34.3. Adding PXE Hosts
After configuring the network server, the interface as shown in Figure 34.1, “Add Hosts” is displayed.

Figure 34.1. Add Hosts
The next step is to configure which hosts are allowed to connect to the PXE boot server. For the command line version of this step, refer to Section 34.3.1, “Command Line Configuration”.
To add hosts, click the button.
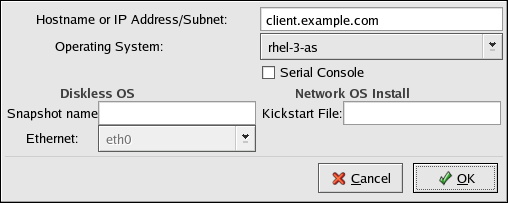
Figure 34.2. Add a Host
Enter the following information:
- Hostname or IP Address/Subnet — The IP address, fully qualified hostname, or a subnet of systems that should be allowed to connect to the PXE server for installations.
Important
Only enter a single IP address. anaconda will not use multiple addresses. - Operating System — The operating system identifier to install on this client. The list is populated from the network install instances created from the Network Installation Dialog.
- Serial Console — This option allows use of a serial console.
- Kickstart File — The location of a kickstart file to use, such as
http://server.example.com/kickstart/ks.cfg. This file can be created with the Kickstart Configurator. Refer to Chapter 32, Kickstart Configurator for details.
Ignore the Snapshot name and Ethernet options. They are only used for diskless environments.
34.3.1. Command Line Configuration
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
If the network server is not running X, the
pxeboot utility, a part of the system-config-netboot package, can be used to add hosts which are allowed to connect to the PXE server:
pxeboot -a -K <kickstart> -O <os-identifier> -r <value> <host>
pxeboot -a -K <kickstart> -O <os-identifier> -r <value> <host>
The following list explains the options:
-a— Specifies that a host is to be added.-K<kickstart> — The location of the kickstart file, if available.-O<os-identifier> — Specifies the operating system identifier as defined in Section 34.2, “PXE Boot Configuration”.-r<value> — Specifies the ram disk size.- <host> — Specifies the IP address or hostname of the host to add.
For more information on command line options available for the
pxeboot command, refer to the pxeboot man page.