168.12.1 dev net1 10.128.10.0/23 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.128.10.18 192.168.12.0/24 dev net1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.12.99 192.168.12.1 dev net1
default via 192.168.12.1 dev net1 10.128.10.0/23 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.128.10.18 192.168.12.0/24 dev net1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.12.99 192.168.12.1 dev net1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.19. Enabling multicast for a project
25.19.1. About multicast
With IP multicast, data is broadcast to many IP addresses simultaneously.
- At this time, multicast is best used for low-bandwidth coordination or service discovery and not a high-bandwidth solution.
-
By default, network policies affect all connections in a namespace. However, multicast is unaffected by network policies. If multicast is enabled in the same namespace as your network policies, it is always allowed, even if there is a
deny-allnetwork policy. Cluster administrators should consider the implications to the exemption of multicast from network policies before enabling it.
Multicast traffic between OpenShift Container Platform pods is disabled by default. If you are using the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin, you can enable multicast on a per-project basis.
25.19.2. Enabling multicast between pods
You can enable multicast between pods for your project.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Run the following command to enable multicast for a project. Replace
<namespace>with the namespace for the project you want to enable multicast for.oc annotate namespace <namespace> \ k8s.ovn.org/multicast-enabled=true$ oc annotate namespace <namespace> \ k8s.ovn.org/multicast-enabled=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the annotation:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that multicast is enabled for a project, complete the following procedure:
Change your current project to the project that you enabled multicast for. Replace
<project>with the project name.oc project <project>
$ oc project <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod to act as a multicast receiver:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod to act as a multicast sender:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a new terminal window or tab, start the multicast listener.
Get the IP address for the Pod:
POD_IP=$(oc get pods mlistener -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')$ POD_IP=$(oc get pods mlistener -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the multicast listener by entering the following command:
oc exec mlistener -i -t -- \ socat UDP4-RECVFROM:30102,ip-add-membership=224.1.0.1:$POD_IP,fork EXEC:hostname$ oc exec mlistener -i -t -- \ socat UDP4-RECVFROM:30102,ip-add-membership=224.1.0.1:$POD_IP,fork EXEC:hostnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Start the multicast transmitter.
Get the pod network IP address range:
CIDR=$(oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ -o jsonpath='{.status.clusterNetwork[0].cidr}')$ CIDR=$(oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ -o jsonpath='{.status.clusterNetwork[0].cidr}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To send a multicast message, enter the following command:
oc exec msender -i -t -- \ /bin/bash -c "echo | socat STDIO UDP4-DATAGRAM:224.1.0.1:30102,range=$CIDR,ip-multicast-ttl=64"$ oc exec msender -i -t -- \ /bin/bash -c "echo | socat STDIO UDP4-DATAGRAM:224.1.0.1:30102,range=$CIDR,ip-multicast-ttl=64"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If multicast is working, the previous command returns the following output:
mlistener
mlistenerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.20. Disabling multicast for a project
25.20.1. Disabling multicast between pods
You can disable multicast between pods for your project.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Disable multicast by running the following command:
oc annotate namespace <namespace> \ k8s.ovn.org/multicast-enabled-$ oc annotate namespace <namespace> \1 k8s.ovn.org/multicast-enabled-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
namespacefor the project you want to disable multicast for.
TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to delete the annotation:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.21. Tracking network flows
As a cluster administrator, you can collect information about pod network flows from your cluster to assist with the following areas:
- Monitor ingress and egress traffic on the pod network.
- Troubleshoot performance issues.
- Gather data for capacity planning and security audits.
When you enable the collection of the network flows, only the metadata about the traffic is collected. For example, packet data is not collected, but the protocol, source address, destination address, port numbers, number of bytes, and other packet-level information is collected.
The data is collected in one or more of the following record formats:
- NetFlow
- sFlow
- IPFIX
When you configure the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) with one or more collector IP addresses and port numbers, the Operator configures Open vSwitch (OVS) on each node to send the network flows records to each collector.
You can configure the Operator to send records to more than one type of network flow collector. For example, you can send records to NetFlow collectors and also send records to sFlow collectors.
When OVS sends data to the collectors, each type of collector receives identical records. For example, if you configure two NetFlow collectors, OVS on a node sends identical records to the two collectors. If you also configure two sFlow collectors, the two sFlow collectors receive identical records. However, each collector type has a unique record format.
Collecting the network flows data and sending the records to collectors affects performance. Nodes process packets at a slower rate. If the performance impact is too great, you can delete the destinations for collectors to disable collecting network flows data and restore performance.
Enabling network flow collectors might have an impact on the overall performance of the cluster network.
25.21.1. Network object configuration for tracking network flows
The fields for configuring network flows collectors in the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) are shown in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The name of the CNO object. This name is always |
|
|
|
One or more of |
|
|
| A list of IP address and network port pairs for up to 10 collectors. |
|
|
| A list of IP address and network port pairs for up to 10 collectors. |
|
|
| A list of IP address and network port pairs for up to 10 collectors. |
After applying the following manifest to the CNO, the Operator configures Open vSwitch (OVS) on each node in the cluster to send network flows records to the NetFlow collector that is listening at 192.168.1.99:2056.
Example configuration for tracking network flows
25.21.2. Adding destinations for network flows collectors
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) to send network flows metadata about the pod network to a network flows collector.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have a network flows collector and know the IP address and port that it listens on.
Procedure
Create a patch file that specifies the network flows collector type and the IP address and port information of the collectors:
spec: exportNetworkFlows: netFlow: collectors: - 192.168.1.99:2056spec: exportNetworkFlows: netFlow: collectors: - 192.168.1.99:2056Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the CNO with the network flows collectors:
oc patch network.operator cluster --type merge -p "$(cat <file_name>.yaml)"
$ oc patch network.operator cluster --type merge -p "$(cat <file_name>.yaml)"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verification is not typically necessary. You can run the following command to confirm that Open vSwitch (OVS) on each node is configured to send network flows records to one or more collectors.
View the Operator configuration to confirm that the
exportNetworkFlowsfield is configured:oc get network.operator cluster -o jsonpath="{.spec.exportNetworkFlows}"$ oc get network.operator cluster -o jsonpath="{.spec.exportNetworkFlows}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
{"netFlow":{"collectors":["192.168.1.99:2056"]}}{"netFlow":{"collectors":["192.168.1.99:2056"]}}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the network flows configuration in OVS from each node:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.21.3. Deleting all destinations for network flows collectors
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) to stop sending network flows metadata to a network flows collector.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster with a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Remove all network flows collectors:
oc patch network.operator cluster --type='json' \ -p='[{"op":"remove", "path":"/spec/exportNetworkFlows"}]'$ oc patch network.operator cluster --type='json' \ -p='[{"op":"remove", "path":"/spec/exportNetworkFlows"}]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
25.22. Configuring hybrid networking
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the Red Hat OpenShift Networking OVN-Kubernetes network plugin to allow Linux and Windows nodes to host Linux and Windows workloads, respectively.
25.22.1. Configuring hybrid networking with OVN-Kubernetes
You can configure your cluster to use hybrid networking with the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin. This allows a hybrid cluster that supports different node networking configurations.
This configuration is necessary to run both Linux and Windows nodes in the same cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to the cluster as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Ensure that the cluster uses the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
Procedure
To configure the OVN-Kubernetes hybrid network overlay, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
cidr- Specify the CIDR configuration used for nodes on the additional overlay network. This CIDR must not overlap with the cluster network CIDR.
hostPrefix-
Specifies the subnet prefix length to assign to each individual node. For example, if
hostPrefixis set to23, then each node is assigned a/23subnet out of the givencidr, which allows for 510 (2^(32 - 23) - 2) pod IP addresses. If you are required to provide access to nodes from an external network, configure load balancers and routers to manage the traffic. hybridOverlayVXLANPort-
Specify a custom VXLAN port for the additional overlay network. This is required for running Windows nodes in a cluster installed on vSphere, and must not be configured for any other cloud provider. The custom port can be any open port excluding the default
4789port. For more information on this requirement, see the Microsoft documentation on Pod-to-pod connectivity between hosts is broken.
NoteWindows Server Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC): Windows Server 2019 is not supported on clusters with a custom
hybridOverlayVXLANPortvalue because this Windows server version does not support selecting a custom VXLAN port.Example output
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patched
network.operator.openshift.io/cluster patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the configuration is active, enter the following command. It can take several minutes for the update to apply.
oc get network.operator.openshift.io -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.defaultNetwork.ovnKubernetesConfig}"$ oc get network.operator.openshift.io -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.defaultNetwork.ovnKubernetesConfig}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 26. OpenShift SDN network plugin
26.1. About the OpenShift SDN network plugin
Part of Red Hat OpenShift Networking, OpenShift SDN is a network plugin that uses a software-defined networking (SDN) approach to provide a unified cluster network that enables communication between pods across the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This pod network is established and maintained by OpenShift SDN, which configures an overlay network by using Open vSwitch (OVS).
For a cloud controller manager (CCM) with the --cloud-provider=external option set to cloud-provider-vsphere, a known issue exists for a cluster that operates in a networking environment with multiple subnets.
When you upgrade your cluster from OpenShift Container Platform 4.12 to OpenShift Container Platform 4.13, the CCM selects a wrong node IP address and this operation generates an error message in the namespaces/openshift-cloud-controller-manager/pods/vsphere-cloud-controller-manager logs. The error message indicates a mismatch with the node IP address and the vsphere-cloud-controller-manager pod IP address in your cluster.
The known issue might not impact the cluster upgrade operation, but you can set the correct IP address in both the nodeNetworking.external.networkSubnetCidr and the nodeNetworking.internal.networkSubnetCidr parameters for the nodeNetworking object that your cluster uses for its networking requirements.
26.1.1. OpenShift SDN network isolation modes
OpenShift SDN provides three SDN modes for configuring the pod network:
-
Network policy mode allows project administrators to configure their own isolation policies using
NetworkPolicyobjects. Network policy is the default mode in OpenShift Container Platform 4.13. - Multitenant mode provides project-level isolation for pods and services. Pods from different projects cannot send packets to or receive packets from pods and services of a different project. You can disable isolation for a project, allowing it to send network traffic to all pods and services in the entire cluster and receive network traffic from those pods and services.
- Subnet mode provides a flat pod network where every pod can communicate with every other pod and service. The network policy mode provides the same functionality as subnet mode.
26.1.2. Supported network plugin feature matrix
Red Hat OpenShift Networking offers two options for the network plugin, OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes, for the network plugin. The following table summarizes the current feature support for both network plugins:
| Feature | OpenShift SDN | OVN-Kubernetes |
|---|---|---|
| Egress IPs | Supported | Supported |
| Egress firewall | Supported | Supported [1] |
| Egress router | Supported | Supported [2] |
| Hybrid networking | Not supported | Supported |
| IPsec encryption for intra-cluster communication | Not supported | Supported |
| IPv4 single-stack | Supported | Supported |
| IPv6 single-stack | Not supported | Supported [3] |
| IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack | Not Supported | Supported [4] |
| IPv6/IPv4 dual-stack | Not supported | Supported [5] |
| Kubernetes network policy | Supported | Supported |
| Kubernetes network policy logs | Not supported | Supported |
| Hardware offloading | Not supported | Supported |
| Multicast | Supported | Supported |
- Egress firewall is also known as egress network policy in OpenShift SDN. This is not the same as network policy egress.
- Egress router for OVN-Kubernetes supports only redirect mode.
- IPv6 single-stack networking on a bare-metal platform.
- IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack networking on bare-metal, VMware vSphere (installer-provisioned infrastructure installations only), IBM Power®, and IBM Z® platforms. On VMware vSphere, dual-stack networking limitations exist.
- IPv6/IPv4 dual-stack networking on bare-metal and IBM Power® platforms.
26.2. Migrating to the OpenShift SDN network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can migrate to the OpenShift SDN network plugin from the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
To learn more about OpenShift SDN, read About the OpenShift SDN network plugin.
26.2.1. How the migration process works
The following table summarizes the migration process by segmenting between the user-initiated steps in the process and the actions that the migration performs in response.
| User-initiated steps | Migration activity |
|---|---|
|
Set the |
|
|
Update the |
|
| Reboot each node in the cluster. |
|
26.2.2. Migrating to the OpenShift SDN network plugin
Cluster administrators can roll back to the OpenShift SDN Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin by using the offline migration method. During the migration you must manually reboot every node in your cluster. With the offline migration method, there is some downtime, during which your cluster is unreachable.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - A cluster installed on infrastructure configured with the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
- A recent backup of the etcd database is available.
- A reboot can be triggered manually for each node.
- The cluster is in a known good state, without any errors.
Procedure
Stop all of the machine configuration pools managed by the Machine Config Operator (MCO):
Stop the
masterconfiguration pool by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": true } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": true } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop the
workermachine configuration pool by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec":{ "paused": true } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec":{ "paused": true } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To prepare for the migration, set the migration field to
nullby entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the migration status is empty for the
Network.config.openshift.ioobject by entering the following command in your CLI. Empty command output indicates that the object is not in a migration operation.oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration}'$ oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the patch to the
Network.operator.openshift.ioobject to set the network plugin back to OpenShift SDN by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantIf you applied the patch to the
Network.config.openshift.ioobject before the patch operation finalizes on theNetwork.operator.openshift.ioobject, the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) enters into a degradation state and this causes a slight delay until the CNO recovers from the degraded state.Confirm that the migration status of the network plugin for the
Network.config.openshift.io clusterobject isOpenShiftSDNby entering the following command in your CLI:oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration.networkType}'$ oc get Network.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.migration.networkType}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the patch to the
Network.config.openshift.ioobject to set the network plugin back to OpenShift SDN by entering the following command in your CLI:oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } }'$ oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OpenShiftSDN" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Disable automatic migration of several OVN-Kubernetes capabilities to the OpenShift SDN equivalents:
- Egress IPs
- Egress firewall
- Multicast
To disable automatic migration of the configuration for any of the previously noted OpenShift SDN features, specify the following keys:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
bool: Specifies whether to enable migration of the feature. The default istrue.Optional: You can customize the following settings for OpenShift SDN to meet your network infrastructure requirements:
- Maximum transmission unit (MTU)
- VXLAN port
To customize either or both of the previously noted settings, customize and enter the following command in your CLI. If you do not need to change the default value, omit the key from the patch.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow mtu-
The MTU for the VXLAN overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically, but if the nodes in your cluster do not all use the same MTU, then you must set this explicitly to
50less than the smallest node MTU value. port-
The UDP port for the VXLAN overlay network. If a value is not specified, the default is
4789. The port cannot be the same as the Geneve port that is used by OVN-Kubernetes. The default value for the Geneve port is6081.
Example patch command
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reboot each node in your cluster. You can reboot the nodes in your cluster with either of the following approaches:
With the
oc rshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow With the
sshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following. The script assumes that you have configured sudo to not prompt for a password.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Wait until the Multus daemon set rollout completes. Run the following command to see your rollout status:
oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multus
$ oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the Multus pods is in the form of
multus-<xxxxx>where<xxxxx>is a random sequence of letters. It might take several moments for the pods to restart.Example output
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled out
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the nodes in your cluster have rebooted and the multus pods are rolled out, start all of the machine configuration pools by running the following commands::
Start the master configuration pool:
oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool master --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the worker configuration pool:
oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'$ oc patch MachineConfigPool worker --type='merge' --patch \ '{ "spec": { "paused": false } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
As the MCO updates machines in each config pool, it reboots each node.
By default the MCO updates a single machine per pool at a time, so the time that the migration requires to complete grows with the size of the cluster.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the following statements are true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<config_name>is the name of the machine config from themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.
Confirm that the migration succeeded:
To confirm that the network plugin is OpenShift SDN, enter the following command in your CLI. The value of
status.networkTypemust beOpenShiftSDN.oc get Network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'$ oc get Network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the cluster nodes are in the
Readystate, enter the following command in your CLI:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If a node is stuck in the
NotReadystate, investigate the machine config daemon pod logs and resolve any errors.To list the pods, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The names for the config daemon pods are in the following format:
machine-config-daemon-<seq>. The<seq>value is a random five character alphanumeric sequence.To display the pod log for each machine config daemon pod shown in the previous output, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
podis the name of a machine config daemon pod.- Resolve any errors in the logs shown by the output from the previous command.
To confirm that your pods are not in an error state, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'$ oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If pods on a node are in an error state, reboot that node.
Complete the following steps only if the migration succeeds and your cluster is in a good state:
To remove the migration configuration from the Cluster Network Operator configuration object, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the OVN-Kubernetes configuration, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "ovnKubernetesConfig":null } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "ovnKubernetesConfig":null } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the OVN-Kubernetes network provider namespace, enter the following command in your CLI:
oc delete namespace openshift-ovn-kubernetes
$ oc delete namespace openshift-ovn-kubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
26.3. Rolling back to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can rollback to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin from the OpenShift SDN network plugin if the migration to OpenShift SDN is unsuccessful.
To learn more about OVN-Kubernetes, read About the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
26.3.1. Migrating to the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin
As a cluster administrator, you can change the network plugin for your cluster to OVN-Kubernetes. During the migration, you must reboot every node in your cluster.
While performing the migration, your cluster is unavailable and workloads might be interrupted. Perform the migration only when an interruption in service is acceptable.
Prerequisites
- You have a cluster configured with the OpenShift SDN CNI network plugin in the network policy isolation mode.
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - You have a recent backup of the etcd database.
- You can manually reboot each node.
- You checked that your cluster is in a known good state without any errors.
-
You created a security group rule that allows User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets on port
6081for all nodes on all cloud platforms.
Procedure
To backup the configuration for the cluster network, enter the following command:
oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster -o yaml > cluster-openshift-sdn.yaml
$ oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster -o yaml > cluster-openshift-sdn.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
OVN_SDN_MIGRATION_TIMEOUTenvironment variable is set and is equal to0sby running the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the configuration from the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) configuration object by running the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{"spec":{"migration":null}}'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{"spec":{"migration":null}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy(NNCP) custom resource (CR) that defines the primary network interface for the OpenShift SDN network plugin by completing the following steps:Check that the existing NNCP CR bonded the primary interface to your cluster by entering the following command:
oc get nncp
$ oc get nncpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS REASON bondmaster0 Available SuccessfullyConfigured
NAME STATUS REASON bondmaster0 Available SuccessfullyConfiguredCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Network Manager stores the connection profile for the bonded primary interface in the
/etc/NetworkManager/system-connectionssystem path.Remove the NNCP from your cluster:
oc delete nncp <nncp_manifest_filename>
$ oc delete nncp <nncp_manifest_filename>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To prepare all the nodes for the migration, set the
migrationfield on the CNO configuration object by running the following command:oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis step does not deploy OVN-Kubernetes immediately. Instead, specifying the
migrationfield triggers the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to apply new machine configs to all the nodes in the cluster in preparation for the OVN-Kubernetes deployment.Check that the reboot is finished by running the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that all cluster Operators are available by running the following command:
oc get co
$ oc get coCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively: You can disable automatic migration of several OpenShift SDN capabilities to the OVN-Kubernetes equivalents:
- Egress IPs
- Egress firewall
- Multicast
To disable automatic migration of the configuration for any of the previously noted OpenShift SDN features, specify the following keys:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
bool: Specifies whether to enable migration of the feature. The default istrue.
Optional: You can customize the following settings for OVN-Kubernetes to meet your network infrastructure requirements:
Maximum transmission unit (MTU). Consider the following before customizing the MTU for this optional step:
- If you use the default MTU, and you want to keep the default MTU during migration, this step can be ignored.
- If you used a custom MTU, and you want to keep the custom MTU during migration, you must declare the custom MTU value in this step.
This step does not work if you want to change the MTU value during migration. Instead, you must first follow the instructions for "Changing the cluster MTU". You can then keep the custom MTU value by performing this procedure and declaring the custom MTU value in this step.
NoteOpenShift-SDN and OVN-Kubernetes have different overlay overhead. MTU values should be selected by following the guidelines found on the "MTU value selection" page.
- Geneve (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) overlay network port
- OVN-Kubernetes IPv4 internal subnet
To customize either of the previously noted settings, enter and customize the following command. If you do not need to change the default value, omit the key from the patch.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
mtu-
The MTU for the Geneve overlay network. This value is normally configured automatically, but if the nodes in your cluster do not all use the same MTU, then you must set this explicitly to
100less than the smallest node MTU value. port-
The UDP port for the Geneve overlay network. If a value is not specified, the default is
6081. The port cannot be the same as the VXLAN port that is used by OpenShift SDN. The default value for the VXLAN port is4789. ipv4_subnet-
An IPv4 address range for internal use by OVN-Kubernetes. You must ensure that the IP address range does not overlap with any other subnet used by your OpenShift Container Platform installation. The IP address range must be larger than the maximum number of nodes that can be added to the cluster. The default value is
100.64.0.0/16.
Example patch command to update
mtufieldCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow As the MCO updates machines in each machine config pool, it reboots each node one by one. You must wait until all the nodes are updated. Check the machine config pool status by entering the following command:
oc get mcp
$ oc get mcpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successfully updated node has the following status:
UPDATED=true,UPDATING=false,DEGRADED=false.NoteBy default, the MCO updates one machine per pool at a time, causing the total time the migration takes to increase with the size of the cluster.
Confirm the status of the new machine configuration on the hosts:
To list the machine configuration state and the name of the applied machine configuration, enter the following command:
oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"
$ oc describe node | egrep "hostname|machineconfig"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: Done
kubernetes.io/hostname=master-0 machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfig: rendered-master-c53e221d9d24e1c8bb6ee89dd3d8ad7b machineconfiguration.openshift.io/reason: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/state: DoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the following statements are true:
-
The value of
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/statefield isDone. -
The value of the
machineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield is equal to the value of themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/desiredConfigfield.
-
The value of
To confirm that the machine config is correct, enter the following command:
oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStart
$ oc get machineconfig <config_name> -o yaml | grep ExecStartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
<config_name>is the name of the machine config from themachineconfiguration.openshift.io/currentConfigfield.The machine config must include the following update to the systemd configuration:
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/configure-ovs.sh OVNKubernetes
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/configure-ovs.sh OVNKubernetesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If a node is stuck in the
NotReadystate, investigate the machine config daemon pod logs and resolve any errors.To list the pods, enter the following command:
oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc get pod -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The names for the config daemon pods are in the following format:
machine-config-daemon-<seq>. The<seq>value is a random five character alphanumeric sequence.Display the pod log for the first machine config daemon pod shown in the previous output by enter the following command:
oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operator
$ oc logs <pod> -n openshift-machine-config-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
podis the name of a machine config daemon pod.- Resolve any errors in the logs shown by the output from the previous command.
To start the migration, configure the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin by using one of the following commands:
To specify the network provider without changing the cluster network IP address block, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='merge' --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } }'$ oc patch Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ --type='merge' --patch '{ "spec": { "networkType": "OVNKubernetes" } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To specify a different cluster network IP address block, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
cidris a CIDR block andprefixis the slice of the CIDR block apportioned to each node in your cluster. You cannot use any CIDR block that overlaps with the100.64.0.0/16CIDR block because the OVN-Kubernetes network provider uses this block internally.ImportantYou cannot change the service network address block during the migration.
Verify that the Multus daemon set rollout is complete before continuing with subsequent steps:
oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multus
$ oc -n openshift-multus rollout status daemonset/multusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the Multus pods is in the form of
multus-<xxxxx>where<xxxxx>is a random sequence of letters. It might take several moments for the pods to restart.Example output
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled out
Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 1 out of 6 new pods have been updated... ... Waiting for daemon set "multus" rollout to finish: 5 of 6 updated pods are available... daemon set "multus" successfully rolled outCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To complete changing the network plugin, reboot each node in your cluster. You can reboot the nodes in your cluster with either of the following approaches:
ImportantThe following scripts reboot all of the nodes in the cluster at the same time. This can cause your cluster to be unstable. Another option is to reboot your nodes manually one at a time. Rebooting nodes one-by-one causes considerable downtime in a cluster with many nodes.
Cluster Operators will not work correctly before you reboot the nodes.
With the
oc rshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow With the
sshcommand, you can use a bash script similar to the following. The script assumes that you have configured sudo to not prompt for a password.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Confirm that the migration succeeded:
To confirm that the network plugin is OVN-Kubernetes, enter the following command. The value of
status.networkTypemust beOVNKubernetes.oc get network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'$ oc get network.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.networkType}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that the cluster nodes are in the
Readystate, enter the following command:oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To confirm that your pods are not in an error state, enter the following command:
oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'$ oc get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --sort-by='{.spec.nodeName}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If pods on a node are in an error state, reboot that node.
To confirm that all of the cluster Operators are not in an abnormal state, enter the following command:
oc get co
$ oc get coCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The status of every cluster Operator must be the following:
AVAILABLE="True",PROGRESSING="False",DEGRADED="False". If a cluster Operator is not available or degraded, check the logs for the cluster Operator for more information.
Complete the following steps only if the migration succeeds and your cluster is in a good state:
To remove the migration configuration from the CNO configuration object, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "migration": null } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove custom configuration for the OpenShift SDN network provider, enter the following command:
oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "openshiftSDNConfig": null } } }'$ oc patch Network.operator.openshift.io cluster --type='merge' \ --patch '{ "spec": { "defaultNetwork": { "openshiftSDNConfig": null } } }'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the OpenShift SDN network provider namespace, enter the following command:
oc delete namespace openshift-sdn
$ oc delete namespace openshift-sdnCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After a successful migration operation, remove the
network.openshift.io/network-type-migration-annotation from thenetwork.configcustom resource by entering the following command:oc annotate network.config cluster network.openshift.io/network-type-migration-
$ oc annotate network.config cluster network.openshift.io/network-type-migration-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Next steps
- Optional: After cluster migration, you can convert your IPv4 single-stack cluster to a dual-network cluster network that supports IPv4 and IPv6 address families. For more information, see "Converting to IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack networking".
26.4. Configuring egress IPs for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the OpenShift SDN Container Network Interface (CNI) network plugin to assign one or more egress IP addresses to a project.
26.4.1. Egress IP address architectural design and implementation
By using the OpenShift Container Platform egress IP address functionality, you can ensure that the traffic from one or more pods in one or more namespaces has a consistent source IP address for services outside the cluster network.
For example, you might have a pod that periodically queries a database that is hosted on a server outside of your cluster. To enforce access requirements for the server, a packet filtering device is configured to allow traffic only from specific IP addresses. To ensure that you can reliably allow access to the server from only that specific pod, you can configure a specific egress IP address for the pod that makes the requests to the server.
An egress IP address assigned to a namespace is different from an egress router, which is used to send traffic to specific destinations.
In some cluster configurations, application pods and ingress router pods run on the same node. If you configure an egress IP address for an application project in this scenario, the IP address is not used when you send a request to a route from the application project.
An egress IP address is implemented as an additional IP address on the primary network interface of a node and must be in the same subnet as the primary IP address of the node. The additional IP address must not be assigned to any other node in the cluster.
Egress IP addresses must not be configured in any Linux network configuration files, such as ifcfg-eth0.
26.4.1.1. Platform support
The Egress IP address feature that runs on a primary host network is supported on the following platforms:
| Platform | Supported |
|---|---|
| Bare metal | Yes |
| VMware vSphere | Yes |
| Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) | Yes |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Yes |
| Google Cloud | Yes |
| Microsoft Azure | Yes |
| IBM Z and IBM® LinuxONE | Yes |
| IBM Z and IBM® LinuxONE for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) KVM | Yes |
| IBM Power | Yes |
The Egress IP address feature that runs on secondary host networks is supported on the following platform:
| Platform | Supported |
|---|---|
| Bare metal | Yes |
The assignment of egress IP addresses to control plane nodes with the EgressIP feature is not supported on a cluster provisioned on Amazon Web Services (AWS). (BZ#2039656)
26.4.1.2. Public cloud platform considerations
Typically, public cloud providers place a limit on egress IPs. This means that there is a constraint on the absolute number of assignable IP addresses per node for clusters provisioned on public cloud infrastructure. The maximum number of assignable IP addresses per node, or the IP capacity, can be described in the following formula:
IP capacity = public cloud default capacity - sum(current IP assignments)
IP capacity = public cloud default capacity - sum(current IP assignments)While the Egress IPs capability manages the IP address capacity per node, it is important to plan for this constraint in your deployments. For example, if a public cloud provider limits IP address capacity to 10 IP addresses per node, and you have 8 nodes, the total number of assignable IP addresses is only 80. To achieve a higher IP address capacity, you would need to allocate additional nodes. For example, if you needed 150 assignable IP addresses, you would need to allocate 7 additional nodes.
To confirm the IP capacity and subnets for any node in your public cloud environment, you can enter the oc get node <node_name> -o yaml command. The cloud.network.openshift.io/egress-ipconfig annotation includes capacity and subnet information for the node.
The annotation value is an array with a single object with fields that provide the following information for the primary network interface:
-
interface: Specifies the interface ID on AWS and Azure and the interface name on Google Cloud. -
ifaddr: Specifies the subnet mask for one or both IP address families. -
capacity: Specifies the IP address capacity for the node. On AWS, the IP address capacity is provided per IP address family. On Azure and Google Cloud, the IP address capacity includes both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Automatic attachment and detachment of egress IP addresses for traffic between nodes are available. This allows for traffic from many pods in namespaces to have a consistent source IP address to locations outside of the cluster. This also supports OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes, which is the default networking plugin in Red Hat OpenShift Networking in OpenShift Container Platform 4.13.
The RHOSP egress IP address feature creates a Neutron reservation port called egressip-<IP address>. Using the same RHOSP user as the one used for the OpenShift Container Platform cluster installation, you can assign a floating IP address to this reservation port to have a predictable SNAT address for egress traffic. When an egress IP address on an RHOSP network is moved from one node to another, because of a node failover, for example, the Neutron reservation port is removed and recreated. This means that the floating IP association is lost and you need to manually reassign the floating IP address to the new reservation port.
When an RHOSP cluster administrator assigns a floating IP to the reservation port, OpenShift Container Platform cannot delete the reservation port. The CloudPrivateIPConfig object cannot perform delete and move operations until an RHOSP cluster administrator unassigns the floating IP from the reservation port.
The following examples illustrate the annotation from nodes on several public cloud providers. The annotations are indented for readability.
Example cloud.network.openshift.io/egress-ipconfig annotation on AWS
Example cloud.network.openshift.io/egress-ipconfig annotation on Google Cloud
The following sections describe the IP address capacity for supported public cloud environments for use in your capacity calculation.
26.4.1.2.1. Amazon Web Services (AWS) IP address capacity limits
On AWS, constraints on IP address assignments depend on the instance type configured. For more information, see IP addresses per network interface per instance type
26.4.1.2.2. Google Cloud IP address capacity limits
On Google Cloud, the networking model implements additional node IP addresses through IP address aliasing, rather than IP address assignments. However, IP address capacity maps directly to IP aliasing capacity.
The following capacity limits exist for IP aliasing assignment:
- Per node, the maximum number of IP aliases, both IPv4 and IPv6, is 100.
- Per VPC, the maximum number of IP aliases is unspecified, but OpenShift Container Platform scalability testing reveals the maximum to be approximately 15,000.
For more information, see Per instance quotas and Alias IP ranges overview.
26.4.1.2.3. Microsoft Azure IP address capacity limits
On Azure, the following capacity limits exist for IP address assignment:
- Per NIC, the maximum number of assignable IP addresses, for both IPv4 and IPv6, is 256.
- Per virtual network, the maximum number of assigned IP addresses cannot exceed 65,536.
For more information, see Networking limits.
26.4.1.3. Limitations
The following limitations apply when using egress IP addresses with the OpenShift SDN network plugin:
- You cannot use manually assigned and automatically assigned egress IP addresses on the same nodes.
- If you manually assign egress IP addresses from an IP address range, you must not make that range available for automatic IP assignment.
- You cannot share egress IP addresses across multiple namespaces using the OpenShift SDN egress IP address implementation.
If you need to share IP addresses across namespaces, the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin egress IP address implementation allows you to span IP addresses across multiple namespaces.
If you use OpenShift SDN in multitenant mode, you cannot use egress IP addresses with any namespace that is joined to another namespace by the projects that are associated with them. For example, if project1 and project2 are joined by running the oc adm pod-network join-projects --to=project1 project2 command, neither project can use an egress IP address. For more information, see BZ#1645577.
26.4.1.4. IP address assignment approaches
You can assign egress IP addresses to namespaces by setting the egressIPs parameter of the NetNamespace object. After an egress IP address is associated with a project, OpenShift SDN allows you to assign egress IP addresses to hosts in two ways:
- In the automatically assigned approach, an egress IP address range is assigned to a node.
- In the manually assigned approach, a list of one or more egress IP address is assigned to a node.
Namespaces that request an egress IP address are matched with nodes that can host those egress IP addresses, and then the egress IP addresses are assigned to those nodes. If the egressIPs parameter is set on a NetNamespace object, but no node hosts that egress IP address, then egress traffic from the namespace will be dropped.
High availability of nodes is automatic. If a node that hosts an egress IP address is unreachable and there are nodes that are able to host that egress IP address, then the egress IP address will move to a new node. When the unreachable node comes back online, the egress IP address automatically moves to balance egress IP addresses across nodes.
26.4.1.4.1. Considerations when using automatically assigned egress IP addresses
When using the automatic assignment approach for egress IP addresses the following considerations apply:
-
You set the
egressCIDRsparameter of each node’sHostSubnetresource to indicate the range of egress IP addresses that can be hosted by a node. OpenShift Container Platform sets theegressIPsparameter of theHostSubnetresource based on the IP address range you specify.
If the node hosting the namespace’s egress IP address is unreachable, OpenShift Container Platform will reassign the egress IP address to another node with a compatible egress IP address range. The automatic assignment approach works best for clusters installed in environments with flexibility in associating additional IP addresses with nodes.
26.4.1.4.2. Considerations when using manually assigned egress IP addresses
This approach allows you to control which nodes can host an egress IP address.
If your cluster is installed on public cloud infrastructure, you must ensure that each node that you assign egress IP addresses to has sufficient spare capacity to host the IP addresses. For more information, see "Platform considerations" in a previous section.
When using the manual assignment approach for egress IP addresses the following considerations apply:
-
You set the
egressIPsparameter of each node’sHostSubnetresource to indicate the IP addresses that can be hosted by a node. - Multiple egress IP addresses per namespace are supported.
If a namespace has multiple egress IP addresses and those addresses are hosted on multiple nodes, the following additional considerations apply:
- If a pod is on a node that is hosting an egress IP address, that pod always uses the egress IP address on the node.
- If a pod is not on a node that is hosting an egress IP address, that pod uses an egress IP address at random.
26.4.2. Configuring automatically assigned egress IP addresses for a namespace
In OpenShift Container Platform you can enable automatic assignment of an egress IP address for a specific namespace across one or more nodes.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Update the
NetNamespaceobject with the egress IP address using the following JSON:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<project_name>- Specifies the name of the project.
<ip_address>-
Specifies one or more egress IP addresses for the
egressIPsarray.
For example, to assign
project1to an IP address of 192.168.1.100 andproject2to an IP address of 192.168.1.101:oc patch netnamespace project1 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.100"]}' oc patch netnamespace project2 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.101"]}'$ oc patch netnamespace project1 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.100"]}' $ oc patch netnamespace project2 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.101"]}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBecause OpenShift SDN manages the
NetNamespaceobject, you can make changes only by modifying the existingNetNamespaceobject. Do not create a newNetNamespaceobject.Indicate which nodes can host egress IP addresses by setting the
egressCIDRsparameter for each host using the following JSON:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<node_name>- Specifies a node name.
<ip_address_range>-
Specifies an IP address range in CIDR format. You can specify more than one address range for the
egressCIDRsarray.
For example, to set
node1andnode2to host egress IP addresses in the range 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255:oc patch hostsubnet node1 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressCIDRs": ["192.168.1.0/24"]}' oc patch hostsubnet node2 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressCIDRs": ["192.168.1.0/24"]}'$ oc patch hostsubnet node1 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressCIDRs": ["192.168.1.0/24"]}' $ oc patch hostsubnet node2 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressCIDRs": ["192.168.1.0/24"]}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform automatically assigns specific egress IP addresses to available nodes in a balanced way. In this case, it assigns the egress IP address 192.168.1.100 to
node1and the egress IP address 192.168.1.101 tonode2or vice versa.
26.4.3. Configuring manually assigned egress IP addresses for a namespace
In OpenShift Container Platform you can associate one or more egress IP addresses with a namespace.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Update the
NetNamespaceobject by specifying the following JSON object with the desired IP addresses:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<project_name>- Specifies the name of the project.
<ip_address>-
Specifies one or more egress IP addresses for the
egressIPsarray.
For example, to assign the
project1project to the IP addresses192.168.1.100and192.168.1.101:oc patch netnamespace project1 --type=merge \ -p '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.100","192.168.1.101"]}'$ oc patch netnamespace project1 --type=merge \ -p '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.100","192.168.1.101"]}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To provide high availability, set the
egressIPsvalue to two or more IP addresses on different nodes. If multiple egress IP addresses are set, then pods use all egress IP addresses roughly equally.NoteBecause OpenShift SDN manages the
NetNamespaceobject, you can make changes only by modifying the existingNetNamespaceobject. Do not create a newNetNamespaceobject.Manually assign the egress IP address to the node hosts.
If your cluster is installed on public cloud infrastructure, you must confirm that the node has available IP address capacity.
Set the
egressIPsparameter on theHostSubnetobject on the node host. Using the following JSON, include as many IP addresses as you want to assign to that node host:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<node_name>- Specifies a node name.
<ip_address>-
Specifies an IP address. You can specify more than one IP address for the
egressIPsarray.
For example, to specify that
node1should have the egress IPs192.168.1.100,192.168.1.101, and192.168.1.102:oc patch hostsubnet node1 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.100", "192.168.1.101", "192.168.1.102"]}'$ oc patch hostsubnet node1 --type=merge -p \ '{"egressIPs": ["192.168.1.100", "192.168.1.101", "192.168.1.102"]}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the previous example, all egress traffic for
project1will be routed to the node hosting the specified egress IP, and then connected through Network Address Translation (NAT) to that IP address.
26.4.4. Additional resources
- If you are configuring manual egress IP address assignment, see Platform considerations for information about IP capacity planning.
26.5. Configuring an egress firewall for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can create an egress firewall for a project that restricts egress traffic leaving your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
26.5.1. How an egress firewall works in a project
As a cluster administrator, you can use an egress firewall to limit the external hosts that some or all pods can access from within the cluster. An egress firewall supports the following scenarios:
- A pod can only connect to internal hosts and cannot start connections to the public internet.
- A pod can only connect to the public internet and cannot start connections to internal hosts that are outside the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- A pod cannot reach specified internal subnets or hosts outside the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- A pod can connect to only specific external hosts.
For example, you can allow one project access to a specified IP range but deny the same access to a different project. Or you can restrict application developers from updating from Python pip mirrors, and force updates to come only from approved sources.
Egress firewall does not apply to the host network namespace. Egress firewall rules do not impact any pods that have host networking enabled.
You configure an egress firewall policy by creating an EgressNetworkPolicy custom resource (CR) object. The egress firewall matches network traffic that meets any of the following criteria:
- An IP address range in CIDR format
- A DNS name that resolves to an IP address
You must have OpenShift SDN configured to use either the network policy or multitenant mode to configure an egress firewall.
If you use network policy mode, an egress firewall is compatible with only one policy per namespace and will not work with projects that share a network, such as global projects.
Egress firewall rules do not apply to traffic that goes through routers. Any user with permission to create a Route CR object can bypass egress firewall policy rules by creating a route that points to a forbidden destination.
26.5.1.1. Limitations of an egress firewall
An egress firewall has the following limitations:
No project can have more than one EgressNetworkPolicy object.
ImportantThe creation of more than one EgressNetworkPolicy object is allowed, however it should not be done. When you create more than one EgressNetworkPolicy object, the following message is returned:
dropping all rules. In actuality, all external traffic is dropped, which can cause security risks for your organization.- A maximum of one EgressNetworkPolicy object with a maximum of 1,000 rules can be defined per project.
-
The
defaultproject cannot use an egress firewall. When using the OpenShift SDN network plugin in multitenant mode, the following limitations apply:
-
Global projects cannot use an egress firewall. You can make a project global by using the
oc adm pod-network make-projects-globalcommand. -
Projects merged by using the
oc adm pod-network join-projectscommand cannot use an egress firewall in any of the joined projects.
-
Global projects cannot use an egress firewall. You can make a project global by using the
-
If you create a selectorless service and manually define endpoints or
EndpointSlicesthat point to external IPs, traffic to the service IP might still be allowed, even if yourEgressNetworkPolicyis configured to deny all egress traffic. This occurs because OpenShift SDN does not fully enforce egress network policies for these external endpoints. Consequently, this might result in unexpected access to external services.
Violating any of these restrictions results in a broken egress firewall for the project. As a result, all external network traffic drops, which can cause security risks for your organization.
You can create an Egress Firewall resource in the kube-node-lease, kube-public, kube-system, openshift and openshift- projects.
26.5.1.2. Matching order for egress firewall policy rules
The OVN-Kubernetes network plugin evaluates egress firewall policy rules based on the first-to-last order of how you defined the rules. The first rule that matches an egress connection from a pod applies. The plugin ignores any subsequent rules for that connection.
26.5.1.3. Domain Name Server (DNS) resolution
If you use DNS names in any of your egress firewall policy rules, proper resolution of the domain names is subject to the following restrictions:
- Domain name updates are polled based on a time-to-live (TTL) duration. By default, the duration is 30 seconds. When the egress firewall controller queries the local name servers for a domain name, if the response includes a TTL that is less than 30 seconds, the controller sets the duration to the returned value. If the TTL in the response is greater than 30 minutes, the controller sets the duration to 30 minutes. If the TTL is between 30 seconds and 30 minutes, the controller ignores the value and sets the duration to 30 seconds.
- The pod must resolve the domain from the same local name servers when necessary. Otherwise the IP addresses for the domain known by the egress firewall controller and the pod can be different. If the IP addresses for a hostname differ, consistent enforcement of the egress firewall does not apply.
- Because the egress firewall controller and pods asynchronously poll the same local name server, the pod might obtain the updated IP address before the egress controller does, which causes a race condition. Due to this current limitation, domain name usage in EgressNetworkPolicy objects is only recommended for domains with infrequent IP address changes.
Using DNS names in your egress firewall policy does not affect local DNS resolution through CoreDNS.
If your egress firewall policy uses domain names, and an external DNS server handles DNS resolution for an affected pod, you must include egress firewall rules that allow access to the IP addresses of your DNS server.
26.5.2. EgressNetworkPolicy custom resource (CR) object
You can define one or more rules for an egress firewall. A rule is either an Allow rule or a Deny rule, with a specification for the traffic that the rule applies to.
The following YAML describes an EgressNetworkPolicy CR object:
EgressNetworkPolicy object
26.5.2.1. EgressNetworkPolicy rules
The following YAML describes an egress firewall rule object. The user can select either an IP address range in CIDR format, a domain name, or use the nodeSelector to allow or deny egress traffic. The egress stanza expects an array of one or more objects.
Egress policy rule stanza
egress:
- type: <type>
to:
cidrSelector: <cidr>
dnsName: <dns_name>
egress:
- type: <type>
to:
cidrSelector: <cidr>
dnsName: <dns_name> 26.5.2.2. Example EgressNetworkPolicy CR objects
The following example defines several egress firewall policy rules:
- 1
- A collection of egress firewall policy rule objects.
26.5.3. Creating an egress firewall policy object
As a cluster administrator, you can create an egress firewall policy object for a project.
If the project already has an EgressNetworkPolicy object defined, you must edit the existing policy to make changes to the egress firewall rules.
Prerequisites
- A cluster that uses the OpenShift SDN network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Create a policy rule:
-
Create a
<policy_name>.yamlfile where<policy_name>describes the egress policy rules. - In the file you created, define an egress policy object.
-
Create a
Enter the following command to create the policy object. Replace
<policy_name>with the name of the policy and<project>with the project that the rule applies to.oc create -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <project>
$ oc create -f <policy_name>.yaml -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example, a new EgressNetworkPolicy object is created in a project named
project1:oc create -f default.yaml -n project1
$ oc create -f default.yaml -n project1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
egressnetworkpolicy.network.openshift.io/v1 created
egressnetworkpolicy.network.openshift.io/v1 createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Optional: Save the
<policy_name>.yamlfile so that you can make changes later.
26.6. Editing an egress firewall for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can modify network traffic rules for an existing egress firewall.
26.6.1. Viewing an EgressNetworkPolicy object
You can view an EgressNetworkPolicy object in your cluster.
Prerequisites
- A cluster using the OpenShift SDN network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift Command-line Interface (CLI), commonly known as
oc. - You must log in to the cluster.
Procedure
Optional: To view the names of the EgressNetworkPolicy objects defined in your cluster, enter the following command:
oc get egressnetworkpolicy --all-namespaces
$ oc get egressnetworkpolicy --all-namespacesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To inspect a policy, enter the following command. Replace
<policy_name>with the name of the policy to inspect.oc describe egressnetworkpolicy <policy_name>
$ oc describe egressnetworkpolicy <policy_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
26.7. Editing an egress firewall for a project
As a cluster administrator, you can modify network traffic rules for an existing egress firewall.
26.7.1. Editing an EgressNetworkPolicy object
As a cluster administrator, you can update the egress firewall for a project.
Prerequisites
- A cluster using the OpenShift SDN network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Find the name of the EgressNetworkPolicy object for the project. Replace
<project>with the name of the project.oc get -n <project> egressnetworkpolicy
$ oc get -n <project> egressnetworkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: If you did not save a copy of the EgressNetworkPolicy object when you created the egress network firewall, enter the following command to create a copy.
oc get -n <project> egressnetworkpolicy <name> -o yaml > <filename>.yaml
$ oc get -n <project> egressnetworkpolicy <name> -o yaml > <filename>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<project>with the name of the project. Replace<name>with the name of the object. Replace<filename>with the name of the file to save the YAML to.After making changes to the policy rules, enter the following command to replace the EgressNetworkPolicy object. Replace
<filename>with the name of the file containing the updated EgressNetworkPolicy object.oc replace -f <filename>.yaml
$ oc replace -f <filename>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
26.8. Removing an egress firewall from a project
As a cluster administrator, you can remove an egress firewall from a project to remove all restrictions on network traffic from the project that leaves the OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
26.8.1. Removing an EgressNetworkPolicy object
As a cluster administrator, you can remove an egress firewall from a project.
Prerequisites
- A cluster using the OpenShift SDN network plugin.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You must log in to the cluster as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Find the name of the EgressNetworkPolicy object for the project. Replace
<project>with the name of the project.oc get -n <project> egressnetworkpolicy
$ oc get -n <project> egressnetworkpolicyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the following command to delete the EgressNetworkPolicy object. Replace
<project>with the name of the project and<name>with the name of the object.oc delete -n <project> egressnetworkpolicy <name>
$ oc delete -n <project> egressnetworkpolicy <name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
26.9. Considerations for the use of an egress router pod
26.9.1. About an egress router pod
The OpenShift Container Platform egress router pod redirects traffic to a specified remote server from a private source IP address that is not used for any other purpose. An egress router pod can send network traffic to servers that are set up to allow access only from specific IP addresses.
The egress router pod is not intended for every outgoing connection. Creating large numbers of egress router pods can exceed the limits of your network hardware. For example, creating an egress router pod for every project or application could exceed the number of local MAC addresses that the network interface can handle before reverting to filtering MAC addresses in software.
The egress router image is not compatible with Amazon AWS, Azure Cloud, or any other cloud platform that does not support layer 2 manipulations due to their incompatibility with macvlan traffic.
26.9.1.1. Egress router modes
In redirect mode, an egress router pod configures iptables rules to redirect traffic from its own IP address to one or more destination IP addresses. Client pods that need to use the reserved source IP address must be configured to access the service for the egress router rather than connecting directly to the destination IP. You can access the destination service and port from the application pod by using the curl command. For example:
curl <router_service_IP> <port>
$ curl <router_service_IP> <port>
In HTTP proxy mode, an egress router pod runs as an HTTP proxy on port 8080. This mode only works for clients that are connecting to HTTP-based or HTTPS-based services, but usually requires fewer changes to the client pods to get them to work. Many programs can be told to use an HTTP proxy by setting an environment variable.
In DNS proxy mode, an egress router pod runs as a DNS proxy for TCP-based services from its own IP address to one or more destination IP addresses. To make use of the reserved, source IP address, client pods must be modified to connect to the egress router pod rather than connecting directly to the destination IP address. This modification ensures that external destinations treat traffic as though it were coming from a known source.
Redirect mode works for all services except for HTTP and HTTPS. For HTTP and HTTPS services, use HTTP proxy mode. For TCP-based services with IP addresses or domain names, use DNS proxy mode.
26.9.1.2. Egress router pod implementation
The egress router pod setup is performed by an initialization container. That container runs in a privileged context so that it can configure the macvlan interface and set up iptables rules. After the initialization container finishes setting up the iptables rules, it exits. Next the egress router pod executes the container to handle the egress router traffic. The image used varies depending on the egress router mode.
The environment variables determine which addresses the egress-router image uses. The image configures the macvlan interface to use EGRESS_SOURCE as its IP address, with EGRESS_GATEWAY as the IP address for the gateway.
Network Address Translation (NAT) rules are set up so that connections to the cluster IP address of the pod on any TCP or UDP port are redirected to the same port on IP address specified by the EGRESS_DESTINATION variable.
If only some of the nodes in your cluster are capable of claiming the specified source IP address and using the specified gateway, you can specify a nodeName or nodeSelector to identify which nodes are acceptable.
26.9.1.3. Deployment considerations
An egress router pod adds an additional IP address and MAC address to the primary network interface of the node. As a result, you might need to configure your hypervisor or cloud provider to allow the additional address.
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP)
If you deploy OpenShift Container Platform on RHOSP, you must allow traffic from the IP and MAC addresses of the egress router pod on your OpenStack environment. If you do not allow the traffic, then communication will fail:
openstack port set --allowed-address \ ip_address=<ip_address>,mac_address=<mac_address> <neutron_port_uuid>
$ openstack port set --allowed-address \ ip_address=<ip_address>,mac_address=<mac_address> <neutron_port_uuid>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Red Hat Virtualization (RHV)
- If you are using RHV, you must select No Network Filter for the Virtual network interface controller (vNIC).
- VMware vSphere
- If you are using VMware vSphere, see the VMware documentation for securing vSphere standard switches. View and change VMware vSphere default settings by selecting the host virtual switch from the vSphere Web Client.
Specifically, ensure that the following are enabled:
26.9.1.4. Failover configuration
To avoid downtime, you can deploy an egress router pod with a Deployment resource, as in the following example. To create a new Service object for the example deployment, use the oc expose deployment/egress-demo-controller command.
26.10. Deploying an egress router pod in redirect mode
As a cluster administrator, you can deploy an egress router pod that is configured to redirect traffic to specified destination IP addresses.
26.10.1. Egress router pod specification for redirect mode
Define the configuration for an egress router pod in the Pod object. The following YAML describes the fields for the configuration of an egress router pod in redirect mode:
- 1
- The annotation tells OpenShift Container Platform to create a macvlan network interface on the primary network interface controller (NIC) and move that macvlan interface into the pod’s network namespace. You must include the quotation marks around the
"true"value. To have OpenShift Container Platform create the macvlan interface on a different NIC interface, set the annotation value to the name of that interface. For example,eth1. - 2
- IP address from the physical network that the node is on that is reserved for use by the egress router pod. Optional: You can include the subnet length, the
/24suffix, so that a proper route to the local subnet is set. If you do not specify a subnet length, then the egress router can access only the host specified with theEGRESS_GATEWAYvariable and no other hosts on the subnet. - 3
- Same value as the default gateway used by the node.
- 4
- External server to direct traffic to. Using this example, connections to the pod are redirected to
203.0.113.25, with a source IP address of192.168.12.99.
Example egress router pod specification
26.10.2. Egress destination configuration format
When an egress router pod is deployed in redirect mode, you can specify redirection rules by using one or more of the following formats:
-
<port> <protocol> <ip_address>- Incoming connections to the given<port>should be redirected to the same port on the given<ip_address>.<protocol>is eithertcporudp. -
<port> <protocol> <ip_address> <remote_port>- As above, except that the connection is redirected to a different<remote_port>on<ip_address>. -
<ip_address>- If the last line is a single IP address, then any connections on any other port will be redirected to the corresponding port on that IP address. If there is no fallback IP address then connections on other ports are rejected.
In the example that follows several rules are defined:
-
The first line redirects traffic from local port
80to port80on203.0.113.25. -
The second and third lines redirect local ports
8080and8443to remote ports80and443on203.0.113.26. - The last line matches traffic for any ports not specified in the previous rules.
Example configuration
80 tcp 203.0.113.25 8080 tcp 203.0.113.26 80 8443 tcp 203.0.113.26 443 203.0.113.27
80 tcp 203.0.113.25
8080 tcp 203.0.113.26 80
8443 tcp 203.0.113.26 443
203.0.113.2726.10.3. Deploying an egress router pod in redirect mode
In redirect mode, an egress router pod sets up iptables rules to redirect traffic from its own IP address to one or more destination IP addresses. Client pods that need to use the reserved source IP address must be configured to access the service for the egress router rather than connecting directly to the destination IP. You can access the destination service and port from the application pod by using the curl command. For example:
curl <router_service_IP> <port>
$ curl <router_service_IP> <port>Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
- Create an egress router pod.
To ensure that other pods can find the IP address of the egress router pod, create a service to point to the egress router pod, as in the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your pods can now connect to this service. Their connections are redirected to the corresponding ports on the external server, using the reserved egress IP address.
26.11. Deploying an egress router pod in HTTP proxy mode
As a cluster administrator, you can deploy an egress router pod configured to proxy traffic to specified HTTP and HTTPS-based services.
26.11.1. Egress router pod specification for HTTP mode
Define the configuration for an egress router pod in the Pod object. The following YAML describes the fields for the configuration of an egress router pod in HTTP mode:
- 1
- The annotation tells OpenShift Container Platform to create a macvlan network interface on the primary network interface controller (NIC) and move that macvlan interface into the pod’s network namespace. You must include the quotation marks around the
"true"value. To have OpenShift Container Platform create the macvlan interface on a different NIC interface, set the annotation value to the name of that interface. For example,eth1. - 2
- IP address from the physical network that the node is on that is reserved for use by the egress router pod. Optional: You can include the subnet length, the
/24suffix, so that a proper route to the local subnet is set. If you do not specify a subnet length, then the egress router can access only the host specified with theEGRESS_GATEWAYvariable and no other hosts on the subnet. - 3
- Same value as the default gateway used by the node.
- 4
- A string or YAML multi-line string specifying how to configure the proxy. Note that this is specified as an environment variable in the HTTP proxy container, not with the other environment variables in the init container.
26.11.2. Egress destination configuration format
When an egress router pod is deployed in HTTP proxy mode, you can specify redirection rules by using one or more of the following formats. Each line in the configuration specifies one group of connections to allow or deny:
-
An IP address allows connections to that IP address, such as
192.168.1.1. -
A CIDR range allows connections to that CIDR range, such as
192.168.1.0/24. -
A hostname allows proxying to that host, such as
www.example.com. -
A domain name preceded by
*.allows proxying to that domain and all of its subdomains, such as*.example.com. -
A
!followed by any of the previous match expressions denies the connection instead. -
If the last line is
*, then anything that is not explicitly denied is allowed. Otherwise, anything that is not allowed is denied.
You can also use * to allow connections to all remote destinations.
Example configuration
!*.example.com !192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.1 *
!*.example.com
!192.168.1.0/24
192.168.2.1
*26.11.3. Deploying an egress router pod in HTTP proxy mode
In HTTP proxy mode, an egress router pod runs as an HTTP proxy on port 8080. This mode only works for clients that are connecting to HTTP-based or HTTPS-based services, but usually requires fewer changes to the client pods to get them to work. Many programs can be told to use an HTTP proxy by setting an environment variable.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
- Create an egress router pod.
To ensure that other pods can find the IP address of the egress router pod, create a service to point to the egress router pod, as in the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Ensure the
httpport is set to8080.
To configure the client pod (not the egress proxy pod) to use the HTTP proxy, set the
http_proxyorhttps_proxyvariables:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The service created in the previous step.
NoteUsing the
http_proxyandhttps_proxyenvironment variables is not necessary for all setups. If the above does not create a working setup, then consult the documentation for the tool or software you are running in the pod.
26.12. Deploying an egress router pod in DNS proxy mode
As a cluster administrator, you can deploy an egress router pod configured to proxy traffic to specified DNS names and IP addresses.
26.12.1. Egress router pod specification for DNS mode
Define the configuration for an egress router pod in the Pod object. The following YAML describes the fields for the configuration of an egress router pod in DNS mode:
- 1
- The annotation tells OpenShift Container Platform to create a macvlan network interface on the primary network interface controller (NIC) and move that macvlan interface into the pod’s network namespace. You must include the quotation marks around the
"true"value. To have OpenShift Container Platform create the macvlan interface on a different NIC interface, set the annotation value to the name of that interface. For example,eth1. - 2
- IP address from the physical network that the node is on that is reserved for use by the egress router pod. Optional: You can include the subnet length, the
/24suffix, so that a proper route to the local subnet is set. If you do not specify a subnet length, then the egress router can access only the host specified with theEGRESS_GATEWAYvariable and no other hosts on the subnet. - 3
- Same value as the default gateway used by the node.
- 4
- Specify a list of one or more proxy destinations.
- 5
- Optional: Specify to output the DNS proxy log output to
stdout.
26.12.2. Egress destination configuration format
When the router is deployed in DNS proxy mode, you specify a list of port and destination mappings. A destination may be either an IP address or a DNS name.
An egress router pod supports the following formats for specifying port and destination mappings:
- Port and remote address
-
You can specify a source port and a destination host by using the two field format:
<port> <remote_address>.
The host can be an IP address or a DNS name. If a DNS name is provided, DNS resolution occurs at runtime. For a given host, the proxy connects to the specified source port on the destination host when connecting to the destination host IP address.
Port and remote address pair example
80 172.16.12.11 100 example.com
80 172.16.12.11
100 example.com- Port, remote address, and remote port
-
You can specify a source port, a destination host, and a destination port by using the three field format:
<port> <remote_address> <remote_port>.
The three field format behaves identically to the two field version, with the exception that the destination port can be different than the source port.
Port, remote address, and remote port example
8080 192.168.60.252 80 8443 web.example.com 443
8080 192.168.60.252 80
8443 web.example.com 44326.12.3. Deploying an egress router pod in DNS proxy mode
In DNS proxy mode, an egress router pod acts as a DNS proxy for TCP-based services from its own IP address to one or more destination IP addresses.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
- Create an egress router pod.
Create a service for the egress router pod:
Create a file named
egress-router-service.yamlthat contains the following YAML. Setspec.portsto the list of ports that you defined previously for theEGRESS_DNS_PROXY_DESTINATIONenvironment variable.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create the service, enter the following command:
oc create -f egress-router-service.yaml
$ oc create -f egress-router-service.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pods can now connect to this service. The connections are proxied to the corresponding ports on the external server, using the reserved egress IP address.
26.13. Configuring an egress router pod destination list from a config map
As a cluster administrator, you can define a ConfigMap object that specifies destination mappings for an egress router pod. The specific format of the configuration depends on the type of egress router pod. For details on the format, refer to the documentation for the specific egress router pod.
26.13.1. Configuring an egress router destination mappings with a config map
For a large or frequently-changing set of destination mappings, you can use a config map to externally maintain the list. An advantage of this approach is that permission to edit the config map can be delegated to users without cluster-admin privileges. Because the egress router pod requires a privileged container, it is not possible for users without cluster-admin privileges to edit the pod definition directly.
The egress router pod does not automatically update when the config map changes. You must restart the egress router pod to get updates.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a file containing the mapping data for the egress router pod, as in the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can put blank lines and comments into this file.
Create a
ConfigMapobject from the file:oc delete configmap egress-routes --ignore-not-found
$ oc delete configmap egress-routes --ignore-not-foundCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc create configmap egress-routes \ --from-file=destination=my-egress-destination.txt
$ oc create configmap egress-routes \ --from-file=destination=my-egress-destination.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the previous command, the
egress-routesvalue is the name of theConfigMapobject to create andmy-egress-destination.txtis the name of the file that the data is read from.TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to create the config map:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an egress router pod definition and specify the
configMapKeyRefstanza for theEGRESS_DESTINATIONfield in the environment stanza:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
26.14. Enabling multicast for a project
26.14.1. About multicast
With IP multicast, data is broadcast to many IP addresses simultaneously.
- At this time, multicast is best used for low-bandwidth coordination or service discovery and not a high-bandwidth solution.
-
By default, network policies affect all connections in a namespace. However, multicast is unaffected by network policies. If multicast is enabled in the same namespace as your network policies, it is always allowed, even if there is a
deny-allnetwork policy. Cluster administrators should consider the implications to the exemption of multicast from network policies before enabling it.
Multicast traffic between OpenShift Container Platform pods is disabled by default. If you are using the OpenShift SDN network plugin, you can enable multicast on a per-project basis.
When using the OpenShift SDN network plugin in networkpolicy isolation mode:
-
Multicast packets sent by a pod will be delivered to all other pods in the project, regardless of
NetworkPolicyobjects. Pods might be able to communicate over multicast even when they cannot communicate over unicast. -
Multicast packets sent by a pod in one project will never be delivered to pods in any other project, even if there are
NetworkPolicyobjects that allow communication between the projects.
When using the OpenShift SDN network plugin in multitenant isolation mode:
- Multicast packets sent by a pod will be delivered to all other pods in the project.
- Multicast packets sent by a pod in one project will be delivered to pods in other projects only if each project is joined together and multicast is enabled in each joined project.
26.14.2. Enabling multicast between pods
You can enable multicast between pods for your project.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Run the following command to enable multicast for a project. Replace
<namespace>with the namespace for the project you want to enable multicast for.oc annotate netnamespace <namespace> \ netnamespace.network.openshift.io/multicast-enabled=true$ oc annotate netnamespace <namespace> \ netnamespace.network.openshift.io/multicast-enabled=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that multicast is enabled for a project, complete the following procedure:
Change your current project to the project that you enabled multicast for. Replace
<project>with the project name.oc project <project>
$ oc project <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod to act as a multicast receiver:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod to act as a multicast sender:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a new terminal window or tab, start the multicast listener.
Get the IP address for the Pod:
POD_IP=$(oc get pods mlistener -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')$ POD_IP=$(oc get pods mlistener -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the multicast listener by entering the following command:
oc exec mlistener -i -t -- \ socat UDP4-RECVFROM:30102,ip-add-membership=224.1.0.1:$POD_IP,fork EXEC:hostname$ oc exec mlistener -i -t -- \ socat UDP4-RECVFROM:30102,ip-add-membership=224.1.0.1:$POD_IP,fork EXEC:hostnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Start the multicast transmitter.
Get the pod network IP address range:
CIDR=$(oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ -o jsonpath='{.status.clusterNetwork[0].cidr}')$ CIDR=$(oc get Network.config.openshift.io cluster \ -o jsonpath='{.status.clusterNetwork[0].cidr}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To send a multicast message, enter the following command:
oc exec msender -i -t -- \ /bin/bash -c "echo | socat STDIO UDP4-DATAGRAM:224.1.0.1:30102,range=$CIDR,ip-multicast-ttl=64"$ oc exec msender -i -t -- \ /bin/bash -c "echo | socat STDIO UDP4-DATAGRAM:224.1.0.1:30102,range=$CIDR,ip-multicast-ttl=64"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If multicast is working, the previous command returns the following output:
mlistener
mlistenerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
26.15. Disabling multicast for a project
26.15.1. Disabling multicast between pods
You can disable multicast between pods for your project.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Disable multicast by running the following command:
oc annotate netnamespace <namespace> \ netnamespace.network.openshift.io/multicast-enabled-$ oc annotate netnamespace <namespace> \1 netnamespace.network.openshift.io/multicast-enabled-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
namespacefor the project you want to disable multicast for.
26.16. Configuring network isolation using OpenShift SDN
When your cluster is configured to use the multitenant isolation mode for the OpenShift SDN network plugin, each project is isolated by default. Network traffic is not allowed between pods or services in different projects in multitenant isolation mode.
You can change the behavior of multitenant isolation for a project in two ways:
- You can join one or more projects, allowing network traffic between pods and services in different projects.
- You can disable network isolation for a project. It will be globally accessible, accepting network traffic from pods and services in all other projects. A globally accessible project can access pods and services in all other projects.
26.16.1. Prerequisites
- You must have a cluster configured to use the OpenShift SDN network plugin in multitenant isolation mode.
26.16.2. Joining projects
You can join two or more projects to allow network traffic between pods and services in different projects.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Use the following command to join projects to an existing project network:
oc adm pod-network join-projects --to=<project1> <project2> <project3>
$ oc adm pod-network join-projects --to=<project1> <project2> <project3>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, instead of specifying specific project names, you can use the
--selector=<project_selector>option to specify projects based upon an associated label.Optional: Run the following command to view the pod networks that you have joined together:
oc get netnamespaces
$ oc get netnamespacesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Projects in the same pod-network have the same network ID in the NETID column.
26.16.3. Isolating a project
You can isolate a project so that pods and services in other projects cannot access its pods and services.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
To isolate the projects in the cluster, run the following command:
oc adm pod-network isolate-projects <project1> <project2>
$ oc adm pod-network isolate-projects <project1> <project2>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, instead of specifying specific project names, you can use the
--selector=<project_selector>option to specify projects based upon an associated label.
26.16.4. Disabling network isolation for a project
You can disable network isolation for a project.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You must log in to the cluster with a user that has the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Run the following command for the project:
oc adm pod-network make-projects-global <project1> <project2>
$ oc adm pod-network make-projects-global <project1> <project2>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, instead of specifying specific project names, you can use the
--selector=<project_selector>option to specify projects based upon an associated label.
26.17. Configuring kube-proxy
The Kubernetes network proxy (kube-proxy) runs on each node and is managed by the Cluster Network Operator (CNO). kube-proxy maintains network rules for forwarding connections for endpoints associated with services.
26.17.1. About iptables rules synchronization
The synchronization period determines how frequently the Kubernetes network proxy (kube-proxy) syncs the iptables rules on a node.
A sync begins when either of the following events occurs:
- An event occurs, such as service or endpoint is added to or removed from the cluster.
- The time since the last sync exceeds the sync period defined for kube-proxy.
26.17.2. kube-proxy configuration parameters
You can modify the following kubeProxyConfig parameters.
Because of performance improvements introduced in OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 and greater, adjusting the iptablesSyncPeriod parameter is no longer necessary.
| Parameter | Description | Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
The refresh period for |
A time interval, such as |
|
|
|
The minimum duration before refreshing |
A time interval, such as |
|
26.17.3. Modifying the kube-proxy configuration
You can modify the Kubernetes network proxy configuration for your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in to a running cluster with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Edit the
Network.operator.openshift.iocustom resource (CR) by running the following command:oc edit network.operator.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit network.operator.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the
kubeProxyConfigparameter in the CR with your changes to the kube-proxy configuration, such as in the following example CR:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the file and exit the text editor.
The syntax is validated by the
occommand when you save the file and exit the editor. If your modifications contain a syntax error, the editor opens the file and displays an error message.Enter the following command to confirm the configuration update:
oc get networks.operator.openshift.io -o yaml
$ oc get networks.operator.openshift.io -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Enter the following command to confirm that the Cluster Network Operator accepted the configuration change:
oc get clusteroperator network
$ oc get clusteroperator networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE network 4.1.0-0.9 True False False 1m
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE network 4.1.0-0.9 True False False 1mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
AVAILABLEfield isTruewhen the configuration update is applied successfully.
Chapter 27. Configuring Routes
27.1. Route configuration
27.1.1. Creating an HTTP-based route
A route allows you to host your application at a public URL. It can either be secure or unsecured, depending on the network security configuration of your application. An HTTP-based route is an unsecured route that uses the basic HTTP routing protocol and exposes a service on an unsecured application port.
The following procedure describes how to create a simple HTTP-based route to a web application, using the hello-openshift application as an example.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You are logged in as an administrator.
- You have a web application that exposes a port and a TCP endpoint listening for traffic on the port.
Procedure
Create a project called
hello-openshiftby running the following command:oc new-project hello-openshift
$ oc new-project hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod in the project by running the following command:
oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/origin/master/examples/hello-openshift/hello-pod.json
$ oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/origin/master/examples/hello-openshift/hello-pod.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a service called
hello-openshiftby running the following command:oc expose pod/hello-openshift
$ oc expose pod/hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an unsecured route to the
hello-openshiftapplication by running the following command:oc expose svc hello-openshift
$ oc expose svc hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To verify that the
routeresource that you created, run the following command:oc get routes -o yaml <name of resource>
$ oc get routes -o yaml <name of resource>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the route is named
hello-openshift.
Sample YAML definition of the created unsecured route:
- 1
- The
hostfield is an alias DNS record that points to the service. This field can be any valid DNS name, such aswww.example.com. The DNS name must follow DNS952 subdomain conventions. If not specified, a route name is automatically generated. - 2
- The
targetPortfield is the target port on pods that is selected by the service that this route points to.NoteTo display your default ingress domain, run the following command:
oc get ingresses.config/cluster -o jsonpath={.spec.domain}$ oc get ingresses.config/cluster -o jsonpath={.spec.domain}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.2. Creating a route for Ingress Controller sharding
A route allows you to host your application at a URL. In this case, the hostname is not set and the route uses a subdomain instead. When you specify a subdomain, you automatically use the domain of the Ingress Controller that exposes the route. For situations where a route is exposed by multiple Ingress Controllers, the route is hosted at multiple URLs.
The following procedure describes how to create a route for Ingress Controller sharding, using the hello-openshift application as an example.
Ingress Controller sharding is useful when balancing incoming traffic load among a set of Ingress Controllers and when isolating traffic to a specific Ingress Controller. For example, company A goes to one Ingress Controller and company B to another.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You are logged in as a project administrator.
- You have a web application that exposes a port and an HTTP or TLS endpoint listening for traffic on the port.
- You have configured the Ingress Controller for sharding.
Procedure
Create a project called
hello-openshiftby running the following command:oc new-project hello-openshift
$ oc new-project hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod in the project by running the following command:
oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/origin/master/examples/hello-openshift/hello-pod.json
$ oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/origin/master/examples/hello-openshift/hello-pod.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a service called
hello-openshiftby running the following command:oc expose pod/hello-openshift
$ oc expose pod/hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a route definition called
hello-openshift-route.yaml:YAML definition of the created route for sharding:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Both the label key and its corresponding label value must match the ones specified in the Ingress Controller. In this example, the Ingress Controller has the label key and value
type: sharded. - 2
- The route will be exposed using the value of the
subdomainfield. When you specify thesubdomainfield, you must leave the hostname unset. If you specify both thehostandsubdomainfields, then the route will use the value of thehostfield, and ignore thesubdomainfield.
Use
hello-openshift-route.yamlto create a route to thehello-openshiftapplication by running the following command:oc -n hello-openshift create -f hello-openshift-route.yaml
$ oc -n hello-openshift create -f hello-openshift-route.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Get the status of the route with the following command:
oc -n hello-openshift get routes/hello-openshift-edge -o yaml
$ oc -n hello-openshift get routes/hello-openshift-edge -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The resulting
Routeresource should look similar to the following:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The hostname the Ingress Controller, or router, uses to expose the route. The value of the
hostfield is automatically determined by the Ingress Controller, and uses its domain. In this example, the domain of the Ingress Controller is<apps-sharded.basedomain.example.net>. - 2
- The hostname of the Ingress Controller.
- 3
- The name of the Ingress Controller. In this example, the Ingress Controller has the name
sharded.
27.1.3. Configuring route timeouts
You can configure the default timeouts for an existing route when you have services in need of a low timeout, which is required for Service Level Availability (SLA) purposes, or a high timeout, for cases with a slow back end.
If you configured a user-managed external load balancer in front of your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, ensure that the timeout value for the user-managed external load balancer is higher than the timeout value for the route. This configuration prevents network congestion issues over the network that your cluster uses.
Prerequisites
- You need a deployed Ingress Controller on a running cluster.
Procedure
Using the
oc annotatecommand, add the timeout to the route:oc annotate route <route_name> \ --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=<timeout><time_unit>$ oc annotate route <route_name> \ --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=<timeout><time_unit>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Supported time units are microseconds (us), milliseconds (ms), seconds (s), minutes (m), hours (h), or days (d).
The following example sets a timeout of two seconds on a route named
myroute:oc annotate route myroute --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=2s
$ oc annotate route myroute --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=2sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.4. HTTP Strict Transport Security
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) policy is a security enhancement, which signals to the browser client that only HTTPS traffic is allowed on the route host. HSTS also optimizes web traffic by signaling HTTPS transport is required, without using HTTP redirects. HSTS is useful for speeding up interactions with websites.
When HSTS policy is enforced, HSTS adds a Strict Transport Security header to HTTP and HTTPS responses from the site. You can use the insecureEdgeTerminationPolicy value in a route to redirect HTTP to HTTPS. When HSTS is enforced, the client changes all requests from the HTTP URL to HTTPS before the request is sent, eliminating the need for a redirect.
Cluster administrators can configure HSTS to do the following:
- Enable HSTS per-route
- Disable HSTS per-route
- Enforce HSTS per-domain, for a set of domains, or use namespace labels in combination with domains
HSTS works only with secure routes, either edge-terminated or re-encrypt. The configuration is ineffective on HTTP or passthrough routes.
27.1.4.1. Enabling HTTP Strict Transport Security per-route
HTTP strict transport security (HSTS) is implemented in the HAProxy template and applied to edge and re-encrypt routes that have the haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header annotation.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster with a user with administrator privileges for the project.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
To enable HSTS on a route, add the
haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_headervalue to the edge-terminated or re-encrypt route. You can use theoc annotatetool to do this by running the following command:oc annotate route <route_name> -n <namespace> --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=31536000;\ includeSubDomains;preload"
$ oc annotate route <route_name> -n <namespace> --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=31536000;\1 includeSubDomains;preload"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- In this example, the maximum age is set to
31536000ms, which is approximately eight and a half hours.
NoteIn this example, the equal sign (
=) is in quotes. This is required to properly execute the annotate command.Example route configured with an annotation
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Required.
max-agemeasures the length of time, in seconds, that the HSTS policy is in effect. If set to0, it negates the policy. - 2
- Optional. When included,
includeSubDomainstells the client that all subdomains of the host must have the same HSTS policy as the host. - 3
- Optional. When
max-ageis greater than 0, you can addpreloadinhaproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_headerto allow external services to include this site in their HSTS preload lists. For example, sites such as Google can construct a list of sites that havepreloadset. Browsers can then use these lists to determine which sites they can communicate with over HTTPS, even before they have interacted with the site. Withoutpreloadset, browsers must have interacted with the site over HTTPS, at least once, to get the header.
27.1.4.2. Disabling HTTP Strict Transport Security per-route
To disable HTTP strict transport security (HSTS) per-route, you can set the max-age value in the route annotation to 0.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster with a user with administrator privileges for the project.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
To disable HSTS, set the
max-agevalue in the route annotation to0, by entering the following command:oc annotate route <route_name> -n <namespace> --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=0"
$ oc annotate route <route_name> -n <namespace> --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=0"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to create the config map:
Example of disabling HSTS per-route
metadata: annotations: haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header: max-age=0metadata: annotations: haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header: max-age=0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To disable HSTS for every route in a namespace, enter the following command:
oc annotate route --all -n <namespace> --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=0"
$ oc annotate route --all -n <namespace> --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=0"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To query the annotation for all routes, enter the following command:
oc get route --all-namespaces -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if .metadata.annotations}}{{$a := index .metadata.annotations "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"}}{{$n := .metadata.name}}{{with $a}}Name: {{$n}} HSTS: {{$a}}{{"\n"}}{{else}}{{""}}{{end}}{{end}}{{end}}'$ oc get route --all-namespaces -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if .metadata.annotations}}{{$a := index .metadata.annotations "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"}}{{$n := .metadata.name}}{{with $a}}Name: {{$n}} HSTS: {{$a}}{{"\n"}}{{else}}{{""}}{{end}}{{end}}{{end}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name: routename HSTS: max-age=0
Name: routename HSTS: max-age=0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.4.3. Enforcing HTTP Strict Transport Security per-domain
To enforce HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) per-domain for secure routes, add a requiredHSTSPolicies record to the Ingress spec to capture the configuration of the HSTS policy.
If you configure a requiredHSTSPolicy to enforce HSTS, then any newly created route must be configured with a compliant HSTS policy annotation.
To handle upgraded clusters with non-compliant HSTS routes, you can update the manifests at the source and apply the updates.
You cannot use oc expose route or oc create route commands to add a route in a domain that enforces HSTS, because the API for these commands does not accept annotations.
HSTS cannot be applied to insecure, or non-TLS routes, even if HSTS is requested for all routes globally.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster with a user with administrator privileges for the project.
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
Edit the Ingress config file:
oc edit ingresses.config.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit ingresses.config.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example HSTS policy
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Required.
requiredHSTSPoliciesare validated in order, and the first matchingdomainPatternsapplies. - 2 7
- Required. You must specify at least one
domainPatternshostname. Any number of domains can be listed. You can include multiple sections of enforcing options for differentdomainPatterns. - 3
- Optional. If you include
namespaceSelector, it must match the labels of the project where the routes reside, to enforce the set HSTS policy on the routes. Routes that only match thenamespaceSelectorand not thedomainPatternsare not validated. - 4
- Required.
max-agemeasures the length of time, in seconds, that the HSTS policy is in effect. This policy setting allows for a smallest and largestmax-ageto be enforced.-
The
largestMaxAgevalue must be between0and2147483647. It can be left unspecified, which means no upper limit is enforced. -
The
smallestMaxAgevalue must be between0and2147483647. Enter0to disable HSTS for troubleshooting, otherwise enter1if you never want HSTS to be disabled. It can be left unspecified, which means no lower limit is enforced.
-
The
- 5
- Optional. Including
preloadinhaproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_headerallows external services to include this site in their HSTS preload lists. Browsers can then use these lists to determine which sites they can communicate with over HTTPS, before they have interacted with the site. Withoutpreloadset, browsers need to interact at least once with the site to get the header.preloadcan be set with one of the following:-
RequirePreload:preloadis required by theRequiredHSTSPolicy. -
RequireNoPreload:preloadis forbidden by theRequiredHSTSPolicy. -
NoOpinion:preloaddoes not matter to theRequiredHSTSPolicy.
-
- 6
- Optional.
includeSubDomainsPolicycan be set with one of the following:-
RequireIncludeSubDomains:includeSubDomainsis required by theRequiredHSTSPolicy. -
RequireNoIncludeSubDomains:includeSubDomainsis forbidden by theRequiredHSTSPolicy. -
NoOpinion:includeSubDomainsdoes not matter to theRequiredHSTSPolicy.
-
You can apply HSTS to all routes in the cluster or in a particular namespace by entering the
oc annotate command.To apply HSTS to all routes in the cluster, enter the
oc annotate command. For example:oc annotate route --all --all-namespaces --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=31536000"
$ oc annotate route --all --all-namespaces --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=31536000"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To apply HSTS to all routes in a particular namespace, enter the
oc annotate command. For example:oc annotate route --all -n my-namespace --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=31536000"
$ oc annotate route --all -n my-namespace --overwrite=true "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"="max-age=31536000"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can review the HSTS policy you configured. For example:
To review the
maxAgeset for required HSTS policies, enter the following command:oc get clusteroperator/ingress -n openshift-ingress-operator -o jsonpath='{range .spec.requiredHSTSPolicies[*]}{.spec.requiredHSTSPolicies.maxAgePolicy.largestMaxAge}{"\n"}{end}'$ oc get clusteroperator/ingress -n openshift-ingress-operator -o jsonpath='{range .spec.requiredHSTSPolicies[*]}{.spec.requiredHSTSPolicies.maxAgePolicy.largestMaxAge}{"\n"}{end}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To review the HSTS annotations on all routes, enter the following command:
oc get route --all-namespaces -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if .metadata.annotations}}{{$a := index .metadata.annotations "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"}}{{$n := .metadata.name}}{{with $a}}Name: {{$n}} HSTS: {{$a}}{{"\n"}}{{else}}{{""}}{{end}}{{end}}{{end}}'$ oc get route --all-namespaces -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if .metadata.annotations}}{{$a := index .metadata.annotations "haproxy.router.openshift.io/hsts_header"}}{{$n := .metadata.name}}{{with $a}}Name: {{$n}} HSTS: {{$a}}{{"\n"}}{{else}}{{""}}{{end}}{{end}}{{end}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name: <_routename_> HSTS: max-age=31536000;preload;includeSubDomains
Name: <_routename_> HSTS: max-age=31536000;preload;includeSubDomainsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.5. Throughput issue troubleshooting methods
Sometimes applications deployed by using OpenShift Container Platform can cause network throughput issues, such as unusually high latency between specific services.
If pod logs do not reveal any cause of the problem, use the following methods to analyze performance issues:
Use a packet analyzer, such as
pingortcpdumpto analyze traffic between a pod and its node.For example, run the
tcpdumptool on each pod while reproducing the behavior that led to the issue. Review the captures on both sides to compare send and receive timestamps to analyze the latency of traffic to and from a pod. Latency can occur in OpenShift Container Platform if a node interface is overloaded with traffic from other pods, storage devices, or the data plane.tcpdump -s 0 -i any -w /tmp/dump.pcap host <podip 1> && host <podip 2>
$ tcpdump -s 0 -i any -w /tmp/dump.pcap host <podip 1> && host <podip 2>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
podipis the IP address for the pod. Run theoc get pod <pod_name> -o widecommand to get the IP address of a pod.
The
tcpdumpcommand generates a file at/tmp/dump.pcapcontaining all traffic between these two pods. You can run the analyzer shortly before the issue is reproduced and stop the analyzer shortly after the issue is finished reproducing to minimize the size of the file. You can also run a packet analyzer between the nodes (eliminating the SDN from the equation) with:tcpdump -s 0 -i any -w /tmp/dump.pcap port 4789
$ tcpdump -s 0 -i any -w /tmp/dump.pcap port 4789Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use a bandwidth measuring tool, such as
iperf, to measure streaming throughput and UDP throughput. Locate any bottlenecks by running the tool from the pods first, and then running it from the nodes.-
For information on installing and using
iperf, see this Red Hat Solution.
-
For information on installing and using
- In some cases, the cluster may mark the node with the router pod as unhealthy due to latency issues. Use worker latency profiles to adjust the frequency that the cluster waits for a status update from the node before taking action.
-
If your cluster has designated lower-latency and higher-latency nodes, configure the
spec.nodePlacementfield in the Ingress Controller to control the placement of the router pod.
27.1.6. Using cookies to keep route statefulness
OpenShift Container Platform provides sticky sessions, which enables stateful application traffic by ensuring all traffic hits the same endpoint. However, if the endpoint pod terminates, whether through restart, scaling, or a change in configuration, this statefulness can disappear.
OpenShift Container Platform can use cookies to configure session persistence. The Ingress controller selects an endpoint to handle any user requests, and creates a cookie for the session. The cookie is passed back in the response to the request and the user sends the cookie back with the next request in the session. The cookie tells the Ingress Controller which endpoint is handling the session, ensuring that client requests use the cookie so that they are routed to the same pod.
Cookies cannot be set on passthrough routes, because the HTTP traffic cannot be seen. Instead, a number is calculated based on the source IP address, which determines the backend.
If backends change, the traffic can be directed to the wrong server, making it less sticky. If you are using a load balancer, which hides source IP, the same number is set for all connections and traffic is sent to the same pod.
27.1.6.1. Annotating a route with a cookie
You can set a cookie name to overwrite the default, auto-generated one for the route. This allows the application receiving route traffic to know the cookie name. By deleting the cookie it can force the next request to re-choose an endpoint. So, if a server was overloaded it tries to remove the requests from the client and redistribute them.
Procedure
Annotate the route with the specified cookie name:
oc annotate route <route_name> router.openshift.io/cookie_name="<cookie_name>"
$ oc annotate route <route_name> router.openshift.io/cookie_name="<cookie_name>"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<route_name>- Specifies the name of the route.
<cookie_name>- Specifies the name for the cookie.
For example, to annotate the route
my_routewith the cookie namemy_cookie:oc annotate route my_route router.openshift.io/cookie_name="my_cookie"
$ oc annotate route my_route router.openshift.io/cookie_name="my_cookie"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Capture the route hostname in a variable:
ROUTE_NAME=$(oc get route <route_name> -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')$ ROUTE_NAME=$(oc get route <route_name> -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:
<route_name>- Specifies the name of the route.
Save the cookie, and then access the route:
curl $ROUTE_NAME -k -c /tmp/cookie_jar
$ curl $ROUTE_NAME -k -c /tmp/cookie_jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the cookie saved by the previous command when connecting to the route:
curl $ROUTE_NAME -k -b /tmp/cookie_jar
$ curl $ROUTE_NAME -k -b /tmp/cookie_jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.7. Path-based routes
Path-based routes specify a path component that can be compared against a URL, which requires that the traffic for the route be HTTP based. Thus, multiple routes can be served using the same hostname, each with a different path. Routers should match routes based on the most specific path to the least.
The following table shows example routes and their accessibility:
| Route | When Compared to | Accessible |
|---|---|---|
| www.example.com/test | www.example.com/test | Yes |
| www.example.com | No | |
| www.example.com/test and www.example.com | www.example.com/test | Yes |
| www.example.com | Yes | |
| www.example.com | www.example.com/text | Yes (Matched by the host, not the route) |
| www.example.com | Yes |
An unsecured route with a path
- 1
- The path is the only added attribute for a path-based route.
Path-based routing is not available when using passthrough TLS, as the router does not terminate TLS in that case and cannot read the contents of the request.
27.1.8. Route-specific annotations
The Ingress Controller can set the default options for all the routes it exposes. An individual route can override some of these defaults by providing specific configurations in its annotations. Red Hat does not support adding a route annotation to an operator-managed route.
To create a whitelist with multiple source IPs or subnets, use a space-delimited list. Any other delimiter type causes the list to be ignored without a warning or error message.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Sets the load-balancing algorithm. Available options are |
|
|
Disables the use of cookies to track related connections. If set to |
|
| Specifies an optional cookie to use for this route. The name must consist of any combination of upper and lower case letters, digits, "_", and "-". The default is the hashed internal key name for the route. |
|
|
Sets the maximum number of connections that are allowed to a backing pod from a router. |
|
|
Setting |
|
|
Limits the number of concurrent TCP connections made through the same source IP address. It accepts a numeric value. |
|
|
Limits the rate at which a client with the same source IP address can make HTTP requests. It accepts a numeric value. |
|
|
Limits the rate at which a client with the same source IP address can make TCP connections. It accepts a numeric value. |
|
| Sets the interval for the back-end health checks. (TimeUnits) |
|
| Sets an allowlist for the route. The allowlist is a space-separated list of IP addresses and CIDR ranges for the approved source addresses. Requests from IP addresses that are not in the allowlist are dropped.
The maximum number of IP addresses and CIDR ranges directly visible in the |
|
| Sets a Strict-Transport-Security header for the edge terminated or re-encrypt route. |
|
| Sets the rewrite path of the request on the backend. |
|
| Sets a value to restrict cookies. The values are:
This value is applicable to re-encrypt and edge routes only. For more information, see the SameSite cookies documentation. |
|
|
Sets the policy for handling the
|
If the number of IP addresses and CIDR ranges in an allowlist exceeds 61, they are written into a separate file that is then referenced from
haproxy.config. This file is stored in thevar/lib/haproxy/router/whitelistsfolder.NoteTo ensure that the addresses are written to the allowlist, check that the full list of CIDR ranges are listed in the Ingress Controller configuration file. The etcd object size limit restricts how large a route annotation can be. Because of this, it creates a threshold for the maximum number of IP addresses and CIDR ranges that you can include in an allowlist.
A route that allows only one specific IP address
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 192.168.1.10
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 192.168.1.10A route that allows several IP addresses
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.11 192.168.1.12
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.11 192.168.1.12A route that allows an IP address CIDR network
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 192.168.1.0/24
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 192.168.1.0/24A route that allows both IP an address and IP address CIDR networks
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 180.5.61.153 192.168.1.0/24 10.0.0.0/8
metadata:
annotations:
haproxy.router.openshift.io/ip_whitelist: 180.5.61.153 192.168.1.0/24 10.0.0.0/8A route specifying a rewrite target
- 1
- Sets
/as rewrite path of the request on the backend.
Setting the haproxy.router.openshift.io/rewrite-target annotation on a route specifies that the Ingress Controller should rewrite paths in HTTP requests using this route before forwarding the requests to the backend application. The part of the request path that matches the path specified in spec.path is replaced with the rewrite target specified in the annotation.
The following table provides examples of the path rewriting behavior for various combinations of spec.path, request path, and rewrite target.
| Route.spec.path | Request path | Rewrite target | Forwarded request path |
|---|---|---|---|
| /foo | /foo | / | / |
| /foo | /foo/ | / | / |
| /foo | /foo/bar | / | /bar |
| /foo | /foo/bar/ | / | /bar/ |
| /foo | /foo | /bar | /bar |
| /foo | /foo/ | /bar | /bar/ |
| /foo | /foo/bar | /baz | /baz/bar |
| /foo | /foo/bar/ | /baz | /baz/bar/ |
| /foo/ | /foo | / | N/A (request path does not match route path) |
| /foo/ | /foo/ | / | / |
| /foo/ | /foo/bar | / | /bar |
27.1.9. Configuring the route admission policy
Administrators and application developers can run applications in multiple namespaces with the same domain name. This is for organizations where multiple teams develop microservices that are exposed on the same hostname.
Allowing claims across namespaces should only be enabled for clusters with trust between namespaces, otherwise a malicious user could take over a hostname. For this reason, the default admission policy disallows hostname claims across namespaces.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator privileges.
Procedure
Edit the
.spec.routeAdmissionfield of theingresscontrollerresource variable using the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"routeAdmission":{"namespaceOwnership":"InterNamespaceAllowed"}}}' --type=merge$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"routeAdmission":{"namespaceOwnership":"InterNamespaceAllowed"}}}' --type=mergeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample Ingress Controller configuration
spec: routeAdmission: namespaceOwnership: InterNamespaceAllowed ...spec: routeAdmission: namespaceOwnership: InterNamespaceAllowed ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to configure the route admission policy:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.10. Creating a route through an Ingress object
Some ecosystem components have an integration with Ingress resources but not with route resources. To cover this case, OpenShift Container Platform automatically creates managed route objects when an Ingress object is created. These route objects are deleted when the corresponding Ingress objects are deleted.
Procedure
Define an Ingress object in the OpenShift Container Platform console or by entering the
oc createcommand:YAML Definition of an Ingress
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
route.openshift.io/terminationannotation can be used to configure thespec.tls.terminationfield of theRouteasIngresshas no field for this. The accepted values areedge,passthroughandreencrypt. All other values are silently ignored. When the annotation value is unset,edgeis the default route. The TLS certificate details must be defined in the template file to implement the default edge route. - 3
- When working with an
Ingressobject, you must specify an explicit hostname, unlike when working with routes. You can use the<host_name>.<cluster_ingress_domain>syntax, for exampleapps.openshiftdemos.com, to take advantage of the*.<cluster_ingress_domain>wildcard DNS record and serving certificate for the cluster. Otherwise, you must ensure that there is a DNS record for the chosen hostname.If you specify the
passthroughvalue in theroute.openshift.io/terminationannotation, setpathto''andpathTypetoImplementationSpecificin the spec:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc apply -f ingress.yaml
$ oc apply -f ingress.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- 2
- The
route.openshift.io/destination-ca-certificate-secretcan be used on an Ingress object to define a route with a custom destination certificate (CA). The annotation references a kubernetes secret,secret-ca-certthat will be inserted into the generated route.-
To specify a route object with a destination CA from an ingress object, you must create a
kubernetes.io/tlsorOpaquetype secret with a certificate in PEM-encoded format in thedata.tls.crtspecifier of the secret.
-
To specify a route object with a destination CA from an ingress object, you must create a
List your routes:
oc get routes
$ oc get routesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The result includes an autogenerated route whose name starts with
frontend-:NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD frontend-gnztq www.example.com frontend 443 reencrypt/Redirect None
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD frontend-gnztq www.example.com frontend 443 reencrypt/Redirect NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you inspect this route, it looks this:
YAML Definition of an autogenerated route
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.11. Creating a route using the default certificate through an Ingress object
If you create an Ingress object without specifying any TLS configuration, OpenShift Container Platform generates an insecure route. To create an Ingress object that generates a secure, edge-terminated route using the default ingress certificate, you can specify an empty TLS configuration as follows.
Prerequisites
- You have a service that you want to expose.
-
You have access to the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a YAML file for the Ingress object. In this example, the file is called
example-ingress.yaml:YAML definition of an Ingress object
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Use this exact syntax to specify TLS without specifying a custom certificate.
Create the Ingress object by running the following command:
oc create -f example-ingress.yaml
$ oc create -f example-ingress.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that OpenShift Container Platform has created the expected route for the Ingress object by running the following command:
oc get routes -o yaml
$ oc get routes -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.12. Creating a route using the destination CA certificate in the Ingress annotation
The route.openshift.io/destination-ca-certificate-secret annotation can be used on an Ingress object to define a route with a custom destination CA certificate.
Prerequisites
- You may have a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded files, where the certificate is valid for the route host.
- You may have a separate CA certificate in a PEM-encoded file that completes the certificate chain.
- You must have a separate destination CA certificate in a PEM-encoded file.
- You must have a service that you want to expose.
Procedure
Create a secret for the destination CA certificate by entering the following command:
oc create secret generic dest-ca-cert --from-file=tls.crt=<file_path>
$ oc create secret generic dest-ca-cert --from-file=tls.crt=<file_path>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc -n test-ns create secret generic dest-ca-cert --from-file=tls.crt=tls.crt
$ oc -n test-ns create secret generic dest-ca-cert --from-file=tls.crt=tls.crtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
secret/dest-ca-cert created
secret/dest-ca-cert createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
route.openshift.io/destination-ca-certificate-secretto the Ingress annotations:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The annotation references a kubernetes secret.
The secret referenced in this annotation will be inserted into the generated route.
Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.1.13. Configuring the OpenShift Container Platform Ingress Controller for dual-stack networking
If your OpenShift Container Platform cluster is configured for IPv4 and IPv6 dual-stack networking, your cluster is externally reachable by OpenShift Container Platform routes.
The Ingress Controller automatically serves services that have both IPv4 and IPv6 endpoints, but you can configure the Ingress Controller for single-stack or dual-stack services.
Prerequisites
- You deployed an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on bare metal.
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
To have the Ingress Controller serve traffic over IPv4/IPv6 to a workload, you can create a service YAML file or modify an existing service YAML file by setting the
ipFamiliesandipFamilyPolicyfields. For example:Sample service YAML file
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow These resources generate corresponding
endpoints. The Ingress Controller now watchesendpointslices.To view
endpoints, enter the following command:oc get endpoints
$ oc get endpointsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view
endpointslices, enter the following command:oc get endpointslices
$ oc get endpointslicesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.2. Secured routes
Secure routes provide the ability to use several types of TLS termination to serve certificates to the client. The following sections describe how to create re-encrypt, edge, and passthrough routes with custom certificates.
If you create routes in Microsoft Azure through public endpoints, the resource names are subject to restriction. You cannot create resources that use certain terms. For a list of terms that Azure restricts, see Resolve reserved resource name errors in the Azure documentation.
27.2.1. Creating a re-encrypt route with a custom certificate
You can configure a secure route using reencrypt TLS termination with a custom certificate by using the oc create route command.
Prerequisites
- You must have a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded files, where the certificate is valid for the route host.
- You may have a separate CA certificate in a PEM-encoded file that completes the certificate chain.
- You must have a separate destination CA certificate in a PEM-encoded file.
- You must have a service that you want to expose.
Password protected key files are not supported. To remove a passphrase from a key file, use the following command:
openssl rsa -in password_protected_tls.key -out tls.key
$ openssl rsa -in password_protected_tls.key -out tls.keyProcedure
This procedure creates a Route resource with a custom certificate and reencrypt TLS termination. The following assumes that the certificate/key pair are in the tls.crt and tls.key files in the current working directory. You must also specify a destination CA certificate to enable the Ingress Controller to trust the service’s certificate. You may also specify a CA certificate if needed to complete the certificate chain. Substitute the actual path names for tls.crt, tls.key, cacert.crt, and (optionally) ca.crt. Substitute the name of the Service resource that you want to expose for frontend. Substitute the appropriate hostname for www.example.com.
Create a secure
Routeresource using reencrypt TLS termination and a custom certificate:oc create route reencrypt --service=frontend --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key --dest-ca-cert=destca.crt --ca-cert=ca.crt --hostname=www.example.com
$ oc create route reencrypt --service=frontend --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key --dest-ca-cert=destca.crt --ca-cert=ca.crt --hostname=www.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you examine the resulting
Routeresource, it should look similar to the following:YAML Definition of the Secure Route
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See
oc create route reencrypt --helpfor more options.
27.2.2. Creating an edge route with a custom certificate
You can configure a secure route using edge TLS termination with a custom certificate by using the oc create route command. With an edge route, the Ingress Controller terminates TLS encryption before forwarding traffic to the destination pod. The route specifies the TLS certificate and key that the Ingress Controller uses for the route.
Prerequisites
- You must have a certificate/key pair in PEM-encoded files, where the certificate is valid for the route host.
- You may have a separate CA certificate in a PEM-encoded file that completes the certificate chain.
- You must have a service that you want to expose.
Password protected key files are not supported. To remove a passphrase from a key file, use the following command:
openssl rsa -in password_protected_tls.key -out tls.key
$ openssl rsa -in password_protected_tls.key -out tls.keyProcedure
This procedure creates a Route resource with a custom certificate and edge TLS termination. The following assumes that the certificate/key pair are in the tls.crt and tls.key files in the current working directory. You may also specify a CA certificate if needed to complete the certificate chain. Substitute the actual path names for tls.crt, tls.key, and (optionally) ca.crt. Substitute the name of the service that you want to expose for frontend. Substitute the appropriate hostname for www.example.com.
Create a secure
Routeresource using edge TLS termination and a custom certificate.oc create route edge --service=frontend --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key --ca-cert=ca.crt --hostname=www.example.com
$ oc create route edge --service=frontend --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key --ca-cert=ca.crt --hostname=www.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you examine the resulting
Routeresource, it should look similar to the following:YAML Definition of the Secure Route
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See
oc create route edge --helpfor more options.
27.2.3. Creating a passthrough route
You can configure a secure route using passthrough termination by using the oc create route command. With passthrough termination, encrypted traffic is sent straight to the destination without the router providing TLS termination. Therefore no key or certificate is required on the route.
Prerequisites
- You must have a service that you want to expose.
Procedure
Create a
Routeresource:oc create route passthrough route-passthrough-secured --service=frontend --port=8080
$ oc create route passthrough route-passthrough-secured --service=frontend --port=8080Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you examine the resulting
Routeresource, it should look similar to the following:A Secured Route Using Passthrough Termination
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The destination pod is responsible for serving certificates for the traffic at the endpoint. This is currently the only method that can support requiring client certificates, also known as two-way authentication.
Chapter 28. Configuring ingress cluster traffic
28.1. Configuring ingress cluster traffic overview
OpenShift Container Platform provides the following methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster.
The methods are recommended, in order or preference:
- If you have HTTP/HTTPS, use an Ingress Controller.
- If you have a TLS-encrypted protocol other than HTTPS. For example, for TLS with the SNI header, use an Ingress Controller.
-
Otherwise, use a Load Balancer, an External IP, or a
NodePort.
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Allows access to HTTP/HTTPS traffic and TLS-encrypted protocols other than HTTPS (for example, TLS with the SNI header). | |
| Automatically assign an external IP using a load balancer service | Allows traffic to non-standard ports through an IP address assigned from a pool. Most cloud platforms offer a method to start a service with a load-balancer IP address. |
| Allows traffic to a specific IP address or address from a pool on the machine network. For bare-metal installations or platforms that are like bare metal, MetalLB provides a way to start a service with a load-balancer IP address. | |
| Allows traffic to non-standard ports through a specific IP address. | |
| Expose a service on all nodes in the cluster. |
28.1.1. Comparision: Fault tolerant access to external IP addresses
For the communication methods that provide access to an external IP address, fault tolerant access to the IP address is another consideration. The following features provide fault tolerant access to an external IP address.
- IP failover
- IP failover manages a pool of virtual IP address for a set of nodes. It is implemented with Keepalived and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP). IP failover is a layer 2 mechanism only and relies on multicast. Multicast can have disadvantages for some networks.
- MetalLB
- MetalLB has a layer 2 mode, but it does not use multicast. Layer 2 mode has a disadvantage that it transfers all traffic for an external IP address through one node.
- Manually assigning external IP addresses
- You can configure your cluster with an IP address block that is used to assign external IP addresses to services. By default, this feature is disabled. This feature is flexible, but places the largest burden on the cluster or network administrator. The cluster is prepared to receive traffic that is destined for the external IP, but each customer has to decide how they want to route traffic to nodes.
28.2. Configuring ExternalIPs for services
As a cluster administrator, you can select an IP address block that is external to the cluster that can send traffic to services in the cluster.
This functionality is generally most useful for clusters installed on bare-metal hardware.
28.2.1. Prerequisites
- Your network infrastructure must route traffic for the external IP addresses to your cluster.
28.2.2. About ExternalIP
For non-cloud environments, OpenShift Container Platform supports the use of the ExternalIP facility to specify external IP addresses in the spec.externalIPs[] parameter of the Service object. A service configured with an ExternalIP functions similarly to a service with type=NodePort, whereby you traffic directs to a local node for load balancing.
For cloud environments, use the load balancer services for automatic deployment of a cloud load balancer to target the endpoints of a service.
After you specify a value for the parameter, OpenShift Container Platform assigns an additional virtual IP address to the service. The IP address can exist outside of the service network that you defined for your cluster.
Because ExternalIP is disabled by default, enabling the ExternalIP functionality might introduce security risks for the service, because in-cluster traffic to an external IP address is directed to that service. This configuration means that cluster users could intercept sensitive traffic destined for external resources.
You can use either a MetalLB implementation or an IP failover deployment to attach an ExternalIP resource to a service in the following ways:
- Automatic assignment of an external IP
-
OpenShift Container Platform automatically assigns an IP address from the
autoAssignCIDRsCIDR block to thespec.externalIPs[]array when you create aServiceobject withspec.type=LoadBalancerset. For this configuration, OpenShift Container Platform implements a cloud version of the load balancer service type and assigns IP addresses to the services. Automatic assignment is disabled by default and must be configured by a cluster administrator as described in the "Configuration for ExternalIP" section. - Manual assignment of an external IP
-
OpenShift Container Platform uses the IP addresses assigned to the
spec.externalIPs[]array when you create aServiceobject. You cannot specify an IP address that is already in use by another service.
After using either the MetalLB implementation or an IP failover deployment to host external IP address blocks, you must configure your networking infrastructure to ensure that the external IP address blocks are routed to your cluster. This configuration means that the IP address is not configured in the network interfaces from nodes. To handle the traffic, you must configure the routing and access to the external IP by using a method, such as static Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) entries.
OpenShift Container Platform extends the ExternalIP functionality in Kubernetes by adding the following capabilities:
- Restrictions on the use of external IP addresses by users through a configurable policy
- Allocation of an external IP address automatically to a service upon request
28.2.3. Additional resources
28.2.4. Configuration for ExternalIP
The following parameters in the Network.config.openshift.io custom resource (CR) govern the use of an external IP address in OpenShift Container Platform:
-
spec.externalIP.autoAssignCIDRsdefines an IP address block used by the load balancer when choosing an external IP address for the service. OpenShift Container Platform supports only a single IP address block for automatic assignment. This configuration requires less steps than manually assigning ExternalIPs to services, which requires managing the port space of a limited number of shared IP addresses. If you enable automatic assignment, the Cloud Controller Manager Operator allocates an external IP address to aServiceobject withspec.type=LoadBalancerdefind in its configuration. -
spec.externalIP.policydefines the permissible IP address blocks when manually specifying an IP address. OpenShift Container Platform does not apply policy rules to IP address blocks that you defined in thespec.externalIP.autoAssignCIDRsparameter.
If routed correctly, external traffic from the configured external IP address block can reach service endpoints through any TCP or UDP port that the service exposes.
As a cluster administrator, you must configure routing to externalIPs. You must also ensure that the IP address block you assign terminates at one or more nodes in your cluster. For more information, see Kubernetes External IPs.
OpenShift Container Platform supports both automatic and manual IP address assignment. This support guarantees that each address gets assigned to a maximum of one service and that each service can expose its chosen ports regardless of the ports exposed by other services.
To use IP address blocks defined by autoAssignCIDRs in OpenShift Container Platform, you must configure the necessary IP address assignment and routing for your host network.
The following YAML shows a Service object with a configured external IP:
If you run a private cluster on a cloud-provider platform, you can change the publishing scope to internal for the load balancer of the Ingress Controller by running the following patch command:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/ingress-controller-with-nlb --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"loadBalancer":{"scope":"Internal"}}}}'
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/ingress-controller-with-nlb --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"loadBalancer":{"scope":"Internal"}}}}'After you run this command, the Ingress Controller restricts access to routes for OpenShift Container Platform applications to internal networks only.
28.2.5. Restrictions on the assignment of an external IP address
As a cluster administrator, you can specify IP address blocks to allow and to reject IP addresses for a service. Restrictions apply only to users without cluster-admin privileges. A cluster administrator can always set the service spec.externalIPs[] field to any IP address.
You configure an IP address policy by specifying Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) address blocks for the spec.ExternalIP.policy parameter in the policy object.
Example in JSON form of a policy object and its CIDR parameters
When configuring policy restrictions, the following rules apply:
-
If
policyis set to{}, creating aServiceobject withspec.ExternalIPs[]results in a failed service. This setting is the default for OpenShift Container Platform. The same behavior exists forpolicy: null. If
policyis set and eitherpolicy.allowedCIDRs[]orpolicy.rejectedCIDRs[]is set, the following rules apply:-
If
allowedCIDRs[]andrejectedCIDRs[]are both set,rejectedCIDRs[]has precedence overallowedCIDRs[]. -
If
allowedCIDRs[]is set, creating aServiceobject withspec.ExternalIPs[]succeeds only if the specified IP addresses are allowed. -
If
rejectedCIDRs[]is set, creating aServiceobject withspec.ExternalIPs[]succeeds only if the specified IP addresses are not rejected.
-
If
28.2.6. Example policy objects
The examples in this section show different spec.externalIP.policy configurations.
In the following example, the policy prevents OpenShift Container Platform from creating any service with a specified external IP address.
Example policy to reject any value specified for
Serviceobjectspec.externalIPs[]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example, both the
allowedCIDRsandrejectedCIDRsfields are set.Example policy that includes both allowed and rejected CIDR blocks
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example,
policyis set to{}. With this configuration, using theoc get networks.config.openshift.io -o yamlcommand to view the configuration meanspolicyparameter does not show on the command output. The same behavior exists forpolicy: null.Example policy to allow any value specified for
Serviceobjectspec.externalIPs[]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.2.7. ExternalIP address block configuration
The configuration for ExternalIP address blocks is defined by a Network custom resource (CR) named cluster. The Network CR is part of the config.openshift.io API group.
During cluster installation, the Cluster Version Operator (CVO) automatically creates a Network CR named cluster. Creating any other CR objects of this type is not supported.
The following YAML describes the ExternalIP configuration:
Network.config.openshift.io CR named cluster
- 1
- Defines the IP address block in CIDR format that is available for automatic assignment of external IP addresses to a service. Only a single IP address range is allowed.
- 2
- Defines restrictions on manual assignment of an IP address to a service. If no restrictions are defined, specifying the
spec.externalIPfield in aServiceobject is not allowed. By default, no restrictions are defined.
The following YAML describes the fields for the policy stanza:
Network.config.openshift.io policy stanza
policy: allowedCIDRs: [] rejectedCIDRs: []
policy:
allowedCIDRs: []
rejectedCIDRs: [] Example external IP configurations
Several possible configurations for external IP address pools are displayed in the following examples:
The following YAML describes a configuration that enables automatically assigned external IP addresses:
Example configuration with
spec.externalIP.autoAssignCIDRssetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following YAML configures policy rules for the allowed and rejected CIDR ranges:
Example configuration with
spec.externalIP.policysetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.2.8. Configure external IP address blocks for your cluster
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the following ExternalIP settings:
-
An ExternalIP address block used by OpenShift Container Platform to automatically populate the
spec.clusterIPfield for aServiceobject. -
A policy object to restrict what IP addresses may be manually assigned to the
spec.clusterIParray of aServiceobject.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Optional: To display the current external IP configuration, enter the following command:
oc describe networks.config cluster
$ oc describe networks.config clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To edit the configuration, enter the following command:
oc edit networks.config cluster
$ oc edit networks.config clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the ExternalIP configuration, as in the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the configuration for the
externalIPstanza.
To confirm the updated ExternalIP configuration, enter the following command:
oc get networks.config cluster -o go-template='{{.spec.externalIP}}{{"\n"}}'$ oc get networks.config cluster -o go-template='{{.spec.externalIP}}{{"\n"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.2.10. Next steps
28.3. Configuring ingress cluster traffic using an Ingress Controller
OpenShift Container Platform provides methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster. This method uses an Ingress Controller.
28.3.1. Using Ingress Controllers and routes
The Ingress Operator manages Ingress Controllers and wildcard DNS.
Using an Ingress Controller is the most common way to allow external access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
An Ingress Controller is configured to accept external requests and proxy them based on the configured routes. This is limited to HTTP, HTTPS using SNI, and TLS using SNI, which is sufficient for web applications and services that work over TLS with SNI.
Work with your administrator to configure an Ingress Controller to accept external requests and proxy them based on the configured routes.
The administrator can create a wildcard DNS entry and then set up an Ingress Controller. Then, you can work with the edge Ingress Controller without having to contact the administrators.
By default, every Ingress Controller in the cluster can admit any route created in any project in the cluster.
The Ingress Controller:
- Has two replicas by default, which means it should be running on two worker nodes.
- Can be scaled up to have more replicas on more nodes.
The procedures in this section require prerequisites performed by the cluster administrator.
28.3.2. Prerequisites
Before starting the following procedures, the administrator must:
- Set up the external port to the cluster networking environment so that requests can reach the cluster.
Make sure there is at least one user with cluster admin role. To add this role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin username
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin usernameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You have an OpenShift Container Platform cluster with at least one master and at least one node and a system outside the cluster that has network access to the cluster. This procedure assumes that the external system is on the same subnet as the cluster. The additional networking required for external systems on a different subnet is out-of-scope for this topic.
28.3.3. Creating a project and service
If the project and service that you want to expose does not exist, create the project and then create the service.
If the project and service already exists, skip to the procedure on exposing the service to create a route.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc) and log in as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Create a new project for your service by running the
oc new-projectcommand:oc new-project <project_name>
$ oc new-project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
oc new-appcommand to create your service:oc new-app nodejs:12~https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex.git
$ oc new-app nodejs:12~https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the service was created, run the following command:
oc get svc -n <project_name>
$ oc get svc -n <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.197.157 <none> 8080/TCP 70s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.197.157 <none> 8080/TCP 70sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, the new service does not have an external IP address.
28.3.4. Exposing the service by creating a route
You can expose the service as a route by using the oc expose command.
Prerequisites
- You logged into OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
Log in to the project where the service you want to expose is located:
oc project <project_name>
$ oc project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the
oc expose servicecommand to expose the route:oc expose service nodejs-ex
$ oc expose service nodejs-exCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
route.route.openshift.io/nodejs-ex exposed
route.route.openshift.io/nodejs-ex exposedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the service is exposed, you can use a tool, such as
curlto check that the service is accessible from outside the cluster.To find the hostname of the route, enter the following command:
oc get route
$ oc get routeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD nodejs-ex nodejs-ex-myproject.example.com nodejs-ex 8080-tcp None
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD nodejs-ex nodejs-ex-myproject.example.com nodejs-ex 8080-tcp NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check that the host responds to a GET request, enter the following command:
Example
curlcommandcurl --head nodejs-ex-myproject.example.com
$ curl --head nodejs-ex-myproject.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.3.5. Ingress sharding in OpenShift Container Platform
In OpenShift Container Platform, an Ingress Controller can serve all routes, or it can serve a subset of routes. By default, the Ingress Controller serves any route created in any namespace in the cluster. You can add additional Ingress Controllers to your cluster to optimize routing by creating shards, which are subsets of routes based on selected characteristics. To mark a route as a member of a shard, use labels in the route or namespace metadata field. The Ingress Controller uses selectors, also known as a selection expression, to select a subset of routes from the entire pool of routes to serve.
Ingress sharding is useful in cases where you want to load balance incoming traffic across multiple Ingress Controllers, when you want to isolate traffic to be routed to a specific Ingress Controller, or for a variety of other reasons described in the next section.
By default, each route uses the default domain of the cluster. However, routes can be configured to use the domain of the router instead.
28.3.6. Ingress Controller sharding
You can use Ingress sharding, also known as router sharding, to distribute a set of routes across multiple routers by adding labels to routes, namespaces, or both. The Ingress Controller uses a corresponding set of selectors to admit only the routes that have a specified label. Each Ingress shard comprises the routes that are filtered by using a given selection expression.
As the primary mechanism for traffic to enter the cluster, the demands on the Ingress Controller can be significant. As a cluster administrator, you can shard the routes to:
- Balance Ingress Controllers, or routers, with several routes to accelerate responses to changes.
- Assign certain routes to have different reliability guarantees than other routes.
- Allow certain Ingress Controllers to have different policies defined.
- Allow only specific routes to use additional features.
- Expose different routes on different addresses so that internal and external users can see different routes, for example.
- Transfer traffic from one version of an application to another during a blue-green deployment.
When Ingress Controllers are sharded, a given route is admitted to zero or more Ingress Controllers in the group. The status of a route describes whether an Ingress Controller has admitted the route. An Ingress Controller only admits a route if the route is unique to a shard.
With sharding, you can distribute subsets of routes over multiple Ingress Controllers. These subsets can be nonoverlapping, also called traditional sharding, or overlapping, otherwise known as overlapped sharding.
The following table outlines three sharding methods:
| Sharding method | Description |
|---|---|
| Namespace selector | After you add a namespace selector to the Ingress Controller, all routes in a namespace that have matching labels for the namespace selector are included in the Ingress shard. Consider this method when an Ingress Controller serves all routes created in a namespace. |
| Route selector | After you add a route selector to the Ingress Controller, all routes with labels that match the route selector are included in the Ingress shard. Consider this method when you want an Ingress Controller to serve only a subset of routes or a specific route in a namespace. |
| Namespace and route selectors | Provides your Ingress Controller scope for both namespace selector and route selector methods. Consider this method when you want the flexibility of both the namespace selector and the route selector methods. |
28.3.6.1. Traditional sharding example
An example of a configured Ingress Controller finops-router that has the label selector spec.namespaceSelector.matchExpressions with key values set to finance and ops:
Example YAML definition for finops-router
An example of a configured Ingress Controller dev-router that has the label selector spec.namespaceSelector.matchLabels.name with the key value set to dev:
Example YAML definition for dev-router
If all application routes are in separate namespaces, such as each labeled with name:finance, name:ops, and name:dev, the configuration effectively distributes your routes between the two Ingress Controllers. OpenShift Container Platform routes for console, authentication, and other purposes should not be handled.
In the previous scenario, sharding becomes a special case of partitioning, with no overlapping subsets. Routes are divided between router shards.
The default Ingress Controller continues to serve all routes unless the namespaceSelector or routeSelector fields contain routes that are meant for exclusion. See this Red Hat Knowledgebase solution and the section "Sharding the default Ingress Controller" for more information on how to exclude routes from the default Ingress Controller.
28.3.6.2. Overlapped sharding example
An example of a configured Ingress Controller devops-router that has the label selector spec.namespaceSelector.matchExpressions with key values set to dev and ops:
Example YAML definition for devops-router
The routes in the namespaces labeled name:dev and name:ops are now serviced by two different Ingress Controllers. With this configuration, you have overlapping subsets of routes.
With overlapping subsets of routes you can create more complex routing rules. For example, you can divert higher priority traffic to the dedicated finops-router while sending lower priority traffic to devops-router.
28.3.6.3. Sharding the default Ingress Controller
After creating a new Ingress shard, there might be routes that are admitted to your new Ingress shard that are also admitted by the default Ingress Controller. This is because the default Ingress Controller has no selectors and admits all routes by default.
You can restrict an Ingress Controller from servicing routes with specific labels using either namespace selectors or route selectors. The following procedure restricts the default Ingress Controller from servicing your newly sharded finance, ops, and dev, routes using a namespace selector. This adds further isolation to Ingress shards.
You must keep all of OpenShift Container Platform’s administration routes on the same Ingress Controller. Therefore, avoid adding additional selectors to the default Ingress Controller that exclude these essential routes.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You are logged in as a project administrator.
Procedure
Modify the default Ingress Controller by running the following command:
oc edit ingresscontroller -n openshift-ingress-operator default
$ oc edit ingresscontroller -n openshift-ingress-operator defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the Ingress Controller to contain a
namespaceSelectorthat excludes the routes with any of thefinance,ops, anddevlabels:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The default Ingress Controller will no longer serve the namespaces labeled name:finance, name:ops, and name:dev.
28.3.6.4. Ingress sharding and DNS
The cluster administrator is responsible for making a separate DNS entry for each router in a project. A router will not forward unknown routes to another router.
Consider the following example:
-
Router A lives on host 192.168.0.5 and has routes with
*.foo.com. -
Router B lives on host 192.168.1.9 and has routes with
*.example.com.
Separate DNS entries must resolve *.foo.com to the node hosting Router A and *.example.com to the node hosting Router B:
-
*.foo.com A IN 192.168.0.5 -
*.example.com A IN 192.168.1.9
28.3.6.5. Configuring Ingress Controller sharding by using route labels
Ingress Controller sharding by using route labels means that the Ingress Controller serves any route in any namespace that is selected by the route selector.
Figure 28.1. Ingress sharding using route labels
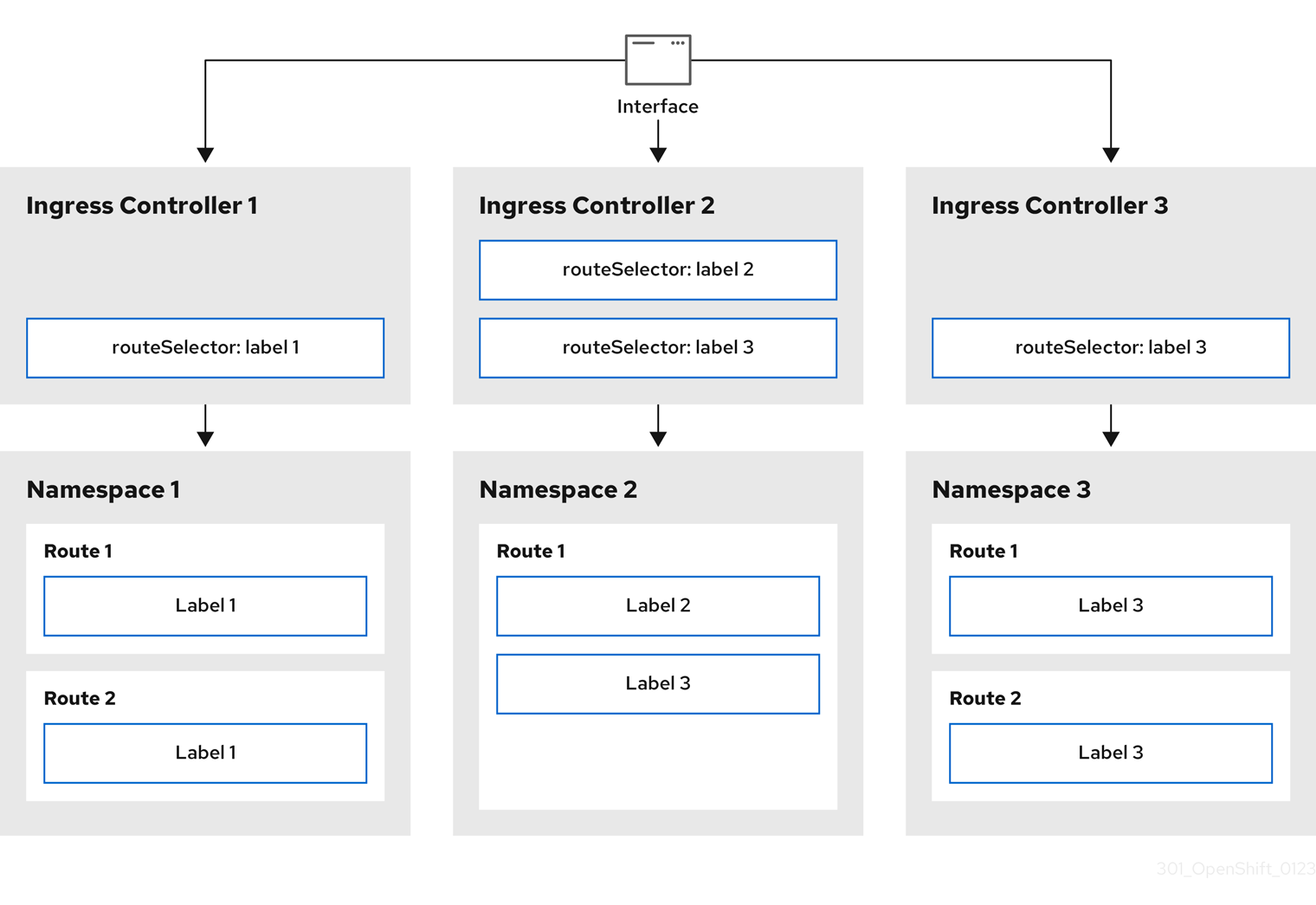
Ingress Controller sharding is useful when balancing incoming traffic load among a set of Ingress Controllers and when isolating traffic to a specific Ingress Controller. For example, company A goes to one Ingress Controller and company B to another.
Procedure
Edit the
router-internal.yamlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify a domain to be used by the Ingress Controller. This domain must be different from the default Ingress Controller domain.
Apply the Ingress Controller
router-internal.yamlfile:oc apply -f router-internal.yaml
# oc apply -f router-internal.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Ingress Controller selects routes in any namespace that have the label
type: sharded.Create a new route using the domain configured in the
router-internal.yaml:oc expose svc <service-name> --hostname <route-name>.apps-sharded.basedomain.example.net
$ oc expose svc <service-name> --hostname <route-name>.apps-sharded.basedomain.example.netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.3.6.6. Configuring Ingress Controller sharding by using namespace labels
Ingress Controller sharding by using namespace labels means that the Ingress Controller serves any route in any namespace that is selected by the namespace selector.
Figure 28.2. Ingress sharding using namespace labels
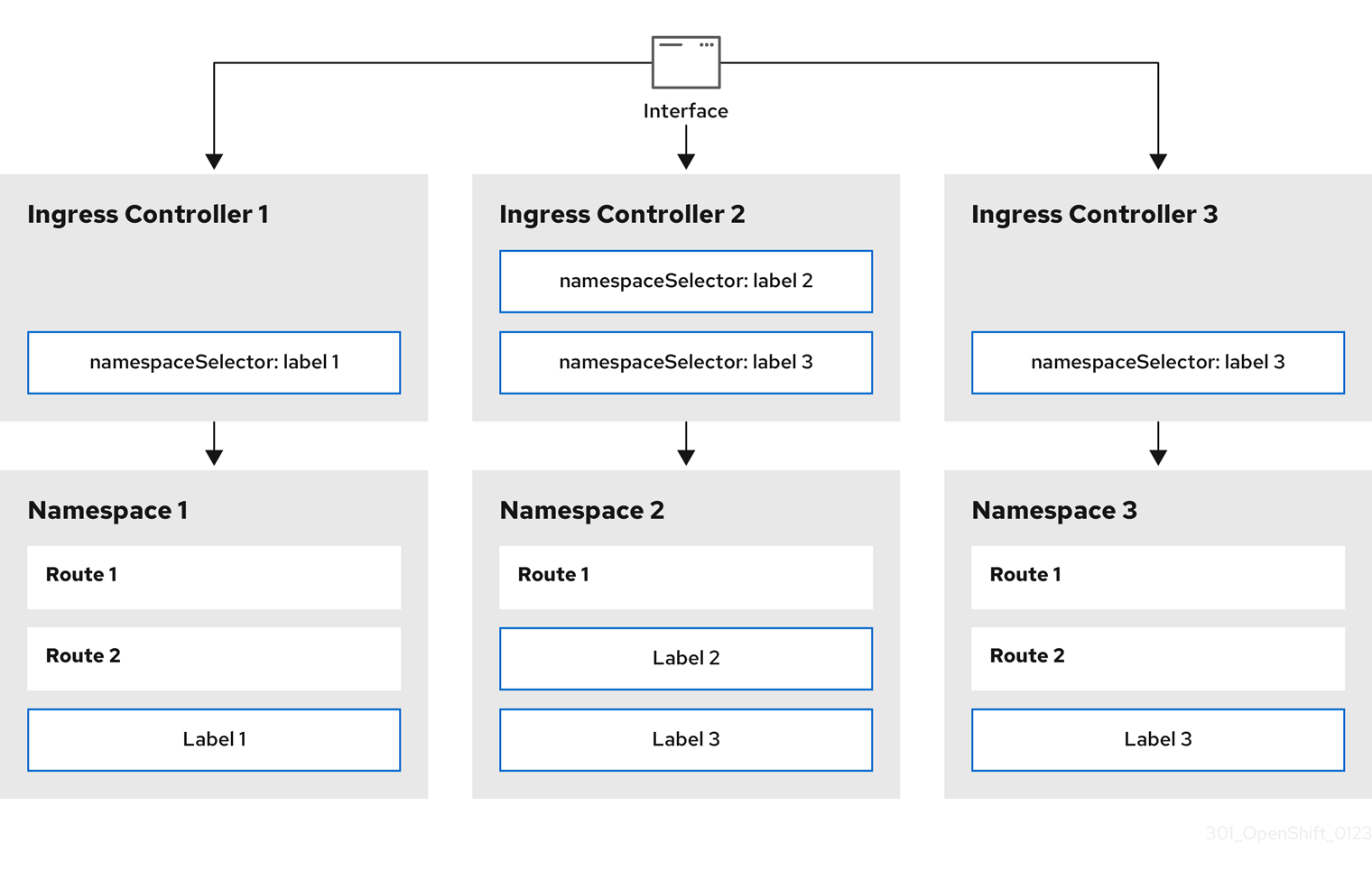
Ingress Controller sharding is useful when balancing incoming traffic load among a set of Ingress Controllers and when isolating traffic to a specific Ingress Controller. For example, company A goes to one Ingress Controller and company B to another.
Procedure
Edit the
router-internal.yamlfile:cat router-internal.yaml
$ cat router-internal.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify a domain to be used by the Ingress Controller. This domain must be different from the default Ingress Controller domain.
Apply the Ingress Controller
router-internal.yamlfile:oc apply -f router-internal.yaml
$ oc apply -f router-internal.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Ingress Controller selects routes in any namespace that is selected by the namespace selector that have the label
type: sharded.Create a new route using the domain configured in the
router-internal.yaml:oc expose svc <service-name> --hostname <route-name>.apps-sharded.basedomain.example.net
$ oc expose svc <service-name> --hostname <route-name>.apps-sharded.basedomain.example.netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.3.6.7. Creating a route for Ingress Controller sharding
A route allows you to host your application at a URL. In this case, the hostname is not set and the route uses a subdomain instead. When you specify a subdomain, you automatically use the domain of the Ingress Controller that exposes the route. For situations where a route is exposed by multiple Ingress Controllers, the route is hosted at multiple URLs.
The following procedure describes how to create a route for Ingress Controller sharding, using the hello-openshift application as an example.
Ingress Controller sharding is useful when balancing incoming traffic load among a set of Ingress Controllers and when isolating traffic to a specific Ingress Controller. For example, company A goes to one Ingress Controller and company B to another.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You are logged in as a project administrator.
- You have a web application that exposes a port and an HTTP or TLS endpoint listening for traffic on the port.
- You have configured the Ingress Controller for sharding.
Procedure
Create a project called
hello-openshiftby running the following command:oc new-project hello-openshift
$ oc new-project hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a pod in the project by running the following command:
oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/origin/master/examples/hello-openshift/hello-pod.json
$ oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/origin/master/examples/hello-openshift/hello-pod.jsonCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a service called
hello-openshiftby running the following command:oc expose pod/hello-openshift
$ oc expose pod/hello-openshiftCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a route definition called
hello-openshift-route.yaml:YAML definition of the created route for sharding:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Both the label key and its corresponding label value must match the ones specified in the Ingress Controller. In this example, the Ingress Controller has the label key and value
type: sharded. - 2
- The route will be exposed using the value of the
subdomainfield. When you specify thesubdomainfield, you must leave the hostname unset. If you specify both thehostandsubdomainfields, then the route will use the value of thehostfield, and ignore thesubdomainfield.
Use
hello-openshift-route.yamlto create a route to thehello-openshiftapplication by running the following command:oc -n hello-openshift create -f hello-openshift-route.yaml
$ oc -n hello-openshift create -f hello-openshift-route.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Get the status of the route with the following command:
oc -n hello-openshift get routes/hello-openshift-edge -o yaml
$ oc -n hello-openshift get routes/hello-openshift-edge -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The resulting
Routeresource should look similar to the following:Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The hostname the Ingress Controller, or router, uses to expose the route. The value of the
hostfield is automatically determined by the Ingress Controller, and uses its domain. In this example, the domain of the Ingress Controller is<apps-sharded.basedomain.example.net>. - 2
- The hostname of the Ingress Controller.
- 3
- The name of the Ingress Controller. In this example, the Ingress Controller has the name
sharded.
Additional resources
28.4. Configuring the Ingress Controller endpoint publishing strategy
The endpointPublishingStrategy is used to publish the Ingress Controller endpoints to other networks, enable load balancer integrations, and provide access to other systems.
On Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the LoadBalancerService endpoint publishing strategy is supported only if a cloud provider is configured to create health monitors. For RHOSP 16.2, this strategy is possible only if you use the Amphora Octavia provider.
For more information, see the "Setting RHOSP Cloud Controller Manager options" section of the RHOSP installation documentation.
28.4.1. Ingress Controller endpoint publishing strategy
NodePortService endpoint publishing strategy
The NodePortService endpoint publishing strategy publishes the Ingress Controller using a Kubernetes NodePort service.
In this configuration, the Ingress Controller deployment uses container networking. A NodePortService is created to publish the deployment. The specific node ports are dynamically allocated by OpenShift Container Platform; however, to support static port allocations, your changes to the node port field of the managed NodePortService are preserved.
Figure 28.3. Diagram of NodePortService

The preceding graphic shows the following concepts pertaining to OpenShift Container Platform Ingress NodePort endpoint publishing strategy:
- All the available nodes in the cluster have their own, externally accessible IP addresses. The service running in the cluster is bound to the unique NodePort for all the nodes.
-
When the client connects to a node that is down, for example, by connecting the
10.0.128.4IP address in the graphic, the node port directly connects the client to an available node that is running the service. In this scenario, no load balancing is required. As the image shows, the10.0.128.4address is down and another IP address must be used instead.
The Ingress Operator ignores any updates to .spec.ports[].nodePort fields of the service.
By default, ports are allocated automatically and you can access the port allocations for integrations. However, sometimes static port allocations are necessary to integrate with existing infrastructure which may not be easily reconfigured in response to dynamic ports. To achieve integrations with static node ports, you can update the managed service resource directly.
For more information, see the Kubernetes Services documentation on NodePort.
HostNetwork endpoint publishing strategy
The HostNetwork endpoint publishing strategy publishes the Ingress Controller on node ports where the Ingress Controller is deployed.
An Ingress Controller with the HostNetwork endpoint publishing strategy can have only one pod replica per node. If you want n replicas, you must use at least n nodes where those replicas can be scheduled. Because each pod replica requests ports 80 and 443 on the node host where it is scheduled, a replica cannot be scheduled to a node if another pod on the same node is using those ports.
The HostNetwork object has a hostNetwork field with the following default values for the optional binding ports: httpPort: 80, httpsPort: 443, and statsPort: 1936. By specifying different binding ports for your network, you can deploy multiple Ingress Controllers on the same node for the HostNetwork strategy.
Example
28.4.1.1. Configuring the Ingress Controller endpoint publishing scope to Internal
When a cluster administrator installs a new cluster without specifying that the cluster is private, the default Ingress Controller is created with a scope set to External. Cluster administrators can change an External scoped Ingress Controller to Internal.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
To change an
Externalscoped Ingress Controller toInternal, enter the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/default --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"scope":"Internal"}}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/default --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"scope":"Internal"}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check the status of the Ingress Controller, enter the following command:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers/default -o yaml
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers/default -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
Progressingstatus condition indicates whether you must take further action. For example, the status condition can indicate that you need to delete the service by entering the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress delete services/router-default
$ oc -n openshift-ingress delete services/router-defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you delete the service, the Ingress Operator recreates it as
Internal.
28.4.1.2. Configuring the Ingress Controller endpoint publishing scope to External
When a cluster administrator installs a new cluster without specifying that the cluster is private, the default Ingress Controller is created with a scope set to External.
The Ingress Controller’s scope can be configured to be Internal during installation or after, and cluster administrators can change an Internal Ingress Controller to External.
On some platforms, it is necessary to delete and recreate the service.
Changing the scope can cause disruption to Ingress traffic, potentially for several minutes. This applies to platforms where it is necessary to delete and recreate the service, because the procedure can cause OpenShift Container Platform to deprovision the existing service load balancer, provision a new one, and update DNS.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the
ocCLI.
Procedure
To change an
Internalscoped Ingress Controller toExternal, enter the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/private --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"scope":"External"}}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontrollers/private --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy":{"type":"LoadBalancerService","loadBalancer":{"scope":"External"}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check the status of the Ingress Controller, enter the following command:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers/default -o yaml
$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator get ingresscontrollers/default -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
Progressingstatus condition indicates whether you must take further action. For example, the status condition can indicate that you need to delete the service by entering the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress delete services/router-default
$ oc -n openshift-ingress delete services/router-defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you delete the service, the Ingress Operator recreates it as
External.
28.4.1.3. Adding a single NodePort service to an Ingress Controller
Instead of creating a NodePort-type Service for each project, you can create a custom Ingress Controller to use the NodePortService endpoint publishing strategy. To prevent port conflicts, consider this configuration for your Ingress Controller when you want to apply a set of routes, through Ingress sharding, to nodes that might already have a HostNetwork Ingress Controller.
Before you set a NodePort-type Service for each project, read the following considerations:
- You must create a wildcard DNS record for the Nodeport Ingress Controller domain. A Nodeport Ingress Controller route can be reached from the address of a worker node. For more information about the required DNS records for routes, see "User-provisioned DNS requirements".
-
You must expose a route for your service and specify the
--hostnameargument for your custom Ingress Controller domain. -
You must append the port that is assigned to the
NodePort-typeServicein the route so that you can access application pods.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You created a wildcard DNS record.
Procedure
Create a custom resource (CR) file for the Ingress Controller:
Example of a CR file that defines information for the
IngressControllerobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the a custom
namefor theIngressControllerCR. - 2
- The DNS name that the Ingress Controller services. As an example, the default ingresscontroller domain is
apps.ipi-cluster.example.com, so you would specify the<custom_ic_domain_name>asnodeportsvc.ipi-cluster.example.com. - 3
- Specify the label for the nodes that include the custom Ingress Controller.
- 4
- Specify the label for a set of namespaces. Substitute
<key>:<value>with a map of key-value pairs where<key>is a unique name for the new label and<value>is its value. For example:ingresscontroller: custom-ic.
Add a label to a node by using the
oc label nodecommand:oc label node <node_name> <key>=<value>
$ oc label node <node_name> <key>=<value>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Where
<value>must match the key-value pair specified in thenodePlacementsection of yourIngressControllerCR.
Create the
IngressControllerobject:oc create -f <ingress_controller_cr>.yaml
$ oc create -f <ingress_controller_cr>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the port for the service created for the
IngressControllerCR:oc get svc -n openshift-ingress
$ oc get svc -n openshift-ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output that shows port
80:32432/TCPfor therouter-nodeport-custom-ic3serviceNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE router-internal-default ClusterIP 172.30.195.74 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP,1936/TCP 223d router-nodeport-custom-ic3 NodePort 172.30.109.219 <none> 80:32432/TCP,443:31366/TCP,1936:30499/TCP 155m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE router-internal-default ClusterIP 172.30.195.74 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP,1936/TCP 223d router-nodeport-custom-ic3 NodePort 172.30.109.219 <none> 80:32432/TCP,443:31366/TCP,1936:30499/TCP 155mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a new project, enter the following command:
oc new-project <project_name>
$ oc new-project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To label the new namespace, enter the following command:
oc label namespace <project_name> <key>=<value>
$ oc label namespace <project_name> <key>=<value>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Where
<key>=<value>must match the value in thenamespaceSelectorsection of your Ingress Controller CR.
Create a new application in your cluster:
oc new-app --image=<image_name>
$ oc new-app --image=<image_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- An example of
<image_name>isquay.io/openshifttest/hello-openshift:multiarch.
Create a
Routeobject for a service, so that the pod can use the service to expose the application external to the cluster.oc expose svc/<service_name> --hostname=<svc_name>-<project_name>.<custom_ic_domain_name>
$ oc expose svc/<service_name> --hostname=<svc_name>-<project_name>.<custom_ic_domain_name>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou must specify the domain name of your custom Ingress Controller in the
--hostnameargument. If you do not do this, the Ingress Operator uses the default Ingress Controller to serve all the routes for your cluster.Check that the route has the
Admittedstatus and that it includes metadata for the custom Ingress Controller:oc get route/hello-openshift -o json | jq '.status.ingress'
$ oc get route/hello-openshift -o json | jq '.status.ingress'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the default
IngressControllerCR to prevent the default Ingress Controller from managing theNodePort-typeService. The default Ingress Controller will continue to monitor all other cluster traffic.oc patch --type=merge -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"namespaceSelector":{"matchExpressions":[{"key":"<key>","operator":"NotIn","values":["<value>]}]}}}'$ oc patch --type=merge -n openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/default --patch '{"spec":{"namespaceSelector":{"matchExpressions":[{"key":"<key>","operator":"NotIn","values":["<value>]}]}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the DNS entry can route inside and outside of your cluster by entering the following command. The command outputs the IP address of the node that received the label from running the
oc label nodecommand earlier in the procedure.dig +short <svc_name>-<project_name>.<custom_ic_domain_name>
$ dig +short <svc_name>-<project_name>.<custom_ic_domain_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that your cluster uses the IP addresses from external DNS servers for DNS resolution, check the connection of your cluster by entering the following command:
curl <svc_name>-<project_name>.<custom_ic_domain_name>:<port>
$ curl <svc_name>-<project_name>.<custom_ic_domain_name>:<port>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Output example
Hello OpenShift!
Hello OpenShift!Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.5. Configuring ingress cluster traffic using a load balancer
OpenShift Container Platform provides methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster. This method uses a load balancer.
28.5.1. Using a load balancer to get traffic into the cluster
If you do not need a specific external IP address, you can configure a load balancer service to allow external access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
A load balancer service allocates a unique IP. The load balancer has a single edge router IP, which can be a virtual IP (VIP), but is still a single machine for initial load balancing.
If a pool is configured, it is done at the infrastructure level, not by a cluster administrator.
The procedures in this section require prerequisites performed by the cluster administrator.
28.5.2. Prerequisites
Before starting the following procedures, the administrator must:
- Set up the external port to the cluster networking environment so that requests can reach the cluster.
Make sure there is at least one user with cluster admin role. To add this role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin username
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin usernameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Have an OpenShift Container Platform cluster with at least one master and at least one node and a system outside the cluster that has network access to the cluster. This procedure assumes that the external system is on the same subnet as the cluster. The additional networking required for external systems on a different subnet is out-of-scope for this topic.
28.5.3. Creating a project and service
If the project and service that you want to expose does not exist, create the project and then create the service.
If the project and service already exists, skip to the procedure on exposing the service to create a route.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc) and log in as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Create a new project for your service by running the
oc new-projectcommand:oc new-project <project_name>
$ oc new-project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
oc new-appcommand to create your service:oc new-app nodejs:12~https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex.git
$ oc new-app nodejs:12~https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the service was created, run the following command:
oc get svc -n <project_name>
$ oc get svc -n <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.197.157 <none> 8080/TCP 70s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.197.157 <none> 8080/TCP 70sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, the new service does not have an external IP address.
28.5.4. Exposing the service by creating a route
You can expose the service as a route by using the oc expose command.
Prerequisites
- You logged into OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
Log in to the project where the service you want to expose is located:
oc project <project_name>
$ oc project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the
oc expose servicecommand to expose the route:oc expose service nodejs-ex
$ oc expose service nodejs-exCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
route.route.openshift.io/nodejs-ex exposed
route.route.openshift.io/nodejs-ex exposedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the service is exposed, you can use a tool, such as
curlto check that the service is accessible from outside the cluster.To find the hostname of the route, enter the following command:
oc get route
$ oc get routeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD nodejs-ex nodejs-ex-myproject.example.com nodejs-ex 8080-tcp None
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD nodejs-ex nodejs-ex-myproject.example.com nodejs-ex 8080-tcp NoneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To check that the host responds to a GET request, enter the following command:
Example
curlcommandcurl --head nodejs-ex-myproject.example.com
$ curl --head nodejs-ex-myproject.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.5.5. Creating a load balancer service
Use the following procedure to create a load balancer service.
Prerequisites
- Make sure that the project and service you want to expose exist.
- Your cloud provider supports load balancers.
Procedure
To create a load balancer service:
- Log in to OpenShift Container Platform.
Load the project where the service you want to expose is located.
oc project project1
$ oc project project1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open a text file on the control plane node and paste the following text, editing the file as needed:
Sample load balancer configuration file
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Enter a descriptive name for the load balancer service.
- 2
- Enter the same port that the service you want to expose is listening on.
- 3
- Enter a list of specific IP addresses to restrict traffic through the load balancer. This field is ignored if the cloud-provider does not support the feature.
- 4
- Enter
Loadbalanceras the type. - 5
- Enter the name of the service.
NoteTo restrict the traffic through the load balancer to specific IP addresses, it is recommended to use the Ingress Controller field
spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.allowedSourceRanges. Do not set theloadBalancerSourceRangesfield.- Save and exit the file.
Run the following command to create the service:
oc create -f <file-name>
$ oc create -f <file-name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc create -f mysql-lb.yaml
$ oc create -f mysql-lb.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the following command to view the new service:
oc get svc
$ oc get svcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE egress-2 LoadBalancer 172.30.22.226 ad42f5d8b303045-487804948.example.com 3306:30357/TCP 15m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE egress-2 LoadBalancer 172.30.22.226 ad42f5d8b303045-487804948.example.com 3306:30357/TCP 15mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The service has an external IP address automatically assigned if there is a cloud provider enabled.
On the master, use a tool, such as cURL, to make sure you can reach the service using the public IP address:
curl <public-ip>:<port>
$ curl <public-ip>:<port>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
curl 172.29.121.74:3306
$ curl 172.29.121.74:3306Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The examples in this section use a MySQL service, which requires a client application. If you get a string of characters with the
Got packets out of ordermessage, you are connecting with the service:If you have a MySQL client, log in with the standard CLI command:
mysql -h 172.30.131.89 -u admin -p
$ mysql -h 172.30.131.89 -u admin -pCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. MySQL [(none)]>
Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. MySQL [(none)]>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.6. Configuring ingress cluster traffic on AWS
OpenShift Container Platform provides methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster. This method uses load balancers on AWS, specifically a Network Load Balancer (NLB) or a Classic Load Balancer (CLB). Both types of load balancers can forward the client’s IP address to the node, but a CLB requires proxy protocol support, which OpenShift Container Platform automatically enables.
There are two ways to configure an Ingress Controller to use an NLB:
-
By force replacing the Ingress Controller that is currently using a CLB. This deletes the
IngressControllerobject and an outage will occur while the new DNS records propagate and the NLB is being provisioned. -
By editing an existing Ingress Controller that uses a CLB to use an NLB. This changes the load balancer without having to delete and recreate the
IngressControllerobject.
Both methods can be used to switch from an NLB to a CLB.
You can configure these load balancers on a new or existing AWS cluster.
28.6.1. Configuring Classic Load Balancer timeouts on AWS
OpenShift Container Platform provides a method for setting a custom timeout period for a specific route or Ingress Controller. Additionally, an AWS Classic Load Balancer (CLB) has its own timeout period with a default time of 60 seconds.
If the timeout period of the CLB is shorter than the route timeout or Ingress Controller timeout, the load balancer can prematurely terminate the connection. You can prevent this problem by increasing both the timeout period of the route and CLB.
28.6.1.1. Configuring route timeouts
You can configure the default timeouts for an existing route when you have services in need of a low timeout, which is required for Service Level Availability (SLA) purposes, or a high timeout, for cases with a slow back end.
If you configured a user-managed external load balancer in front of your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, ensure that the timeout value for the user-managed external load balancer is higher than the timeout value for the route. This configuration prevents network congestion issues over the network that your cluster uses.
Prerequisites
- You need a deployed Ingress Controller on a running cluster.
Procedure
Using the
oc annotatecommand, add the timeout to the route:oc annotate route <route_name> \ --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=<timeout><time_unit>$ oc annotate route <route_name> \ --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=<timeout><time_unit>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Supported time units are microseconds (us), milliseconds (ms), seconds (s), minutes (m), hours (h), or days (d).
The following example sets a timeout of two seconds on a route named
myroute:oc annotate route myroute --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=2s
$ oc annotate route myroute --overwrite haproxy.router.openshift.io/timeout=2sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.6.1.2. Configuring Classic Load Balancer timeouts
You can configure the default timeouts for a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) to extend idle connections.
Prerequisites
- You must have a deployed Ingress Controller on a running cluster.
Procedure
Set an AWS connection idle timeout of five minutes for the default
ingresscontrollerby running the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Restore the default value of the timeout by running the following command:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default \ --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy": \ {"loadBalancer":{"providerParameters":{"aws":{"classicLoadBalancer": \ {"connectionIdleTimeout":null}}}}}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default \ --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy": \ {"loadBalancer":{"providerParameters":{"aws":{"classicLoadBalancer": \ {"connectionIdleTimeout":null}}}}}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You must specify the scope field when you change the connection timeout value unless the current scope is already set. When you set the scope field, you do not need to do so again if you restore the default timeout value.
28.6.2. Configuring ingress cluster traffic on AWS using a Network Load Balancer
OpenShift Container Platform provides methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services that run in the cluster. One such method uses a Network Load Balancer (NLB). You can configure an NLB on a new or existing AWS cluster.
28.6.2.1. Switching the Ingress Controller from using a Classic Load Balancer to a Network Load Balancer
You can switch the Ingress Controller that is using a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) to one that uses a Network Load Balancer (NLB) on AWS.
Switching between these load balancers will not delete the IngressController object.
This procedure might cause the following issues:
- An outage that can last several minutes due to new DNS records propagation, new load balancers provisioning, and other factors. IP addresses and canonical names of the Ingress Controller load balancer might change after applying this procedure.
- Leaked load balancer resources due to a change in the annotation of the service.
Procedure
Modify the existing Ingress Controller that you want to switch to using an NLB. This example assumes that your default Ingress Controller has an
Externalscope and no other customizations:Example
ingresscontroller.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do not specify a value for the
spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.providerParameters.aws.typefield, the Ingress Controller uses thespec.loadBalancer.platform.aws.typevalue from the clusterIngressconfiguration that was set during installation.TipIf your Ingress Controller has other customizations that you want to update, such as changing the domain, consider force replacing the Ingress Controller definition file instead.
Apply the changes to the Ingress Controller YAML file by running the command:
oc apply -f ingresscontroller.yaml
$ oc apply -f ingresscontroller.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expect several minutes of outages while the Ingress Controller updates.
28.6.2.2. Switching the Ingress Controller from using a Network Load Balancer to a Classic Load Balancer
You can switch the Ingress Controller that is using a Network Load Balancer (NLB) to one that uses a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) on AWS.
Switching between these load balancers will not delete the IngressController object.
This procedure might cause an outage that can last several minutes due to new DNS records propagation, new load balancers provisioning, and other factors. IP addresses and canonical names of the Ingress Controller load balancer might change after applying this procedure.
Procedure
Modify the existing Ingress Controller that you want to switch to using a CLB. This example assumes that your default Ingress Controller has an
Externalscope and no other customizations:Example
ingresscontroller.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do not specify a value for the
spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.providerParameters.aws.typefield, the Ingress Controller uses thespec.loadBalancer.platform.aws.typevalue from the clusterIngressconfiguration that was set during installation.TipIf your Ingress Controller has other customizations that you want to update, such as changing the domain, consider force replacing the Ingress Controller definition file instead.
Apply the changes to the Ingress Controller YAML file by running the command:
oc apply -f ingresscontroller.yaml
$ oc apply -f ingresscontroller.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expect several minutes of outages while the Ingress Controller updates.
28.6.2.3. Replacing Ingress Controller Classic Load Balancer with Network Load Balancer
You can replace an Ingress Controller that is using a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) with one that uses a Network Load Balancer (NLB) on AWS.
This procedure might cause the following issues:
- An outage that can last several minutes due to new DNS records propagation, new load balancers provisioning, and other factors. IP addresses and canonical names of the Ingress Controller load balancer might change after applying this procedure.
- Leaked load balancer resources due to a change in the annotation of the service.
Procedure
Create a file with a new default Ingress Controller. The following example assumes that your default Ingress Controller has an
Externalscope and no other customizations:Example
ingresscontroller.ymlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If your default Ingress Controller has other customizations, ensure that you modify the file accordingly.
TipIf your Ingress Controller has no other customizations and you are only updating the load balancer type, consider following the procedure detailed in "Switching the Ingress Controller from using a Classic Load Balancer to a Network Load Balancer".
Force replace the Ingress Controller YAML file:
oc replace --force --wait -f ingresscontroller.yml
$ oc replace --force --wait -f ingresscontroller.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until the Ingress Controller is replaced. Expect several of minutes of outages.
28.6.2.4. Configuring an Ingress Controller Network Load Balancer on an existing AWS cluster
You can create an Ingress Controller backed by an AWS Network Load Balancer (NLB) on an existing cluster.
Prerequisites
- You must have an installed AWS cluster.
PlatformStatusof the infrastructure resource must be AWS.To verify that the
PlatformStatusis AWS, run:oc get infrastructure/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.platformStatus.type}' AWS$ oc get infrastructure/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.platformStatus.type}' AWSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
Create an Ingress Controller backed by an AWS NLB on an existing cluster.
Create the Ingress Controller manifest:
cat ingresscontroller-aws-nlb.yaml
$ cat ingresscontroller-aws-nlb.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
$my_ingress_controllerwith a unique name for the Ingress Controller. - 2
- Replace
$my_unique_ingress_domainwith a domain name that is unique among all Ingress Controllers in the cluster. This variable must be a subdomain of the DNS name<clustername>.<domain>. - 3
- You can replace
ExternalwithInternalto use an internal NLB.
Create the resource in the cluster:
oc create -f ingresscontroller-aws-nlb.yaml
$ oc create -f ingresscontroller-aws-nlb.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Before you can configure an Ingress Controller NLB on a new AWS cluster, you must complete the Creating the installation configuration file procedure.
28.6.2.5. Configuring an Ingress Controller Network Load Balancer on a new AWS cluster
You can create an Ingress Controller backed by an AWS Network Load Balancer (NLB) on a new cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Create the
install-config.yamlfile and complete any modifications to it.
Procedure
Create an Ingress Controller backed by an AWS NLB on a new cluster.
Change to the directory that contains the installation program and create the manifests:
./openshift-install create manifests --dir <installation_directory>
$ ./openshift-install create manifests --dir <installation_directory>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
<installation_directory>, specify the name of the directory that contains theinstall-config.yamlfile for your cluster.
Create a file that is named
cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlin the<installation_directory>/manifests/directory:touch <installation_directory>/manifests/cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yaml
$ touch <installation_directory>/manifests/cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
<installation_directory>, specify the directory name that contains themanifests/directory for your cluster.
After creating the file, several network configuration files are in the
manifests/directory, as shown:ls <installation_directory>/manifests/cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yaml
$ ls <installation_directory>/manifests/cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yaml
cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open the
cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlfile in an editor and enter a custom resource (CR) that describes the Operator configuration you want:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Save the
cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlfile and quit the text editor. -
Optional: Back up the
manifests/cluster-ingress-default-ingresscontroller.yamlfile. The installation program deletes themanifests/directory when creating the cluster.
28.7. Configuring ingress cluster traffic for a service external IP
You can use either a MetalLB implementation or an IP failover deployment to attach an ExternalIP resource to a service so that the service is available to traffic outside your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. Hosting an external IP address in this way is only applicable for a cluster installed on bare-metal hardware.
You must ensure that you correctly configure the external network infrastructure to route traffic to the service.
28.7.1. Prerequisites
Your cluster is configured with ExternalIPs enabled. For more information, read Configuring ExternalIPs for services.
NoteDo not use the same ExternalIP for the egress IP.
28.7.2. Attaching an ExternalIP to a service
You can attach an ExternalIP resource to a service. If you configured your cluster to automatically attach the resource to a service, you might not need to manually attach an ExternalIP to the service.
The examples in the procedure use a scenario that manually attaches an ExternalIP resource to a service in a cluster with an IP failover configuration.
Procedure
Confirm compatible IP address ranges for the ExternalIP resource by entering the following command in your CLI:
oc get networks.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.spec.externalIP}{"\n"}'$ oc get networks.config cluster -o jsonpath='{.spec.externalIP}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf
autoAssignCIDRsis set and you did not specify a value forspec.externalIPsin the ExternalIP resource, OpenShift Container Platform automatically assigns ExternalIP to a newServiceobject.Choose one of the following options to attach an ExternalIP resource to the service:
If you are creating a new service, specify a value in the
spec.externalIPsfield and array of one or more valid IP addresses in theallowedCIDRsparameter.Example of service YAML configuration file that supports an ExternalIP resource
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you are attaching an ExternalIP to an existing service, enter the following command. Replace
<name>with the service name. Replace<ip_address>with a valid ExternalIP address. You can provide multiple IP addresses separated by commas.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc patch svc mysql-55-rhel7 -p '{"spec":{"externalIPs":["192.174.120.10"]}}'$ oc patch svc mysql-55-rhel7 -p '{"spec":{"externalIPs":["192.174.120.10"]}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
"mysql-55-rhel7" patched
"mysql-55-rhel7" patchedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To confirm that an ExternalIP address is attached to the service, enter the following command. If you specified an ExternalIP for a new service, you must create the service first.
oc get svc
$ oc get svcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql-55-rhel7 172.30.131.89 192.174.120.10 3306/TCP 13m
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql-55-rhel7 172.30.131.89 192.174.120.10 3306/TCP 13mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.8. Configuring ingress cluster traffic by using a NodePort
OpenShift Container Platform provides methods for communicating from outside the cluster with services running in the cluster. This method uses a NodePort.
28.8.1. Using a NodePort to get traffic into the cluster
Use a NodePort-type Service resource to expose a service on a specific port on all nodes in the cluster. The port is specified in the Service resource’s .spec.ports[*].nodePort field.
Using a node port requires additional port resources.
A NodePort exposes the service on a static port on the node’s IP address. NodePorts are in the 30000 to 32767 range by default, which means a NodePort is unlikely to match a service’s intended port. For example, port 8080 may be exposed as port 31020 on the node.
The administrator must ensure the external IP addresses are routed to the nodes.
NodePorts and external IPs are independent and both can be used concurrently.
The procedures in this section require prerequisites performed by the cluster administrator.
28.8.2. Prerequisites
Before starting the following procedures, the administrator must:
- Set up the external port to the cluster networking environment so that requests can reach the cluster.
Make sure there is at least one user with cluster admin role. To add this role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user_name>
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Have an OpenShift Container Platform cluster with at least one master and at least one node and a system outside the cluster that has network access to the cluster. This procedure assumes that the external system is on the same subnet as the cluster. The additional networking required for external systems on a different subnet is out-of-scope for this topic.
28.8.3. Creating a project and service
If the project and service that you want to expose does not exist, create the project and then create the service.
If the project and service already exists, skip to the procedure on exposing the service to create a route.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc) and log in as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
Create a new project for your service by running the
oc new-projectcommand:oc new-project <project_name>
$ oc new-project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
oc new-appcommand to create your service:oc new-app nodejs:12~https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex.git
$ oc new-app nodejs:12~https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the service was created, run the following command:
oc get svc -n <project_name>
$ oc get svc -n <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.197.157 <none> 8080/TCP 70s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.197.157 <none> 8080/TCP 70sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, the new service does not have an external IP address.
28.8.4. Exposing the service by creating a route
You can expose the service as a route by using the oc expose command.
Prerequisites
- You logged into OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
Log in to the project where the service you want to expose is located:
oc project <project_name>
$ oc project <project_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To expose a node port for the application, modify the custom resource definition (CRD) of a service by entering the following command:
oc edit svc <service_name>
$ oc edit svc <service_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To confirm the service is available with a node port exposed, enter the following command:
oc get svc -n myproject
$ oc get svc -n myprojectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.217.127 <none> 3306/TCP 9m44s nodejs-ex-ingress NodePort 172.30.107.72 <none> 3306:31345/TCP 39s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nodejs-ex ClusterIP 172.30.217.127 <none> 3306/TCP 9m44s nodejs-ex-ingress NodePort 172.30.107.72 <none> 3306:31345/TCP 39sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To remove the service created automatically by the
oc new-appcommand, enter the following command:oc delete svc nodejs-ex
$ oc delete svc nodejs-exCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To check that the service node port is updated with a port in the
30000-32767range, enter the following command:oc get svc
$ oc get svcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following example output, the updated port is
30327:Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE httpd NodePort 172.xx.xx.xx <none> 8443:30327/TCP 109s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE httpd NodePort 172.xx.xx.xx <none> 8443:30327/TCP 109sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
28.9. Configuring ingress cluster traffic using load balancer allowed source ranges
You can specify a list of IP address ranges for the IngressController. This restricts access to the load balancer service when the endpointPublishingStrategy is LoadBalancerService.
28.9.1. Configuring load balancer allowed source ranges
You can enable and configure the spec.endpointPublishingStrategy.loadBalancer.allowedSourceRanges field. By configuring load balancer allowed source ranges, you can limit the access to the load balancer for the Ingress Controller to a specified list of IP address ranges. The Ingress Operator reconciles the load balancer Service and sets the spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field based on AllowedSourceRanges.
If you have already set the spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field or the load balancer service anotation service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges in a previous version of OpenShift Container Platform, Ingress Controller starts reporting Progressing=True after an upgrade. To fix this, set AllowedSourceRanges that overwrites the spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field and clears the service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges annotation. Ingress Controller starts reporting Progressing=False again.
Prerequisites
- You have a deployed Ingress Controller on a running cluster.
Procedure
Set the allowed source ranges API for the Ingress Controller by running the following command:
oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default \ --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy": \ {"type":"LoadBalancerService", "loadbalancer": \ {"scope":"External", "allowedSourceRanges":["0.0.0.0/0"]}}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default \ --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy": \ {"type":"LoadBalancerService", "loadbalancer": \ {"scope":"External", "allowedSourceRanges":["0.0.0.0/0"]}}}}'1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The example value
0.0.0.0/0specifies the allowed source range.
28.9.2. Migrating to load balancer allowed source ranges
If you have already set the annotation service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges, you can migrate to load balancer allowed source ranges. When you set the AllowedSourceRanges, the Ingress Controller sets the spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field based on the AllowedSourceRanges value and unsets the service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges annotation.
If you have already set the spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field or the load balancer service anotation service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges in a previous version of OpenShift Container Platform, the Ingress Controller starts reporting Progressing=True after an upgrade. To fix this, set AllowedSourceRanges that overwrites the spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field and clears the service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges annotation. The Ingress Controller starts reporting Progressing=False again.
Prerequisites
-
You have set the
service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-rangesannotation.
Procedure
Ensure that the
service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-rangesis set:oc get svc router-default -n openshift-ingress -o yaml
$ oc get svc router-default -n openshift-ingress -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges: 192.168.0.1/32apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-source-ranges: 192.168.0.1/32Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure that the
spec.loadBalancerSourceRangesfield is unset:oc get svc router-default -n openshift-ingress -o yaml
$ oc get svc router-default -n openshift-ingress -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
... spec: loadBalancerSourceRanges: - 0.0.0.0/0 ...
... spec: loadBalancerSourceRanges: - 0.0.0.0/0 ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Update your cluster to OpenShift Container Platform 4.13.
Set the allowed source ranges API for the
ingresscontrollerby running the following command:oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default \ --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy": \ {"loadBalancer":{"allowedSourceRanges":["0.0.0.0/0"]}}}}'$ oc -n openshift-ingress-operator patch ingresscontroller/default \ --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"endpointPublishingStrategy": \ {"loadBalancer":{"allowedSourceRanges":["0.0.0.0/0"]}}}}'1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The example value
0.0.0.0/0specifies the allowed source range.
28.10. Patching existing ingress objects
You can update or modify the following fields of existing Ingress objects without recreating the objects or disrupting services to them:
- Specifications
- Host
- Path
- Backend services
- SSL/TLS settings
- Annotations
28.10.1. Patching Ingress objects to resolve an ingressWithoutClassName alert
The ingressClassName field specifies the name of the IngressClass object. You must define the ingressClassName field for each Ingress object.
If you have not defined the ingressClassName field for an Ingress object, you could experience routing issues. After 24 hours, you will receive an ingressWithoutClassName alert to remind you to set the ingressClassName field.
Procedure
Patch the Ingress objects with a completed ingressClassName field to ensure proper routing and functionality.
List all
IngressClassobjects:oc get ingressclass
$ oc get ingressclassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List all
Ingressobjects in all namespaces:oc get ingress -A
$ oc get ingress -ACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Patch the
Ingressobject:oc patch ingress/<ingress_name> --type=merge --patch '{"spec":{"ingressClassName":"openshift-default"}}'$ oc patch ingress/<ingress_name> --type=merge --patch '{"spec":{"ingressClassName":"openshift-default"}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<ingress_name>with the name of theIngressobject. This command patches theIngressobject to include the desired ingress class name.
Chapter 29. Kubernetes NMState
29.1. About the Kubernetes NMState Operator
The Kubernetes NMState Operator provides a Kubernetes API for performing state-driven network configuration across the OpenShift Container Platform cluster’s nodes with NMState. The Kubernetes NMState Operator provides users with functionality to configure various network interface types, DNS, and routing on cluster nodes. Additionally, the daemons on the cluster nodes periodically report on the state of each node’s network interfaces to the API server.
Red Hat supports the Kubernetes NMState Operator in production environments on bare-metal, IBM Power, IBM Z, IBM® LinuxONE, VMware vSphere, and OpenStack installations.
Before you can use NMState with OpenShift Container Platform, you must install the Kubernetes NMState Operator.
The Kubernetes NMState Operator updates the network configuration of a secondary NIC. It cannot update the network configuration of the primary NIC or the br-ex bridge.
OpenShift Container Platform uses nmstate to report on and configure the state of the node network. This makes it possible to modify the network policy configuration, such as by creating a Linux bridge on all nodes, by applying a single configuration manifest to the cluster.
Node networking is monitored and updated by the following objects:
NodeNetworkState- Reports the state of the network on that node.
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy-
Describes the requested network configuration on nodes. You update the node network configuration, including adding and removing interfaces, by applying a
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicymanifest to the cluster. NodeNetworkConfigurationEnactment- Reports the network policies enacted upon each node.
29.1.1. Installing the Kubernetes NMState Operator
You can install the Kubernetes NMState Operator by using the web console or the CLI.
29.1.1.1. Installing the Kubernetes NMState Operator using the web console
You can install the Kubernetes NMState Operator by using the web console. After it is installed, the Operator can deploy the NMState State Controller as a daemon set across all of the cluster nodes.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
- Select Operators → OperatorHub.
-
In the search field below All Items, enter
nmstateand click Enter to search for the Kubernetes NMState Operator. - Click on the Kubernetes NMState Operator search result.
- Click on Install to open the Install Operator window.
- Click Install to install the Operator.
- After the Operator finishes installing, click View Operator.
-
Under Provided APIs, click Create Instance to open the dialog box for creating an instance of
kubernetes-nmstate. In the Name field of the dialog box, ensure the name of the instance is
nmstate.NoteThe name restriction is a known issue. The instance is a singleton for the entire cluster.
- Accept the default settings and click Create to create the instance.
Summary
Once complete, the Operator has deployed the NMState State Controller as a daemon set across all of the cluster nodes.
29.1.1.2. Installing the Kubernetes NMState Operator by using the CLI
You can install the Kubernetes NMState Operator by using the OpenShift CLI (oc). After it is installed, the Operator can deploy the NMState State Controller as a daemon set across all of the cluster nodes.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create the
nmstateOperator namespace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
OperatorGroup:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Subscribe to the
nmstateOperator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create instance of the
nmstateoperator:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Confirm that the deployment for the
nmstateoperator is running:oc get clusterserviceversion -n openshift-nmstate \ -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phase
oc get clusterserviceversion -n openshift-nmstate \ -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phaseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name Phase kubernetes-nmstate-operator.4.13.0-202210210157 Succeeded
Name Phase kubernetes-nmstate-operator.4.13.0-202210210157 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
29.1.2. Uninstalling the Kubernetes NMState Operator
You can use the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) to uninstall the Kubernetes NMState Operator, but by design OLM does not delete any associated custom resource definitions (CRDs), custom resources (CRs), or API Services.
Before you uninstall the Kubernetes NMState Operator from the Subcription resource used by OLM, identify what Kubernetes NMState Operator resources to delete. This identification ensures that you can delete resources without impacting your running cluster.
If you need to reinstall the Kubernetes NMState Operator, see "Installing the Kubernetes NMState Operator by using the CLI" or "Installing the Kubernetes NMState Operator by using the web console".
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Unsubscribe the Kubernetes NMState Operator from the
Subcriptionresource by running the following command:oc delete --namespace openshift-nmstate subscription kubernetes-nmstate-operator
$ oc delete --namespace openshift-nmstate subscription kubernetes-nmstate-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the
ClusterServiceVersion(CSV) resource that associates with the Kubernetes NMState Operator:oc get --namespace openshift-nmstate clusterserviceversion
$ oc get --namespace openshift-nmstate clusterserviceversionCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output that lists a CSV resource
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE kubernetes-nmstate-operator.v4.18.0 Kubernetes NMState Operator 4.18.0 Succeeded
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE kubernetes-nmstate-operator.v4.18.0 Kubernetes NMState Operator 4.18.0 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the CSV resource. After you delete the file, OLM deletes certain resources, such as
RBAC, that it created for the Operator.oc delete --namespace openshift-nmstate clusterserviceversion kubernetes-nmstate-operator.v4.18.0
$ oc delete --namespace openshift-nmstate clusterserviceversion kubernetes-nmstate-operator.v4.18.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the
nmstateCR and any associatedDeploymentresources by running the following commands:oc -n openshift-nmstate delete nmstate nmstate
$ oc -n openshift-nmstate delete nmstate nmstateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete --all deployments --namespace=openshift-nmstate
$ oc delete --all deployments --namespace=openshift-nmstateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete all the custom resource definition (CRD), such as
nmstates, that exist in thenmstate.ionamespace by running the following commands:oc delete crd nmstates.nmstate.io
$ oc delete crd nmstates.nmstate.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd nodenetworkconfigurationenactments.nmstate.io
$ oc delete crd nodenetworkconfigurationenactments.nmstate.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd nodenetworkstates.nmstate.io
$ oc delete crd nodenetworkstates.nmstate.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc delete crd nodenetworkconfigurationpolicies.nmstate.io
$ oc delete crd nodenetworkconfigurationpolicies.nmstate.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the namespace:
oc delete namespace kubernetes-nmstate
$ oc delete namespace kubernetes-nmstateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
29.2. Observing and updating the node network state and configuration
For more information about how to install the NMState Operator, see Kubernetes NMState Operator.
29.2.1. Viewing the network state of a node
Node network state is the network configuration for all nodes in the cluster. A NodeNetworkState object exists on every node in the cluster. This object is periodically updated and captures the state of the network for that node.
Procedure
List all the
NodeNetworkStateobjects in the cluster:oc get nns
$ oc get nnsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Inspect a
NodeNetworkStateobject to view the network on that node. The output in this example has been redacted for clarity:oc get nns node01 -o yaml
$ oc get nns node01 -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the
NodeNetworkStateobject is taken from the node. - 2
- The
currentStatecontains the complete network configuration for the node, including DNS, interfaces, and routes. - 3
- Timestamp of the last successful update. This is updated periodically as long as the node is reachable and can be used to evalute the freshness of the report.
29.2.2. The NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest file
A NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy (NNCP) manifest file defines policies that the Kubernetes NMState Operator uses to configure networking for nodes that exist in an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you want to apply multiple NNCP CRs to a node, you must create the NNCPs in a logical order that is based on the alphanumeric sorting of the policy names. The Kubernetes NMState Operator continuously checks for a newly created NNCP CR so that the Operator can instantly apply the CR to node. Consider the following logical order issue example:
-
You create NNCP 1 for defining the bridge interface that listens on a VLAN port, such as
eth1.1000. -
You create NNCP 2 for defining the VLAN interface and specify the port for this interface, such as
eth1.1000. - You apply NNCP 1 before you apply NNCP 2 to the node.
The node experiences a node connectivity issue because port eth1.1000 does not exist. As a result, the cluster fails.
After you apply a node network policy to a node, the Kubernetes NMState Operator configures the networking configuration for nodes according to the node network policy details.
You can create an NNCP by using either the OpenShift CLI (oc) or the OpenShift Container Platform web console. As a postinstallation task you can create an NNCP or edit an existing NNCP.
Before you create an NNCP, ensure that you read the "Example policy configurations for different interfaces" document.
If you want to delete an NNCP, you can use the oc delete nncp command to complete this action. However, this command does not delete any objects, such as a bridge interface.
Deleting the node network policy that added an interface to a node does not change the configuration of the policy on the node. Similarly, removing an interface does not delete the policy, because the Kubernetes NMState Operator re-adds the removed interface whenever a pod or a node is restarted.
To effectively delete the NNCP, the node network policy, and any interfaces would typically require the following actions:
-
Edit the NNCP and remove interface details from the file. Ensure that you do not remove
name,state, andtypeparameters from the file. -
Add
state: absentunder theinterfaces.statesection of the NNCP. -
Run
oc apply -f <nncp_file_name>. After the Kubernetes NMState Operator applies the node network policy to each node in your cluster, any interface that exists on each node is now marked as absent. -
Run
oc delete nncpto delete the NNCP.
Additional resources
29.2.3. Managing policy by using the CLI
29.2.3.1. Creating an interface on nodes
Create an interface on nodes in the cluster by applying a NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy (NNCP) manifest to the cluster. The manifest details the requested configuration for the interface.
By default, the manifest applies to all nodes in the cluster. To add the interface to specific nodes, add the spec: nodeSelector parameter and the appropriate <key>:<value> for your node selector.
You can configure multiple nmstate-enabled nodes concurrently. The configuration applies to 50% of the nodes in parallel. This strategy prevents the entire cluster from being unavailable if the network connection fails. To apply the policy configuration in parallel to a specific portion of the cluster, use the maxUnavailable parameter in the NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest configuration file.
If you have two nodes and you apply an NNCP manifest with the maxUnavailable parameter set to 50% to these nodes, one node at a time receives the NNCP configuration. If you then introduce an additional NNCP manifest file with the maxUnavailable parameter set to 50%, this NCCP is independent of the initial NNCP; this means that if both NNCP manifests apply a bad configuration to nodes, you can no longer guarantee that half of your cluster is functional.
Procedure
Create the
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicymanifest. The following example configures a Linux bridge on all worker nodes and configures the DNS resolver:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses the
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""node selector to select all worker nodes in the cluster. - 4
- Optional: Specifies the maximum number of nmstate-enabled nodes that the policy configuration can be applied to concurrently. This parameter can be set to either a percentage value (string), for example,
"10%", or an absolute value (number), such as3. - 5
- Optional: Human-readable description for the interface.
- 6
- Optional: Specifies the search and server settings for the DNS server.
Create the node network policy:
oc apply -f br1-eth1-policy.yaml
$ oc apply -f br1-eth1-policy.yaml1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- File name of the node network configuration policy manifest.
Additional resources
29.2.4. Confirming node network policy updates on nodes
When you apply a node network policy, a NodeNetworkConfigurationEnactment object is created for every node in the cluster. The node network configuration enactment is a read-only object that represents the status of execution of the policy on that node. If the policy fails to be applied on the node, the enactment for that node includes a traceback for troubleshooting.
Procedure
To confirm that a policy has been applied to the cluster, list the policies and their status:
oc get nncp
$ oc get nncpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: If a policy is taking longer than expected to successfully configure, you can inspect the requested state and status conditions of a particular policy:
oc get nncp <policy> -o yaml
$ oc get nncp <policy> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: If a policy is taking longer than expected to successfully configure on all nodes, you can list the status of the enactments on the cluster:
oc get nnce
$ oc get nnceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To view the configuration of a particular enactment, including any error reporting for a failed configuration:
oc get nnce <node>.<policy> -o yaml
$ oc get nnce <node>.<policy> -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
29.2.5. Removing an interface from nodes
You can remove an interface from one or more nodes in the cluster by editing the NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy object and setting the state of the interface to absent.
Removing an interface from a node does not automatically restore the node network configuration to a previous state. If you want to restore the previous state, you will need to define that node network configuration in the policy.
If you remove a bridge or bonding interface, any node NICs in the cluster that were previously attached or subordinate to that bridge or bonding interface are placed in a down state and become unreachable. To avoid losing connectivity, configure the node NIC in the same policy so that it has a status of up and either DHCP or a static IP address.
Deleting the node network policy that added an interface does not change the configuration of the policy on the node. Although a NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy is an object in the cluster, the object only represents the requested configuration. Similarly, removing an interface does not delete the policy.
Procedure
Update the
NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicymanifest used to create the interface. The following example removes a Linux bridge and configures theeth1NIC with DHCP to avoid losing connectivity:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses the
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""node selector to select all worker nodes in the cluster. - 4
- Changing the state to
absentremoves the interface. - 5
- The name of the interface that is to be unattached from the bridge interface.
- 6
- The type of interface. This example creates an Ethernet networking interface.
- 7
- The requested state for the interface.
- 8
- Optional: If you do not use
dhcp, you can either set a static IP or leave the interface without an IP address. - 9
- Enables
ipv4in this example.
Update the policy on the node and remove the interface:
oc apply -f <br1-eth1-policy.yaml>
$ oc apply -f <br1-eth1-policy.yaml>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- File name of the policy manifest.
29.2.6. Example policy configurations for different interfaces
Before you read the different example NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy (NNCP) manifest configurations, consider the following factors when you apply a policy to nodes so that your cluster runs under its best performance conditions:
- If you want to apply multiple NNCP CRs to a node, you must create the NNCPs in a logical order that is based on the alphanumeric sorting of the policy names. The Kubernetes NMState Operator continuously checks for a newly created NNCP CR so that the Operator can instantly apply the CR to node.
-
When you need to apply a policy to many nodes but you only want to create a single NNCP for all the nodes, the Kubernetes NMState Operator applies the policy to each node in sequence. You can set the speed and coverage of policy application for target nodes with the
maxUnavailableparameter in the cluster’s configuration file. By setting a lower percentage value for the parameter, you can reduce the risk of a cluster-wide outage if the outage impacts the small percentage of nodes that are receiving the policy application. -
If you set the
maxUnavailableparameter to50%in two NNCP manifests, the policy configuration coverage applies to 100% of the nodes in your cluster. - When a node restarts, the Kubernetes NMState Operator cannot control the order to which it applies policies to nodes. The Kubernetes NMState Operator might apply interdependent policies in a sequence that results in a degraded network object.
- Consider specifying all related network configurations in a single policy.
29.2.6.1. Example: Linux bridge interface node network configuration policy
Create a Linux bridge interface on nodes in the cluster by applying a NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest to the cluster.
The following YAML file is an example of a manifest for a Linux bridge interface. It includes samples values that you must replace with your own information.
- 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses a
hostnamenode selector. - 4
- Name of the interface.
- 5
- Optional: Human-readable description of the interface.
- 6
- The type of interface. This example creates a bridge.
- 7
- The requested state for the interface after creation.
- 8
- Optional: If you do not use
dhcp, you can either set a static IP or leave the interface without an IP address. - 9
- Enables
ipv4in this example. - 10
- Disables
stpin this example. - 11
- The node NIC to which the bridge attaches.
29.2.6.2. Example: VLAN interface node network configuration policy
Create a VLAN interface on nodes in the cluster by applying a NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest to the cluster.
Define all related configurations for the VLAN interface of a node in a single NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest. For example, define the VLAN interface for a node and the related routes for the VLAN interface in the same NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest.
When a node restarts, the Kubernetes NMState Operator cannot control the order in which policies are applied. Therefore, if you use separate policies for related network configurations, the Kubernetes NMState Operator might apply these policies in a sequence that results in a degraded network object.
The following YAML file is an example of a manifest for a VLAN interface. It includes samples values that you must replace with your own information.
- 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses a
hostnamenode selector. - 4
- Name of the interface. When deploying on bare metal, only the
<interface_name>.<vlan_number>VLAN format is supported. - 5
- Optional: Human-readable description of the interface.
- 6
- The type of interface. This example creates a VLAN.
- 7
- The requested state for the interface after creation.
- 8
- The node NIC to which the VLAN is attached.
- 9
- The VLAN tag.
29.2.6.3. Example: Bond interface node network configuration policy
Create a bond interface on nodes in the cluster by applying a NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform only supports the following bond modes:
-
active-backup
-
balance-xor
-
802.3ad
Other bond modes are not supported.
The balance-xor and 802.3ad bond modes require switch configuration to establish an "EtherChannel" or similar port grouping. Those two modes also require additional load-balancing configuration, depending on the source and destination of traffic being passed through the interface. The active-backup bond mode does not require any switch configuration. Other bond modes are not supported.
The following YAML file is an example of a manifest for a bond interface. It includes samples values that you must replace with your own information.
- 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses a
hostnamenode selector. - 4
- Name of the interface.
- 5
- Optional: Human-readable description of the interface.
- 6
- The type of interface. This example creates a bond.
- 7
- The requested state for the interface after creation.
- 8
- Optional: If you do not use
dhcp, you can either set a static IP or leave the interface without an IP address. - 9
- Enables
ipv4in this example. - 10
- The driver mode for the bond. This example uses
active backup. - 11
- Optional: This example uses miimon to inspect the bond link every 140ms.
- 12
- The subordinate node NICs in the bond.
- 13
- Optional: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) for the bond. If not specified, this value is set to
1500by default.
29.2.6.4. Example: Ethernet interface node network configuration policy
Configure an Ethernet interface on nodes in the cluster by applying a NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest to the cluster.
The following YAML file is an example of a manifest for an Ethernet interface. It includes sample values that you must replace with your own information.
- 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses a
hostnamenode selector. - 4
- Name of the interface.
- 5
- Optional: Human-readable description of the interface.
- 6
- The type of interface. This example creates an Ethernet networking interface.
- 7
- The requested state for the interface after creation.
- 8
- Optional: If you do not use
dhcp, you can either set a static IP or leave the interface without an IP address. - 9
- Enables
ipv4in this example.
29.2.6.5. Example: Multiple interfaces in the same node network configuration policy
You can create multiple interfaces in the same node network configuration policy. These interfaces can reference each other, allowing you to build and deploy a network configuration by using a single policy manifest.
The following example YAML file creates a bond that is named bond10 across two NICs and VLAN that is named bond10.103 that connects to the bond.
- 1
- Name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. - 3
- This example uses
hostnamenode selector. - 4 11
- Name of the interface.
- 5 12
- Optional: Human-readable description of the interface.
- 6 13
- The type of interface.
- 7 14
- The requested state for the interface after creation.
- 8
- The driver mode for the bond.
- 9
- Optional: This example uses miimon to inspect the bond link every 140ms.
- 10
- The subordinate node NICs in the bond.
- 15
- The node NIC to which the VLAN is attached.
- 16
- The VLAN tag.
- 17
- Optional: If you do not use dhcp, you can either set a static IP or leave the interface without an IP address.
- 18
- Enables ipv4 in this example.
29.2.7. Capturing the static IP of a NIC attached to a bridge
Capturing the static IP of a NIC is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
Create a Linux bridge interface on nodes in the cluster and transfer the static IP configuration of the NIC to the bridge by applying a single NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy manifest to the cluster.
The following YAML file is an example of a manifest for a Linux bridge interface. It includes sample values that you must replace with your own information.
- 1
- The name of the policy.
- 2
- Optional: If you do not include the
nodeSelectorparameter, the policy applies to all nodes in the cluster. This example uses thenode-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""node selector to select all worker nodes in the cluster. - 3
- The reference to the node NIC to which the bridge attaches.
- 4
- The type of interface. This example creates a bridge.
- 5
- The IP address of the bridge interface. This value matches the IP address of the NIC which is referenced by the
spec.capture.eth1-nicentry. - 6
- The node NIC to which the bridge attaches.
29.2.8. Examples: IP management
The following example configuration snippets show different methods of IP management.
These examples use the ethernet interface type to simplify the example while showing the related context in the policy configuration. These IP management examples can be used with the other interface types.
29.2.8.1. Static
The following snippet statically configures an IP address on the Ethernet interface:
- 1
- Replace this value with the static IP address for the interface.
29.2.8.2. No IP address
The following snippet ensures that the interface has no IP address:
Always set the state parameter to up when you set both the ipv4.enabled and the ipv6.enabled parameter to false to disable an interface. If you set state: down with this configuration, the interface receives a DHCP IP address because of automatic DHCP assignment.
29.2.8.3. Dynamic host configuration
The following snippet configures an Ethernet interface that uses a dynamic IP address, gateway address, and DNS:
The following snippet configures an Ethernet interface that uses a dynamic IP address but does not use a dynamic gateway address or DNS:
29.2.8.4. DNS
By default, the nmstate API stores DNS values globally as against storing them in a network interface. For certain situations, you must configure a network interface to store DNS values.
Setting a DNS configuration is comparable to modifying the /etc/resolv.conf file.
To define a DNS configuration for a network interface, you must initially specify the dns-resolver section in the network interface’s YAML configuration file. To apply an NNCP configuration to your network interface, you need to run the oc apply -f <nncp_file_name> command.
The following example shows a default situation that stores DNS values globally:
Configure a static DNS without a network interface. Note that when updating the
/etc/resolv.conffile on a host node, you do not need to specify an interface, IPv4 or IPv6, in theNodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy(NNCP) manifest.Example of a DNS configuration for a network interface that globally stores DNS values
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantYou can specify DNS options under the
dns-resolver.configsection of your NNCP file as demonstrated in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you want to remove the DNS options from your network interface, apply the following configuration to your NNCP and then run the
oc apply -f <nncp_file_name>command:# ... dns-resolver: config: {} interfaces: [] # ...# ... dns-resolver: config: {} interfaces: [] # ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The following examples show situations that require configuring a network interface to store DNS values:
If you want to rank a static DNS name server over a dynamic DNS name server, define the interface that runs either the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or the IPv6 Autoconfiguration (
autoconf) mechanism in the network interface YAML configuration file.Example configuration that adds
192.0.2.1to DNS name servers retrieved from the DHCPv4 network protocolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you need to configure a network interface to store DNS values instead of adopting the default method, which uses the
nmstateAPI to store DNS values globally, you can set static DNS values and static IP addresses in the network interface YAML file.ImportantStoring DNS values at the network interface level might cause name resolution issues after you attach the interface to network components, such as an Open vSwitch (OVS) bridge, a Linux bridge, or a bond.
Example configuration that stores DNS values at the interface level
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you want to set static DNS search domains and static DNS name servers for your network interface, define the static interface that runs either the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or the IPv6 Autoconfiguration (
autoconf) mechanism in the network interface YAML configuration file.ImportantSpecifying the following
dns-resolverconfigurations in the network interface YAML file might cause a race condition at reboot that prevents theNodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy(NNCP) from applying to pods that run in your cluster:- Setting static DNS search domains and dynamic DNS name servers for your network interface.
-
Specifying domain suffixes for the
searchparameter and not setting IP addresses for theserverparameter.
Example configuration that sets
example.comandexample.orgstatic DNS search domains along with static DNS name server settingsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
29.2.8.5. Static routing
The following snippet configures a static route and a static IP on interface eth1.
You cannot use the OVN-Kubernetes br-ex bridge as the next hop interface when configuring a static route.
29.3. Troubleshooting node network configuration
If the node network configuration encounters an issue, the policy is automatically rolled back and the enactments report failure. This includes issues such as:
- The configuration fails to be applied on the host.
- The host loses connection to the default gateway.
- The host loses connection to the API server.
29.3.1. Troubleshooting an incorrect node network configuration policy configuration
You can apply changes to the node network configuration across your entire cluster by applying a node network configuration policy.
If you applied an incorrect configuration, you can use the following example to troubleshoot and correct the failed node network policy. The example attempts to apply a Linux bridge policy to a cluster that has three control plane nodes and three compute nodes. The policy is not applied because the policy references the wrong interface.
To find an error, you need to investigate the available NMState resources. You can then update the policy with the correct configuration.
Prerequisites
-
You ensured that an
ens01interface does not exist on your Linux system.
Procedure
Create a policy on your cluster. The following example creates a simple bridge,
br1that hasens01as its member:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the policy to your network interface:
oc apply -f ens01-bridge-testfail.yaml
$ oc apply -f ens01-bridge-testfail.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
nodenetworkconfigurationpolicy.nmstate.io/ens01-bridge-testfail created
nodenetworkconfigurationpolicy.nmstate.io/ens01-bridge-testfail createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the status of the policy by running the following command:
oc get nncp
$ oc get nncpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows that the policy failed:
Example output
NAME STATUS ens01-bridge-testfail FailedToConfigure
NAME STATUS ens01-bridge-testfail FailedToConfigureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The policy status alone does not indicate if it failed on all nodes or a subset of nodes.
List the node network configuration enactments to see if the policy was successful on any of the nodes. If the policy failed for only a subset of nodes, the output suggests that the problem is with a specific node configuration. If the policy failed on all nodes, the output suggests that the problem is with the policy.
oc get nnce
$ oc get nnceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows that the policy failed on all nodes:
Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View one of the failed enactments. The following command uses the output tool
jsonpathto filter the output:oc get nnce compute-1.ens01-bridge-testfail -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[?(@.type=="Failing")].message}'$ oc get nnce compute-1.ens01-bridge-testfail -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[?(@.type=="Failing")].message}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
[2024-10-10T08:40:46Z INFO nmstatectl] Nmstate version: 2.2.37 NmstateError: InvalidArgument: Controller interface br1 is holding unknown port ens01
[2024-10-10T08:40:46Z INFO nmstatectl] Nmstate version: 2.2.37 NmstateError: InvalidArgument: Controller interface br1 is holding unknown port ens01Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The previous example shows the output from an
InvalidArgumenterror that indicates that theens01is an unknown port. For this example, you might need to change the port configuration in the policy configuration file.To ensure that the policy is configured properly, view the network configuration for one or all of the nodes by requesting the
NodeNetworkStateobject. The following command returns the network configuration for thecontrol-plane-1node:oc get nns control-plane-1 -o yaml
$ oc get nns control-plane-1 -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows that the interface name on the nodes is
ens1but the failed policy incorrectly usesens01:Example output
- ipv4: # ... name: ens1 state: up type: ethernet- ipv4: # ... name: ens1 state: up type: ethernetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Correct the error by editing the existing policy:
oc edit nncp ens01-bridge-testfail
$ oc edit nncp ens01-bridge-testfailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow # ... port: - name: ens1# ... port: - name: ens1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the policy to apply the correction.
Check the status of the policy to ensure it updated successfully:
oc get nncp
$ oc get nncpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS ens01-bridge-testfail SuccessfullyConfigured
NAME STATUS ens01-bridge-testfail SuccessfullyConfiguredCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The updated policy is successfully configured on all nodes in the cluster.
29.3.2. Troubleshooting DNS connectivity issues in a disconnected environment
If you experience DNS connectivity issues when configuring nmstate in a disconnected environment, you can configure the DNS server to resolve the list of name servers for the domain root-servers.net.
Ensure that the DNS server includes a name server (NS) entry for the root-servers.net zone. The DNS server does not need to forward a query to an upstream resolver, but the server must return a correct answer for the NS query.
29.3.2.1. Configuring the bind9 DNS named server
For a cluster configured to query a bind9 DNS server, you can add the root-servers.net zone to a configuration file that contains at least one NS record. For example you can use the /var/named/named.localhost as a zone file that already matches this criteria.
Procedure
Add the
root-servers.netzone at the end of the/etc/named.confconfiguration file by running the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the
namedservice by running the following command:systemctl restart named
$ systemctl restart namedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the
root-servers.netzone is present by running the following command:journalctl -u named|grep root-servers.net
$ journalctl -u named|grep root-servers.netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Jul 03 15:16:26 rhel-8-10 bash[xxxx]: zone root-servers.net/IN: loaded serial 0 Jul 03 15:16:26 rhel-8-10 named[xxxx]: zone root-servers.net/IN: loaded serial 0
Jul 03 15:16:26 rhel-8-10 bash[xxxx]: zone root-servers.net/IN: loaded serial 0 Jul 03 15:16:26 rhel-8-10 named[xxxx]: zone root-servers.net/IN: loaded serial 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the DNS server can resolve the NS record for the
root-servers.netdomain by running the following command:host -t NS root-servers.net. 127.0.0.1
$ host -t NS root-servers.net. 127.0.0.1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Using domain server: Name: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.53 Aliases: root-servers.net name server root-servers.net.
Using domain server: Name: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.53 Aliases: root-servers.net name server root-servers.net.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
29.3.2.2. Configuring the dnsmasq DNS server
If you are using dnsmasq as the DNS server, you can delegate resolution of the root-servers.net domain to another DNS server, for example, by creating a new configuration file that resolves root-servers.net using a DNS server that you specify.
Create a configuration file that delegates the domain
root-servers.netto another DNS server by running the following command:echo 'server=/root-servers.net/<DNS_server_IP>'> /etc/dnsmasq.d/delegate-root-servers.net.conf
$ echo 'server=/root-servers.net/<DNS_server_IP>'> /etc/dnsmasq.d/delegate-root-servers.net.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the
dnsmasqservice by running the following command:systemctl restart dnsmasq
$ systemctl restart dnsmasqCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the
root-servers.netdomain is delegated to another DNS server by running the following command:journalctl -u dnsmasq|grep root-servers.net
$ journalctl -u dnsmasq|grep root-servers.netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Jul 03 15:31:25 rhel-8-10 dnsmasq[1342]: using nameserver 192.168.1.1#53 for domain root-servers.net
Jul 03 15:31:25 rhel-8-10 dnsmasq[1342]: using nameserver 192.168.1.1#53 for domain root-servers.netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the DNS server can resolve the NS record for the
root-servers.netdomain by running the following command:host -t NS root-servers.net. 127.0.0.1
$ host -t NS root-servers.net. 127.0.0.1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Using domain server: Name: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Aliases: root-servers.net name server root-servers.net.
Using domain server: Name: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Aliases: root-servers.net name server root-servers.net.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 30. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy
Production environments can deny direct access to the internet and instead have an HTTP or HTTPS proxy available. You can configure OpenShift Container Platform to use a proxy by modifying the Proxy object for existing clusters or by configuring the proxy settings in the install-config.yaml file for new clusters.
After you enable a cluster-wide egress proxy for your cluster on a supported platform, Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) populates the status.noProxy parameter with the values of the networking.machineNetwork[].cidr, networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr, and networking.serviceNetwork[] fields from your install-config.yaml file that exists on the supported platform.
As a postinstallation task, you can change the networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr value, but not the networking.machineNetwork[].cidr and the networking.serviceNetwork[] values. For more information, see "Configuring the cluster network range".
For installations on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the status.noProxy parameter is also populated with the instance metadata endpoint, 169.254.169.254.
Example of values added to the status: segment of a Proxy object by RHCOS
- 1
- Specify IP address blocks from which pod IP addresses are allocated. The default value is
10.128.0.0/14with a host prefix of/23. - 2
- Specify the IP address blocks for machines. The default value is
10.0.0.0/16. - 3
- Specify IP address block for services. The default value is
172.30.0.0/16. - 4
- You can find the URL of the internal API server by running the
oc get infrastructures.config.openshift.io cluster -o jsonpath='{.status.etcdDiscoveryDomain}'command.
If your installation type does not include setting the networking.machineNetwork[].cidr field, you must include the machine IP addresses manually in the .status.noProxy field to make sure that the traffic between nodes can bypass the proxy.
30.1. Prerequisites
Review the sites that your cluster requires access to and determine whether any of them must bypass the proxy. By default, all cluster system egress traffic is proxied, including calls to the cloud provider API for the cloud that hosts your cluster. The system-wide proxy affects system components only, not user workloads. If necessary, add sites to the spec.noProxy parameter of the Proxy object to bypass the proxy.
30.2. Enabling the cluster-wide proxy
The Proxy object is used to manage the cluster-wide egress proxy. When a cluster is installed or upgraded without the proxy configured, a Proxy object is still generated but it will have a nil spec. For example:
A cluster administrator can configure the proxy for OpenShift Container Platform by modifying this cluster Proxy object.
Only the Proxy object named cluster is supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
Enabling the cluster-wide proxy causes the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to trigger node reboot.
Prerequisites
- You have cluster administrator permissions.
-
You installed the OpenShift Container Platform
ocCLI tool.
Procedure
Create a config map that contains any additional CA certificates required for proxying HTTPS connections.
NoteYou can skip this step if the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle.
Create a file called
user-ca-bundle.yamlwith the following contents, and provide the values of your PEM-encoded certificates:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the config map from this file:
oc create -f user-ca-bundle.yaml
$ oc create -f user-ca-bundle.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Use the
oc editcommand to modify theProxyobject:oc edit proxy/cluster
$ oc edit proxy/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the necessary fields for the proxy:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- 1
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. - 2
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be either
httporhttps. Specify a URL for the proxy that supports the URL scheme. For example, most proxies will report an error if they are configured to usehttpsbut they only supporthttp. This failure message may not propagate to the logs and can appear to be a network connection failure instead. If using a proxy that listens forhttpsconnections from the cluster, you may need to configure the cluster to accept the CAs and certificates that the proxy uses. - 3
- A comma-separated list of destination domain names, domains, IP addresses (or other network CIDRs), and port numbers to exclude proxying.Note
Port numbers are only supported when configuring IPv6 addresses. Port numbers are not supported when configuring IPv4 addresses.
Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass proxy for all destinations. If you scale up workers that are not included in the network defined by thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidrfield from the installation configuration, you must add them to this list to prevent connection issues.This field is ignored if neither the
httpProxyorhttpsProxyfields are set. - 4
- One or more URLs external to the cluster to use to perform a readiness check before writing the
httpProxyandhttpsProxyvalues to status. - 5
- A reference to the config map in the
openshift-confignamespace that contains additional CA certificates required for proxying HTTPS connections. Note that the config map must already exist before referencing it here. This field is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle.
- Save the file to apply the changes.
30.3. Removing the cluster-wide proxy
The cluster Proxy object cannot be deleted. To remove the proxy from a cluster, remove all spec fields from the Proxy object.
Prerequisites
- Cluster administrator permissions
-
OpenShift Container Platform
ocCLI tool installed
Procedure
Use the
oc editcommand to modify the proxy:oc edit proxy/cluster
$ oc edit proxy/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove all
specfields from the Proxy object. For example:apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Proxy metadata: name: cluster spec: {}apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Proxy metadata: name: cluster spec: {}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file to apply the changes.
30.4. Verifying the cluster-wide proxy configuration
After the cluster-wide proxy configuration is deployed, you can verify that it is working as expected. Follow these steps to check the logs and validate the implementation.
Prerequisites
- You have cluster administrator permissions.
-
You have the OpenShift Container Platform
ocCLI tool installed.
Procedure
Check the proxy configuration status using the
occommand:oc get proxy/cluster -o yaml
$ oc get proxy/cluster -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Verify the proxy fields in the output to ensure they match your configuration. Specifically, check the
spec.httpProxy,spec.httpsProxy,spec.noProxy, andspec.trustedCAfields. Inspect the status of the
Proxyobject:oc get proxy/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status}'$ oc get proxy/cluster -o jsonpath='{.status}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the logs of the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to ensure that the configuration changes were applied successfully:
oc logs -n openshift-machine-config-operator $(oc get pods -n openshift-machine-config-operator -l k8s-app=machine-config-operator -o name)
$ oc logs -n openshift-machine-config-operator $(oc get pods -n openshift-machine-config-operator -l k8s-app=machine-config-operator -o name)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Look for messages that indicate the proxy settings were applied and the nodes were rebooted if necessary.
Verify that system components are using the proxy by checking the logs of a component that makes external requests, such as the Cluster Version Operator (CVO):
oc logs -n openshift-cluster-version $(oc get pods -n openshift-cluster-version -l k8s-app=machine-config-operator -o name)
$ oc logs -n openshift-cluster-version $(oc get pods -n openshift-cluster-version -l k8s-app=machine-config-operator -o name)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Look for log entries that show that external requests have been routed through the proxy.
Additional resources
Chapter 31. Configuring a custom PKI
Some platform components, such as the web console, use Routes for communication and must trust other components' certificates to interact with them. If you are using a custom public key infrastructure (PKI), you must configure it so its privately signed CA certificates are recognized across the cluster.
You can leverage the Proxy API to add cluster-wide trusted CA certificates. You must do this either during installation or at runtime.
During installation, configure the cluster-wide proxy. You must define your privately signed CA certificates in the
install-config.yamlfile’sadditionalTrustBundlesetting.The installation program generates a ConfigMap that is named
user-ca-bundlethat contains the additional CA certificates you defined. The Cluster Network Operator then creates atrusted-ca-bundleConfigMap that merges these CA certificates with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) trust bundle; this ConfigMap is referenced in the Proxy object’strustedCAfield.-
At runtime, modify the default Proxy object to include your privately signed CA certificates (part of cluster’s proxy enablement workflow). This involves creating a ConfigMap that contains the privately signed CA certificates that should be trusted by the cluster, and then modifying the proxy resource with the
trustedCAreferencing the privately signed certificates' ConfigMap.
The installer configuration’s additionalTrustBundle field and the proxy resource’s trustedCA field are used to manage the cluster-wide trust bundle; additionalTrustBundle is used at install time and the proxy’s trustedCA is used at runtime.
The trustedCA field is a reference to a ConfigMap containing the custom certificate and key pair used by the cluster component.
31.1. Configuring the cluster-wide proxy during installation
Production environments can deny direct access to the internet and instead have an HTTP or HTTPS proxy available. You can configure a new OpenShift Container Platform cluster to use a proxy by configuring the proxy settings in the install-config.yaml file.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing
install-config.yamlfile. You reviewed the sites that your cluster requires access to and determined whether any of them need to bypass the proxy. By default, all cluster egress traffic is proxied, including calls to hosting cloud provider APIs. You added sites to the
Proxyobject’sspec.noProxyfield to bypass the proxy if necessary.NoteThe
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is populated with the values of thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidr,networking.clusterNetwork[].cidr, andnetworking.serviceNetwork[]fields from your installation configuration.For installations on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), the
Proxyobjectstatus.noProxyfield is also populated with the instance metadata endpoint (169.254.169.254).
Procedure
Edit your
install-config.yamlfile and add the proxy settings. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. - 2
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster.
- 3
- A comma-separated list of destination domain names, IP addresses, or other network CIDRs to exclude from proxying. Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass the proxy for all destinations. If you have added the AmazonEC2,Elastic Load Balancing, andS3VPC endpoints to your VPC, you must add these endpoints to thenoProxyfield. - 4
- If provided, the installation program generates a config map that is named
user-ca-bundlein theopenshift-confignamespace that contains one or more additional CA certificates that are required for proxying HTTPS connections. The Cluster Network Operator then creates atrusted-ca-bundleconfig map that merges these contents with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) trust bundle, and this config map is referenced in thetrustedCAfield of theProxyobject. TheadditionalTrustBundlefield is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle. - 5
- Optional: The policy to determine the configuration of the
Proxyobject to reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map in thetrustedCAfield. The allowed values areProxyonlyandAlways. UseProxyonlyto reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map only whenhttp/httpsproxy is configured. UseAlwaysto always reference theuser-ca-bundleconfig map. The default value isProxyonly.
NoteThe installation program does not support the proxy
readinessEndpointsfield.NoteIf the installer times out, restart and then complete the deployment by using the
wait-forcommand of the installer. For example:./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debug
$ ./openshift-install wait-for install-complete --log-level debugCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file and reference it when installing OpenShift Container Platform.
The installation program creates a cluster-wide proxy that is named cluster that uses the proxy settings in the provided install-config.yaml file. If no proxy settings are provided, a cluster Proxy object is still created, but it will have a nil spec.
Only the Proxy object named cluster is supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
31.2. Enabling the cluster-wide proxy
The Proxy object is used to manage the cluster-wide egress proxy. When a cluster is installed or upgraded without the proxy configured, a Proxy object is still generated but it will have a nil spec. For example:
A cluster administrator can configure the proxy for OpenShift Container Platform by modifying this cluster Proxy object.
Only the Proxy object named cluster is supported, and no additional proxies can be created.
Enabling the cluster-wide proxy causes the Machine Config Operator (MCO) to trigger node reboot.
Prerequisites
- You have cluster administrator permissions.
-
You installed the OpenShift Container Platform
ocCLI tool.
Procedure
Create a config map that contains any additional CA certificates required for proxying HTTPS connections.
NoteYou can skip this step if the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle.
Create a file called
user-ca-bundle.yamlwith the following contents, and provide the values of your PEM-encoded certificates:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the config map from this file:
oc create -f user-ca-bundle.yaml
$ oc create -f user-ca-bundle.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Use the
oc editcommand to modify theProxyobject:oc edit proxy/cluster
$ oc edit proxy/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the necessary fields for the proxy:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- 1
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTP connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be
http. - 2
- A proxy URL to use for creating HTTPS connections outside the cluster. The URL scheme must be either
httporhttps. Specify a URL for the proxy that supports the URL scheme. For example, most proxies will report an error if they are configured to usehttpsbut they only supporthttp. This failure message may not propagate to the logs and can appear to be a network connection failure instead. If using a proxy that listens forhttpsconnections from the cluster, you may need to configure the cluster to accept the CAs and certificates that the proxy uses. - 3
- A comma-separated list of destination domain names, domains, IP addresses (or other network CIDRs), and port numbers to exclude proxying.Note
Port numbers are only supported when configuring IPv6 addresses. Port numbers are not supported when configuring IPv4 addresses.
Preface a domain with
.to match subdomains only. For example,.y.commatchesx.y.com, but noty.com. Use*to bypass proxy for all destinations. If you scale up workers that are not included in the network defined by thenetworking.machineNetwork[].cidrfield from the installation configuration, you must add them to this list to prevent connection issues.This field is ignored if neither the
httpProxyorhttpsProxyfields are set. - 4
- One or more URLs external to the cluster to use to perform a readiness check before writing the
httpProxyandhttpsProxyvalues to status. - 5
- A reference to the config map in the
openshift-confignamespace that contains additional CA certificates required for proxying HTTPS connections. Note that the config map must already exist before referencing it here. This field is required unless the proxy’s identity certificate is signed by an authority from the RHCOS trust bundle.
- Save the file to apply the changes.
31.3. Certificate injection using Operators
Once your custom CA certificate is added to the cluster via ConfigMap, the Cluster Network Operator merges the user-provided and system CA certificates into a single bundle and injects the merged bundle into the Operator requesting the trust bundle injection.
After adding a config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle="true" label to the config map, existing data in it is deleted. The Cluster Network Operator takes ownership of a config map and only accepts ca-bundle as data. You must use a separate config map to store service-ca.crt by using the service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=true annotation or a similar configuration. Adding a config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle="true" label and service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=true annotation on the same config map can cause issues.
Operators request this injection by creating an empty ConfigMap with the following label:
config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle="true"
config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle="true"An example of the empty ConfigMap:
- 1
- Specifies the empty ConfigMap name.
The Operator mounts this ConfigMap into the container’s local trust store.
Adding a trusted CA certificate is only needed if the certificate is not included in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) trust bundle.
Certificate injection is not limited to Operators. The Cluster Network Operator injects certificates across any namespace when an empty ConfigMap is created with the config.openshift.io/inject-trusted-cabundle=true label.
The ConfigMap can reside in any namespace, but the ConfigMap must be mounted as a volume to each container within a pod that requires a custom CA. For example:
Chapter 32. Load balancing on RHOSP
32.1. Limitations of load balancer services
OpenShift Container Platform clusters on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) use Octavia to handle load balancer services. As a result of this choice, such clusters have a number of functional limitations.
RHOSP Octavia has two supported providers: Amphora and OVN. These providers differ in terms of available features as well as implementation details. These distinctions affect load balancer services that are created on your cluster.
32.1.1. Local external traffic policies
You can set the external traffic policy (ETP) parameter, .spec.externalTrafficPolicy, on a load balancer service to preserve the source IP address of incoming traffic when it reaches service endpoint pods. However, if your cluster uses the Amphora Octavia provider, the source IP of the traffic is replaced with the IP address of the Amphora VM. This behavior does not occur if your cluster uses the OVN Octavia provider.
Having the ETP option set to Local requires that health monitors be created for the load balancer. Without health monitors, traffic can be routed to a node that doesn’t have a functional endpoint, which causes the connection to drop. To force Cloud Provider OpenStack to create health monitors, you must set the value of the create-monitor option in the cloud provider configuration to true.
In RHOSP 16.2, the OVN Octavia provider does not support health monitors. Therefore, setting the ETP to local is unsupported.
In RHOSP 16.2, the Amphora Octavia provider does not support HTTP monitors on UDP pools. As a result, UDP load balancer services have UDP-CONNECT monitors created instead. Due to implementation details, this configuration only functions properly with the OVN-Kubernetes CNI plugin. When the OpenShift SDN CNI plugin is used, the UDP services alive nodes are detected unreliably.
32.1.2. Load balancer source ranges
Use the .spec.loadBalancerSourceRanges property to restrict the traffic that can pass through the load balancer according to source IP. This property is supported for use with the Amphora Octavia provider only. If your cluster uses the OVN Octavia provider, the option is ignored and traffic is unrestricted.
32.2. Using the Octavia OVN load balancer provider driver with Kuryr SDN
Kuryr is a deprecated feature. Deprecated functionality is still included in OpenShift Container Platform and continues to be supported; however, it will be removed in a future release of this product and is not recommended for new deployments.
For the most recent list of major functionality that has been deprecated or removed within OpenShift Container Platform, refer to the Deprecated and removed features section of the OpenShift Container Platform release notes.
If your OpenShift Container Platform cluster uses Kuryr and was installed on a Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) 13 cloud that was later upgraded to RHOSP 16, you can configure it to use the Octavia OVN provider driver.
Kuryr replaces existing load balancers after you change provider drivers. This process results in some downtime.
Prerequisites
-
Install the RHOSP CLI,
openstack. -
Install the OpenShift Container Platform CLI,
oc. Verify that the Octavia OVN driver on RHOSP is enabled.
TipTo view a list of available Octavia drivers, on a command line, enter
openstack loadbalancer provider list.The
ovndriver is displayed in the command’s output.
Procedure
To change from the Octavia Amphora provider driver to Octavia OVN:
Open the
kuryr-configConfigMap. On a command line, enter:oc -n openshift-kuryr edit cm kuryr-config
$ oc -n openshift-kuryr edit cm kuryr-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the ConfigMap, delete the line that contains
kuryr-octavia-provider: default. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Delete this line. The cluster will regenerate it with
ovnas the value.
Wait for the Cluster Network Operator to detect the modification and to redeploy the
kuryr-controllerandkuryr-cnipods. This process might take several minutes.Verify that the
kuryr-configConfigMap annotation is present withovnas its value. On a command line, enter:oc -n openshift-kuryr edit cm kuryr-config
$ oc -n openshift-kuryr edit cm kuryr-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
ovnprovider value is displayed in the output:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that RHOSP recreated its load balancers.
On a command line, enter:
openstack loadbalancer list | grep amphora
$ openstack loadbalancer list | grep amphoraCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A single Amphora load balancer is displayed. For example:
a4db683b-2b7b-4988-a582-c39daaad7981 | ostest-7mbj6-kuryr-api-loadbalancer | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.0.1 | ACTIVE | amphora
a4db683b-2b7b-4988-a582-c39daaad7981 | ostest-7mbj6-kuryr-api-loadbalancer | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.0.1 | ACTIVE | amphoraCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Search for
ovnload balancers by entering:openstack loadbalancer list | grep ovn
$ openstack loadbalancer list | grep ovnCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The remaining load balancers of the
ovntype are displayed. For example:2dffe783-98ae-4048-98d0-32aa684664cc | openshift-apiserver-operator/metrics | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.167.119 | ACTIVE | ovn 0b1b2193-251f-4243-af39-2f99b29d18c5 | openshift-etcd/etcd | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.143.226 | ACTIVE | ovn f05b07fc-01b7-4673-bd4d-adaa4391458e | openshift-dns-operator/metrics | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.152.27 | ACTIVE | ovn
2dffe783-98ae-4048-98d0-32aa684664cc | openshift-apiserver-operator/metrics | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.167.119 | ACTIVE | ovn 0b1b2193-251f-4243-af39-2f99b29d18c5 | openshift-etcd/etcd | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.143.226 | ACTIVE | ovn f05b07fc-01b7-4673-bd4d-adaa4391458e | openshift-dns-operator/metrics | 84c99c906edd475ba19478a9a6690efd | 172.30.152.27 | ACTIVE | ovnCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
32.3. Scaling clusters for application traffic by using Octavia
OpenShift Container Platform clusters that run on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) can use the Octavia load balancing service to distribute traffic across multiple virtual machines (VMs) or floating IP addresses. This feature mitigates the bottleneck that single machines or addresses create.
If your cluster uses Kuryr, the Cluster Network Operator created an internal Octavia load balancer at deployment. You can use this load balancer for application network scaling.
If your cluster does not use Kuryr, you must create your own Octavia load balancer to use it for application network scaling.
32.3.1. Scaling clusters by using Octavia
If you want to use multiple API load balancers, or if your cluster does not use Kuryr, create an Octavia load balancer and then configure your cluster to use it.
Prerequisites
- Octavia is available on your Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) deployment.
Procedure
From a command line, create an Octavia load balancer that uses the Amphora driver:
openstack loadbalancer create --name API_OCP_CLUSTER --vip-subnet-id <id_of_worker_vms_subnet>
$ openstack loadbalancer create --name API_OCP_CLUSTER --vip-subnet-id <id_of_worker_vms_subnet>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can use a name of your choice instead of
API_OCP_CLUSTER.After the load balancer becomes active, create listeners:
openstack loadbalancer listener create --name API_OCP_CLUSTER_6443 --protocol HTTPS--protocol-port 6443 API_OCP_CLUSTER
$ openstack loadbalancer listener create --name API_OCP_CLUSTER_6443 --protocol HTTPS--protocol-port 6443 API_OCP_CLUSTERCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteTo view the status of the load balancer, enter
openstack loadbalancer list.Create a pool that uses the round robin algorithm and has session persistence enabled:
openstack loadbalancer pool create --name API_OCP_CLUSTER_pool_6443 --lb-algorithm ROUND_ROBIN --session-persistence type=<source_IP_address> --listener API_OCP_CLUSTER_6443 --protocol HTTPS
$ openstack loadbalancer pool create --name API_OCP_CLUSTER_pool_6443 --lb-algorithm ROUND_ROBIN --session-persistence type=<source_IP_address> --listener API_OCP_CLUSTER_6443 --protocol HTTPSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To ensure that control plane machines are available, create a health monitor:
openstack loadbalancer healthmonitor create --delay 5 --max-retries 4 --timeout 10 --type TCP API_OCP_CLUSTER_pool_6443
$ openstack loadbalancer healthmonitor create --delay 5 --max-retries 4 --timeout 10 --type TCP API_OCP_CLUSTER_pool_6443Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the control plane machines as members of the load balancer pool:
for SERVER in $(MASTER-0-IP MASTER-1-IP MASTER-2-IP) do openstack loadbalancer member create --address $SERVER --protocol-port 6443 API_OCP_CLUSTER_pool_6443 done
$ for SERVER in $(MASTER-0-IP MASTER-1-IP MASTER-2-IP) do openstack loadbalancer member create --address $SERVER --protocol-port 6443 API_OCP_CLUSTER_pool_6443 doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: To reuse the cluster API floating IP address, unset it:
openstack floating ip unset $API_FIP
$ openstack floating ip unset $API_FIPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add either the unset
API_FIPor a new address to the created load balancer VIP:openstack floating ip set --port $(openstack loadbalancer show -c <vip_port_id> -f value API_OCP_CLUSTER) $API_FIP
$ openstack floating ip set --port $(openstack loadbalancer show -c <vip_port_id> -f value API_OCP_CLUSTER) $API_FIPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Your cluster now uses Octavia for load balancing.
If Kuryr uses the Octavia Amphora driver, all traffic is routed through a single Amphora virtual machine (VM).
You can repeat this procedure to create additional load balancers, which can alleviate the bottleneck.
32.3.2. Scaling clusters that use Kuryr by using Octavia
Kuryr is a deprecated feature. Deprecated functionality is still included in OpenShift Container Platform and continues to be supported; however, it will be removed in a future release of this product and is not recommended for new deployments.
For the most recent list of major functionality that has been deprecated or removed within OpenShift Container Platform, refer to the Deprecated and removed features section of the OpenShift Container Platform release notes.
If your cluster uses Kuryr, associate the API floating IP address of your cluster with the pre-existing Octavia load balancer.
Prerequisites
- Your OpenShift Container Platform cluster uses Kuryr.
- Octavia is available on your Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) deployment.
Procedure
Optional: From a command line, to reuse the cluster API floating IP address, unset it:
openstack floating ip unset $API_FIP
$ openstack floating ip unset $API_FIPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add either the unset
API_FIPor a new address to the created load balancer VIP:openstack floating ip set --port $(openstack loadbalancer show -c <vip_port_id> -f value ${OCP_CLUSTER}-kuryr-api-loadbalancer) $API_FIP$ openstack floating ip set --port $(openstack loadbalancer show -c <vip_port_id> -f value ${OCP_CLUSTER}-kuryr-api-loadbalancer) $API_FIPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Your cluster now uses Octavia for load balancing.
If Kuryr uses the Octavia Amphora driver, all traffic is routed through a single Amphora virtual machine (VM).
You can repeat this procedure to create additional load balancers, which can alleviate the bottleneck.
32.4. Scaling for ingress traffic by using RHOSP Octavia
Kuryr is a deprecated feature. Deprecated functionality is still included in OpenShift Container Platform and continues to be supported; however, it will be removed in a future release of this product and is not recommended for new deployments.
For the most recent list of major functionality that has been deprecated or removed within OpenShift Container Platform, refer to the Deprecated and removed features section of the OpenShift Container Platform release notes.
You can use Octavia load balancers to scale Ingress controllers on clusters that use Kuryr.
Prerequisites
- Your OpenShift Container Platform cluster uses Kuryr.
- Octavia is available on your RHOSP deployment.
Procedure
To copy the current internal router service, on a command line, enter:
oc -n openshift-ingress get svc router-internal-default -o yaml > external_router.yaml
$ oc -n openshift-ingress get svc router-internal-default -o yaml > external_router.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the file
external_router.yaml, change the values ofmetadata.nameandspec.typetoLoadBalancer.Example router file
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can delete timestamps and other information that is irrelevant to load balancing.
From a command line, create a service from the
external_router.yamlfile:oc apply -f external_router.yaml
$ oc apply -f external_router.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the external IP address of the service is the same as the one that is associated with the load balancer:
On a command line, retrieve the external IP address of the service:
oc -n openshift-ingress get svc
$ oc -n openshift-ingress get svcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE router-external-default LoadBalancer 172.30.235.33 10.46.22.161 80:30112/TCP,443:32359/TCP,1936:30317/TCP 3m38s router-internal-default ClusterIP 172.30.115.123 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP,1936/TCP 22h
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE router-external-default LoadBalancer 172.30.235.33 10.46.22.161 80:30112/TCP,443:32359/TCP,1936:30317/TCP 3m38s router-internal-default ClusterIP 172.30.115.123 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP,1936/TCP 22hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Retrieve the IP address of the load balancer:
openstack loadbalancer list | grep router-external
$ openstack loadbalancer list | grep router-externalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
| 21bf6afe-b498-4a16-a958-3229e83c002c | openshift-ingress/router-external-default | 66f3816acf1b431691b8d132cc9d793c | 172.30.235.33 | ACTIVE | octavia |
| 21bf6afe-b498-4a16-a958-3229e83c002c | openshift-ingress/router-external-default | 66f3816acf1b431691b8d132cc9d793c | 172.30.235.33 | ACTIVE | octavia |Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the addresses you retrieved in the previous steps are associated with each other in the floating IP list:
openstack floating ip list | grep 172.30.235.33
$ openstack floating ip list | grep 172.30.235.33Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
| e2f80e97-8266-4b69-8636-e58bacf1879e | 10.46.22.161 | 172.30.235.33 | 655e7122-806a-4e0a-a104-220c6e17bda6 | a565e55a-99e7-4d15-b4df-f9d7ee8c9deb | 66f3816acf1b431691b8d132cc9d793c |
| e2f80e97-8266-4b69-8636-e58bacf1879e | 10.46.22.161 | 172.30.235.33 | 655e7122-806a-4e0a-a104-220c6e17bda6 | a565e55a-99e7-4d15-b4df-f9d7ee8c9deb | 66f3816acf1b431691b8d132cc9d793c |Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can now use the value of EXTERNAL-IP as the new Ingress address.
If Kuryr uses the Octavia Amphora driver, all traffic is routed through a single Amphora virtual machine (VM).
You can repeat this procedure to create additional load balancers, which can alleviate the bottleneck.
32.5. Services for an external load balancer
You can configure an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) to use an external load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
Configuring an external load balancer depends on your vendor’s load balancer.
The information and examples in this section are for guideline purposes only. Consult the vendor documentation for more specific information about the vendor’s load balancer.
Red Hat supports the following services for an external load balancer:
- Ingress Controller
- OpenShift API
- OpenShift MachineConfig API
You can choose whether you want to configure one or all of these services for an external load balancer. Configuring only the Ingress Controller service is a common configuration option. To better understand each service, view the following diagrams:
Figure 32.1. Example network workflow that shows an Ingress Controller operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment
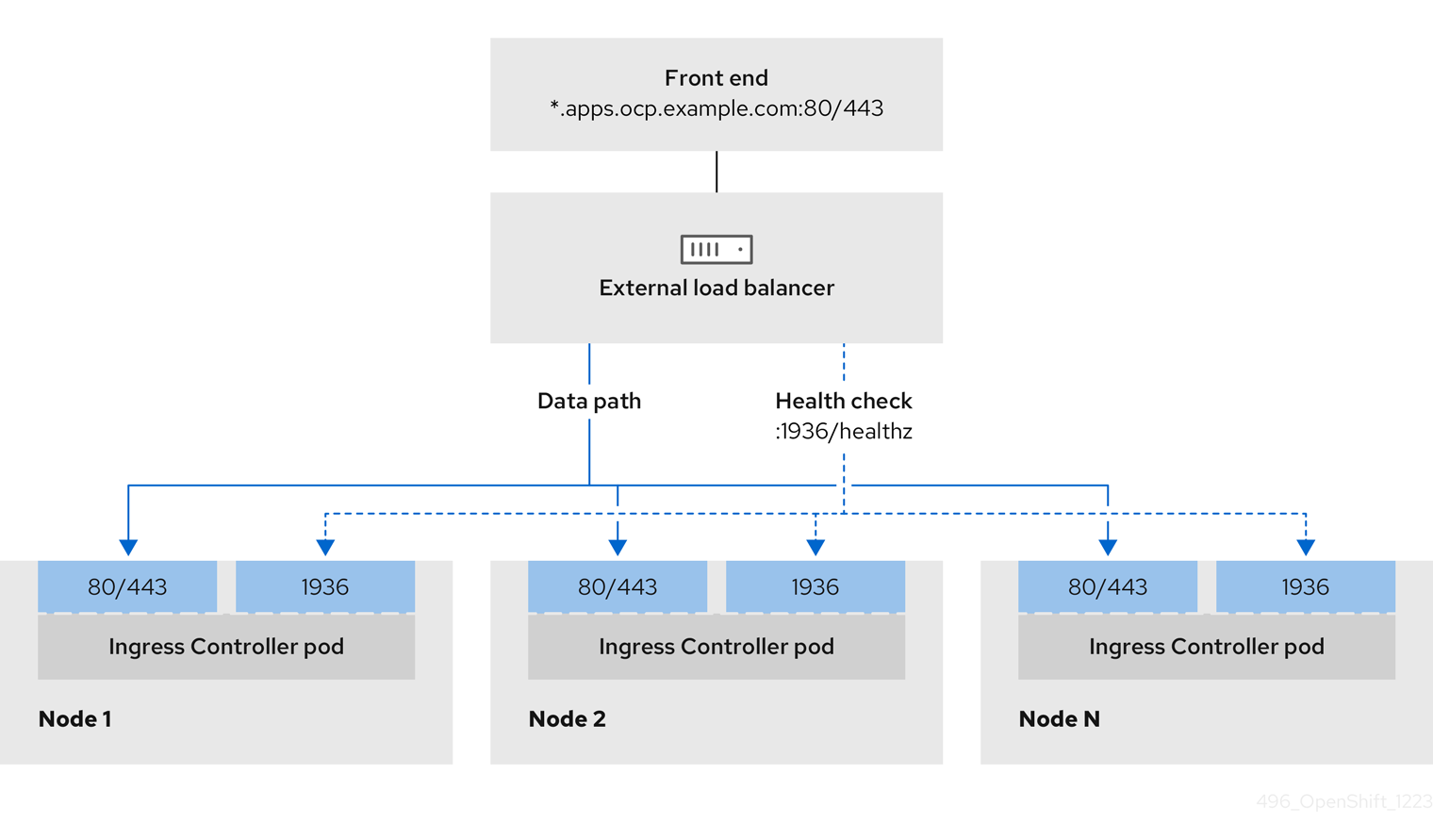
Figure 32.2. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment
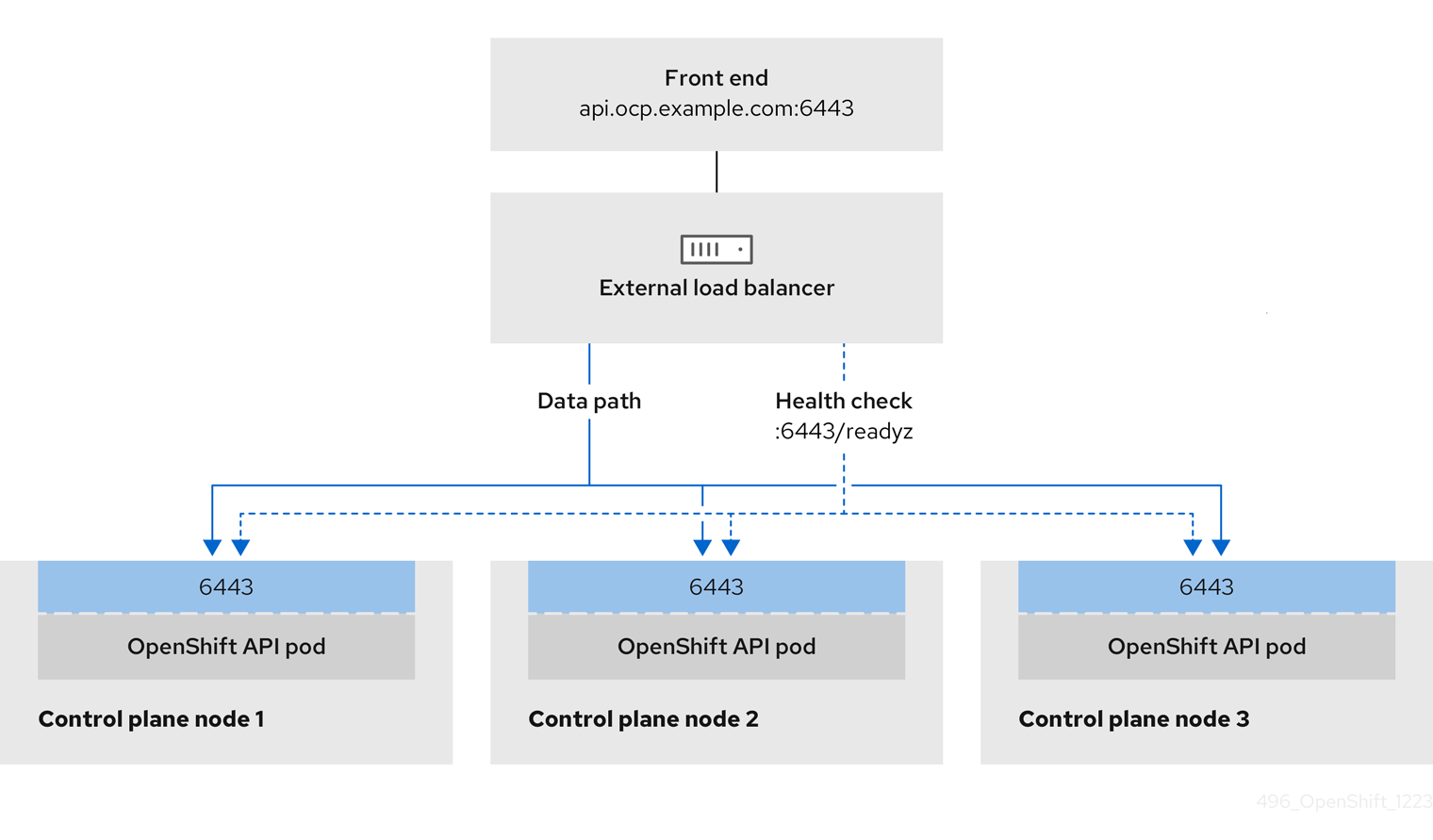
Figure 32.3. Example network workflow that shows an OpenShift MachineConfig API operating in an OpenShift Container Platform environment
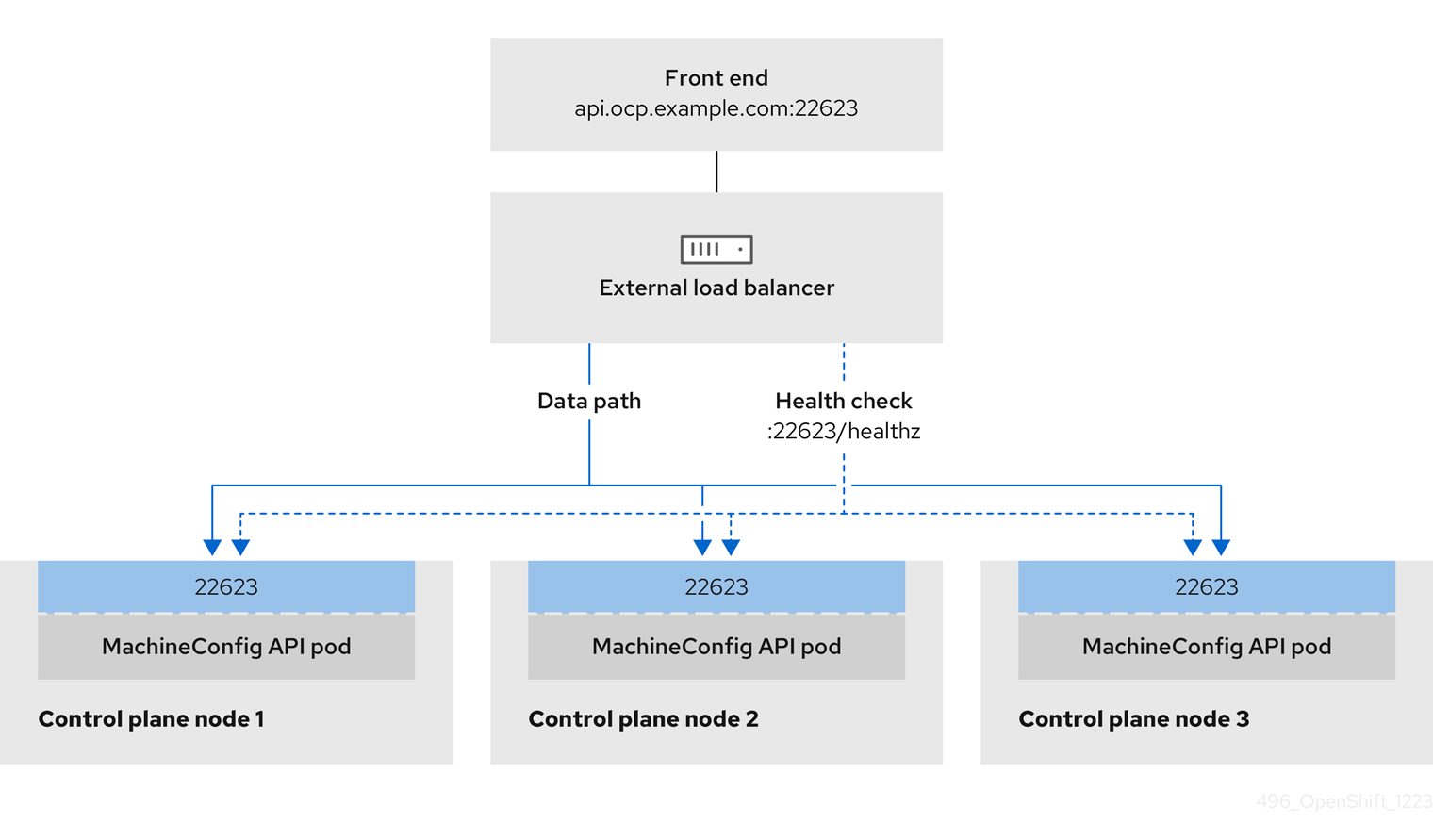
The following configuration options are supported for external load balancers:
- Use a node selector to map the Ingress Controller to a specific set of nodes. You must assign a static IP address to each node in this set, or configure each node to receive the same IP address from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Infrastructure nodes commonly receive this type of configuration.
Target all IP addresses on a subnet. This configuration can reduce maintenance overhead, because you can create and destroy nodes within those networks without reconfiguring the load balancer targets. If you deploy your ingress pods by using a machine set on a smaller network, such as a
/27or/28, you can simplify your load balancer targets.TipYou can list all IP addresses that exist in a network by checking the machine config pool’s resources.
Before you configure an external load balancer for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, consider the following information:
- For a front-end IP address, you can use the same IP address for the front-end IP address, the Ingress Controller’s load balancer, and API load balancer. Check the vendor’s documentation for this capability.
For a back-end IP address, ensure that an IP address for an OpenShift Container Platform control plane node does not change during the lifetime of the external load balancer. You can achieve this by completing one of the following actions:
- Assign a static IP address to each control plane node.
- Configure each node to receive the same IP address from the DHCP every time the node requests a DHCP lease. Depending on the vendor, the DHCP lease might be in the form of an IP reservation or a static DHCP assignment.
- Manually define each node that runs the Ingress Controller in the external load balancer for the Ingress Controller back-end service. For example, if the Ingress Controller moves to an undefined node, a connection outage can occur.
32.5.1. Configuring an external load balancer
You can configure an OpenShift Container Platform cluster on Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) to use an external load balancer in place of the default load balancer.
Before you configure an external load balancer, ensure that you read the "Services for an external load balancer" section.
Read the following prerequisites that apply to the service that you want to configure for your external load balancer.
MetalLB, that runs on a cluster, functions as an external load balancer.
OpenShift API prerequisites
- You defined a front-end IP address.
TCP ports 6443 and 22623 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer. Check the following items:
- Port 6443 provides access to the OpenShift API service.
- Port 22623 can provide ignition startup configurations to nodes.
- The front-end IP address and port 6443 are reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address and port 22623 are reachable only by OpenShift Container Platform nodes.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform control plane nodes on port 6443 and 22623.
Ingress Controller prerequisites
- You defined a front-end IP address.
- TCP ports 443 and 80 are exposed on the front-end IP address of your load balancer.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are be reachable by all users of your system with a location external to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The front-end IP address, port 80 and port 443 are reachable to all nodes that operate in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- The load balancer backend can communicate with OpenShift Container Platform nodes that run the Ingress Controller on ports 80, 443, and 1936.
Prerequisite for health check URL specifications
You can configure most load balancers by setting health check URLs that determine if a service is available or unavailable. OpenShift Container Platform provides these health checks for the OpenShift API, Machine Configuration API, and Ingress Controller backend services.
The following examples demonstrate health check specifications for the previously listed backend services:
Example of a Kubernetes API health check specification
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:6443/readyz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10Example of a Machine Config API health check specification
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 10 Interval: 10
Path: HTTPS:22623/healthz
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 10
Interval: 10Example of an Ingress Controller health check specification
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready Healthy threshold: 2 Unhealthy threshold: 2 Timeout: 5 Interval: 10
Path: HTTP:1936/healthz/ready
Healthy threshold: 2
Unhealthy threshold: 2
Timeout: 5
Interval: 10Procedure
Configure the HAProxy Ingress Controller, so that you can enable access to the cluster from your load balancer on ports 6443, 443, and 80:
Example HAProxy configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the external load balancer and its resources are operational:Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Kubernetes API server resource, by running the following command and observing the response:
curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the cluster machine configuration API is accessible to the Machine config server resource, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://<loadbalancer_ip_address>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 80, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>
$ curl -I -L -H "Host: console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>" http://<load_balancer_front_end_IP_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cache
HTTP/1.1 302 Found content-length: 0 location: https://console-openshift-console.apps.ocp4.private.opequon.net/ cache-control: no-cacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the controller is accessible to the Ingress Controller resource on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>
$ curl -I -L --insecure --resolve console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:443:<Load Balancer Front End IP Address> https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure the DNS records for your cluster to target the front-end IP addresses of the external load balancer. You must update records to your DNS server for the cluster API and applications over the load balancer.
Examples of modified DNS records
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front End
<load_balancer_ip_address> A apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> A record pointing to Load Balancer Front EndCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantDNS propagation might take some time for each DNS record to become available. Ensure that each DNS record propagates before validating each record.
Use the
curlCLI command to verify that the external load balancer and DNS record configuration are operational:Verify that you can access the cluster API, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecure
$ curl https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:6443/version --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, you receive a JSON object in response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access the cluster machine configuration, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecure
$ curl -v https://api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>:22623/healthz --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl http://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that you can access each cluster application on port 443, by running the following command and observing the output:
curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecure
$ curl https://console-openshift-console.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> -I -L --insecureCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the configuration is correct, the output from the command shows the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 33. Load balancing with MetalLB
33.1. About MetalLB and the MetalLB Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can add the MetalLB Operator to your cluster so that when a service of type LoadBalancer is added to the cluster, MetalLB can add an external IP address for the service. The external IP address is added to the host network for your cluster.
33.1.1. When to use MetalLB
Using MetalLB is valuable when you have a bare-metal cluster, or an infrastructure that is like bare metal, and you want fault-tolerant access to an application through an external IP address.
You must configure your networking infrastructure to ensure that network traffic for the external IP address is routed from clients to the host network for the cluster.
After deploying MetalLB with the MetalLB Operator, when you add a service of type LoadBalancer, MetalLB provides a platform-native load balancer.
MetalLB operating in layer2 mode provides support for failover by utilizing a mechanism similar to IP failover. However, instead of relying on the virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP) and keepalived, MetalLB leverages a gossip-based protocol to identify instances of node failure. When a failover is detected, another node assumes the role of the leader node, and a gratuitous ARP message is dispatched to broadcast this change.
MetalLB operating in layer3 or border gateway protocol (BGP) mode delegates failure detection to the network. The BGP router or routers that the OpenShift Container Platform nodes have established a connection with will identify any node failure and terminate the routes to that node.
Using MetalLB instead of IP failover is preferable for ensuring high availability of pods and services.
33.1.2. MetalLB Operator custom resources
The MetalLB Operator monitors its own namespace for the following custom resources:
MetalLB-
When you add a
MetalLBcustom resource to the cluster, the MetalLB Operator deploys MetalLB on the cluster. The Operator only supports a single instance of the custom resource. If the instance is deleted, the Operator removes MetalLB from the cluster. IPAddressPoolMetalLB requires one or more pools of IP addresses that it can assign to a service when you add a service of type
LoadBalancer. AnIPAddressPoolincludes a list of IP addresses. The list can be a single IP address that is set using a range, such as 1.1.1.1-1.1.1.1, a range specified in CIDR notation, a range specified as a starting and ending address separated by a hyphen, or a combination of the three. AnIPAddressPoolrequires a name. The documentation uses names likedoc-example,doc-example-reserved, anddoc-example-ipv6. The MetalLBcontrollerassigns IP addresses from a pool of addresses in anIPAddressPool.L2AdvertisementandBGPAdvertisementcustom resources enable the advertisement of a given IP from a given pool. You can assign IP addresses from anIPAddressPoolto services and namespaces by using thespec.serviceAllocationspecification in theIPAddressPoolcustom resource.NoteA single
IPAddressPoolcan be referenced by a L2 advertisement and a BGP advertisement.BGPPeer- The BGP peer custom resource identifies the BGP router for MetalLB to communicate with, the AS number of the router, the AS number for MetalLB, and customizations for route advertisement. MetalLB advertises the routes for service load-balancer IP addresses to one or more BGP peers.
BFDProfile- The BFD profile custom resource configures Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for a BGP peer. BFD provides faster path failure detection than BGP alone provides.
L2Advertisement-
The L2Advertisement custom resource advertises an IP coming from an
IPAddressPoolusing the L2 protocol. BGPAdvertisement-
The BGPAdvertisement custom resource advertises an IP coming from an
IPAddressPoolusing the BGP protocol.
After you add the MetalLB custom resource to the cluster and the Operator deploys MetalLB, the controller and speaker MetalLB software components begin running.
MetalLB validates all relevant custom resources.
33.1.3. MetalLB software components
When you install the MetalLB Operator, the metallb-operator-controller-manager deployment starts a pod. The pod is the implementation of the Operator. The pod monitors for changes to all the relevant resources.
When the Operator starts an instance of MetalLB, it starts a controller deployment and a speaker daemon set.
You can configure deployment specifications in the MetalLB custom resource to manage how controller and speaker pods deploy and run in your cluster. For more information about these deployment specifications, see the Additional resources section.
controllerThe Operator starts the deployment and a single pod. When you add a service of type
LoadBalancer, Kubernetes uses thecontrollerto allocate an IP address from an address pool. In case of a service failure, verify you have the following entry in yourcontrollerpod logs:Example output
"event":"ipAllocated","ip":"172.22.0.201","msg":"IP address assigned by controller
"event":"ipAllocated","ip":"172.22.0.201","msg":"IP address assigned by controllerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow speakerThe Operator starts a daemon set for
speakerpods. By default, a pod is started on each node in your cluster. You can limit the pods to specific nodes by specifying a node selector in theMetalLBcustom resource when you start MetalLB. If thecontrollerallocated the IP address to the service and service is still unavailable, read thespeakerpod logs. If thespeakerpod is unavailable, run theoc describe pod -ncommand.For layer 2 mode, after the
controllerallocates an IP address for the service, thespeakerpods use an algorithm to determine whichspeakerpod on which node will announce the load balancer IP address. The algorithm involves hashing the node name and the load balancer IP address. For more information, see "MetalLB and external traffic policy". Thespeakeruses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to announce IPv4 addresses and Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) to announce IPv6 addresses.
For Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) mode, after the controller allocates an IP address for the service, each speaker pod advertises the load balancer IP address with its BGP peers. You can configure which nodes start BGP sessions with BGP peers.
Requests for the load balancer IP address are routed to the node with the speaker that announces the IP address. After the node receives the packets, the service proxy routes the packets to an endpoint for the service. The endpoint can be on the same node in the optimal case, or it can be on another node. The service proxy chooses an endpoint each time a connection is established.
33.1.4. MetalLB and external traffic policy
With layer 2 mode, one node in your cluster receives all the traffic for the service IP address. With BGP mode, a router on the host network opens a connection to one of the nodes in the cluster for a new client connection. How your cluster handles the traffic after it enters the node is affected by the external traffic policy.
clusterThis is the default value for
spec.externalTrafficPolicy.With the
clustertraffic policy, after the node receives the traffic, the service proxy distributes the traffic to all the pods in your service. This policy provides uniform traffic distribution across the pods, but it obscures the client IP address and it can appear to the application in your pods that the traffic originates from the node rather than the client.localWith the
localtraffic policy, after the node receives the traffic, the service proxy only sends traffic to the pods on the same node. For example, if thespeakerpod on node A announces the external service IP, then all traffic is sent to node A. After the traffic enters node A, the service proxy only sends traffic to pods for the service that are also on node A. Pods for the service that are on additional nodes do not receive any traffic from node A. Pods for the service on additional nodes act as replicas in case failover is needed.This policy does not affect the client IP address. Application pods can determine the client IP address from the incoming connections.
The following information is important when configuring the external traffic policy in BGP mode.
Although MetalLB advertises the load balancer IP address from all the eligible nodes, the number of nodes loadbalancing the service can be limited by the capacity of the router to establish equal-cost multipath (ECMP) routes. If the number of nodes advertising the IP is greater than the ECMP group limit of the router, the router will use less nodes than the ones advertising the IP.
For example, if the external traffic policy is set to local and the router has an ECMP group limit set to 16 and the pods implementing a LoadBalancer service are deployed on 30 nodes, this would result in pods deployed on 14 nodes not receiving any traffic. In this situation, it would be preferable to set the external traffic policy for the service to cluster.
33.1.5. MetalLB concepts for layer 2 mode
In layer 2 mode, the speaker pod on one node announces the external IP address for a service to the host network. From a network perspective, the node appears to have multiple IP addresses assigned to a network interface.
In layer 2 mode, MetalLB relies on ARP and NDP. These protocols implement local address resolution within a specific subnet. In this context, the client must be able to reach the VIP assigned by MetalLB that exists on the same subnet as the nodes announcing the service in order for MetalLB to work.
The speaker pod responds to ARP requests for IPv4 services and NDP requests for IPv6.
In layer 2 mode, all traffic for a service IP address is routed through one node. After traffic enters the node, the service proxy for the CNI network provider distributes the traffic to all the pods for the service.
Because all traffic for a service enters through a single node in layer 2 mode, in a strict sense, MetalLB does not implement a load balancer for layer 2. Rather, MetalLB implements a failover mechanism for layer 2 so that when a speaker pod becomes unavailable, a speaker pod on a different node can announce the service IP address.
When a node becomes unavailable, failover is automatic. The speaker pods on the other nodes detect that a node is unavailable and a new speaker pod and node take ownership of the service IP address from the failed node.
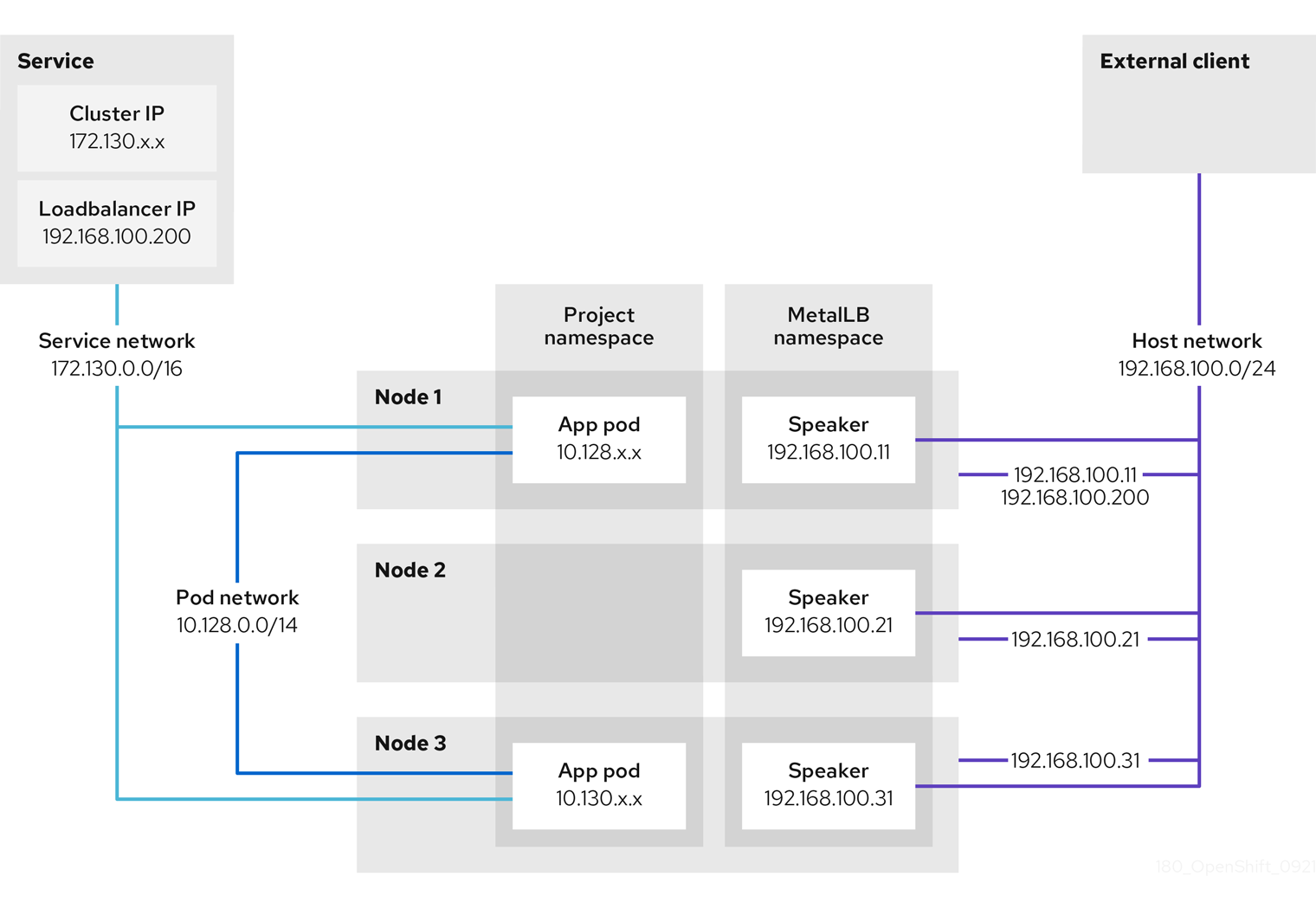
The preceding graphic shows the following concepts related to MetalLB:
-
An application is available through a service that has a cluster IP on the
172.130.0.0/16subnet. That IP address is accessible from inside the cluster. The service also has an external IP address that MetalLB assigned to the service,192.168.100.200. - Nodes 1 and 3 have a pod for the application.
-
The
speakerdaemon set runs a pod on each node. The MetalLB Operator starts these pods. -
Each
speakerpod is a host-networked pod. The IP address for the pod is identical to the IP address for the node on the host network. -
The
speakerpod on node 1 uses ARP to announce the external IP address for the service,192.168.100.200. Thespeakerpod that announces the external IP address must be on the same node as an endpoint for the service and the endpoint must be in theReadycondition. Client traffic is routed to the host network and connects to the
192.168.100.200IP address. After traffic enters the node, the service proxy sends the traffic to the application pod on the same node or another node according to the external traffic policy that you set for the service.-
If the external traffic policy for the service is set to
cluster, the node that advertises the192.168.100.200load balancer IP address is selected from the nodes where aspeakerpod is running. Only that node can receive traffic for the service. -
If the external traffic policy for the service is set to
local, the node that advertises the192.168.100.200load balancer IP address is selected from the nodes where aspeakerpod is running and at least an endpoint of the service. Only that node can receive traffic for the service. In the preceding graphic, either node 1 or 3 would advertise192.168.100.200.
-
If the external traffic policy for the service is set to
-
If node 1 becomes unavailable, the external IP address fails over to another node. On another node that has an instance of the application pod and service endpoint, the
speakerpod begins to announce the external IP address,192.168.100.200and the new node receives the client traffic. In the diagram, the only candidate is node 3.
33.1.6. MetalLB concepts for BGP mode
In BGP mode, by default each speaker pod advertises the load balancer IP address for a service to each BGP peer. It is also possible to advertise the IPs coming from a given pool to a specific set of peers by adding an optional list of BGP peers. BGP peers are commonly network routers that are configured to use the BGP protocol. When a router receives traffic for the load balancer IP address, the router picks one of the nodes with a speaker pod that advertised the IP address. The router sends the traffic to that node. After traffic enters the node, the service proxy for the CNI network plugin distributes the traffic to all the pods for the service.
The directly-connected router on the same layer 2 network segment as the cluster nodes can be configured as a BGP peer. If the directly-connected router is not configured as a BGP peer, you need to configure your network so that packets for load balancer IP addresses are routed between the BGP peers and the cluster nodes that run the speaker pods.
Each time a router receives new traffic for the load balancer IP address, it creates a new connection to a node. Each router manufacturer has an implementation-specific algorithm for choosing which node to initiate the connection with. However, the algorithms commonly are designed to distribute traffic across the available nodes for the purpose of balancing the network load.
If a node becomes unavailable, the router initiates a new connection with another node that has a speaker pod that advertises the load balancer IP address.
Figure 33.1. MetalLB topology diagram for BGP mode
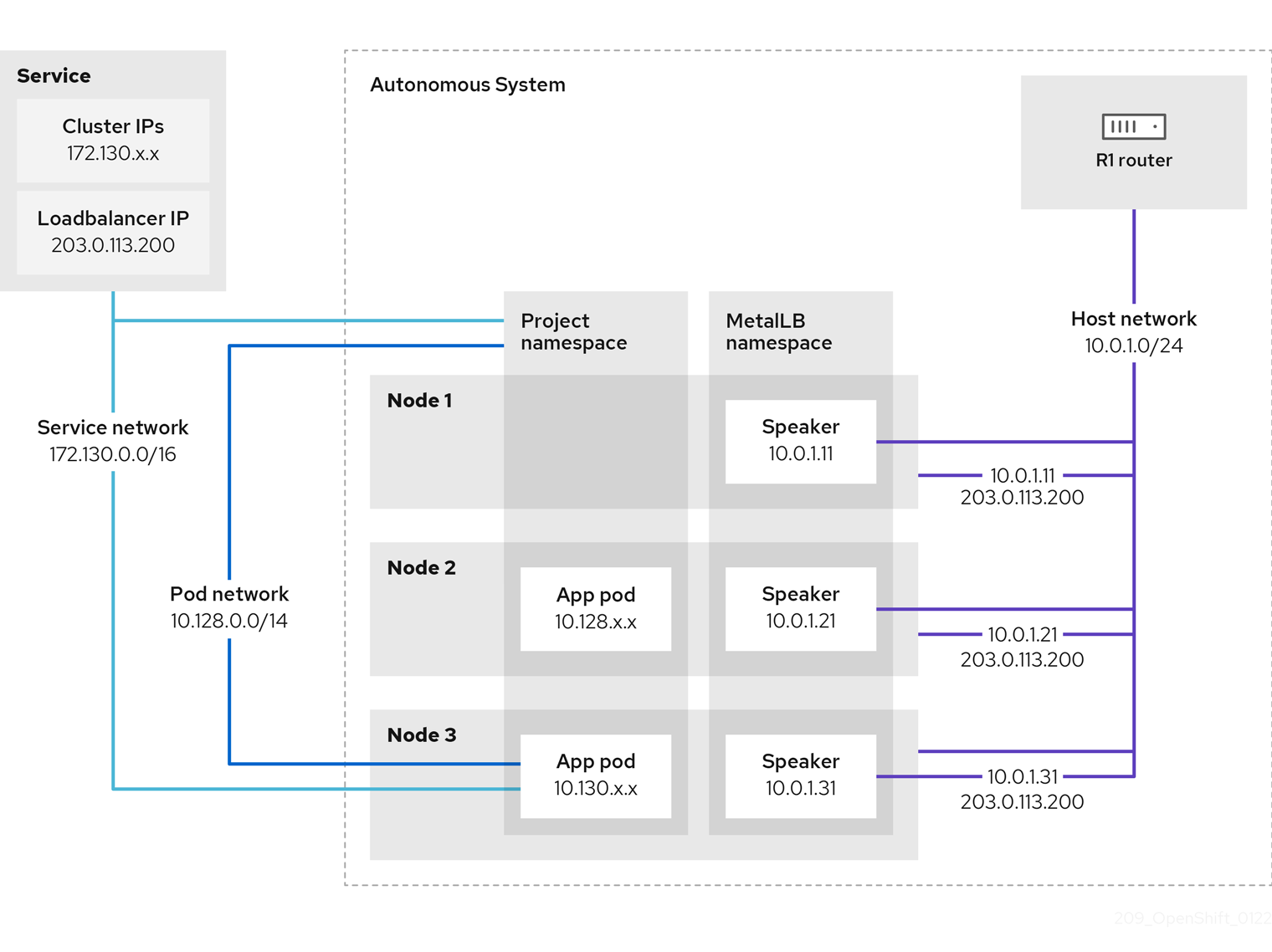
The preceding graphic shows the following concepts related to MetalLB:
-
An application is available through a service that has an IPv4 cluster IP on the
172.130.0.0/16subnet. That IP address is accessible from inside the cluster. The service also has an external IP address that MetalLB assigned to the service,203.0.113.200. - Nodes 2 and 3 have a pod for the application.
-
The
speakerdaemon set runs a pod on each node. The MetalLB Operator starts these pods. You can configure MetalLB to specify which nodes run thespeakerpods. -
Each
speakerpod is a host-networked pod. The IP address for the pod is identical to the IP address for the node on the host network. -
Each
speakerpod starts a BGP session with all BGP peers and advertises the load balancer IP addresses or aggregated routes to the BGP peers. Thespeakerpods advertise that they are part of Autonomous System 65010. The diagram shows a router, R1, as a BGP peer within the same Autonomous System. However, you can configure MetalLB to start BGP sessions with peers that belong to other Autonomous Systems. All the nodes with a
speakerpod that advertises the load balancer IP address can receive traffic for the service.-
If the external traffic policy for the service is set to
cluster, all the nodes where a speaker pod is running advertise the203.0.113.200load balancer IP address and all the nodes with aspeakerpod can receive traffic for the service. The host prefix is advertised to the router peer only if the external traffic policy is set to cluster. -
If the external traffic policy for the service is set to
local, then all the nodes where aspeakerpod is running and at least an endpoint of the service is running can advertise the203.0.113.200load balancer IP address. Only those nodes can receive traffic for the service. In the preceding graphic, nodes 2 and 3 would advertise203.0.113.200.
-
If the external traffic policy for the service is set to
-
You can configure MetalLB to control which
speakerpods start BGP sessions with specific BGP peers by specifying a node selector when you add a BGP peer custom resource. - Any routers, such as R1, that are configured to use BGP can be set as BGP peers.
- Client traffic is routed to one of the nodes on the host network. After traffic enters the node, the service proxy sends the traffic to the application pod on the same node or another node according to the external traffic policy that you set for the service.
- If a node becomes unavailable, the router detects the failure and initiates a new connection with another node. You can configure MetalLB to use a Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) profile for BGP peers. BFD provides faster link failure detection so that routers can initiate new connections earlier than without BFD.
33.1.7. Limitations and restrictions
33.1.7.1. Infrastructure considerations for MetalLB
MetalLB is primarily useful for on-premise, bare metal installations because these installations do not include a native load-balancer capability. In addition to bare metal installations, installations of OpenShift Container Platform on some infrastructures might not include a native load-balancer capability. For example, the following infrastructures can benefit from adding the MetalLB Operator:
- Bare metal
- VMware vSphere
- IBM Z and IBM® LinuxONE
- IBM Z and IBM® LinuxONE for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) KVM
- IBM Power
MetalLB Operator and MetalLB are supported with the OpenShift SDN and OVN-Kubernetes network providers.
33.1.7.2. Limitations for layer 2 mode
33.1.7.2.1. Single-node bottleneck
MetalLB routes all traffic for a service through a single node, the node can become a bottleneck and limit performance.
Layer 2 mode limits the ingress bandwidth for your service to the bandwidth of a single node. This is a fundamental limitation of using ARP and NDP to direct traffic.
33.1.7.2.2. Slow failover performance
Failover between nodes depends on cooperation from the clients. When a failover occurs, MetalLB sends gratuitous ARP packets to notify clients that the MAC address associated with the service IP has changed.
Most client operating systems handle gratuitous ARP packets correctly and update their neighbor caches promptly. When clients update their caches quickly, failover completes within a few seconds. Clients typically fail over to a new node within 10 seconds. However, some client operating systems either do not handle gratuitous ARP packets at all or have outdated implementations that delay the cache update.
Recent versions of common operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux implement layer 2 failover correctly. Issues with slow failover are not expected except for older and less common client operating systems.
To minimize the impact from a planned failover on outdated clients, keep the old node running for a few minutes after flipping leadership. The old node can continue to forward traffic for outdated clients until their caches refresh.
During an unplanned failover, the service IPs are unreachable until the outdated clients refresh their cache entries.
33.1.7.2.3. Additional Network and MetalLB cannot use same network
Using the same VLAN for both MetalLB and an additional network interface set up on a source pod might result in a connection failure. This occurs when both the MetalLB IP and the source pod reside on the same node.
To avoid connection failures, place the MetalLB IP in a different subnet from the one where the source pod resides. This configuration ensures that traffic from the source pod will take the default gateway. Consequently, the traffic can effectively reach its destination by using the OVN overlay network, ensuring that the connection functions as intended.
33.1.7.3. Limitations for BGP mode
33.1.7.3.1. Node failure can break all active connections
MetalLB shares a limitation that is common to BGP-based load balancing. When a BGP session terminates, such as when a node fails or when a speaker pod restarts, the session termination might result in resetting all active connections. End users can experience a Connection reset by peer message.
The consequence of a terminated BGP session is implementation-specific for each router manufacturer. However, you can anticipate that a change in the number of speaker pods affects the number of BGP sessions and that active connections with BGP peers will break.
To avoid or reduce the likelihood of a service interruption, you can specify a node selector when you add a BGP peer. By limiting the number of nodes that start BGP sessions, a fault on a node that does not have a BGP session has no affect on connections to the service.
33.1.7.3.2. Support for a single ASN and a single router ID only
When you add a BGP peer custom resource, you specify the spec.myASN field to identify the Autonomous System Number (ASN) that MetalLB belongs to. OpenShift Container Platform uses an implementation of BGP with MetalLB that requires MetalLB to belong to a single ASN. If you attempt to add a BGP peer and specify a different value for spec.myASN than an existing BGP peer custom resource, you receive an error.
Similarly, when you add a BGP peer custom resource, the spec.routerID field is optional. If you specify a value for this field, you must specify the same value for all other BGP peer custom resources that you add.
The limitation to support a single ASN and single router ID is a difference with the community-supported implementation of MetalLB.
33.2. Installing the MetalLB Operator
As a cluster administrator, you can add the MetallB Operator so that the Operator can manage the lifecycle for an instance of MetalLB on your cluster.
MetalLB and IP failover are incompatible. If you configured IP failover for your cluster, perform the steps to remove IP failover before you install the Operator.
33.2.1. Installing the MetalLB Operator from the OperatorHub using the web console
As a cluster administrator, you can install the MetalLB Operator by using the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
Prerequisites
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
- In the OpenShift Container Platform web console, navigate to Operators → OperatorHub.
Type a keyword into the Filter by keyword box or scroll to find the Operator you want. For example, type
metallbto find the MetalLB Operator.You can also filter options by Infrastructure Features. For example, select Disconnected if you want to see Operators that work in disconnected environments, also known as restricted network environments.
- On the Install Operator page, accept the defaults and click Install.
Verification
To confirm that the installation is successful:
- Navigate to the Operators → Installed Operators page.
-
Check that the Operator is installed in the
openshift-operatorsnamespace and that its status isSucceeded.
If the Operator is not installed successfully, check the status of the Operator and review the logs:
-
Navigate to the Operators → Installed Operators page and inspect the
Statuscolumn for any errors or failures. -
Navigate to the Workloads → Pods page and check the logs in any pods in the
openshift-operatorsproject that are reporting issues.
-
Navigate to the Operators → Installed Operators page and inspect the
33.2.2. Installing from OperatorHub by using the CLI
Instead of using the OpenShift Container Platform web console, you can install an Operator from OperatorHub using the CLI. You can use the OpenShift CLI (oc) to install the MetalLB Operator.
It is recommended that when using the CLI you install the Operator in the metallb-system namespace.
Prerequisites
- A cluster installed on bare-metal hardware.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a namespace for the MetalLB Operator by entering the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an Operator group custom resource (CR) in the namespace:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm the Operator group is installed in the namespace:
oc get operatorgroup -n metallb-system
$ oc get operatorgroup -n metallb-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME AGE metallb-operator 14m
NAME AGE metallb-operator 14mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
SubscriptionCR:Define the
SubscriptionCR and save the YAML file, for example,metallb-sub.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- You must specify the
redhat-operatorsvalue.
To create the
SubscriptionCR, run the following command:oc create -f metallb-sub.yaml
$ oc create -f metallb-sub.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Optional: To ensure BGP and BFD metrics appear in Prometheus, you can label the namespace as in the following command:
oc label ns metallb-system "openshift.io/cluster-monitoring=true"
$ oc label ns metallb-system "openshift.io/cluster-monitoring=true"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
The verification steps assume the MetalLB Operator is installed in the metallb-system namespace.
Confirm the install plan is in the namespace:
oc get installplan -n metallb-system
$ oc get installplan -n metallb-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED install-wzg94 metallb-operator.4.13.0-nnnnnnnnnnnn Automatic true
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED install-wzg94 metallb-operator.4.13.0-nnnnnnnnnnnn Automatic trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteInstallation of the Operator might take a few seconds.
To verify that the Operator is installed, enter the following command:
oc get clusterserviceversion -n metallb-system \ -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phase
$ oc get clusterserviceversion -n metallb-system \ -o custom-columns=Name:.metadata.name,Phase:.status.phaseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Name Phase metallb-operator.4.13.0-nnnnnnnnnnnn Succeeded
Name Phase metallb-operator.4.13.0-nnnnnnnnnnnn SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.2.3. Starting MetalLB on your cluster
After you install the Operator, you need to configure a single instance of a MetalLB custom resource. After you configure the custom resource, the Operator starts MetalLB on your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Install the MetalLB Operator.
Procedure
This procedure assumes the MetalLB Operator is installed in the metallb-system namespace. If you installed using the web console substitute openshift-operators for the namespace.
Create a single instance of a MetalLB custom resource:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Confirm that the deployment for the MetalLB controller and the daemon set for the MetalLB speaker are running.
Verify that the deployment for the controller is running:
oc get deployment -n metallb-system controller
$ oc get deployment -n metallb-system controllerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE controller 1/1 1 1 11m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE controller 1/1 1 1 11mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the daemon set for the speaker is running:
oc get daemonset -n metallb-system speaker
$ oc get daemonset -n metallb-system speakerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE speaker 6 6 6 6 6 kubernetes.io/os=linux 18m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE speaker 6 6 6 6 6 kubernetes.io/os=linux 18mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The example output indicates 6 speaker pods. The number of speaker pods in your cluster might differ from the example output. Make sure the output indicates one pod for each node in your cluster.
33.2.4. Deployment specifications for MetalLB
When you start an instance of MetalLB using the MetalLB custom resource, you can configure deployment specifications in the MetalLB custom resource to manage how the controller or speaker pods deploy and run in your cluster. Use these deployment specifications to manage the following tasks:
- Select nodes for MetalLB pod deployment.
- Manage scheduling by using pod priority and pod affinity.
- Assign CPU limits for MetalLB pods.
- Assign a container RuntimeClass for MetalLB pods.
- Assign metadata for MetalLB pods.
33.2.4.1. Limit speaker pods to specific nodes
By default, when you start MetalLB with the MetalLB Operator, the Operator starts an instance of a speaker pod on each node in the cluster. Only the nodes with a speaker pod can advertise a load balancer IP address. You can configure the MetalLB custom resource with a node selector to specify which nodes run the speaker pods.
The most common reason to limit the speaker pods to specific nodes is to ensure that only nodes with network interfaces on specific networks advertise load balancer IP addresses. Only the nodes with a running speaker pod are advertised as destinations of the load balancer IP address.
If you limit the speaker pods to specific nodes and specify local for the external traffic policy of a service, then you must ensure that the application pods for the service are deployed to the same nodes.
Example configuration to limit speaker pods to worker nodes
<.> The example configuration specifies to assign the speaker pods to worker nodes, but you can specify labels that you assigned to nodes or any valid node selector. <.> In this example configuration, the pod that this toleration is attached to tolerates any taint that matches the key value and effect value using the operator.
After you apply a manifest with the spec.nodeSelector field, you can check the number of pods that the Operator deployed with the oc get daemonset -n metallb-system speaker command. Similarly, you can display the nodes that match your labels with a command like oc get nodes -l node-role.kubernetes.io/worker=.
You can optionally allow the node to control which speaker pods should, or should not, be scheduled on them by using affinity rules. You can also limit these pods by applying a list of tolerations. For more information about affinity rules, taints, and tolerations, see the additional resources.
33.2.4.2. Configuring pod priority and pod affinity in a MetalLB deployment
You can optionally assign pod priority and pod affinity rules to controller and speaker pods by configuring the MetalLB custom resource. The pod priority indicates the relative importance of a pod on a node and schedules the pod based on this priority. Set a high priority on your controller or speaker pod to ensure scheduling priority over other pods on the node.
Pod affinity manages relationships among pods. Assign pod affinity to the controller or speaker pods to control on what node the scheduler places the pod in the context of pod relationships. For example, you can use pod affinity rules to ensure that certain pods are located on the same node or nodes, which can help improve network communication and reduce latency between those components.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have installed the MetalLB Operator.
- You have started the MetalLB Operator on your cluster.
Procedure
Create a
PriorityClasscustom resource, such asmyPriorityClass.yaml, to configure the priority level. This example defines aPriorityClassnamedhigh-prioritywith a value of1000000. Pods that are assigned this priority class are considered higher priority during scheduling compared to pods with lower priority classes:apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1 kind: PriorityClass metadata: name: high-priority value: 1000000
apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1 kind: PriorityClass metadata: name: high-priority value: 1000000Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the
PriorityClasscustom resource configuration:oc apply -f myPriorityClass.yaml
$ oc apply -f myPriorityClass.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
MetalLBcustom resource, such asMetalLBPodConfig.yaml, to specify thepriorityClassNameandpodAffinityvalues:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the priority class for the MetalLB controller pods. In this case, it is set to
high-priority. - 2
- Specifies that you are configuring pod affinity rules. These rules dictate how pods are scheduled in relation to other pods or nodes. This configuration instructs the scheduler to schedule pods that have the label
app: metallbonto nodes that share the same hostname. This helps to co-locate MetalLB-related pods on the same nodes, potentially optimizing network communication, latency, and resource usage between these pods.
Apply the
MetalLBcustom resource configuration:oc apply -f MetalLBPodConfig.yaml
$ oc apply -f MetalLBPodConfig.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To view the priority class that you assigned to pods in the
metallb-systemnamespace, run the following command:oc get pods -n metallb-system -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,PRIORITY:.spec.priorityClassName
$ oc get pods -n metallb-system -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,PRIORITY:.spec.priorityClassNameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME PRIORITY controller-584f5c8cd8-5zbvg high-priority metallb-operator-controller-manager-9c8d9985-szkqg <none> metallb-operator-webhook-server-c895594d4-shjgx <none> speaker-dddf7 high-priority
NAME PRIORITY controller-584f5c8cd8-5zbvg high-priority metallb-operator-controller-manager-9c8d9985-szkqg <none> metallb-operator-webhook-server-c895594d4-shjgx <none> speaker-dddf7 high-priorityCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the scheduler placed pods according to pod affinity rules, view the metadata for the pod’s node or nodes by running the following command:
oc get pod -o=custom-columns=NODE:.spec.nodeName,NAME:.metadata.name -n metallb-system
$ oc get pod -o=custom-columns=NODE:.spec.nodeName,NAME:.metadata.name -n metallb-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.2.4.3. Configuring pod CPU limits in a MetalLB deployment
You can optionally assign pod CPU limits to controller and speaker pods by configuring the MetalLB custom resource. Defining CPU limits for the controller or speaker pods helps you to manage compute resources on the node. This ensures all pods on the node have the necessary compute resources to manage workloads and cluster housekeeping.
Prerequisites
-
You are logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - You have installed the MetalLB Operator.
Procedure
Create a
MetalLBcustom resource file, such asCPULimits.yaml, to specify thecpuvalue for thecontrollerandspeakerpods:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the
MetalLBcustom resource configuration:oc apply -f CPULimits.yaml
$ oc apply -f CPULimits.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
To view compute resources for a pod, run the following command, replacing
<pod_name>with your target pod:oc describe pod <pod_name>
$ oc describe pod <pod_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.2.6. Next steps
33.3. Upgrading the MetalLB
A Subscription custom resource (CR) that subscribes the namespace to metallb-system by default, automatically sets the installPlanApproval parameter to Automatic. This means that when Red Hat-provided Operator catalogs include a newer version of the MetalLB Operator, the MetalLB Operator is automatically upgraded.
If you need to manually control upgrading the MetalLB Operator, set the installPlanApproval parameter to Manual.
33.3.1. Manually upgrading the MetalLB Operator
To manually control upgrading the MetalLB Operator, you must edit the Subscription custom resource (CR) that subscribes the namespace to metallb-system. A Subscription CR is created as part of the Operator installation and the CR has the installPlanApproval parameter set to Automatic by default.
Prerequisites
- You updated your cluster to the latest z-stream release.
- You used OperatorHub to install the MetalLB Operator.
-
Access the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Get the YAML definition of the
metallb-operatorsubscription in themetallb-systemnamespace by entering the following command:oc -n metallb-system get subscription metallb-operator -o yaml
$ oc -n metallb-system get subscription metallb-operator -o yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
SubscriptionCR by setting theinstallPlanApprovalparameter toManual:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the latest OpenShift Container Platform 4.13 version of the MetalLB Operator by entering the following command:
oc -n metallb-system get csv
$ oc -n metallb-system get csvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE metallb-operator.v4.13.0 MetalLB Operator 4.13.0 Succeeded
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE metallb-operator.v4.13.0 MetalLB Operator 4.13.0 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the install plan that exists in the namespace by entering the following command.
oc -n metallb-system get installplan
$ oc -n metallb-system get installplanCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output that shows install-tsz2g as a manual install plan
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED install-shpmd metallb-operator.v4.13.0-202502261233 Automatic true install-tsz2g metallb-operator.v4.13.0-202503102139 Manual false
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED install-shpmd metallb-operator.v4.13.0-202502261233 Automatic true install-tsz2g metallb-operator.v4.13.0-202503102139 Manual falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the install plan that exists in the namespace by entering the following command. Ensure that you replace
<name_of_installplan>with the name of the install plan, such asinstall-tsz2g.oc edit installplan <name_of_installplan> -n metallb-system
$ oc edit installplan <name_of_installplan> -n metallb-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow With the install plan open in your editor, set the
spec.approvalparameter toManualand set thespec.approvedparameter totrue.NoteAfter you edit the install plan, the upgrade operation starts. If you enter the
oc -n metallb-system get csvcommand during the upgrade operation, the output might show theReplacingor thePendingstatus.
Verification
Verify the upgrade was successful by entering the following command:
oc -n metallb-system get csv
$ oc -n metallb-system get csvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACE PHASE metallb-operator.v<latest>.0-202503102139 MetalLB Operator {product-version}.0-202503102139 metallb-operator.v{product-version}.0-202502261233 SucceededNAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACE PHASE metallb-operator.v<latest>.0-202503102139 MetalLB Operator {product-version}.0-202503102139 metallb-operator.v{product-version}.0-202502261233 SucceededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.3.2. Additional resources
33.4. Configuring MetalLB address pools
As a cluster administrator, you can add, modify, and delete address pools. The MetalLB Operator uses the address pool custom resources to set the IP addresses that MetalLB can assign to services. The namespace used in the examples assume the namespace is metallb-system.
33.4.1. About the IPAddressPool custom resource
The address pool custom resource definition (CRD) and API documented in "Load balancing with MetalLB" in OpenShift Container Platform 4.10 can still be used in 4.13. However, the enhanced functionality associated with advertising an IP address from an IPAddressPool with layer 2 protocols, or the BGP protocol, is not supported when using the AddressPool CRD.
The fields for the IPAddressPool custom resource are described in the following tables.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Specifies the name for the address pool. When you add a service, you can specify this pool name in the |
|
|
| Specifies the namespace for the address pool. Specify the same namespace that the MetalLB Operator uses. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies the key value pair assigned to the |
|
|
| Specifies a list of IP addresses for MetalLB Operator to assign to services. You can specify multiple ranges in a single pool; they will all share the same settings. Specify each range in CIDR notation or as starting and ending IP addresses separated with a hyphen. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies whether MetalLB automatically assigns IP addresses from this pool. Specify Note
For IP address pool configurations, ensure the addresses field specifies only IPs that are available and not in use by other network devices, especially gateway addresses, to prevent conflicts when |
|
|
|
Optional: This ensures when enabled that IP addresses ending |
You can assign IP addresses from an IPAddressPool to services and namespaces by configuring the spec.serviceAllocation specification.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Optional: Defines the priority between IP address pools when more than one IP address pool matches a service or namespace. A lower number indicates a higher priority. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies a list of namespaces that you can assign to IP addresses in an IP address pool. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies namespace labels that you can assign to IP addresses from an IP address pool by using label selectors in a list format. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies service labels that you can assign to IP addresses from an address pool by using label selectors in a list format. |
33.4.2. Configuring an address pool
As a cluster administrator, you can add address pools to your cluster to control the IP addresses that MetalLB can assign to load-balancer services.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- This label assigned to the
IPAddressPoolcan be referenced by theipAddressPoolSelectorsin theBGPAdvertisementCRD to associate theIPAddressPoolwith the advertisement.
Apply the configuration for the IP address pool:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
View the address pool by entering the following command:
oc describe -n metallb-system IPAddressPool doc-example
$ oc describe -n metallb-system IPAddressPool doc-exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Confirm that the address pool name, such as
doc-example, and the IP address ranges exist in the output.
33.4.3. Example address pool configurations
The following examples show address pool configurations for specific scenarios.
33.4.3.1. Example: IPv4 and CIDR ranges
You can specify a range of IP addresses in classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) notation. You can combine CIDR notation with the notation that uses a hyphen to separate lower and upper bounds.
33.4.3.2. Example: Assign IP addresses
You can set the autoAssign field to false to prevent MetalLB from automatically assigning IP addresses from the address pool. You can then assign a single IP address or multiple IP addresses from an IP address pool. To assign an IP address, append the /32 CIDR notation to the target IP address in the spec.addresses parameter. This setting ensures that only the specific IP address is avilable for assignment, leaving non-reserved IP addresses for application use.
Example IPAddressPool CR that assigns multiple IP addresses
When you add a service, you can request a specific IP address from the address pool or you can specify the pool name in an annotation to request any IP address from the pool.
33.4.3.3. Example: IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
You can add address pools that use IPv4 and IPv6. You can specify multiple ranges in the addresses list, just like several IPv4 examples.
Whether the service is assigned a single IPv4 address, a single IPv6 address, or both is determined by how you add the service. The spec.ipFamilies and spec.ipFamilyPolicy fields control how IP addresses are assigned to the service.
- 1
- Where
10.0.100.0/28is the local network IP address followed by the/28network prefix.
33.4.3.4. Example: Assign IP address pools to services or namespaces
You can assign IP addresses from an IPAddressPool to services and namespaces that you specify.
If you assign a service or namespace to more than one IP address pool, MetalLB uses an available IP address from the higher-priority IP address pool. If no IP addresses are available from the assigned IP address pools with a high priority, MetalLB uses available IP addresses from an IP address pool with lower priority or no priority.
You can use the matchLabels label selector, the matchExpressions label selector, or both, for the namespaceSelectors and serviceSelectors specifications. This example demonstrates one label selector for each specification.
- 1
- Assign a priority to the address pool. A lower number indicates a higher priority.
- 2
- Assign one or more namespaces to the IP address pool in a list format.
- 3
- Assign one or more namespace labels to the IP address pool by using label selectors in a list format.
- 4
- Assign one or more service labels to the IP address pool by using label selectors in a list format.
33.4.4. Next steps
33.5. About advertising for the IP address pools
You can configure MetalLB so that the IP address is advertised with layer 2 protocols, the BGP protocol, or both. With layer 2, MetalLB provides a fault-tolerant external IP address. With BGP, MetalLB provides fault-tolerance for the external IP address and load balancing.
MetalLB supports advertising using L2 and BGP for the same set of IP addresses.
MetalLB provides the flexibility to assign address pools to specific BGP peers effectively to a subset of nodes on the network. This allows for more complex configurations, for example facilitating the isolation of nodes or the segmentation of the network.
33.5.1. About the BGPAdvertisement custom resource
The fields for the BGPAdvertisements object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies the name for the BGP advertisement. |
|
|
| Specifies the namespace for the BGP advertisement. Specify the same namespace that the MetalLB Operator uses. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies the number of bits to include in a 32-bit CIDR mask. To aggregate the routes that the speaker advertises to BGP peers, the mask is applied to the routes for several service IP addresses and the speaker advertises the aggregated route. For example, with an aggregation length of |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies the number of bits to include in a 128-bit CIDR mask. For example, with an aggregation length of |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies one or more BGP communities. Each community is specified as two 16-bit values separated by the colon character. Well-known communities must be specified as 16-bit values:
|
|
|
| Optional: Specifies the local preference for this advertisement. This BGP attribute applies to BGP sessions within the Autonomous System. |
|
|
|
Optional: The list of |
|
|
|
Optional: A selector for the |
|
|
|
Optional: |
|
|
|
Optional: Use a list to specify the |
33.5.2. Configuring MetalLB with a BGP advertisement and a basic use case
Configure MetalLB as follows so that the peer BGP routers receive one 203.0.113.200/32 route and one fc00:f853:ccd:e799::1/128 route for each load-balancer IP address that MetalLB assigns to a service. Because the localPref and communities fields are not specified, the routes are advertised with localPref set to zero and no BGP communities.
33.5.2.1. Example: Advertise a basic address pool configuration with BGP
Configure MetalLB as follows so that the IPAddressPool is advertised with the BGP protocol.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool.
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a BGP advertisement.
Create a file, such as
bgpadvertisement.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f bgpadvertisement.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgpadvertisement.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.5.3. Configuring MetalLB with a BGP advertisement and an advanced use case
Configure MetalLB as follows so that MetalLB assigns IP addresses to load-balancer services in the ranges between 203.0.113.200 and 203.0.113.203 and between fc00:f853:ccd:e799::0 and fc00:f853:ccd:e799::f.
To explain the two BGP advertisements, consider an instance when MetalLB assigns the IP address of 203.0.113.200 to a service. With that IP address as an example, the speaker advertises two routes to BGP peers:
-
203.0.113.200/32, withlocalPrefset to100and the community set to the numeric value of theNO_ADVERTISEcommunity. This specification indicates to the peer routers that they can use this route but they should not propagate information about this route to BGP peers. -
203.0.113.200/30, aggregates the load-balancer IP addresses assigned by MetalLB into a single route. MetalLB advertises the aggregated route to BGP peers with the community attribute set to8000:800. BGP peers propagate the203.0.113.200/30route to other BGP peers. When traffic is routed to a node with a speaker, the203.0.113.200/32route is used to forward the traffic into the cluster and to a pod that is associated with the service.
As you add more services and MetalLB assigns more load-balancer IP addresses from the pool, peer routers receive one local route, 203.0.113.20x/32, for each service, as well as the 203.0.113.200/30 aggregate route. Each service that you add generates the /30 route, but MetalLB deduplicates the routes to one BGP advertisement before communicating with peer routers.
33.5.3.1. Example: Advertise an advanced address pool configuration with BGP
Configure MetalLB as follows so that the IPAddressPool is advertised with the BGP protocol.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool.
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a BGP advertisement.
Create a file, such as
bgpadvertisement1.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f bgpadvertisement1.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgpadvertisement1.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a file, such as
bgpadvertisement2.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f bgpadvertisement2.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgpadvertisement2.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.5.4. Advertising an IP address pool from a subset of nodes
To advertise an IP address from an IP addresses pool, from a specific set of nodes only, use the .spec.nodeSelector specification in the BGPAdvertisement custom resource. This specification associates a pool of IP addresses with a set of nodes in the cluster. This is useful when you have nodes on different subnets in a cluster and you want to advertise an IP addresses from an address pool from a specific subnet, for example a public-facing subnet only.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool by using a custom resource:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Control which nodes in the cluster the IP address from
pool1advertises from by defining the.spec.nodeSelectorvalue in the BGPAdvertisement custom resource:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
In this example, the IP address from pool1 advertises from NodeA and NodeB only.
33.5.5. About the L2Advertisement custom resource
The fields for the l2Advertisements object are defined in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies the name for the L2 advertisement. |
|
|
| Specifies the namespace for the L2 advertisement. Specify the same namespace that the MetalLB Operator uses. |
|
|
|
Optional: The list of |
|
|
|
Optional: A selector for the |
|
|
|
Optional: Important Limiting the nodes to announce as next hops is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process. For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope. |
|
|
|
Optional: The list of |
33.5.6. Configuring MetalLB with an L2 advertisement
Configure MetalLB as follows so that the IPAddressPool is advertised with the L2 protocol.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool.
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a L2 advertisement.
Create a file, such as
l2advertisement.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f l2advertisement.yaml
$ oc apply -f l2advertisement.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.5.7. Configuring MetalLB with a L2 advertisement and label
The ipAddressPoolSelectors field in the BGPAdvertisement and L2Advertisement custom resource definitions is used to associate the IPAddressPool to the advertisement based on the label assigned to the IPAddressPool instead of the name itself.
This example shows how to configure MetalLB so that the IPAddressPool is advertised with the L2 protocol by configuring the ipAddressPoolSelectors field.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool.
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a L2 advertisement advertising the IP using
ipAddressPoolSelectors.Create a file, such as
l2advertisement.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f l2advertisement.yaml
$ oc apply -f l2advertisement.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.5.8. Configuring MetalLB with an L2 advertisement for selected interfaces
By default, the IP addresses from IP address pool that has been assigned to the service, is advertised from all the network interfaces. The interfaces field in the L2Advertisement custom resource definition is used to restrict those network interfaces that advertise the IP address pool.
This example shows how to configure MetalLB so that the IP address pool is advertised only from the network interfaces listed in the interfaces field of all nodes.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool.
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, and enter the configuration details like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool like the following example:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a L2 advertisement advertising the IP with
interfacesselector.Create a YAML file, such as
l2advertisement.yaml, and enter the configuration details like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the advertisement like the following example:
oc apply -f l2advertisement.yaml
$ oc apply -f l2advertisement.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The interface selector does not affect how MetalLB chooses the node to announce a given IP by using L2. The chosen node does not announce the service if the node does not have the selected interface.
33.6. Configuring MetalLB BGP peers
As a cluster administrator, you can add, modify, and delete Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) peers. The MetalLB Operator uses the BGP peer custom resources to identify which peers that MetalLB speaker pods contact to start BGP sessions. The peers receive the route advertisements for the load-balancer IP addresses that MetalLB assigns to services.
33.6.1. About the BGP peer custom resource
The fields for the BGP peer custom resource are described in the following table.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies the name for the BGP peer custom resource. |
|
|
| Specifies the namespace for the BGP peer custom resource. |
|
|
|
Specifies the Autonomous System number for the local end of the BGP session. Specify the same value in all BGP peer custom resources that you add. The range is |
|
|
|
Specifies the Autonomous System number for the remote end of the BGP session. The range is |
|
|
| Specifies the IP address of the peer to contact for establishing the BGP session. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies the IP address to use when establishing the BGP session. The value must be an IPv4 address. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies the network port of the peer to contact for establishing the BGP session. The range is |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies the duration for the hold time to propose to the BGP peer. The minimum value is 3 seconds ( |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies the maximum interval between sending keep-alive messages to the BGP peer. If you specify this field, you must also specify a value for the |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies the router ID to advertise to the BGP peer. If you specify this field, you must specify the same value in every BGP peer custom resource that you add. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies the MD5 password to send to the peer for routers that enforce TCP MD5 authenticated BGP sessions. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies name of the authentication secret for the BGP Peer. The secret must live in the |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies the name of a BFD profile. |
|
|
| Optional: Specifies a selector, using match expressions and match labels, to control which nodes can connect to the BGP peer. |
|
|
|
Optional: Specifies that the BGP peer is multiple network hops away. If the BGP peer is not directly connected to the same network, the speaker cannot establish a BGP session unless this field is set to |
The passwordSecret field is mutually exclusive with the password field, and contains a reference to a secret containing the password to use. Setting both fields results in a failure of the parsing.
33.6.2. Configuring a BGP peer
As a cluster administrator, you can add a BGP peer custom resource to exchange routing information with network routers and advertise the IP addresses for services.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - Configure MetalLB with a BGP advertisement.
Procedure
Create a file, such as
bgppeer.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the BGP peer:
oc apply -f bgppeer.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgppeer.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.6.3. Configure a specific set of BGP peers for a given address pool
This procedure illustrates how to:
-
Configure a set of address pools (
pool1andpool2). -
Configure a set of BGP peers (
peer1andpeer2). -
Configure BGP advertisement to assign
pool1topeer1andpool2topeer2.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create address pool
pool1.Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool1.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool
pool1:oc apply -f ipaddresspool1.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool1.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create address pool
pool2.Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool2.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool
pool2:oc apply -f ipaddresspool2.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool2.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create BGP
peer1.Create a file, such as
bgppeer1.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the BGP peer:
oc apply -f bgppeer1.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgppeer1.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create BGP
peer2.Create a file, such as
bgppeer2.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the BGP peer2:
oc apply -f bgppeer2.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgppeer2.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create BGP advertisement 1.
Create a file, such as
bgpadvertisement1.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f bgpadvertisement1.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgpadvertisement1.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create BGP advertisement 2.
Create a file, such as
bgpadvertisement2.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f bgpadvertisement2.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgpadvertisement2.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.6.4. Example BGP peer configurations
33.6.4.1. Example: Limit which nodes connect to a BGP peer
You can specify the node selectors field to control which nodes can connect to a BGP peer.
33.6.4.2. Example: Specify a BFD profile for a BGP peer
You can specify a BFD profile to associate with BGP peers. BFD compliments BGP by providing more rapid detection of communication failures between peers than BGP alone.
Deleting the bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) profile and removing the bfdProfile added to the border gateway protocol (BGP) peer resource does not disable the BFD. Instead, the BGP peer starts using the default BFD profile. To disable BFD from a BGP peer resource, delete the BGP peer configuration and recreate it without a BFD profile. For more information, see BZ#2050824.
33.6.4.3. Example: Specify BGP peers for dual-stack networking
To support dual-stack networking, add one BGP peer custom resource for IPv4 and one BGP peer custom resource for IPv6.
33.6.5. Next steps
33.7. Configuring community alias
As a cluster administrator, you can configure a community alias and use it across different advertisements.
33.7.1. About the community custom resource
The community custom resource is a collection of aliases for communities. Users can define named aliases to be used when advertising ipAddressPools using the BGPAdvertisement. The fields for the community custom resource are described in the following table.
The community CRD applies only to BGPAdvertisement.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Specifies the name for the |
|
|
|
Specifies the namespace for the |
|
|
|
Specifies a list of BGP community aliases that can be used in BGPAdvertisements. A community alias consists of a pair of name (alias) and value (number:number). Link the BGPAdvertisement to a community alias by referring to the alias name in its |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The name of the alias for the |
|
|
|
The BGP |
33.7.2. Configuring MetalLB with a BGP advertisement and community alias
Configure MetalLB as follows so that the IPAddressPool is advertised with the BGP protocol and the community alias set to the numeric value of the NO_ADVERTISE community.
In the following example, the peer BGP router doc-example-peer-community receives one 203.0.113.200/32 route and one fc00:f853:ccd:e799::1/128 route for each load-balancer IP address that MetalLB assigns to a service. A community alias is configured with the NO_ADVERTISE community.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create an IP address pool.
Create a file, such as
ipaddresspool.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the IP address pool:
oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yaml
$ oc apply -f ipaddresspool.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a community alias named
community1.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a BGP peer named
doc-example-bgp-peer.Create a file, such as
bgppeer.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the BGP peer:
oc apply -f bgppeer.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgppeer.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a BGP advertisement with the community alias.
Create a file, such as
bgpadvertisement.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specify the
CommunityAlias.namehere and not the community custom resource (CR) name.
Apply the configuration:
oc apply -f bgpadvertisement.yaml
$ oc apply -f bgpadvertisement.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.8. Configuring MetalLB BFD profiles
As a cluster administrator, you can add, modify, and delete Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) profiles. The MetalLB Operator uses the BFD profile custom resources to identify which BGP sessions use BFD to provide faster path failure detection than BGP alone provides.
33.8.1. About the BFD profile custom resource
The fields for the BFD profile custom resource are described in the following table.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies the name for the BFD profile custom resource. |
|
|
| Specifies the namespace for the BFD profile custom resource. |
|
|
| Specifies the detection multiplier to determine packet loss. The remote transmission interval is multiplied by this value to determine the connection loss detection timer.
For example, when the local system has the detect multiplier set to
The range is |
|
|
|
Specifies the echo transmission mode. If you are not using distributed BFD, echo transmission mode works only when the peer is also FRR. The default value is
When echo transmission mode is enabled, consider increasing the transmission interval of control packets to reduce bandwidth usage. For example, consider increasing the transmit interval to |
|
|
|
Specifies the minimum transmission interval, less jitter, that this system uses to send and receive echo packets. The range is |
|
|
| Specifies the minimum expected TTL for an incoming control packet. This field applies to multi-hop sessions only. The purpose of setting a minimum TTL is to make the packet validation requirements more stringent and avoid receiving control packets from other sessions.
The default value is |
|
|
| Specifies whether a session is marked as active or passive. A passive session does not attempt to start the connection. Instead, a passive session waits for control packets from a peer before it begins to reply. Marking a session as passive is useful when you have a router that acts as the central node of a star network and you want to avoid sending control packets that you do not need the system to send.
The default value is |
|
|
|
Specifies the minimum interval that this system is capable of receiving control packets. The range is |
|
|
|
Specifies the minimum transmission interval, less jitter, that this system uses to send control packets. The range is |
33.8.2. Configuring a BFD profile
As a cluster administrator, you can add a BFD profile and configure a BGP peer to use the profile. BFD provides faster path failure detection than BGP alone.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Create a file, such as
bfdprofile.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration for the BFD profile:
oc apply -f bfdprofile.yaml
$ oc apply -f bfdprofile.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.8.3. Next steps
- Configure a BGP peer to use the BFD profile.
33.9. Configuring services to use MetalLB
As a cluster administrator, when you add a service of type LoadBalancer, you can control how MetalLB assigns an IP address.
33.9.1. Request a specific IP address
Like some other load-balancer implementations, MetalLB accepts the spec.loadBalancerIP field in the service specification.
If the requested IP address is within a range from any address pool, MetalLB assigns the requested IP address. If the requested IP address is not within any range, MetalLB reports a warning.
Example service YAML for a specific IP address
If MetalLB cannot assign the requested IP address, the EXTERNAL-IP for the service reports <pending> and running oc describe service <service_name> includes an event like the following example.
Example event when MetalLB cannot assign a requested IP address
... Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Warning AllocationFailed 3m16s metallb-controller Failed to allocate IP for "default/invalid-request": "4.3.2.1" is not allowed in config
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning AllocationFailed 3m16s metallb-controller Failed to allocate IP for "default/invalid-request": "4.3.2.1" is not allowed in config33.9.2. Request an IP address from a specific pool
To assign an IP address from a specific range, but you are not concerned with the specific IP address, then you can use the metallb.universe.tf/address-pool annotation to request an IP address from the specified address pool.
Example service YAML for an IP address from a specific pool
If the address pool that you specify for <address_pool_name> does not exist, MetalLB attempts to assign an IP address from any pool that permits automatic assignment.
33.9.3. Accept any IP address
By default, address pools are configured to permit automatic assignment. MetalLB assigns an IP address from these address pools.
To accept any IP address from any pool that is configured for automatic assignment, no special annotation or configuration is required.
Example service YAML for accepting any IP address
33.9.5. Configuring a service with MetalLB
You can configure a load-balancing service to use an external IP address from an address pool.
Prerequisites
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - Install the MetalLB Operator and start MetalLB.
- Configure at least one address pool.
- Configure your network to route traffic from the clients to the host network for the cluster.
Procedure
Create a
<service_name>.yamlfile. In the file, ensure that thespec.typefield is set toLoadBalancer.Refer to the examples for information about how to request the external IP address that MetalLB assigns to the service.
Create the service:
oc apply -f <service_name>.yaml
$ oc apply -f <service_name>.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
service/<service_name> created
service/<service_name> createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Describe the service:
oc describe service <service_name>
$ oc describe service <service_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> The annotation is present if you request an IP address from a specific pool. <.> The service type must indicate
LoadBalancer. <.> The load-balancer ingress field indicates the external IP address if the service is assigned correctly. <.> The events field indicates the node name that is assigned to announce the external IP address. If you experience an error, the events field indicates the reason for the error.
33.10. MetalLB logging, troubleshooting, and support
If you need to troubleshoot MetalLB configuration, see the following sections for commonly used commands.
33.10.1. Setting the MetalLB logging levels
MetalLB uses FRRouting (FRR) in a container with the default setting of info generates a lot of logging. You can control the verbosity of the logs generated by setting the logLevel as illustrated in this example.
Gain a deeper insight into MetalLB by setting the logLevel to debug as follows:
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Create a file, such as
setdebugloglevel.yaml, with content like the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the configuration:
oc replace -f setdebugloglevel.yaml
$ oc replace -f setdebugloglevel.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteUse
oc replaceas the understanding is themetallbCR is already created and here you are changing the log level.Display the names of the
speakerpods:oc get -n metallb-system pods -l component=speaker
$ oc get -n metallb-system pods -l component=speakerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE speaker-2m9pm 4/4 Running 0 9m19s speaker-7m4qw 3/4 Running 0 19s speaker-szlmx 4/4 Running 0 9m19s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE speaker-2m9pm 4/4 Running 0 9m19s speaker-7m4qw 3/4 Running 0 19s speaker-szlmx 4/4 Running 0 9m19sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteSpeaker and controller pods are recreated to ensure the updated logging level is applied. The logging level is modified for all the components of MetalLB.
View the
speakerlogs:oc logs -n metallb-system speaker-7m4qw -c speaker
$ oc logs -n metallb-system speaker-7m4qw -c speakerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the FRR logs:
oc logs -n metallb-system speaker-7m4qw -c frr
$ oc logs -n metallb-system speaker-7m4qw -c frrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.10.1.1. FRRouting (FRR) log levels
The following table describes the FRR logging levels.
| Log level | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Supplies all logging information for all logging levels. |
|
|
Information that is diagnostically helpful to people. Set to |
|
| Provides information that always should be logged but under normal circumstances does not require user intervention. This is the default logging level. |
|
|
Anything that can potentially cause inconsistent |
|
|
Any error that is fatal to the functioning of |
|
| Turn off all logging. |
33.10.2. Troubleshooting BGP issues
The BGP implementation that Red Hat supports uses FRRouting (FRR) in a container in the speaker pods. As a cluster administrator, if you need to troubleshoot BGP configuration issues, you need to run commands in the FRR container.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Display the names of the
speakerpods:oc get -n metallb-system pods -l component=speaker
$ oc get -n metallb-system pods -l component=speakerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE speaker-66bth 4/4 Running 0 56m speaker-gvfnf 4/4 Running 0 56m ...
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE speaker-66bth 4/4 Running 0 56m speaker-gvfnf 4/4 Running 0 56m ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the running configuration for FRR:
oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show running-config"
$ oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show running-config"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> The
router bgpsection indicates the ASN for MetalLB. <.> Confirm that aneighbor <ip-address> remote-as <peer-ASN>line exists for each BGP peer custom resource that you added. <.> If you configured BFD, confirm that the BFD profile is associated with the correct BGP peer and that the BFD profile appears in the command output. <.> Confirm that thenetwork <ip-address-range>lines match the IP address ranges that you specified in address pool custom resources that you added.Display the BGP summary:
oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show bgp summary"
$ oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show bgp summary"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the BGP peers that received an address pool:
oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show bgp ipv4 unicast 203.0.113.200/30"
$ oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show bgp ipv4 unicast 203.0.113.200/30"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
ipv4withipv6to display the BGP peers that received an IPv6 address pool. Replace203.0.113.200/30with an IPv4 or IPv6 IP address range from an address pool.Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> Confirm that the output includes an IP address for a BGP peer.
33.10.3. Troubleshooting BFD issues
The Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) implementation that Red Hat supports uses FRRouting (FRR) in a container in the speaker pods. The BFD implementation relies on BFD peers also being configured as BGP peers with an established BGP session. As a cluster administrator, if you need to troubleshoot BFD configuration issues, you need to run commands in the FRR container.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. -
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Display the names of the
speakerpods:oc get -n metallb-system pods -l component=speaker
$ oc get -n metallb-system pods -l component=speakerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE speaker-66bth 4/4 Running 0 26m speaker-gvfnf 4/4 Running 0 26m ...
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE speaker-66bth 4/4 Running 0 26m speaker-gvfnf 4/4 Running 0 26m ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Display the BFD peers:
oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show bfd peers brief"
$ oc exec -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -c frr -- vtysh -c "show bfd peers brief"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Session count: 2 SessionId LocalAddress PeerAddress Status ========= ============ =========== ====== 3909139637 10.0.1.2 10.0.2.3 up <.>
Session count: 2 SessionId LocalAddress PeerAddress Status ========= ============ =========== ====== 3909139637 10.0.1.2 10.0.2.3 up <.>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <.> Confirm that the
PeerAddresscolumn includes each BFD peer. If the output does not list a BFD peer IP address that you expected the output to include, troubleshoot BGP connectivity with the peer. If the status field indicatesdown, check for connectivity on the links and equipment between the node and the peer. You can determine the node name for the speaker pod with a command likeoc get pods -n metallb-system speaker-66bth -o jsonpath='{.spec.nodeName}'.
33.10.4. MetalLB metrics for BGP and BFD
OpenShift Container Platform captures the following Prometheus metrics for MetalLB that relate to BGP peers and BFD profiles.
-
metallb_bfd_control_packet_inputcounts the number of BFD control packets received from each BFD peer. -
metallb_bfd_control_packet_outputcounts the number of BFD control packets sent to each BFD peer. -
metallb_bfd_echo_packet_inputcounts the number of BFD echo packets received from each BFD peer. -
metallb_bfd_echo_packet_outputcounts the number of BFD echo packets sent to each BFD peer. -
metallb_bfd_session_down_eventscounts the number of times the BFD session with a peer entered thedownstate. -
metallb_bfd_session_upindicates the connection state with a BFD peer.1indicates the session isupand0indicates the session isdown. -
metallb_bfd_session_up_eventscounts the number of times the BFD session with a peer entered theupstate. -
metallb_bfd_zebra_notificationscounts the number of BFD Zebra notifications for each BFD peer. -
metallb_bgp_announced_prefixes_totalcounts the number of load balancer IP address prefixes that are advertised to BGP peers. The terms prefix and aggregated route have the same meaning. -
metallb_bgp_session_upindicates the connection state with a BGP peer.1indicates the session isupand0indicates the session isdown. -
metallb_bgp_updates_totalcounts the number of BGPupdatemessages that were sent to a BGP peer.
Additional resources
- See Querying metrics for information about using the monitoring dashboard.
33.10.5. About collecting MetalLB data
You can use the oc adm must-gather CLI command to collect information about your cluster, your MetalLB configuration, and the MetalLB Operator. The following features and objects are associated with MetalLB and the MetalLB Operator:
- The namespace and child objects that the MetalLB Operator is deployed in
- All MetalLB Operator custom resource definitions (CRDs)
The oc adm must-gather CLI command collects the following information from FRRouting (FRR) that Red Hat uses to implement BGP and BFD:
-
/etc/frr/frr.conf -
/etc/frr/frr.log -
/etc/frr/daemonsconfiguration file -
/etc/frr/vtysh.conf
The log and configuration files in the preceding list are collected from the frr container in each speaker pod.
In addition to the log and configuration files, the oc adm must-gather CLI command collects the output from the following vtysh commands:
-
show running-config -
show bgp ipv4 -
show bgp ipv6 -
show bgp neighbor -
show bfd peer
No additional configuration is required when you run the oc adm must-gather CLI command.
Additional resources
Chapter 34. Associating secondary interfaces metrics to network attachments
Administrators can use the pod_network_info metric to classify and monitor secondary network interfaces. The metric does this by adding a label that identifies the interface type, typically based on the associated NetworkAttachmentDefinition resource.
34.1. Extending secondary network metrics for monitoring
Secondary devices, or interfaces, are used for different purposes. Metrics from secondary network interfaces need to be classified to allow for effective aggregation and monitoring.
Exposed metrics contain the interface but do not specify where the interface originates. This is workable when there are no additional interfaces. However, relying on interface names alone becomes problematic when secondary interfaces are added because it is difficult to identify their purpose and use their metrics effectively..
When adding secondary interfaces, their names depend on the order in which they are added. Secondary interfaces can belong to distinct networks that can each serve a different purposes.
With pod_network_name_info it is possible to extend the current metrics with additional information that identifies the interface type. In this way, it is possible to aggregate the metrics and to add specific alarms to specific interface types.
The network type is generated from the name of the NetworkAttachmentDefinition resource, which distinguishes different secondary network classes. For example, different interfaces belonging to different networks or using different CNIs use different network attachment definition names.
34.2. Network Metrics Daemon
The Network Metrics Daemon is a daemon component that collects and publishes network related metrics.
The kubelet is already publishing network related metrics you can observe. These metrics are:
-
container_network_receive_bytes_total -
container_network_receive_errors_total -
container_network_receive_packets_total -
container_network_receive_packets_dropped_total -
container_network_transmit_bytes_total -
container_network_transmit_errors_total -
container_network_transmit_packets_total -
container_network_transmit_packets_dropped_total
The labels in these metrics contain, among others:
- Pod name
- Pod namespace
-
Interface name (such as
eth0)
These metrics work well until new interfaces are added to the pod, for example via Multus, as it is not clear what the interface names refer to.
The interface label refers to the interface name, but it is not clear what that interface is meant for. In case of many different interfaces, it would be impossible to understand what network the metrics you are monitoring refer to.
This is addressed by introducing the new pod_network_name_info described in the following section.
34.3. Metrics with network name
The Network Metrics daemonset publishes a pod_network_name_info gauge metric, with a fixed value of 0.
Example of pod_network_name_info
pod_network_name_info{interface="net0",namespace="namespacename",network_name="nadnamespace/firstNAD",pod="podname"} 0
pod_network_name_info{interface="net0",namespace="namespacename",network_name="nadnamespace/firstNAD",pod="podname"} 0The network name label is produced using the annotation added by Multus. It is the concatenation of the namespace the network attachment definition belongs to, plus the name of the network attachment definition.
The new metric alone does not provide much value, but combined with the network related container_network_* metrics, it offers better support for monitoring secondary networks.
Using a promql query like the following ones, it is possible to get a new metric containing the value and the network name retrieved from the k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/network-status annotation:
Legal Notice
Copyright © Red Hat
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of the OpenJS Foundation.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.