Chapter 8. Preparing for users
After installing OpenShift Container Platform, you can further expand and customize your cluster to your requirements, including taking steps to prepare for users.
8.1. Understanding identity provider configuration
The OpenShift Container Platform control plane includes a built-in OAuth server. Developers and administrators obtain OAuth access tokens to authenticate themselves to the API.
As an administrator, you can configure OAuth to specify an identity provider after you install your cluster.
8.1.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a custom resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
8.1.2. Supported identity providers
You can configure the following types of identity providers:
| Identity provider | Description |
|---|---|
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure an |
After you define an identity provider, you can use RBAC to define and apply permissions.
8.1.3. Identity provider parameters
The following parameters are common to all identity providers:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The provider name is prefixed to provider user names to form an identity name. |
|
| Defines how new identities are mapped to users when they log in. Enter one of the following values:
|
When adding or changing identity providers, you can map identities from the new provider to existing users by setting the mappingMethod parameter to add.
8.1.4. Sample identity provider CR
The following custom resource (CR) shows the parameters and default values that you use to configure an identity provider. This example uses the htpasswd identity provider.
Sample identity provider CR
8.2. Using RBAC to define and apply permissions
Understand and apply role-based access control.
8.2.1. RBAC overview
Role-based access control (RBAC) objects determine whether a user is allowed to perform a given action within a project.
Cluster administrators can use the cluster roles and bindings to control who has various access levels to the OpenShift Container Platform platform itself and all projects.
Developers can use local roles and bindings to control who has access to their projects. Note that authorization is a separate step from authentication, which is more about determining the identity of who is taking the action.
Authorization is managed using:
| Authorization object | Description |
|---|---|
| Rules |
Sets of permitted verbs on a set of objects. For example, whether a user or service account can |
| Roles | Collections of rules. You can associate, or bind, users and groups to multiple roles. |
| Bindings | Associations between users and/or groups with a role. |
There are two levels of RBAC roles and bindings that control authorization:
| RBAC level | Description |
|---|---|
| Cluster RBAC | Roles and bindings that are applicable across all projects. Cluster roles exist cluster-wide, and cluster role bindings can reference only cluster roles. |
| Local RBAC | Roles and bindings that are scoped to a given project. While local roles exist only in a single project, local role bindings can reference both cluster and local roles. |
A cluster role binding is a binding that exists at the cluster level. A role binding exists at the project level. The cluster role view must be bound to a user using a local role binding for that user to view the project. Create local roles only if a cluster role does not provide the set of permissions needed for a particular situation.
This two-level hierarchy allows reuse across multiple projects through the cluster roles while allowing customization inside of individual projects through local roles.
During evaluation, both the cluster role bindings and the local role bindings are used. For example:
- Cluster-wide "allow" rules are checked.
- Locally-bound "allow" rules are checked.
- Deny by default.
8.2.1.1. Default cluster roles
OpenShift Container Platform includes a set of default cluster roles that you can bind to users and groups cluster-wide or locally.
It is not recommended to manually modify the default cluster roles. Modifications to these system roles can prevent a cluster from functioning properly.
| Default cluster role | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A project manager. If used in a local binding, an |
|
| A user that can get basic information about projects and users. |
|
| A super-user that can perform any action in any project. When bound to a user with a local binding, they have full control over quota and every action on every resource in the project. |
|
| A user that can get basic cluster status information. |
|
| A user that can get or view most of the objects but cannot modify them. |
|
| A user that can modify most objects in a project but does not have the power to view or modify roles or bindings. |
|
| A user that can create their own projects. |
|
| A user who cannot make any modifications, but can see most objects in a project. They cannot view or modify roles or bindings. |
Be mindful of the difference between local and cluster bindings. For example, if you bind the cluster-admin role to a user by using a local role binding, it might appear that this user has the privileges of a cluster administrator. This is not the case. Binding the cluster-admin to a user in a project grants super administrator privileges for only that project to the user. That user has the permissions of the cluster role admin, plus a few additional permissions like the ability to edit rate limits, for that project. This binding can be confusing via the web console UI, which does not list cluster role bindings that are bound to true cluster administrators. However, it does list local role bindings that you can use to locally bind cluster-admin.
The relationships between cluster roles, local roles, cluster role bindings, local role bindings, users, groups and service accounts are illustrated below.
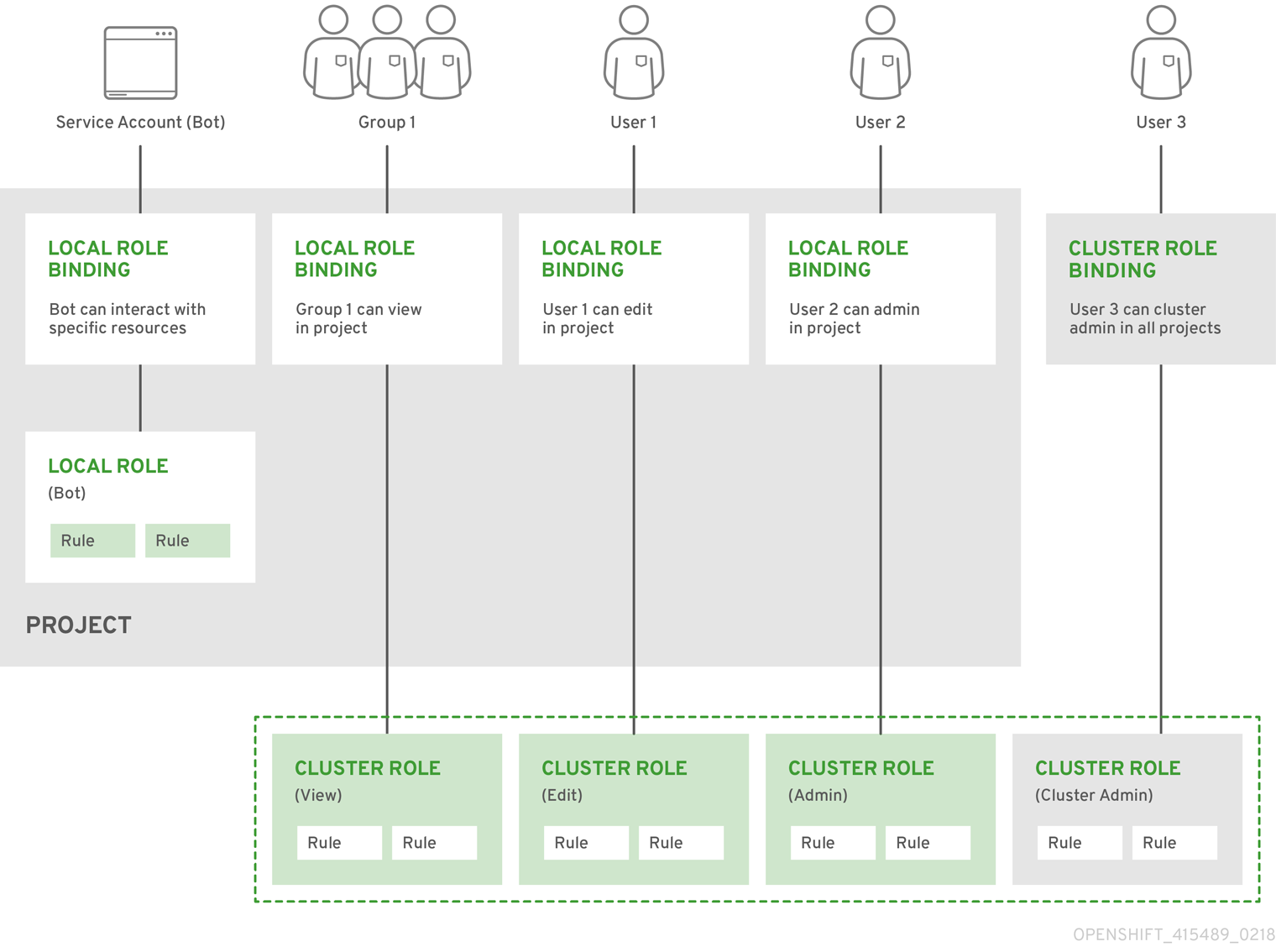
8.2.1.2. Evaluating authorization
OpenShift Container Platform evaluates authorization by using:
- Identity
- The user name and list of groups that the user belongs to.
- Action
The action you perform. In most cases, this consists of:
- Project: The project you access. A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations that allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities.
-
Verb : The action itself:
get,list,create,update,delete,deletecollection, orwatch. - Resource name: The API endpoint that you access.
- Bindings
- The full list of bindings, the associations between users or groups with a role.
OpenShift Container Platform evaluates authorization by using the following steps:
- The identity and the project-scoped action is used to find all bindings that apply to the user or their groups.
- Bindings are used to locate all the roles that apply.
- Roles are used to find all the rules that apply.
- The action is checked against each rule to find a match.
- If no matching rule is found, the action is then denied by default.
Remember that users and groups can be associated with, or bound to, multiple roles at the same time.
Project administrators can use the CLI to view local roles and bindings, including a matrix of the verbs and resources each are associated with.
The cluster role bound to the project administrator is limited in a project through a local binding. It is not bound cluster-wide like the cluster roles granted to the cluster-admin or system:admin.
Cluster roles are roles defined at the cluster level but can be bound either at the cluster level or at the project level.
8.2.1.2.1. Cluster role aggregation
The default admin, edit, view, and cluster-reader cluster roles support cluster role aggregation, where the cluster rules for each role are dynamically updated as new rules are created. This feature is relevant only if you extend the Kubernetes API by creating custom resources.
8.2.2. Projects and namespaces
A Kubernetes namespace provides a mechanism to scope resources in a cluster. The Kubernetes documentation has more information on namespaces.
Namespaces provide a unique scope for:
- Named resources to avoid basic naming collisions.
- Delegated management authority to trusted users.
- The ability to limit community resource consumption.
Most objects in the system are scoped by namespace, but some are excepted and have no namespace, including nodes and users.
A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations and is the central vehicle by which access to resources for regular users is managed. A project allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities. Users must be given access to projects by administrators, or if allowed to create projects, automatically have access to their own projects.
Projects can have a separate name, displayName, and description.
-
The mandatory
nameis a unique identifier for the project and is most visible when using the CLI tools or API. The maximum name length is 63 characters. -
The optional
displayNameis how the project is displayed in the web console (defaults toname). -
The optional
descriptioncan be a more detailed description of the project and is also visible in the web console.
Each project scopes its own set of:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Pods, services, replication controllers, etc. |
|
| Rules for which users can or cannot perform actions on objects. |
|
| Quotas for each kind of object that can be limited. |
|
| Service accounts act automatically with designated access to objects in the project. |
Cluster administrators can create projects and delegate administrative rights for the project to any member of the user community. Cluster administrators can also allow developers to create their own projects.
Developers and administrators can interact with projects by using the CLI or the web console.
8.2.3. Default projects
OpenShift Container Platform comes with a number of default projects, and projects starting with openshift- are the most essential to users. These projects host master components that run as pods and other infrastructure components. The pods created in these namespaces that have a critical pod annotation are considered critical, and the have guaranteed admission by kubelet. Pods created for master components in these namespaces are already marked as critical.
You cannot assign an SCC to pods created in one of the default namespaces: default, kube-system, kube-public, openshift-node, openshift-infra, and openshift. You cannot use these namespaces for running pods or services.
8.2.4. Viewing cluster roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view cluster roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. - Obtain permission to view the cluster roles and bindings.
Users with the cluster-admin default cluster role bound cluster-wide can perform any action on any resource, including viewing cluster roles and bindings.
Procedure
To view the cluster roles and their associated rule sets:
oc describe clusterrole.rbac
$ oc describe clusterrole.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the current set of cluster role bindings, which shows the users and groups that are bound to various roles:
oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.2.5. Viewing local roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view local roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. Obtain permission to view the local roles and bindings:
-
Users with the
cluster-admindefault cluster role bound cluster-wide can perform any action on any resource, including viewing local roles and bindings. -
Users with the
admindefault cluster role bound locally can view and manage roles and bindings in that project.
-
Users with the
Procedure
To view the current set of local role bindings, which show the users and groups that are bound to various roles for the current project:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the local role bindings for a different project, add the
-nflag to the command:oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe-project
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe-projectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.2.6. Adding roles to users
You can use the oc adm administrator CLI to manage the roles and bindings.
Binding, or adding, a role to users or groups gives the user or group the access that is granted by the role. You can add and remove roles to and from users and groups using oc adm policy commands.
You can bind any of the default cluster roles to local users or groups in your project.
Procedure
Add a role to a user in a specific project:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, you can add the
adminrole to thealiceuser injoeproject by running:oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joe
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipYou can alternatively apply the following YAML to add the role to the user:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the local role bindings and verify the addition in the output:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to view the local role bindings for the
joeproject:oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joe
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aliceuser has been added to theadminsRoleBinding.
8.2.7. Creating a local role
You can create a local role for a project and then bind it to a user.
Procedure
To create a local role for a project, run the following command:
oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>
$ oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role -
<resource>, the resources that the role applies to -
<project>, the project name
For example, to create a local role that allows a user to view pods in the
blueproject, run the following command:oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blue
$ oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To bind the new role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blue
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.2.8. Creating a cluster role
You can create a cluster role.
Procedure
To create a cluster role, run the following command:
oc create clusterrole <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource>
$ oc create clusterrole <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role -
<resource>, the resources that the role applies to
For example, to create a cluster role that allows a user to view pods, run the following command:
oc create clusterrole podviewonly --verb=get --resource=pod
$ oc create clusterrole podviewonly --verb=get --resource=podCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
8.2.9. Local role binding commands
When you manage a user or group’s associated roles for local role bindings using the following operations, a project may be specified with the -n flag. If it is not specified, then the current project is used.
You can use the following commands for local RBAC management.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicates which users can perform an action on a resource. |
|
| Binds a specified role to specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified users and all of their roles in the current project. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified groups and all of their roles in the current project. |
8.2.10. Cluster role binding commands
You can also manage cluster role bindings using the following operations. The -n flag is not used for these operations because cluster role bindings use non-namespaced resources.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Binds a given role to specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
8.2.11. Creating a cluster admin
The cluster-admin role is required to perform administrator level tasks on the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, such as modifying cluster resources.
Prerequisites
- You must have created a user to define as the cluster admin.
Procedure
Define the user as a cluster admin:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user>
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3. The kubeadmin user
OpenShift Container Platform creates a cluster administrator, kubeadmin, after the installation process completes.
This user has the cluster-admin role automatically applied and is treated as the root user for the cluster. The password is dynamically generated and unique to your OpenShift Container Platform environment. After installation completes the password is provided in the installation program’s output. For example:
INFO Install complete! INFO Run 'export KUBECONFIG=<your working directory>/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI. INFO The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p <provided>' succeeds (wait a few minutes). INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.demo1.openshift4-beta-abcorp.com INFO Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: <provided>
INFO Install complete!
INFO Run 'export KUBECONFIG=<your working directory>/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI.
INFO The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p <provided>' succeeds (wait a few minutes).
INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.demo1.openshift4-beta-abcorp.com
INFO Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: <provided>8.3.1. Removing the kubeadmin user
After you define an identity provider and create a new cluster-admin user, you can remove the kubeadmin to improve cluster security.
If you follow this procedure before another user is a cluster-admin, then OpenShift Container Platform must be reinstalled. It is not possible to undo this command.
Prerequisites
- You must have configured at least one identity provider.
-
You must have added the
cluster-adminrole to a user. - You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Remove the
kubeadminsecrets:oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-system
$ oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.4. Image configuration
Understand and configure image registry settings.
8.4.1. Image controller configuration parameters
The image.config.openshift.io/cluster resource holds cluster-wide information about how to handle images. The canonical, and only valid name is cluster. Its spec offers the following configuration parameters.
Parameters such as DisableScheduledImport, MaxImagesBulkImportedPerRepository, MaxScheduledImportsPerMinute, ScheduledImageImportMinimumIntervalSeconds, InternalRegistryHostname are not configurable.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Limits the container image registries from which normal users can import images. Set this list to the registries that you trust to contain valid images, and that you want applications to be able to import from. Users with permission to create images or Every element of this list contains a location of the registry specified by the registry domain name.
|
|
|
A reference to a config map containing additional CAs that should be trusted during
The namespace for this config map is |
|
|
Provides the hostnames for the default external image registry. The external hostname should be set only when the image registry is exposed externally. The first value is used in |
|
| Contains configuration that determines how the container runtime should treat individual registries when accessing images for builds and pods. For instance, whether or not to allow insecure access. It does not contain configuration for the internal cluster registry.
Either |
When the allowedRegistries parameter is defined, all registries, including registry.redhat.io and quay.io registries and the default internal image registry, are blocked unless explicitly listed. When using the parameter, to prevent pod failure, add all registries including the registry.redhat.io and quay.io registries and the internalRegistryHostname to the allowedRegistries list, as they are required by payload images within your environment. For disconnected clusters, mirror registries should also be added.
The status field of the image.config.openshift.io/cluster resource holds observed values from the cluster.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Set by the Image Registry Operator, which controls the |
|
|
Set by the Image Registry Operator, provides the external hostnames for the image registry when it is exposed externally. The first value is used in |
8.4.2. Configuring image registry settings
You can configure image registry settings by editing the image.config.openshift.io/cluster custom resource (CR). The Machine Config Operator (MCO) watches the image.config.openshift.io/cluster CR for any changes to the registries and reboots the nodes when it detects changes.
Procedure
Edit the
image.config.openshift.io/clustercustom resource:oc edit image.config.openshift.io/cluster
$ oc edit image.config.openshift.io/clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following is an example
image.config.openshift.io/clusterCR:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
Image: Holds cluster-wide information about how to handle images. The canonical, and only valid name iscluster.- 2
allowedRegistriesForImport: Limits the container image registries from which normal users may import images. Set this list to the registries that you trust to contain valid images, and that you want applications to be able to import from. Users with permission to create images orImageStreamMappingsfrom the API are not affected by this policy. Typically only cluster administrators have the appropriate permissions.- 3
additionalTrustedCA: A reference to a config map containing additional certificate authorities (CA) that are trusted during image stream import, pod image pull,openshift-image-registrypullthrough, and builds. The namespace for this config map isopenshift-config. The format of the config map is to use the registry hostname as the key, and the PEM certificate as the value, for each additional registry CA to trust.- 4
registrySources: Contains configuration that determines whether the container runtime allows or blocks individual registries when accessing images for builds and pods. Either theallowedRegistriesparameter or theblockedRegistriesparameter can be set, but not both. You can also define whether or not to allow access to insecure registries or registries that allow registries that use image short names. This example uses theallowedRegistriesparameter, which defines the registries that are allowed to be used. The insecure registryinsecure.comis also allowed. TheregistrySourcesparamter does not contain configuration for the internal cluster registry.
NoteWhen the
allowedRegistriesparameter is defined, all registries, including the registry.redhat.io and quay.io registries and the default internal image registry, are blocked unless explicitly listed. If you use the parameter, to prevent pod failure, you must add theregistry.redhat.ioandquay.ioregistries and theinternalRegistryHostnameto theallowedRegistrieslist, as they are required by payload images within your environment. Do not add theregistry.redhat.ioandquay.ioregistries to theblockedRegistrieslist.When using the
allowedRegistries,blockedRegistries, orinsecureRegistriesparameter, you can specify an individual repository within a registry. For example:reg1.io/myrepo/myapp:latest.Insecure external registries should be avoided to reduce possible security risks.
To check that the changes are applied, list your nodes:
oc get nodes
$ oc get nodesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For more information on the allowed, blocked, and insecure registry parameters, see Configuring image registry settings.
8.4.2.1. Configuring additional trust stores for image registry access
The image.config.openshift.io/cluster custom resource can contain a reference to a config map that contains additional certificate authorities to be trusted during image registry access.
Prerequisites
- The certificate authorities (CA) must be PEM-encoded.
Procedure
You can create a config map in the openshift-config namespace and use its name in AdditionalTrustedCA in the image.config.openshift.io custom resource to provide additional CAs that should be trusted when contacting external registries.
The config map key is the hostname of a registry with the port for which this CA is to be trusted, and the base64-encoded certificate is the value, for each additional registry CA to trust.
Image registry CA config map example
- 1
- If the registry has the port, such as
registry-with-port.example.com:5000,:should be replaced with...
You can configure additional CAs with the following procedure.
To configure an additional CA:
oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=<external_registry_address>=ca.crt -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap registry-config --from-file=<external_registry_address>=ca.crt -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc edit image.config.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit image.config.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow spec: additionalTrustedCA: name: registry-configspec: additionalTrustedCA: name: registry-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.4.2.2. Configuring image registry repository mirroring
Setting up container registry repository mirroring enables you to do the following:
- Configure your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to redirect requests to pull images from a repository on a source image registry and have it resolved by a repository on a mirrored image registry.
- Identify multiple mirrored repositories for each target repository, to make sure that if one mirror is down, another can be used.
The attributes of repository mirroring in OpenShift Container Platform include:
- Image pulls are resilient to registry downtimes.
- Clusters in disconnected environments can pull images from critical locations, such as quay.io, and have registries behind a company firewall provide the requested images.
- A particular order of registries is tried when an image pull request is made, with the permanent registry typically being the last one tried.
-
The mirror information you enter is added to the
/etc/containers/registries.conffile on every node in the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. - When a node makes a request for an image from the source repository, it tries each mirrored repository in turn until it finds the requested content. If all mirrors fail, the cluster tries the source repository. If successful, the image is pulled to the node.
Setting up repository mirroring can be done in the following ways:
At OpenShift Container Platform installation:
By pulling container images needed by OpenShift Container Platform and then bringing those images behind your company’s firewall, you can install OpenShift Container Platform into a datacenter that is in a disconnected environment.
After OpenShift Container Platform installation:
Even if you don’t configure mirroring during OpenShift Container Platform installation, you can do so later using the
ImageContentSourcePolicyobject.
The following procedure provides a post-installation mirror configuration, where you create an ImageContentSourcePolicy object that identifies:
- The source of the container image repository you want to mirror.
- A separate entry for each mirror repository you want to offer the content requested from the source repository.
You can only configure global pull secrets for clusters that have an ImageContentSourcePolicy object. You cannot add a pull secret to a project.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Configure mirrored repositories, by either:
- Setting up a mirrored repository with Red Hat Quay, as described in Red Hat Quay Repository Mirroring. Using Red Hat Quay allows you to copy images from one repository to another and also automatically sync those repositories repeatedly over time.
Using a tool such as
skopeoto copy images manually from the source directory to the mirrored repository.For example, after installing the skopeo RPM package on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7 or RHEL 8 system, use the
skopeocommand as shown in this example:skopeo copy \ docker://registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6 \ docker://example.io/example/ubi-minimal
$ skopeo copy \ docker://registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6 \ docker://example.io/example/ubi-minimalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, you have a container image registry that is named
example.iowith an image repository namedexampleto which you want to copy theubi8/ubi-minimalimage fromregistry.access.redhat.com. After you create the registry, you can configure your OpenShift Container Platform cluster to redirect requests made of the source repository to the mirrored repository.
- Log in to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
Create an
ImageContentSourcePolicyfile (for example,registryrepomirror.yaml), replacing the source and mirrors with your own registry and repository pairs and images:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Indicates the name of the image registry and repository.
- 2
- Indicates the registry and repository containing the content that is mirrored.
- 3
- You can configure a namespace inside a registry to use any image in that namespace. If you use a registry domain as a source, the
ImageContentSourcePolicyresource is applied to all repositories from the registry.
Create the new
ImageContentSourcePolicyobject:oc create -f registryrepomirror.yaml
$ oc create -f registryrepomirror.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the
ImageContentSourcePolicyobject is created, the new settings are deployed to each node and the cluster starts using the mirrored repository for requests to the source repository.To check that the mirrored configuration settings, are applied, do the following on one of the nodes.
List your nodes:
oc get node
$ oc get nodeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can see that scheduling on each worker node is disabled as the change is being applied.
Start the debugging process to access the node:
oc debug node/ip-10-0-147-35.ec2.internal
$ oc debug node/ip-10-0-147-35.ec2.internalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Starting pod/ip-10-0-147-35ec2internal-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host`
Starting pod/ip-10-0-147-35ec2internal-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host`Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change your root directory to
/host:chroot /host
sh-4.2# chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the
/etc/containers/registries.conffile to make sure the changes were made:cat /etc/containers/registries.conf
sh-4.2# cat /etc/containers/registries.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pull an image digest to the node from the source and check if it is resolved by the mirror.
ImageContentSourcePolicyobjects support image digests only, not image tags.podman pull --log-level=debug registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6
sh-4.2# podman pull --log-level=debug registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal@sha256:5cfbaf45ca96806917830c183e9f37df2e913b187adb32e89fd83fa455ebaa6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Troubleshooting repository mirroring
If the repository mirroring procedure does not work as described, use the following information about how repository mirroring works to help troubleshoot the problem.
- The first working mirror is used to supply the pulled image.
- The main registry is only used if no other mirror works.
-
From the system context, the
Insecureflags are used as fallback. -
The format of the
/etc/containers/registries.conffile has changed recently. It is now version 2 and in TOML format.
8.5. About Operator installation with OperatorHub
OperatorHub is a user interface for discovering Operators; it works in conjunction with Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM), which installs and manages Operators on a cluster.
As a cluster administrator, you can install an Operator from OperatorHub using the OpenShift Container Platform web console or CLI. Subscribing an Operator to one or more namespaces makes the Operator available to developers on your cluster.
During installation, you must determine the following initial settings for the Operator:
- Installation Mode
- Choose All namespaces on the cluster (default) to have the Operator installed on all namespaces or choose individual namespaces, if available, to only install the Operator on selected namespaces. This example chooses All namespaces… to make the Operator available to all users and projects.
- Update Channel
- If an Operator is available through multiple channels, you can choose which channel you want to subscribe to. For example, to deploy from the stable channel, if available, select it from the list.
- Approval Strategy
You can choose automatic or manual updates.
If you choose automatic updates for an installed Operator, when a new version of that Operator is available in the selected channel, Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) automatically upgrades the running instance of your Operator without human intervention.
If you select manual updates, when a newer version of an Operator is available, OLM creates an update request. As a cluster administrator, you must then manually approve that update request to have the Operator updated to the new version.
8.5.1. Installing from OperatorHub using the web console
You can install and subscribe to an Operator from OperatorHub using the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
Prerequisites
-
Access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions.
Procedure
-
Navigate in the web console to the Operators
OperatorHub page. Scroll or type a keyword into the Filter by keyword box to find the Operator you want. For example, type
jaegerto find the Jaeger Operator.You can also filter options by Infrastructure Features. For example, select Disconnected if you want to see Operators that work in disconnected environments, also known as restricted network environments.
Select the Operator to display additional information.
NoteChoosing a Community Operator warns that Red Hat does not certify Community Operators; you must acknowledge the warning before continuing.
- Read the information about the Operator and click Install.
On the Install Operator page:
Select one of the following:
-
All namespaces on the cluster (default) installs the Operator in the default
openshift-operatorsnamespace to watch and be made available to all namespaces in the cluster. This option is not always available. - A specific namespace on the cluster allows you to choose a specific, single namespace in which to install the Operator. The Operator will only watch and be made available for use in this single namespace.
-
All namespaces on the cluster (default) installs the Operator in the default
- Select an Update Channel (if more than one is available).
- Select Automatic or Manual approval strategy, as described earlier.
Click Install to make the Operator available to the selected namespaces on this OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
If you selected a Manual approval strategy, the upgrade status of the subscription remains Upgrading until you review and approve the install plan.
After approving on the Install Plan page, the subscription upgrade status moves to Up to date.
- If you selected an Automatic approval strategy, the upgrade status should resolve to Up to date without intervention.
After the upgrade status of the subscription is Up to date, select Operators
Installed Operators to verify that the cluster service version (CSV) of the installed Operator eventually shows up. The Status should ultimately resolve to InstallSucceeded in the relevant namespace. NoteFor the All namespaces… installation mode, the status resolves to InstallSucceeded in the
openshift-operatorsnamespace, but the status is Copied if you check in other namespaces.If it does not:
-
Check the logs in any pods in the
openshift-operatorsproject (or other relevant namespace if A specific namespace… installation mode was selected) on the WorkloadsPods page that are reporting issues to troubleshoot further.
-
Check the logs in any pods in the
8.5.2. Installing from OperatorHub using the CLI
Instead of using the OpenShift Container Platform web console, you can install an Operator from OperatorHub using the CLI. Use the oc command to create or update a Subscription object.
Prerequisites
-
Access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions. -
Install the
occommand to your local system.
Procedure
View the list of Operators available to the cluster from OperatorHub:
oc get packagemanifests -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc get packagemanifests -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note the catalog for your desired Operator.
Inspect your desired Operator to verify its supported install modes and available channels:
oc describe packagemanifests <operator_name> -n openshift-marketplace
$ oc describe packagemanifests <operator_name> -n openshift-marketplaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow An Operator group, defined by an
OperatorGroupobject, selects target namespaces in which to generate required RBAC access for all Operators in the same namespace as the Operator group.The namespace to which you subscribe the Operator must have an Operator group that matches the install mode of the Operator, either the
AllNamespacesorSingleNamespacemode. If the Operator you intend to install uses theAllNamespaces, then theopenshift-operatorsnamespace already has an appropriate Operator group in place.However, if the Operator uses the
SingleNamespacemode and you do not already have an appropriate Operator group in place, you must create one.NoteThe web console version of this procedure handles the creation of the
OperatorGroupandSubscriptionobjects automatically behind the scenes for you when choosingSingleNamespacemode.Create an
OperatorGroupobject YAML file, for exampleoperatorgroup.yaml:Example
OperatorGroupobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
OperatorGroupobject:oc apply -f operatorgroup.yaml
$ oc apply -f operatorgroup.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a
Subscriptionobject YAML file to subscribe a namespace to an Operator, for examplesub.yaml:Example
SubscriptionobjectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- For
AllNamespacesinstall mode usage, specify theopenshift-operatorsnamespace. Otherwise, specify the relevant single namespace forSingleNamespaceinstall mode usage. - 2
- Name of the channel to subscribe to.
- 3
- Name of the Operator to subscribe to.
- 4
- Name of the catalog source that provides the Operator.
- 5
- Namespace of the catalog source. Use
openshift-marketplacefor the default OperatorHub catalog sources. - 6
- The
envparameter defines a list of Environment Variables that must exist in all containers in the pod created by OLM. - 7
- The
envFromparameter defines a list of sources to populate Environment Variables in the container. - 8
- The
volumesparameter defines a list of Volumes that must exist on the pod created by OLM. - 9
- The
volumeMountsparameter defines a list of VolumeMounts that must exist in all containers in the pod created by OLM. If avolumeMountreferences avolumethat does not exist, OLM fails to deploy the Operator. - 10
- The
tolerationsparameter defines a list of Tolerations for the pod created by OLM. - 11
- The
resourcesparameter defines resource constraints for all the containers in the pod created by OLM. - 12
- The
nodeSelectorparameter defines aNodeSelectorfor the pod created by OLM.
Create the
Subscriptionobject:oc apply -f sub.yaml
$ oc apply -f sub.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow At this point, OLM is now aware of the selected Operator. A cluster service version (CSV) for the Operator should appear in the target namespace, and APIs provided by the Operator should be available for creation.