此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
18.4. Configuring Locations
A location is a set of maps, which are all stored in
auto.master, and a location can store multiple maps. The location entry only works as a container for map entries; it is not an automount configuration in and of itself.
Important
Identity Management does not set up or configure autofs. That must be done separately. Identity Management works with an existing autofs deployment.
18.4.1. Configuring Locations through the Web UI
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
- Click the Policy tab.
- Click the Automount subtab.
- Click the Add link at the top of the list of automount locations.
- Enter the name for the new location.
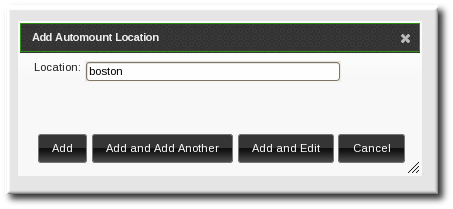
- Click the button to go to the map configuration for the new location. Create maps, as described in Section 18.5.1.1, “Configuring Direct Maps from the Web UI” and Section 18.5.2.1, “Configuring Indirect Maps from the Web UI”.
18.4.2. Configuring Locations through the Command Line
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To create a map, using the
Copy to Clipboard
Copied!
Toggle word wrap
Toggle overflow
For example:
automountlocation-add and give the location name.
ipa automountlocation-add location
$ ipa automountlocation-add locationipa automountlocation-add raleigh ---------------------------------- Added automount location "raleigh" ---------------------------------- Location: raleigh
$ ipa automountlocation-add raleigh
----------------------------------
Added automount location "raleigh"
----------------------------------
Location: raleigh
When a new location is created, two maps are automatically created for it,
auto.master and auto.direct. auto.master is the root map for all automount maps for the location. auto.direct is the default map for direct mounts and is mounted on /-.
To view all of the maps configured for a location as if they were deployed on a filesystem, use the
automountlocation-tofiles command:
ipa automountlocation-tofiles raleigh /etc/auto.master: /- /etc/auto.direct --------------------------- /etc/auto.direct:
$ ipa automountlocation-tofiles raleigh
/etc/auto.master:
/- /etc/auto.direct
---------------------------
/etc/auto.direct: